-
摘要:
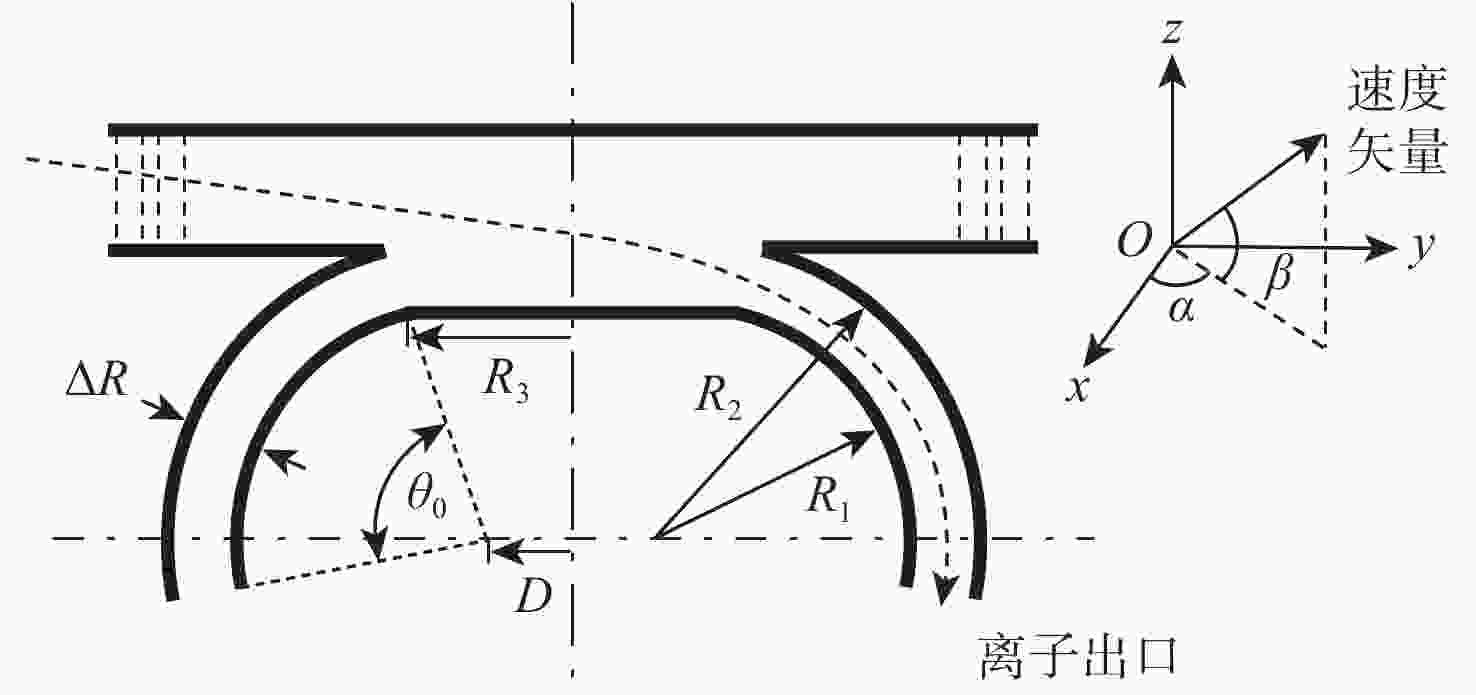
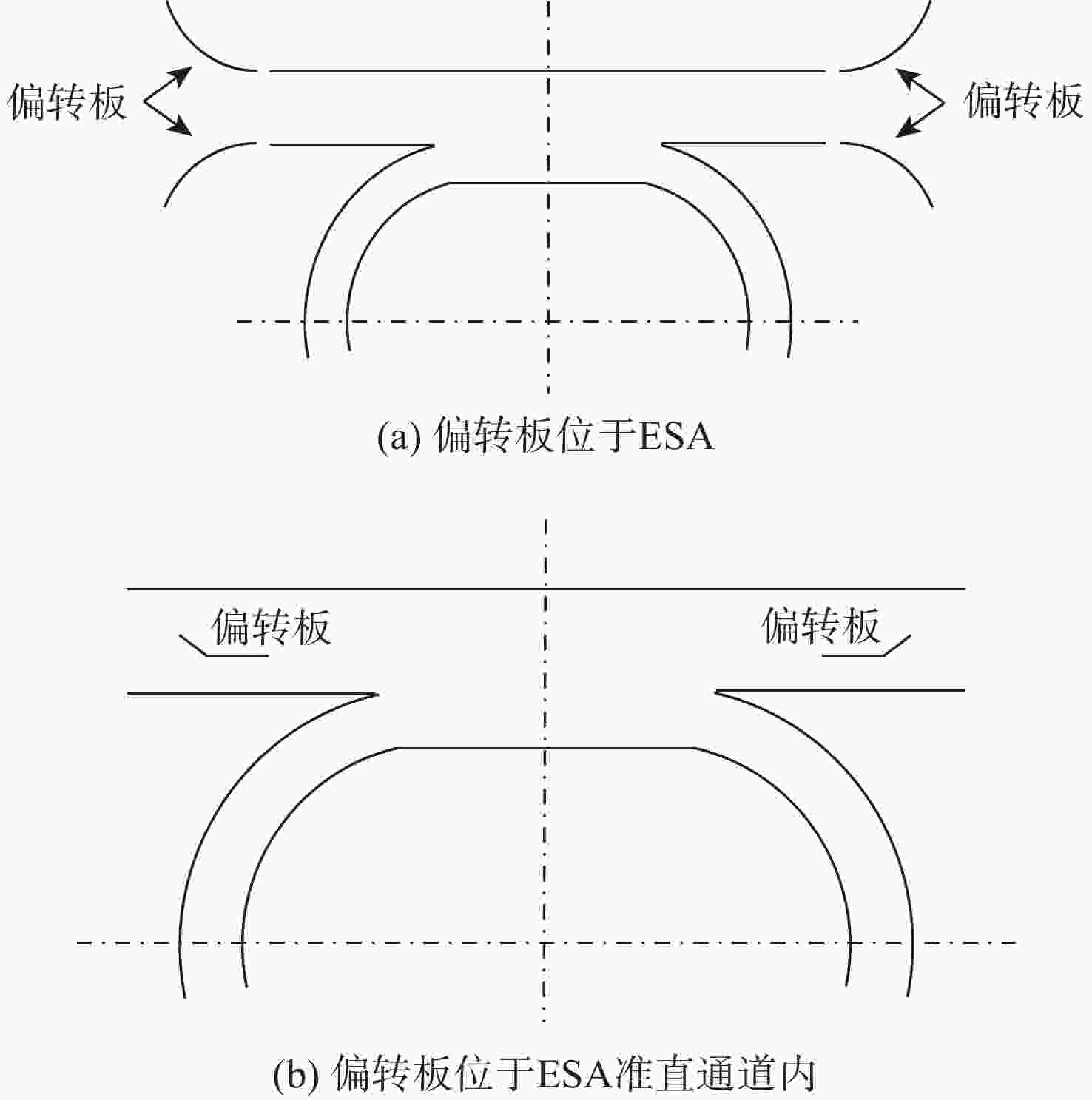
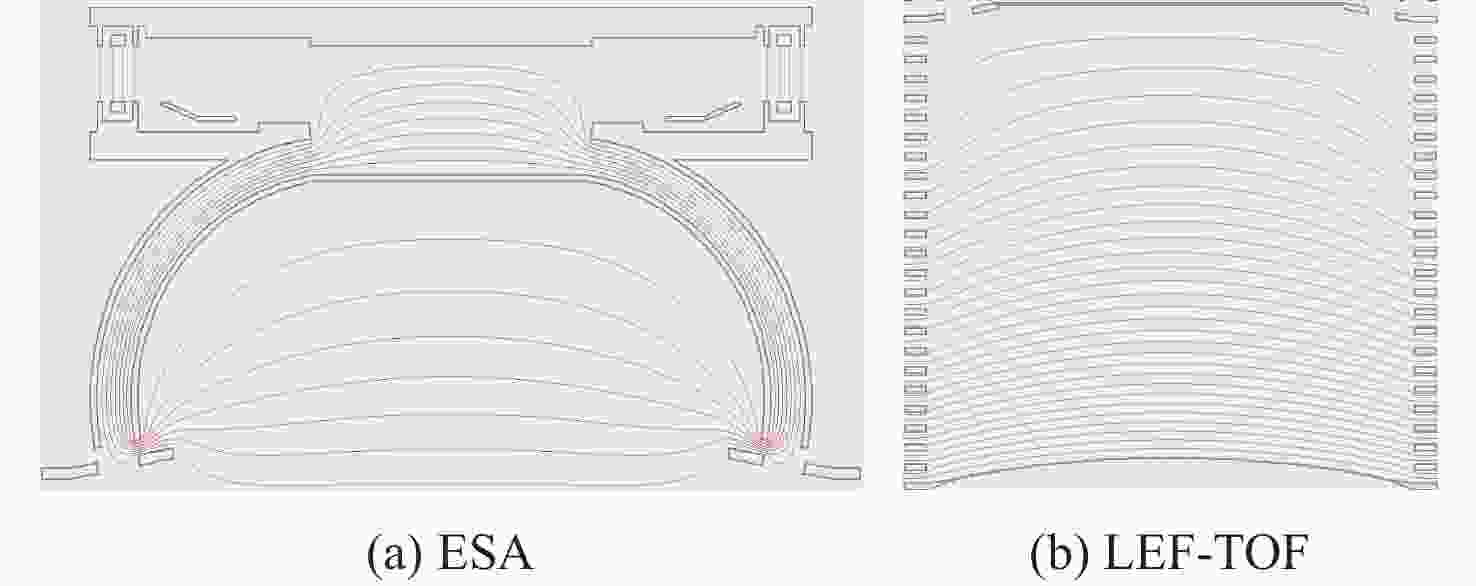
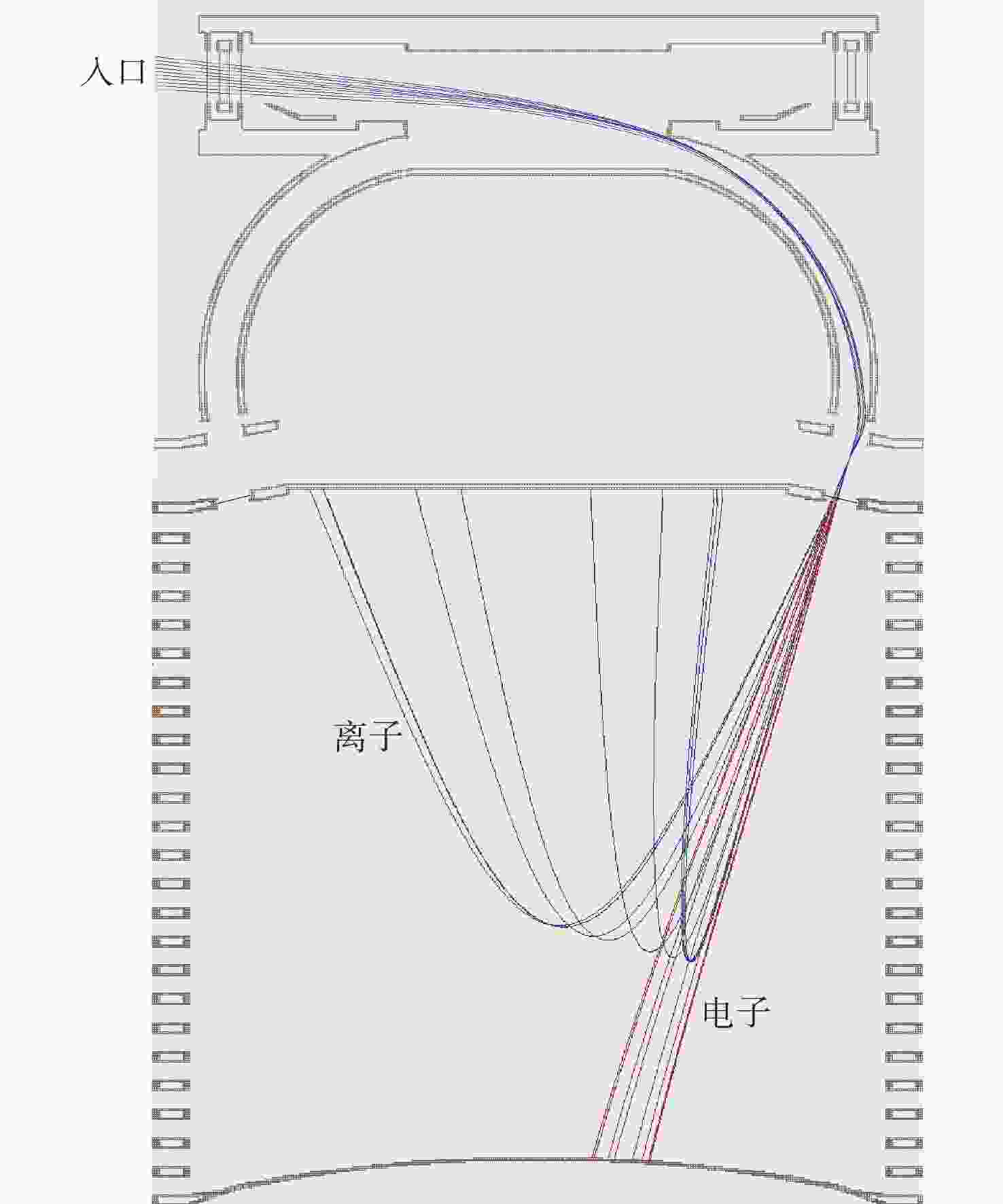
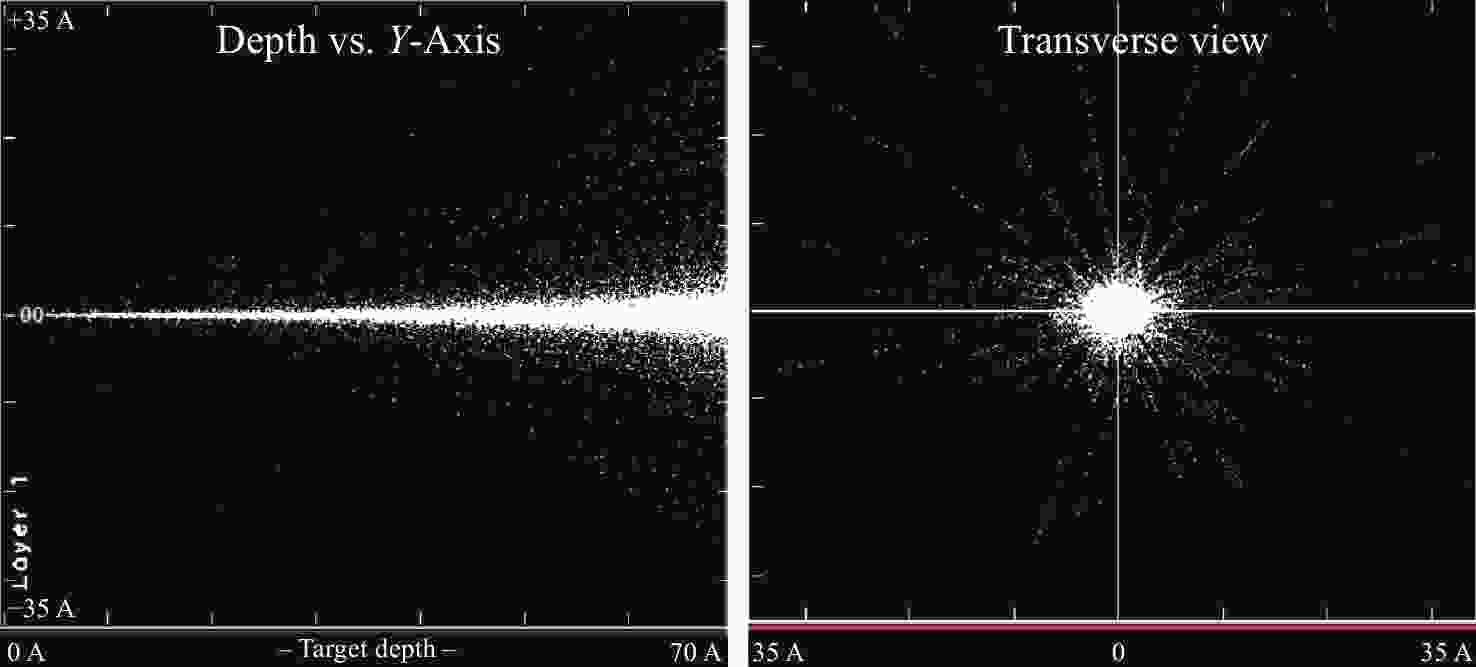
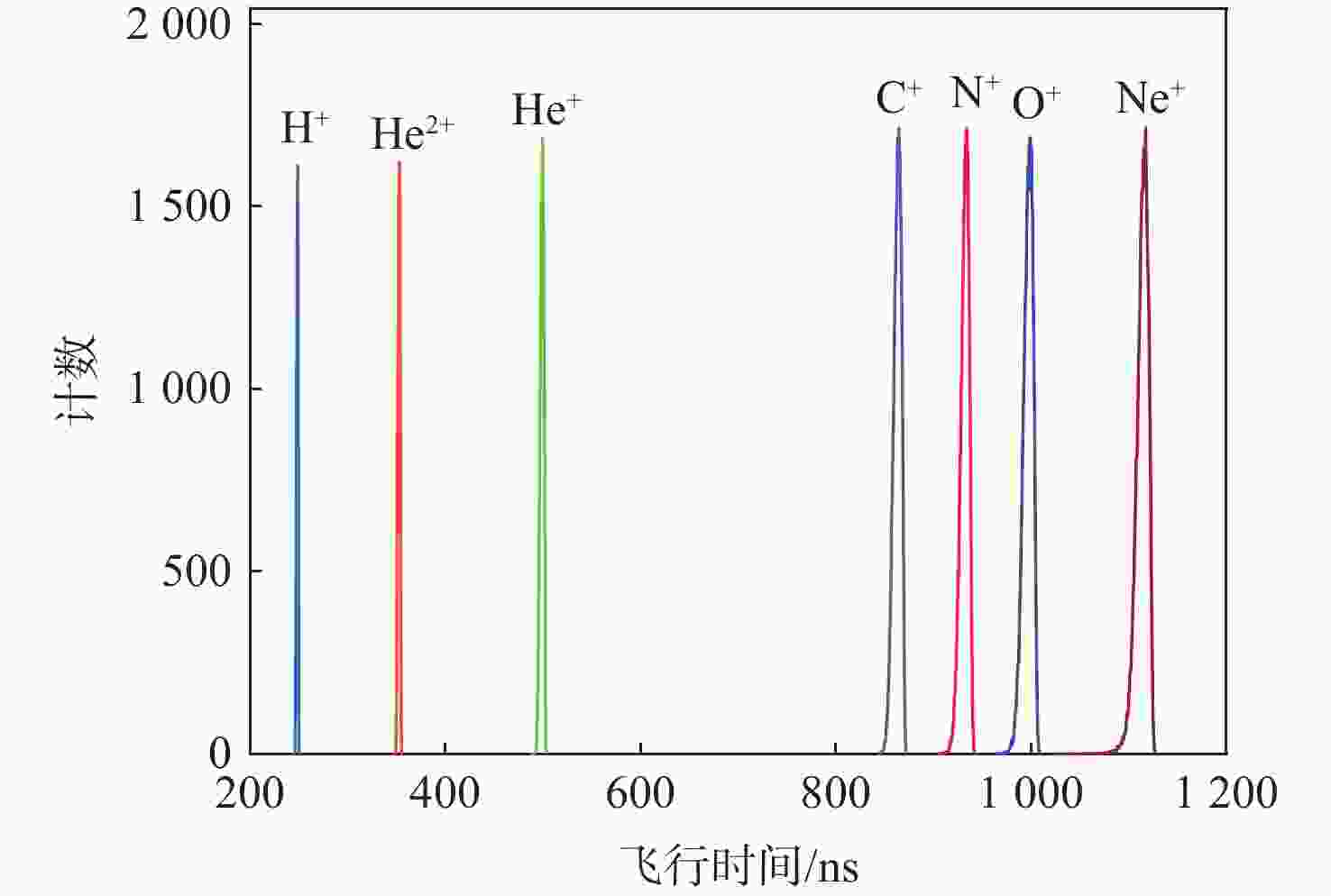
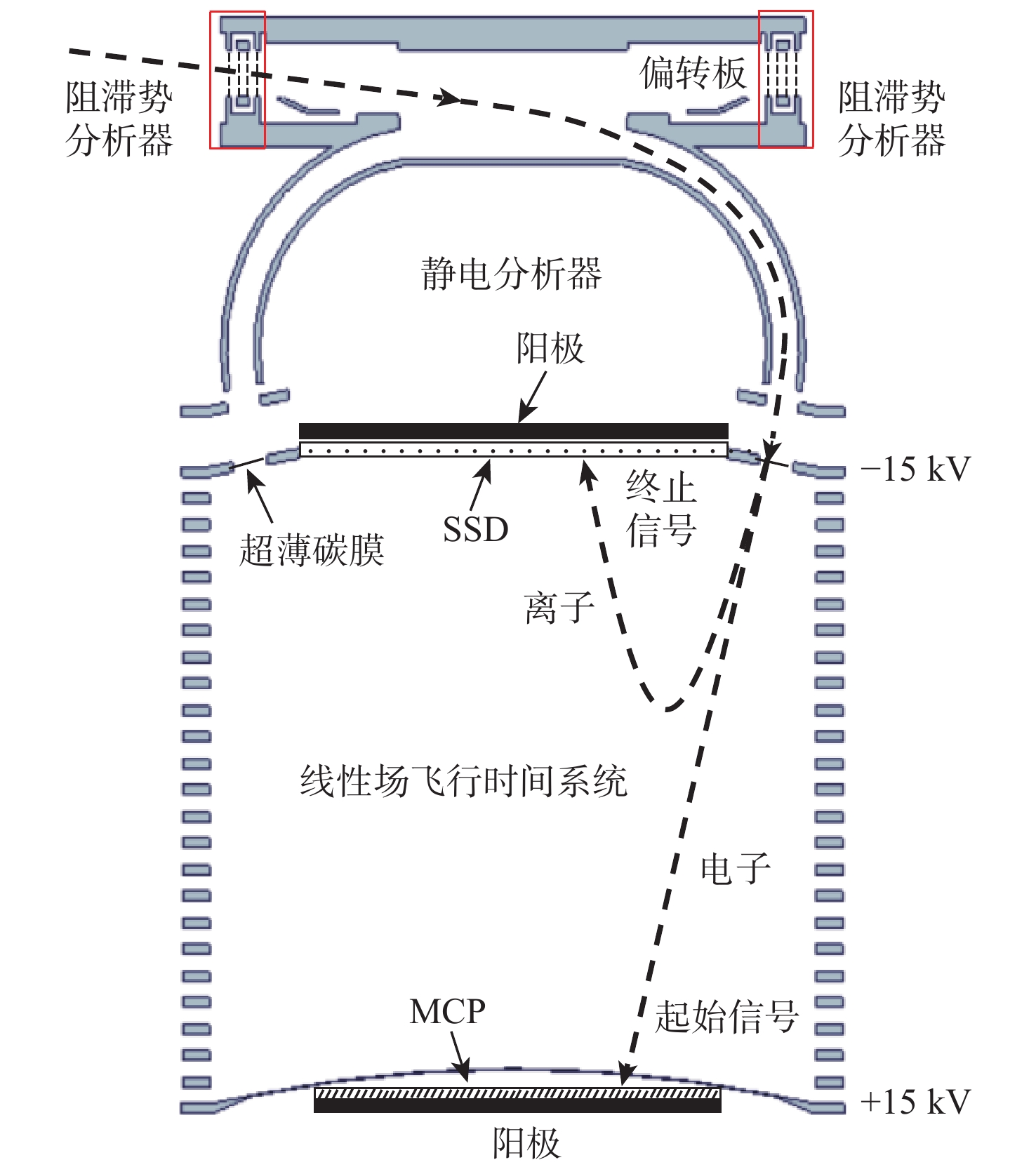
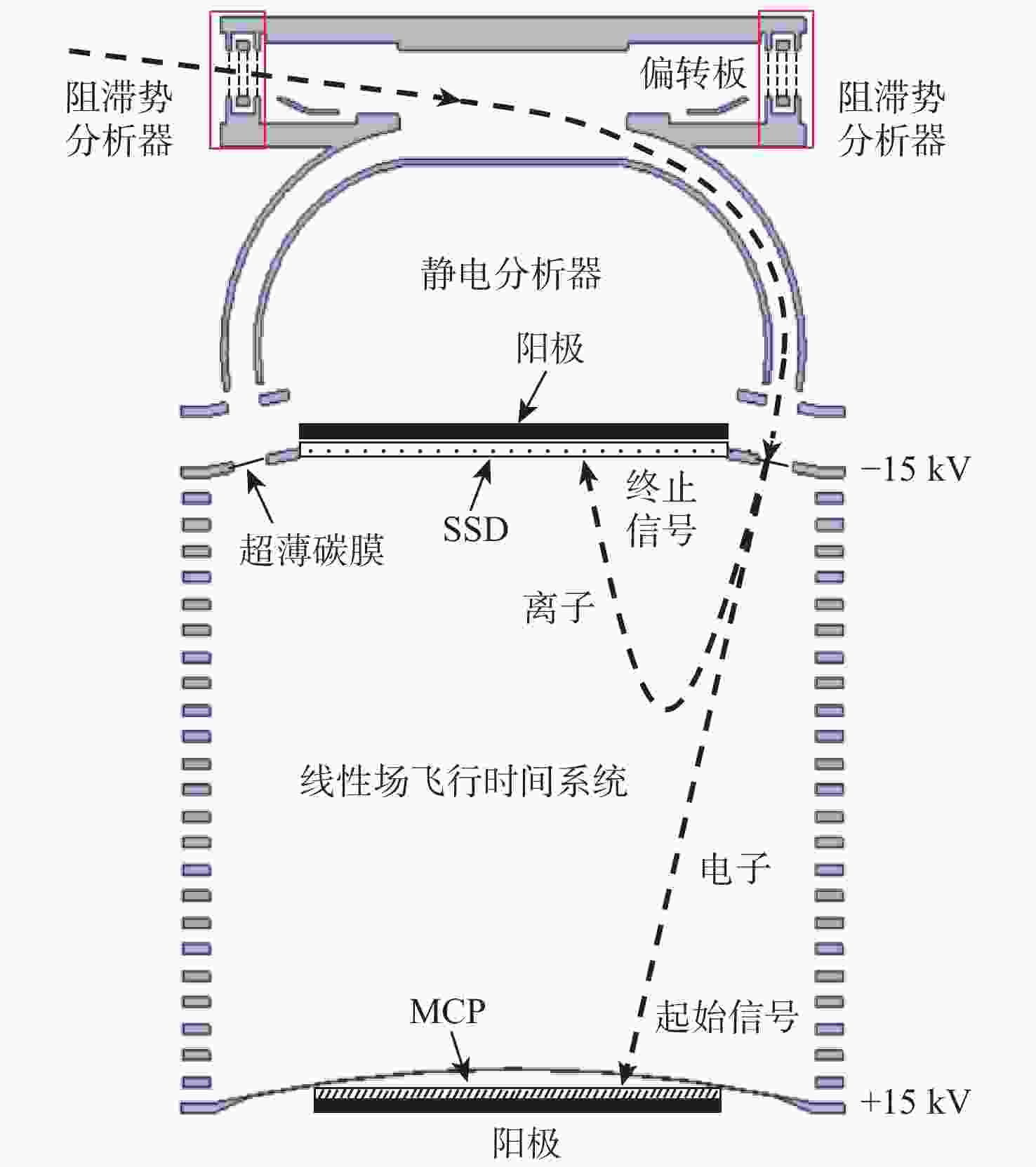
针对外日球层低速、低密度、低温的拾起离子(PUIs)的高分辨探测需求,以带顶盖超环面静电分析器、阻滞势分析器和线性场飞行时间系统为基础设计了一种新型高分辨拾起离子探测器。经过有限元仿真分析,探测器可实现离子(氢)的速度范围15.7 ~1072.2 km/s,密度范围0.0001 ~100 cm−3,温度高于474.9 K的探测,同时可实现典型拾起离子(氢、氦、碳、氮、氧、氖)的成分分辨,质谱分辨率(
M/ ΔM )大于40。Abstract:To enable the high-resolution detection of low-speed, low-density and low-temperature pickup ions (PUIs) in the outer heliosphere, a new high-resolution detector is designed based on the toroidal top-hat electrostatic analyzer, retarding potential analyzer and linear-electric-field time-of-flight analyzer. Using finite element simulation, the velocity range of PUIs (hydrogen) can be detected at 15.7~1072.2 km/s, with the density range being 0.0001~100 cm−3 and the temperature higher than 474.9 K. Component discrimination can also be achieved for typical pickup ions (hydrogen, helium, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and neon), with the mass spectral resolution (
M /ΔM ) larger than 40. -
表 1 拾起离子探测器技术指标仿真结果
Table 1. Simulation specifications of pickup ion detector
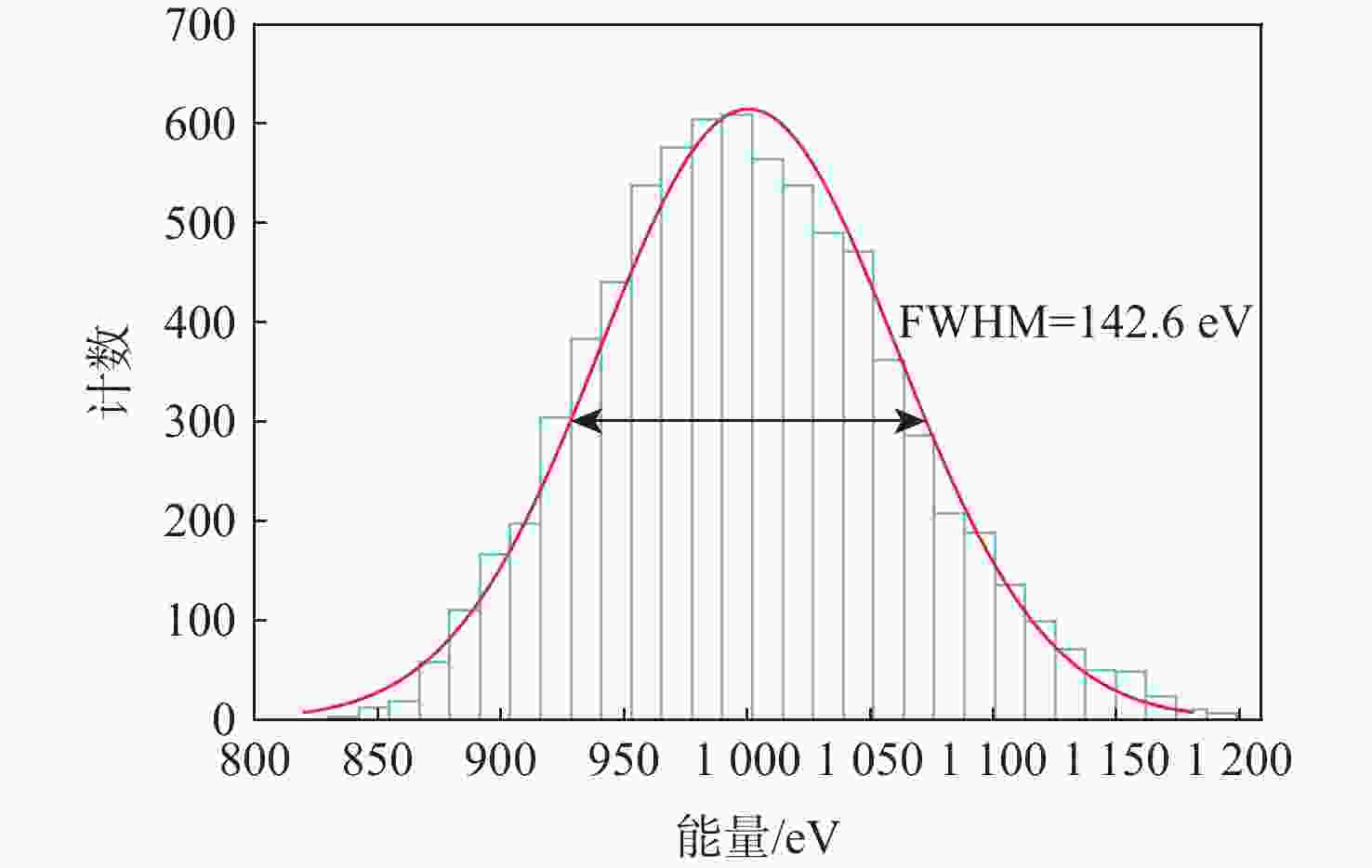
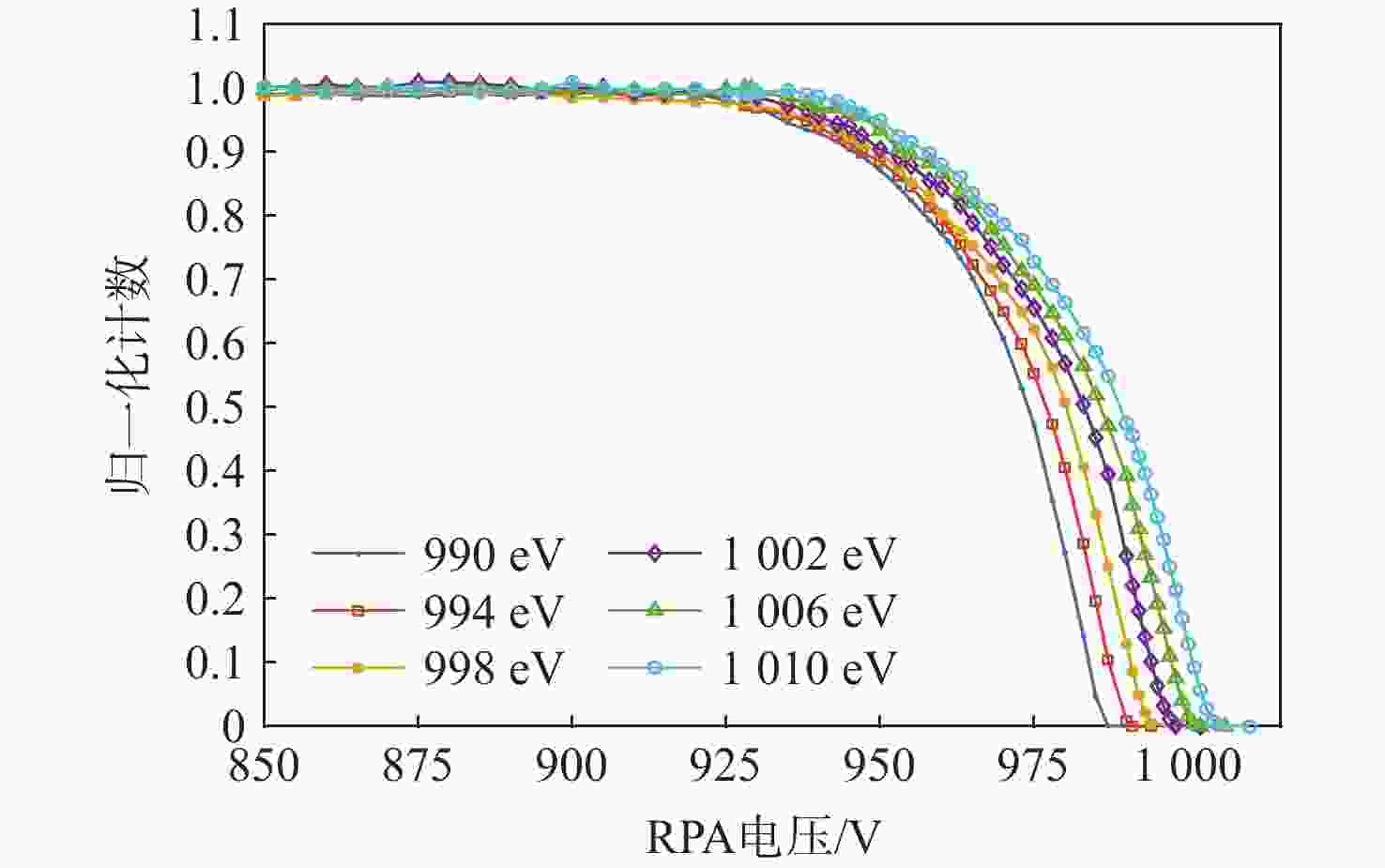
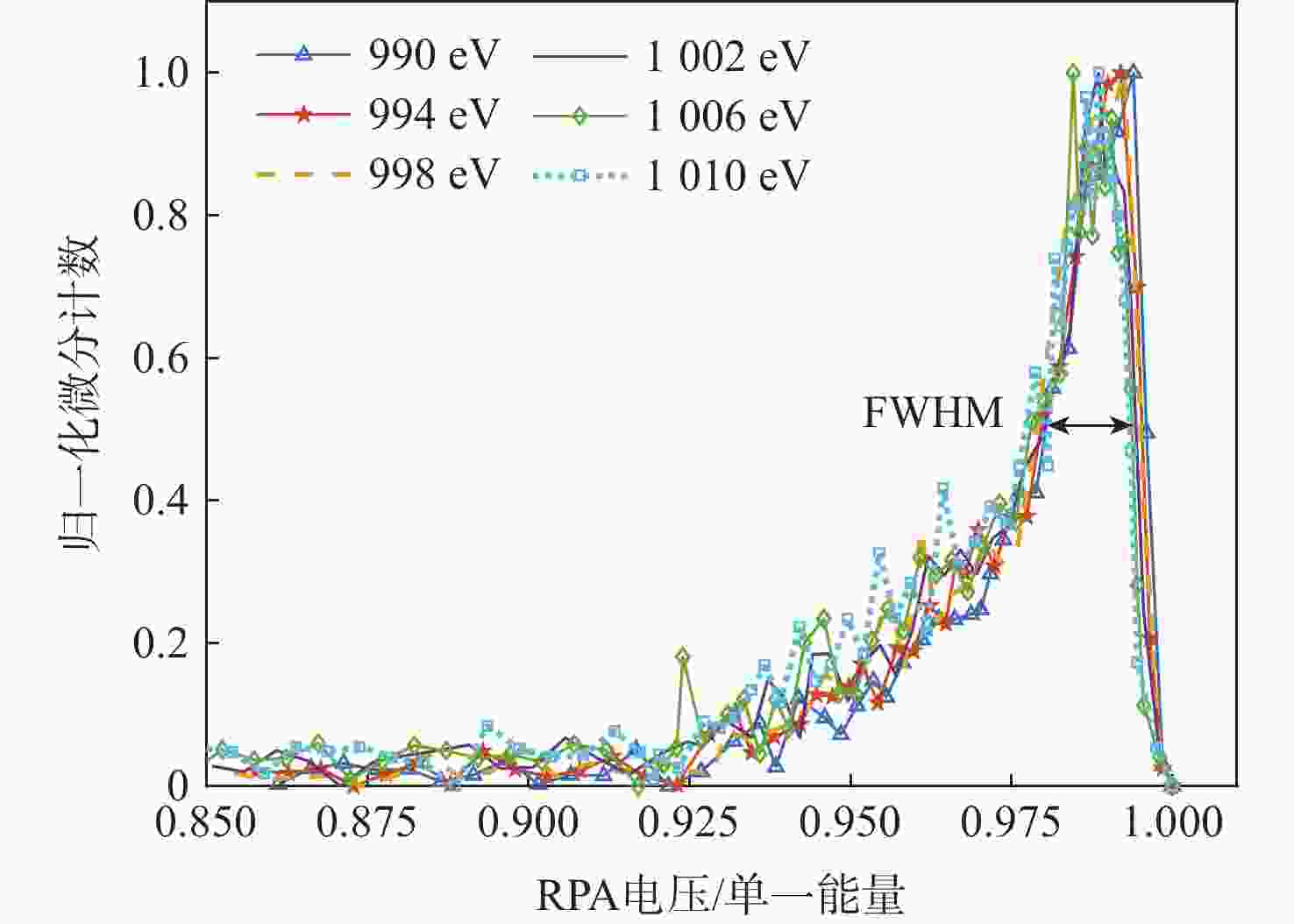
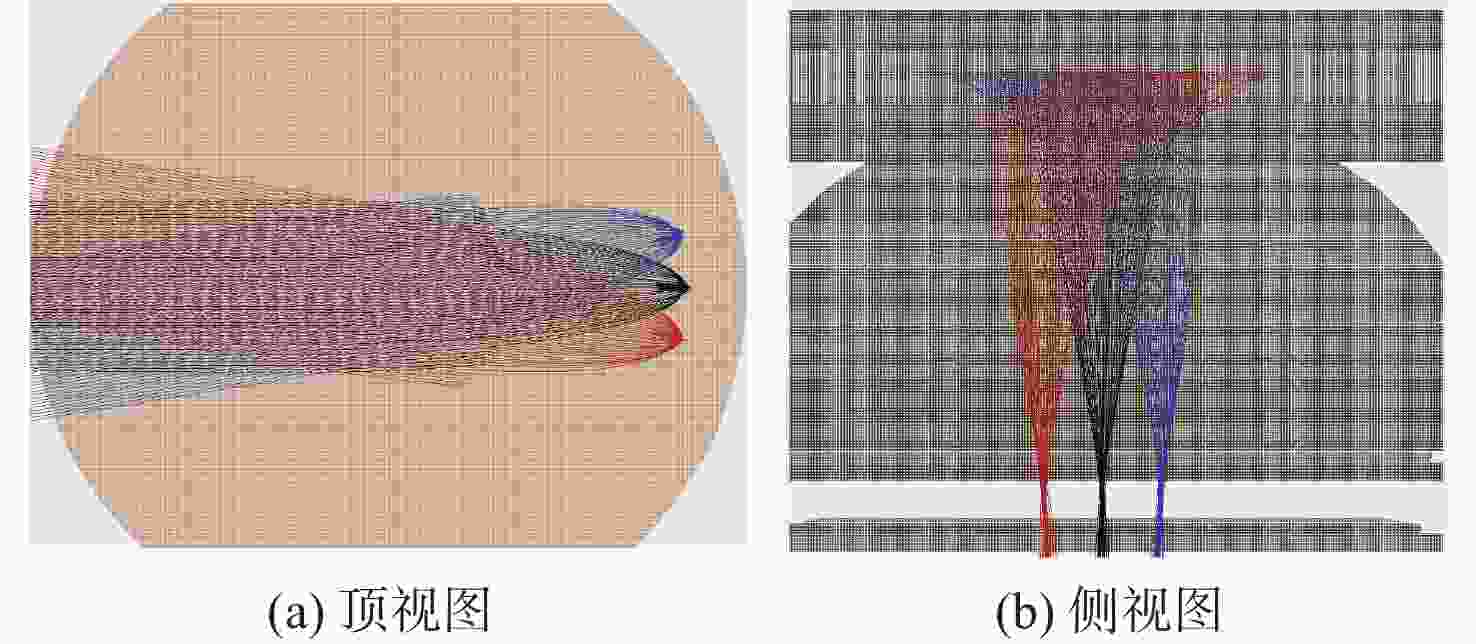
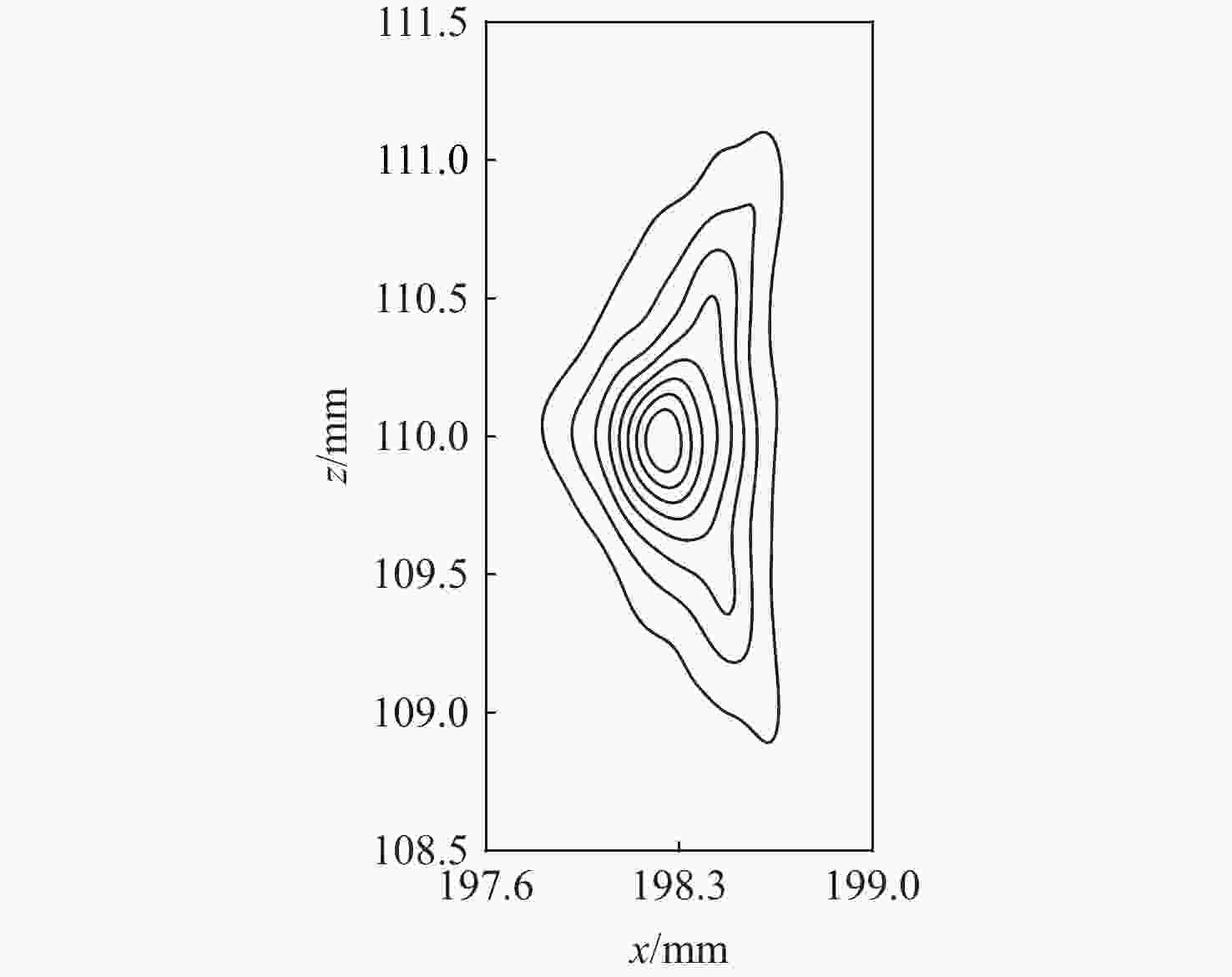
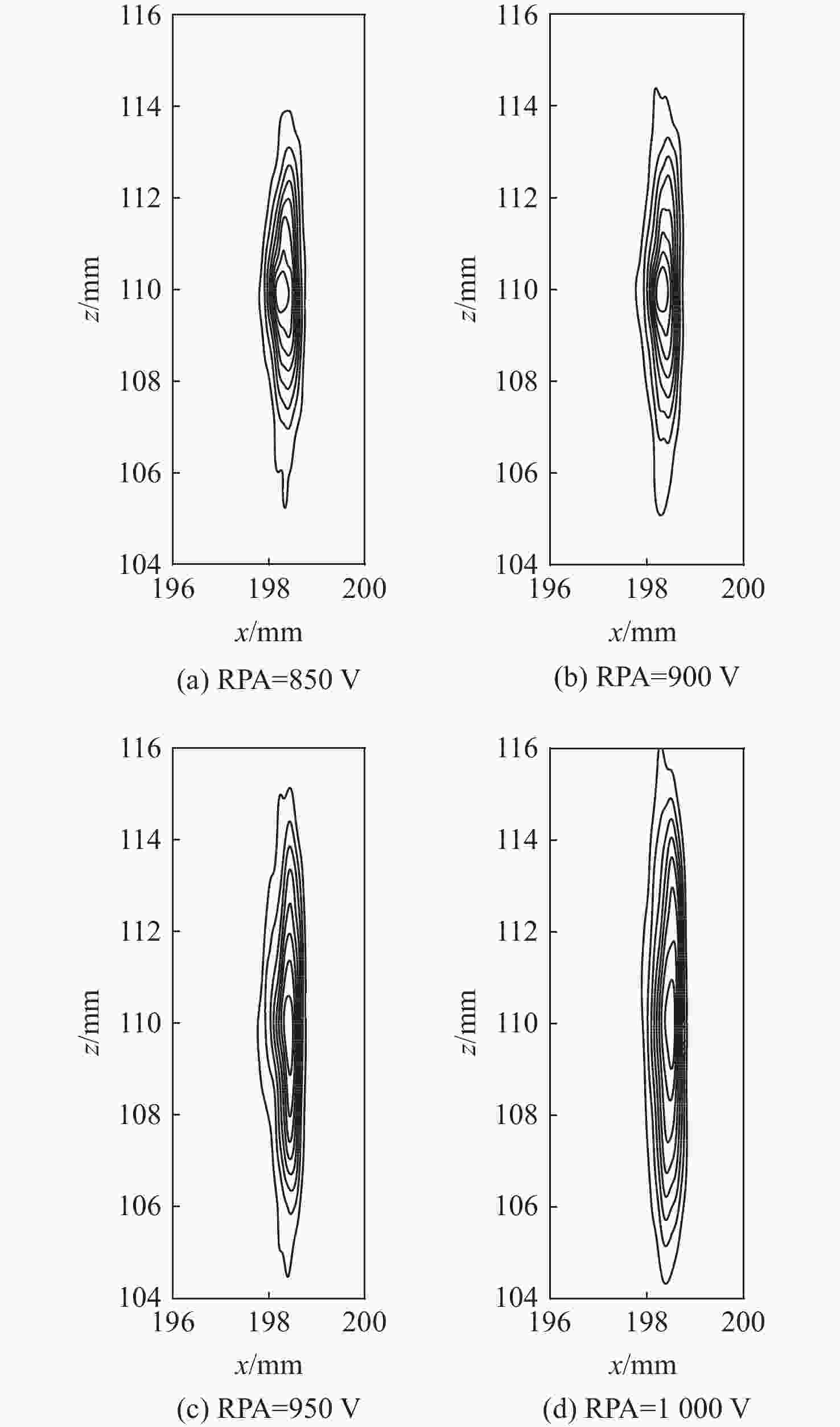
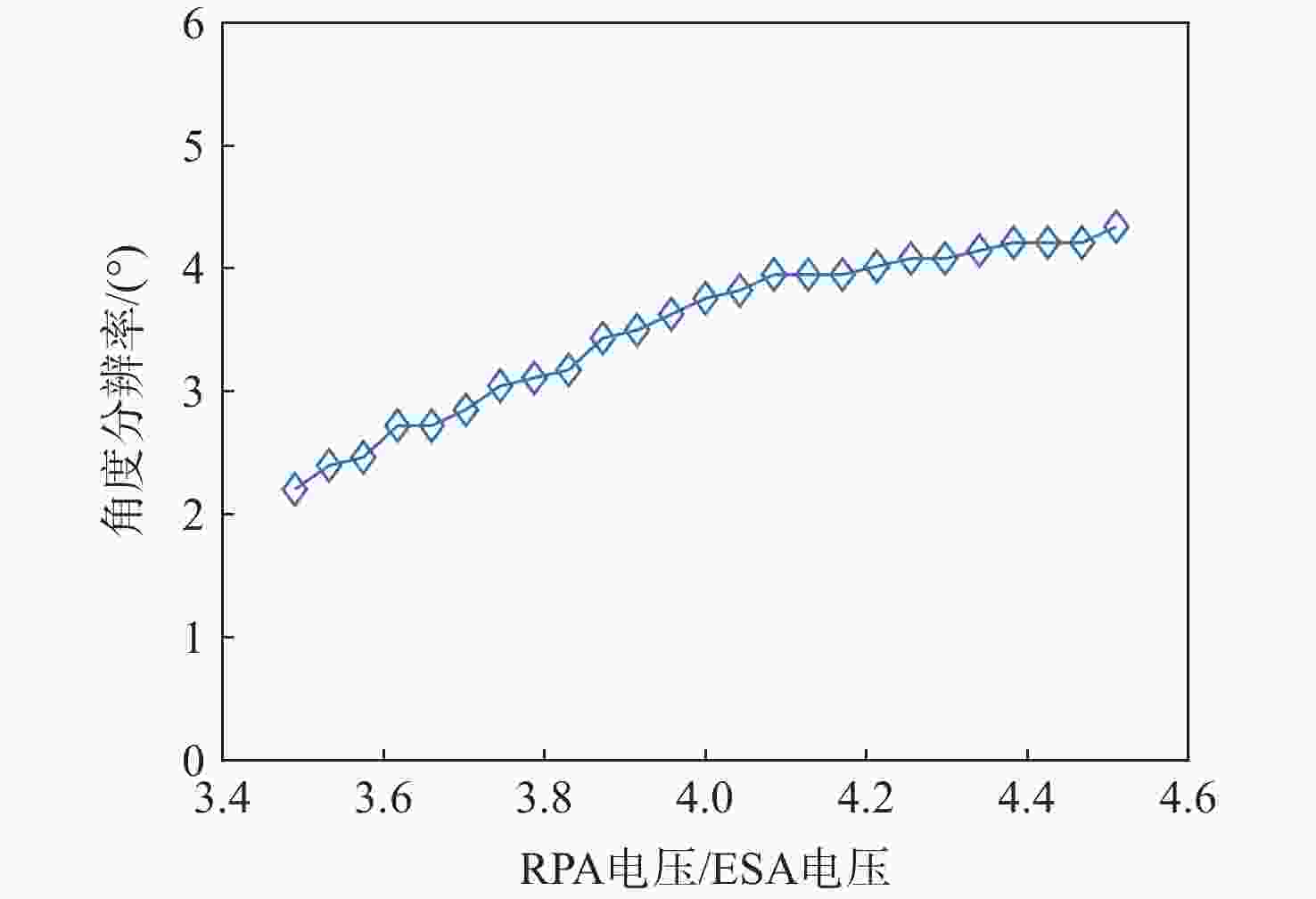
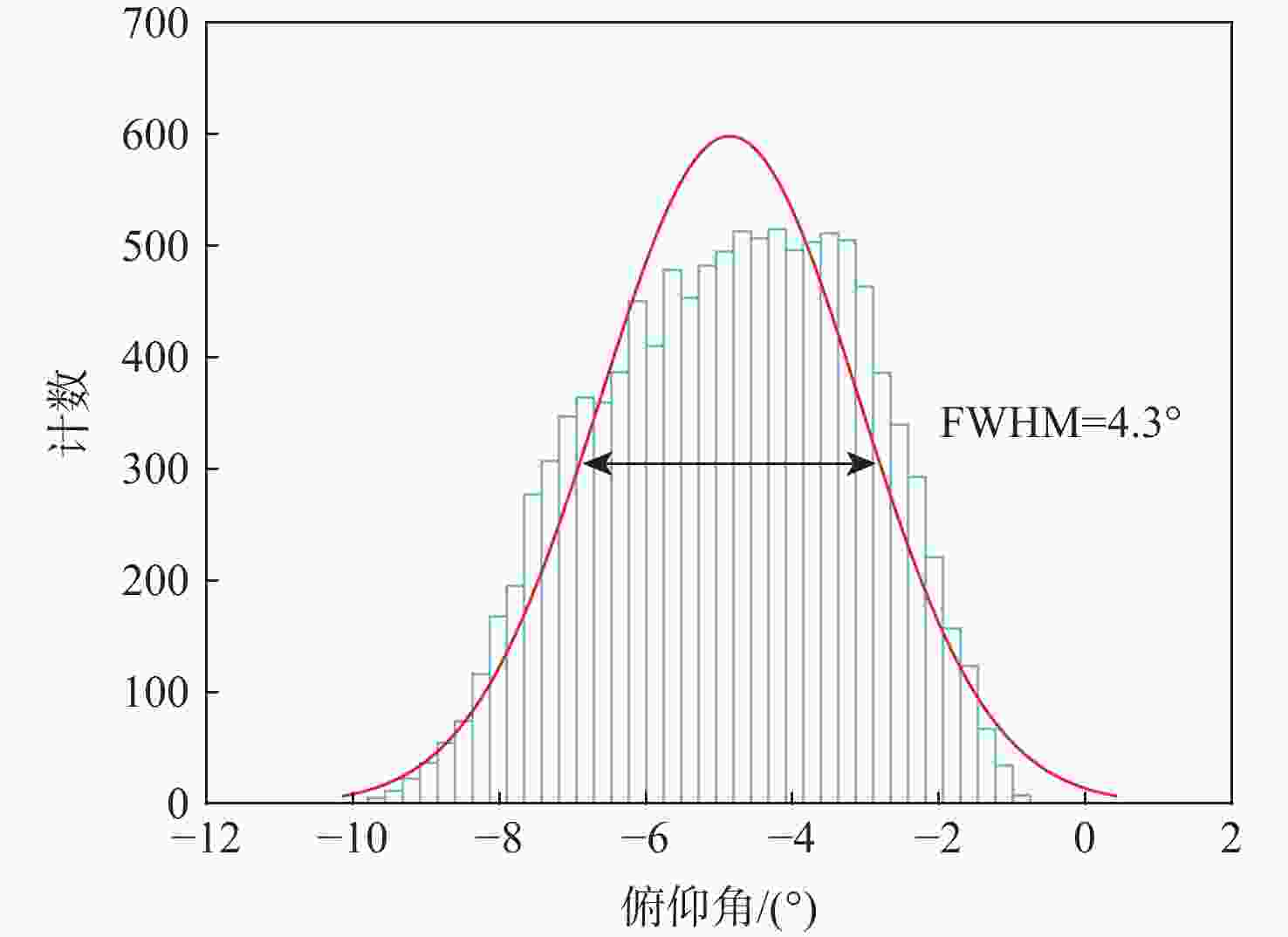
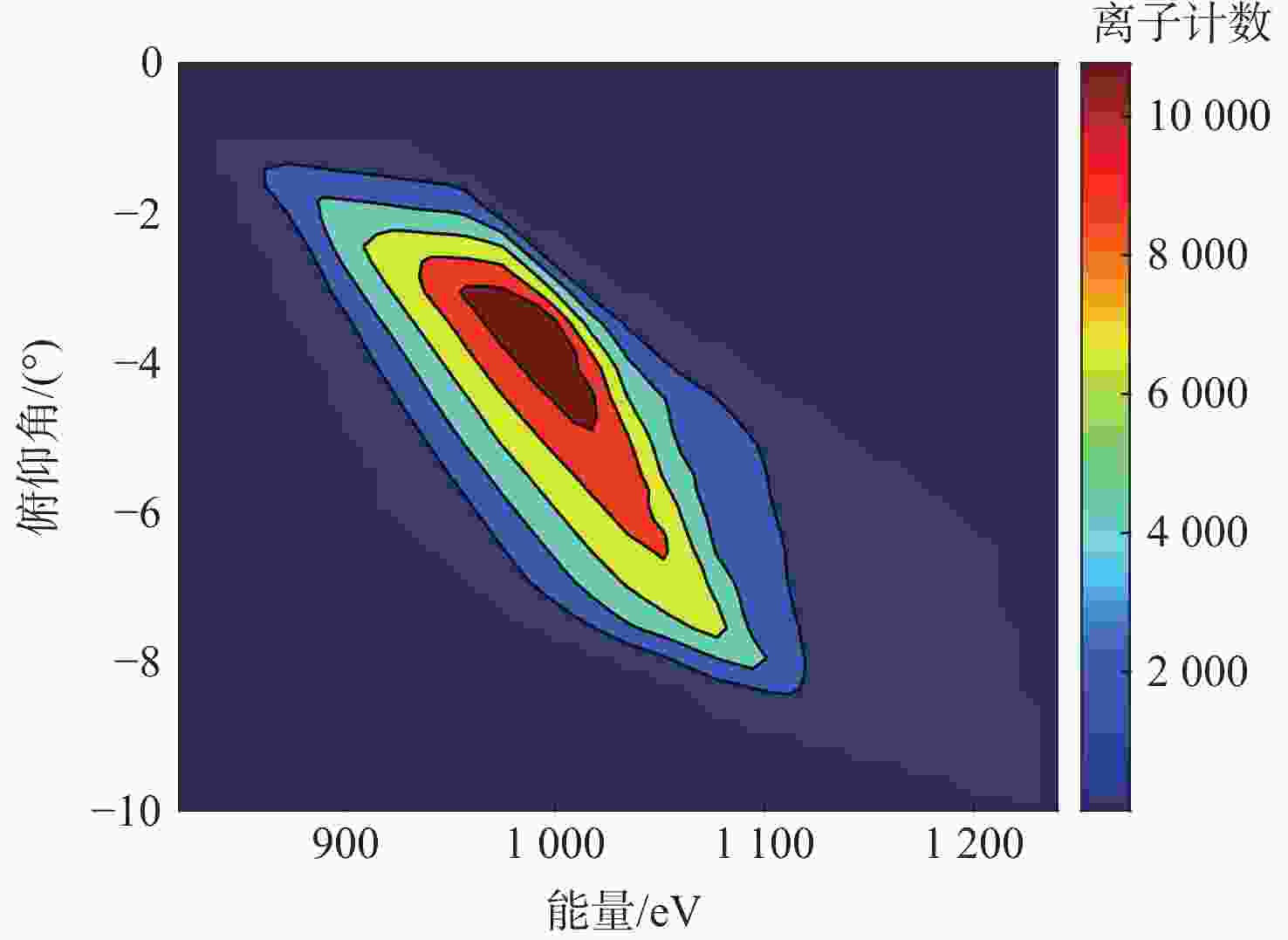
技术指标 仿真结果 能量范围/eV 1.28~6 000 能量分辨率/% ESA(ΔE/E) 14.26 ESA+RPA 1.60 静电分析器常数 4.26 方位角范围/(°) 0~360 俯仰角范围/(°) −6.9~3.6(FWHM) 方位角分辨率/(°) 0.78(固有极限)
15.00(实际设计)几何因子/cm2·sr 0.02096 速度/(km·s−1) 15.7~1072.2 @H+ 密度/cm−3 1×10−4~100 @H+ 温度/K ≥474.9 质谱分辨率 >40 for M=1~20(54.5@H+) -
[1] HOLLICK S J, SMITH C W, PINE Z B, et al. Magnetic waves excited by newborn interstellar pickup ions measured by the Voyager spacecraft from 1 to 45 au. I. wave properties[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2018, 863(1): 75-93. doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/aac83b [2] SWACZYNA P, MCCOMAS D J, ZIRNSTEIN E J. He+ ions comoving with the solar wind in the outer heliosphere[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2019, 875(1): 36-48. doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ab1081 [3] STILWELL D E, JOYCE R M, TEEGARDEN B J, et al. The Pioneer 10/11 and Helios A/B cosmic ray instruments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2007, 22(1): 570-574. [4] BRIDGE H S, BELCHER J W, BUTLER R J, et al. The plasma experiment on the 1977 Voyager Mission[J]. Space Science Review, 1977, 21(3): 259-287. [5] MÖBIUS E, HOVESTADT D, KLECKER B, et al. Direct observation of He+ pick-up ions of interstellar origin in the solar wind[J]. Nature, 1985, 318(6045): 426-429. doi: 10.1038/318426a0 [6] GLOECKLER G, GEISS J, BALSIGER H, et al. The Ulysses solar wind plasma experiment[J]. Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series, 1992, 92(2): 237-265. [7] FRANK L A, ACKERSON K L, LEE J A, et al. The plasma instrumentation for the Galileo Mission[J]. Space Science Reviews, 1992, 60(1-4): 283-304. [8] HOVESTADT D, HILCHENBACH M, BÜRGI A, et al. CELIAS-charge, element and isotope analysis system for SOHO[J]. Solar Physics, 1995, 162(1-2): 441-481. doi: 10.1007/BF00733436 [9] GLOECKLER G, CAIN J, IPAVICH F M, et al. Investigation of the composition of solar and interstellar matter using solar wind and pickup ion measurements with SWICS and SWIMS on the ACE spacecraft[J]. Space Science Reviews, 1998, 86(1-4): 497-539. [10] YOUNG D T, BARRACLOUGH B L, BERTHELIER J J, et al. Cassini plasma spectrometer investigation[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2004, 114(1-4): 1-112. doi: 10.1007/s11214-004-1406-4 [11] MCCOMAS D, ALLEGRINI F, BAGENAL F, et al. The solar wind around Pluto (SWAP) instrument aboard new horizons[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2008, 140(1-4): 261-313. doi: 10.1007/s11214-007-9205-3 [12] GALVIN A B, KISTLER L M, POPECKI M A, et al. The plasma and suprathermal ion composition (PLASTIC) investigation on the STEREO observatories[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2008, 136(1-4): 437-486. doi: 10.1007/s11214-007-9296-x [13] ZHONG J, XIE L, ZHANG H, et al. Chang'E-1 observations of pickup ions near the moon under different interplanetary magnetic field conditions[J]. Planetary and Space Science, 2013, 79-80(1): 56-63. [14] MCFADDEN J P, KORTMANN O, CURTIS D, et al. MAVEN suprathermal and thermal ion compostion (STATIC) instrument[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2015, 195(1-4): 199-256. doi: 10.1007/s11214-015-0175-6 [15] GOLDSTEIN R, BURCH J L, MOKASHI P, et al. The rosetta ion and electron sensor (IES) measurement of the development of pickup ions from comet 67P/churyumov-gerasimenko[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(9): 3093-3099. doi: 10.1002/2015GL063939 [16] MCCOMAS D J, ALEXANDER N, ALLEGRINI F, et al. The jovian auroral distributions experiment (JADE) on the juno mission to Jupiter[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2017, 213(1-4): 547-643. doi: 10.1007/s11214-013-9990-9 [17] ZANK G P. Pickup ion-mediated plasma physics of the outer heliosphere and very local interstellar medium[J/OL]. (2016-07-15)[2021-05-08].https://geoscienceletters. springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s40562-016-0055-2. [18] KALLENBACH R, GEISS J, GLOECKLER G, et al. Pick-up ion measurements in the heliosphere–a review[J]. Astrophysics and Space Science, 2000, 274(1-2): 97-114. [19] GEISS J, GLOECKLER G, MALL U, et al. Interstellar oxygen, nitrogen and neon in the heliosphere[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 1994, 282(3): 924-933. [20] QUINN P, SCHWADRON N, MÖBIUS E, et al. Inner source C+/O+ pickup ions produced by solar wind recycling, neutralization, backscattering, sputtering, and sputtering-induced recycling[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2018, 861(2): 98-110. doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/aac6ca [21] WU Y, FLORINSKI V, GUO X. Interstellar pickup ion production in the global heliosphere and heliosheath[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2016, 832(1): 61-68. doi: 10.3847/0004-637X/832/1/61 [22] ISENBERG P A. Interaction of the solar wind with interstellar neutral hydrogen: Three-fluid model[J/OL]. (1986-09-01)[2021-05-08].https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/JA091iA09p09965. [23] WANG C, RICHARDSON J D. Energy partition between solar wind protons and pickup ions in the distant heliosphere: A three-fluid approach[J/OL]. (2001-12-01)[2021-05-08].https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2001JA000190. [24] WHANG Y C. The global solar wind between 1 AU and the termination shock[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2010, 713(2): 721-730. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/713/2/721 [25] USMANOV A V, GOLDSTEIN M L. A three-dimensional MHD solar wind model with pickup protons[J/OL]. (2006-07-07)[2021-05-08].https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2005JA011533. [26] DELCOURT D, SAITO Y, LEBLANC F, et al. The mass spectrum analyzer (MSA) on board the BepiColombo MMO[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Space Physics, 2016, 121(7): 6749-6762. doi: 10.1002/2016JA022380 [27] YOUNG D T, BAME S J, THOMSEN M F, et al. 2π-radian field-of-view toroidal electrostatic analyzer[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1988, 59(5): 743-751. doi: 10.1063/1.1139821 [28] GILBERT J A, LUNDGREN R A, PANNING M H, et al. An optimized three-dimensional linear-electric-field time-of-flight analyzer[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2010, 81(5): 053302. doi: 10.1063/1.3429941 [29] PUDJORAHARDJO D S, SUPRAPTO S, DARSONO D, et al. Simulation study of electron beam spot size from thermionic electron gun using SIMION 8.1 software[C]//AIP Conference Proceedings. New York: American Institute of Physics, 2018: 020156. [30] SILVA R, BUNDALESKI N, FONSECA A L, et al. 3D-simulation of a Bayard Alpert ionisation gauge using SIMION program[J]. Vacuum, 2019, 164(5): 300-307. [31] PFAFF R F, BOROVSKY J E, YOUNG D T. Measurement techniques in space plasmas: Particles[M]. Washington, D. C. : American Geophysical Union, 2013: 125-140. [32] BERTAUX J L, LALLEMENT R, KURT V G, et al. Characteristics of the local interstellar hydrogen determined from POGNOZ 5 and 6 interplanetary lyman-alpha line profile measurements with a hydrogen absorption cell[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 1985, 150(1): 1-20. -






 下载:
下载: