Micro immune optimization algorithm for single objective probabilistic constrained programming
-
摘要:
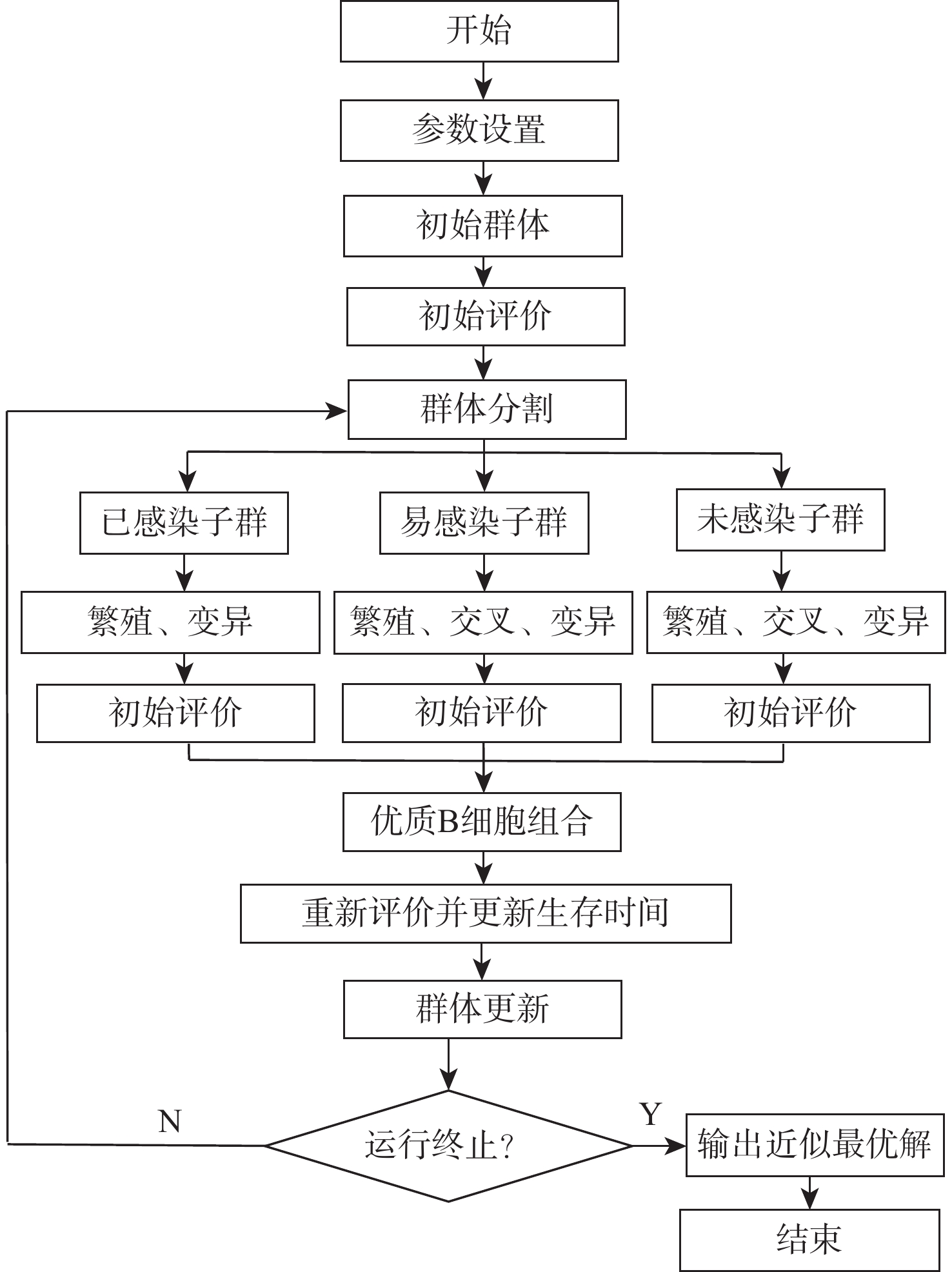
针对无先验随机分布信息的单目标概率约束规划,探讨了微种群免疫优化算法。算法设计中,受危险理论启发设计微种群免疫优化算法进化框架;借助估计值的误差幅度,提出2个方法分别估计概率值和目标值;依据个体间的优劣关系,划分群体为3个类型子群协同进化;构建生命周期模型,设计自适应的交叉与变异概率、变异策略,结合交叉算子促进子群信息有效交流,并沿不同方向协同进化。数值实验统计结果说明:所提算法拥有良好的搜索效率、搜索效果及降噪能力,具有一定的竞争力和应用潜力。
Abstract:An immune optimization algorithm with a small population is proposed to solve a single objective probability constrained programming with no prior random distribution information. In the design of the algorithm, we develop an evolutionary framework with a micro population inspired by danger theory. Based on the amplitude of error of the estimated value, two approaches are proposed to estimate the individual’s objective values and each chance constraint’s probability respectively. According to the superior and inferior relationships among individuals, the population was divided into three types of sub-population for co-evolution. A version of individual life cycle is constructed, while adaptive crossover probability, adaptive mutation probability and adaptive mutation strategy as well as crossover strategy are designed to promote effective information exchange among the above sub-populations to co-evolve individuals in different directions. The results of numerical experiments show that the proposed algorithm has good search efficiency, search effect and noise reduction ability, and has certain competitiveness and application potential.
-
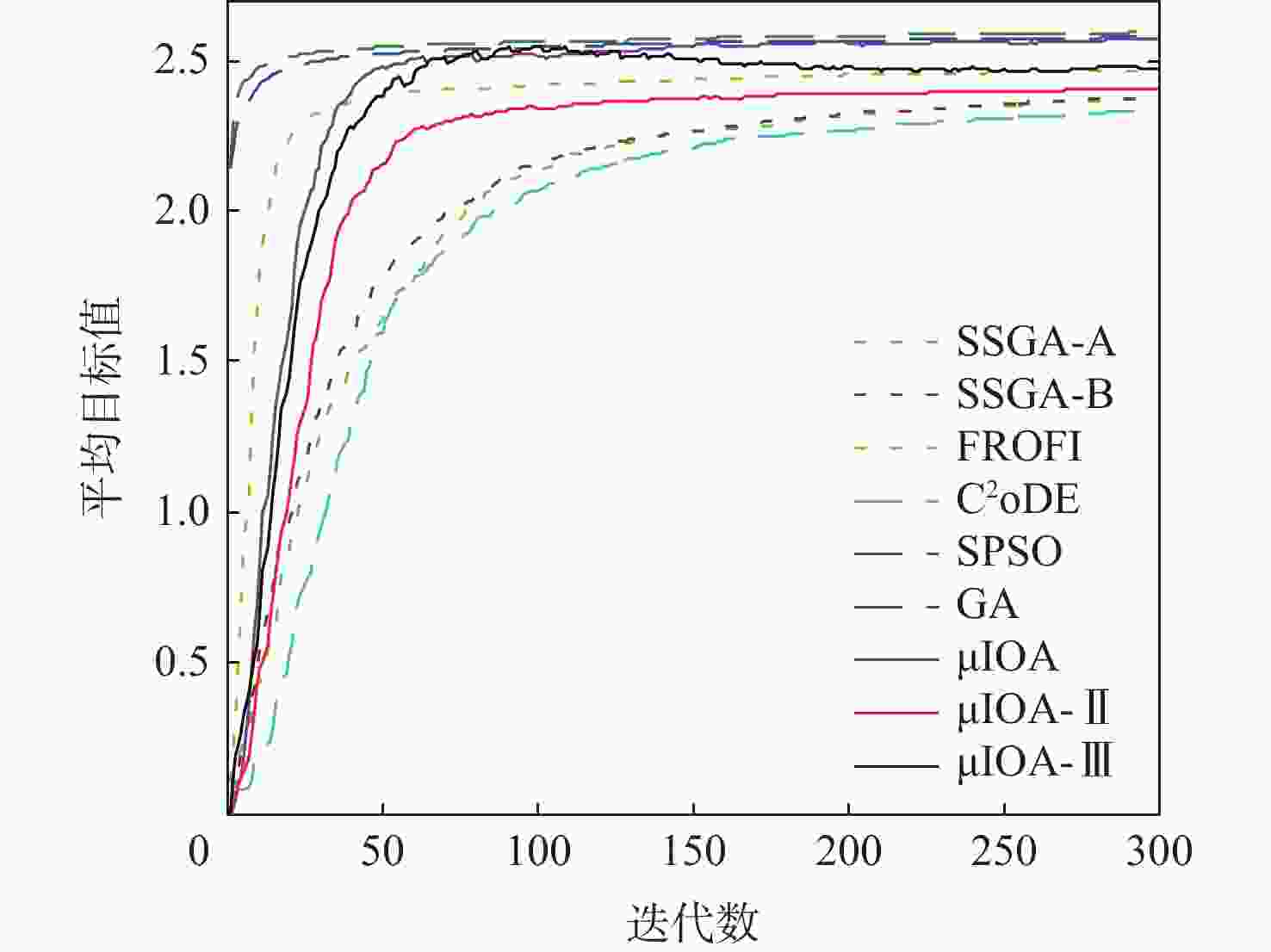
表 1 问题1的统计结果比较
Table 1. Comparison of statistical results for problem 1
算法 min max mean St.Dev CI IAE FR/% AR/s SSGA-A 1.8830 2.3235 2.2163 0.0784 [2.2033,2.2294] 0.0021 83 3.30 SSGA-B 1.9448 2.3416 2.2221 0.0788 [2.2090,2.2352] 0.00212 84 3.13 FROFI 2.1653 2.3449 2.2740 0.0378 [2.2677,2.2802] 0.0031 78 6.52 C2oDE 1.9114 2.3222 2.1834 0.0890 [2.1686,2.1982] 0.0010 94 20.78 SPSO 2.1334 2.3533 2.3027 0.0299 [2.2978,2.3077] 0.0114 47 15.44 GA 2.2031 2.3466 2.3075 0.0249 [2.3033,2.3116] 0.0051 67 20.18 μIOA 2.1024 2.3098 2.2383 0.0477 [2.2304,2.2462] 0 100 0.84 μIOA-Ⅱ 2.1505 2.3191 2.2658 0.0319 [2.2605,2.2711] 0 100 0.54 μIOA-Ⅲ 2.1322 2.3163 2.2614 0.0372 [2.2552,2.2675] 0 100 0.49 表 2 问题2的统计结果比较
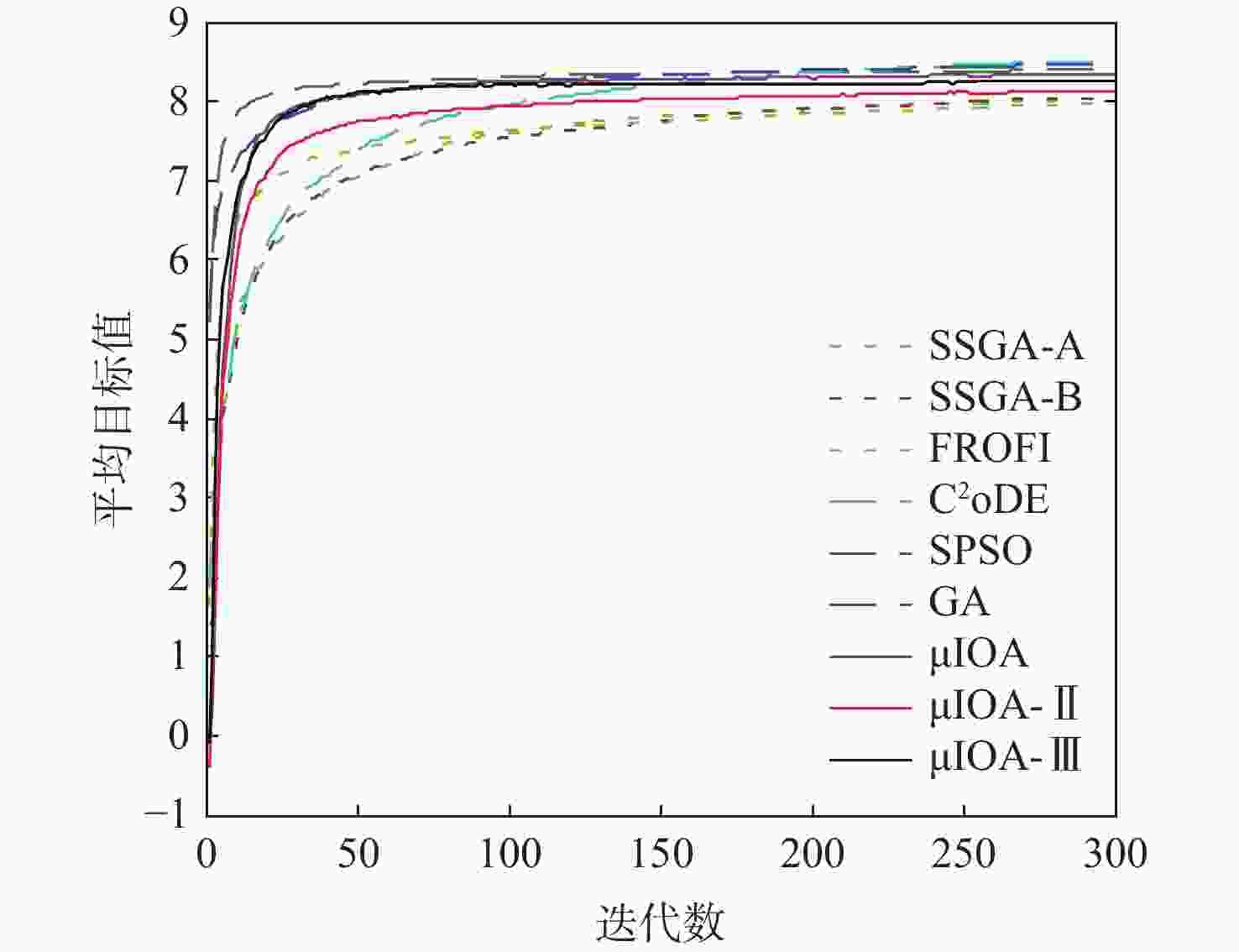
Table 2. Comparison of statistical results for problem 2
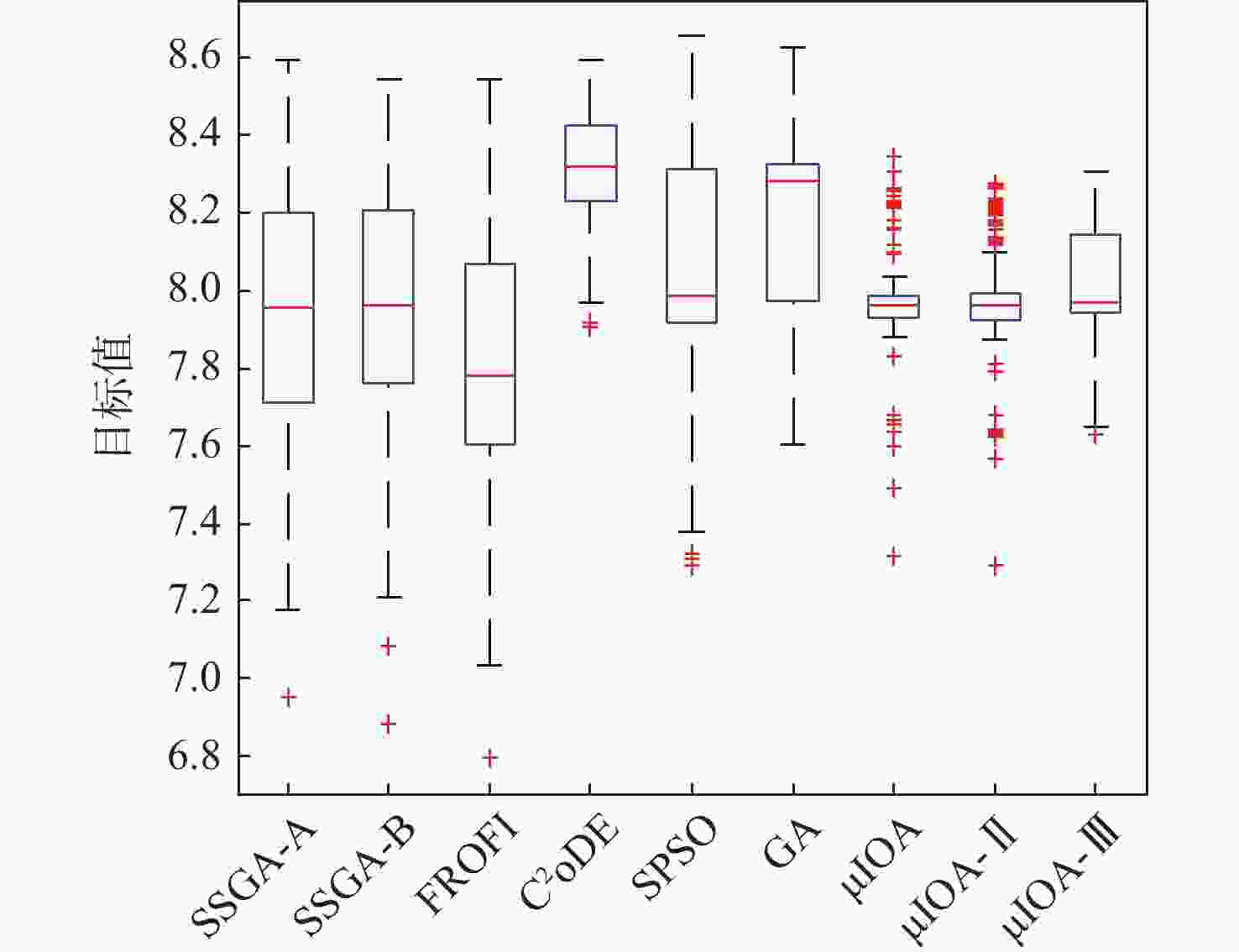
算法 min max mean St.Dev CI IAE FR/% AR/s SSGA-A 6.9541 8.5975 7.9401 0.3230 [7.8864,7.9937] 0.0027 83 2.98 SSGA-B 6.8847 8.5468 7.9321 0.3354 [7.8764,7.9878] 0.0038 79 2.98 FROFI 6.7969 8.5459 7.8194 0.3055 [7.7687,7.8701] 0.0005 92 5.87 C2oDE 7.9063 8.5972 8.3185 0.1419 [8.2950,8.3421] 0.0024 84 17.42 SPSO 7.2901 8.6559 8.0652 0.3424 [8.0083,8.1220] 0.0126 61 9.01 GA 7.6029 8.6293 8.1729 0.2719 [8.1277,8.2180] 0.0057 66 11.52 μIOA 7.3172 8.3427 7.9726 0.1607 [7.9459,7.9993] 8.50×10−5 99 1.08 μIOA-Ⅱ 7.2904 8.2779 7.9697 0.1590 [7.9433,7.9961] 3.56×10−5 99 0.91 μIOA-Ⅲ 7.6316 8.3092 8.0273 0.1504 [8.0023,8.0523] 0 100 0.70 表 3 问题3的统计结果比较
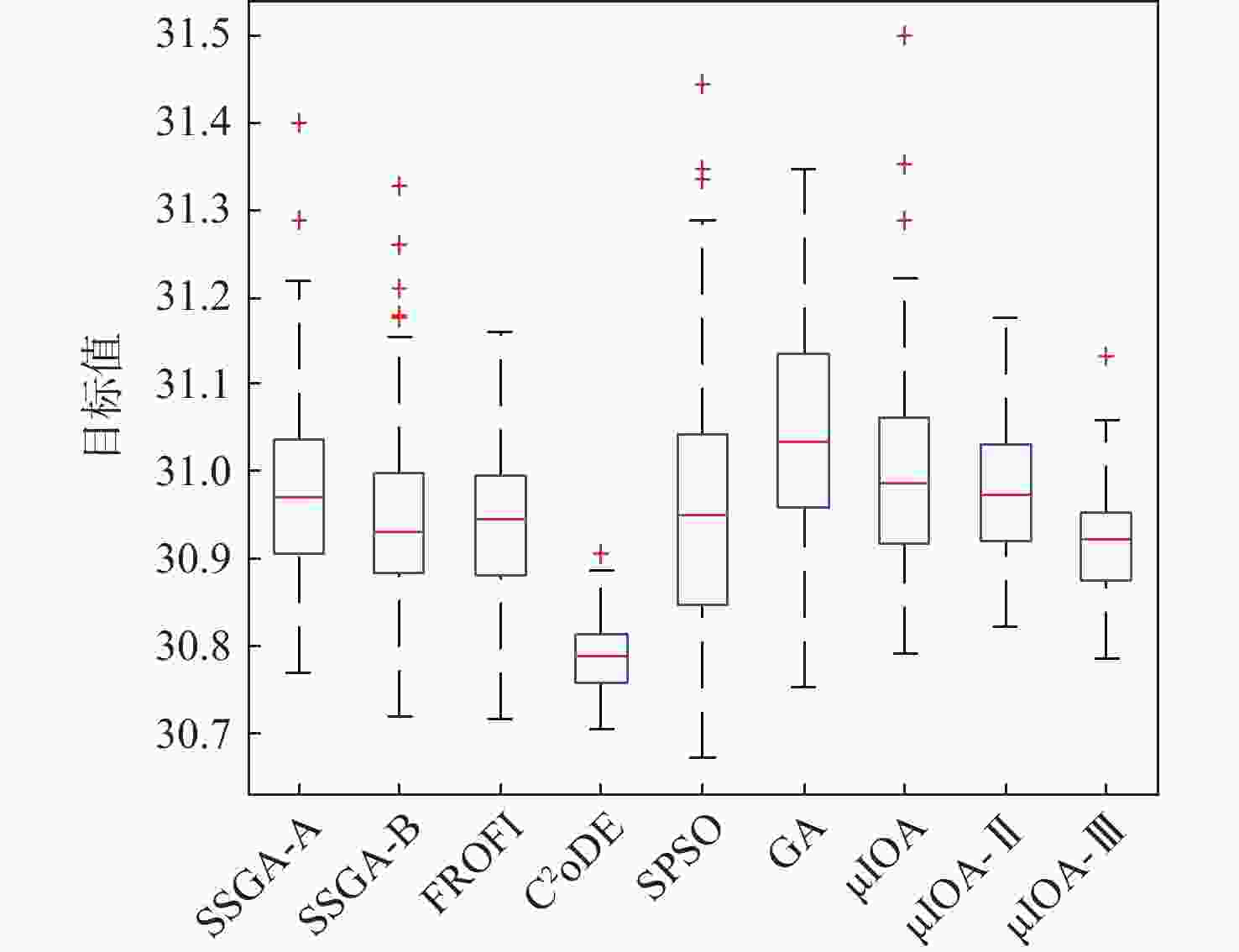
Table 3. Comparison of statistical results for problem 3
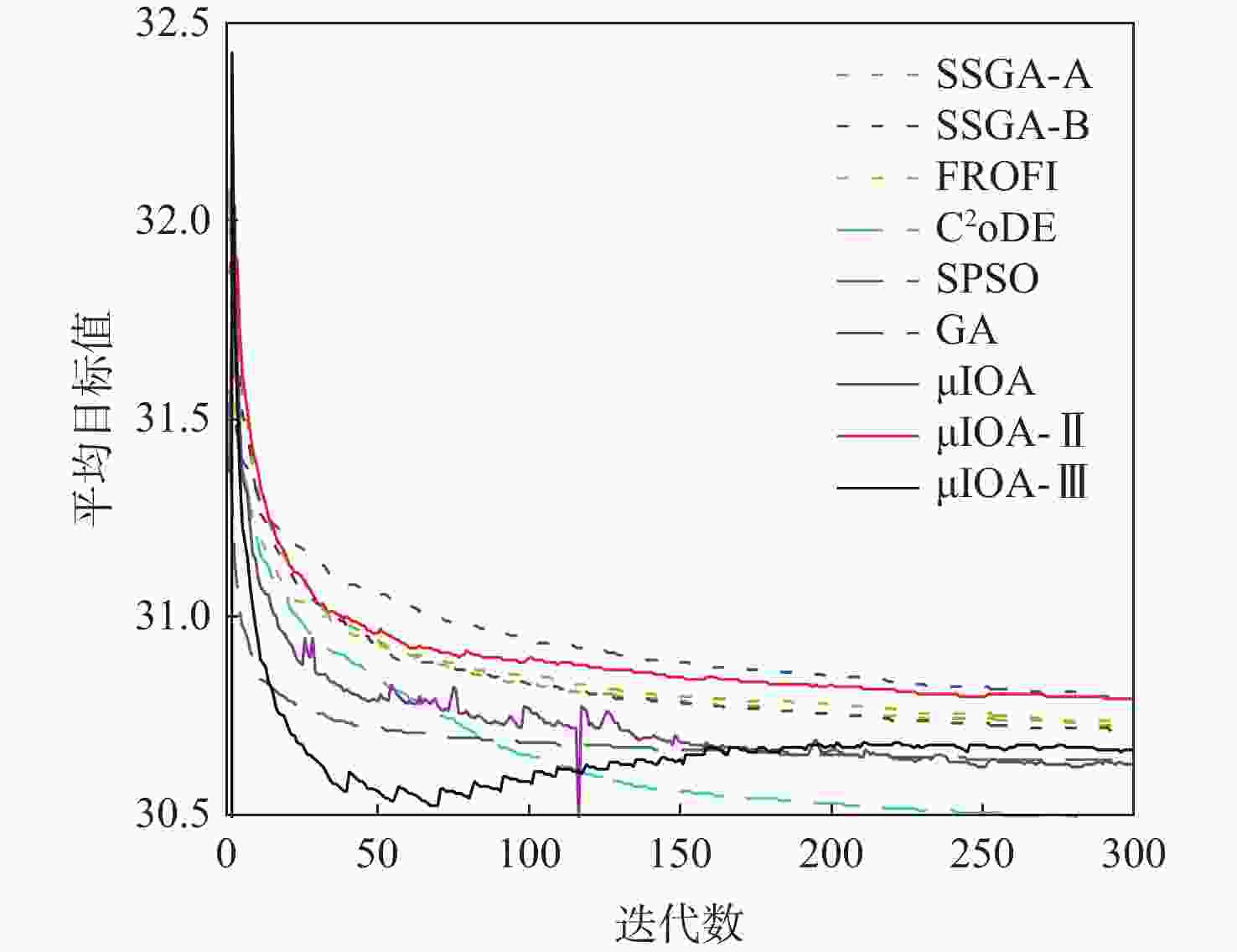
算法 min max mean St.Dev CI IAE FR/% AR/s SSGA-A 30.7685 31.4010 30.9803 0.1120 [30.9617,30.9989] 0.0023 74 2.83 SSGA-B 30.7169 31.3281 30.9484 0.1124 [30.9297,30.9671] 0.0025 76 2.79 FROFI 30.7158 31.1585 30.9431 0.0877 [30.9286,30.9577] 0.0022 76 5.88 C2oDE 30.7047 30.9062 30.7905 0.0404 [30.7838,30.7972] 0.0065 39 17.51 SPSO 30.6716 31.4457 30.9633 0.1470 [30.9389,30.9877] 0.0107 28 7.43 GA 30.7531 31.3484 31.0419 0.1194 [31.0221,31.0617] 0.0024 83 6.88 μIOA 30.7905 31.4999 31.0048 0.1135 [30.9860,31.0237] 4.54×10−5 99 0.72 μIOA-Ⅱ 30.8213 31.1777 30.9781 0.0782 [30.9651,30.9911] 0 100 0.93 μIOA-Ⅲ 30.7857 31.1326 30.9185 0.0608 [30.9084,30.9286] 0 100 0.75 表 4 问题4的统计结果比较
Table 4. Comparison of statistical results for problem 4
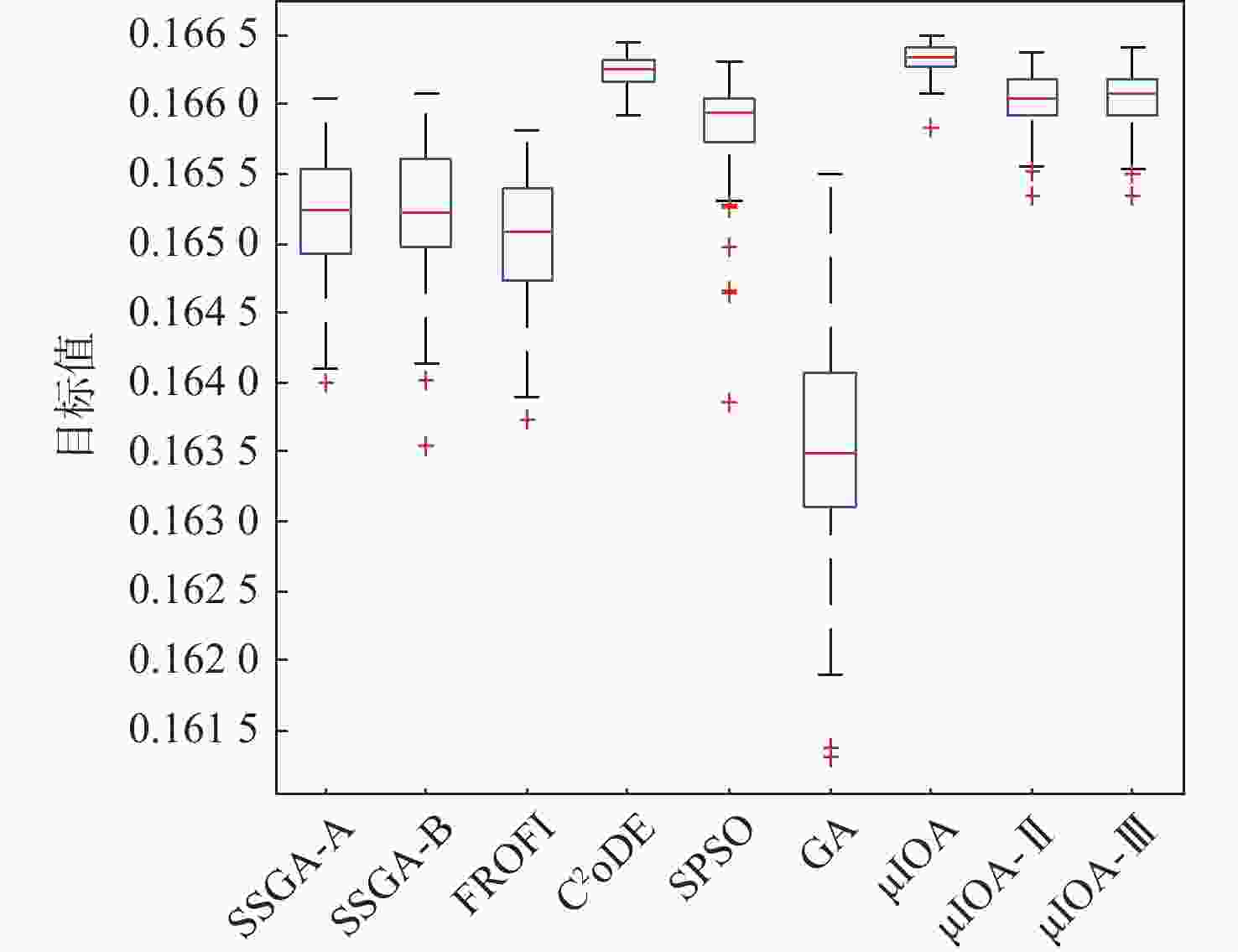
算法 min max mean St.Dev CI IAE FR/% AR/s SSGA-A 0.1640 0.1660 0.1652 0.0004 [0.1651,0.1653] 0 100 6.25 SSGA-B 0.1636 0.1661 0.1652 0.0005 [0.1651,0.1653] 0 100 6.20 FROFI 0.1637 0.1658 0.1650 0.0004 [0.1650,0.1651] 0 100 13.16 C2oDE 0.1659 0.1664 0.1662 0.0001 [0.1662,0.1663] 0 100 38.17 SPSO 0.1639 0.1663 0.1658 0.0004 [0.1658,0.1659] 0 100 26.94 GA 0.1613 0.1655 0.1635 0.0008 [0.1634,0.1637] 0 100 26.54 μIOA 0.1658 0.1665 0.1663 0.0001 [0.1663,0.1663] 0 100 3.71 μIOA-Ⅱ 0.1654 0.1664 0.1660 0.0002 [0.1660,0.1661] 0 100 2.09 μIOA-Ⅲ 0.1653 0.1664 0.1660 0.0002 [0.1660,0.1661] 0 100 1.58 表 5 μIOA-Ⅲ在不同参数设置下求解问题2的统计结果比较
Table 5. Comparison of statistical results for solving problem 2 of μIA-Ⅲ in different parameter settings
参数组合 min max mean St.Dev CI IAE FR/% AR/s N=4, M=10,W=5 7.3814 8.3225 7.936 0.1779 [7.9064,7.9654] 0 100 0.41 N=5 , M=10, W=5 7.6319 8.3747 8.0229 0.1348 [8.0005,8.0453] 0 100 0.60 N=6, M=10, W=5 7.8466 8.3446 8.0579 0.1390 [8.0348,8.0810] 0 100 0.88 N=5, M=10, W=4 7.6121 8.3154 8.0074 0.1460 [7.9832,8.0317] 0 100 0.60 N=5, M=10, W=6 7.6535 8.3397 8.0308 0.1384 [8.0078,8.0538] 0 100 0.63 N=5, M=8, W=5 7.6079 8.3044 7.9843 0.1436 [7.9604,8.0081] 1.19×10−4 99 0.43 N=5, M=12, W=5 7.5852 8.3423 8.0422 0.1642 [8.0150,8.0695] 0 100 0.79 -
[1] CHEN Y, LI Y, SUN B, et al. A chance-constrained programming approach for a zinc hydrometallurgy blending problem under uncertainty[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2020, 140: 106893. [2] 卢福强, 陈伟东, 毕华玲, 等. 考虑随机需求和多种运输方式的第四方物流路径问题[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2020, 26(10): 2864-2876. doi: 10.13196/j.cims.2020.10.025LU F Q, CHEN W D, BI H L, et al. Fourth party logistics routing problem considering stochastic demand and multiple transportation modes[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2020, 26(10): 2864-2876(in Chinese). doi: 10.13196/j.cims.2020.10.025 [3] LONG J, SUN Z, PARDALOS P M, et al. A robust dynamic scheduling approach based on release time series forecasting for the steelmaking-continuous casting production[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2020, 92: 106271. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106271 [4] LONG J, SUN Z, HONG Y, et al. Robust dynamic scheduling with uncertain release time for the steelmaking-continuous casting production[C]//2018 International Conference on Sensing, Diagnostics, Prognostics, and Control. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 531-536. [5] SONG H, DONG M, HAN R, et al. Stochastic programming-based fault diagnosis in power systems under imperfect and incomplete information[J]. Energies, 2018, 11(10): 2565. doi: 10.3390/en11102565 [6] HONG Z, ZHANG Q, GONG T, et al. Peak load regulation and cost optimization for microgrids by installing a heat storage tank and a portable energy system[J]. Applied Sciences, 2018, 8(4): 567. doi: 10.3390/app8040567 [7] ZHANG H, HA M, ZHAO H, et al. Inexact multistage stochastic chance constrained programming model for water resources management under uncertainties[J]. Scientific Programming, 2017, 2017: 1-14. [8] AHMED S. Convex relaxations of chance constrained optimization problems[J]. Optimization Letters, 2014, 8(1): 1-12. doi: 10.1007/s11590-013-0624-7 [9] SUN X L, BAI X D, ZHENG X J. A survey on probabilistically constrained optimization problems[J]. Operations Research Transactions, 2012, 16(3): 65-73. [10] 刘宝碇, 赵瑞清. 随机规划与模糊规划[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 1998: 79-87.LIU B D, ZHAO R Q. Stochastic programming and fuzz programming[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 1998: 79-87(in Chinese). [11] YANG L, YANG Z, LI G, et al. Optimal scheduling of an isolated microgrid with battery storage considering load and renewable generation uncertainties[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(2): 1565-1575. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2840498 [12] HOMEN-DE-MELLO T, BAYRAKSAN G. Monte Carlo sampling-based methods for stochastic optimization[J]. Surveys in Operations Research and Management Science, 2014, 19(1): 56-85. doi: 10.1016/j.sorms.2014.05.001 [13] ZHANG Z H. Noisy immune optimization for chance-constrained programming problems[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2011, 48-49: 740-744. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.48-49.740 [14] ZHANG Z H, WANG L, LIAO M. Adaptive sampling immune algorithm solving joint chance-constrained programming[J]. Journal of Control Theory and Applications, 2013, 11(2): 237-246. doi: 10.1007/s11768-013-1186-z [15] YANG K, ZHANG Z H. Adaptive sampling detection based immune optimization approach and its application to chance constrained programming[M]//SUN H, YANG C Y, LIN C W, et al. Genetic and evolutionary computing. Berlin: Springer International Publishing, 2015: 19-28. [16] ZHANG Z H, LI L, ZHANG R C. Danger theory based micro immune optimization algorithm solving probabilistic constrained optimization[C]//2017 2nd IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Applications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 103-107. [17] ZHANG Z H, ZHANG R C. Danger theory inspired micro-population immune optimization for probabilistic constrained programming[J]. Evolving Systems, 2020, 11(2): 333-348. doi: 10.1007/s12530-019-09277-6 [18] 张著洪, 张仁崇. 求解概率优化问题的微种群免疫优化算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(9): 1785-1794. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2015.0563ZHANG Z H, ZHANG R C. Micro immune optimization algorithm for solving probabilistic optimization problems[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42(9): 1785-1794(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2015.0563 [19] 张仁崇, 张著洪. 非线性多目标概率约束规划免疫优化算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(5): 900-914. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0350ZHANG R C, ZHANG Z H. Immune optimization algorithm for nonlinear multi-objective probabilistic constrained programming[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(5): 900-914(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0350 [20] 张仁崇, 潘春燕, 武星, 等. 非线性多目标概率优化问题的自适应采样免疫优化算法[J]. 电子学报, 2021, 49(4): 647-660. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20200171ZHANG R C, PAN C Y, WU X, et al. Adaptive sampling immune optimization algorithm for nonlinear multi-objective probabilistic optimization problems[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2021, 49(4): 647-660(in Chinese). doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20200171 [21] LIU B D. Theory and practice of uncertain programming[M]. 3rd ed. Berlin: Springer International Publishing, 2009: 50-53. [22] 沈依婷, 张菁, 武鹏, 等. 含电动汽车的配电网双重不确定性网架规划方法[J]. 中国电力, 2020, 53(4): 139-146.SHEN Y T, ZHANG J, WU P, et al. Bi-uncertainty network frame planning method for distribution network with electric vehicles[J]. Electric Power, 2020, 53(4): 139-146(in Chinese). [23] XIAO N. An algorithm for solving stochastic chance-constrained programming problem[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2014, 912: 1138-1141. [24] HUANG D, XIE L, WU Z. Dynamic economic dispatch for microgrid based on the chance-constrained programming[J]. Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology, 2017, 12(3): 1064-1072. [25] 李鹏, 蔡永青, 韩肖清, 等. 计及随机模糊双重不确定性的交直流混合微网优化运行[J]. 高电压技术, 2020, 46(7): 2269-2279. doi: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20200619001LI P, CAI Y Q, HAN X Q, et al. Optimization operation of AC/DC hybrid microgrid considering random fuzzy double uncertainties[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2020, 46(7): 2269-2279(in Chinese). doi: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20200619001 [26] 德格吉日夫, 谭忠富, 李梦露, 等. 考虑不确定性的风储电站参与电力现货市场竞价策略[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43(8): 2799-2807. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2019.0547DE G J R F, TAN Z F, LI M L, et al. Bidding strategy of wind-storage power plant participation in electricity spot market considering uncertainty[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43(8): 2799-2807(in Chinese). doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2019.0547 [27] 马丽叶, 王志强, 陆肖宇, 等. 基于机会约束规划的风-火-蓄联合系统优化调度[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43(9): 3311-3320.MA L Y, WANG Z Q, LU X Y, et al. Optimal scheduling of combined wind-thermo-storage system based on chance constrained programming[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43(9): 3311-3320(in Chinese). [28] ZHAO Q, YANG R, DUAN F. An immune clonal hybrid algorithm for solving stochastic chance-constrained programming[J]. Journal of Computational Information Systems, 2012, 8(20): 8295-8302. [29] 韩畅, 梁博淼, 林振智, 等. 防灾应急电源优化调度的机会约束规划方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2018, 38(3): 147-154. doi: 10.16081/j.issn.1006-6047.2018.03.020HAN C, LIANG B M, LIN Z Z, et al. Chance-constrained programming method for optimal scheduling of emergency power source[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2018, 38(3): 147-154(in Chinese). doi: 10.16081/j.issn.1006-6047.2018.03.020 [30] 贾伯岩, 马天祥, 张智远, 等. 计及不确定性的含分布式发电并网的配电网故障区段定位方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48(14): 35-42. doi: 10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.191002JIA B Y, MA T X, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Fault section location method for distribution networks with distributed generation and grid connection considering uncertainty[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48(14): 35-42(in Chinese). doi: 10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.191002 [31] 茆诗松, 程依明, 濮晓龙, 等. 概率论与数理统计教程[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2004: 226-237.MAO S S, CHENG Y M, PU X L, et al. Probability theory and mathematical statistics course[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2004: 226-237(Chinese). [32] MATZINGER P. Tolerance, danger, and the extended family[J]. Annual Review of Immunology, 1994, 12(1): 991-1045. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.005015 [33] POOJARI C A, VARGHESE B. Genetic algorithm based technique for solving chance constrained problems[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2008, 185(3): 1128-1154. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2006.06.045 [34] WANG Y, WANG B C, LI H X, et al. Incorporating objective function information into the feasibility rule for constrained evolutionary optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016, 46(12): 2938-2952. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2015.2493239 [35] WANG B C, LI H X, LI J P, et al. Composite differential evolution for constrained evolutionary optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems Man and Cybernetics Systems, 2018, 49(7): 1482-1495. [36] SALEHINEJAD H, RAHNAMAYAN S, TIZHOOSH H R. Micro-differential evolution: diversity enhancement and a comparative study[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2017, 52: 812-833. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2016.09.042 [37] YASUI T, SUGISAKA J, HIRAYAMA K. Structural optimization of silica-based 2×2 multimode interference coupler using a real-coded micro-genetic algorithm[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research, 2017, 55: 169-178. doi: 10.2528/PIERM17012204 [38] CAMERO A, ARELLANO-VERDEJO J, ALBA E. Road map partitioning for routing by using a micro steady state evolutionary algorithm[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2018, 71: 155-165. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2018.02.016 [39] VARGHESE B, POOJARI C A. Genetic algorithm based technique for solving chance constrained problems arising in risk management[R]. CARISMA Technical Report, 2004: 1-49. [40] 程晓娟, 韩庆兰, 全春光. 不确定条件下机械产品设计方案费效权衡优化[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2015, 21(8): 1988-1994. doi: 10.13196/j.cims.2015.08.003CHENG X J, HAN Q L, QUAN C G. Cost-effective trade-off of mechanical product design scheme under uncertainty[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing System, 2015, 21(8): 1988-1994(in Chinese). doi: 10.13196/j.cims.2015.08.003 -







 下载:
下载: