GNSS-R BSAR range-Doppler imaging algorithm based on synchronization of direct and echo signal
-
摘要:
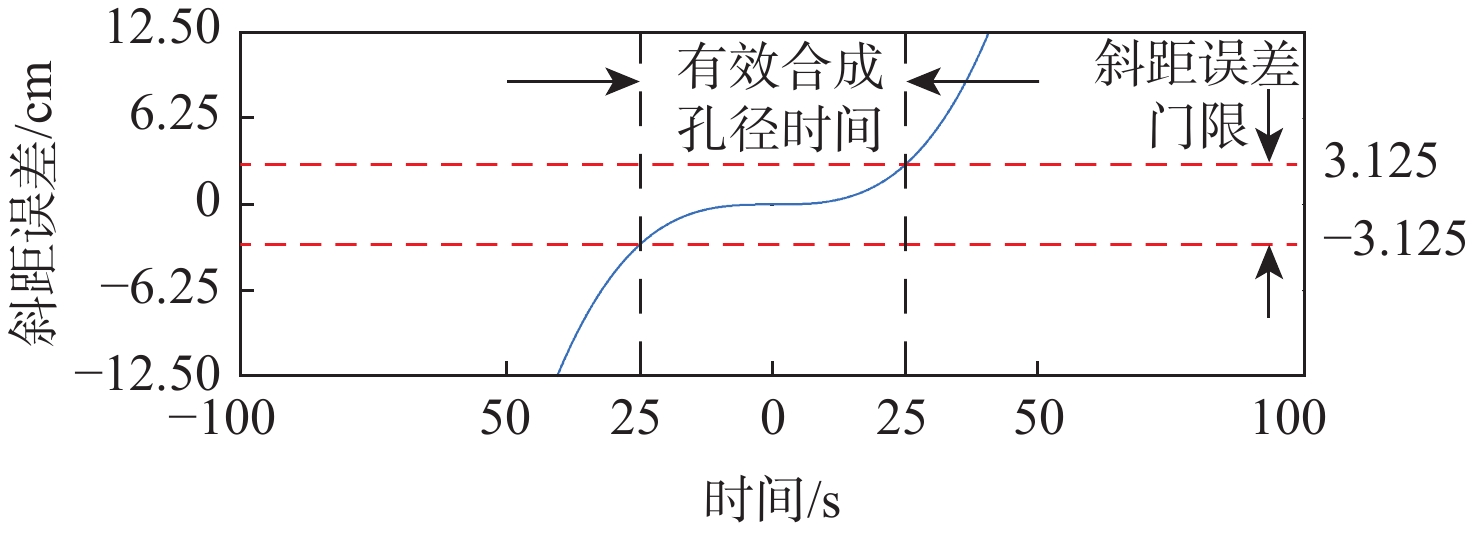
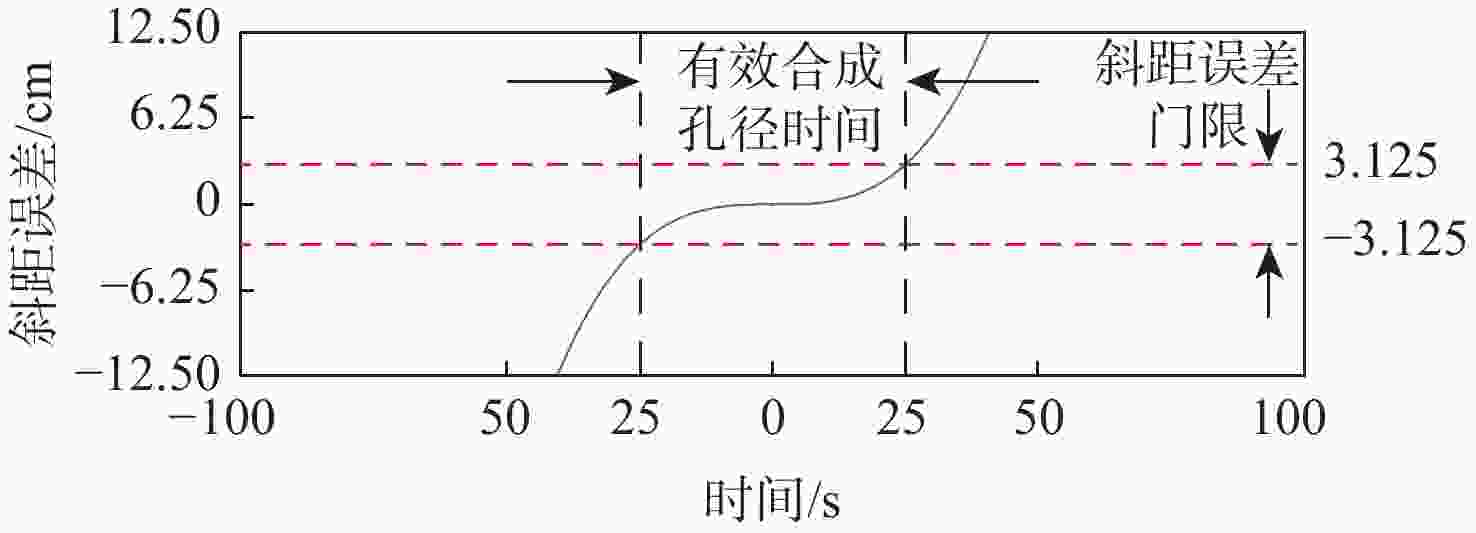
针对目前基于全球导航卫星系统反射信号的双基地合成孔径雷达(GNSS-R BSAR)在一站固定模式下的大斜视,斜距历程复杂,回波信号方位空变导致回波信号难以处理的问题,提出改进的距离多普勒成像新算法。所提算法采用GNSS信号作为辐射源,根据一站固定模式下GNSS-R BSAR合成孔径时间长的特点,引入高阶等效斜视距离模型,得到导航卫星与目标斜距相对时间变化的精确描述。先通过直射信号与回波信号时域对消进行距离徙动校正,实现全场景目标距离徙动的精确校正;再通过方位向分块混合相关处理来克服回波信号方位向的移变性质,实现全场景高效精确成像。所提算法的成像效率优于传统后向投影时域(BP)算法,成像精度与BP算法相当,且可根据需要通过调整方位分块的宽度来提升聚焦效果。最后,用GPS-L5 信号进行仿真和实验,仿真和实验结果验证了所提算法的可行性和高效性。
-
关键词:
- 全球导航卫星系统反射信号 /
- 双基地合成孔径雷达 /
- 方位空变处理 /
- 距离多普勒算法 /
- 距离徙动校正
Abstract:Aiming at the problems that the current global navigation satellite system-reflectometry bistatic synthetic aperture radar (GNSS-R BSAR) has a large squint in the fixed mode of one station, the slant range history is complicated, and the echo signal's azimuth is changed, the echo signal is difficult to process, an improved Range Doppler imaging algorithm is proposed. The method uses GNSS signal as the radiation source, and introduces a high-order squint range model based on the long GNSS-R BSAR synthetic aperture time in the one-stop fixed mode to obtain an accurate description of the relative time variation of the squint range between the navigation satellite and the target. Based on this model, firstly, the range migration is corrected by the time-domain cancellation of the direct signal and the echo signal to realize the accurate correction of the target range migration in the whole scene; By azimuth-block hybrid correlation processing, the azimuth shifting nature of the echo signal is overcome, and efficient and accurate imaging of the whole scene is realized. The imaging efficiency of the proposed algorithm is better than that of the traditional BP algorithm, the imaging accuracy is comparable to that of the back projection (BP) algorithm, and the focusing effect can be improved by adjusting the width of the orientation bins as needed. Finally, to validate the proposed algorithm, we conducted simulations and experiments with GPS-L5 signals , the simulation and experimental results verified the feasibility and efficiency of the proposed algorithm.
-
表 1 残差项仿真参数
Table 1. Residual simulation parameters
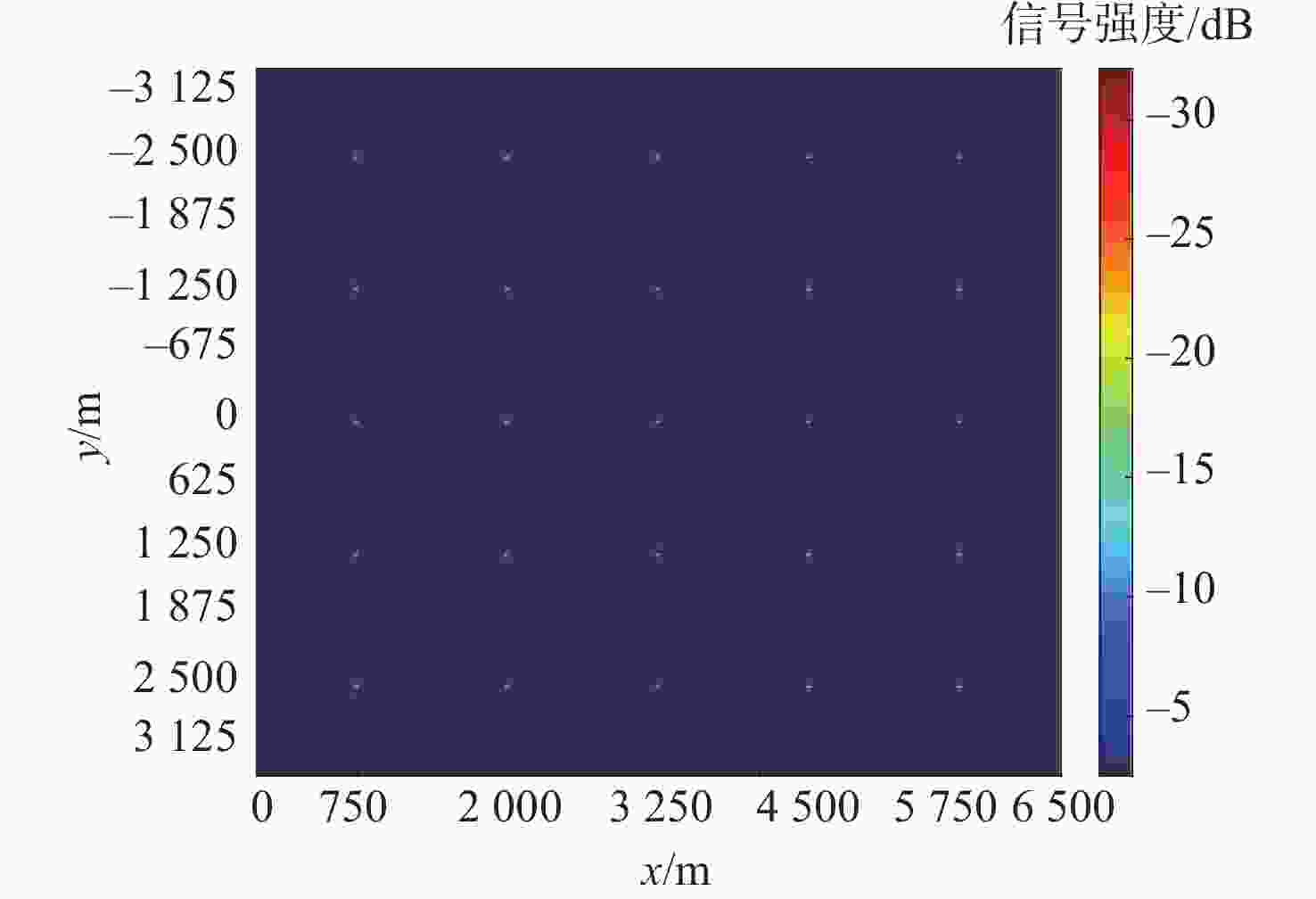
坐标 卫星位置/km 卫星速度/(m·s−1) 接收机位置/m 目标点/m x 11769 500.96 0 1~5000 y 1124.8 2891.8 0 0 z 12482 −369.24 1000 0 表 2 仿真参数
Table 2. Simulation parameters
参数 距离向
采样频率/
MHz载波
频率/
MHz信号
带宽/
MHz成像区域
大小/
(km×km)合成
孔径
时间/s脉冲
重复
频率/Hz数值 62 1176.45 20.46 6.5×6.5 300 1000 表 3 场景参数
Table 3. Scene parameters
坐标 接收机位置/
m场景中心位置/
km卫星位置/
km卫星速度/
(m·s−1)x 0 12.5 20133.7258 1392.7068 y 0 0 10697.3032 −2766.6856 z 100 0 728.0291 138.3063 表 4 所选点目标的评估参数
Table 4. Evaluation parameters of selected point target
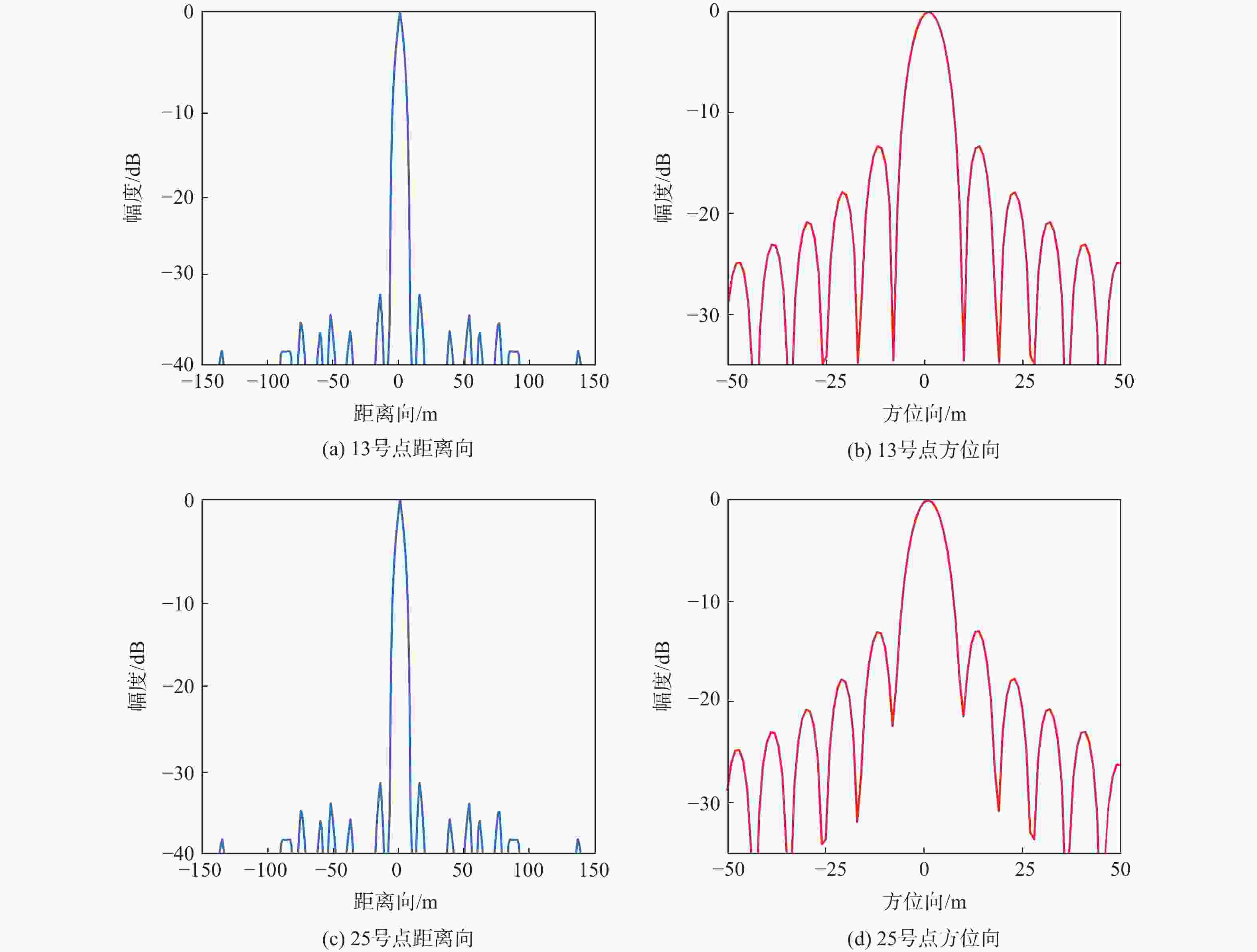
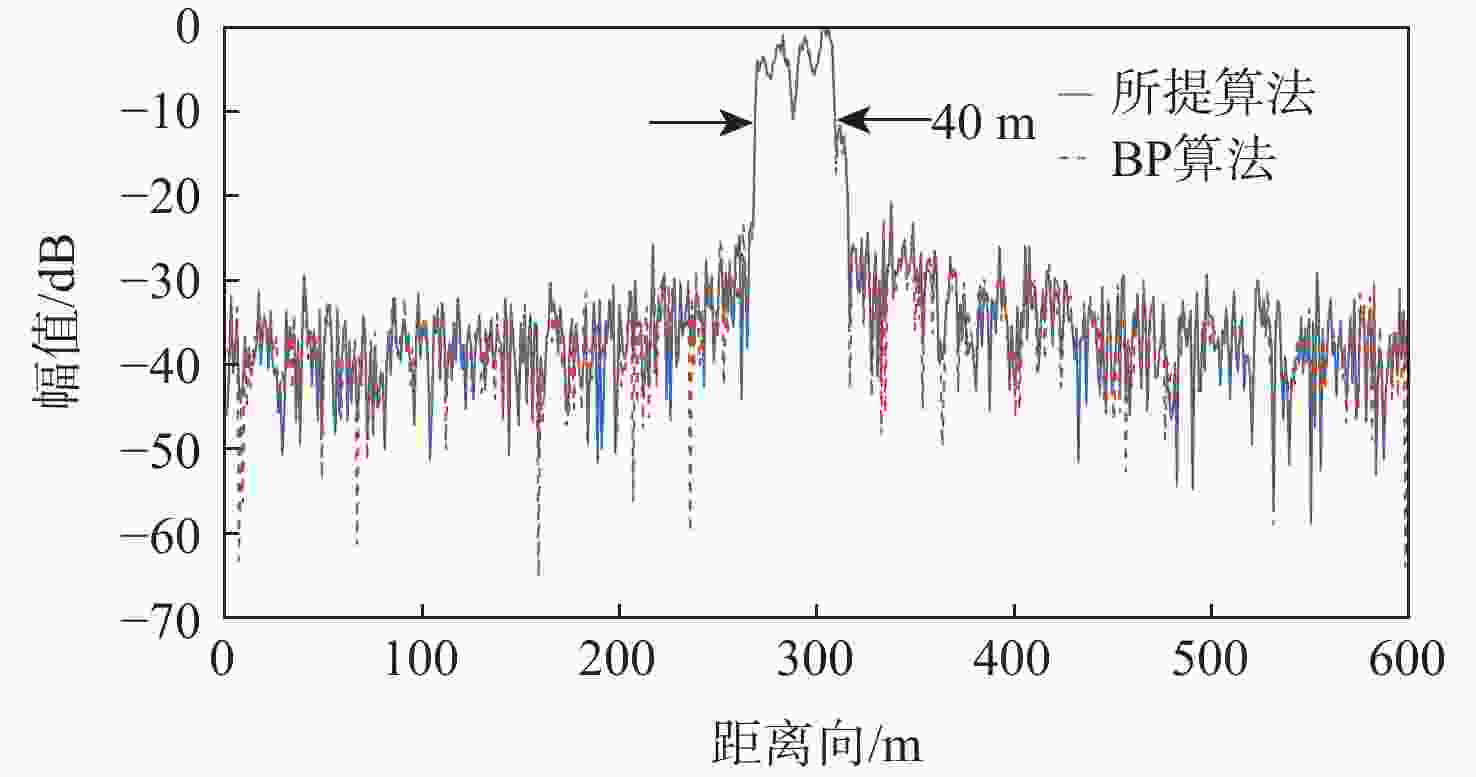
参数 距离向 方位向 PSLR/dB ISLR/dB 分辨率/m PSLR/dB ISLR/dB 分辨率/m 目标13 −34.8 −12.8 16.8 −13.3 −9.94 5.625 目标25 −34.8 −12.6 16.8 −13.11 −9.76 5.626 理论值 −35 −12.8 16.3 −13.3 −9.95 5.625 表 5 实验场景主要回波目标
Table 5. Main echo target of experimental scene
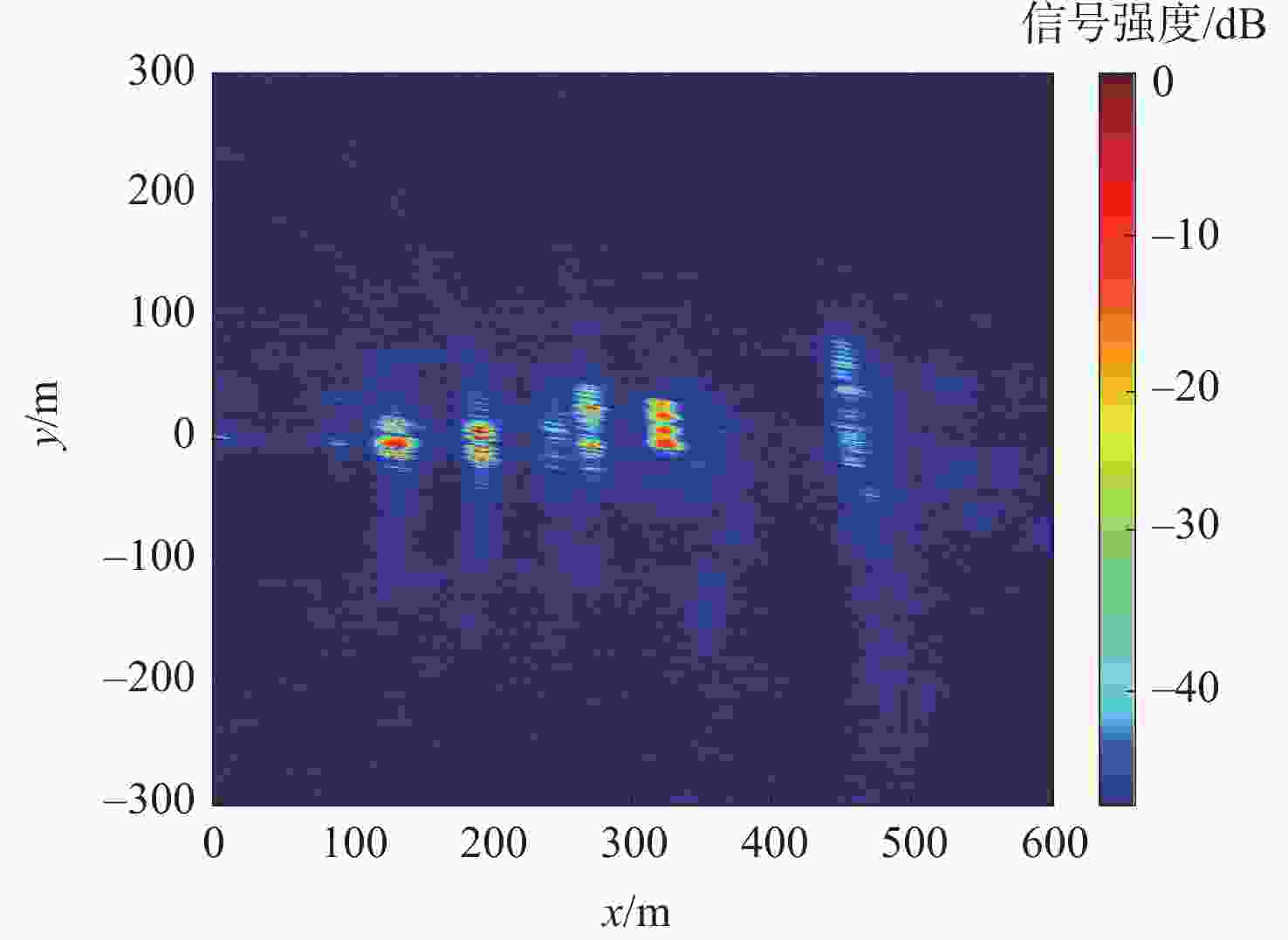
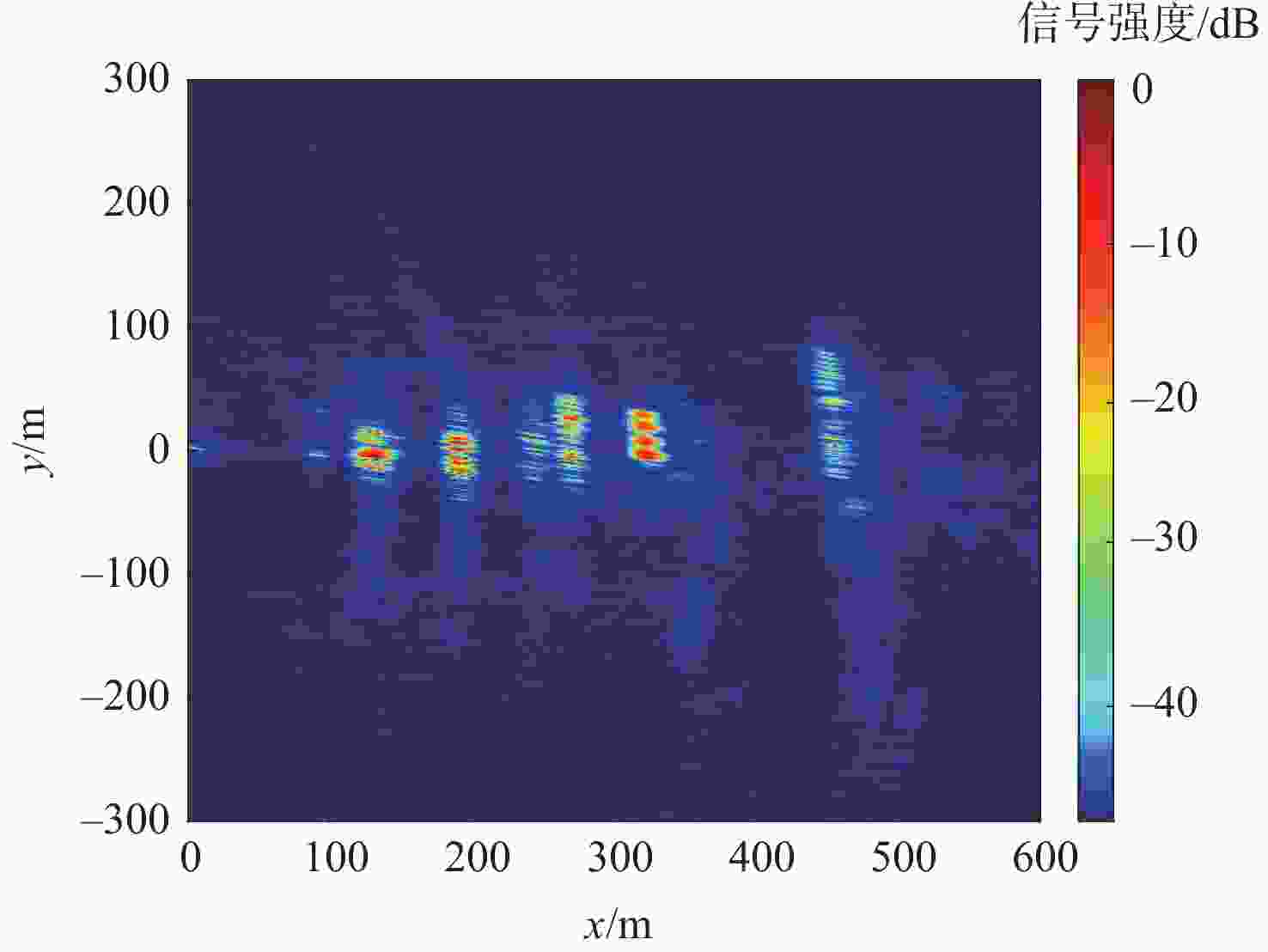
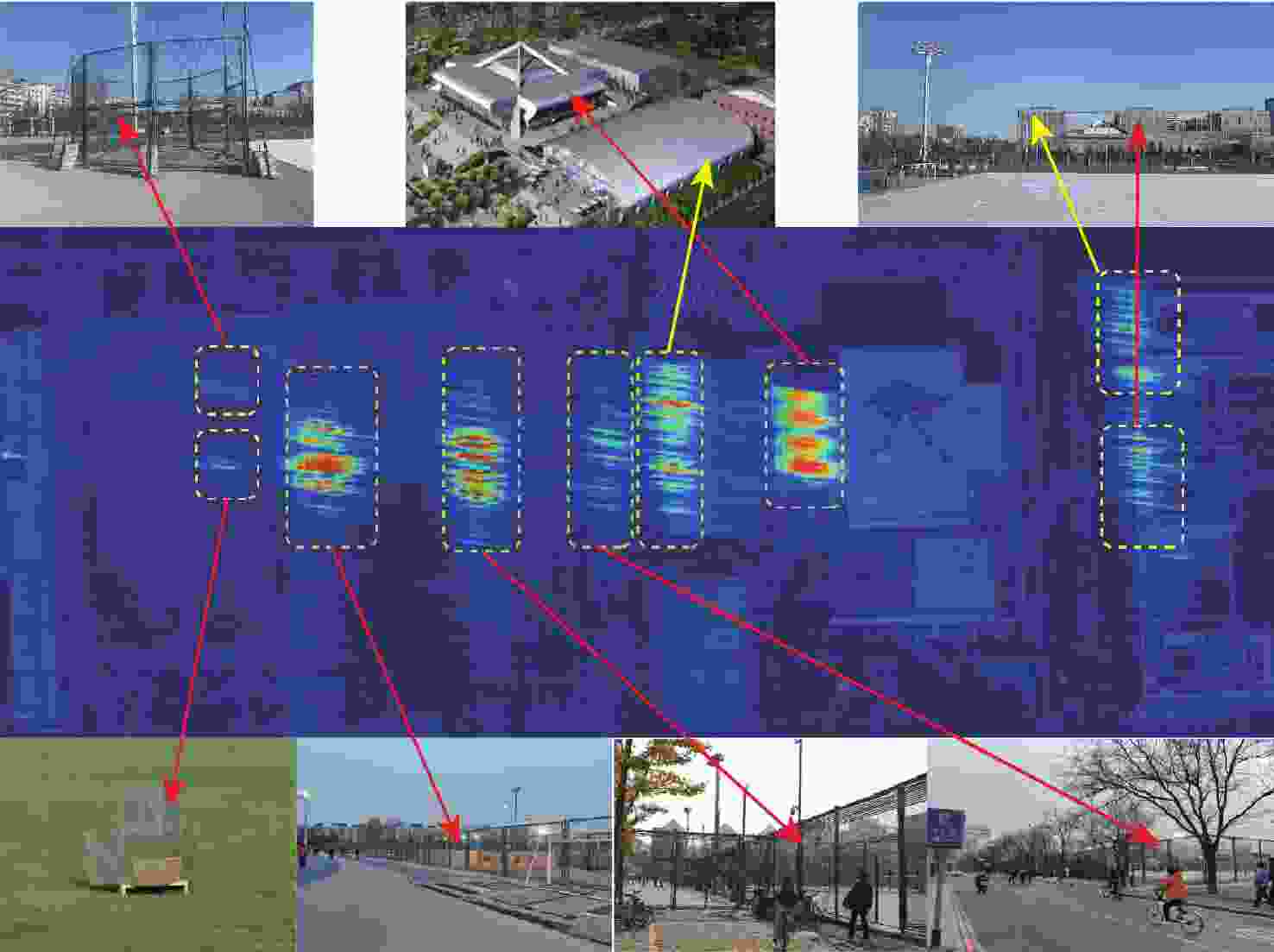
编号 建筑物 目标0 链球围栏 目标1 角反射器 目标2 两道铁栅栏 目标3 篮球场铁栅栏 目标4 篮球场铁栅栏 目标5 游泳馆 目标6 体育馆 目标7 体育馆顶部 目标8 新主楼 表 6 数据采集系统及成像参数
Table 6. Data acquisition system and imaging parameters
参数 数值 采样频率/MHz 62 量化比特/bit 14 载频/MHz 1176.45 信号带宽/MHz 20.46 合成孔径时间/s 1800 成像区域大小/(m×m) 600×600 脉冲重复频率/Hz 1000 回波天线海拔高度/m 60.52 表 7 GPS PRN03卫星的位置和速度信息
Table 7. GPS PRN03 satellite position and speed information
坐标 卫星位置/km 速度/(m·s−1) x 20133.7258 1392.7068 y 10697.3032 −2766.6856 z 728.0291 138.3063 -
[1] ANTONIOU M, CHERNIAKOV M. GNSS-based bistatic SAR: A signal processing view[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2013(1): 1-16. [2] ANTONIOU M, STOVE A, SAYIN A, et al. Passive SAR satellite constellation for near-persistent earth observation: Prospects and issues[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2018, 33: 4-15. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2018.8650001 [3] WANG F, YANG D, YANG L. Feasibility of wind direction observation using low-altitude global navigation satellite system-reflectometry[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(12): 5063-5075. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2877388 [4] MARTIN-NEIRA M. A passive reflectometry and interferometry system (PARIS): Application to ocean altimetry[J]. ESA Journal, 1993, 17: 331-355. [5] RODRIGUEZ-ALVAREZ N, BOSCH-LLUIS X, CAMPS A, et al. Soil moisture retrieval ssing GNSS-R techniques: Experimental results over a bare soil field[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(11): 3616-3624. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2030672 [6] 洪学宝, 张波, 阮宏梁, 等. 基于相关功率修正的地基GNSS-R土壤湿度反演[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(8): 1558-1564. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2020.0154HONG X B, ZHANG B, RUAN H L, et al. Ground-based GNSS-R soil moisture retrieval based on correlation power correction[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(8): 1558-1564(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2020.0154 [7] ZHOU X, WANG P, CHEN J, et al. A modified radon fourier transform for GNSS-based bistatic radar target detection[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020(99): 1-5. [8] GAO C, YANG D, HONG X, et al. Experimental results about traffic flow detection by using GPS reflected signals[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(12): 5076-5087. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2882232 [9] LIU F, FAN X, ZHANG T, et al. GNSS-Based SAR interferometry for 3-D deformation retrieval: Algorithms and feasibility study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(10): 5736-5748. [10] LIU F, ANTONIOU M, ZENG Z, et al. Coherent change detection using passive GNSS-Based BSAR: Experimental proof of concept[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(8): 4544-4555. [11] 仇晓兰, 丁赤飚, 胡东辉. 双站SAR成像处理技术[M]. 北京: 科学技术出版社, 2010: 147-148.QIU X L, DING C B, HU D H. Double-station SAR imaging processing technology[M]. Beijing: Science and Technology Press, 2010: 147-148 (in chinese ) . [12] SHAO Y F, WANG R, DENG Y K, et al. Fast backprojection algorithm for bistatic SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transations on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 10(5): 1080-1084. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2230243 [13] ANTONIOU M, SAINI R, CHERNIAKOV M. Results of a space-surface bistatic SAR image formation algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(11): 3359-3371. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.902124 [14] ZENG T, WANG R, LI F, et al. A modified nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm for spaceborne/stationary bistatic SAR based on series reversion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(5): 3108-3118. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2219057 [15] ZHOU X K, CHEN J, WANG P B, et al. An efficient imaging algorithm for GNSS-R bi-static SAR[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(24): 2945. doi: 10.3390/rs11242945 [16] WANG P, LIU W, CHEN J, et al. A high-order imaging algorithm for high-resolution spaceborne SAR based on a modified equivalent squint range model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(3): 1225-1235. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2336241 [17] 黄岩, 李春升, 陈杰, 等. 高分辨星载SAR改进ChirpScaling成像算法[J]. 电子学报, 2000, 28(3): 35-38. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2000.03.010HUANG Y, LI C S, CHEN J, et al. Improved ChirpScaling imaging algorithm for high resolution spaceborne SAR[J]. Acta Electronics, 2000, 28(3): 35-38(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2000.03.010 [18] ZENG H C, WANG P B, CHEN J, et al. A novel general imaging formation algorithm for GNSS-based bistatic SAR[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(3): s16030294. -






 下载:
下载: