Air combat maneuver trajectory prediction of target based on Volterra series optimized by SABA algorithm
-
摘要:
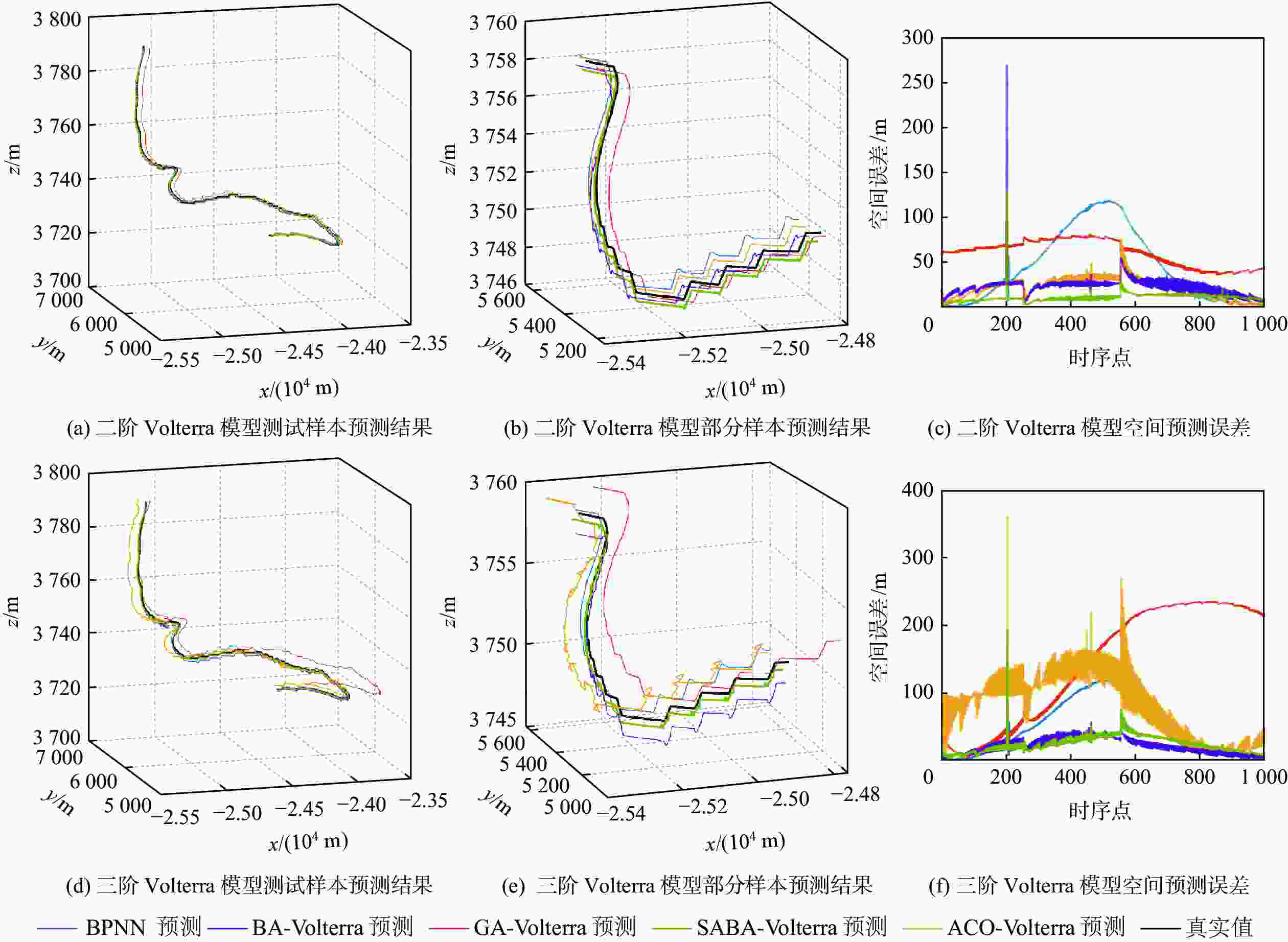
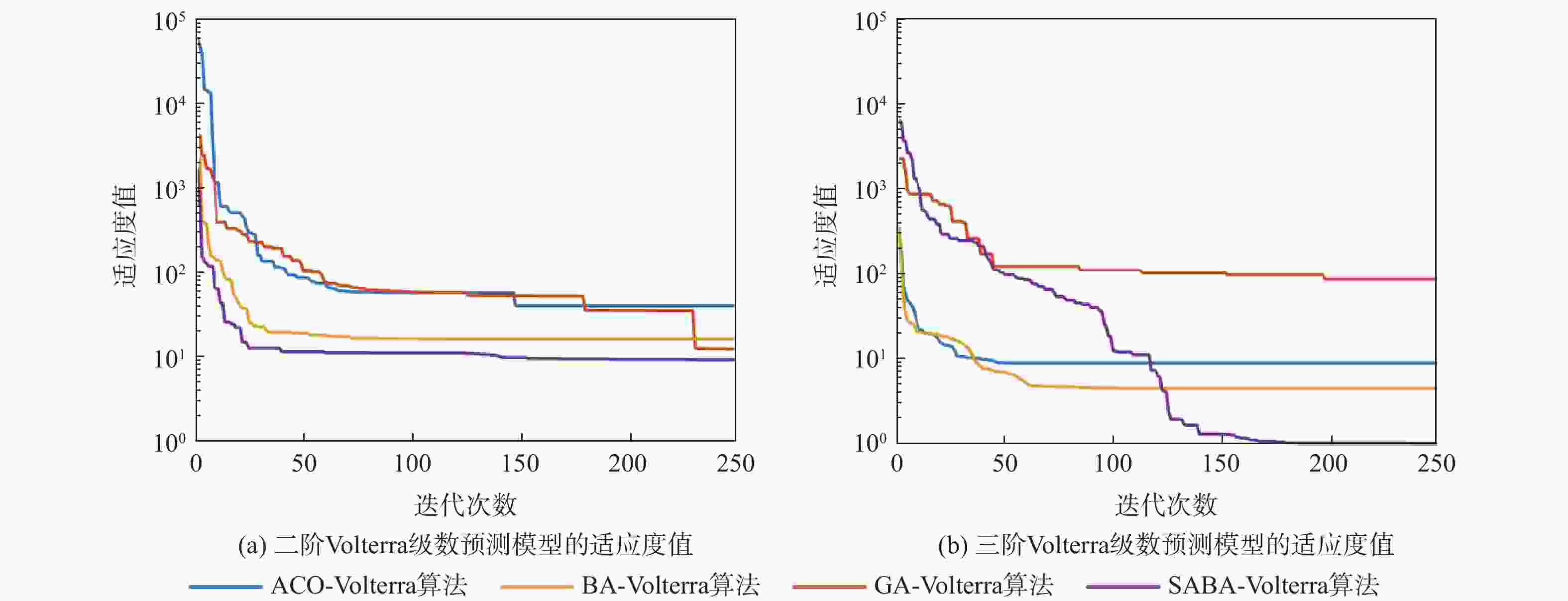
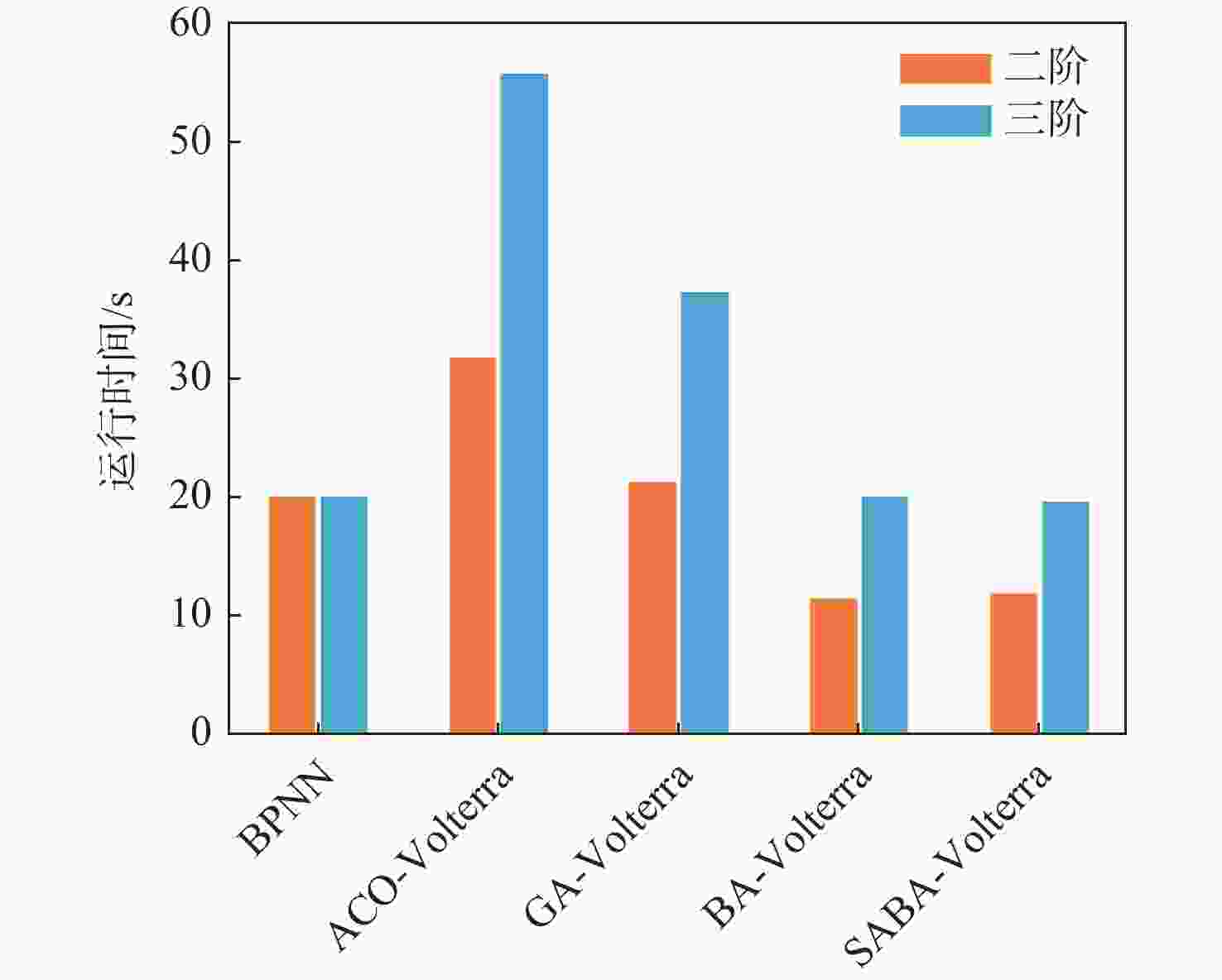
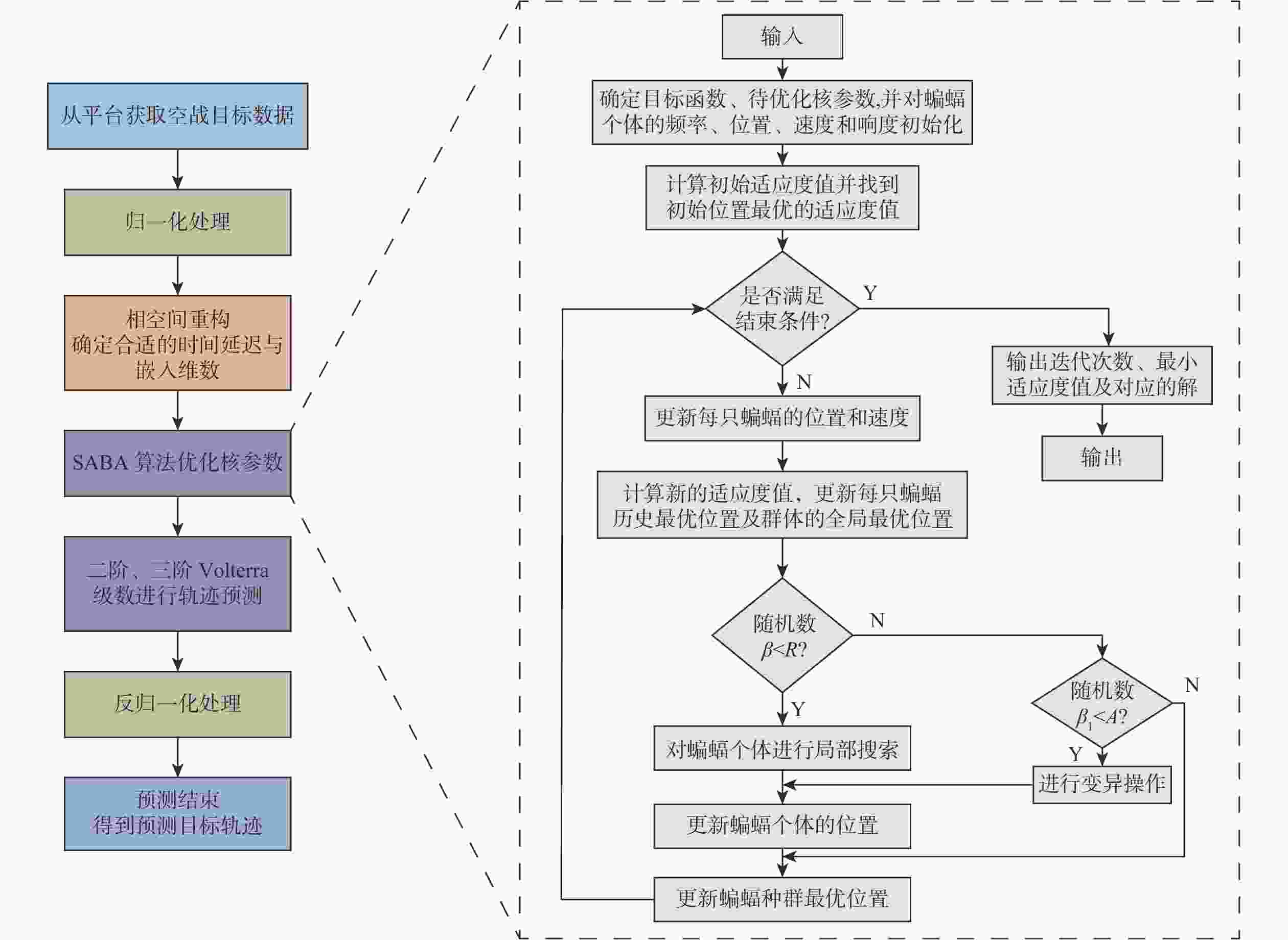
目标机动轨迹预测是空战态势感知和目标威胁评估的重要前提。针对传统目标机动轨迹预测模型复杂度大、预测精度低等问题,通过分析并结合目标机动轨迹时序数据所具备的混沌特性,引入Volterra泛函级数模型进行目标机动轨迹预测。为解决Volterra泛函级数模型中存在高阶核函数难以求解的问题,利用变异机制和自适应步长控制机制改进蝙蝠算法的寻优能力,进而构建了一种基于自适应蝙蝠算法(SABA)优化的Volterra泛函级数目标机动轨迹预测模型,并利用优化后不同阶数的Volterra泛函级数模型对目标未来机动轨迹进行预测。仿真实验中,通过与其他优化算法改进的Volterra泛函级数模型的预测精度对比,验证了所提预测模型的可行性,同时也说明了二阶Volterra泛函级数模型更加适用于目标机动轨迹预测。
-
关键词:
- 轨迹预测 /
- Volterra泛函级数模型 /
- 核参数优化 /
- 自适应蝙蝠算法 /
- 截断阶数
Abstract:Target maneuver trajectory prediction is an important prerequisite for air combat situation awareness and target threat assessment. Aiming at the problems of high complexity and low prediction accuracy of traditional target maneuvering trajectory prediction model, Volterra functional series model was introduced to predict the target maneuvering trajectory by analyzing and combining the chaotic characteristics of target maneuvering trajectory time series data. To solve the problem that it is difficult to solve the high-order kernel function in Volterra functional series model, the mutation mechanism and adaptive step control mechanism were used to improve the optimization ability of bat algorithm. Then, a Volterra functional series target maneuver trajectory prediction model based on self-adaptive bat algorithm (SABA) optimization was constructed, and the future maneuvering trajectory of the target was predicted by using the optimized Volterra series model with different orders. In the simulation experiment, the feasibility of the prediction model is verified by comparing with the prediction accuracy of the Volterra series prediction model improved by other optimization algorithms, and the second-order Volterra series model is proved to bemore suitable for target maneuver trajectory prediction.
-
表 1 不同预测模型进行2步预测的性能对比
Table 1. Performance comparison of two-step prediction with different prediction models
算法 阶数 Mad Mse Mape Cor BA-Volterra 二阶 21.9137 6.563 3×102 0.0009 0.9983 BA-Volterra 三阶 30.5021 1.460 4×103 0.0012 0.9976 SABA-Volterra 二阶 15.4337 2.424 6×102 0.0006 0.9987 SABA-Volterra 三阶 25.1874 8.296 9×102 0.0010 0.9978 ACO-Volterra 二阶 24.4320 8.006 2×102 0.0010 0.9979 ACO-Volterra 三阶 112.5901 1.684 0×104 0.0043 0.9891 GA-Volterra 二阶 35.4252 1.355 7×103 0.0014 0.9975 GA-Volterra 三阶 202.4583 5.289 1×104 0.0080 0.9836 BPNN 83.7994 9.162 4×103 0.0033 0.9971 表 2 不同预测模型进行4步预测的性能对比
Table 2. Performance comparison of four-step prediction with different prediction models
算法 阶数 Mad Mse Mape Cor BA-Volterra 二阶 85.6052 8.851 1×103 0.0033 0.9899 BA-Volterra 三阶 134.2922 2.223 0×104 0.0053 0.9886 SABA-Volterra 二阶 27.9075 1.269 8×103 0.0011 0.9982 SABA-Volterra 三阶 27.9597 1.104 6×103 0.0011 0.9983 ACO-Volterra 二阶 30.5999 1.143 9×103 0.0013 0.9978 ACO-Volterra 三阶 114.2622 1.695 3×104 0.0045 0.9890 GA-Volterra 二阶 53.7130 3.015 4×103 0.0021 0.9970 GA-Volterra 三阶 210.4822 5.956 8×104 0.0082 0.9834 BPNN 221.7636 7.253 6×104 0.0087 0.9830 表 3 不同预测模型进行8步预测的性能对比
Table 3. Performance comparison of eight-step prediction with different prediction models
算法 阶数 Mad Mse Mape Cor BA-Volterra 二阶 108.0024 1.475 9×104 0.0042 0.9887 BA-Volterra 三阶 125.6733 1.900 8×104 0.0049 0.9888 SABA-Volterra 二阶 39.5275 1.589 9×103 0.0015 0.9976 SABA-Volterra 三阶 71.7624 6.519 5×103 0.0028 0.9968 ACO-Volterra 二阶 294.7023 1.395 2×105 0.0114 0.9811 ACO-Volterra 三阶 545.3952 3.806 3×105 0.0212 0.9689 GA-Volterra 二阶 100.6532 1.049 8×104 0.0039 0.9890 GA-Volterra 三阶 430.5977 2.278 4×105 0.0167 0.9753 BPNN 369.8697 1.923 3×105 0.0144 0.9773 -
[1] 寇英信, 李战武, 陈哨东, 等. 火控系统在航空作战中的作用——作战飞机之“魂”[J]. 电光与控制, 2013, 20(12): 1-5.KOU Y X, LI Z W, CHEN S D, et al. The important role of fire control system in air combat—Soul of fighters[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2013, 20(12): 1-5(in Chinese). [2] 姜佰辰, 关键, 周伟, 等. 基于多项式卡尔曼滤波的船舶轨迹预测算法[J]. 信号处理, 2019, 35(5): 741-746.JIANG B C, GUAN J, ZHOU W, et al. Vessel trajectory prediction algorithm based on polynomial fitting Kalman filtering[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2019, 35(5): 741-746(in Chinese). [3] 赵帅兵, 唐诚, 梁山, 等. 基于改进卡尔曼滤波的控制河段船舶航迹预测[J]. 计算机应用, 2012, 32(11): 3247-3250.ZHAO S B, TANG C, LIANG S, et al. Track prediction of vessel in controlled waterway based on improved Kalman filter[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2012, 32(11): 3247-3250(in Chinese). [4] 乔少杰, 韩楠, 朱新文, 等. 基于卡尔曼滤波的动态轨迹预测算法[J]. 电子学报, 2018, 46(2): 418-423.QIAO S J, HAN N, ZHU X W, et al. A dynamic trajectory prediction algorithm based on Kalman filter[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2018, 46(2): 418-423(in Chinese). [5] 翟岱亮, 雷虎民, 李炯, 等. 基于自适应IMM的高超声速飞行器轨迹预测[J]. 航空学报, 2016, 37(11): 3466-3475.ZHAI D L, LEI H M, LI J, et al. Trajectory prediction of hypersonic vehicle based on adaptive IMM[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2016, 37(11): 3466-3475(in Chinese). [6] 杨彬, 贺正洪. 一种GRNN神经网络的高超声速飞行器轨迹预测方法[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2015, 32(7): 239-243.YANG B, HE Z H. Hypersonic vehicle track prediction based on GRNN[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2015, 32(7): 239-243(in Chinese). [7] 谭伟, 陆百川, 黄美灵. 神经网络结合遗传算法用于航迹预测[J]. 重庆交通大学学报, 2010, 291(1): 147-150.TAN W, LU B C, HUANG M L. Track prediction based on neural networks and genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2010, 291(1): 147-150(in Chinese). [8] 甘旭升, 端木京顺, 孟月波, 等. 基于粒子群优化的WNN飞行数据气动力建模[J]. 航空学报, 2012, 33(7): 1209-1217.GAN X S, DUANGMU J S, MENG Y B, et al. Aerodynamic modeling from flight data based on WNN optimized by particle swarm[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2012, 33(7): 1209-1217(in Chinese). [9] SLATTERY R, ZHAO Y. Trajectory synthesis for air traffic automation[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamic, 1997, 20(2): 232-238. doi: 10.2514/2.4056 [10] 张家良, 曹建福, 高峰. 大型装备传动系统非线性频谱特征提取与故障诊断[J]. 控制与决策, 2012, 27(1): 135-138.ZHANG J L, CAO J F, GAO F. Feature extraction and fault diagnosis of large-scale equipment transmission system based on nonlinear frequency spectrum[J]. Control and Decision, 2012, 27(1): 135-138(in Chinese). [11] 张华君. 基于递推批量最小二乘的Volterra级数辨识方法[J]. 小型微型计算机, 2004, 25(12): 2282-2285.ZHANG H J. Volterra series identification method based on recursive least square algorithm[J]. Mini-Micro Systems, 2004, 25(12): 2282-2285(in Chinese). [12] 孔祥玉, 韩崇昭, 马红光, 等. 基于Volterra级数的全解耦RLS自适应辨识算法[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2004, 16(4): 807-809.KONG X Y, HAN C Z, MA H G, et al. Fully decoupled RLS adaptive identification algorithm based on Volterra series[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2004, 16(4): 807-809(in Chinese). [13] 孔祥玉, 韩崇昭, 马红光, 等. 一种总体最小二乘算法及在Volterra滤波器中的应用[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2004, 38(4): 339-342.KONG X Y, HAN C Z, MA H G, et al. Total least square algorithm and its application to Volterra filter[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiao Tong University, 2004, 38(4): 339-342(in Chinese). [14] 唐浩, 屈梁生, 温广瑞. 基于Volterra级数的转子故障诊断研究[J]. 中国机械工程, 2009, 20(4): 447-454.TANG H, QU L S, WEN G R. Fault diagnosis for rotor system based on Volterra series[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2009, 20(4): 447-454(in Chinese). [15] ABBAS H M, BAYOUMI M M. Volterra system identification using adaptive genetic algorithms[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2005, 5(1): 75-86. [16] 李志农, 唐高松, 肖尧先, 等. 基于自适应蚁群优化的Volterra核辨识算法研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2011, 30(10): 35-38.LI Z N, TANG G S, XIAO Y X, et al. Volterra series identification method based on adaptive ant colony optimizations[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2011, 30(10): 35-38(in Chinese). [17] 李志农, 蒋静, 陈金刚, 等. 基于量子粒子群优化的Volterra核辨识算法研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2013, 32(3): 60-63.LI Z N, JIANG J, CHEN J G, et al. Volterra series identification method based on quantum particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2013, 32(3): 60-63(in Chinese). [18] 李志农, 蒋静, 冯辅周, 等. 基于量子粒子群优化Volterra时域核辨识的隐Markov模型识别方法[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2011, 32(12): 2693-2698.LI Z N, JIANG J, FENG F Z, et al. Hidden Markov model recognition method based on Volterra kernel identified with particle swarm optimization[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2011, 32(12): 2693-2698(in Chinese). [19] YANG X. A new metaheuristic bat-inspired algorithm[C]//Nature Inspired Cooperative Strategies for Optimization. Berlin: Springer, 2010, 284: 65-74. [20] 吕石磊, 黄永霖, 陈海强, 等. 基于自适应步长的改进蝙蝠算法[J]. 控制与决策, 2018, 33(3): 557-567.LV S L, HUANG Y L, CHEN H Q, et al. Improved bat algorithm using self-adaptive step[J]. Control and Decision, 2018, 33(3): 557-567(in Chinese). [21] FISTER I, FISTER D, YANG X S. A hybrid bat algorithm[J]. Elektrotehniski Vestnik, 2013, 80(1): 1-7. [22] TAN L, JIANG J. Adaptive second-order Volterra filtered-XRLS algorithms with sequential and partial updates for non-linear active noise control[C]//Proceedings of 4th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2009: 1625-1630. [23] CHENG C M, PENG Z K, ZHANG W M, et al. Volterra-series-based nonlinear system modeling and its engineering applications: A state-of-the-art review[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2017, 87: 340-364. [24] 卫晓娟, 丁旺才, 李宁洲, 等. 基于改进粒子群算法的Volterra模型参数辨识[J]. 振动与冲击, 2015, 34(21): 105-112.WEI X J, DING W C, LI N Z, et al. Parametric identification of nonlinear Volterra model based on improved PSO algorithm[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2015, 34(21): 105-112(in Chinese). [25] SONG J, MENG D, WANG Y. Analysis of chaotic behavior based on phase space reconstruction methods[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 6th International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Design. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 414-417. [26] 陆振波, 蔡志明, 姜可宇. 基于改进的C-C方法的相空间重构参数选择[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2007, 19(11): 2527-2529. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-731X.2007.11.036LU Z B, CAI Z M, JIANG K Y. Determination of embedding parameters for phase space reconstruction based on improved C-C methods[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2007, 19(11): 2527-2529(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-731X.2007.11.036 [27] 赵玮, 王强, 何晓晖, 等. 基于BA优化核参数的非线性Volterra滤波方法研究[J]. 仪表技术与传感器, 2019(6): 77-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1841.2019.06.018ZHAO W, WANG Q, HE X H, et al. Research on nonlinear Volterra filter method with kernel parameters optimized based on BA[J]. Instrument Technique and Sensor, 2019(6): 77-81(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1841.2019.06.018 [28] 姜学鹏, 洪贝. 基于AP的Volterra级数自适应多重回归及其多步预测应用[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2014, 36(12): 2652-2655.JIANG X P, HONG B. Multi-step predicting model based on multi-recursive AP algorithm of Volterra series[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2014, 36(12): 2652-2655(in Chinese). [29] 韩敏. 混沌时间序列预测理论与方法[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2007: 24-30.HAN M. Theory and method of chaotic time series prediction[M]. Beijing: China Water Resources and Hydropower Press, 2007: 24-30(in Chinese). [30] 张家树, 肖先赐. 混沌时间序列的自适应高阶非线性滤波预测[J]. 物理学报, 2000, 49(7): 1222-1226. doi: 10.7498/aps.49.1221ZHANG J S, XIAO X C. Prediction of chaotic time series by using adaptive higher-order nonlinear Fourier infrared filters[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2000, 49(7): 1222-1226(in Chinese). doi: 10.7498/aps.49.1221 -






 下载:
下载: