-
摘要:
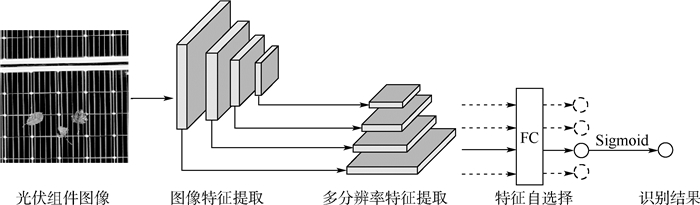
光伏组件的遮挡物识别是光伏运维系统中不可或缺的环节,传统识别算法多依赖人工巡检,成本高昂且效率低下。基于卷积神经网络,提出了一种面向光伏组件的遮挡物识别算法PORNet。通过引入特征金字塔,构建多个分辨率下具有丰富语义信息的图像特征,提升对遮挡物尺度和密度的敏感性。通过特征自选择,筛选出语义最具代表性的特征图,以加强物体环境的语义信息表达。用筛选出的特征图完成遮挡物识别,从而提升识别准确率。在自建光伏组件落叶遮挡数据集上进行了实验比较和分析,并对识别性能进行了评估,通过与现有物体识别算法相比,所提算法的准确率和召回率分别提升了9.21%和15.79%。
Abstract:The identification of obstructions of photovoltaic modules is an indispensable link in modern photovoltaic operation and maintenance systems. Traditional identification methods mostly rely on manual inspections, but they are costly and inefficient. Therefore, based on the convolutional neural network, PORNet, an occlusion recognition algorithm for photovoltaic modules, is proposed. By introducing feature pyramids, image features with rich semantic information at multiple resolutions are constructed, enhancing the sensitivity to the scale and density of occlusions. Through feature auto-selection, the most representative feature maps are screened out to strengthen the semantic information expression of the object contexts. Finally, the screened feature map is used to complete the occlusion recognition, improving the recognition accuracy. Experimental comparison and analysis are carried out on the self-built photovoltaic module falling leaf occlusion dataset, and the recognition performance is evaluated. Compared with existing object recognition methods, the accuracy and recall rate of the proposed method are increased by 9.21% and 15.79%, respectively.
-
表 1 符号表示
Table 1. Summary of main notations' representation
符号 含义 yi 第i张图片类别 ReLU ReLU函数 Sigmoid Sigmoid函数 BN 批归一化层 FC 全连接层 GAP 全局平均池化 Lcls 分类损失函数 Conv 卷积层 表 2 各模块特征图信息
Table 2. Feature map information of different modules
特征图名称 尺度 通道数 C1 56 64 C2 28 128 C3 14 256 C4 7 512 P1 56 256 P2 28 256 P3 14 256 P4 7 256 表 3 不同算法测试结果
Table 3. Test results of different algorithms
算法 准确率/% 召回率/% AUC VGG11 84.21 68.42 0.916 2 VGG13 86.84 73.68 0.941 8 VGG16 92.11 84.21 0.981 3 Res18 89.47 81.58 0.965 4 FuseRes18 89.47 78.95 0.943 2 PORNet 98.68 97.37 0.991 5 表 4 不同算法运行时参数
Table 4. Runtime parameters of different algorithms
算法 参数量/106 MAC/109 速度/(帧·s-1) VGG11 8.79 6.98 201.79 VGG13 8.97 10.43 180.74 VGG16 14.03 14.31 156.14 Res18 10.66 1.69 125.38 FuseRes18 13.15 4.07 120.08 PORNet 13.15 4.07 115.83 -
[1] JIA D, WEI D, SOCHER R, et al. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2009: 248-255. [2] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2012: 1106-1114. [3] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]//International Conference on Learning Representations, 2015: 1-14. [4] SCHROFF F, KALENICHENKO D, PHILBIN J. FaceNet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 815-823. [5] LIU W, WEN Y, YU Z, et al. SphereFace: Deep hypersphere embedding for face recognition[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 6738-6746. [6] LI W, ZHU X, GONG S. Person re-identification by deep joint learning of multi-loss classification[C]//Proceedings of International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York: ACM, 2017: 2194-2200. [7] ZHONG Z, LIANG Z, CAO D, et al. Re-ranking person re-identification with k-reciprocal encoding[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 3652-3661. [8] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [9] ZAGORUYKO S, KOMODAKIS N. Wide residual networks[C]//Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, 2016: 1-12. [10] HUANG G, LIU Z, LAURENS V, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2261-2269. [11] XIE S, GIRSHICK R, DOLLÁR P, et al. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 5987-5995. [12] SUN K, XIAO B, LIU D, et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 5693-5703. [13] YU F, KOLTUN V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1-9. [14] DAI J, QI H, XIONG Y, et al. Deformable convolutional networks[C]//IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 764-773. [15] LI D, HU J, WANG C, et al. Involution: Inverting the inherence of convolution for visual recognition[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021. [16] ZHANG H, CISSE M, DAUPHIN Y N, et al. Mixup: Beyond empirical risk minimization[C]//International Conference on Learning Representations, 2018. [17] DEVRIES T, TAYLOR G W. Improved regularization of convolutional neural networks with cutout[EB/OL]. (2017-08-15)[2021-06-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1708.04552. [18] YUN S, HAN D, OH S J, et al. CutMix: Regularization strategy to train strong classifiers with localizable features[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 6023-6032. [19] CUBUK E D, ZOPH B, MANE D, et al. AutoAugment: Learning augmentation policies from data[EB/OL]. (2018-05-24)[2021-06-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1805.09501. [20] HO D, LIANG E, STOICA I, et al. Population based augmentation: Efficient learning of augmentation policy schedules[C]//Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2019: 2731-2741. [21] LIM S, KIM I, KIM T, et al. Fast AutoAugment[EB/OL]. (2019-05-01)[2021-06-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1905.00397. [22] LIN T Y, DOLLAR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 936-944. [23] SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[J] International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(2): 336-359. -







 下载:
下载: