Dynamic analysis of deployment impact of trim-wing mechanism of Mars entry capsules
-
摘要:
在着陆巡视器进入火星大气的过程中,配平翼机构会根据指令由收拢状态展开,并在到达指定位置后锁定,进而将进入舱配平攻角降至合理范围内,因此,其展开动力学性能对后续任务的成败至关重要。以配平翼机构功能的顺利实现为背景,研究复合材料构件的冲击动力学分析方法,建立了其有限元分析模型并基于隐式动力学算法对其展开过程进行了仿真。通过与地面试验结果对比,验证了展开动力学分析模型的正确性。在此基础上,对配平翼机构进入火星大气过程中的2种气动载荷工况下的展开过程进行了分析;基于Hashin理论对碳纤维蒙皮翼板的强度进行了校核,在2种气动载荷工况下各铺层的纤维拉伸、纤维压缩、基体拉伸及基体压缩4种失效模式所对应的失效因子均处于安全范围。可对类似机构的展开冲击问题研究提供参考。
Abstract:When a landing rover is entering the Martian atmosphere, its trim wing will be deployed from the retracted state and locked following instructions when arriving the target position. Then, the attack angle of the entry capsule will be trimmed to an appropriate range. Hence, the dynamic performance of the deployment is critical to subsequent missions. To realize the function of the trim wing deployment, an impact dynamics analysis of its composite material components was conducted. First, a finite element model for the trim wing deployment was established, and then the deployment process was simulated based on the implicit dynamic algorithm. The accuracy of the deployment dynamic analysis model was later verified by the ground test results. On this basis, the deployment process of the trim wing under two aerodynamic load conditions in entering the Martian atmosphere was analyzed, and the strength margin of the carbon fiber-skinned wing is calculated using the Hashin theory. Results show that under the two aerodynamic load conditions, the values of the four failure factors, which correspond to fiber stretching, fiber compression, matrix stretching, and matrix compression of each composite layer, are in a safe range. The findings provide a reference for future researches on the deployment and impact analysis of similar mechanism.
-
Key words:
- trim-wing mechanism /
- finite element analysis /
- deployment lock /
- impact /
- Hashin theory
-
表 1 试验气动载荷数据
Table 1. Data of the aerodynamic load test
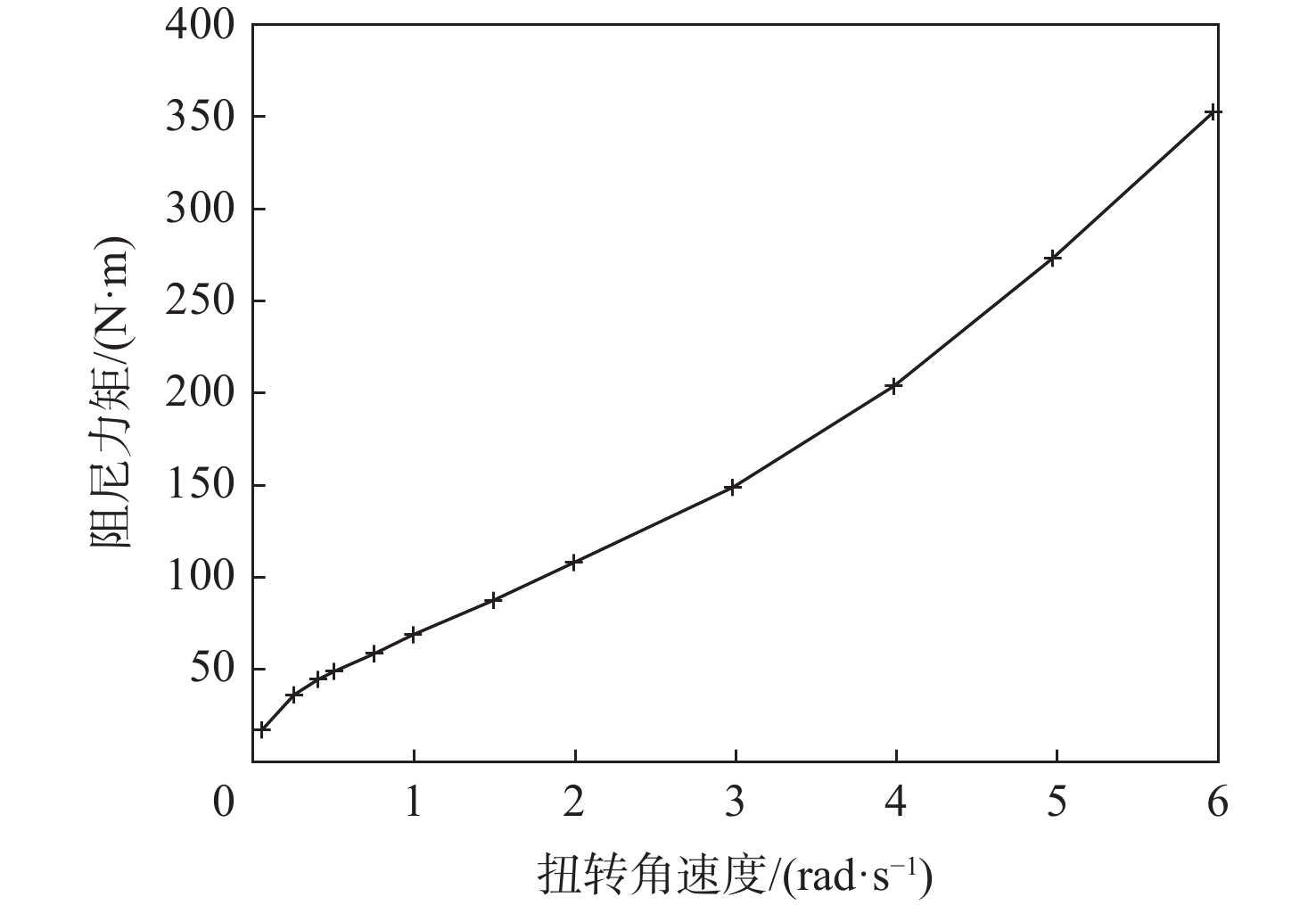
转角/(°) 试验气动载荷/(N·m) 0 0 24 3.79 54 8.53 84 13.26 18 114 表 2 试验气动载荷下仿真结果与试验结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of simulation results and results of aerodynamic load test
内容 展开时间/ms 传感器测点处x方向
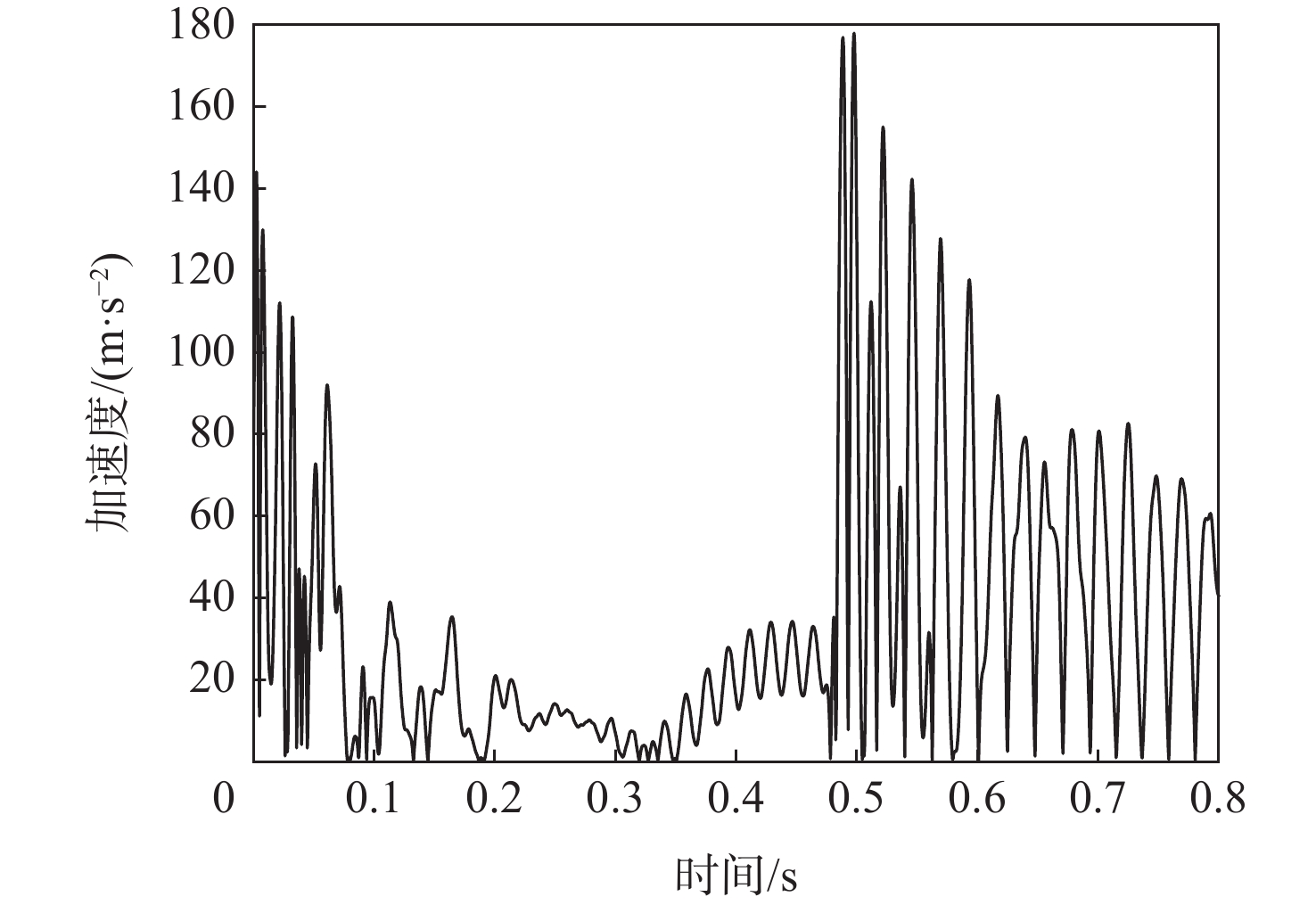
加速度/(m·s−2)试验数据 500 194.3 仿真数据 478 185.5 注:展开时间误差、传感器测点处x方向加速度误差分别为4.4%,4.5%。 表 3 不同工况下计算结果统计
Table 3. Statistics of calculation results under different conditions
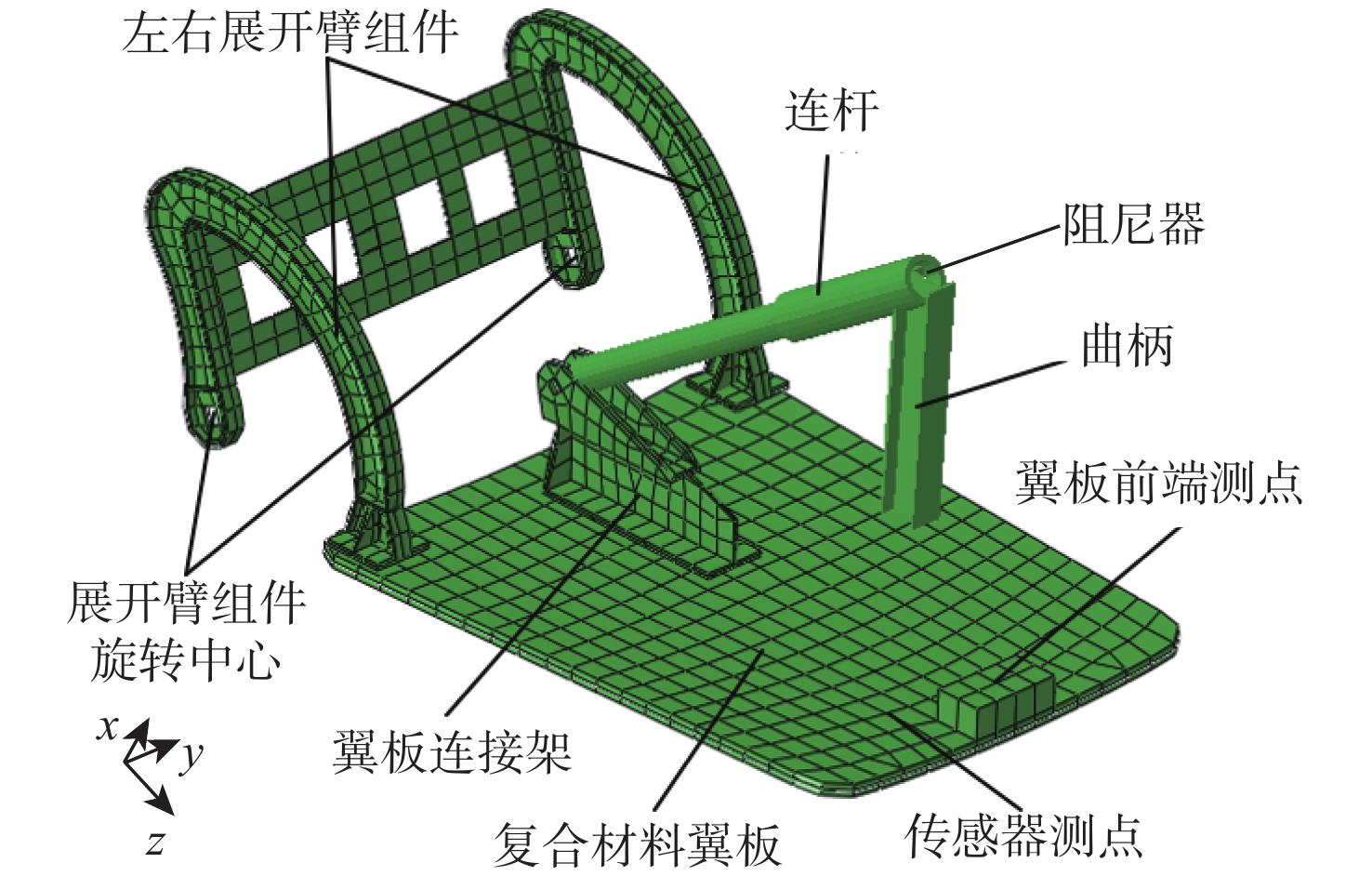
工况 展开时间/ms 翼板前端测点加速度/(m·s−2) 传感器测点加速度/(m·s−2) x向 y向 z向 幅值 x向 y向 z向 幅值 最小气动载荷工况 486.8 46.3 1.15 50.7 51.1 29.7 0.8 96.7 29 最大气动载荷工况 767.5 55.5 1.19 74.6 70.1 42.9 1.0 37.8 44.2 表 4 不同工况下翼板各铺层主应力统计
Table 4. Statistics of principal stress of each wing layer under different conditions
MPa 工况 主应力类型 上蒙皮各铺层主应力 下蒙皮各铺层主应力 0°铺层 45°铺层 −45°铺层 90°铺层 90°铺层 −45°铺层 45°铺层 0°铺层 最小气动载荷工况 最大主应力 233.5 130.9 130.7 172.9 171.7 206.5 206.8 216.9 最小主应力 −40.4 −63.5 −63 −66.5 −60.7 −102.9 −103.5 −16.9 最大气动载荷工况 最大主应力 270.3 117.6 117.7 91.9 208.2 206.1 206.5 223.6 最小主应力 −3.8 −63.1 −63.3 −42 −59.2 −100.6 −101.2 −23.7 表 5 不同工况下翼板各铺层的Hashin损伤因子统计
Table 5. Statistics of Hashin damage factor for each wing layer under different conditions
工况 失效模式 上蒙皮各铺层损伤因子 下蒙皮各铺层损伤因子 0°铺层 45°铺层 −45°铺层 90°铺层 90°铺层 −45°铺层 45°铺层 0°铺层 最小气动载荷工况 纤维受压破坏 0.2105 0.0827 0.0823 0.1010 0.0372 0.0583 0.0585 0.0501 纤维受拉破坏 0.0136 0.0043 0.0043 0.0075 0.0099 0.0114 0.0115 0.0119 基体受压破坏 0.0081 0.0029 0.0024 0.0013 0.0001 0.0012 0.0010 0.0102 基体受拉破坏 0.0096 0.0129 0.0124 0.0146 0.0166 0.0164 0.0173 0.0181 最大气动载荷工况 纤维受压破坏 0.2220 0.0874 0.0870 0.1051 0.0157 0.0447 0.0451 0.0602 纤维受拉破坏 0.0190 0.0041 0.0041 0.0022 0.0109 0.0118 0.0119 0.0125 基体受压破坏 0.0088 0.0028 0.0025 0.0013 0.0009 0.0017 0.0018 0.0102 基体受拉破坏 0.0097 0.0172 0.0165 0.0201 0.0176 0.0175 0.0185 0.0198 -
[1] 任守志, 刘立平. 零重力试验装置对太阳翼展开影响分析[J]. 航天器工程, 2008, 17(6): 73-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2008.06.011REN S Z, LIU L P. Influence of the zero-gravity test facility on the solar array's deployment test[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2008, 17(6): 73-78(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2008.06.011 [2] 王晛, 陈天智, 柴洪友. 太阳翼地面展开锁定的动力学仿真分析[J]. 航天器工程, 2011, 20(3): 86-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2011.03.014WANG X, CHEN T Z, CHAI H Y. Dynamics simulation analysis of solar array ground deployment and locking[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2011, 20(3): 86-92(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2011.03.014 [3] 濮海玲, 王晛, 杨巧龙. 黏滞型阻尼器对太阳翼展开性能的影响分析[J]. 航天器工程, 2013, 22(1): 54-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2013.01.011PU H L, WANG X, YANG Q L. Analysis of viscous damper effect on solar array deployment[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2013, 22(1): 54-59(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2013.01.011 [4] ZHANG Z J, YUAN G Z, ZOU Y J. Study on latch-up impact loads during solar wing deployment[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2012, 21(1): 31-36. [5] 荣吉利, 宋逸博, 刘志超, 等. 圆形薄膜太阳翼展开动力学分析与模态分析[J]. 宇航学报, 2020, 41(9): 1125-1131. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2020.09.002RONG J L, SONG Y B, LIU Z C, et al. Deployment dynamic analysis and modal analysis of circular membrane solar arrays[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2020, 41(9): 1125-1131(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2020.09.002 [6] 吴宏宇, 王春洁, 丁宗茂, 等. 着陆姿态不确定下的着陆器缓冲机构优化设计[J]. 宇航学报, 2018, 39(12): 1323-1331. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2018.12.002WU H Y, WANG C J, DING Z M, et al. Optimization design of a landing gear under uncertain landing attitude[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2018, 39(12): 1323-1331(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2018.12.002 [7] 吴宏宇, 王春洁, 丁宗茂, 等. 两种着陆模式下的着陆器缓冲机构构型优化[J]. 宇航学报, 2017, 38(10): 1032-1040. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2017.10.003WU H Y, WANG C J, DING Z M, et al. Configuration optimization of landing gear under two kinds of landing modes[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2017, 38(10): 1032-1040(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2017.10.003 [8] 逯运通, 宋顺广, 王春洁, 等. 基于刚柔耦合模型的月球着陆器动力学分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2010, 36(11): 1348-1352. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2010.11.004LU Y T, SONG S G, WANG C J, et al. Dynamic analysis for lunar lander based on rigid-flexible coupled model[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2010, 36(11): 1348-1352(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2010.11.004 [9] 吴宏宇, 王春洁, 丁建中, 等. 基于多工况的新型着陆器软着陆性能优化[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2017, 43(4): 776-781. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0296WU H Y, WANG C J, DING J Z, et al. Soft landing performance optimization for novel lander based on multiple working conditions[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017, 43(4): 776-781(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0296 [10] 梁东平, 柴洪友. 着陆冲击仿真月壤本构模型及有限元建模[J]. 航天器工程, 2012, 21(1): 18-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2012.01.006LIANG D P, CHAI H Y. Lunar soil constitutive model and finite element modeling for landing impact simulation[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2012, 21(1): 18-24(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2012.01.006 [11] 梁东平, 柴洪友, 曾福明. 月球着陆器着陆腿非线性有限元建模与仿真[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2013, 39(1): 11-15. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2013.01.012LIANG D P, CHAI H Y, ZENG F M. Nonlinear finite element modeling and simulation for landing leg of lunar lander[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2013, 39(1): 11-15(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2013.01.012 [12] LI T J, WANG Y. Deployment dynamic analysis of deployable antennas considering thermal effect[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2009, 13(4): 210-215. [13] 李培. 大型星载环形桁架天线展开动力学研究[D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2016: 72-88.LI P. Deployment dynamics of the large-scale hoop truss antenna of satellite[D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2016: 72-88(in Chinese). [14] 李团结, 张琰, 段宝岩. 周边桁架可展开天线展开过程仿真方法[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2008, 20(8): 2081-2084. doi: 10.16182/j.cnki.joss.2008.08.032LI T J, ZHANG Y, DUAN B Y. Approach to deployable process simulation of circular truss deployable antenna[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2008, 20(8): 2081-2084(in Chinese). doi: 10.16182/j.cnki.joss.2008.08.032 [15] BATHE K J. 有限元法(下)[M]. 轩建平, 译. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2016: 319-339.BATHE K J. Finite element procedures(II)[M]. XUAN J P, translated. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2016: 319-339(in Chinese). [16] HASHIN Z. Failure criteria for unidirectional fiber composites[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1980, 47(2): 329-334. [17] HASHIN Z, ROTEM A. A fatigue failure criterion for fiber reinforced materials[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 1973, 7(4): 448-464. doi: 10.1177/002199837300700404 -







 下载:
下载: