Comparison of turbulence models for unsteady flow simulation in a long and narrow cabin
-
摘要:
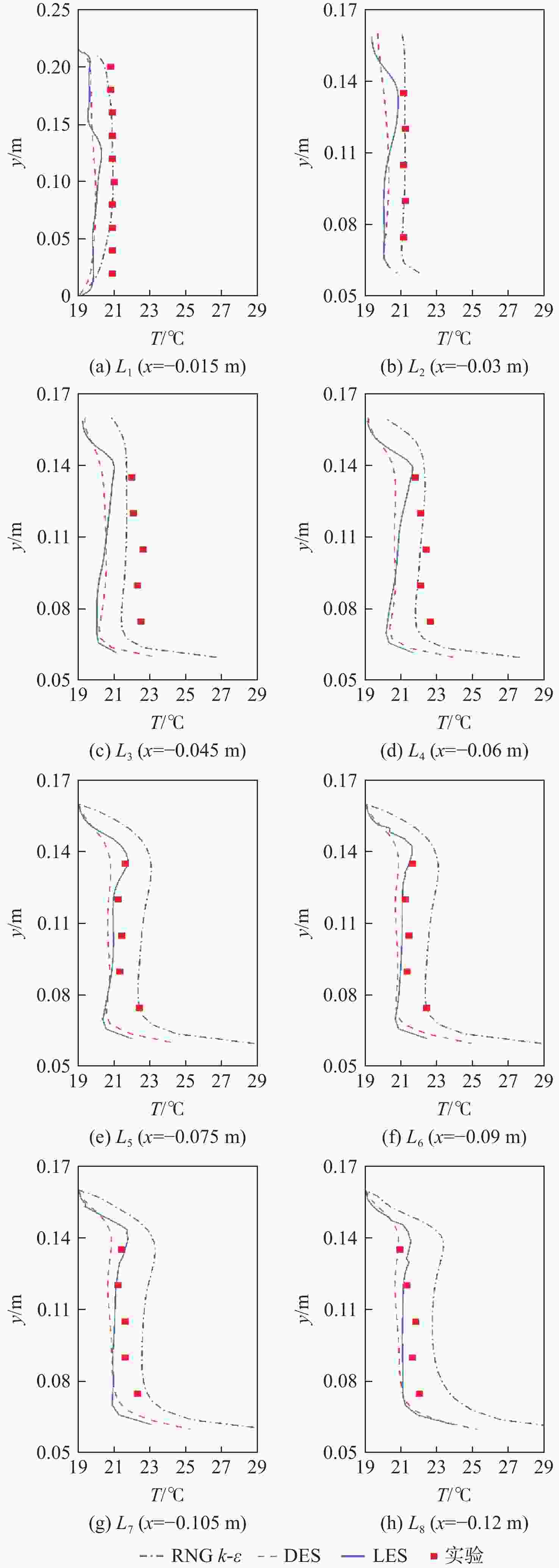
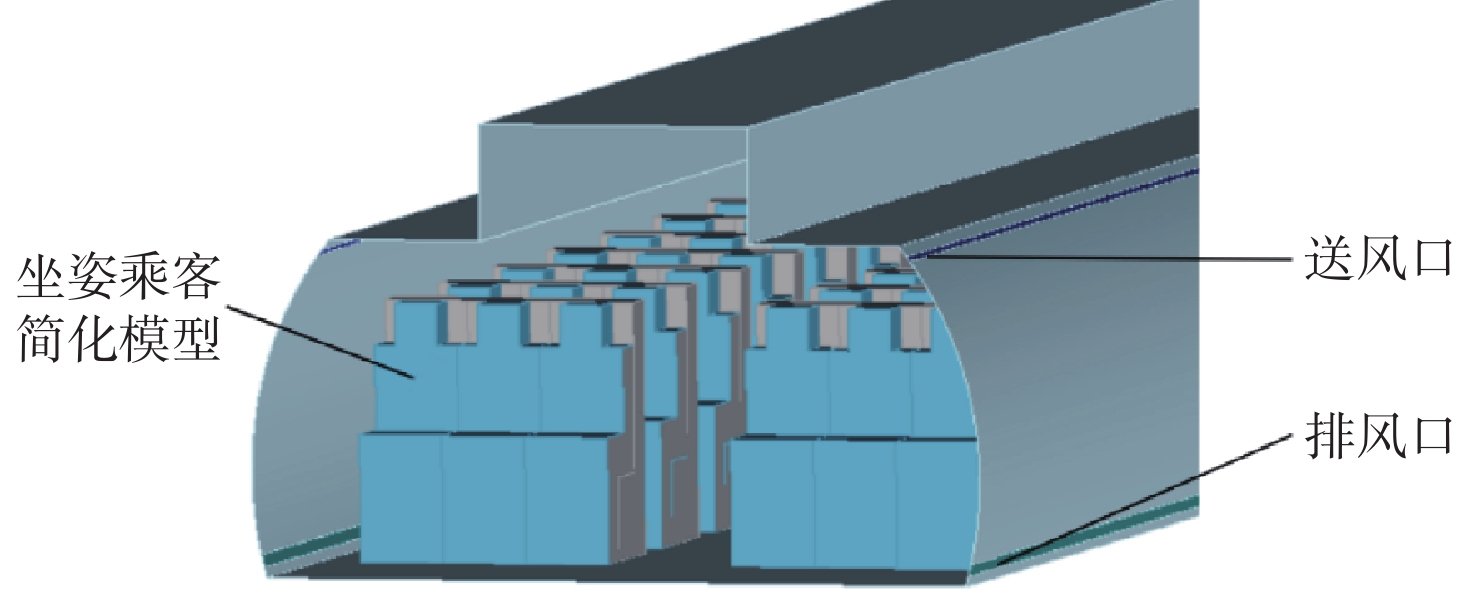
针对狭长型封闭舱室内非定常流动模拟的湍流模型选择问题,以飞机舱室为典型环境,使用相似准则为依据的热缩比法搭建了实验平台。将实验结果与RNG
k -ε 、DES、LES三种湍流模型的数值模拟结果进行对比和分析,评估狭长型封闭舱室内非定常流动特征研究中合适的湍流模型。结果显示,RNGk -ε 和DES模型可以定性描述流动变化趋势,但是LES模型在流场非定常性和不稳定性捕捉更为准确,其流场结构更接近实验结果。模拟结果与实验结果对比显示,LES模型能更加真实地反映狭长型封闭舱室非定常流动的情况。Abstract:Aiming at the problem of turbulence model selection for unsteady flow simulation in a long and narrow enclosed cabin, this study uses an aircraft cabin as a typical environment and uses the heat shrinkage ratio method based on similar criteria to build a simplified experimental platform. The experimental results are compared and analyzed with the numerical simulation results obtained by the three turbulence models of RNG
k -ε , DES and LES, and the appropriate turbulence model in the study of unsteady flow characteristics in the long and narrow enclosed cabin is evaluated. The results demonstrate that the RNGk -ε and DES models are capable of qualitatively describing the flow trend, but the LES model is more accurate in capturing the unpredictability and instability of the flow field, and its flow field structure is more in line with the experimental findings. Therefore, the LES model can more truly reflect the unsteady flow of the long and narrow enclosed cabin.-
Key words:
- numerical simulation /
- turbulence model /
- air distribution /
- scaled model /
- long-narrow cabin
-
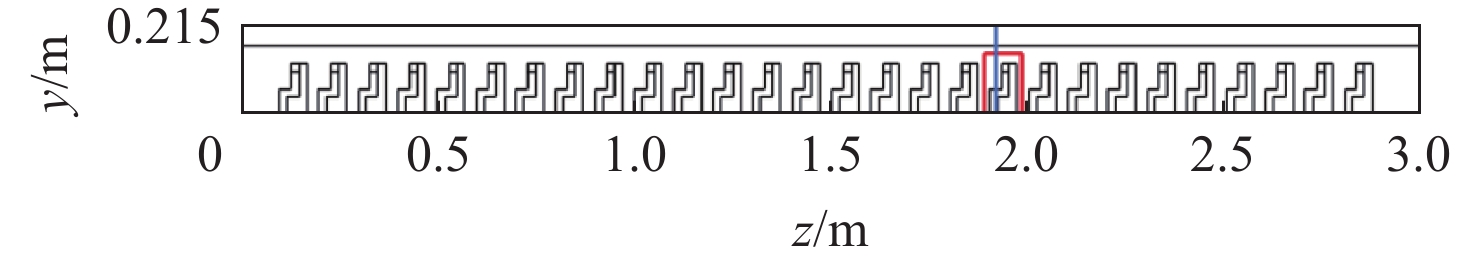
表 1 相似比例尺
Table 1. Similar scale
比例尺 几何比例尺$ {C_L} $ 速度比例尺$ {C_V} $ 流量比例尺$ {C_G} $ 流量比例尺$ {C_Q} $ 数值 $ 1:10 $ $ \sqrt {10} :10 $ $\sqrt {10} :1\;000$ $\sqrt {10} :1\;000$ 表 2 机舱实际与模型参数
Table 2. Actual and model parameters of cabin
模型 机舱长/
m纵横比 总风量/
(L·s−1)送风速度/
(m·s−1)总体发热量/
W机舱实型 30 10∶1 1579.2 1.15 16530 机舱模型 3 10∶1 5 0.36 50 -
[1] 刘鹤. 中英两国民航产业政策比较分析[J]. 民航管理, 2019(9): 14-16.LIU H. A comparative analysis of civil aviation industry policies between China and Britain[J]. Civil Aviation Management, 2019(9): 14-16(in Chinese). [2] 庞丽萍, 巩萌萌, 王浚, 等. 基于人体热调节模型的民机座舱热舒适性分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2012, 38(2): 166-169. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2012.02.019PANG L P, GONG M M, WANG J, et al. Aircraft cabin comfort analysis with human thermoregulation model[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2012, 38(2): 166-169(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2012.02.019 [3] LI J Y, LIU J J, PEI J J, et al. Experimental study of human thermal plumes in a small space via large-scale TR PIV system[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 127: 970-980. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.07.138 [4] ZHANG Y Z, LI J Y, LIU J J. Experimental study of the impact of passenger behavior on the aircraft cabin environment[J]. Science and Technology for the Built Environment, 2021, 27(4): 427-435. doi: 10.1080/23744731.2020.1849795 [5] MAHMOUD S, BENNETT J S, HOSNI M H, et al. Comparison of pathogens dispersion in an aircraft cabin using gas injection source versus a coughing manikin[C]//Proceedings of ASME 2020 Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting. New York: ASME, 2020: V001 T 01A013. [6] CAO X D, LIU J J, PEI J J, et al. 2D-PIV measurement of aircraft cabin air distribution with a high spatial resolution[J]. Building and Environment, 2014, 82: 9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2014.07.027 [7] LIU W, DUAN R, CHEN C, et al. Inverse design of the thermal environment in an airliner cabin by use of the CFD-based adjoint method[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2015, 104: 147-155. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2015.07.011 [8] KIM J Y, KIM K Y. Experimental and numerical analyses of train-induced unsteady tunnel flow in subway[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology Incorporating Trenchless Technology Research, 2007, 22(2): 166-172. [9] 朱学良. 客舱内自然对流运动对流场影响的实验研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2016.ZHU X L. The experimental research about the influence of natural convection on the flow field in the cabin mockup[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2016(in Chinese). [10] LIU W, WEN J Z, LIN C H, et al. Evaluation of various categories of turbulence models for predicting air distribution in an airliner cabin[J]. Building and Environment, 2013, 65: 118-131. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2013.03.018 [11] LIN C H, HORSTMAN R H, AHLERS M F, et al. Numerical simulation of airflow and airborne pathogen transport in aircraft cabins- Part Ⅰ: Numerical simulation of the flow field[J]. ASHRAE Transactions, 2005, 111(1): 755-763. [12] EBRAHIMI K, ZHENG Z C, HOSNI M H. LES and RANS simulation of turbulent airflow and tracer gas injection in a generic aircraft cabin model[C]//Proceedings of the Roceeding of ASME-joint Us-european Fluids Engineering Summer Meeting & International Conference on Nanochannels. New York: ASME, 2010: 227-240. [13] 胡滋艳. 基于地铁车厢内流动结构优化的数值模拟研究[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2019.HU Z Y. Numerical simulation research on flow structure optimization in subway cabin[D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2019(in Chinese). [14] TANABE S, ARENS E A, BAUMAN F, et al. Evaluating thermal environments by using a thermal manikin with controlled skin surface temperature[J]. ASHRAE Transactions, 1994, 100(1): 39-48. [15] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 热环境人类工效学 代谢率的测定: GB/T 18048—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Replublic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Ergonomics of the thermal environment-Determination of metabolic rate: GB/T 18048—2008[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2009(in Chinese). [16] YAN Y H, LI X D, TU J Y. Effects of passenger thermal plume on the transport and distribution characteristics of airborne particles in an airliner cabin section[J]. Science and Technology for the Built Environment, 2016, 22(2): 153-163. doi: 10.1080/23744731.2015.1090254 [17] ZHANG T, CHEN Q. Novel air distribution systems for commercial aircraft cabins[J]. Building and Environment, 2007, 42(4): 1675-1684. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2006.02.014 [18] ZHANG Z, CHEN X, MAZUMDAR S, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation of airflow and contaminant transport in an airliner cabin mockup[J]. Building and Environment, 2009, 44(1): 85-94. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2008.01.012 [19] ZHANG Z, ZHANG W, ZHAI J Z, et al. Evaluation of various turbulence models in predicting airflow and turbulence in enclosed environments by CFD. Part 2: Comparison with experimental data from literature[J]. HVAC & R Research, 2007, 13(6): 871-886. [20] ZHANG T T, LEE K, CHEN Q Y. A simplified approach to describe complex diffusers in displacement ventilation for CFD simulations[J]. Indoor Air, 2009, 19(3): 255-267. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0668.2009.00590.x [21] YANG C W, ZHANG X W, CAO X D, et al. Numerical simulations of the instantaneous flow fields in a generic aircraft cabin with various categories turbulence models[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2015, 121: 1827-1835. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2015.09.163 -







 下载:
下载: