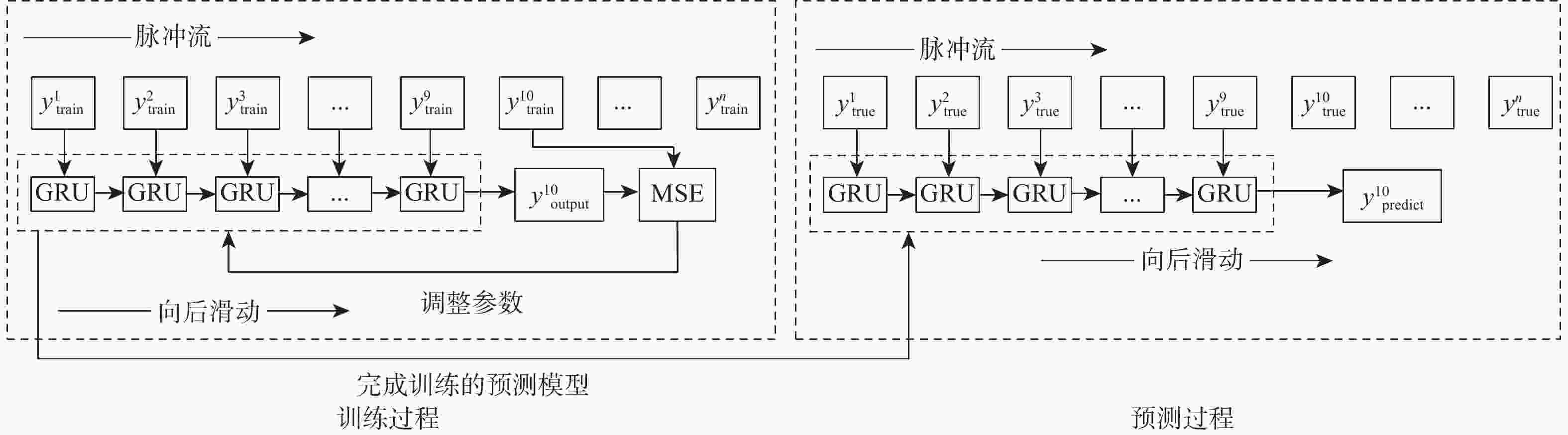
Improved intelligent detection algorithm for SPMA protocol channel state based on recurrent neural network
-
摘要:
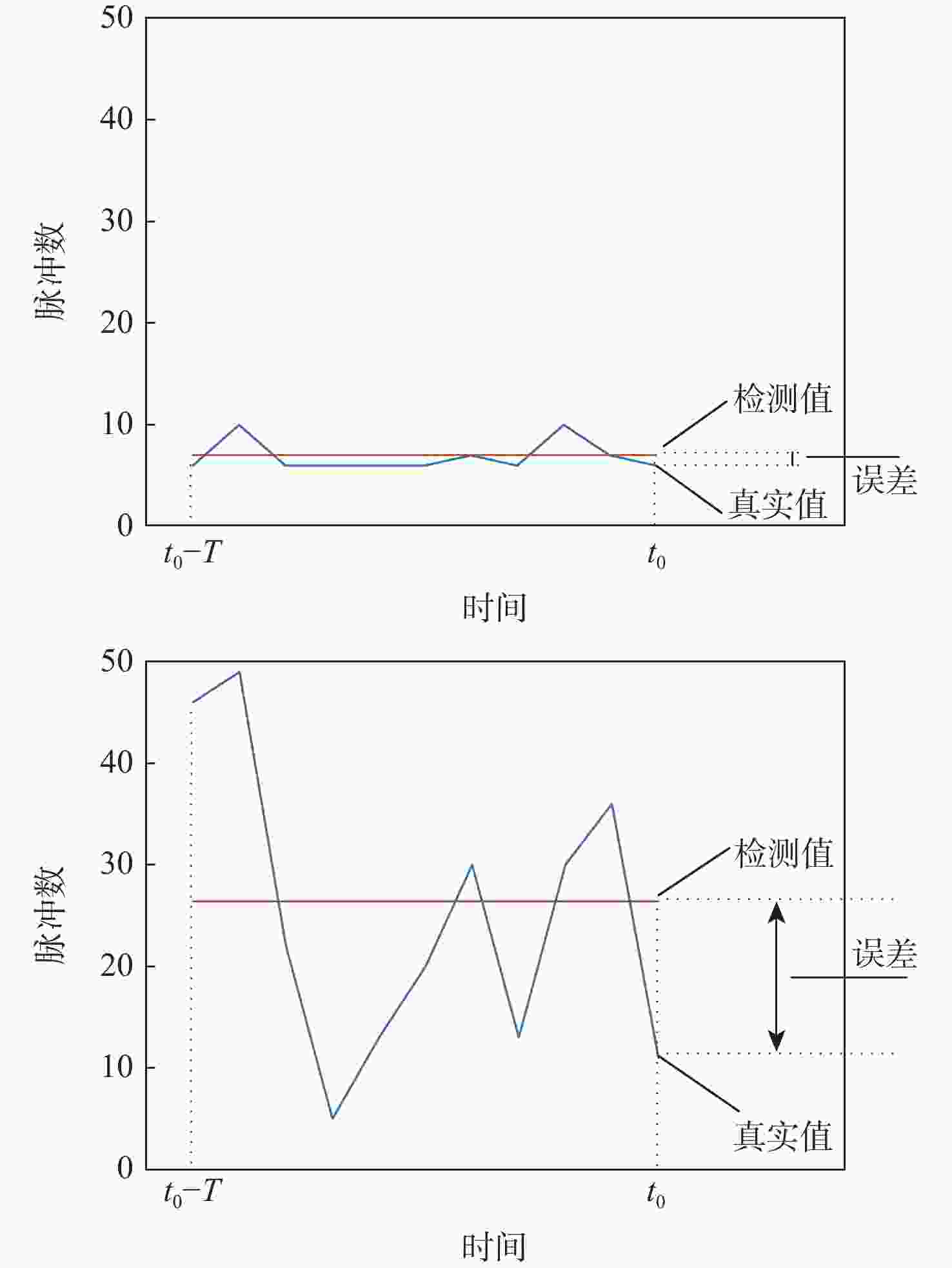
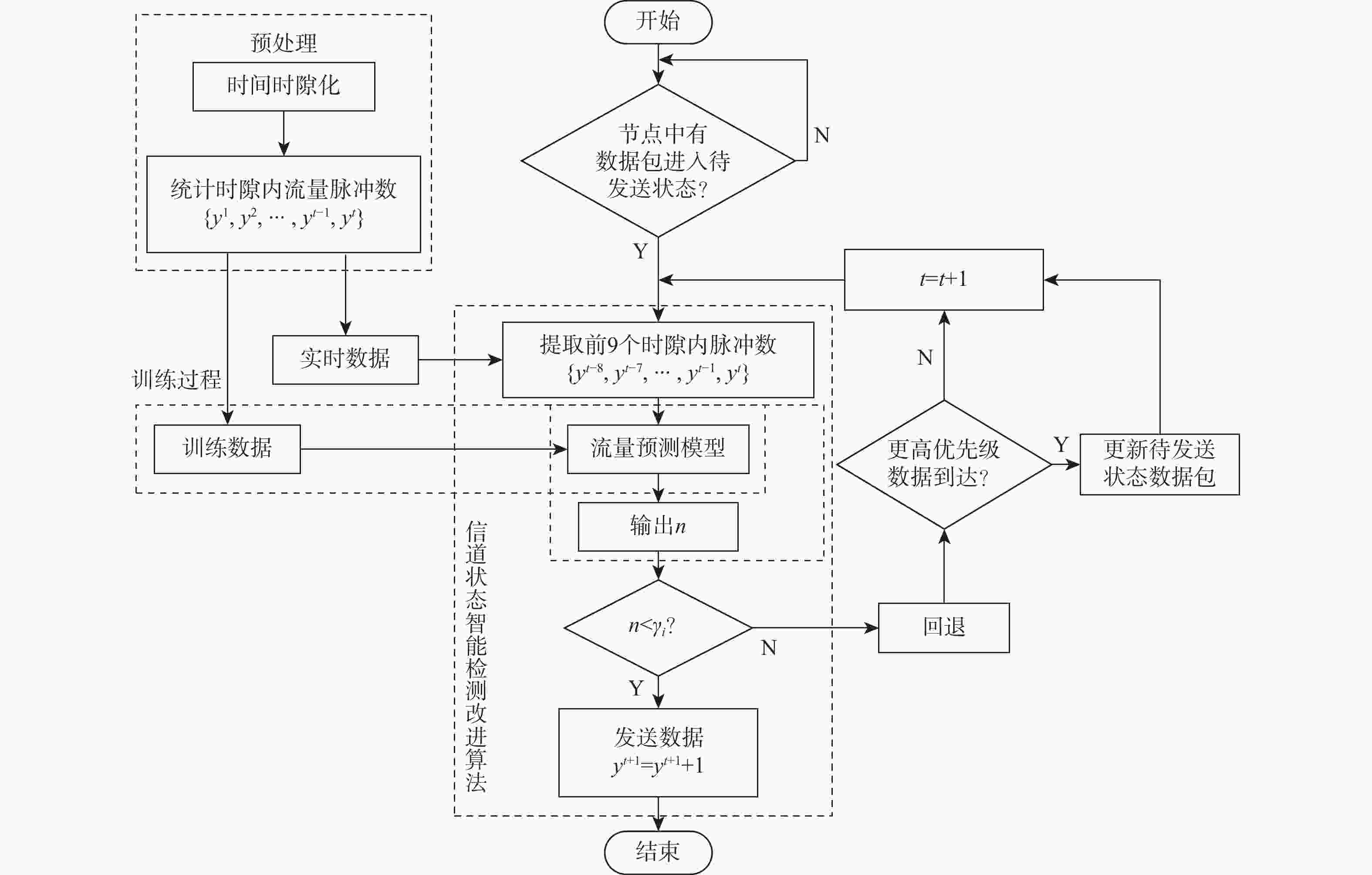
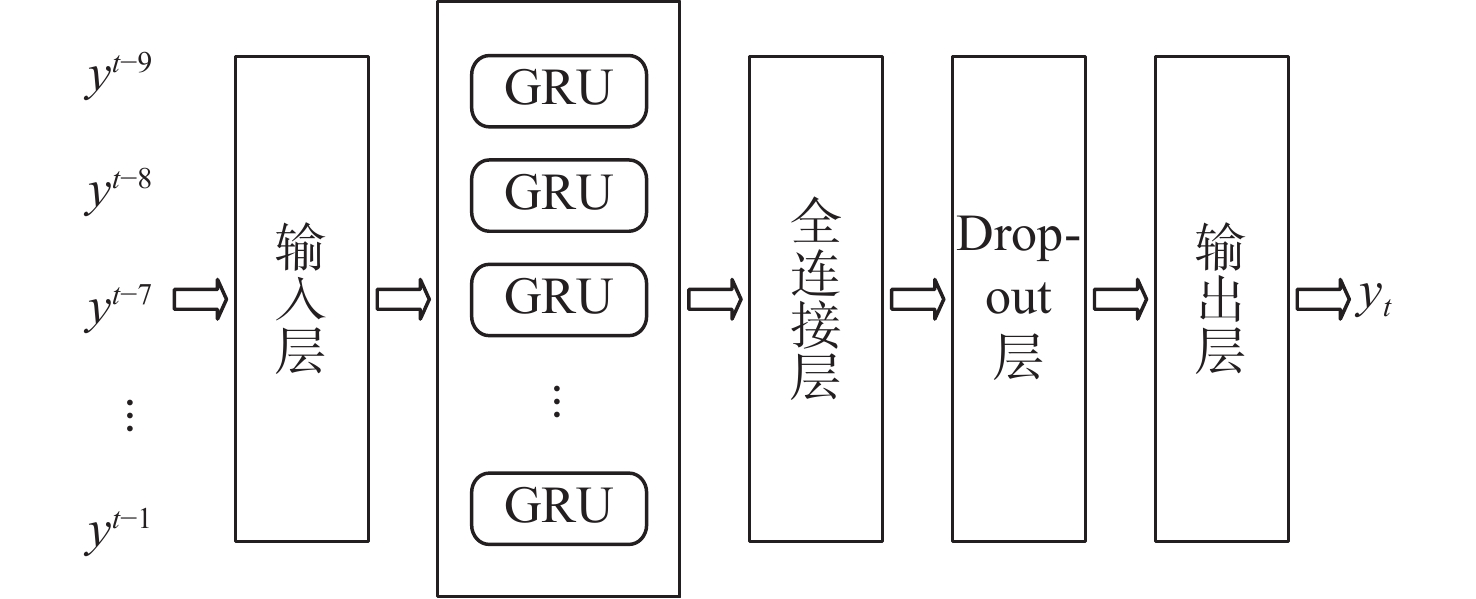
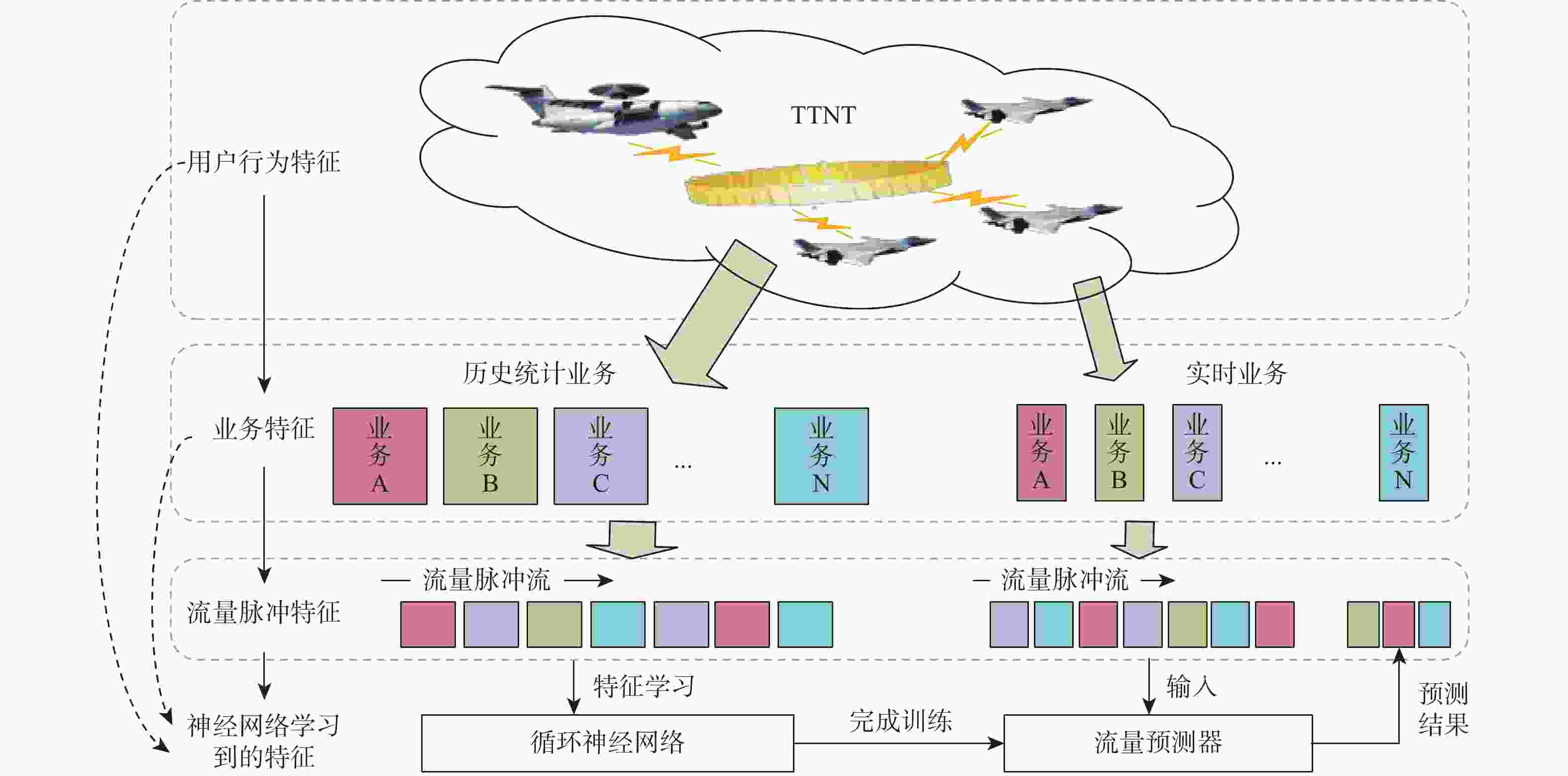
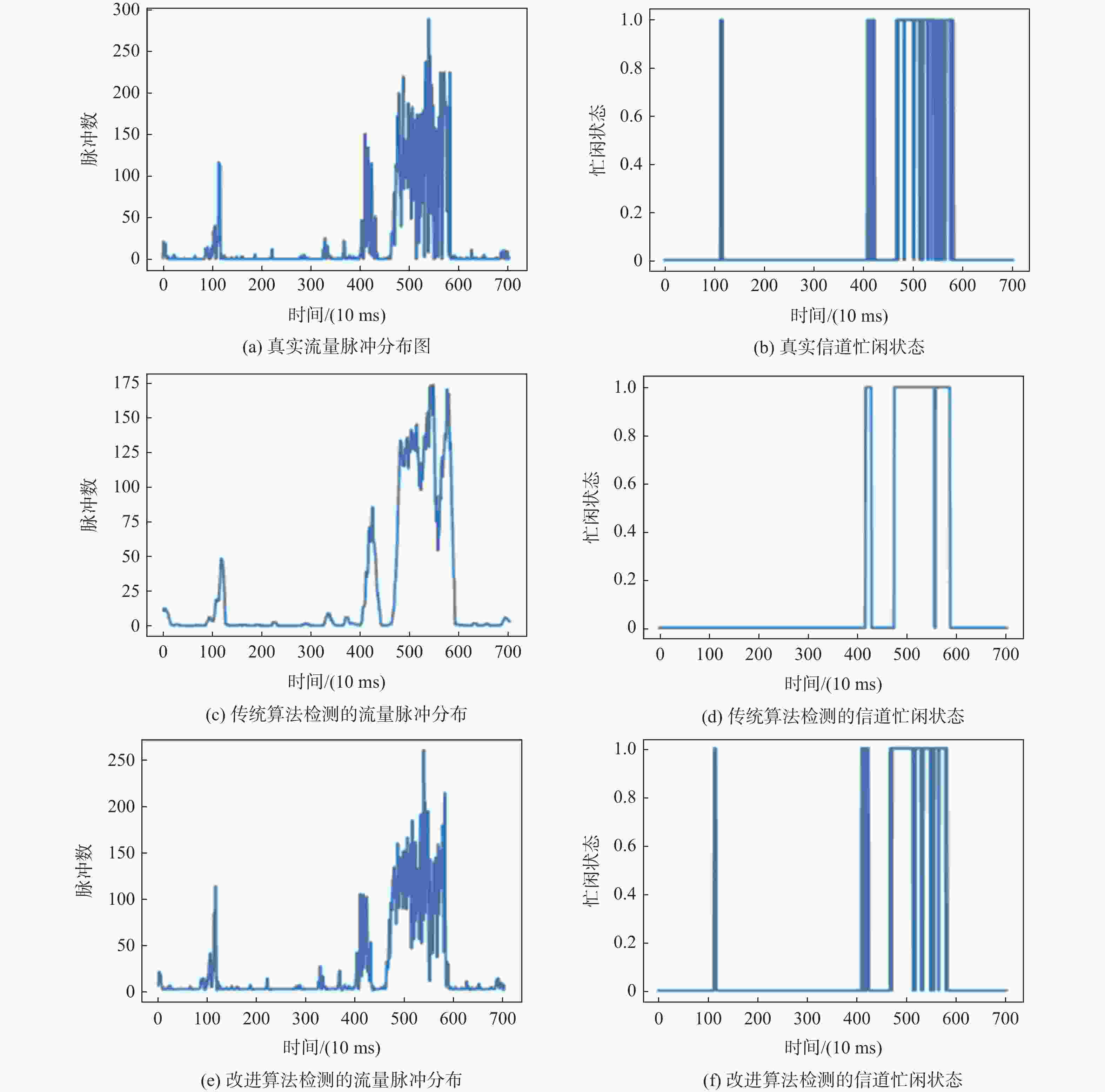
为实现对时敏目标的快速探测、定位和打击,战术瞄准网络技术(TTNT)对战术信息接入信道、交互传输的实时性、可靠性提出高要求。TTNT采用基于统计优先的多址接入 (SPMA) 协议,通过周期性计算统计平均的思想,估计当前信道状态,控制战术信息接入信道的时机。该思想仅适用于流量相对平稳的情况,在流量非平稳时会导致较大的信道状态检测误差。针对此问题,引入流量预测技术,提出基于循环神经网络的SPMA协议信道状态智能检测改进算法。利用循环神经网络的学习特点学习历史流量数据的隐含特征,构建流量预测器对瞬时时刻的流量脉冲到达数进行实时预测,从而准确获取当前信道状态。实验结果表明:所提算法对信道状态的检测结果更接近真实值,显著降低了信道忙闲状态的误判率。
-
关键词:
- 统计优先的多址接入协议 /
- 信道状态检测 /
- 流量预测 /
- 循环神经网络 /
- 战术瞄准网络技术
Abstract:By connecting sensors and shooters, tactical target network technology (TTNT) can realize rapid detection, positioning and strike of time-sensitive targets in denial environments. To that end, real-time and reliable channel access is highly required for tactical information transmission. TTNT uses the statistical priority-based multiple access (SPMA) protocol, which periodically calculates the statistical average number of arrival traffic pulses, to estimate the current channel state and thus control the timing of tactical information access. However, methods based on statistical average are merely suitable for stationary traffic, and will lead to large error in channel state detection when the traffic is non-stationary. To solve this problem, the traffic prediction technology was adopted and an improved detection algorithm for SPMA protocol channel state based on recurrent neural network was proposed. Meanwhile, in order to accurately obtain the current channel state, the recurrent neural network was employed to learn the hidden characteristics of historical traffic data, and a traffic predictor was constructed to timely predict the number of traffic pulses arriving at an instant. Experiments showed that the results of communication state detection with our algorithm is more realistic, which can significantly reduce the false judgment rate of the channel state.
-
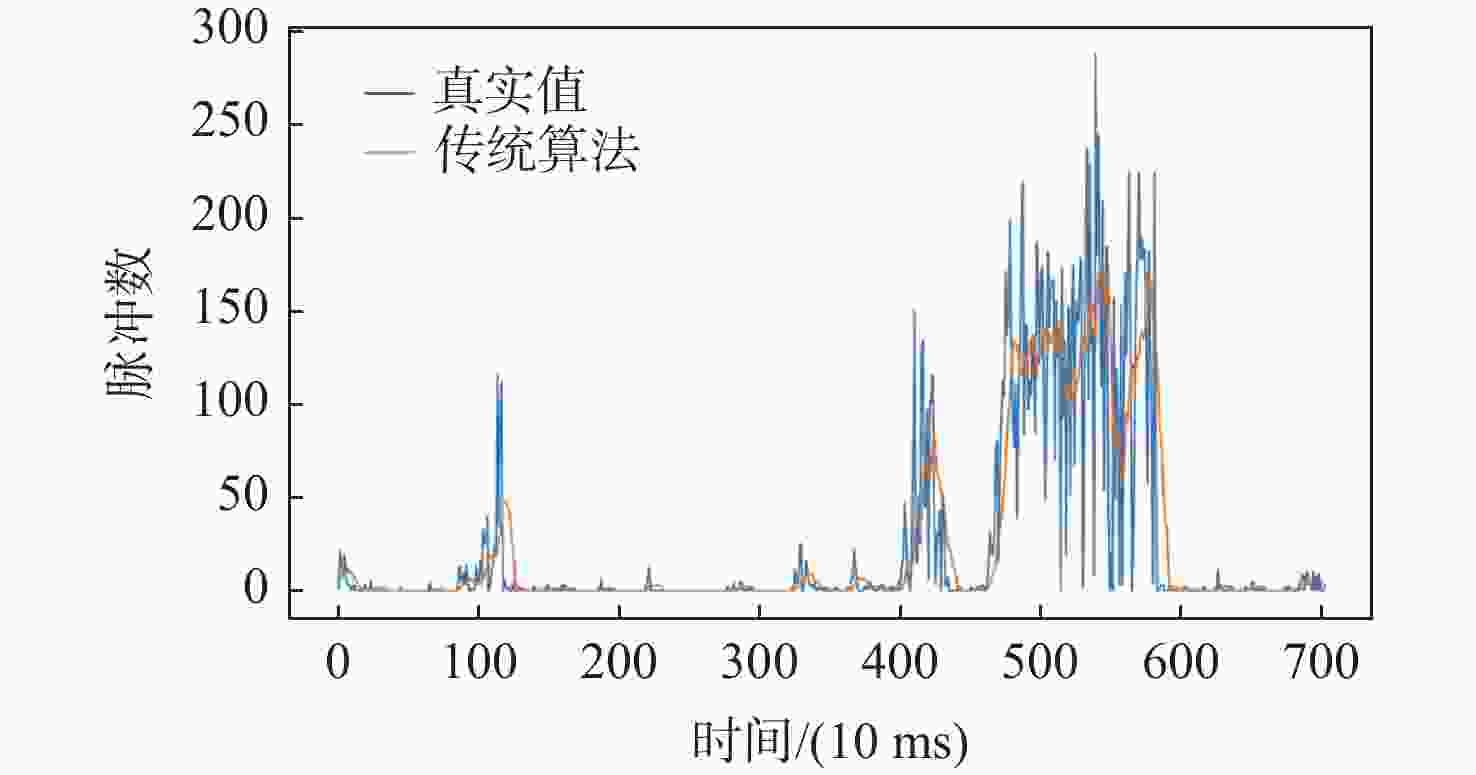
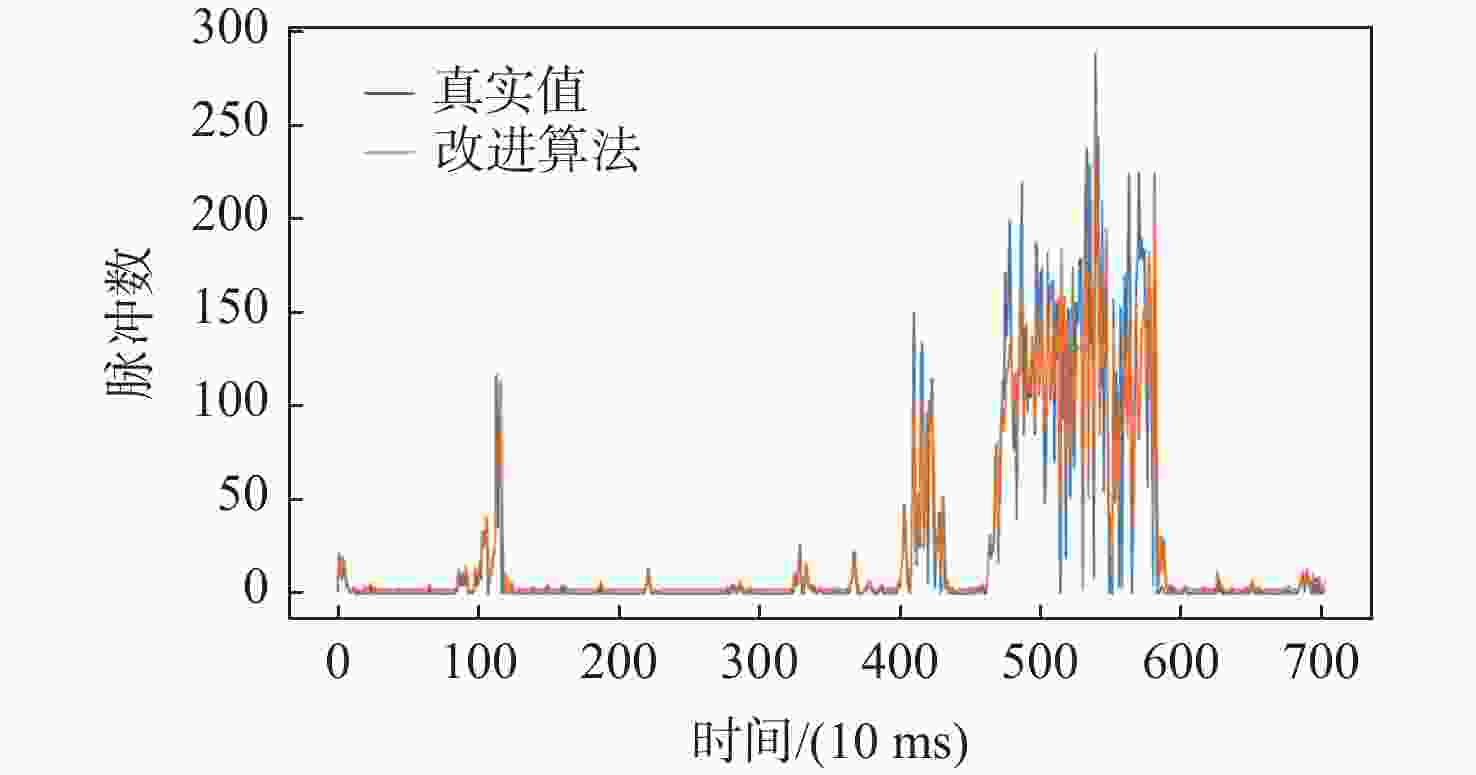
表 1 两种算法检测准确性对比
Table 1. Comparison of detection accuracy of two algorithms
算法 MSE RMSE MAE R2 传统算法 931.53 30.52 13.71 0.67 改进算法 313.56 17.70 7.78 0.89 表 2 两种算法在不同类型流量下对低中高优先级消息的忙闲状态误判率
Table 2. Misjudgment probability of busy and idle status of two algorithms for low, medium and high priority messages under different types of traffic
流量类型 所用算法 低优先级消
息误判率/%中优先级消
息误判率/%高优先级消
息误判率/%突发流量
[100,120]传统算法 20 0 0 改进算法 5 0 0 稳定流量
[200,400]传统算法 0 0 0 改进算法 0 0 0 强波动流量
[400,600]传统算法 22.61 25.55 13.76 改进算法 7.38 12.28 8.85 表 3 两种算法时延对比
Table 3. Time Delay comparison of two algorithms
算法 1000次时延/ms 平均单次时延/ms 传统算法 4.24 0.004 2 改进算法 48.30 0.048 3 -
[1] 吕娜, 张岳彤, 陈柯帆, 等. 数据链理论与系统[M]. 2版. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2018: 5-6.LV N, ZHANG Y T, CHEN K F, et al. Data link theory and system[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2018: 5-6(in Chinese). [2] 黄振, 周永将. 美军网络中心战的重要元素——协同数据链[J]. 现代导航, 2017, 8(1): 70-73.HUANG Z, ZHOU Y J. Element of US army network centric warfare—Cooperative sata link[J]. Modern Navigation, 2017, 8(1): 70-73(in Chinese). [3] 戴辉. 武器协同数据链发展需求[J]. 指挥信息系统与技术, 2011, 2(5): 11-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-909X.2011.05.004DAI H. Development requirement of weapon cooperative data link[J]. Command Information System and Technology, 2011, 2(5): 11-14(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-909X.2011.05.004 [4] 金荣, 张衡阳. 美军TTNT数据链发展应用现状[J]. 现代导航, 2014, 5(2): 154-156.JIN R, ZHANG H Y. Development situation of tactical targeting networks for US force[J]. Modern Navigation, 2014, 5(2): 154-156(in Chinese). [5] 陈志辉, 李大双. 对美军下一代数据链TTNT数据链技术的分析与探讨[J]. 信息安全与通信保密, 2011(5): 76-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8054.2011.05.038CHEN Z H, LI D S. Analysis and exploration on tactical targeting network technology for the next generation tactical data link[J]. Information Security and Communications Privacy, 2011(5): 76-79(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8054.2011.05.038 [6] HERDER J C , STEVENS J A. Method and architecture for TTNT symbol rate scaling modes: U. S. Patent 7, 839, 900[P]. 2010-11-23. [7] 周礼明. 统计优先级无线多址接入访问技术研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2019: 10-18.ZHOU L M. Research on statistical priority based multiple access[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2019: 10-18(in Chinese). [8] 李志林. 面向高时敏业务的统计优先级多址接入技术研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2019: 17-20, 45-66.LI Z L. Research on statistical priority-based multiple access technology for high time-sensitive services[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019: 17-20, 45-66(in Chinese). [9] LIU J, PENG T, QUAN Q Y, et al. Performance analysis of the statistical priority-based multiple access[C]//3rd IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 30-35. [10] 刘健. 基于优先级概率统计的多址接入协议研究[D]. 北京: 北京邮电大学, 2018: 19-23.LIU J. Performance analysis of the statistical priority-based multiple access[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunication, 2018: 19-23(in Chinese). [11] 王希洋. 基于统计优先级的数据链MAC协议研究[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2017: 21-31.WANG X Y. Research on statistical priority-based MAC protocol for data link[D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2017: 21-31(in Chinese). [12] 吴琼. 基于统计优先级的链路层协议性能仿真与研究[D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2014: 17-22.WU Q. Performance simulation and research of the statistical priority-based multiple access[D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2014: 17-22(in Chinese). [13] 王玉龙. TTNT数据链战术数据链媒体接入控制协议关键技术研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2018: 21-36.WANG Y L. Research on key technologies of MAC protocol in TTNT tactical data link[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2018: 21-36(in Chinese). [14] 郑文庆, 金虎, 郭建蓬, 等. 一种新型数据链MAC协议及其信道占用研究[J]. 计算机仿真, 2019, 36(7): 148-152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2019.07.030ZHENG W Q, JIN H, GUO J P, et al. Research on a new data link MAC protocol and its channel occupancy[J]. Computer Simulation, 2019, 36(7): 148-152(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2019.07.030 [15] 程文驰, 张施施. 一种数据链动态门限统计优先级多址接入协议[J]. 指挥与控制学报, 2020, 6(1): 75-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2020.01.0075CHENG W C, ZHANG S S. A data link-oriented dynamic threshold statistical priority multiple access protocol[J]. Journal of Command and Control, 2020, 6(1): 75-80(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2020.01.0075 [16] 臧运娟. 无线通信网络流量预测综述[J]. 电子设计工程, 2017, 25(4): 150-153. doi: 10.14022/j.cnki.dzsjgc.2017.04.038ZANG Y J. Traffic prediction in wireless communication network: A survey[J]. Electronic Design Engineering, 2017, 25(4): 150-153(in Chinese). doi: 10.14022/j.cnki.dzsjgc.2017.04.038 [17] FENG H F, SHU Y T. Study on network traffic prediction techniques[C]//International Conference on Wireless Communications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2005: 1041-1044. [18] 刘杰, 黄亚楼. 基于BP神经网络的非线性网络流量预测[J]. 计算机应用, 2007, 27(7): 1770-1772.LIU J, HUANG Y L. Nonlinear network traffic prediction based on BP neural network[J]. Computer Applications, 2007, 27(7): 1770-1772(in Chinese). [19] OLIVERIRA T P, BARBAR J S, SOARES A S. Computer network traffic prediction: a comparison between traditional and deep learning neural networks.[J]. International Journal of Big Data Intelligence, 2016, 3(1): 28-37. doi: 10.1504/IJBDI.2016.073903 [20] VINAYAKUMAR R, SOMAN K P, POORNACHANDRAN P. Applying deep learning approaches for network traffic prediction[C]//International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2353-2358. [21] 杜爽, 徐展琦, 马涛, 等. 基于神经网络模型的网络流量预测综述[J]. 无线电通信技术, 2020, 46(2): 216-222. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2020.02.013DU S, XU Z Q, MA T, et al. A survey of network traffic prediction based on neural network models[J]. Radio Communications Technology, 2020, 46(2): 216-222(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2020.02.013 [22] 郭佳, 余永斌, 杨晨阳. 基于全注意力机制的多步网络流量预测[J]. 信号处理, 2019, 35(5): 758-767.GUO J, YU Y B, YANG C Y. Multi-step prediction of traffic load with all-attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2019, 35(5): 758-767(in Chinese). [23] LI M, WANG Y W, WANG Z W, et al. A deep learning method based on an attention mechanism for wireless network traffic prediction[J]. Ad Hoc networks, 2020, 107: 102258. doi: 10.1016/j.adhoc.2020.102258 [24] CHO K, MERRIENBOER B V, GULCEHRE C, et al. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation[C]//Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in natural Language Processing, 2014: 1724-1734. -







 下载:
下载: