-
摘要:
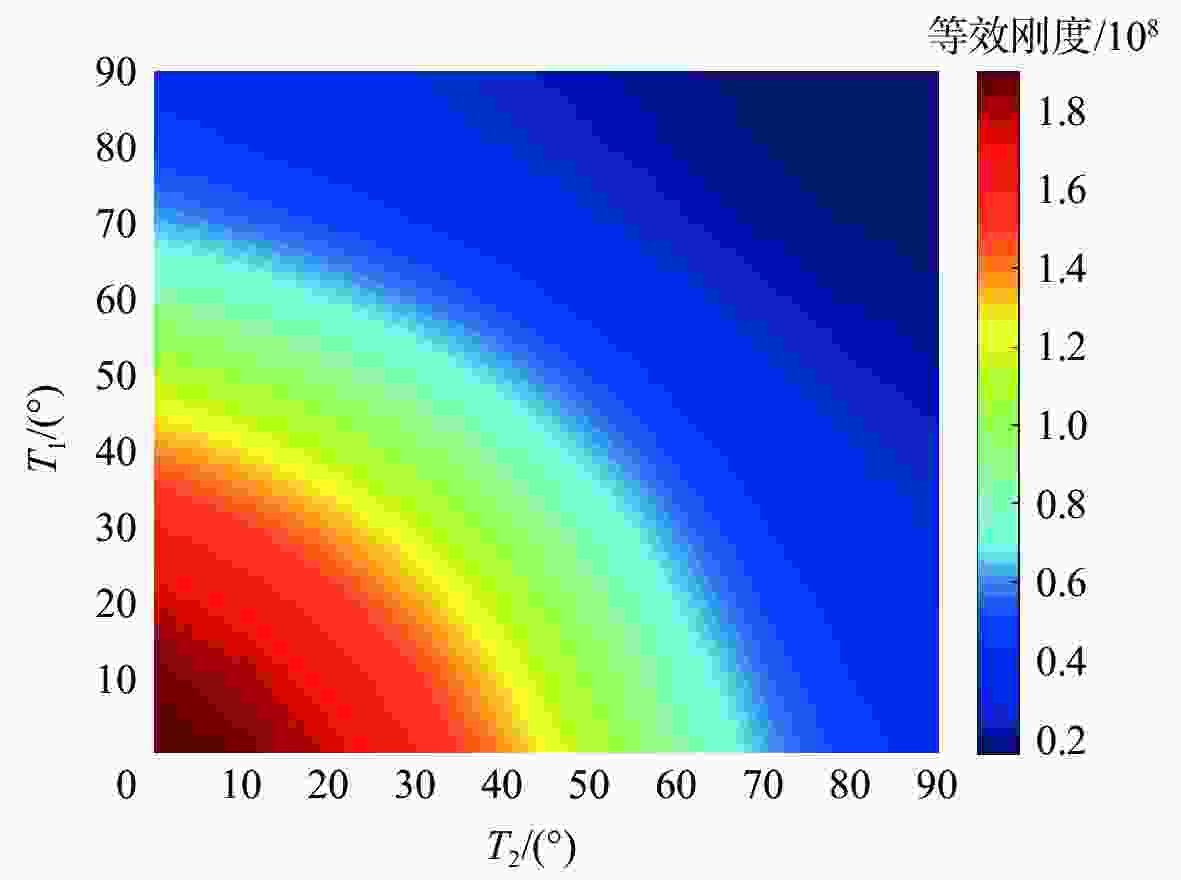
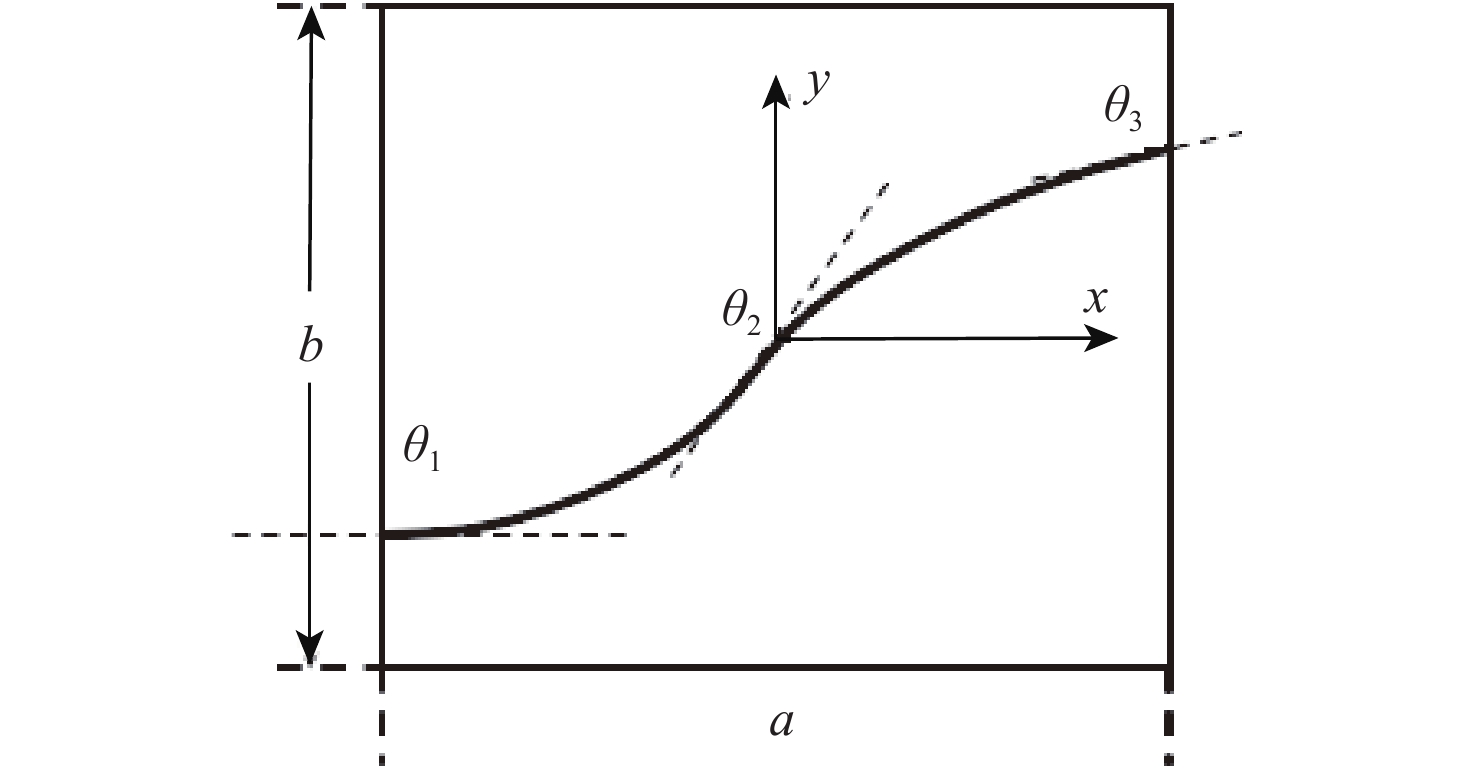
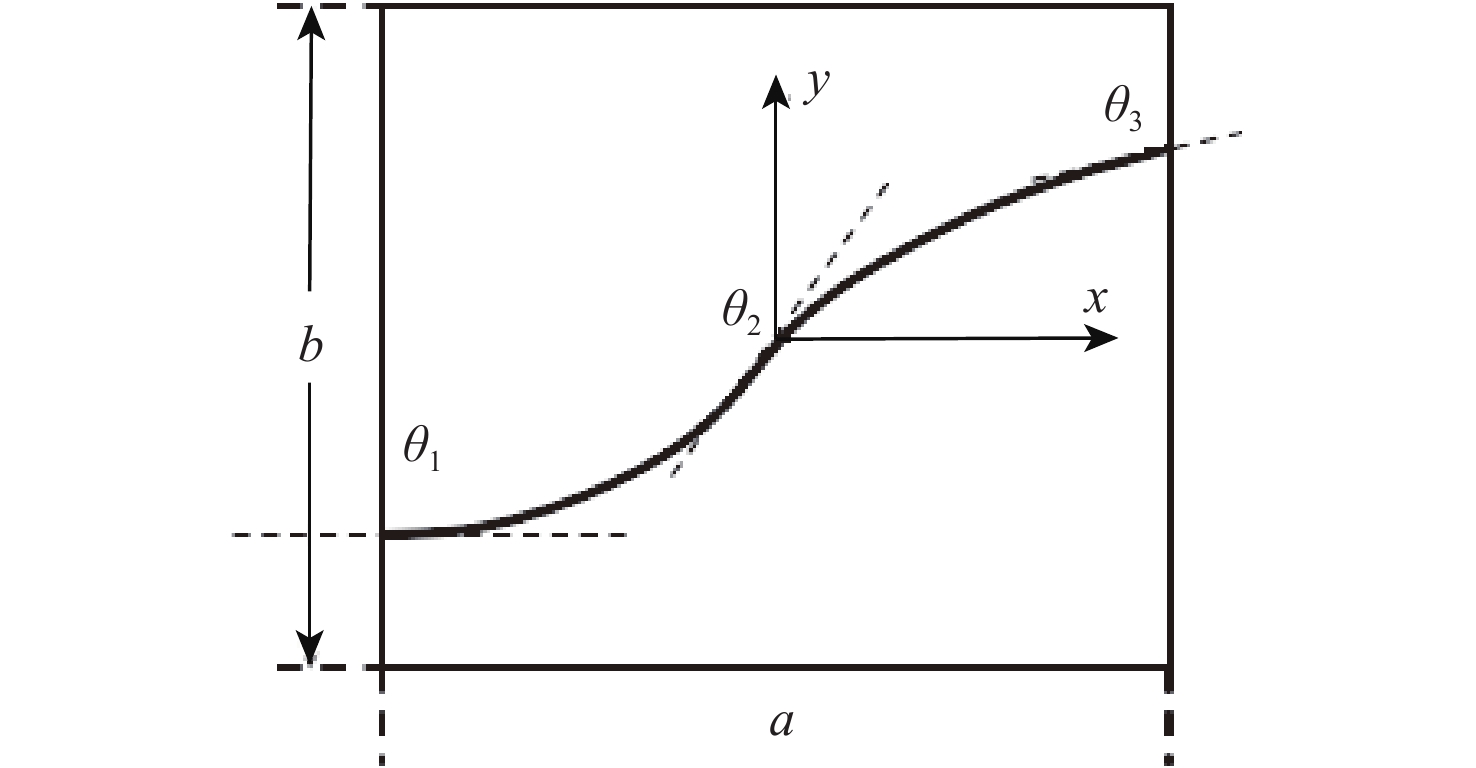
曲线(VAT)纤维复合材料壁板相比广泛应用的直线纤维形式具有更优的面内稳定性,作为机翼壁板,在同等质量时具有更高的抗屈曲潜力。为深入研究纤维路径对于曲线纤维壁板稳定性的影响规律,从各向同性薄板的理论出发,推导曲线纤维壁板在面内载荷下的稳定性分析方法;通过Airy应力函数和拉格朗日乘子描述边界条件,建立曲线纤维壁板适用于任意位移及载荷边界条件的单一变分方程,避免了非线性平衡方程和非线性相容方程间由于反复迭代对求解速度的制约。基于冯卡门大变形方程发展了曲线纤维壁板后屈曲状态下的非线性稳定性问题求解模型,并采用瑞利-里兹法建立了屈曲/后屈曲一体化半解析快速求解框架,该框架的求解精度与商用软件MSC.Nastran一致,但求解时间远低于商业软件;利用此优势,可以快速分析给定任意位移边界条件下的曲线纤维壁板屈曲响应特性,并得到纤维路径的影响规律。
Abstract:Benefiting from the curved fibre paths, variable-angle-tow (VAT) fibre composites feature a larger design space than traditional straight-fibre reinforced plastics. VAT fiber composite has better in-plane stability than the straight fiber, hence it has a higher buckling resistance potential at the same weight as a wing panel. To deeply analyze the influence law of fiber path on the stability of VAT fiber composite, the stability analysis method of curved fiber siding under in-plane load is derived, based on the theory of isotropic thin plate. By introducing the Airy stress function and the Lagrange multiplier which describes the arbitrary boundary conditions, a single variational equation suitable for arbitrary displacement and load boundary conditions of VAT fiber composite is established, which avoids the restriction on the solution speed by repeated iterations between nonlinear equilibrium equations and nonlinear compatibility equations. Based on the Von Karman large deformation equation, a solution model for linear and geometry nonlinear stability problem in the post-buckling state is derived, and then approached by Rayleigh-Ritz method. The accuracy of the established fast tool is the same as that of the commercial software MSC.Nastran, but the solution time is highly reduced. Thanks to this advantage, the buckling and nonlinear performance of VAT panel under arbitrary displacement boundary conditions can be quickly captured, and the influence law of fiber path on buckling and post-buckling of a VAT panel is effectively summarized.
-
Key words:
- composite structure /
- variable-angle-tow fiber /
- stability /
- buckling /
- post-buckling /
- Rayleigh-Ritz approach
-
表 1 壁板采用材料的材料属性
Table 1. Material properties of composite used in panel
材料属性 数值 材料属性 数值 ${E_1}$/MPa 98000 ${v_{12}}$ 0.28 ${E_2}$/MPa 7900 密度/(kg·m−3) 1520 ${G_{12}}$/MPa 5600 单层厚度/mm 0.134 -
[1] MANGALGIRI P D. Composite materials for aerospace applications[J]. Bulletin of Materials Science, 1999, 22(3): 657-664. doi: 10.1007/BF02749982 [2] LIANG L, WAN Z Q, YANG C. Aeroelastic optimization on composite skins of large aircraft wings[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2012, 55(4): 1078-1085. doi: 10.1007/s11431-011-4734-0 [3] WAGNER M, NORRIS G. Boeing 787 dreamliner[M]. Minneapolis: Zenith Press, 2009: 59-60 [4] GÜRDAL Z, TATTING B F, WU C K. Variable stiffness composite panels: Effects of stiffness variation on the in-plane and buckling response[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2008, 39: 911-22. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2007.11.015 [5] GÜRDAL Z, OLMEDO R. In-plane response of laminates with spatially varying fiber orientations: variable stiffness concept[J]. AIAA Journal, 1993, 31: 751-8. doi: 10.2514/3.11613 [6] HAO P, YUAN X, LIU C, et al. An integrated framework of exact modeling, isogeometric analysis and optimization for variable-stiffness composite panels[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 339: 205-238. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2018.04.046 [7] GROH R M, WEAVER P. Mass optimisation of variable angle tow, variable thickness panels with static failure and buckling constraints[C] //Aiaa/asce/ahs/asc Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference. Kissimmee: AIAA, 2013: 452. [8] KIM B C, WEAVER P M, POTTER K. Computer aided modelling of variable angle tow composites manufactured by continuous tow shearing[J]. Composite Structures, 2015, 129: 256-267. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.04.012 [9] BROOKS T R, MARTINS J R R A, KENNEDY G J. Aerostructural tradeoffs for tow-steered composite wings[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2020, 57(5): 787-799. doi: 10.2514/1.C035699 [10] STANFORD B K, JUTTE C V. Comparison of curvilinear stiffeners and tow steered composites for aeroelastic tailoring of aircraft wings[J]. Computers & Structures, 2017, 183: 48-60. [11] NARDO S V. An exact solution for the buckling load of flat sandwich panels with loaded edges clamped[J]. Journal of the Aeronautical Sciences, 1953, 20(9): 605-612. [12] THIELEMANN W. Contribution to the problem of buckling of orthotropic plates, with special reference to plywood: NACA-TM-1263[R]. Washington D. C. : NACA, 1950: 43-58. [13] GREEN A E. The buckling of flat rectangular plates: The philosophical magazine[J]. Journal of Experimental and Applied Physics, 1945, 36(7): 261. [14] ASHTON J E, WADDOUPS M E. Analysis of anisotropic plates[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 1969, 3(1): 148-165. doi: 10.1177/002199836900300111 [15] LOJA M A R, BARBOSA J I, SOARES C M M. Dynamic instability of variable stiffness composite plates[J]. Composite Structures, 2017, 182: 402-411. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.09.046 [16] WU Z, RAJU G, WEAVER P M. Postbuckling analysis of variable angle tow composite plates[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2013, 50(10): 1770-1780. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2013.02.001 [17] WU Z, CHEN X, WEAVER P M. Buckling analysis of variable angle tow composite plates with one circular delaminationp[C]//21st International Conference on Composite Materials. Xi’an: Chinese Society for Composite Materials, 2017: 3733. [18] 秦永利, 祝颖丹, 范欣愉, 等. 纤维曲线铺放制备变刚度复合材料层合板的研究进展[J]. 玻璃钢/复合材料, 2012(1): 61-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0999.2012.01.013QIN Y L, ZHU Y D, FAN X Y, et al. Research progress on fabrication of variable stiffness composite laminates by fiber curve laying[J]. Fiber Reinforced Plastics/Composites, 2012(1): 61-66(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0999.2012.01.013 [19] 马永前, 张淑杰, 许震宇. 纤维曲线铺放的变刚度复合材料层合板的屈曲[J]. 玻璃钢/复合材料, 2009(5): 31-35.MA Y Q, ZHANG S J, XU Z Y. Buckling of variable stiffness composite laminates with fiber curve laying[J]. Fiber Reinforced Plastics/Composites, 2009(5): 31-35(in Chinese). [20] 杜宇, 杨涛, 戴维蓉, 等. 纤维曲线铺放的变刚度复合材料损伤失效试验研究[J]. 固体火箭技术, 2013, 36(6): 826-830.DU Y, YANG T, DAI W R, et al. Experimental research of damaging failure of variable-stiffness composite[J]. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology, 2013, 36(6): 826-830(in Chinese). [21] 牛雪娟, 杨涛, 杜宇, 等. 变刚度纤维曲线铺放复合材料层合板的有限元建模和拉伸特性分析[J]. 宇航材料工艺, 2014, 44(4): 19-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2330.2014.04.003NIU X J, YANG T, DU Y, et al. Finite element modeling and tensile properties analysis of curvelinear fiber-placed variable-stiffness composite laminates[J]. Aerospace Materials and Technology, 2014, 44(4): 19-24(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2330.2014.04.003 [22] 卫宇璇, 张明, 刘佳, 等. 基于自动铺放技术的高精度变刚度复合材料层合板屈曲性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(11): 2807-2815. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200218.001WEI Y X, ZHANG M, LIU J, et al. Buckling performance of high-precision variable stiffness composites laminate based on automatic placement technology[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2020, 37(11): 2807-2815(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200218.001 [23] KIM B C, WEAVER P M, POTTER K. Manufacturing characteristics of the continuous tow shearing method for manufacturing of variable angle tow composites[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing. 2014, 61: 141-51. [24] REDDY J N. A genera lization of two-dimensional theories of laminated composite plates[J]. Communications in Applied Numerical Methods, 1987, 3(3): 173-180. [25] BISAGNI C, VESCOVINI R. Analytical formulation for local buckling and post-buckling analysis of stiffened laminated panels[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2009, 47(3): 318-334. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2008.07.006 -






 下载:
下载: