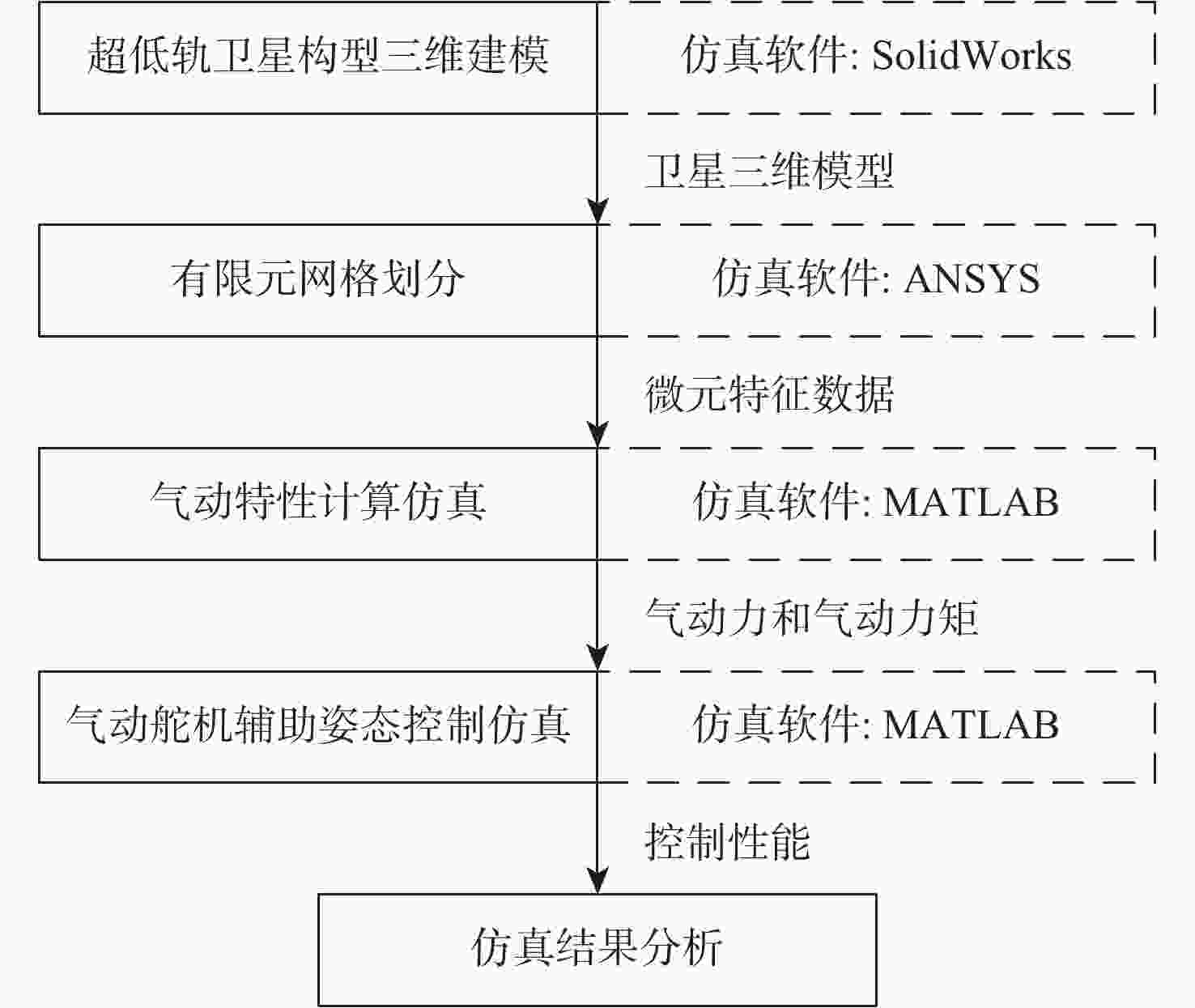
Design of attitude control method for ultra-low-orbit satellite with pneumatic steering gear
-
摘要:
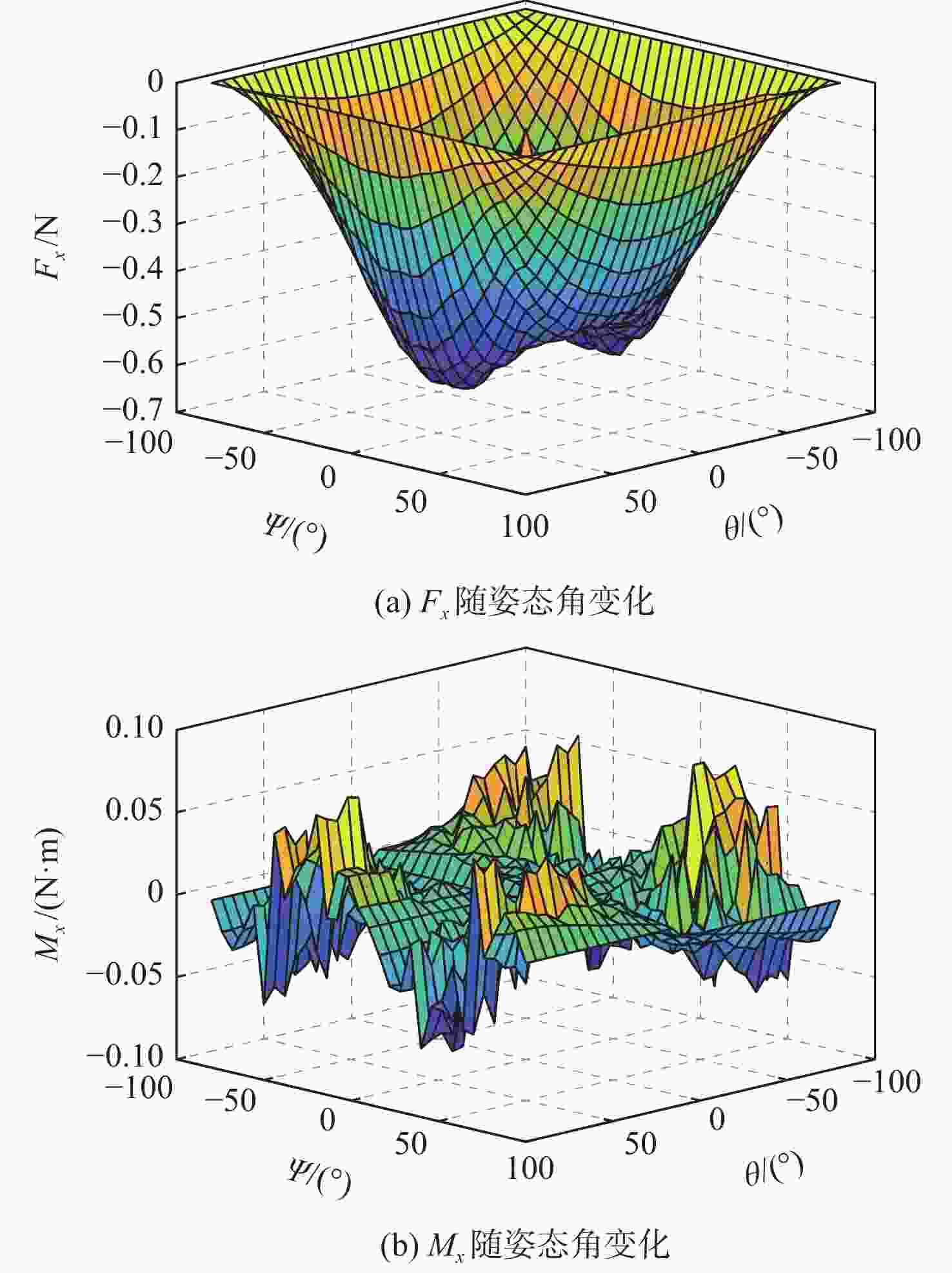
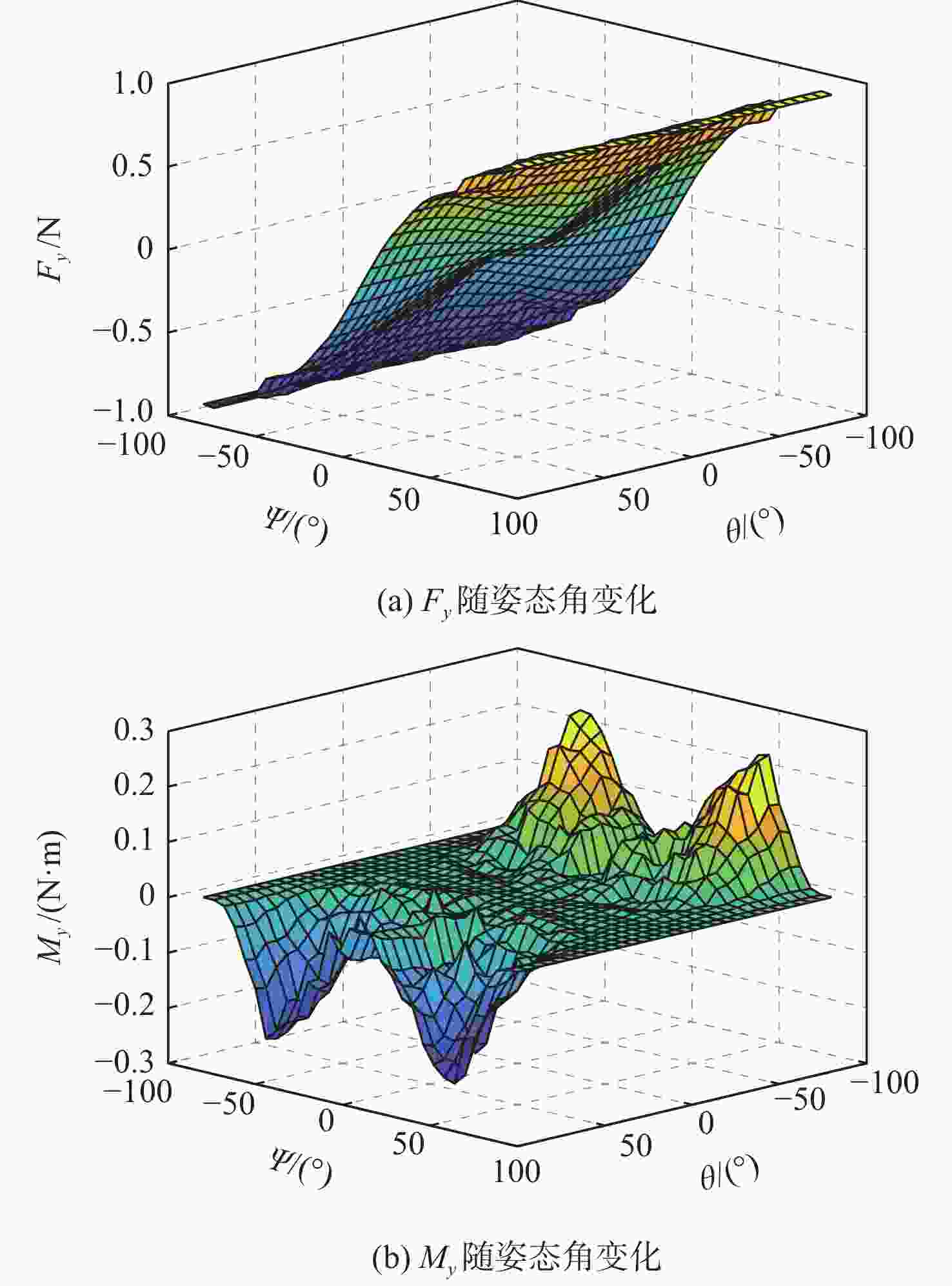
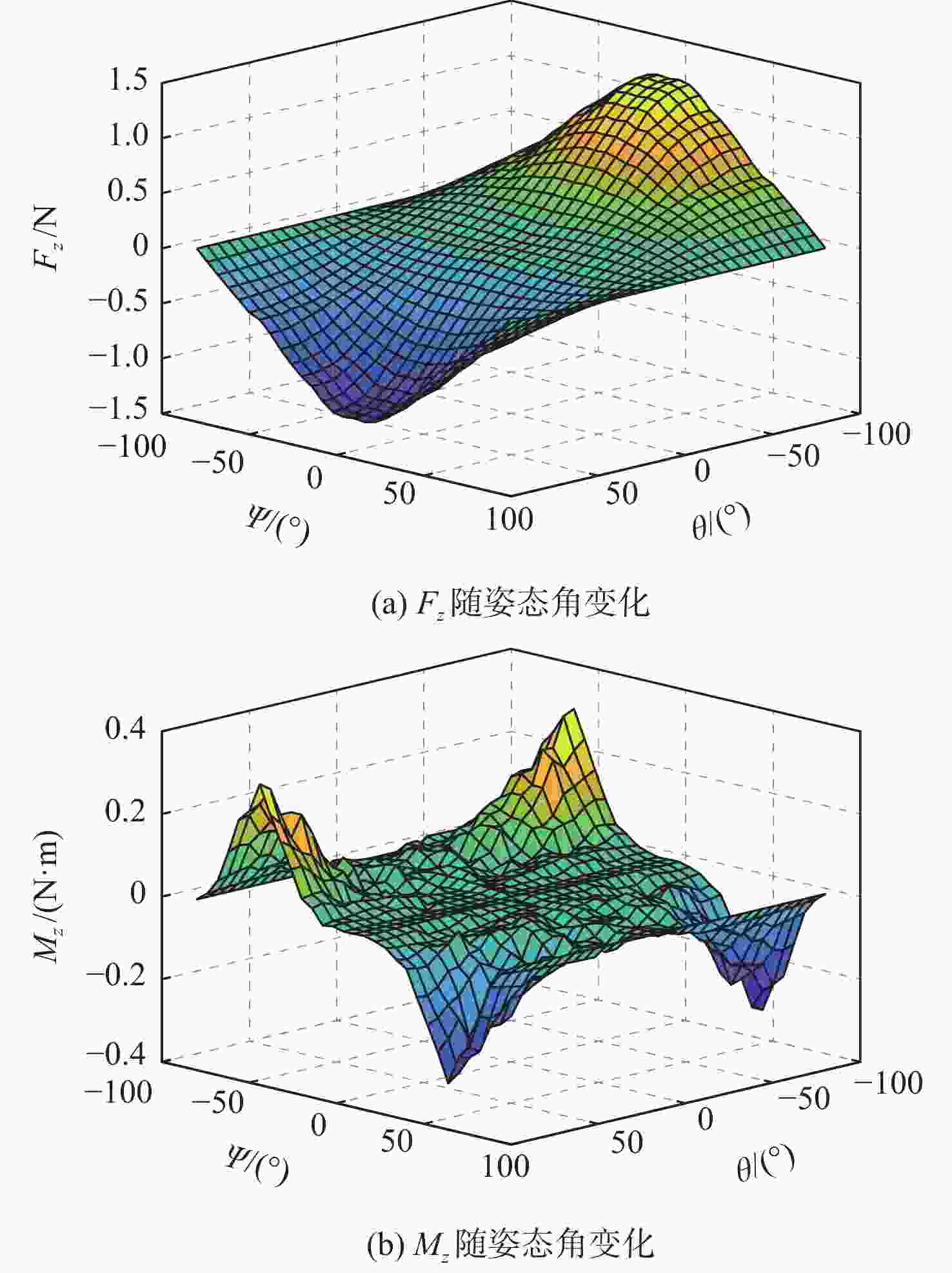
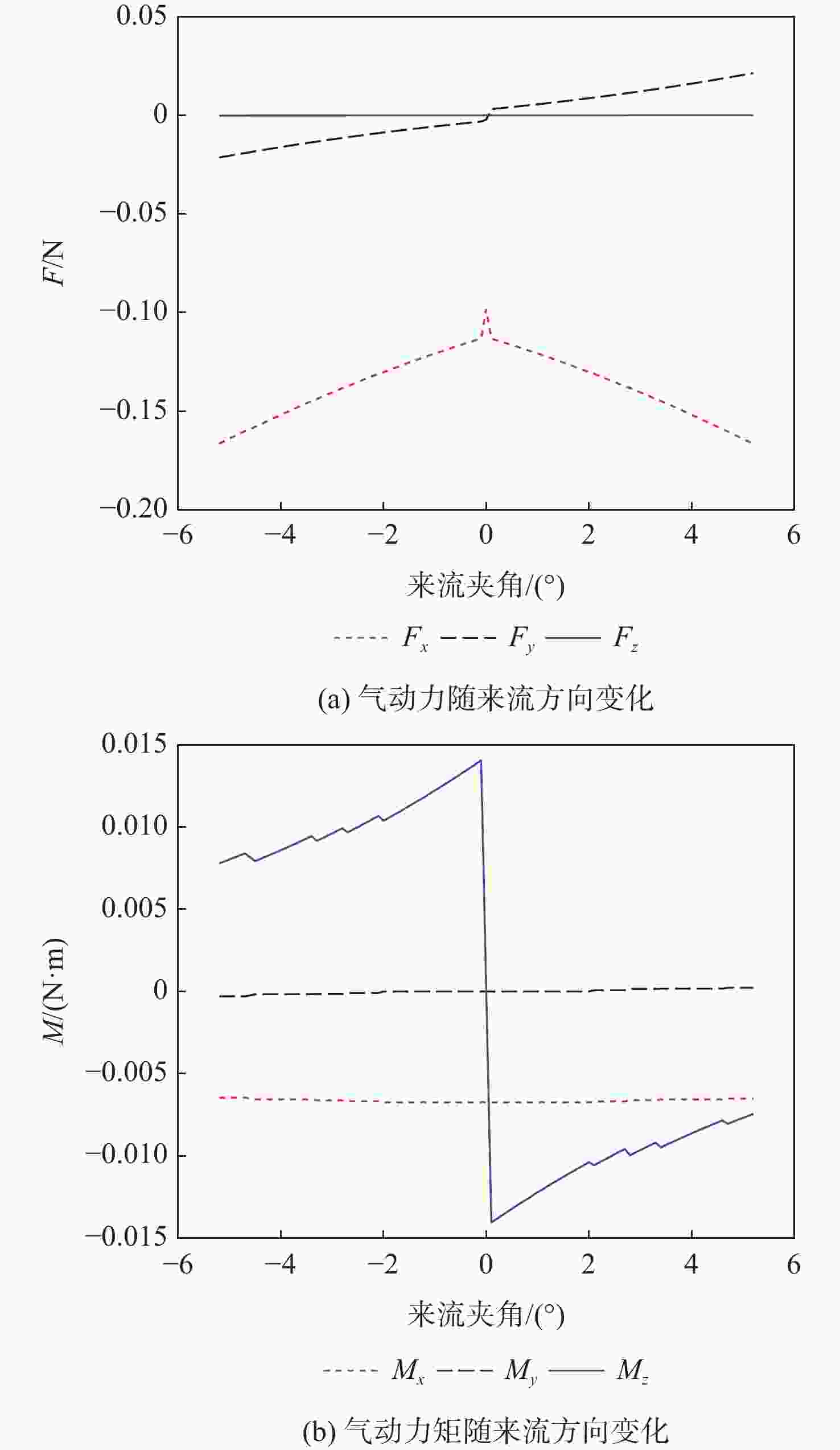
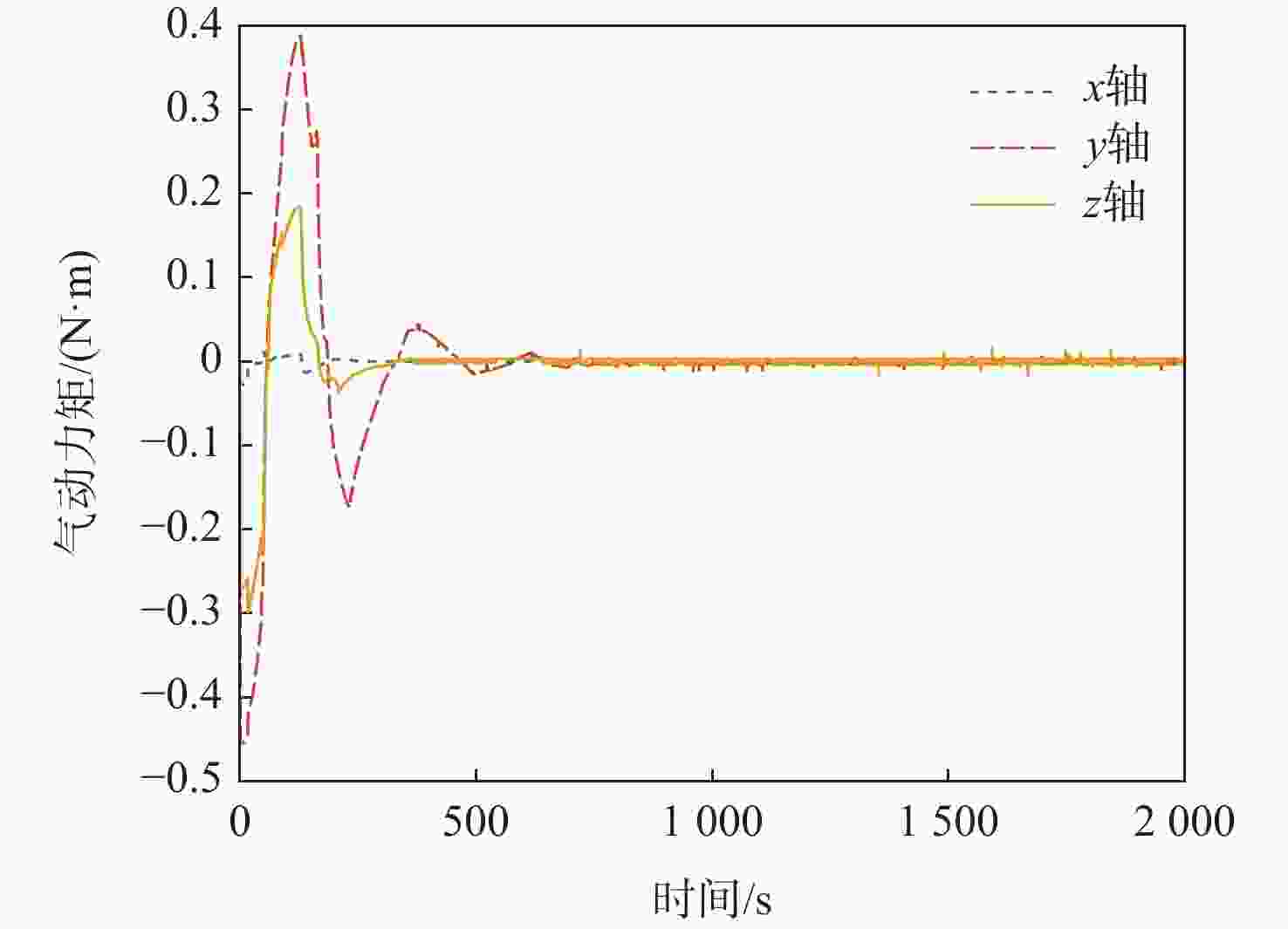
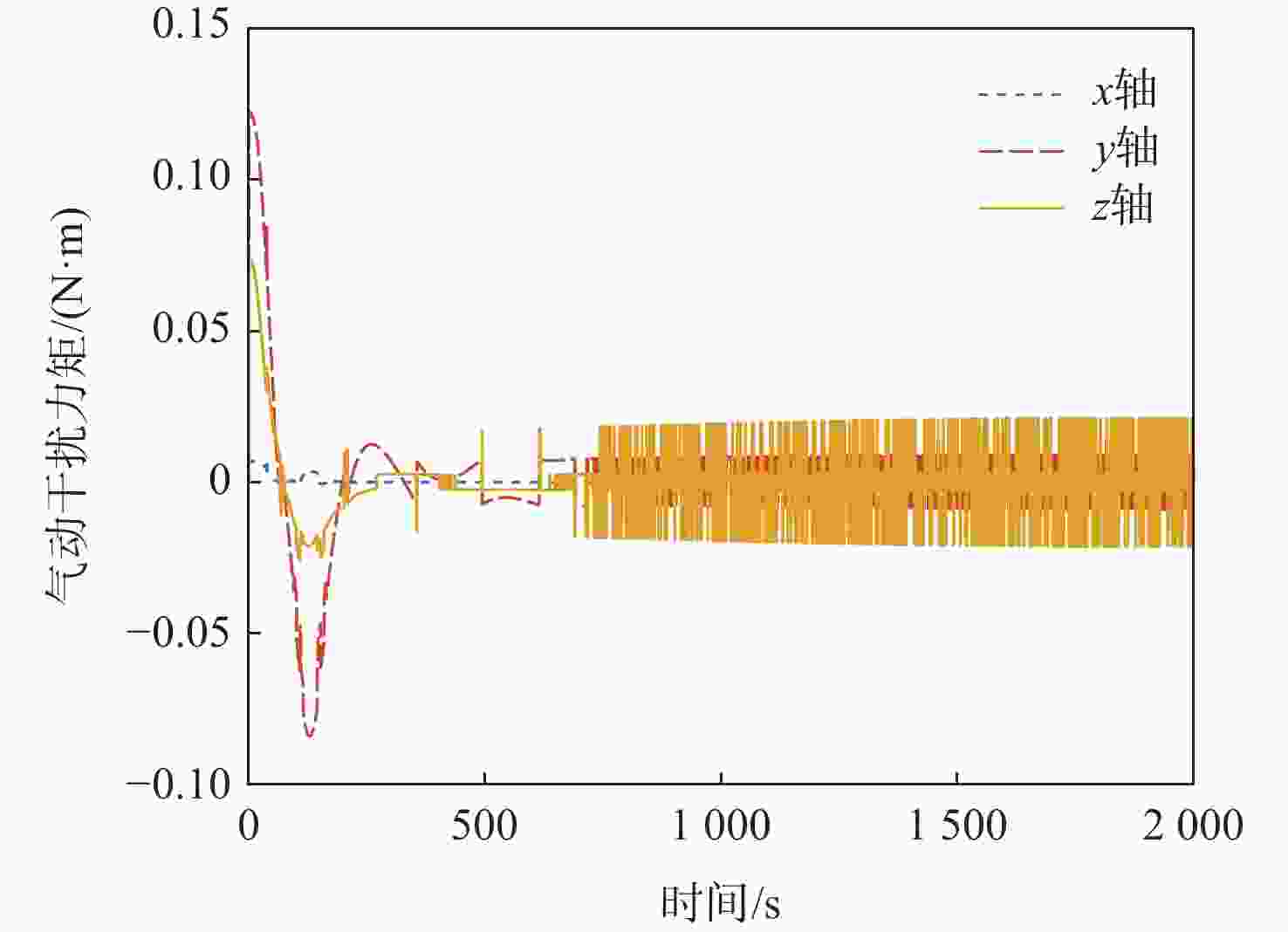
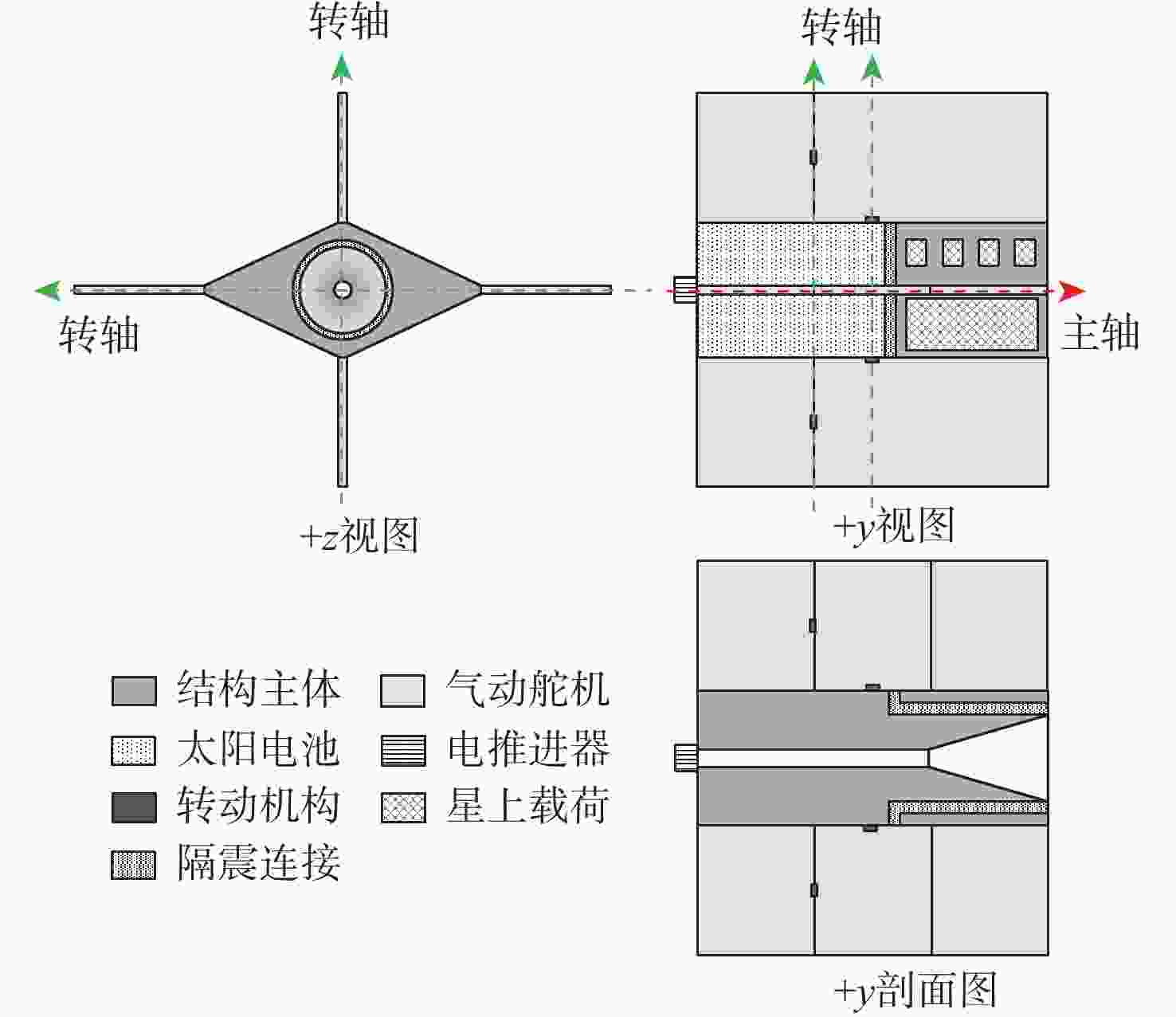
针对超低轨卫星姿态控制差异化需求,开展了基于气动舵机辅助的姿态控制策略研究。完成了超低轨道稀薄大气下卫星气动舵机布局设计与气动特性研究,理论气动力可达10−1 N量级,气动力矩可达10−1 N·m量级。在此基础上,完成了基于气动舵机辅助的姿态控制策略研究。通过仿真验证,在
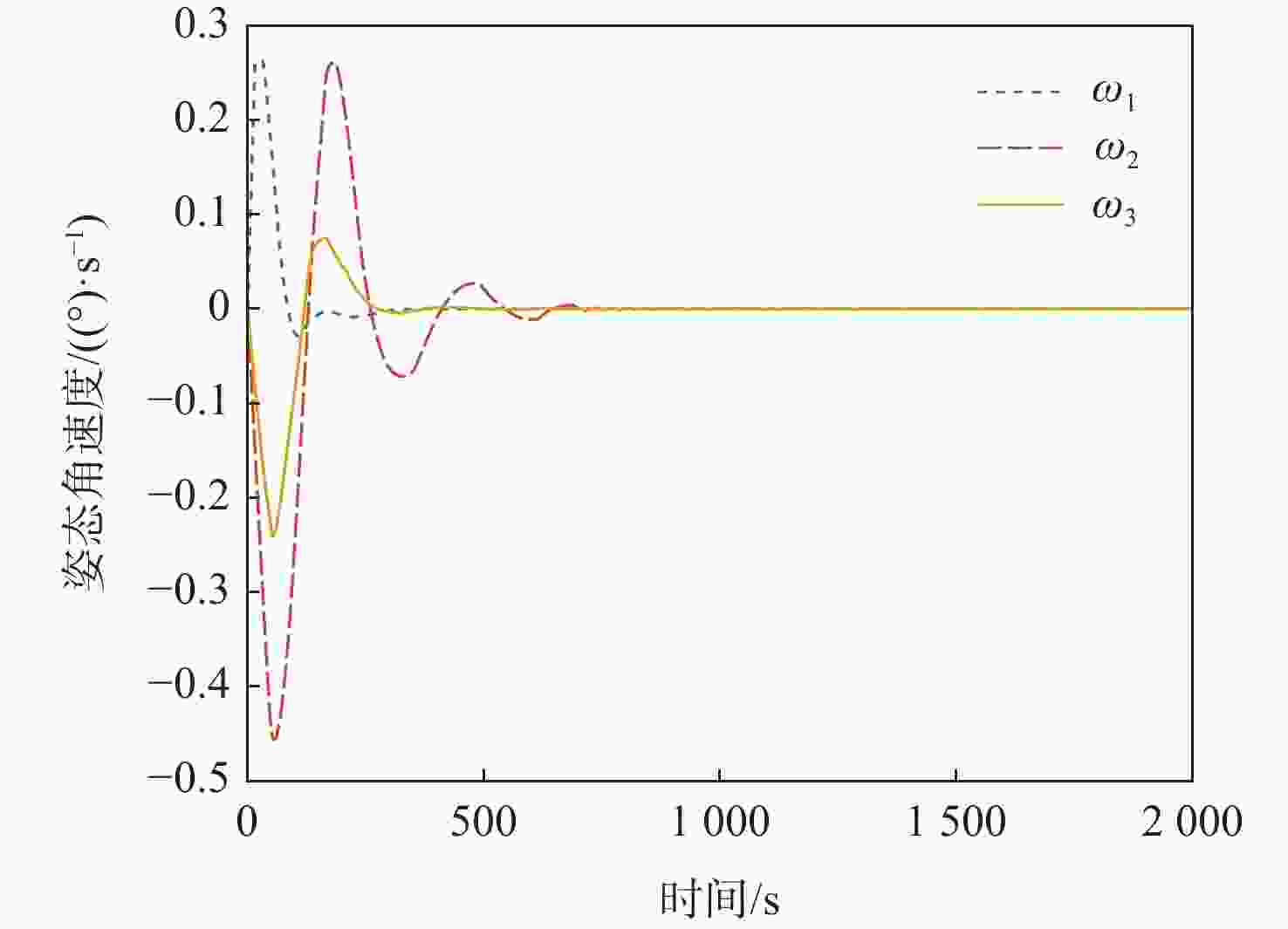
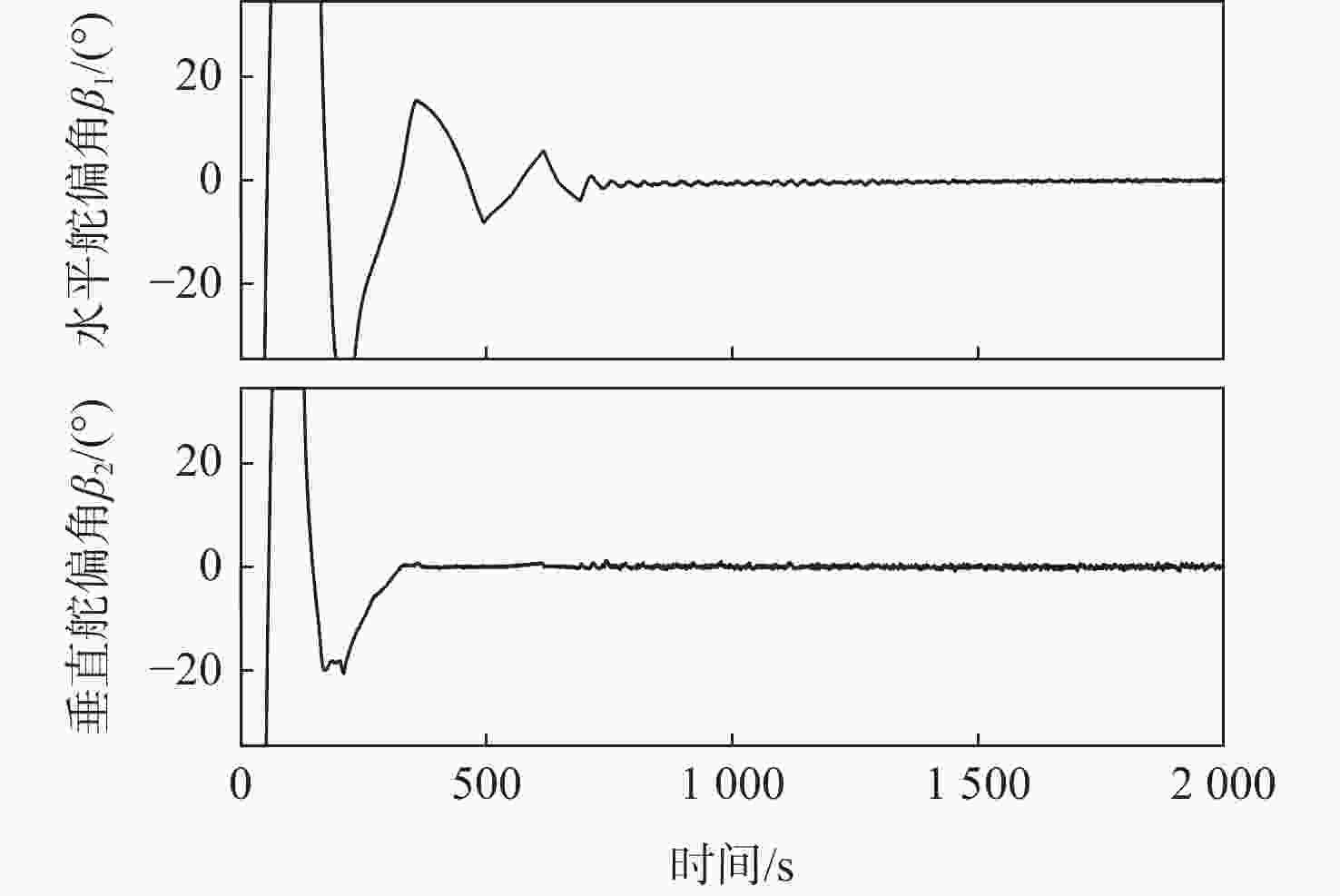
x 轴采用动量轮控制、y 轴和z 轴采用气动舵机辅助控制情况下,可实现优于0.004°的三轴指向精度和优于0.0007(°)/s的三轴姿态稳定度。所设计气动舵机辅助姿态控制策略对超低轨卫星技术应用与发展具有重要技术价值和工程意义。Abstract:To meet the differentiated needs of the attitude control of ultra-low orbit satellites, this study investigates the attitude control strategy with the assistance of pneumatic steering gears. The layout of the gear is designed and its aerodynamic characteristics are analyzed under the thin atmosphere of the ultra-low orbit, with the theoretical aerodynamic force up to the order of 10−1 N, and the aerodynamic torque the order of 10−1 N·m. On this basis, an attitude control strategy assisted by pneumatic steering gears is designed. Simulation results show that when the
x -axis is controlled by the momentum wheel and they -axis andz -axis are controlled by pneumatic steering gears, the three-axis pointing accuracy larger than 0.004° and the three-axis attitude stability larger than 0.0007(°)/s can be achieved. The attitude control strategy designed in this paper has important technical and engineering value for the application and development of ultra-low orbit satellites. -
表 1 仿真参数设置
Table 1. Simulation parameters setting
参数 实际高度
h/km来流速度
V∞/(m·s−1)法向动量
适应系数σn切向动量
适应系数στ数值 200 7500 0.99 0.99 表 2 气动力矩与副翼偏转对照关系
Table 2. Relationship between aerodynamic moment and rotation angle of ailerons
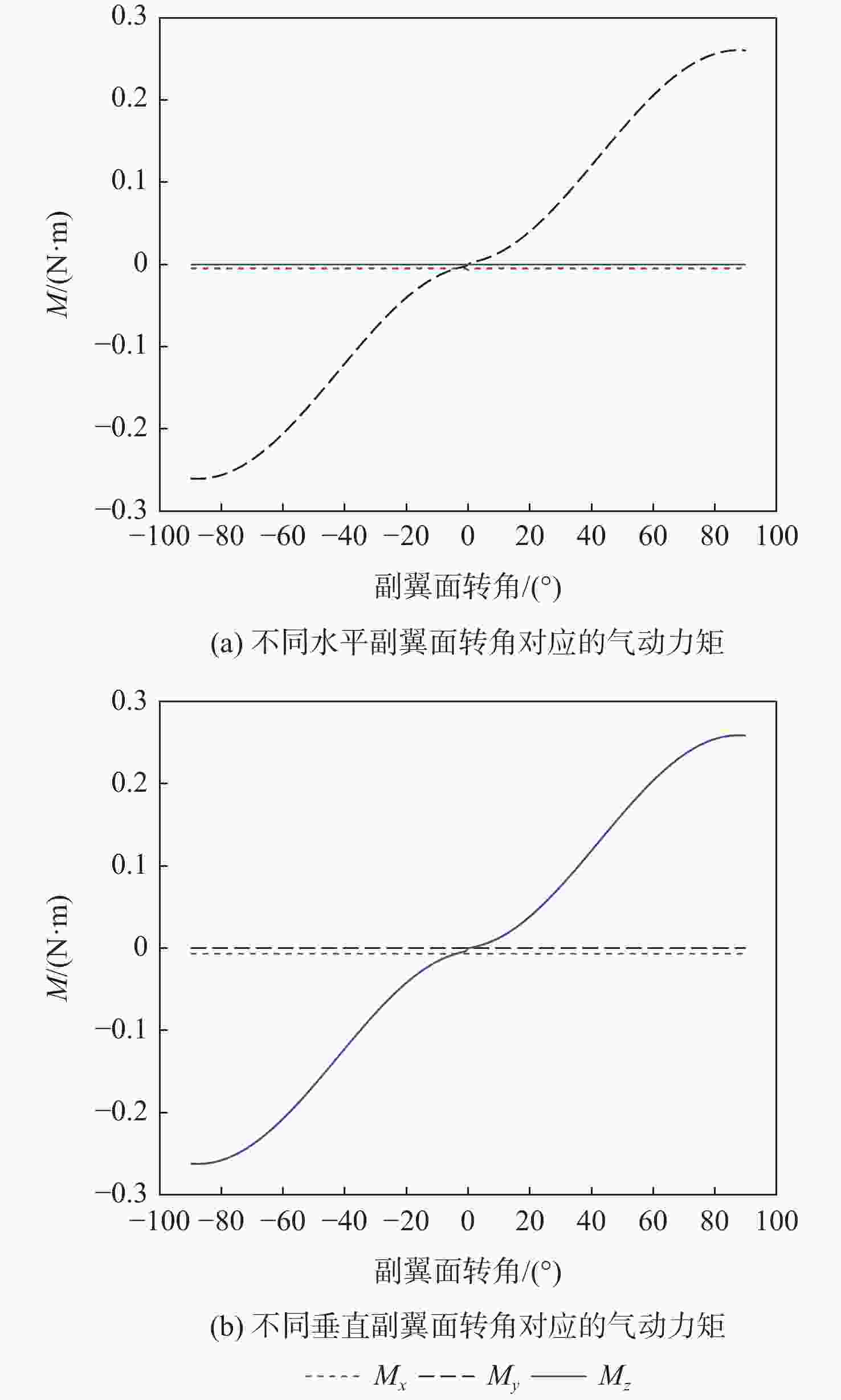
主翼面转角 所需气动力矩为正 所需气动力矩为负 主翼面转角为正 (20°, 0.11 N·m) (−20°, −0.13 N·m) 主翼面转角为零 (80°, 0.256 N·m) (−80°, −0.256 N·m) 主翼面转角为负 (20°, 0.13 N·m) (−20°, −0.11 N·m) 表 3 仿真参数说明
Table 3. Description of simulation parameters
参数 数值 初始姿态角/(°) [−10,20,10] 初始姿态角速度/((°)·s−1) [0,0,0] x轴转动惯量Jx/(kg·m2) 600 y轴转动惯量Jy/(kg·m2) 2000 z轴转动惯量Jz/(kg·m2) 2000 动量轮转动惯量/(kg·m2) 0.008 动量轮组每根轴输出力矩上限/(N·m) 0.2 动量轮组每根轴角动量上限/(N·m·s) 3 动量轮初始动量/(N·m·s) [0,0,0] 期望姿态角/(°) [0,0,0] 期望姿态角速度/((°)·s−1) [0,0,0] 表 4 仿真加入的随机干扰
Table 4. Random disturbance in simulations
误差类型 随机干扰的3σ 姿态角测量偏差/(°) [0.01,0.01,0.01] 姿态角速度测量偏差/((°)·s−1) [0.001,0.001,0.001] 动量轮组角加速度控制偏差/((°)·s−2) 0.001 气动翼转角控制偏差/(°) 0.01 -
[1] BACON A, OLIVIER B S. Bringing down the cost of earth observation[C]//Proceedings of the 12th Reinventing Space Conference. Berlin: Springer, 2017: 1-7. [2] ROBERT P C E, ROMANO F, HERDRICH G, et al. Keynote: Discoverer-making commercial satellite operations in very low earth orbit a reality[C]//70th International Astronautical Congress (IAC). Reston: AIAA, 2019: 21-25. [3] DE FLORIO S, D’AMICO S, RADICE G. Virtual formation method for precise autonomous absolute orbit control[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2014, 37(2): 425-438. doi: 10.2514/1.61575 [4] DE FLORIO S, D’AMICO S, RADICE G. Precise autonomous orbit control in low earth orbit[C]//Astrodynamics Specialist Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2012: 4811. [5] WERTZ J R, SHAO A, TAYLOR C, et al. Moderately elliptical very low orbits (MEVLOs) as a long-term solution to orbital debris[C]//26th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satelites. Reston: AIAA, 2012: SSC12-IV-6. [6] 吴勤. 透视俄罗斯军用卫星发展现状[J]. 太空探索, 2008(12): 46-49.WU Q. Perspective of Russian military satellite development status[J]. Space Exploration, 2008(12): 46-49(in Chinese). [7] 曾其鋆. 气动力矩在超低轨道卫星姿态控制方面的应用研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2009: 41-56.ZENG Q J. Applications of aerodynamic torque to ultra-low-orbit satellite attitude control[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2009: 41-56(in Chinese). [8] 田春华, 马广富, 李传江, 等. 三轴稳定卫星姿态控制系统的一般性问题[J]. 自动化技术与应用, 2001(1): 9-12.TIAN C H, MA G F, LI C J, et al. General problems of satellite attitude control[J]. Techniques of Automation and Applications, 2001(1): 9-12(in Chinese). [9] 黄静. 三轴稳定航天器姿态最优控制方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2010: 75-78.HUANG J. Optimal attitude control for three-axis stabilized spacecrafts[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2010: 75-78(in Chinese). [10] 段广仁, 钟震, 姜苍华. 航天器的一种无源自适应姿态控制方法[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2011, 43(5): 1-7. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.2011.05.001DUAN G R, ZHONG Z, JIANG C H. One scheme of passive adaptive attitude control for spacecraft[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2011, 43(5): 1-7(in Chinese). doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.2011.05.001 [11] 邵汉斌. 基于滑模控制的超低轨道航天器姿态控制方法研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2014: 12-16.SHAO H B. Ultra-low-orbit spacecraft attitude control based on sliding mode control[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2014: 12-16(in Chinese). [12] KUMAR R R, MAZANEK D D, HECK M L. Simulation and Shuttle Hitchhiker validation of passive satellite aerostabilization[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 1995, 32(5): 806-811. [13] KUMAR R R, MAZANEK D D, HECK M L. Parametric and classical resonance in passive satellite aerostabilization[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 1996, 33(2): 228-234. doi: 10.2514/3.26745 [14] PSIAKI M L. Spacecraft attitude stabilization using passive aerodynamics and acting magnetic torquing: AIAA-2003-5420[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2003. [15] PSIAKI M L. Magnetic torquer attitude control via asymptotic periodic linear quadratic regulation[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2001, 24(2): 386-394. doi: 10.2514/2.4723 [16] GUETTLER D B. Satellite attitude control using atmospheric drag [D]. Dayton: Air Force Institute of Technology, 2007: 23-33. [17] 刘辉, 伍斯宾斯基. 利用喷气装置卸载航天器积累角动量的最小工质损耗控制[J]. 航天控制, 2004, 22(5): 32-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3242.2004.05.008LIU H, USPENSKY V B. Minimize propellant consumption during gyro system unloading process of spacecraft[J]. Aerospace Control, 2004, 22(5): 32-35(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3242.2004.05.008 [18] 张利宾. 基于磁控和轮控的微小卫星姿态控制算法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2007: 26-51.ZHANG L B. Study on attitude control algorithm for micro-satellite using magnetotorquers and reaction wheels[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2007: 26-51(in Chinese). [19] 李太玉, 张育林. 基于能量最优解析解的飞轮磁卸载方法[J]. 上海航天, 2006, 23(6): 1-9. doi: 10.19328/j.cnki.1006-1630.2006.06.001LI T Y, ZHANG Y L. Momentum magnetic unloading basing on analytic equation of energy optimization[J]. Aerospace Shanghai, 2006, 23(6): 1-9(in Chinese). doi: 10.19328/j.cnki.1006-1630.2006.06.001 [20] STEIGER C, ROMANAZZO M, EMANUELLI P P. The deorbiting of ESA’s gravity mission GOCE–Spacecraft operations in extreme drag conditions[C]//International Conference on Space Operations. Reston: AIAA, 2014: 1934. [21] 何慧东. 日本“超低轨道技术试验卫星”任务及应用[J]. 国际太空, 2018(9): 50-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2366.2018.09.010HE H D. Japan’s super low altitude test satellite mission and application[J]. Space International, 2018(9): 50-53(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2366.2018.09.010 [22] 温生林. 超低轨道卫星动力学建模与控制方法研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2016: 20-35.WEN S L. Dynamic modeling and flight control for super low altitude satellite[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2016: 20-35(in Chinese). [23] 周伟勇, 张育林, 刘昆. 超低轨航天器气动力分析与减阻设计[J]. 宇航学报, 2010, 31(2): 342-348. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2010.02.007ZHOU W Y, ZHANG Y L, LIU K. Aerodynamics analysis and reduced drag design for the lower LEO spacecraft[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2010, 31(2): 342-348(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2010.02.007 [24] 胡凌云, 张立华, 程晓丽, 等. 超低轨航天器气动设计与计算方法探讨[J]. 航天器工程, 2016, 25(1): 10-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2016.01.002HU L Y, ZHANG L H, CHENG X L, et al. Method of aerodynamic design and calculation for ultra-LEO spacecraft[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2016, 25(1): 10-18(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2016.01.002 -






 下载:
下载: