Remaining useful life prediction method of rolling bearing based on Transformer model
-
摘要:
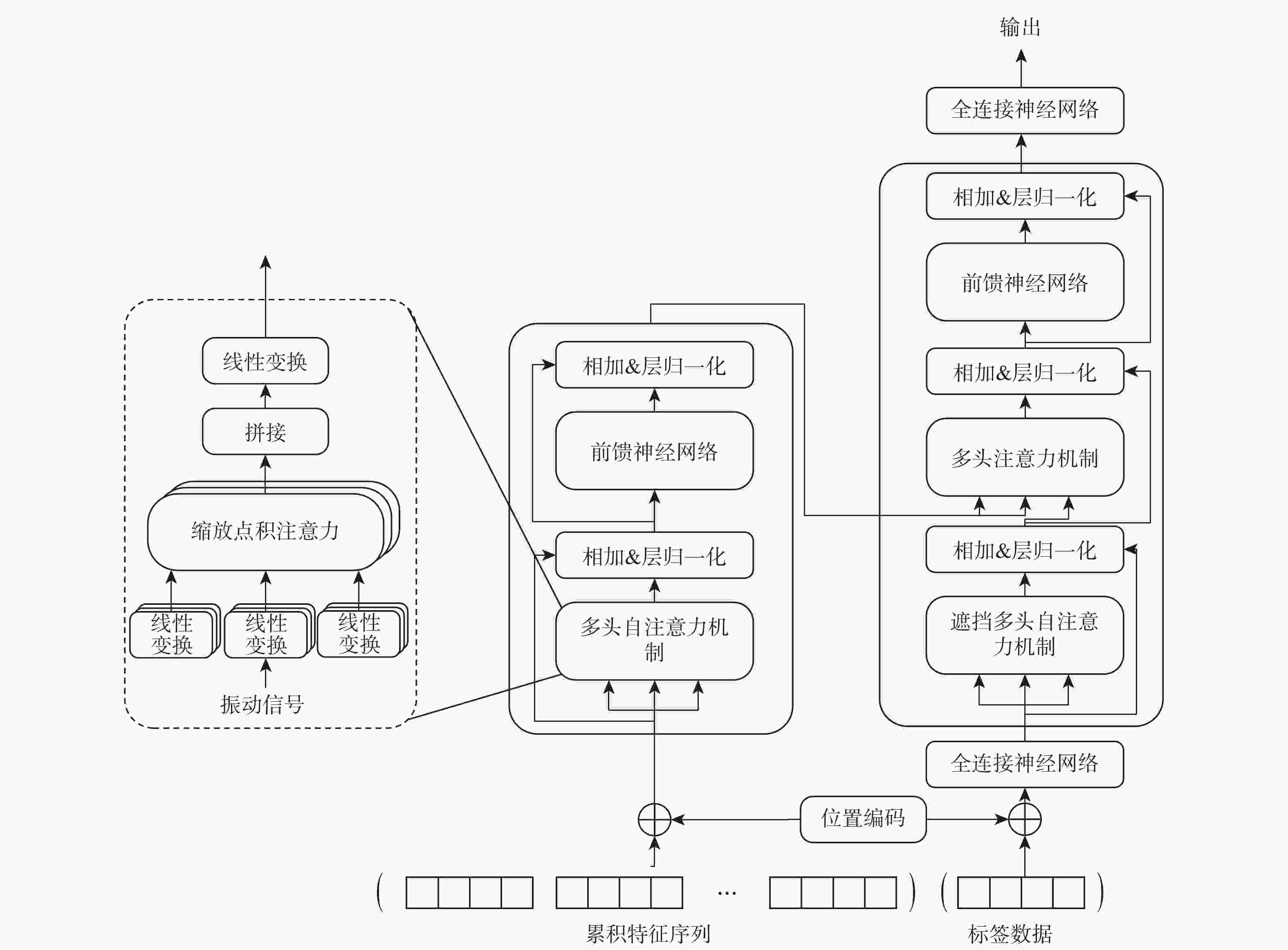
准确的滚动轴承剩余使用寿命(RUL)预测对保证机械安全运行和减小维修损失起着至关重要的作用。为提高滚动轴承RUL预测准确率,提出一种基于Transformer模型的轴承RUL预测方法,充分利用其自注意力机制与编码器-解码器结构的优势,解决轴承RUL预测中序列过长而导致的记忆力退化问题,挖掘出输入特征与轴承RUL之间复杂映射关系。同时,采用三角函数变换与累积变换来修正输入特征的单调性与趋势性,使其能更好地表征滚动轴承的退化过程。在PHM2012数据集上的实验结果表明:所提方法相比于对比方法平均绝对误差分别降低了9.25%、28.63%、34.14%,平均得分分别提高了2.78%、19.79%、29.38%;在XJTU-SY数据集上的实验结果表明,所提方法相比于对比方法均方根误差降低了17.4%,平均得分提高了18.6%,进一步证明了其可行性与优越性。
-
关键词:
- 滚动轴承 /
- 剩余使用寿命预测 /
- Transformer模型 /
- 自注意力机制 /
- 累积变换
Abstract:Accurate rolling bearing remaining useful life (RUL) prediction is extremely important to assure the machine’s safety and decrease damage repair. To improve the accuracy of rolling bearing RUL prediction, proposed a bearing RUL prediction method based on the Transformer model, made full use of its self-attention mechanism and the advantages of encoder-decoder structure, solved the memory degradation problem caused by the too-long sequence in bearing RUL prediction, found out the dependent relationship between the input feature and the bearing degradation degree. Meanwhile, trigonometric function transform and cumulative transform are used to correct the feature's monotony and tendency, representing the rolling bearing degradation process better. The average absolute error of RUL prediction based on the Transformer model is reduced by 9.25%, 28.63%, and 34.14%, while the average ss were increased by 2.78%, 19.79%, and 29.38%, according to experimental results on the PHM2012 dataset. Experimental results on the XJTU-SY dataset showed that compared with other prediction methods, the proposed model is reduced by 17.4%, and the average ss were increased by 18.6%, which indicates higher feasibility and superiority.
-
Key words:
- rolling bearing /
- remaining useful life /
- Transformer model /
- self-attention /
- cumulative operation
-
表 1 特征和相应的计算公式
Table 1. Feature and corresponding formulas
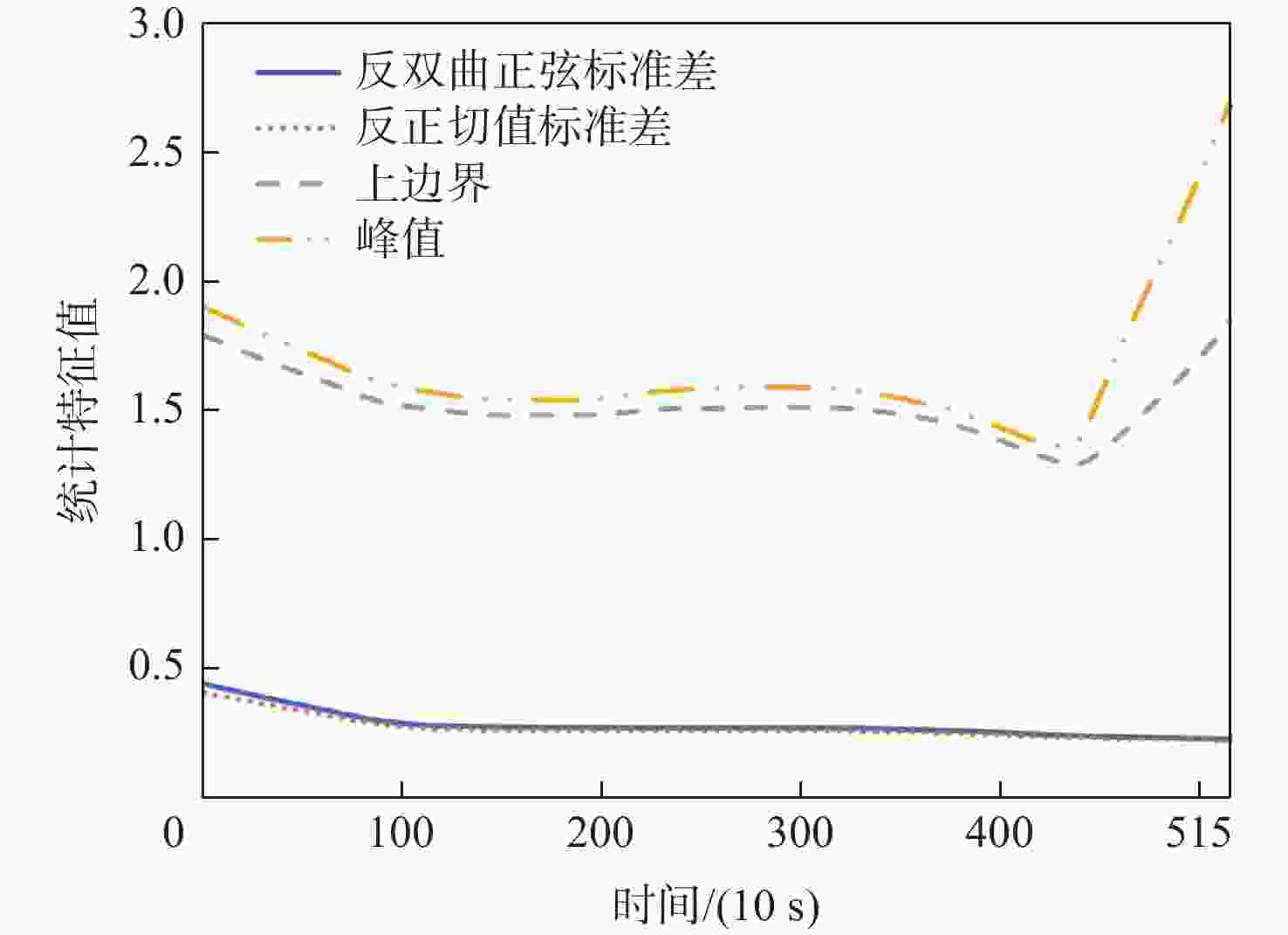
特征 公式 反正切值标准差 $ {X_{{\text{atan}}}} = \sigma \left( {\ln [{x_i} + \sqrt {{x_i}^2 + 1} ]} \right) $ 反双曲正弦标准差 ${X_{ {\text{asinh} } } } = \sigma \left( {\dfrac{i}{2}\ln \left( {\dfrac{ {i + {x_i} } }{ {i - {x_i} } } } \right)} \right)$ 标准差 ${X_{ {\text{sd} } } } = \sqrt {\dfrac{1}{n}{ {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {\left( { {x_i} - \mu } \right)^2} }} }$ 峰值 ${X_{\text{P} } } = {\rm{max}}\left| X \right|$ 峰峰值 ${X_{ {\text{p - p} } } } = {\rm{max}}\left( { {x_i} } \right) - {\rm{min}}\left( { {x_i} } \right)$ 均方根 ${X_{ {\text{rms} } } } = \sqrt {\dfrac{1}{n}{ {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n { {x_i}^2 } }} }$ 上边界 ${X_{ {\text{upper} } } } = {\rm{max} }\left( { {x_i} } \right) + \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{ { {\rm{max} }\left( { {x_i} } \right) - {\rm{min}}\left( { {x_i} } \right)} }{ {n - 1} }$ 脉冲因子 ${X_{ {\text{if} } } } = \dfrac{ { {X_{\text{P} } } } }{ {\dfrac{1}{n}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {\left| { {x_i} } \right|} } }$ 峰值因子 ${X_{ {\text{cf} } } } = \dfrac{ { {X_{\text{P} } } }}{ { {X_{ {\text{rms} } } } } }$ 裕度系数 ${X_{ {\text{mf} } } } = \dfrac{ { {X_{\text{P} } } } }{ { { {\left( {\dfrac{1}{n}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {\sqrt {\left| { {x_i} } \right|} } } \right)}^2} } }$ 能量 ${X_{\text{e} } } = {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n { {x_i} } ^2}$ 峭度 ${X_{\text{k} } } = \dfrac{ {\dfrac{1}{n}{ {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {\left( { {x_i} - \mu } \right)^4} }} } }{ { {X_{ {\rm{sd} } ^4} } } }$ 平均绝对值 ${X_{ {\text{mav} } } } = \dfrac{1}{n}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {\left| { {x_i} } \right|}$ 偏度 ${X_{ {\text{sk} } } } = \dfrac{ {\dfrac{1}{n}{ {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {\left( { {x_i} - \mu } \right)^3} }} } }{ { {X_{ {\text{sd} } } }^3} }$ 表 2 PHM2012数据集工况信息
Table 2. Operating condition information of PHM2012 dataset
工况 径向力/N 转速/(r·min−1) 训练集 测试集 工况1 4000 1800 轴承1_1、轴承1_2 轴承1_3、轴承1_4、轴承1_5 轴承1_6 轴承1_7 工况2 4200 1650 轴承2_1、轴承2_2 轴承2_3、轴承2_4、轴承2_5、轴承2_6、轴承2_7 工况3 5000 1500 轴承3_1、轴承3_2 轴承3_3 表 3 累积变换前后比较
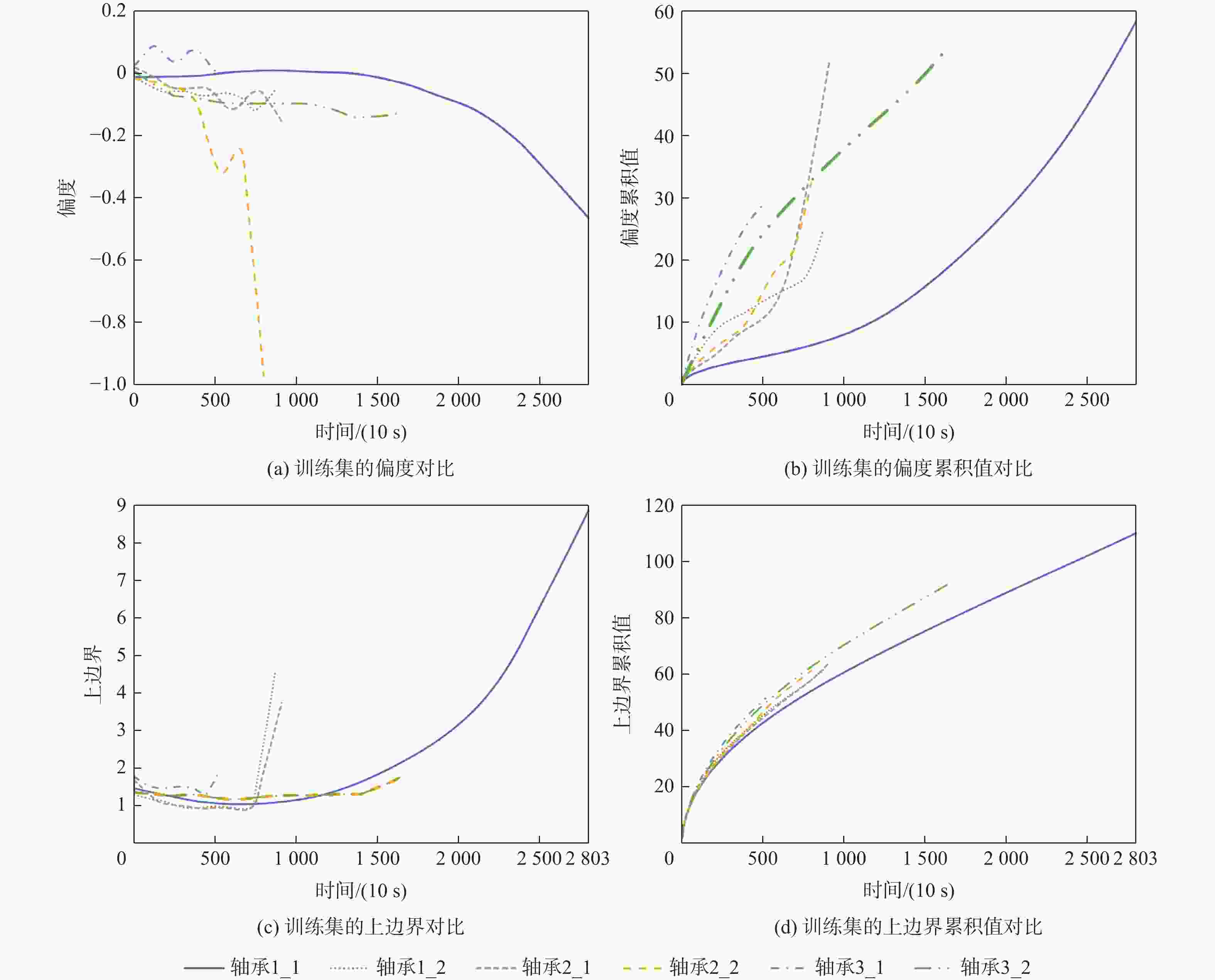
Table 3. Comparison before and after cumulative transformation
传统特征 单调性 趋势性 累积特征 单调性 趋势性 反双曲正弦标准差 0.57 0.71 反双曲正弦标准差 1 1 反正切值标准差 0.58 0.76 反正切值标准差 1 1 能量 0.50 0.64 能量 1 1 偏度 0.60 0.83 偏度 1 1 峭度 0.39 0.80 峭度 1 1 上边界 0.26 0.36 上边界 1 1 均方根 0.50 0.61 均方根 1 1 脉冲因子 0.54 0.78 脉冲因子 1 1 峰值因子 0.52 0.75 峰值因子 1 1 峰峰值 0.27 0.37 峰峰值 1 1 裕度系数 0.51 0.77 裕度系数 1 1 标准差 0.50 0.60 标准差 1 1 平均绝对值 0.59 0.70 平均绝对值 0.87 0.96 表 4 实验数据(PHM2012轴承数据集)
Table 4. Experimental data(PHM2012 Datasets)
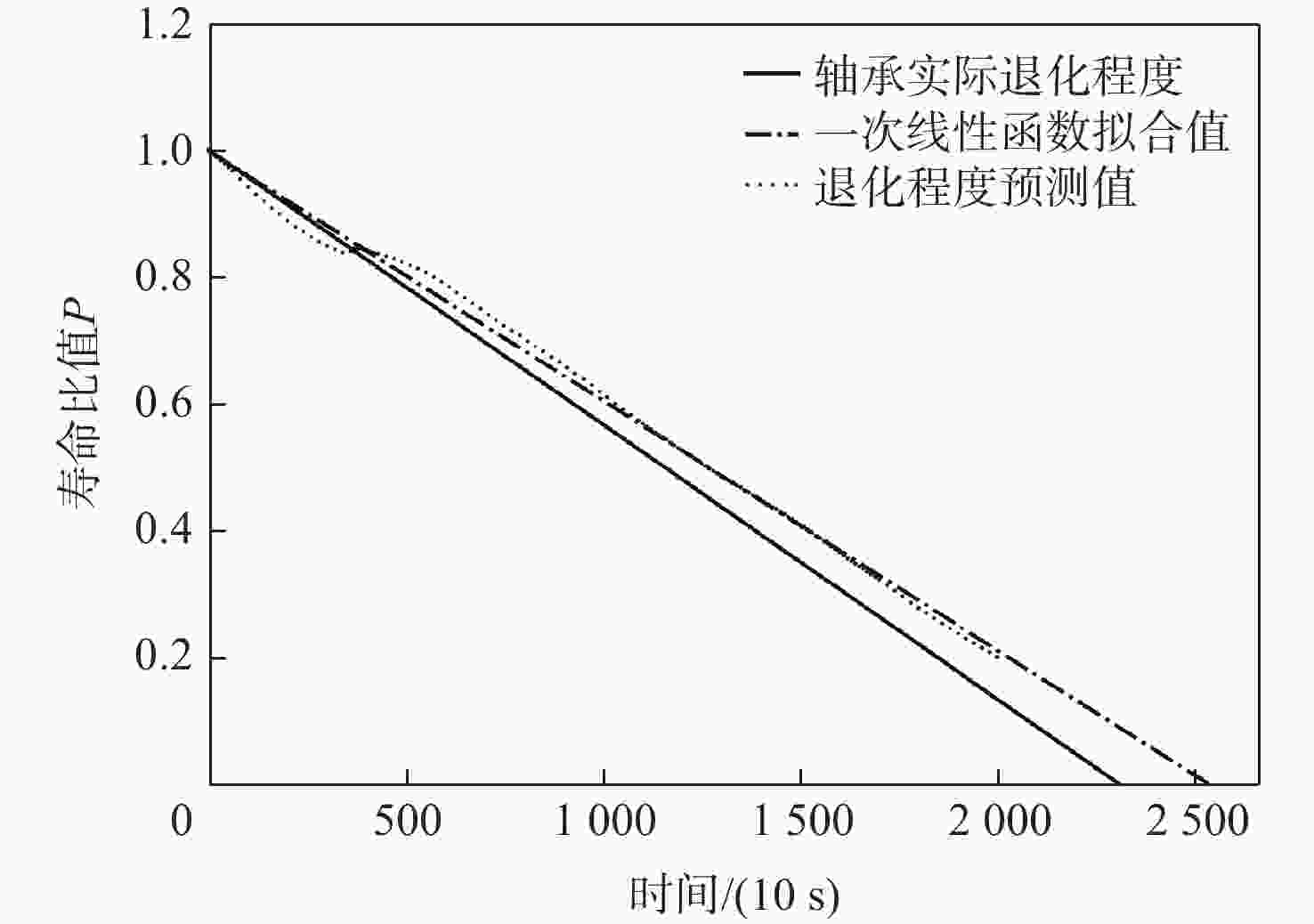
数据集划分 轴承编号 非全寿命时间/(10s) 全寿命时间/
(10s)训练集 1_1 2803 1_2 871 2_1 911 2_2 797 3_1 515 3_2 1637 测试集 1_3 1802 2375 1_4 1139 1428 1_5 2302 2463 1_6 2302 2448 1_7 1502 2259 2_3 1202 1955 2_4 612 751 2_5 2002 2311 2_6 572 701 2_7 172 230 3_3 352 434 表 5 运行速度对比结果
Table 5. Running speed comparison results
预测模型 运行时间/ms Transformer 2.15 LSTM 3.47 GRU 3.33 BiLSTM 4.00 表 6 所提方法与其他2种方案的构成
Table 6. Composition of the proposed prediction method and other two schemes
预测方法 特征提取模型 预测模型 所提方法 累积特征 编码器-解码器结构
Transformer模型方案1 经典统计特征 编码器-解码器结构
Transformer模型方案2 累积特征 单编码器结构
Transformer模型表 7 所提方法和对比方法在PHM 2012数据集RUL预测结果
Table 7. The RUL prediction results of the proposed method and comparison method in the PHM 2012 dataset
轴承型号 误差El 所提方法 方案1 方案2 文献[11] 文献[25] 文献[26] 1_3 74.17 −4131 67.66 7.62 54.73 −1.04 1_4 −0.69 23.31 −98.81 69.77 38.48 85.81 1_5 9.9 336.75 10.45 −72.57 −99.4 −278.2 1_6 −12.33 102.39 −7.18 0.93 −120.0 19.18 1_7 83.62 132.32 82.48 85.99 70.65 −7.13 2_3 61.35 90.14 65.08 81.24 75.53 10.49 2_4 5.06 −196.3 14.49 9.04 19.81 51.8 2_5 −70.22 60.04 −53.99 28.19 8.2 28.8 2_6 0.78 102.82 5.13 24.92 17.87 −20.93 2_7 44.83 77.44 47.03 19.06 1.69 44.83 3_3 1.22 118.27 −1.23 2.09 2.93 −3.66 表 9 实验方案
Table 9. The experimental scheme
径向力/N 转速/(r·min−1) 训练集 测试集 11000 2250 轴承2_1
轴承2_2
轴承2_3轴承2_4
轴承2_510000 2400 轴承3_1
轴承3_2
轴承3_3轴承3_4
轴承3_5表 10 XJTU-SY数据集RUL预测结果与比较
Table 10. RUL prognostics results and comparisons on XJTU-SY dataset
模型 RMSE 平均得分 DSCN 0.0749 0.4165 RCNN 0.0803 0.3586 RVM 0.1082 0.2911 TCN-RSA 0.0659 0.4803 所提方法 0.0544 0.5697 -
[1] 刘建昌, 权贺, 于霞, 等. 基于参数优化VMD和样本熵的滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(3): 808-819. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190345LIU J C, QUAN H, YU X, et al. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on parameter optimization VMD and sample entropy[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(3): 808-819(in Chinese). doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190345 [2] 张振良, 刘君强, 黄亮, 等. 基于半监督迁移学习的轴承故障诊断方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(11): 2291-2300. ZHANG Z L, LIU J Q, HUANG L, et al. A bearing fault diagnosis method based on semi-supervised and transfer learning[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(11): 2291-2300 (in Chinese). [3] 田利梅, 龚梦彤, 唐荻音, 等. 基于功耗残差的航天器CMG退化特征提取方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(10): 1899-1905. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2021.0060TIAN L M, GONG M T, TANG D Y, et al. Degradation indicator extraction for aerospace CMG based on power consumption analysis[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(10): 1899-1905(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2021.0060 [4] 袁烨, 张永, 丁汉. 工业人工智能的关键技术及其在预测性维护中的应用现状[J]. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(10): 2013-2030.YUAN Y, ZHANG Y, DING H. Research on key technology of industrial artificial intelligence and its application in predictive maintenance[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(10): 2013-2030(in Chinese). [5] LEI Y G, LI N P, GUO L, et al. Machinery health prognostics: A systematic review from data acquisition to RUL prediction[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 104: 799-834. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2017.11.016 [6] 王冰, 李洪儒, 许葆华. 基于多尺度形态分解谱熵的电机轴承预测特征提取及退化状态评估[J]. 振动与冲击, 2013, 32(22): 124-128.WANG B, LI H R, XU B H. Motor bearing forecast feature extracting and degradation status identification based on multi-scale morphological decomposition spectral entropy[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2013, 32(22): 124-128 (in Chinese). [7] 李洪儒, 于贺, 田再克, 等. 基于二元多尺度熵的滚动轴承退化趋势预测[J]. 中国机械工程, 2017, 28(20): 2420-2425. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2017.20.005LI H R, YU H, TIAN Z K, et al. Degradation trend prediction of rolling bearings based on two-element multiscale entropy[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 28(20): 2420-2425(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2017.20.005 [8] REN L, LIU Y X, WANG X K, et al. Cloud–edge-based lightweight temporal convolutional networks for remaining useful life prediction in IIoT[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(16): 12578-12587. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3008170 [9] 杨宇, 张娜, 程军圣. 全参数动态学习深度信念网络在滚动轴承寿命预测中的应用[J]. 振动与冲击, 2019, 38(10): 199-205. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2019.10.030YANG Y, ZHANG N, CHENG J S. Global parameters dynamic learning deep belief networks and its application in rolling bearing life prediction[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2019, 38(10): 199-205(in Chinese). doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2019.10.030 [10] GUO L, LI N P, JIA F, et al. A recurrent neural network based health indicator for remaining useful life prediction of bearings[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 240: 98-109. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.02.045 [11] CHEN Y H, PENG G L, ZHU Z Y, et al. A novel deep learning method based on attention mechanism for bearing remaining useful life prediction[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2020, 86: 105919. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105919 [12] 康守强, 周月, 王玉静, 等. 基于改进SAE和双向LSTM的滚动轴承RUL预测方法[J]. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(9): 2327-2336.KANG S Q, ZHOU Y, WANG Y J, et al. RUL prediction method of a rolling bearing based on improved SAE and Bi-LSTM[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(9): 2327-2336(in Chinese). [13] 邱大伟, 刘子辰, 周一青, 等. 基于Transformer神经网络的滚动轴承故障类型识别[J]. 高技术通讯, 2021, 31(1): 1-11.QIU D W, LIU Z C, ZHOU Y Q, et al. A novel fault type detection method of rolling bearing using Transformer neural networks[J]. Chinese High Technology Letters, 2021, 31(1): 1-11(in Chinese). [14] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[J/OL]. (2017-06-12)[2021-03-20].https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762. [15] WANG B, LEI Y G, YAN T, et al. Recurrent convolutional neural network: A new framework for remaining useful life prediction of machinery[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 379: 117-129. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.10.064 [16] MA M, MAO Z. Deep-convolution-based LSTM network for remaining useful life prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(3): 1658-1667. doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.2991796 [17] WANG B, LEI Y G, LI N P, et al. Deep separable convolutional network for remaining useful life prediction of machinery[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2019, 134: 106330. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2019.106330 [18] ZENG F C, LI Y M, JIANG Y H, et al. An online transfer learning-based remaining useful life prediction method of ball bearings[J]. Measurement, 2021, 176: 109201. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109201 [19] NECTOUX P, GOURIVEAU R, MEDJAHER K, et al. PRONOSTIA: An ex-perimental platform for bearings accelerated degradation tests[C]//IEEE International Conference on Prognostics and Health M-anagement. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2012: 1-8. [20] SOUALHI A, MEDJAHER K, ZERHOUNI N. Bearing health monitoring based on Hilbert–Huang transform, support vector machine, and regression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2015, 64(1): 52-62. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2014.2330494 [21] SINGLETON R K, STRANGAS E G, AVIYENTE S. Extended Kalman filtering for remaining-useful-life estimation of bearings[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(3): 1781-1790. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2014.2336616 [22] WANG F T, LIU X F, DENG G, et al. Remaining life prediction method for rolling bearing based on the long short-term memory network[J]. Neural Processing Letters, 2019, 50(3): 2437-2454. doi: 10.1007/s11063-019-10016-w [23] LUO J H, ZHANG X. Convolutional neural network based on attention mechanism and Bi-LSTM for bearing remaining life prediction[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2022, 52(1): 1076-1091. doi: 10.1007/s10489-021-02503-2 [24] MO Y, WU Q H, LI X, et al. Remaining useful life estimation via transformer encoder enhanced by a gated convolutional unit[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2021, 32(7): 1997-2006. doi: 10.1007/s10845-021-01750-x [25] HINCHI A Z, TKIOUAT M. Rolling element bearing remaining useful life estimation based on a convolutional long-short-term memory network[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2018, 127: 123-132. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2018.01.106 [26] HONG S, ZHOU Z, ZIO E, et al. Condition assessment for the performance degradation of bearing based on a combinatorial feature extraction method[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2014, 27: 159-166. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2013.12.010 [27] WANG B, LEI Y G, LI N P, et al. A hybrid prognostics approach for estimating remaining useful life of rolling element bearings[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2020, 69(1): 401-412. doi: 10.1109/TR.2018.2882682 [28] CAO Y D, DING Y F, JIA M P, et al. A novel temporal convolutional network with residual self-attention mechanism for remaining useful life prediction of rolling bearings[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2021, 215: 107813. -






 下载:
下载: