Current chopping control strategy of switched reluctance motor based on inductance characteristics
-
摘要:
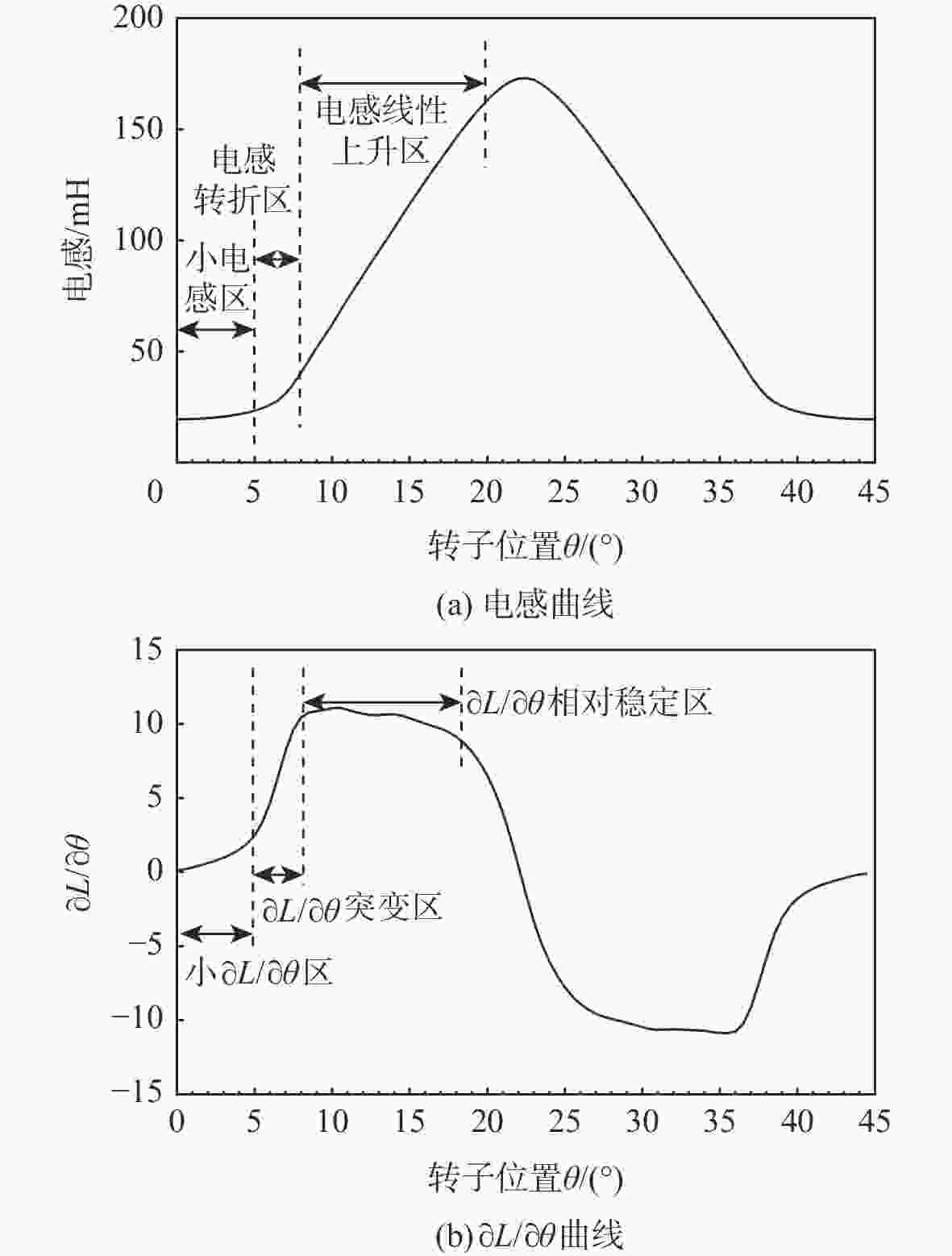
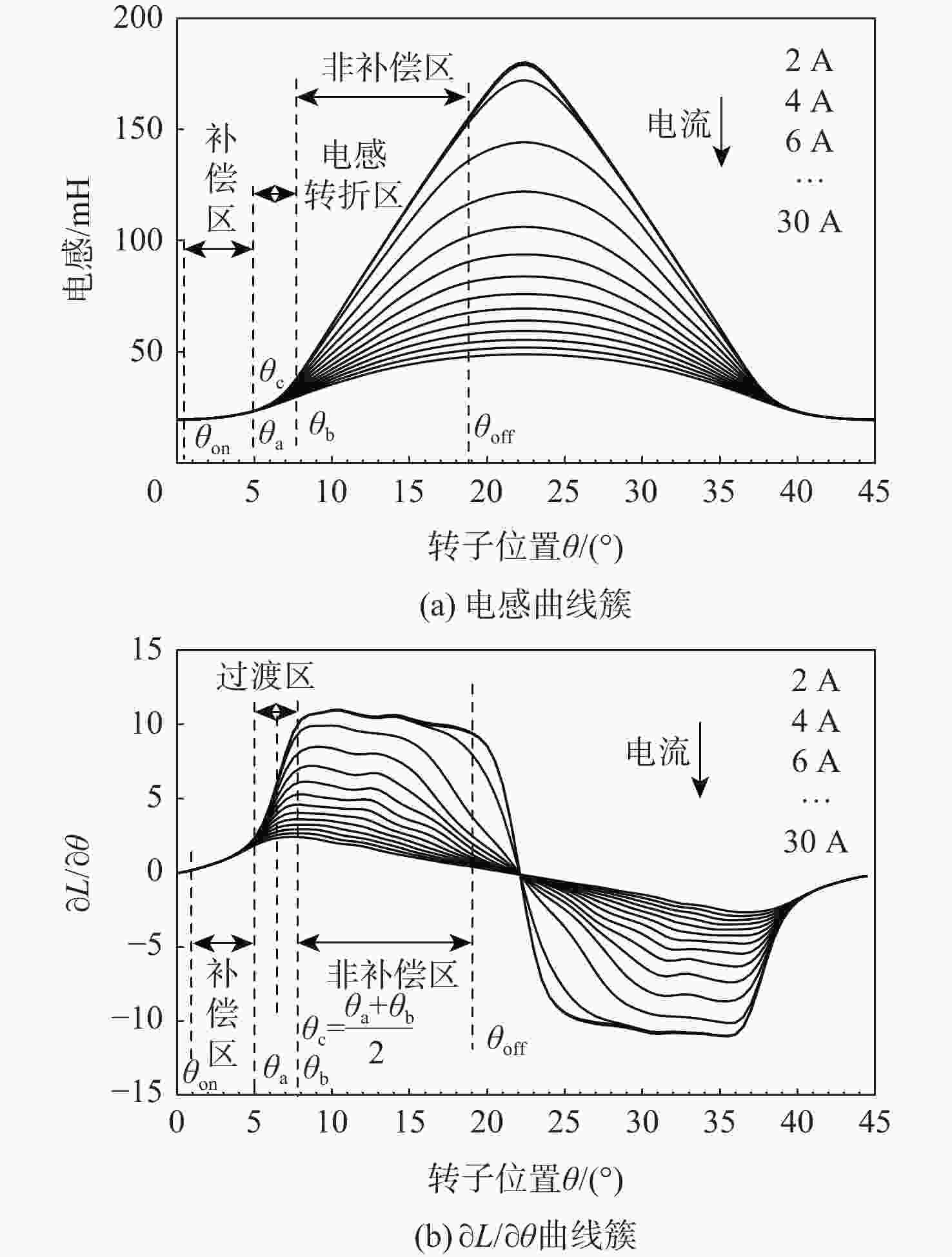
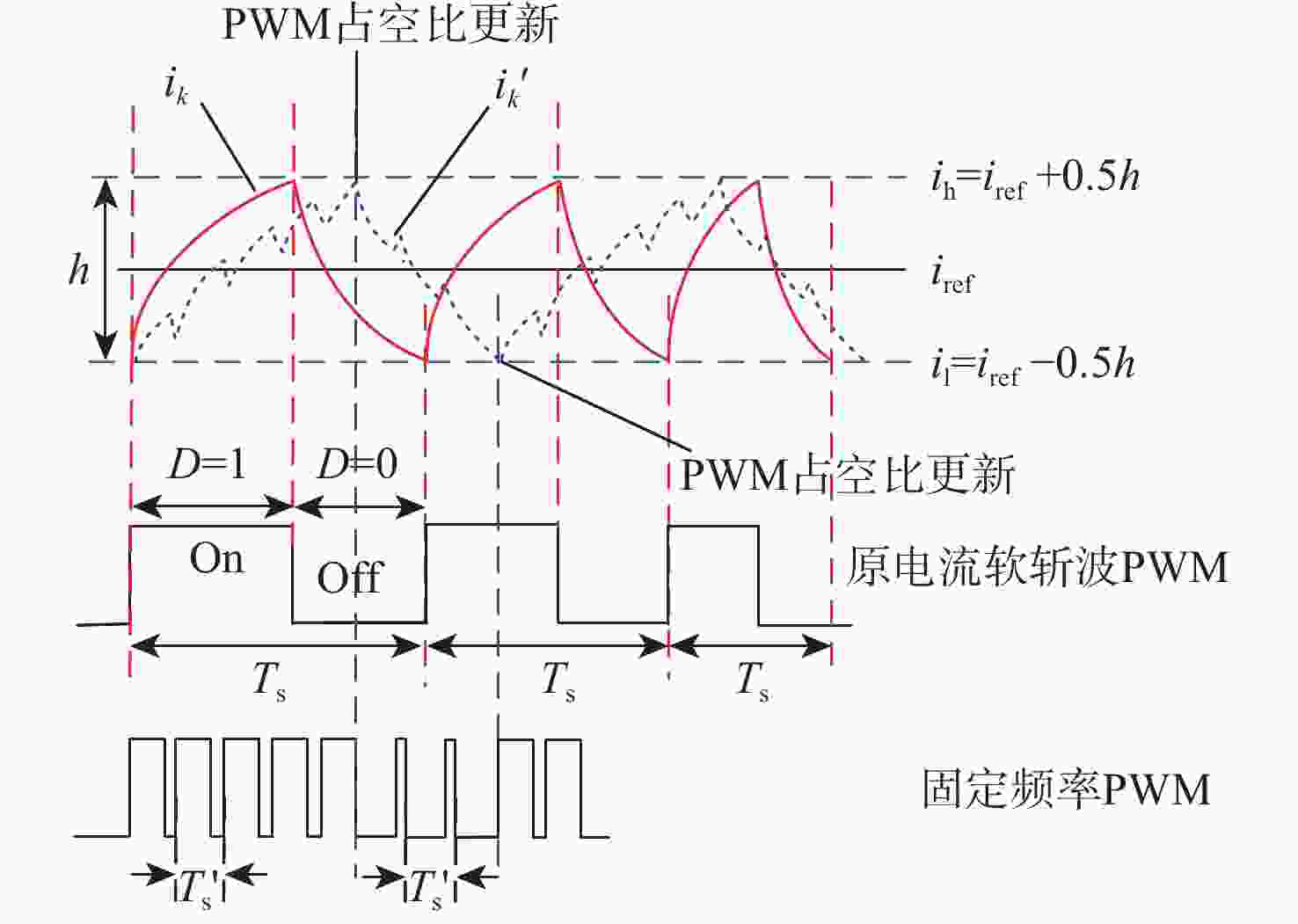
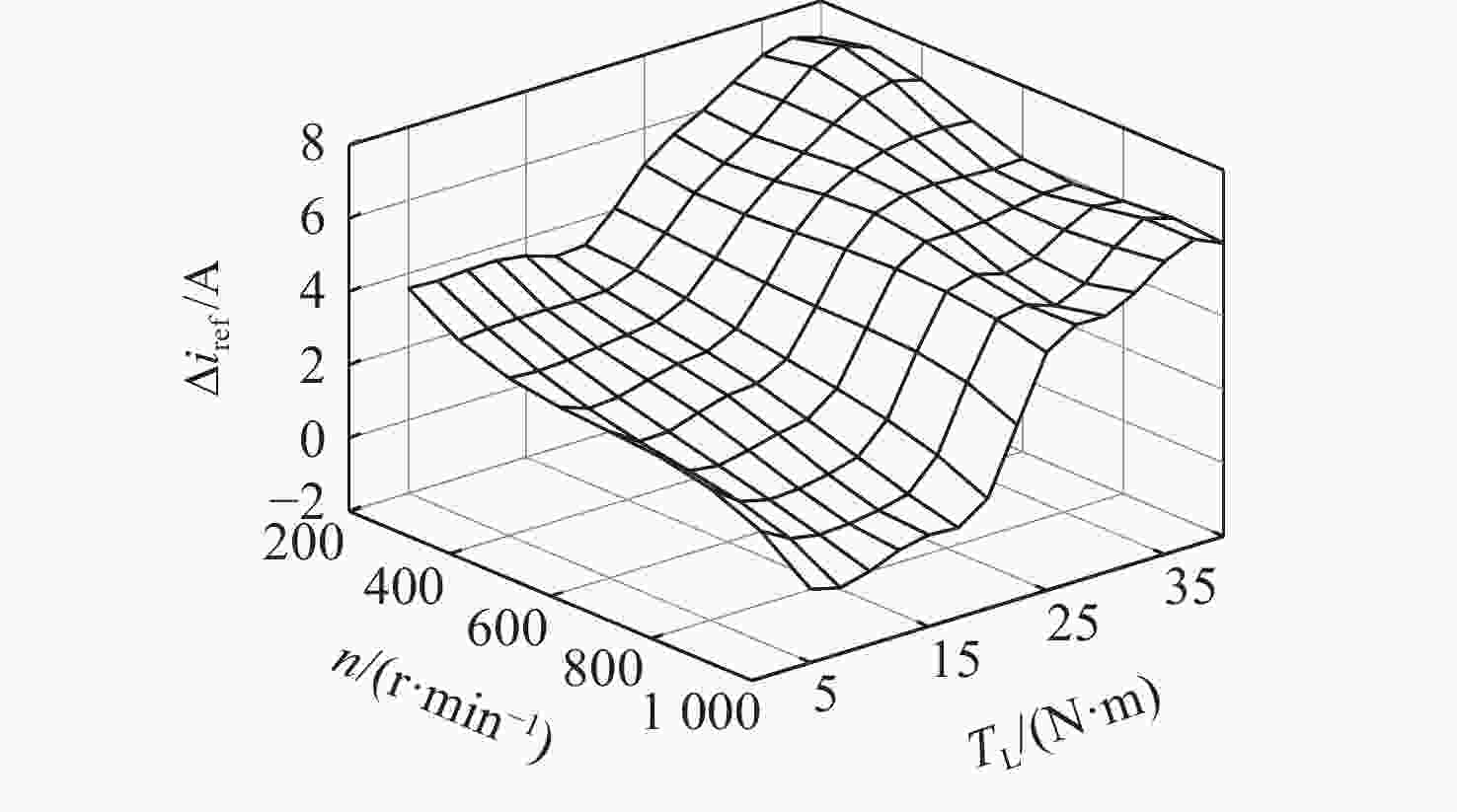
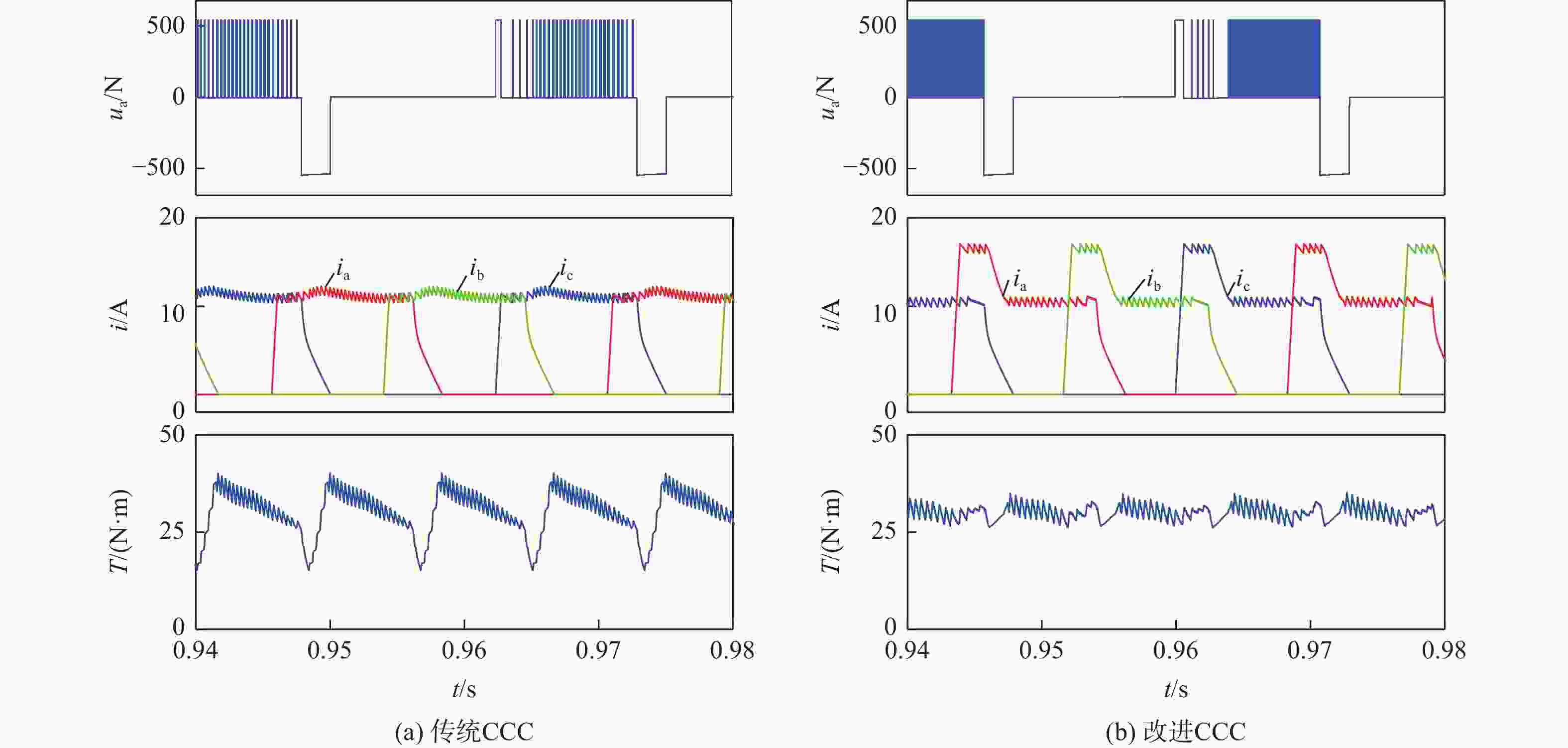
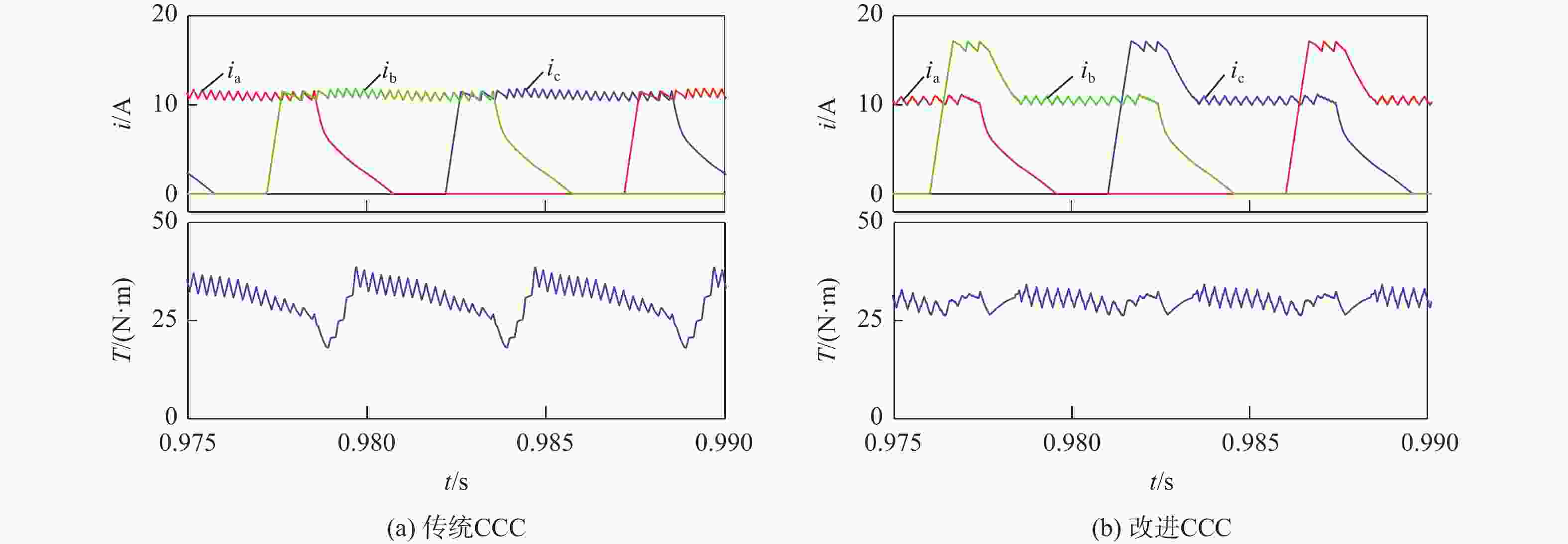
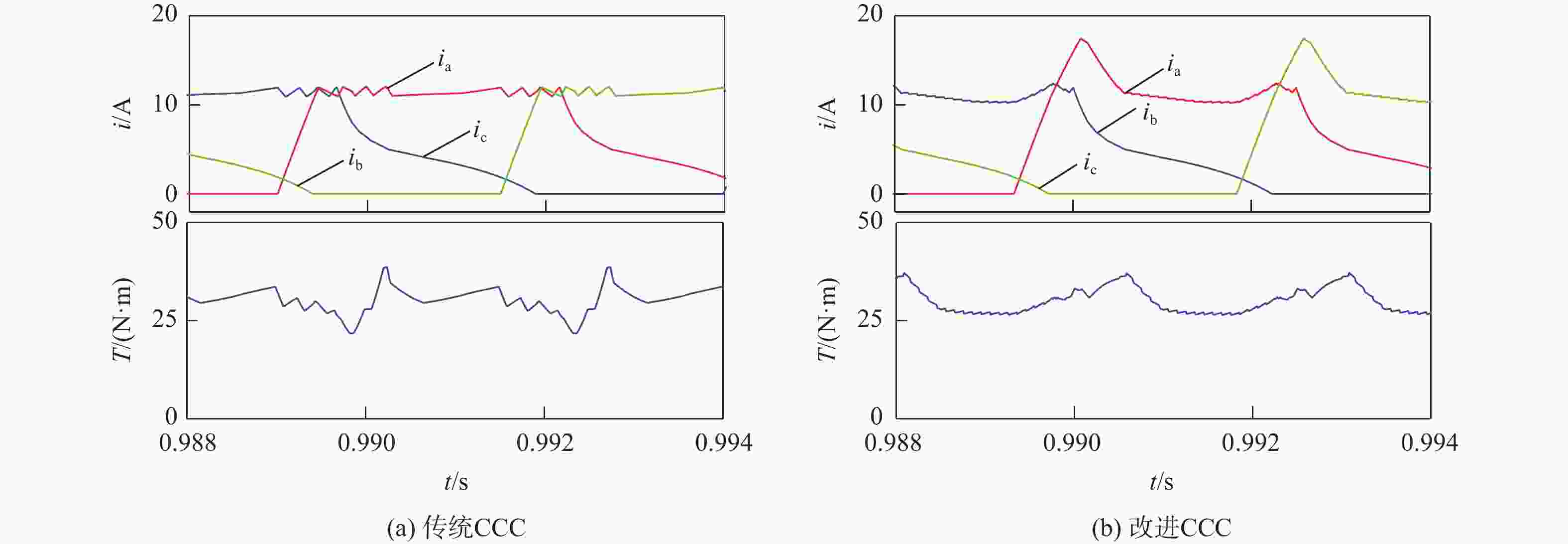
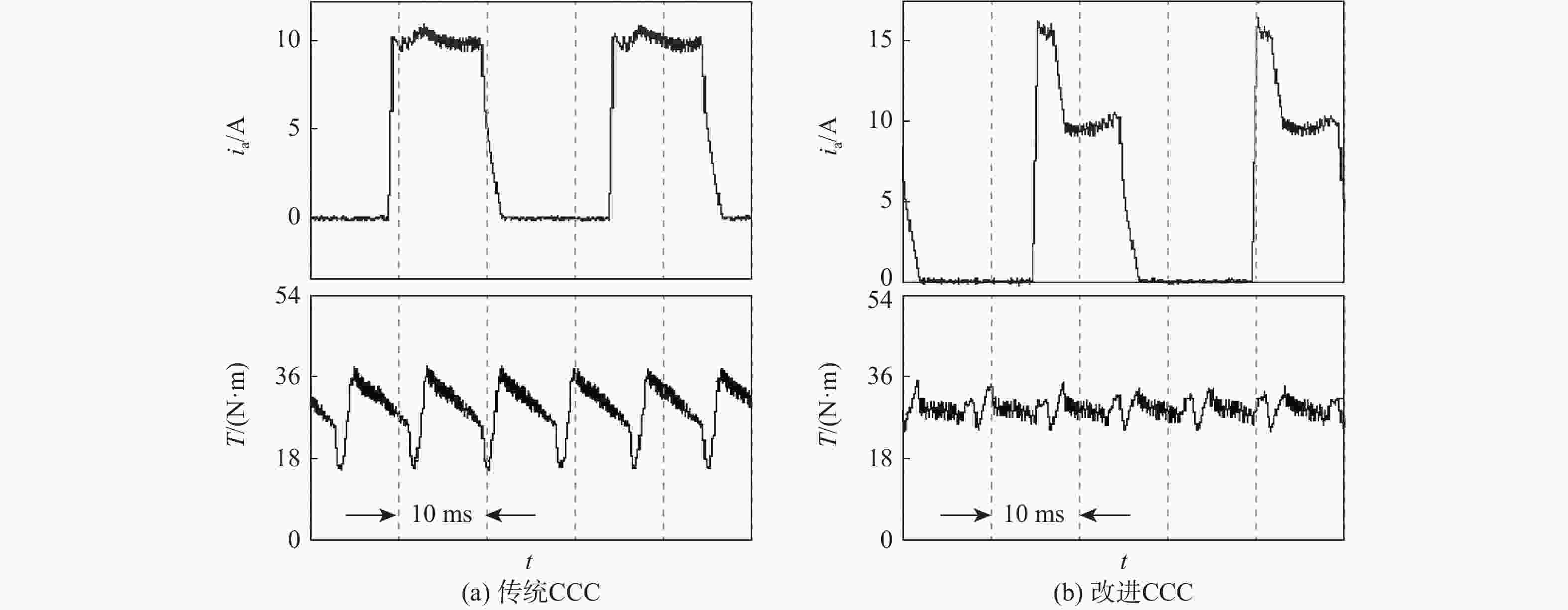
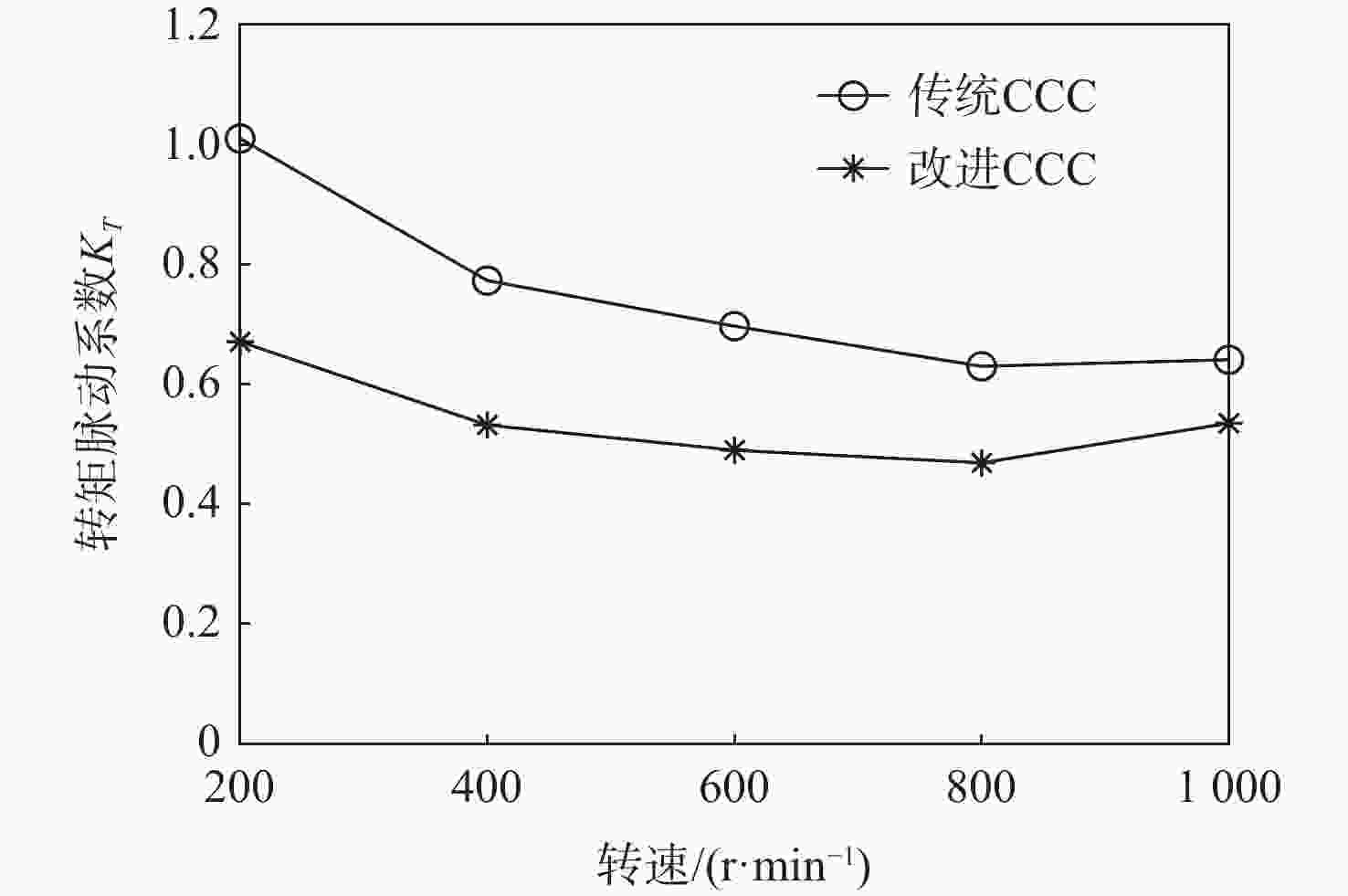
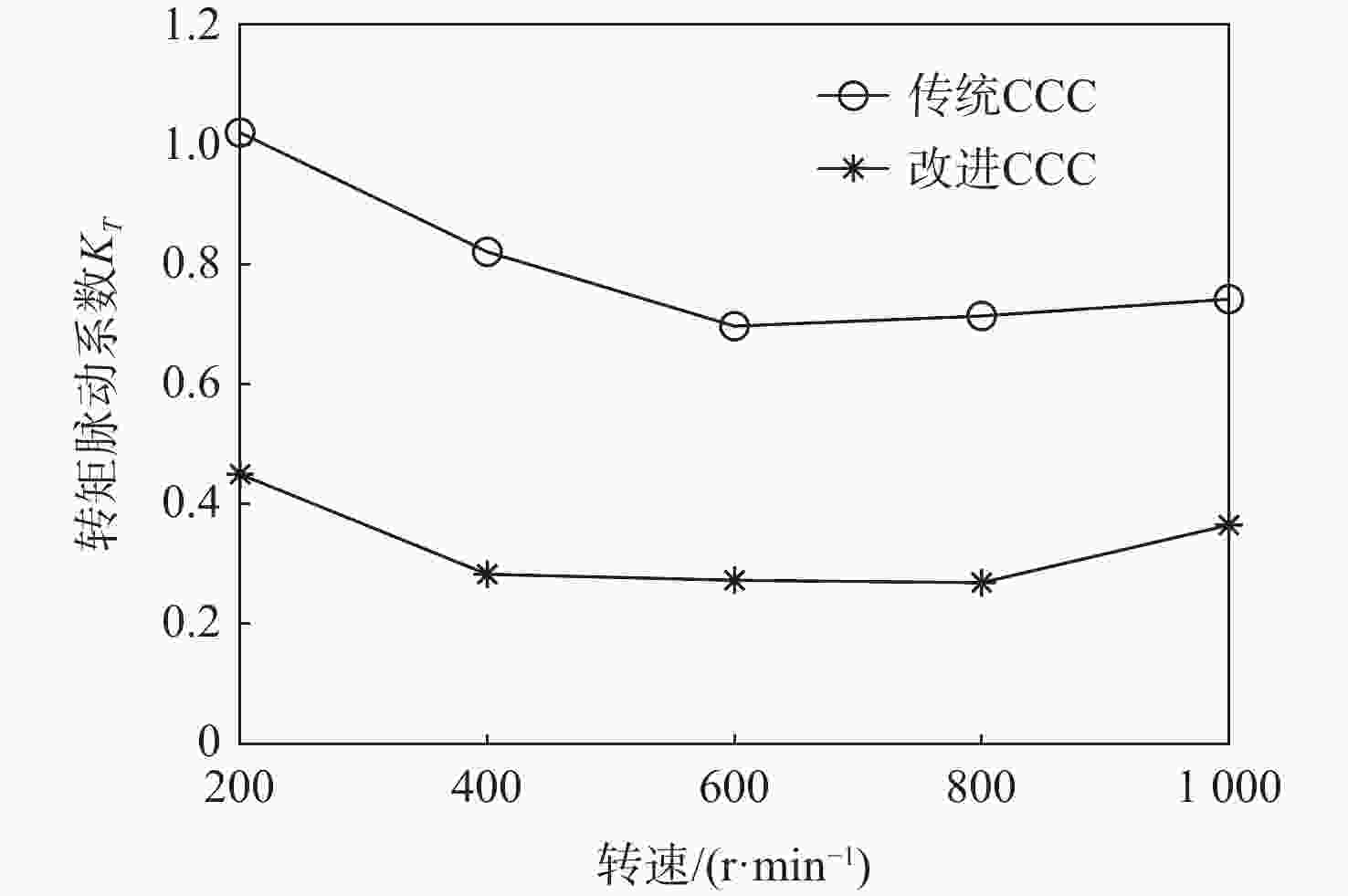
开关磁阻电机(SRM)运行在基速以下时常采用电流斩波控制(CCC),针对传统电流斩波控制中电流动态跟踪能力弱、换相区内转矩脉动大及功率器件开关频率不固定的问题,根据电感曲线的变化特征进行区间分段,提出一种基于参考电流补偿的电流斩波控制策略。在低电感区段内根据电机转速、负载的大小对参考电流进行补偿,提高相绕组在换相过程中的转矩输出能力和动态响应能力;在电感曲线的线性上升阶段,采用固定频率的脉冲宽度调制(PWM)波进行控制,使输出转矩更平滑。搭建三相12/8极开关磁阻电机仿真模型及硬件在环实验平台,考虑电机在不同转速、负载下的运行工况,选取转矩脉动指标进行对比。仿真与实验结果表明:所提控制策略能有效减小开关磁阻电机的转矩脉动,提高电机的运行性能。
Abstract:Switched reluctance motors (SRMs) often use current chopping control (CCC) when running below the base speed. In the traditional control, however, the dynamic tracking ability of current is weak, the torque ripple in the commutation area is large, and the switching frequency of power devices is not fixed. A soft chopping current control strategy is proposed based on reference current compensation and the interval segmented according to the characteristics of inductance curve changes. In the low-inductance section, the reference current is compensated according to motor speed and load to improve the torque output capability and dynamic response capability of the phase winding during commutation. In the linear rising stage of the inductance curve, a fixed frequency pulse width modulation (PWM) wave is used to control the output torque to make it smoother. Then this study sets up a three-phase 12/8 pole switched reluctance motor simulation model and a semi-physical experiment platform. Considering the operating conditions of the motor with different speeds and loads, the torque ripple index is chosen for comparison. Simulation and experimental results show that the control method proposed in this paper can effectively reduce the torque ripple of SRMS and improve the performance of the motor.
-
-
[1] ZUO S G, LIU M T, HU S L, et al. Torque ripple reduction of switched reluctance motor by optimising switch angle based on analytical modelling[J]. IET Electric Power Applications, 2020, 14(8): 1488-1495. doi: 10.1049/iet-epa.2019.0776 [2] 匡斯建, 张小平, 刘苹, 等. 基于相电感非饱和区定位的开关磁阻电机无位置传感器控制方法[J]. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35(20): 4296-4305. doi: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.191077KUANG S J, ZHANG X P, LIU P, et al. Sensorless control method for switched reluctance motors based on locations of phase inductance characteristic points[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35(20): 4296-4305(in Chinese). doi: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.191077 [3] YE J, BILGIN B, EMADI A. An offline torque sharing function for torque ripple reduction in switched reluctance motor drives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2015, 30(2): 726-735. doi: 10.1109/TEC.2014.2383991 [4] XUE X D, CHENG K W E, HO S L. Optimization and evaluation of torque-sharing functions for torque ripple minimization in switched reluctance motor drives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2009, 24(9): 2076-2090. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2009.2019581 [5] 颜宁, 曹鑫, 邓智泉. 基于全桥变换器的开关磁阻电机直接转矩控制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38(S1): 235-242.YAN N, CAO X, DENG Z Q. Direct torque control of switched reluctance motors based on full-bridge converter[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38(S1): 235-242 (in Chinese). [6] YAN N, CAO X, DENG Z Q. Direct torque control for switched reluctance motor to obtain high torque–ampere ratio[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(7): 5144-5152. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2870355 [7] 程勇, 曹晓晓, 张怡龙. 开关磁阻电机滞环-脉宽调制直接瞬时转矩控制[J]. 电机与控制学报, 2020, 24(8): 74-82. doi: 10.15938/j.emc.2020.08.010CHENG Y, CAO X X, ZHANG Y L. Hysteresis-PWM direct instantaneous torque control of switched reluctance motor[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2020, 24(8): 74-82(in Chinese). doi: 10.15938/j.emc.2020.08.010 [8] LIANG J, LEE D H, AHN J W. Direct instantaneous torque control of switched reluctance machines using 4-level converters[J]. IET Electric Power Applications, 2009, 3(4): 313-323. doi: 10.1049/iet-epa.2008.0002 [9] 朱叶盛, 章国宝, 黄永明. 基于PWM的开关磁阻电机直接瞬时转矩控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2017, 32(7): 31-39. doi: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.2017.07.004ZHU Y S, ZHANG G B, HUANG Y M. PWM-based direct instantaneous torque control of switched reluctance machine[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2017, 32(7): 31-39(in Chinese). doi: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.2017.07.004 [10] 王喜莲, 许振亮. 基于PI参数自适应的开关磁阻电机调速控制研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2015, 35(16): 4215-4223. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2015.16.025WANG X L, XU Z L. Speed regulation control of switched reluctance motors based on PI parameter self-adaptation[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2015, 35(16): 4215-4223(in Chinese). doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2015.16.025 [11] DÚBRAVKA P, RAFAJDUS P, MAKYŠ P, et al. Control of switched reluctance motor by current profiling under normal and open phase operating condition[J]. IET Electric Power Applications, 2017, 11(4): 548-556. doi: 10.1049/iet-epa.2016.0543 [12] 蔡辉, 王辉, 李孟秋, 等. 基于预测电流控制算法的开关磁阻电机转矩脉动抑制策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39(16): 4899-4909. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.171488CAI H, WANG H, LI M Q, et al. Predictive current control of switched reluctance motor for torque ripples minimization[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39(16): 4899-4909(in Chinese). doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.171488 [13] LIN Z Y, REAY D S, WILLIAMS B W, et al. Torque ripple reduction in switched reluctance motor drives using B-spline neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2006, 42(6): 1445-1453. doi: 10.1109/TIA.2006.882671 [14] LI C H, WANG G F, LI Y, et al. Robust adaptive neural network control for switched reluctance motor drives[J]. Automatika, 2018, 59(1): 24-34. doi: 10.1080/00051144.2018.1486797 [15] 潘再平, 罗星宝. 基于迭代学习控制的开关磁阻电机转矩脉动抑制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2010, 25(7): 51-55. doi: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.2010.07.009PAN Z P, LUO X B. Torque ripple minimization of switched reluctance motor based on iterative learning control[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2010, 25(7): 51-55(in Chinese). doi: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.2010.07.009 [16] XU Y Z, ZHONG R, CHEN L, et al. Analytical method to optimise turn-on angle and turn-off angle for switched reluctance motor drives[J]. IET Electric Power Applications, 2012, 6(9): 593-603. doi: 10.1049/iet-epa.2012.0157 -







 下载:
下载: