Mural inpainting with generative adversarial networks based on multi-scale feature and attention fusion
-
摘要:
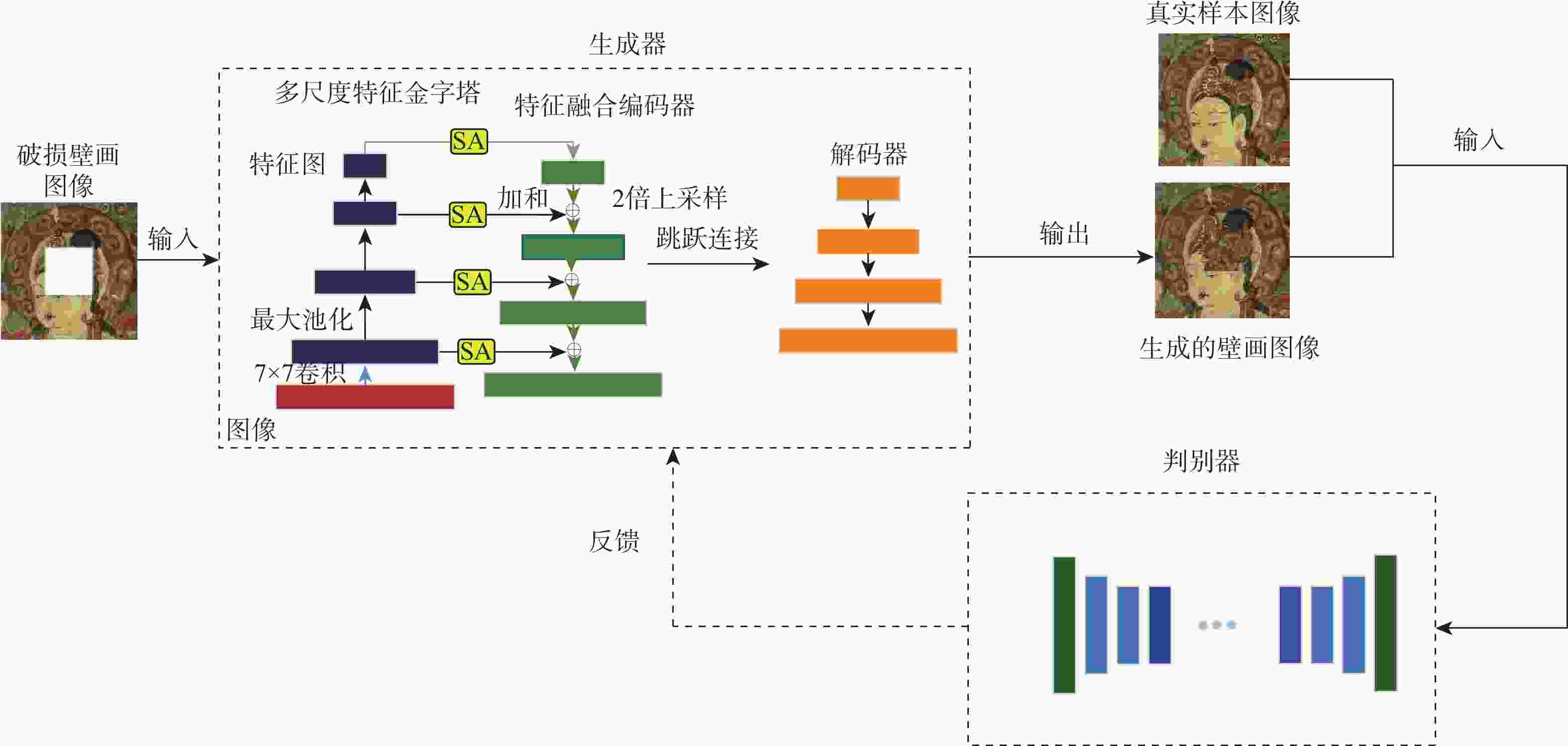
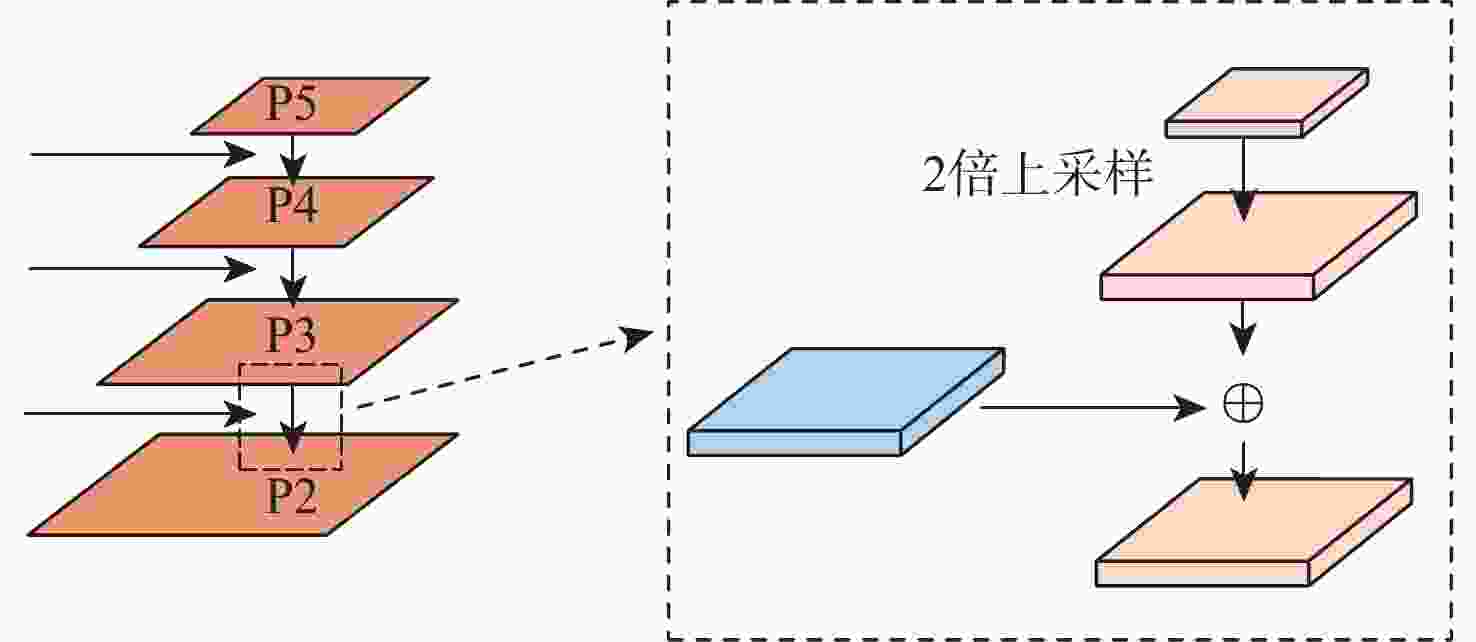
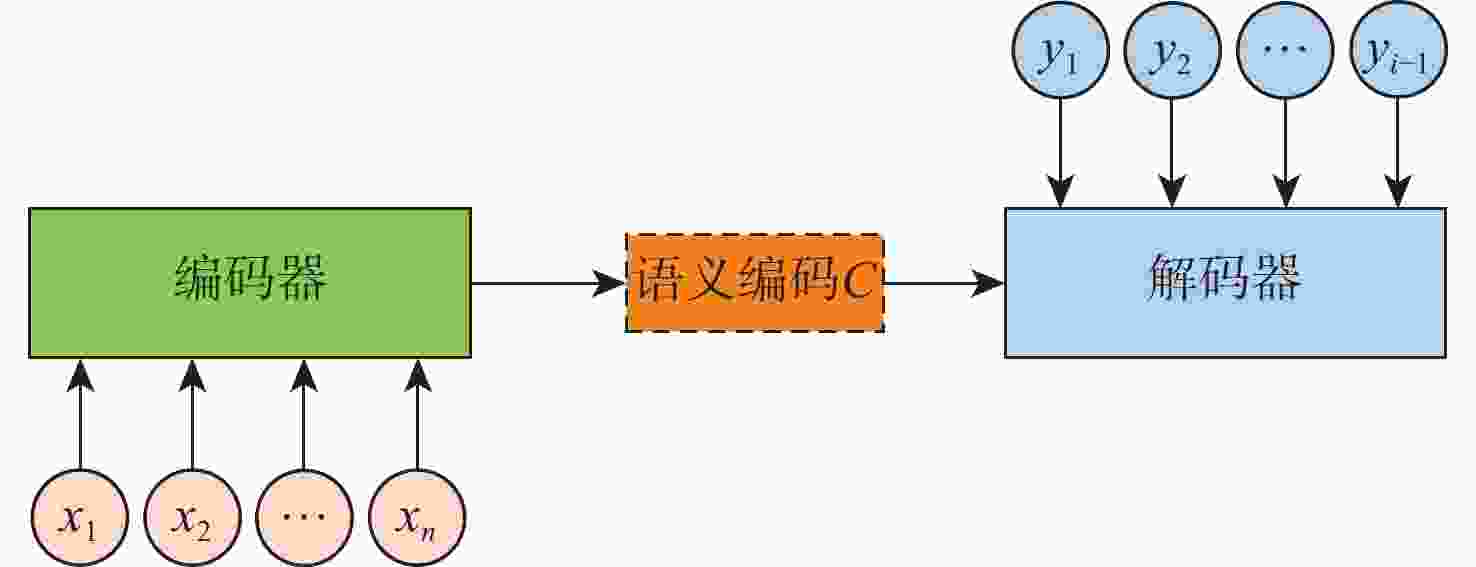
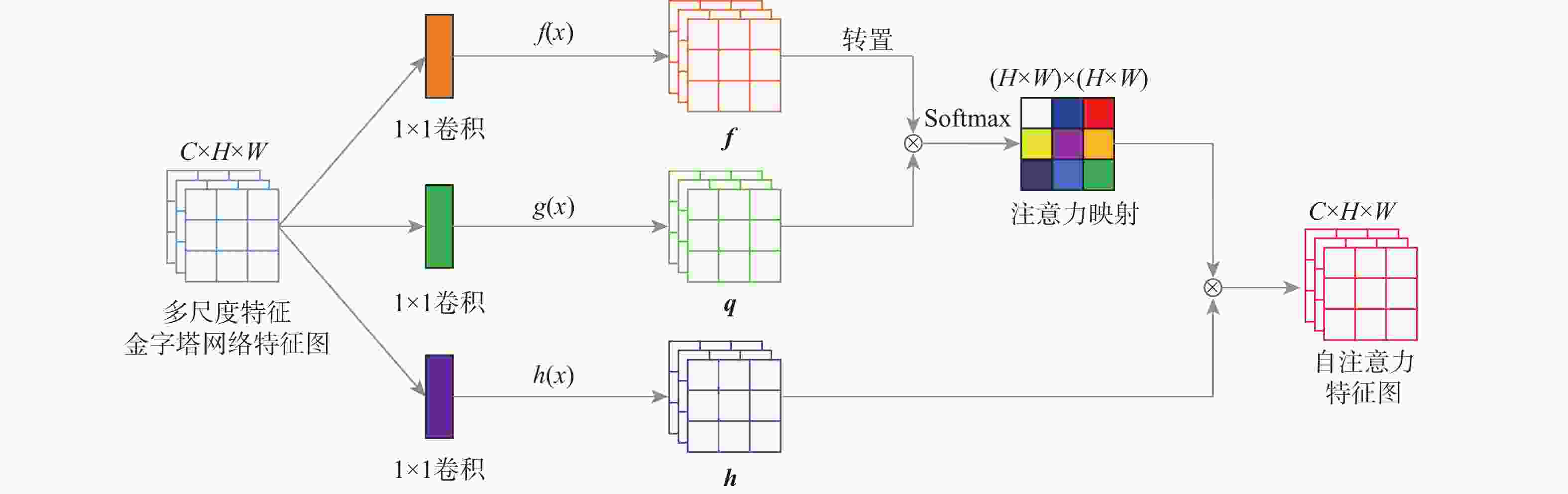
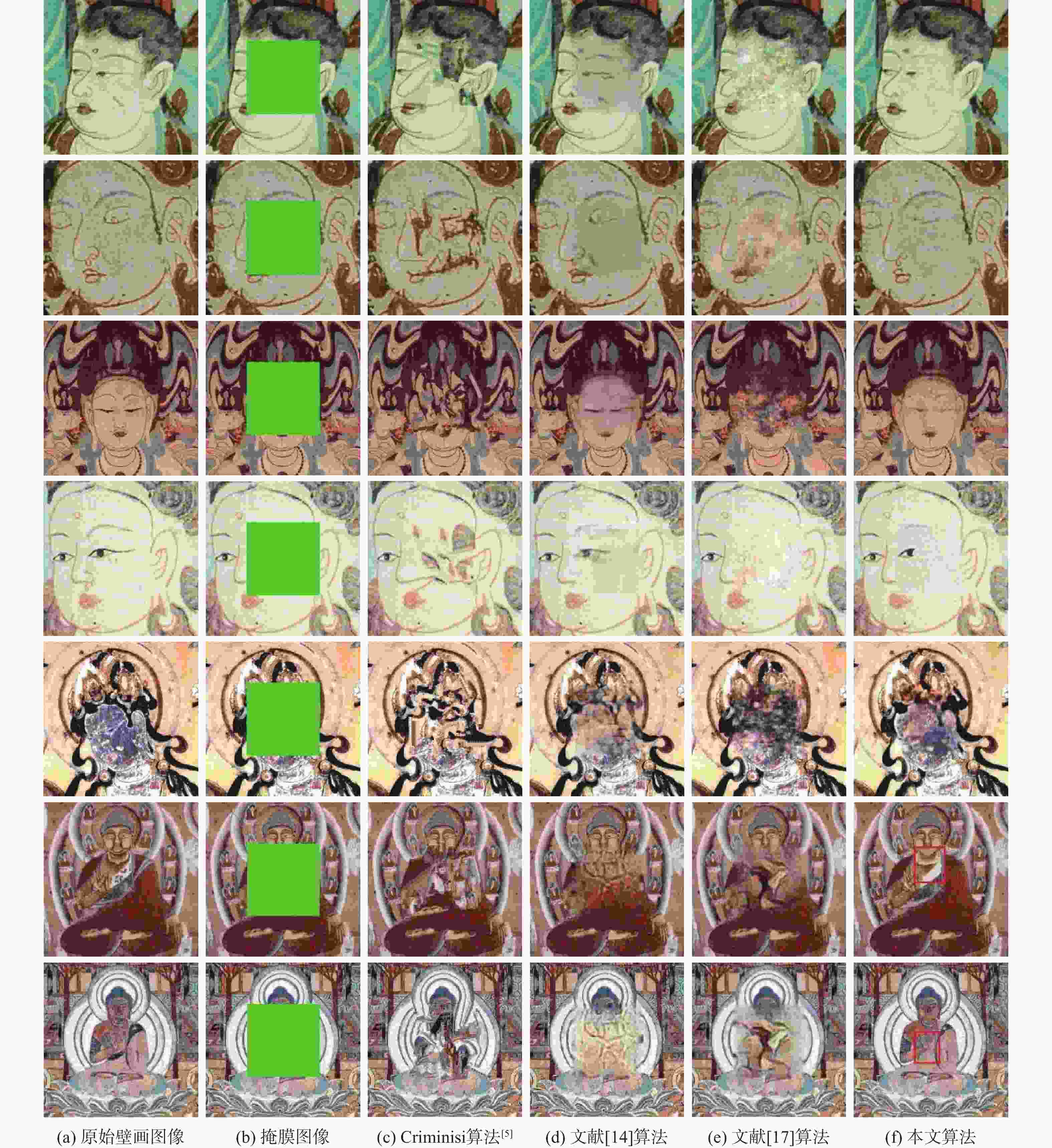
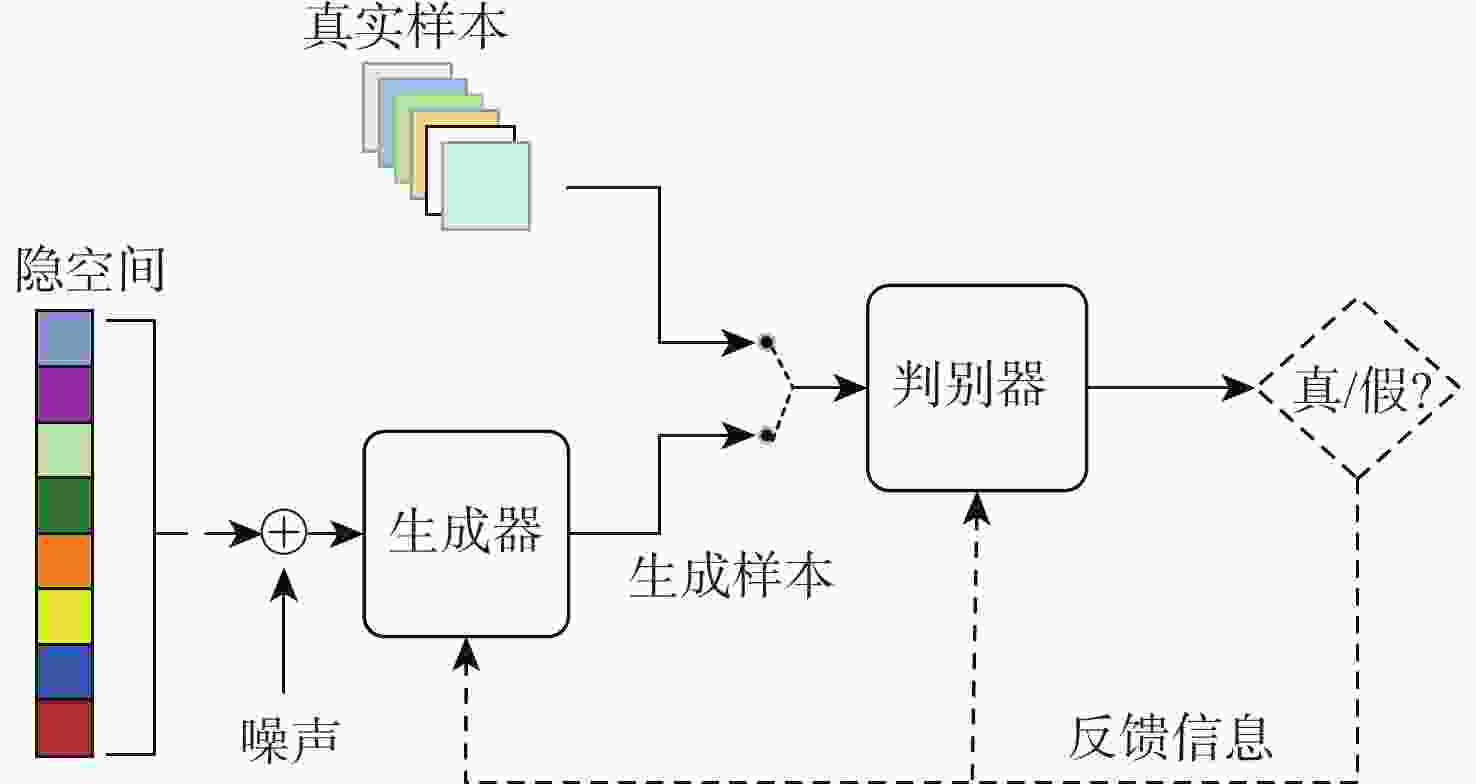
针对现有深度学习图像修复算法修复壁画时,存在特征提取不足及细节重构丢失等问题,提出了一种多尺度特征和注意力融合的生成对抗壁画修复深度学习模型。设计多尺度特征金字塔网络提取壁画中不同尺度的特征信息,增强特征关联性;采用自注意力机制及特征融合模块构建多尺度特征生成器,以获取丰富的上下文信息,提升网络的修复能力;引入最小化对抗损失与均方误差促进判别器的残差反馈,从而结合不同尺度的特征信息完成壁画修复。通过对真实敦煌壁画数字化修复的实验结果表明,所提算法能够有效保护壁画图像的边缘和纹理等重要特征信息,并且主观视觉效果及客观评价指标均优于比较算法。
Abstract:This study proposes a deep learning model for mural restoration based on generative adversarial networks with multi-scale feature and attention fusions, addressing insufficient feature extraction and detail loss of the existing deep learning image inpainting algorithms during reconstruction. Firstly, a multi-scale feature pyramid network is designed to extract feature information of different scales in mural images, which enhances the feature relevance. Secondly, using the self-attention mechanism and feature fusion module, a multi-scale feature generator is constructed to obtain rich context information and improve the restoration ability of the network. Finally, the minimal confrontation loss and the mean square error are introduced to promote the residual feedback of the discriminator, which completes the mural restoration by combining the feature information of different scales. The experimental results of digital restoration of real Dunhuang murals show that the proposed algorithm can effectively protect important feature information such as the edges and textures, and that the subjective visual effects and objective evaluation indicators are superior to those of the algorithms for comparison.
-
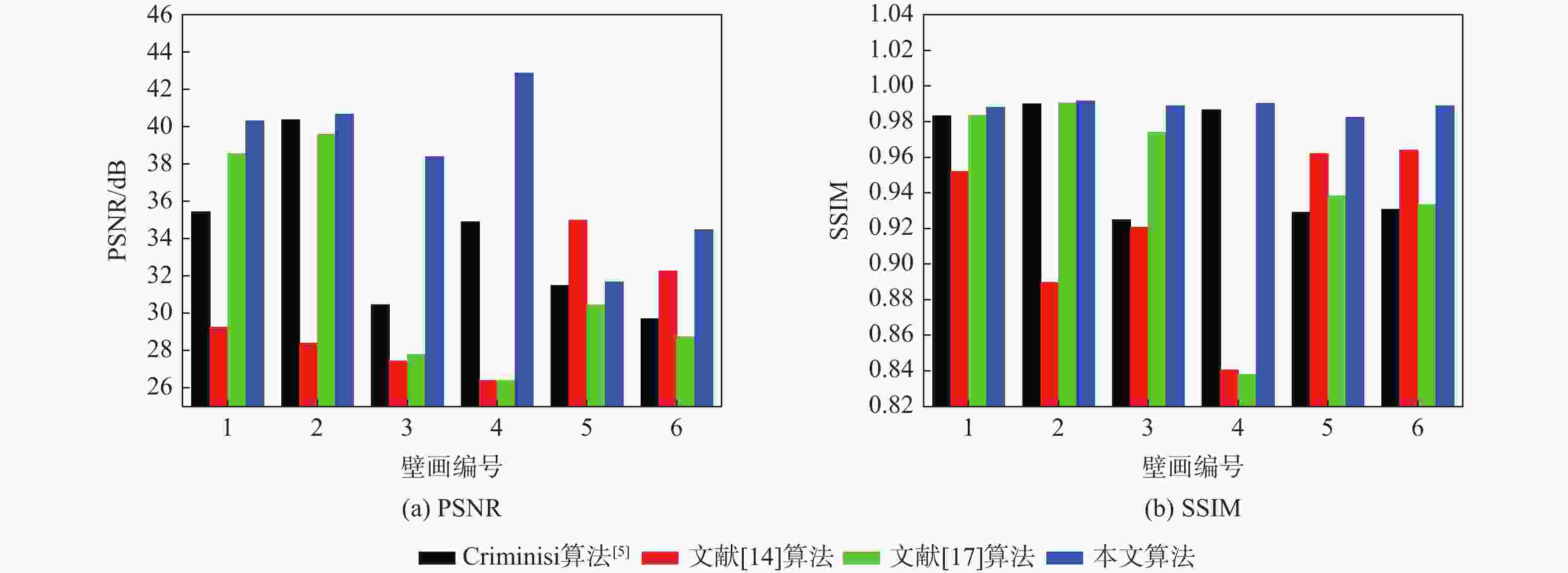
表 1 不同算法修复结果PSNR和SSIM对比
Table 1. Comparison of PSNR and SSIM repair results of different algorithms
原始壁画
图像Criminisi算法[5] 文献[14]算法 文献[17]算法 本文算法 PSNR/dB SSIM PSNR/dB SSIM PSNR/dB SSIM PSNR/dB SSIM 1 21.46 0.8113 26.74 0.8888 27.33 0.8229 34.17 0.9153 2 22.59 0.8035 31.16 0.8899 28.55 0.8366 33.96 0.9048 3 18.94 0.7806 28.41 0.8685 20.51 0.7834 29.42 0.8737 4 24.38 0.8448 31.16 0.8935 27.95 0.8721 32.78 0.9212 5 16.41 0.6826 21.19 0.8163 18.49 0.7581 24.78 0.8593 6 20.57 0.7589 23.40 0.7894 22.06 0.7823 27.19 0.9199 7 19.29 0.7408 19.52 0.7718 20.94 0.7587 26.93 0.9155 -
[1] WANG H, LI Q Q, JIA S. A global and local feature weighted method for ancient murals inpainting[J]. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2020, 11(6): 1197-1216. doi: 10.1007/s13042-019-01032-2 [2] BERTALMIO M, SAPIRO G, CASELLES V, et al. Image inpainting[C]//Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques. New York: ACM, 2000: 417-424. [3] CHAN T F, SHEN J H. Nontexture inpainting by curvature-driven diffusions[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2001, 12(4): 436-449. doi: 10.1006/jvci.2001.0487 [4] SHEN J H, CHAN T F. Mathematical models for local nontexture inpaintings[J]. SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 2002, 62(3): 1019-1043. doi: 10.1137/S0036139900368844 [5] CRIMINISI A, PEREZ P, TOYAMA K. Region filling and object removal by exemplar-based image inpainting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(9): 1200-1212. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2004.833105 [6] LI P, CHEN W G, MICHAEL K N. Compressive total variation for image reconstruction and restoration[J]. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 2020, 80(5): 874-893. doi: 10.1016/j.camwa.2020.05.006 [7] FAN Y. Damaged region filling by improved criminisi image inpainting algorithm for thangka[J]. Cluster Computing, 2019, 22(6): 13683-13691. [8] 陈永, 艾亚鹏, 郭红光. 改进曲率驱动模型的敦煌壁画修复算法[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2020, 32(5): 787-796.CHEN Y, AI Y P, GUO H G. Improved curvature-driven model of Dunhuang mural restoration algorithm[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design and Graphics, 2020, 32(5): 787-796(in Chinese). [9] YANG X H, GUO B L, XIAO Z L, et al. Improved structure tensor for fine-grained texture inpainting[J]. Signal Processing:Image Communication, 2019, 73: 84-95. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2018.02.006 [10] XU S X, LIU D, XIONG Z W. E2I: Generative inpainting from edge to image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2021, 31(4): 1308-1322. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2020.3001267 [11] QIN J, BAI H H, ZHAO Y. Multi-scale attention network for image inpainting[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2021, 204: 103155. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2020.103155 [12] ZENG Y H, FU J L, CHAO H Y, et al. Learning pyramid-context encoder network for high-quality image inpainting[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1486-1494. [13] IIZUKA S, SIMO-SERRA E, ISHIKAWA H. Globally and locally consistent image completion[J]. ACM Transaction on Graphics, 2017, 36(4): 1-14. [14] YAN Z Y, LI X M, LI M, et al. Shift-Net: Image inpainting via deep feature rearrangement[EB/OL]. (2018-04-13) [2021-05-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.09392v2. [15] ZENG Y, GONG Y, ZENG X. Controllable digital restoration of ancient paintings using convolutional neural network and nearest neighbor[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2020, 133: 158-164. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2020.02.033 [16] 曹建芳, 李艳飞, 崔红艳, 等. 自适应样本块局部搜索算法对古代寺观壁画的修复[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2019, 31(11): 2030-2037.CAO J F, LI Y F, CUI H Y, et al. Restoration of ancient temple and temple mural paintings by adaptive local search algorithm of Sample blocks[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design and Graphics, 2019, 31(11): 2030-2037(in Chinese). [17] LIU H Y, JIANG B, SONG Y B, et al. Rethinking image inpainting via a mutual encoder-decoder with feature equalizations[C]// Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020, 12347: 725-741. [18] 胡凯, 赵健, 刘昱, 等. 结构引导的图像修复[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(7): 1269-1277.HU K, ZHAO J, LIU Y, et al. Structure-guided image restoration[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(7): 1269-1277(in Chinese). [19] GADIPUDI A, DEIVALAKSHMI S, SEOK-BUM K. Deep dilated and densely connected parallel convolutional groups for compression artifacts reduction[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2020, 106: 102804. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2020.102804 [20] GUO X P, MENG L Y, MEI L Y, et al. Multi-focus image fusion with Siamese self-attention network[J]. IET Image Processing, 2020, 14(7): 1339-1346. doi: 10.1049/iet-ipr.2019.0883 -






 下载:
下载: