-
摘要:
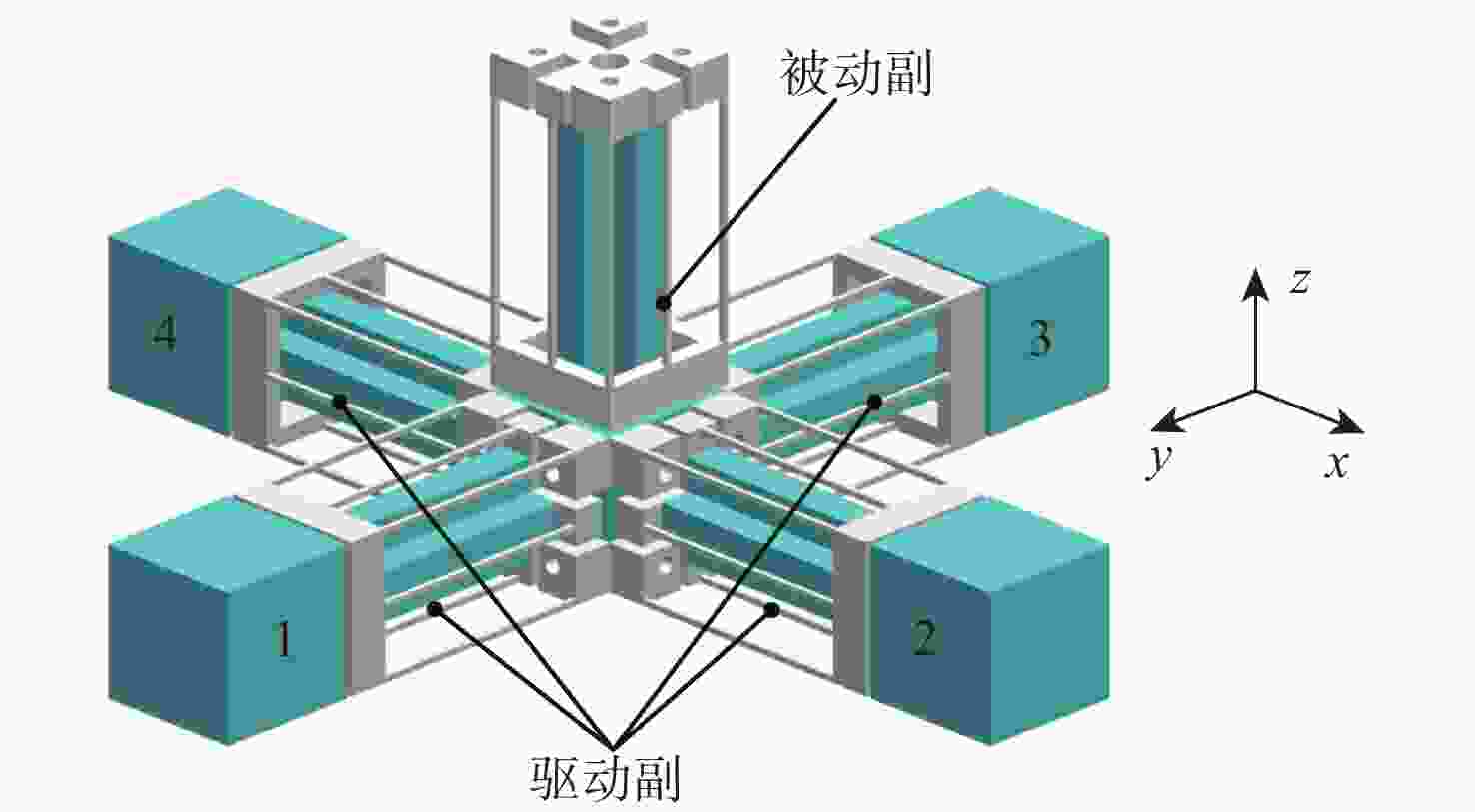
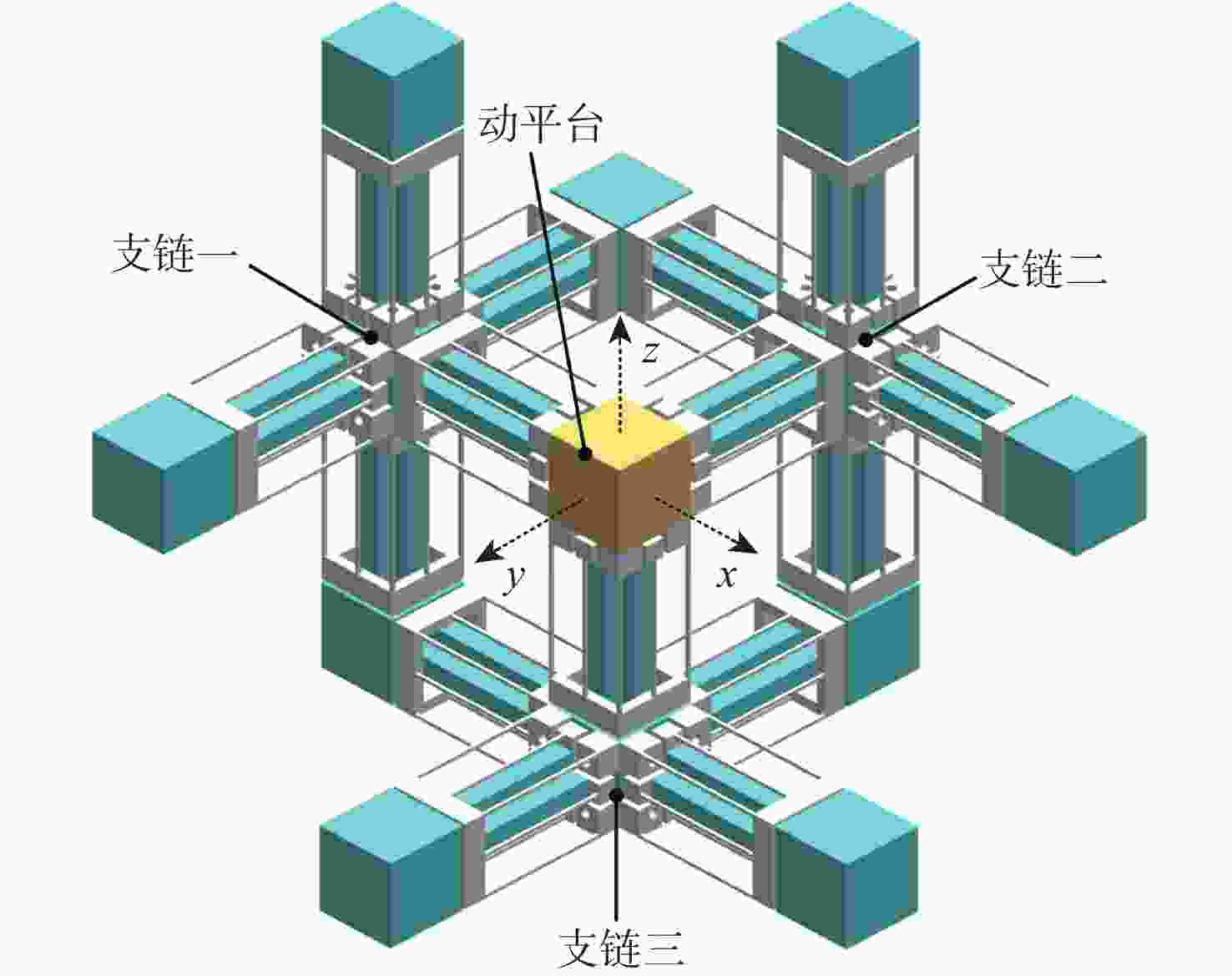
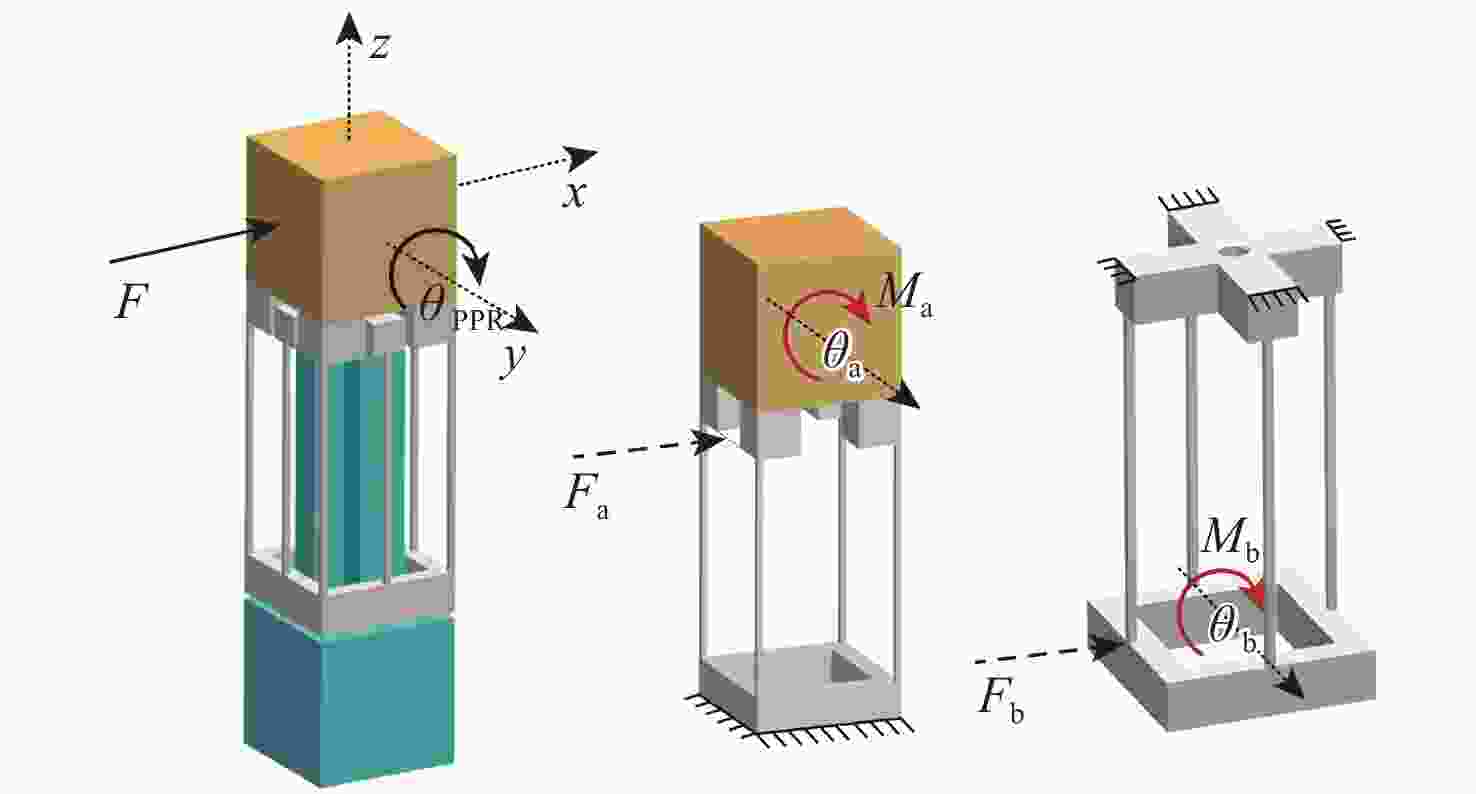
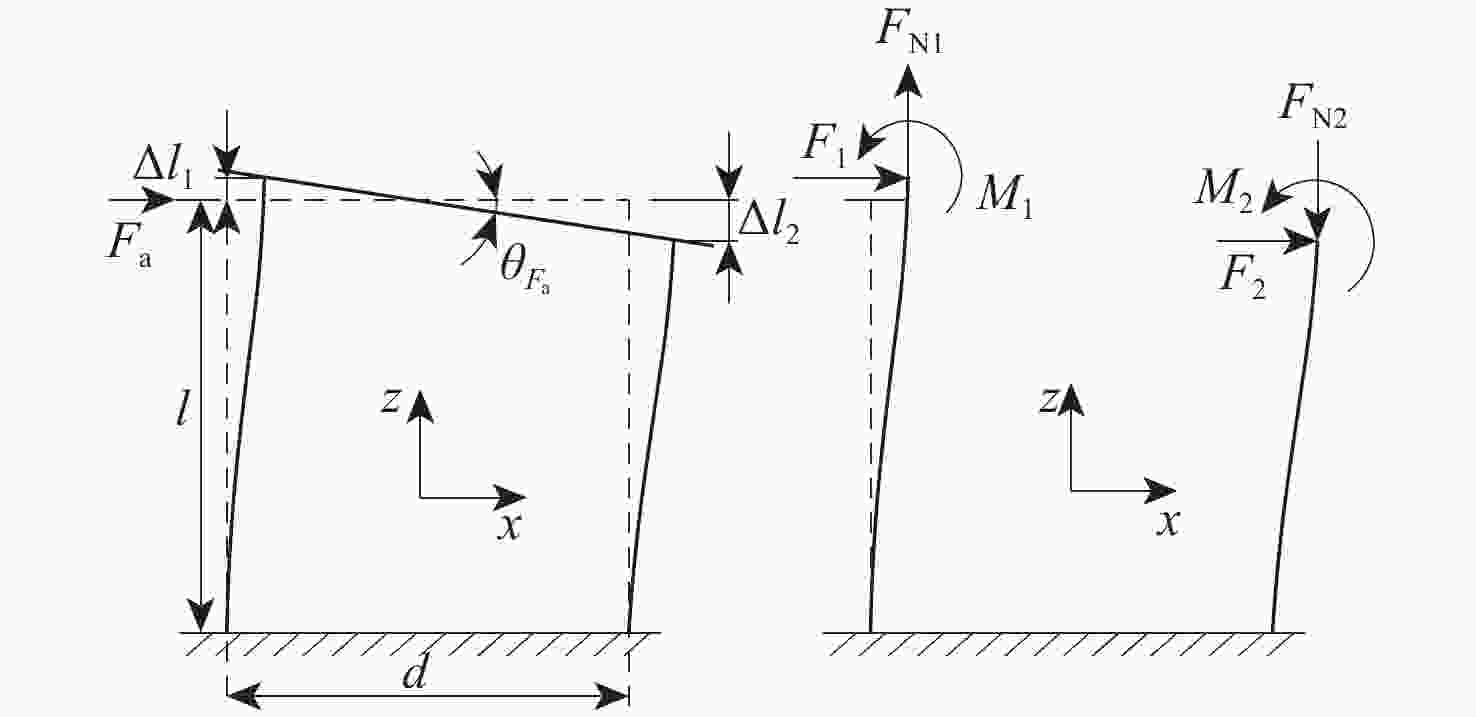
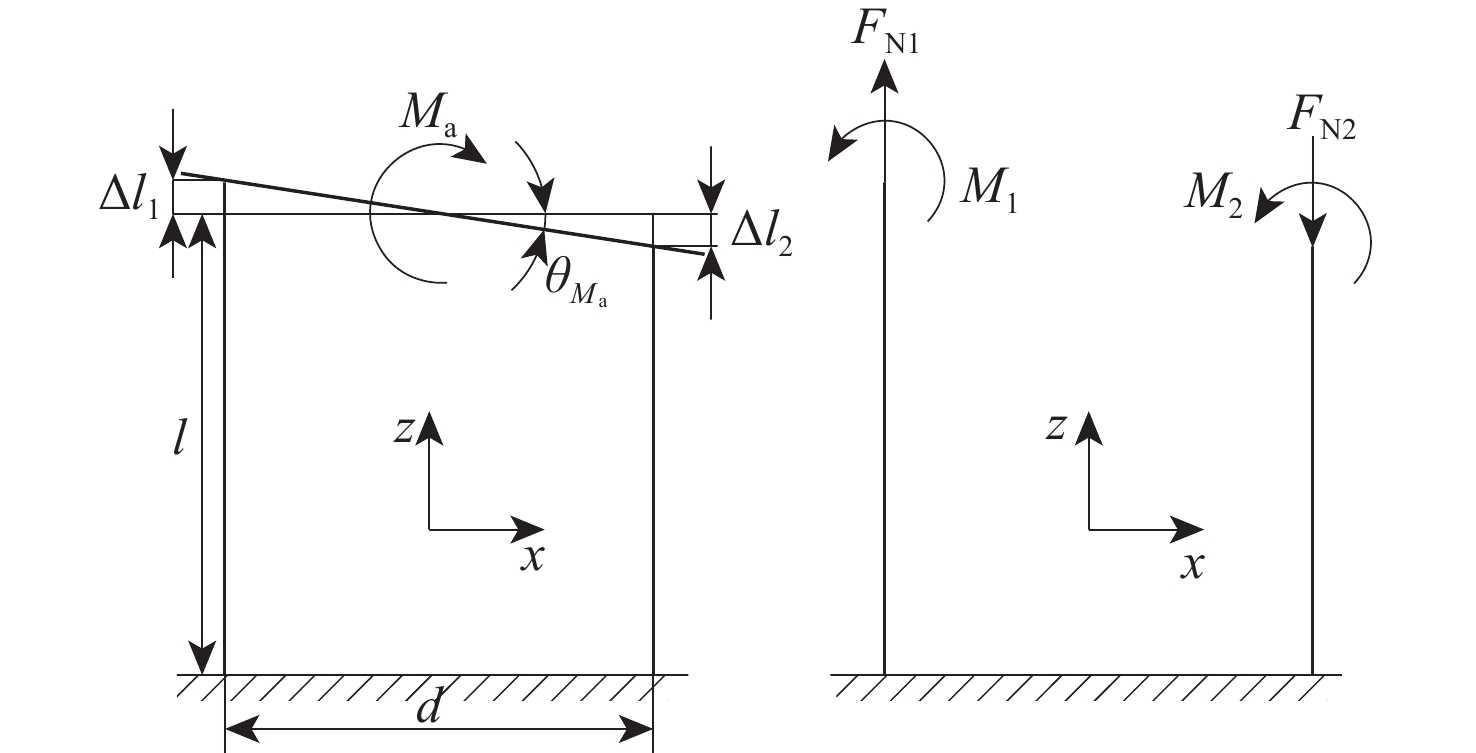
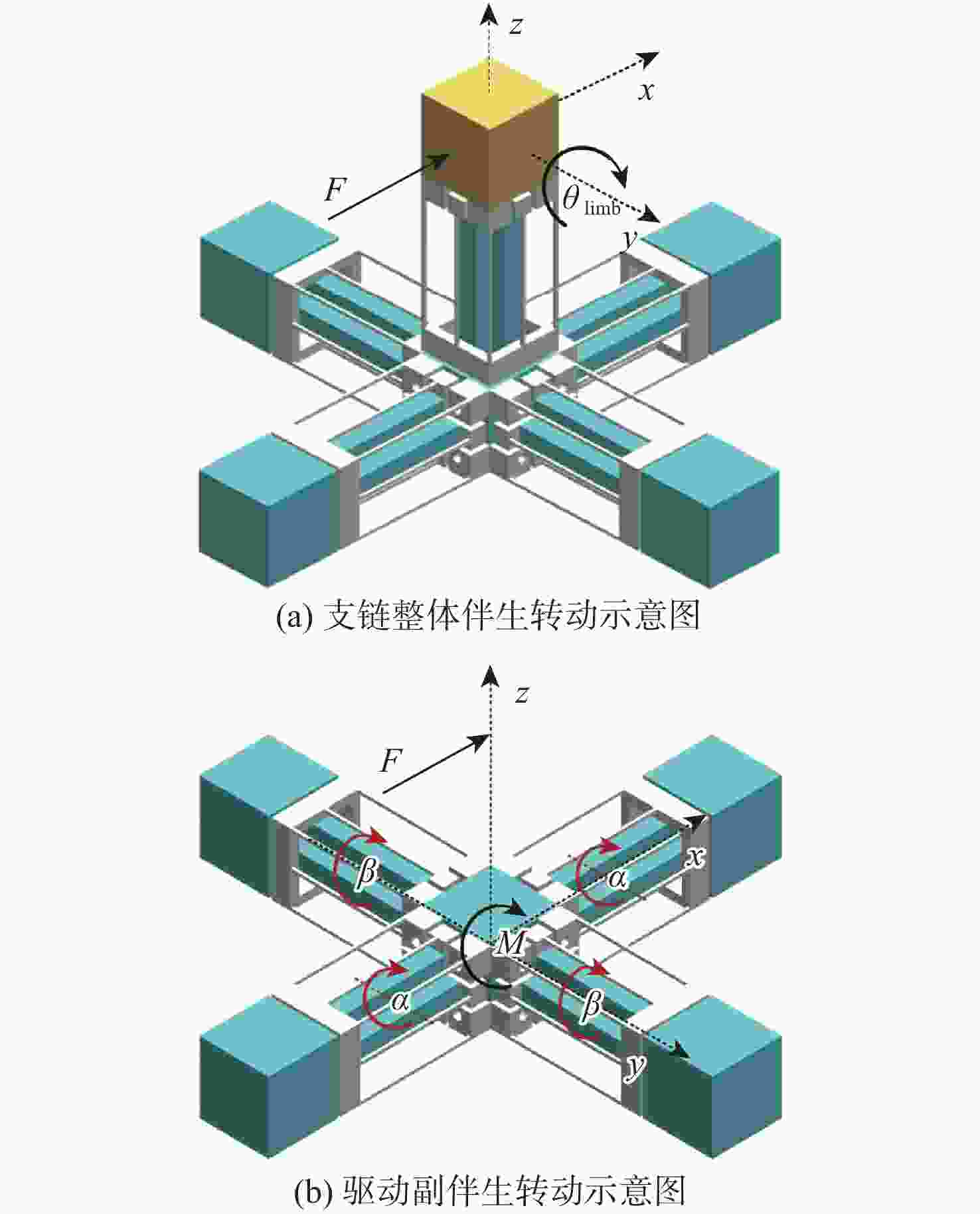
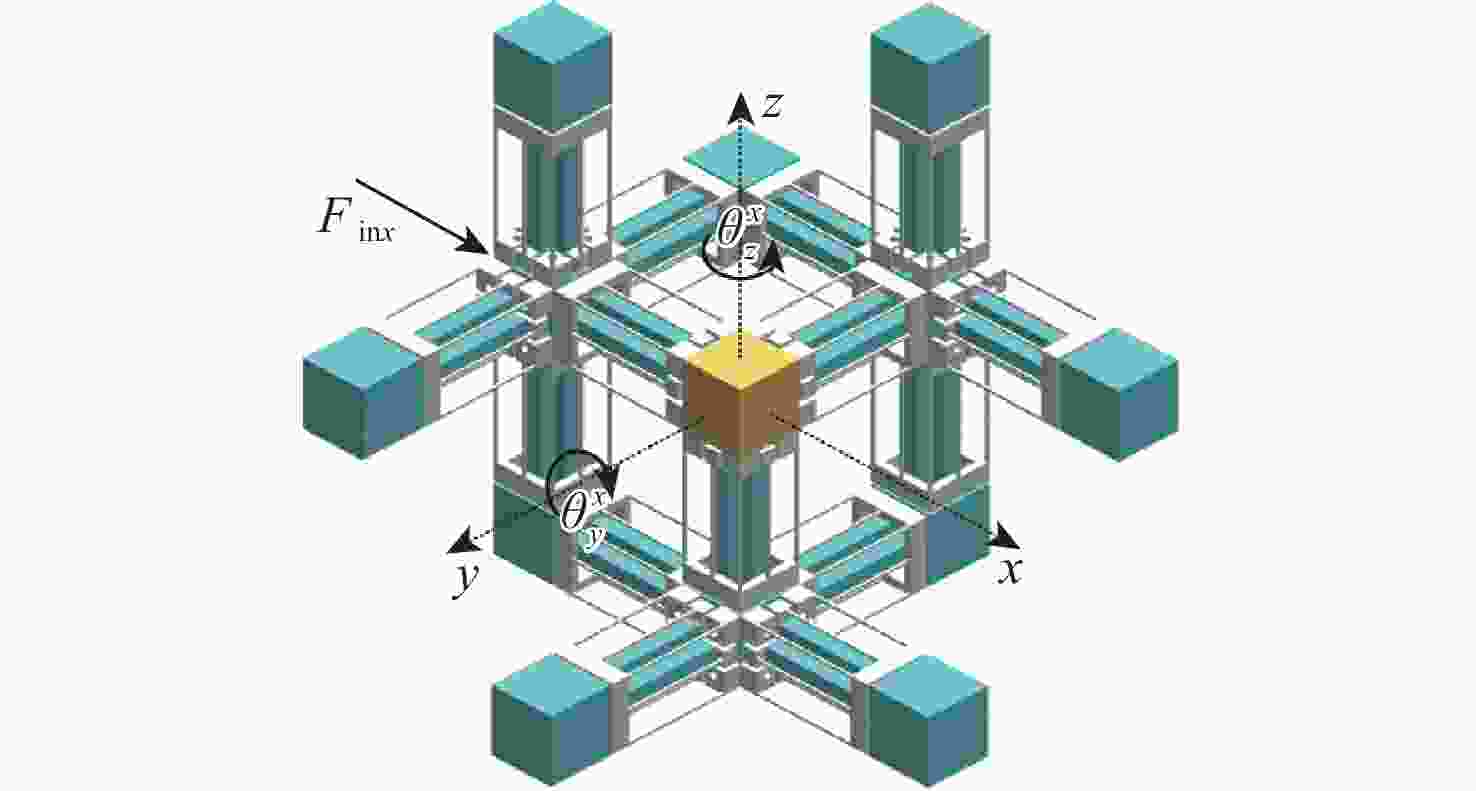
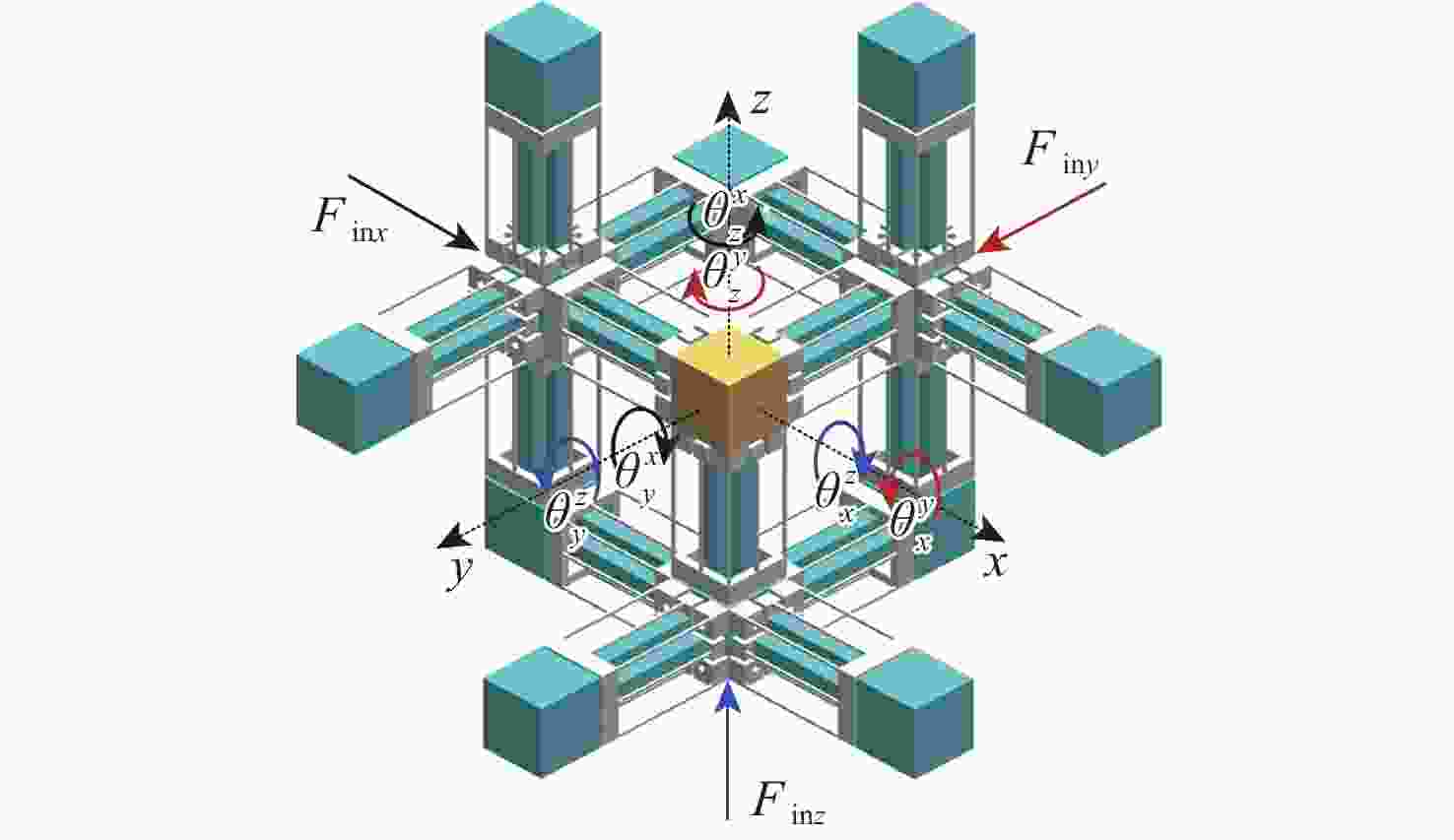
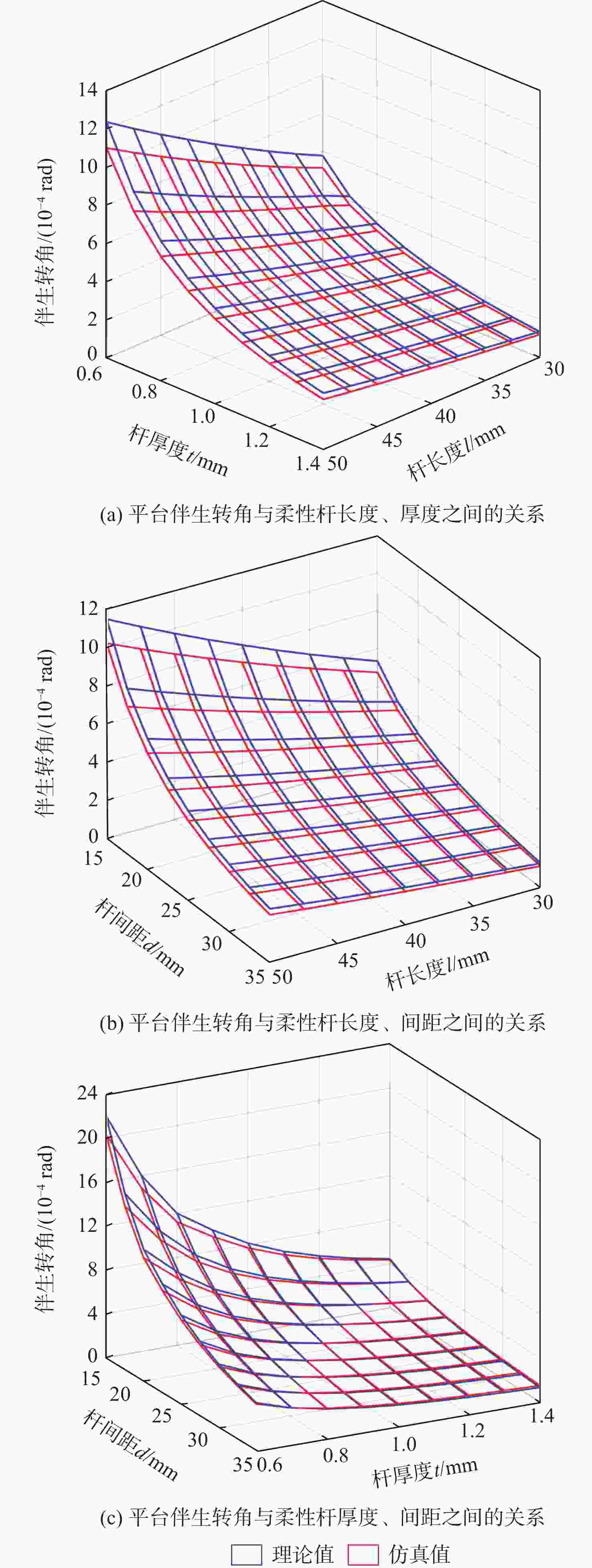
大行程柔性微定位平台在运动过程中不可避免地产生伴生转动现象,并对其定位精度造成消极影响。为降低伴生转动对平台定位精度的影响,提出一种基于柔性杆的三移一转(3-PPPR)型大行程柔性微定位平台,基于线弹性梁理论模型并考虑柔性杆轴向形变,对两移一转(PPR)柔性运动副伴生转角进行了理论建模,并基于此完成了对所提平台在单轴、双轴及三轴驱动时产生伴生转角的理论分析;再采用有限元分析对理论模型进行验证。最后探究了柔性杆尺寸参数与平台伴生转角之间的灵敏度关系,为所提平台性能提升奠定了基础,并据此提出了改善所提平台运动性能的优化方案。结果表明:3种驱动条件下平台伴生转角理论值与仿真值最大相对误差为2.46%。
Abstract:Parasitic rotation is inevitable during the movement of large stroke compliant micro-positioning platforms, causing a negative impact on their positioning precision. To reduce this effect, a 3-PPPR compliant micro-positioning platform with large stroke is proposed based on compliant beams. Then, based on linear elastic beam theory, the theoretical parasitic rotational angle of the PPR compliant kinematic joint is modeled considering the axial deformations of the beams. The parasitic rotational angles of the platform are also analyzed theoretically in uniaxial, biaxial and triaxial cases. Furthermore, the theoretical models are verified by finite element analysis. Finally, the sensitivity between the dimension parameters of the compliant beams and the parasitic rotational angle of the platform is analyzed, laying a foundation for the improvement of the platform. On this basis, the optimization schemes are proposed to improve the motion performance of the platform. results show that the maximum relative errors of the theoretical and simulated values of the parasitic rotational angle is 2.46% in three driven cases.
-
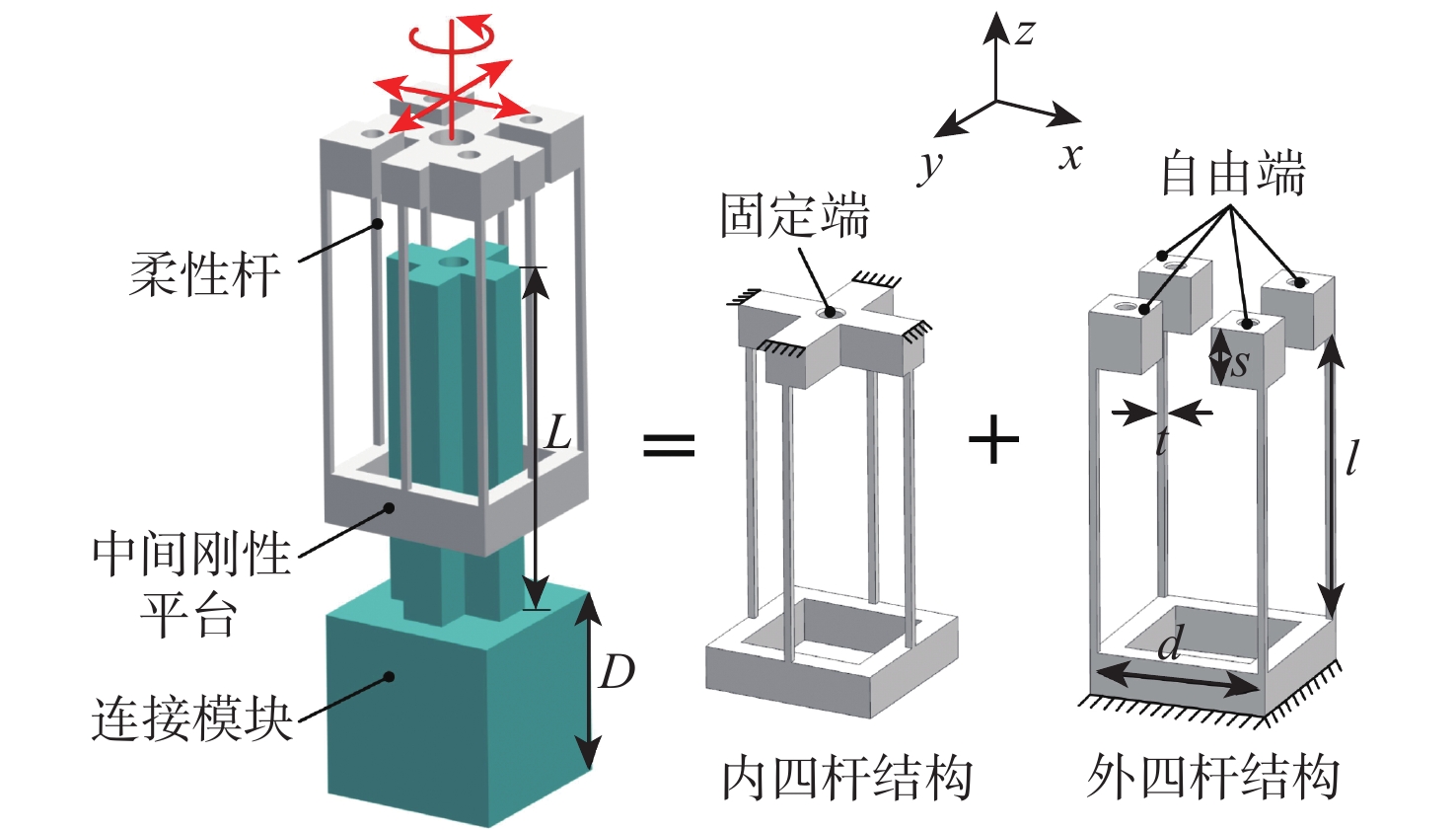
表 1 平台材料及尺寸参数
Table 1. Material and dimension parameters of platform
参数 数值 参数 数值 l/mm 40 弹性模量E/GPa 71.7 t/mm 1 剪切模量G/GPa 26.9 d/mm 24 泊松比ν 0.33 s/mm 6 屈服强度σ/MPa 503 L/mm 47 密度ρ/(kg·m−3) 2 810 D/mm 25 表 2 平台伴生转角理论、仿真值及其相对误差
Table 2. Theoretical values, simulation values and relative errors of parasitic rotational angles
运动状态 伴生转角 理论值/rad 仿真值/rad 相对误差/% 单支链 ${\theta _{{\text{limb}}}}$ 8.96×10−4 8.77×10−4 2.12 x单轴 $\theta _y^x$ 4.48×10−4 4.39×10−4 2.01 $\theta _z^x$ 4.48×10−4 4.40×10−4 1.79 x、y
双轴$\theta _x^{xy}$ 4.48×10−4 4.37×10−4 2.46 $\theta _y^{xy}$ 4.48×10−4 4.42×10−4 1.34 $\theta _z^{xy}$ 0 1.2×10−7 x、y、z
三轴$\theta _x^{xyz}$ 0 4.0×10−7 $\theta _y^{xyz}$ 0 8.8×10−7 $\theta _z^{xyz}$ 0 4.0×10−7 -
[1] 于靖军, 郝广波, 陈贵敏, 等. 柔性机构及其应用研究进展[J]. 机械工程学报, 2015, 51(13): 53-68. doi: 10.3901/JME.2015.13.053YU J J, HAO G B, CHEN G M, et al. State-of-art of compliant mechanisms and their applications[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 51(13): 53-68(in Chinese). doi: 10.3901/JME.2015.13.053 [2] HOWELL L L. Compliant mechanisms[M]. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 2001: 2-14. [3] 贾晓辉, 刘今越, 田延岭. 空间全柔性并联机构动力学分析[J]. 农业机械学报, 2012, 43(8): 210-214. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2012.08.038JIA X H, LIU J Y, TIAN Y L. Dynamics analysis of spatial compliant parallel mechanism[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2012, 43(8): 210-214(in Chinese). doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2012.08.038 [4] 周睿, 周辉, 桂和利, 等. 基于柔性铰链的二自由度微动平台分析及优化[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(9): 1982-1990.ZHOU R, ZHOU H, GUI H L, et al. Analysis and optimization of 2-DoF micro-positioning stage based on flexible hinges[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics. 2018, 44(9): 1982-1990 (in Chinese). [5] 曹毅, 王保兴, 孟刚, 等. 大行程三平动柔性微定位平台的设计分析及优化[J]. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56(17): 71-81. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.17.071CAO Y, WANG B X, MENG G, et al. Design analysis and optimization of large range spatial translational compliant micro-positioning stage[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(17): 71-81(in Chinese). doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.17.071 [6] 王萍萍, 刘磊. 柔性航天器高精度隔振与定向研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2012, 33(9): 1195-1202.WANG P P, LIU L. Research on high accuracy pointing of the flexible spacecraft with Stewart platform[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2012, 33(9): 1195-1202(in Chinese). [7] 刘璟龙, 张崇峰, 邹怀武, 等. 基于干扰观测器的柔性空间机器人在轨精细操作控制方法[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(1): 523899.LIU J L, ZHANG C F, ZOU H W, et al. On-orbit precise operation control method for flexible joint space robots based on disturbance observer[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(1): 523899(in Chinese). [8] DI GIAMBERARDINO P, BAGOLINI A, BELLUTTI P, et al. New MEMS tweezers for the viscoelastic characterization of soft materials at the microscale[J]. Micromachines, 2017, 9(1): 15. doi: 10.3390/mi9010015 [9] 李杨民, 汤晖, 徐青松, 等. 面向生物医学应用的微操作机器人技术发展态势[J]. 机械工程学报, 2011, 47(23): 1-13. doi: 10.3901/JME.2011.23.001LI Y M, TANG H, XU Q S, et al. Development status of micromanipulator technology for biomedical applications[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2011, 47(23): 1-13(in Chinese). doi: 10.3901/JME.2011.23.001 [10] WANG R Z, ZHANG X M. A planar 3-DOF nanopositioning platform with large magnification[J]. Precision Engineering, 2016, 46: 221-231. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2016.04.016 [11] HAO G B, KONG X W. Design and modeling of a large-range modular XYZ compliant parallel manipulator using identical spatial modules[J]. Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics, 2012, 4(2): 1-10. [12] 牟新明, 王建华, 杨密. 平行簧片机构力学分析与计算[J]. 纳米技术与精密工程, 2005, 3(4): 278-282. doi: 10.13494/j.npe.2005.051MU X M, WANG J H, YANG M. Mechanical analysis and computation of parallel springs[J]. Nanotechnology and Precision Engineering, 2005, 3(4): 278-282(in Chinese). doi: 10.13494/j.npe.2005.051 [13] LUO Y Q, LIU W Q. Analysis of the displacement of distributed compliant parallel-guiding mechanism considering parasitic rotation and deflection on the guiding plate[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2014, 80: 151-165. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2014.06.005 [14] HAO G B. Towards the design of monolithic decoupled XYZ compliant parallel mechanisms for multi-function applications[J]. Mechanical Sciences, 2013, 4(2): 291-302. doi: 10.5194/ms-4-291-2013 [15] HAO G B, LI H Y. Design of 3-legged XYZ compliant parallel manipulators with minimised parasitic rotations[J]. Robotica, 2015, 33(4): 787-806. doi: 10.1017/S0263574714000575 [16] SU H J, SHI H, YU J J. A symbolic formulation for analytical compliance analysis and synthesis of flexure mechanisms[J]. Journal of Mechanical Design, 2012, 134(5): 051009. doi: 10.1115/1.4006441 [17] AWTAR S, USTICK J, SEN S. An XYZ parallel kinematic flexure mechanism with geometrically decoupled degrees of freedom[J]. Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics, 2013, 5(1): 015001. doi: 10.1115/1.4007768 [18] LIN H R, CHENG C H, HUNG S K. Design and quasi-static characteristics study on a planar piezoelectric nanopositioner with ultralow parasitic rotation[J]. Mechatronics, 2015, 31(1): 180-188. [19] DONG W, SUN L N, DU Z J. Design of a precision compliant parallel positioner driven by dual piezoelectric actuators[J]. Sensors and Actuators A:Physical, 2007, 135(1): 250-256. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2006.07.011 [20] HERPE X, WALKER R, DUNNIGAN M, et al. On a simplified nonlinear analytical model for the characterisation and design optimisation of a compliant XY micro-motion stage[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2018, 49: 66-76. doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2017.05.012 [21] 李海洋, 郝广波, 于靖军, 等. 空间平动柔性并联机构的系统设计方法研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2018, 54(13): 57-65. doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.13.057LI H Y, HAO G B, YU J J. et al. Systematic approach to the design of spatial translational compliant parallel mechanisms[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 54(13): 57-65(in Chinese). doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.13.057 [22] HOPKINS J B, CULPEPPER M L. Synthesis of multi-degree of freedom, parallel flexure system concepts via freedom and constraint topology (FACT) Part I: Principles[J]. Precision Engineering, 2010, 34(2): 259-270. [23] HOPKINS J B, CULPEPPER M L. Synthesis of multi-degree of freedom, parallel flexure system concepts via Freedom and constraint topology (FACT) Part II: Principles[J]. Precision Engineering, 2010, 34(2): 271-278. [24] 黄真, 刘婧芳, 曾达幸. 基于约束螺旋理论的机构自由度分析的普遍方法[J]. 中国科学, 2009, 39(1): 84-93.HUANG Z, LIU J F, ZENG D X. A general methodology for mobility analysis of mechanism based on the constraint screw theory[J]. Science in China, 2009, 39(1): 84-93 (in Chinese). [25] MURANAKA Y, INABA M, ASANO T, et al. Parasitic rotation in parallel spring movements[J]. International Journal of The Japan Society for Precision Engineering, 1991, 25(3): 208-213. [26] KOSEKI Y, TANIKAWA T, KOYACHI N, et al. Kinematic analysis of translational 3-DOF micro parallel mechanism using matrix method[C]// IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2000 : 786-792. [27] 王保兴, 孟刚, 林苗, 等. 3-PPP型柔性并联微定位平台的设计与分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(4): 798-807.WANG B X, MENG G, LIN M, et al. Design and analysis of a 3-PPP compliant parallel micro-positioning stage[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(4): 798-807(in Chinese). [28] TANG H, LI Y M. Design analysis and test of a novel 2-DOF nanopositioning system driven by dual mode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2013, 29(3): 650-662. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2013.2248536 -







 下载:
下载: