Structural safety assessment model of large liquid tanks considering environmental disturbance
-
摘要:
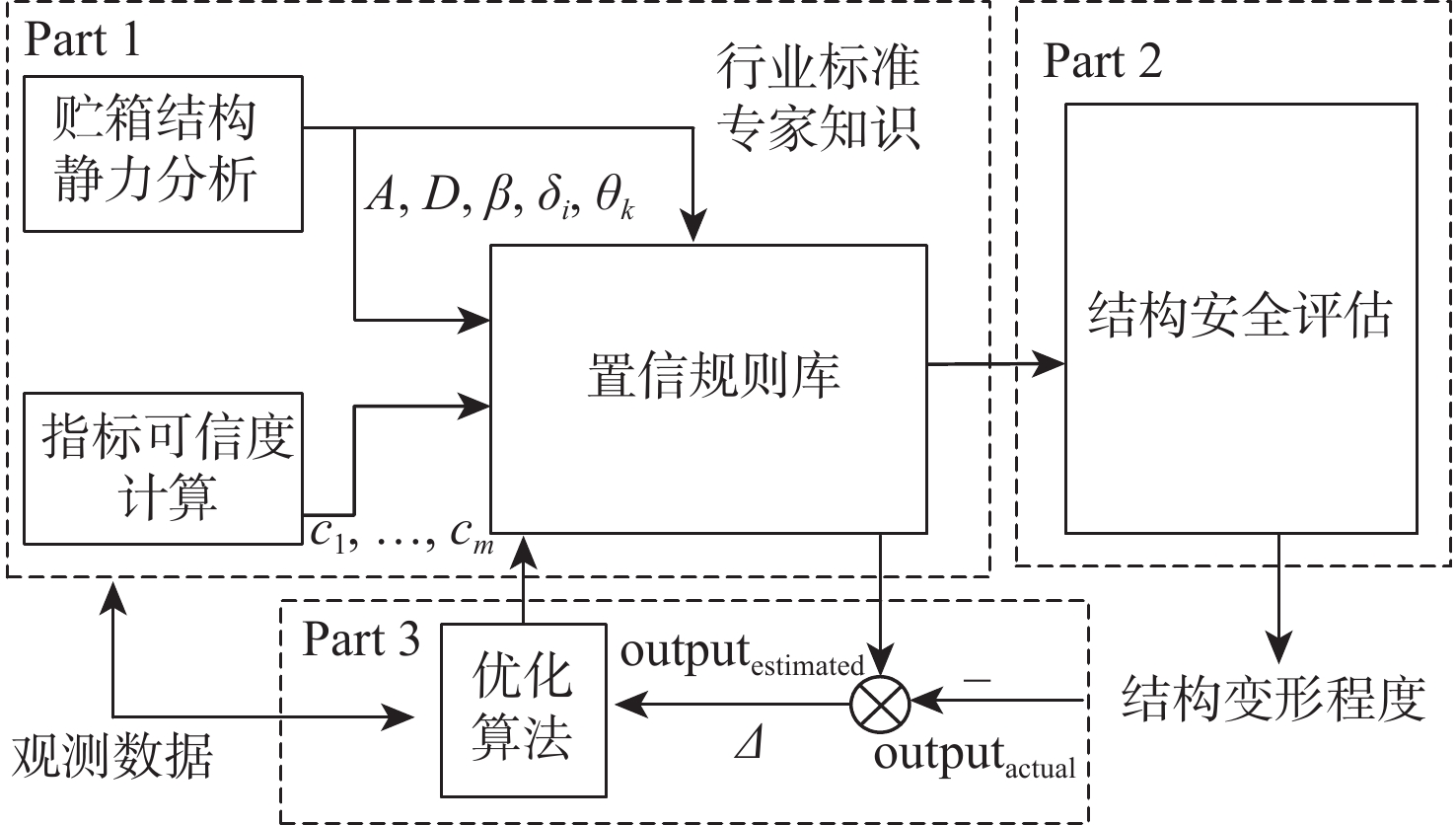
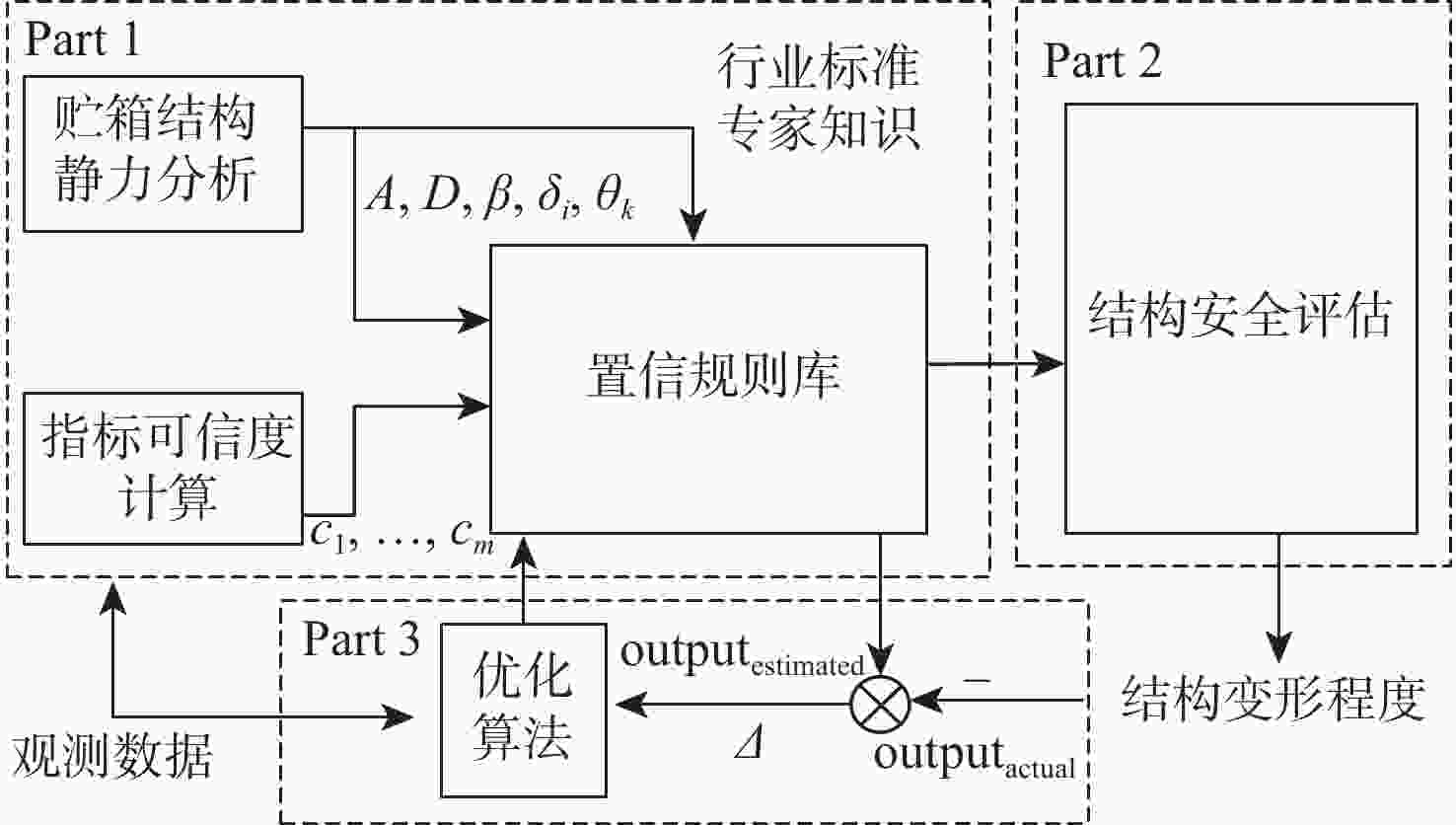
针对大型贮液箱(LLT)结构安全评估面临的先验信息缺失、监测信息不完全可靠等问题,基于置信规则库(BRB)和有限元方法(FEM),提出了一种考虑环境干扰的大型贮液箱结构安全评估模型。基于行业标准和专家知识,借助有限元方法进行评估模型初始参数的估计;基于信息一致性方法计算指标可信度,以反映实际工程中扰动因素对监测数据的影响;提出一种新的融合方法,将指标可信度合理融合到模型推理过程中,完成评估模型的构建;选用105 m3石油储罐作为研究对象,对所提模型的有效性进行验证。研究结果表明:所提模型不仅能有效处理监测数据不可靠问题,也能够将大型贮液箱复杂系统内部结构机理考虑在内,有效克服先验信息不足给评估精度带来的影响。
Abstract:To solve the problems of lack of prior information and incomplete reliability of monitoring data in structural safety assessment of large liquid tanks (LLT), a structural safety assessment model of large liquid tanks considering environmental disturbance is proposed based on the belief rule base (BRB) and finite element method (FEM). First, the FEM estimates the basic parameters of the proposed model using industry standards and subject-matter knowledge. Secondly, the index credibility is calculated based on the information consistency method to reflect the influence of disturbance factors on the monitoring data in actual engineering. Then, a new fusion method can be used to integrate the index credibility into the model reasoning process to complete the construction of the proposed model. Finally, a 100,000 m3 oil storage tank is selected as the research object to verify the effectiveness of the proposed model. The results show that the proposed model can not only effectively deal with the problem of unreliable monitoring data, but also take into account the internal structure mechanism of large liquid tanks, thereby minimizing the negative effects of a lack of prior knowledge on the accuracy of the assessment.
-
表 1 结构变形程度的参考值
Table 1. Referential values of structural deformation states
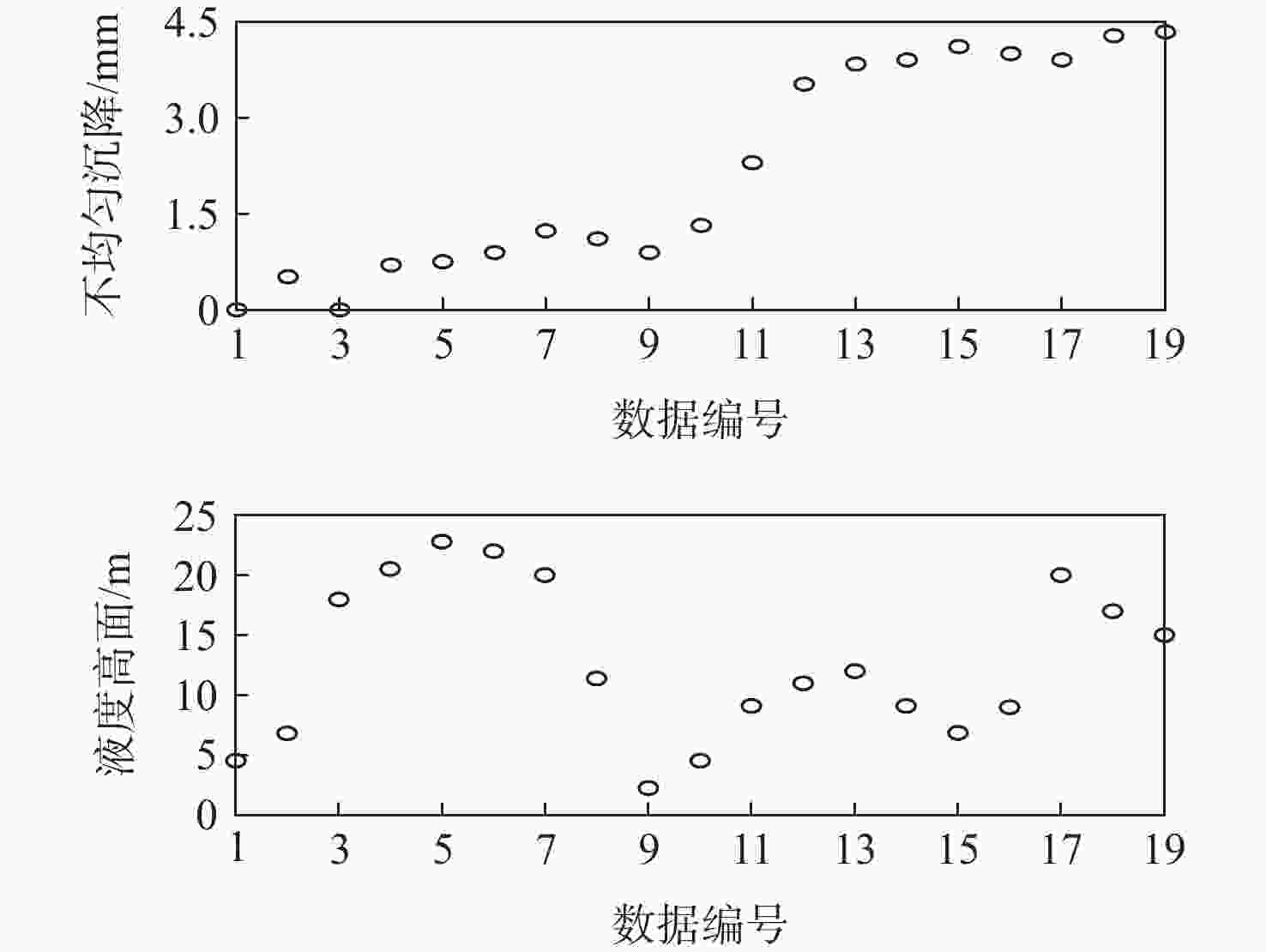
参考等级 VS M H VH 效用值 0 0.3 0.7 1 表 2 不均匀沉降载荷的参考值
Table 2. Referential values of uneven settlement
参考等级 NL NM NS Z S M L 参考值/mm −41.89 −20.95 −10 0 10 20.95 41.89 表 3 液面高度载荷的参考值
Table 3. Referential values of liquid level load
参考等级 空罐 半罐 满罐 参考值/m 0 11.4 22.8 表 4 初始置信规则库
Table 4. Initial belief rule base
编号 规则
权重指标 结构变形尺寸
置信分布编号 规则
权重指标 结构变形尺寸
置信分布$ x_{1} $ $x_{2}$ $ x_{1} $ $ x_{k} $ 1 1 NL 空罐 0,0,0.000 7,0.999 3 12 1 Z 满罐 0,0.721 3,0.278 7,0 2 1 NL 半罐 0,0,0,1 13 1 S 空罐 0.331 3,0.668 7,0,0 3 1 NL 满罐 0,0,0.015, 0.985 0 14 1 S 半罐 0.336 7,0.663 3,0,0 4 1 NM 空罐 0,0.502 5,0.497 5,0 15 1 S 满罐 0,0.511 5,0.488 5,0 5 1 NM 半罐 0,0.502 0,0.498 0,0 16 1 M 空罐 0,0.693 3,0.306 7,0 6 1 NM 满罐 0,0.388 0,0.612 0,0 17 1 M 半罐 0,0.697 5,0.302 5,0 7 1 NS 空罐 0.209 0,0.791 0,0,0 18 1 M 满罐 0,0.167 3,0.832 7,0 8 1 NS 半罐 0.208 3,0.791 7,0,0 19 1 L 空罐 0,0,0.508 0,0.492 0 9 1 NS 满罐 0,0.618 0,0.382 0,0 20 1 L 半罐 0,0,0.513 7,0.486 3 10 1 Z 空罐 1,0,0,0 21 1 L 满罐 0,0,0.256 3,0.743 7 11 1 Z 半罐 0.623 7,0.376 3,0,0 表 5 BP和模糊推理算法的参数设置细节
Table 5. Parameter setting details of BP and fuzzy inference method
方法 模型参数 参数设置 BP 训练次数 100 训练目标最小误差 1×10−3 学习速率 0.01 隐含层神经元节点个数 9 模糊推理 模糊矩阵 $ {\mathbf{\beta }} $ 规则的隶属度 $ {\alpha _k} = \alpha _1^k \wedge \alpha _2^k $ 注:“$ \wedge $”表示取小运算 表 6 不同模型交叉验证后产生的评估精度
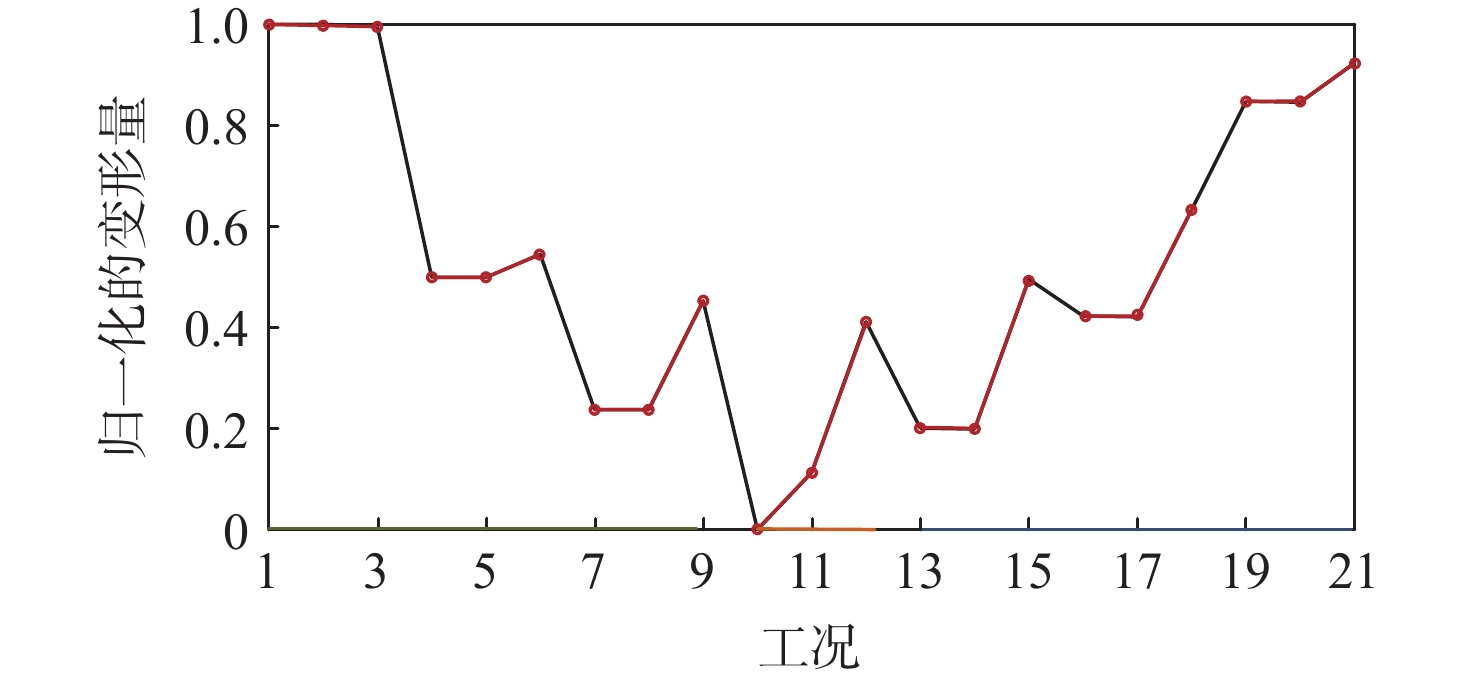
Table 6. Different models evaluation accuracy resulting from cross-validation
方法 MSE 最大值 最小值 平均值 FEM-BRB-c 2.54×10−3 6.79×10−4 6.45×10−4 FEM-BRB 6.89×10−3 3.68×10−4 1.31×10−3 BP 1.38×10−2 1.97×10−6 3.09×10−3 模糊推理 8.52×10−2 6.03×10−2 3.97×10−2 -
[1] YANG L C, CHEN Z P, CAO G W, et al. An analytical formula for elastic-plastic instability of large oil storage tanks[J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 2013, 101: 72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpvp.2012.10.006 [2] LIU W Y, CHEN C H, CHEN W T, et al. A study of caprolactam storage tank accident through root cause analysis with a computational approach[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2017, 50: 80-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jlp.2017.09.004 [3] PASMAN H J, ROGERS W J. Risk assessment by means of Bayesian networks: A comparative study of compressed and liquefied H2 transportation and tank station risks[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(22): 17415-17425. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.04.051 [4] HYUN K C, MIN S, CHOI H, et al. Risk analysis using fault-tree analysis (FTA) and analytic hierarchy process (AHP) applicable to shield TBM tunnels[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2015, 49: 121-129. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2015.04.007 [5] YANG Y F, CHEN G H, RENIERS G. Vulnerability assessment of atmospheric storage tanks to floods based on logistic regression[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2020, 196: 106721. [6] 杨继星, 佘笑梅, 黄玉钏, 等. 基于BP神经网络的苯储罐泄漏事故风险评价模型研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2019, 15(1): 157-162.YANG J X, SHE X M, HUANG Y C, et al. Research on risk assessment model for leakage accident of benzene tank based on BP neural network[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2019, 15(1): 157-162(in Chinese). [7] ŽARKOVIĆ M, STOJKOVIĆ Z. Analysis of artificial intelligence expert systems for power transformer condition monitoring and diagnostics[J]. Electric Power Systems Research, 2017, 149: 125-136. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgr.2017.04.025 [8] VEMA V, SUDHEER K P, CHAUBEY I. Fuzzy inference system for site suitability evaluation of water harvesting structures in rainfed regions[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2019, 218: 82-93. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2019.03.028 [9] YANG J B, LIU J, WANG J, et al. Belief rule-base inference methodology using the evidential reasoning approach-RIMER[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part A: Systems and Humans, 2006, 36(2): 266-285. doi: 10.1109/TSMCA.2005.851270 [10] ZHOU Z J, HU G Y, HU C H, et al. A survey of belief rule-base expert system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics:Systems, 2021, 51(8): 4944-4958. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2019.2944893 [11] 鱼蒙, 黄健, 孔江涛. 输入信息不完整的置信规则库推理方法[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2019, 51(4): 51-59.YU M, HUANG J, KONG J T. Belief rule-base inference methodology with incomplete input[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019, 51(4): 51-59(in Chinese). [12] CHEN Y, ZHOU Z J, YANG L H, et al. A novel structural safety assessment method of large liquid tank based on the belief rule base and finite element method[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part O: Journal of Risk and Reliability, 2022, 236(3): 458-476. doi: 10.1177/1748006X211021690 [13] WANG X J, LI X L, ZHAO Y L, et al. Credibility analysis of air quality data based on improved measurement method[C]//2019 Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 4421-4425. [14] 周志杰, 刘涛源, 胡冠宇, 等. 一种基于数据可靠性和区间证据推理的故障检测方法[J]. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(12): 2628-2637.ZHOU Z J, LIU T Y, HU G Y, et al. A fault detection method based on data reliability and interval evidence reasoning[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(12): 2628-2637(in Chinese). [15] 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 锅炉和压力容器用钢板: GB 713-2014[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014.Standardization administration of the P.R.C., General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Steel plates for boilers and pressure vessels: GB 713-2014[S]. Beijing: the Standards Press of China, 2014. [16] American Petroleum Institute. Tank inspection, repair, alteration, and reconstruction: API 653-2009[S]. Washington, D.C.: American Petroleum Institute. [17] CLOUGH R W. The finite element method in plane stress analysis[C]// Proceedings of 2nd ASCE Conference on Electronic Computation. Pittsburgh: ASCE Press, 1960: 345-78. [18] PAVOL L, MIROSLAV P, JOZEF B. Static structural analysis of water tank[J]. American Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 3(6): 230-234. [19] AKSU G, GÜZELLER C O, ESER M T. The effect of the normalization method used in different sample sizes on the success of artificial neural network model[J]. International Journal of Assessment Tools in Education, 2019, 6(2): 170-192. [20] YANG J B. Rule and utility based evidential reasoning approach for multiattribute decision analysis under uncertainties[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2001, 131(1): 31-61. doi: 10.1016/S0377-2217(99)00441-5 [21] YOU Y Q, SUN J B, JIANG J, et al. A new modeling and inference approach for the belief rule base with attribute reliability[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2020, 50(3): 976-992. doi: 10.1007/s10489-019-01586-2 [22] ZHOU Z J, HU G Y, ZHANG B C, et al. A model for hidden behavior prediction of complex systems based on belief rule base and power set[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2018, 48(9): 1649-1655. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2017.2665880 -






 下载:
下载: