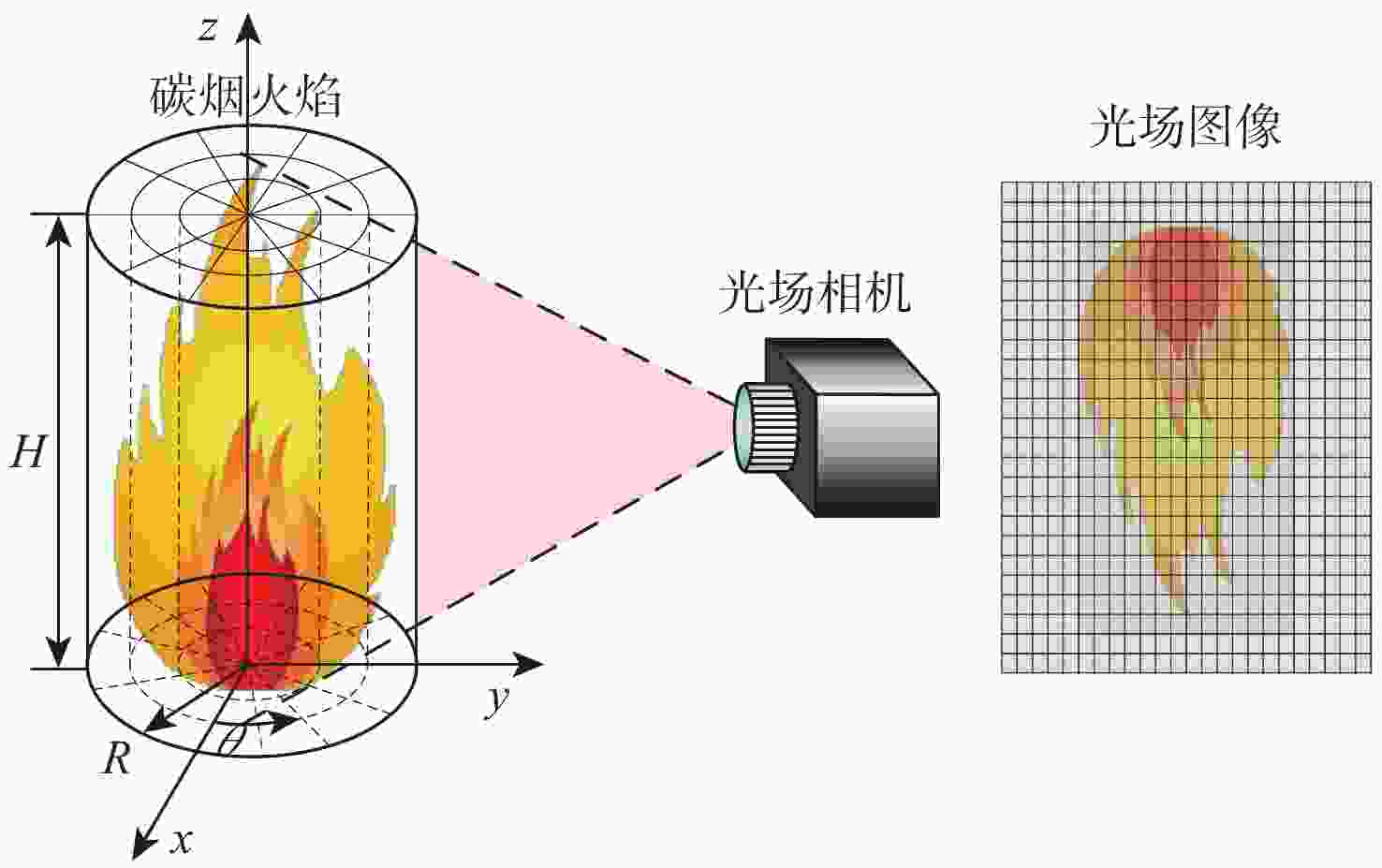
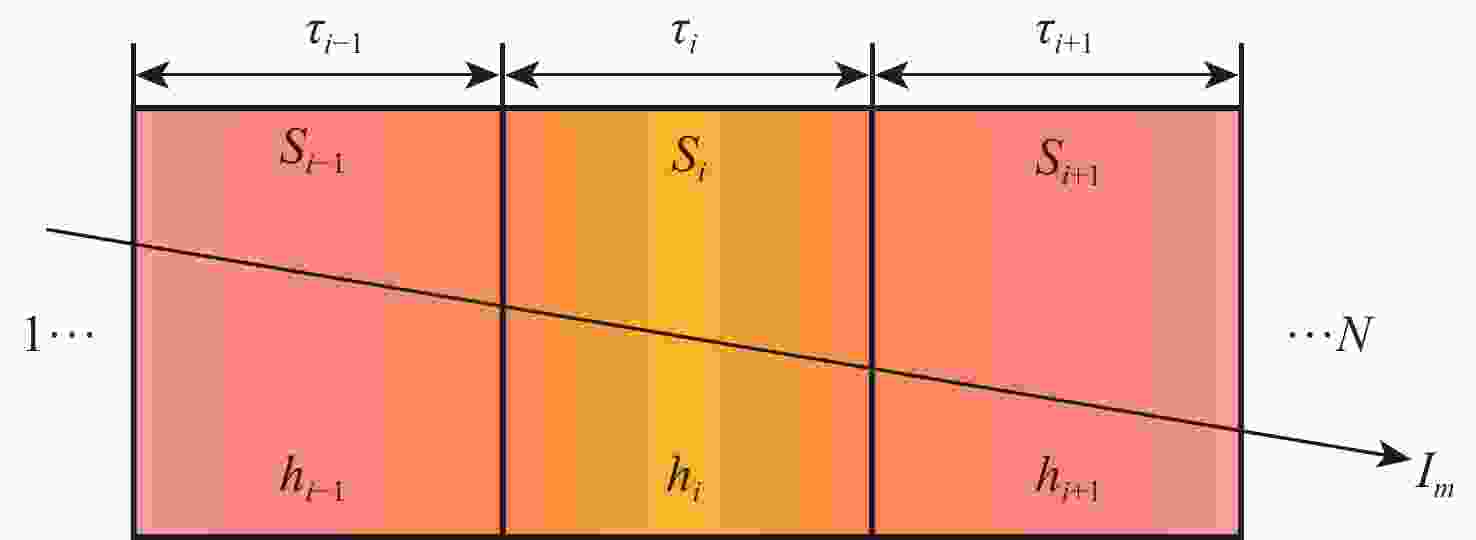
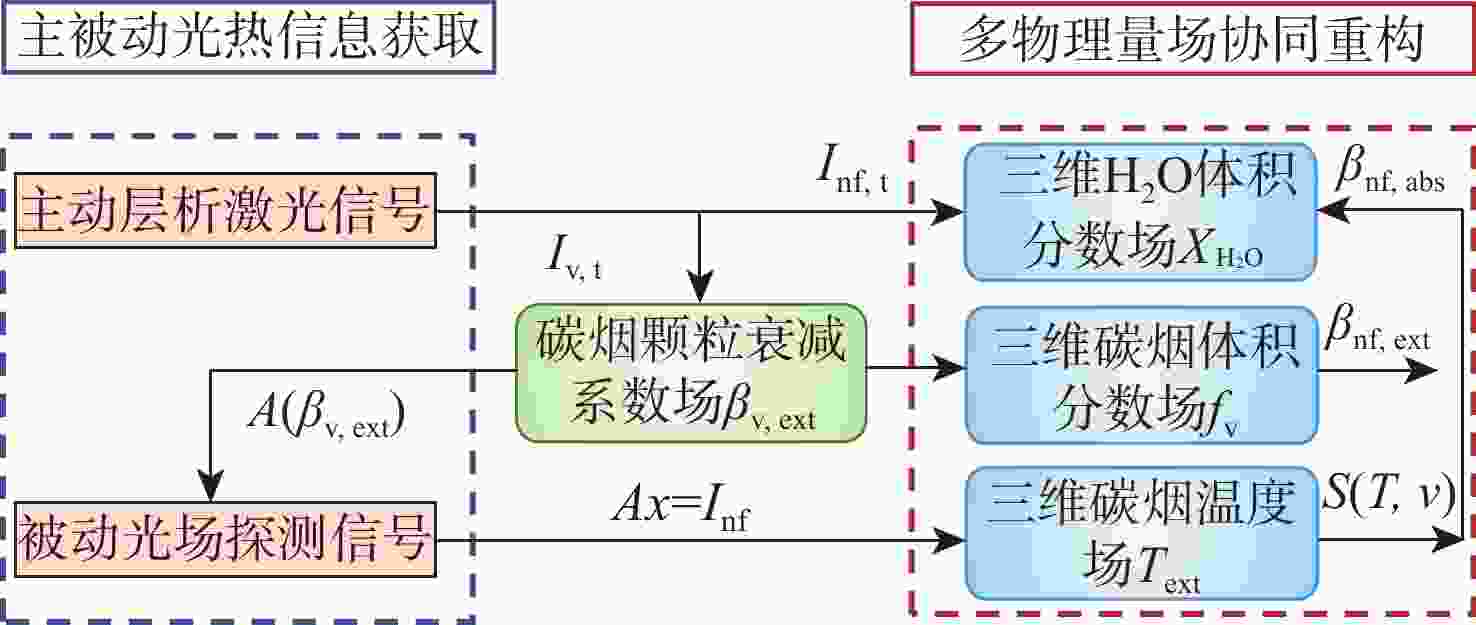
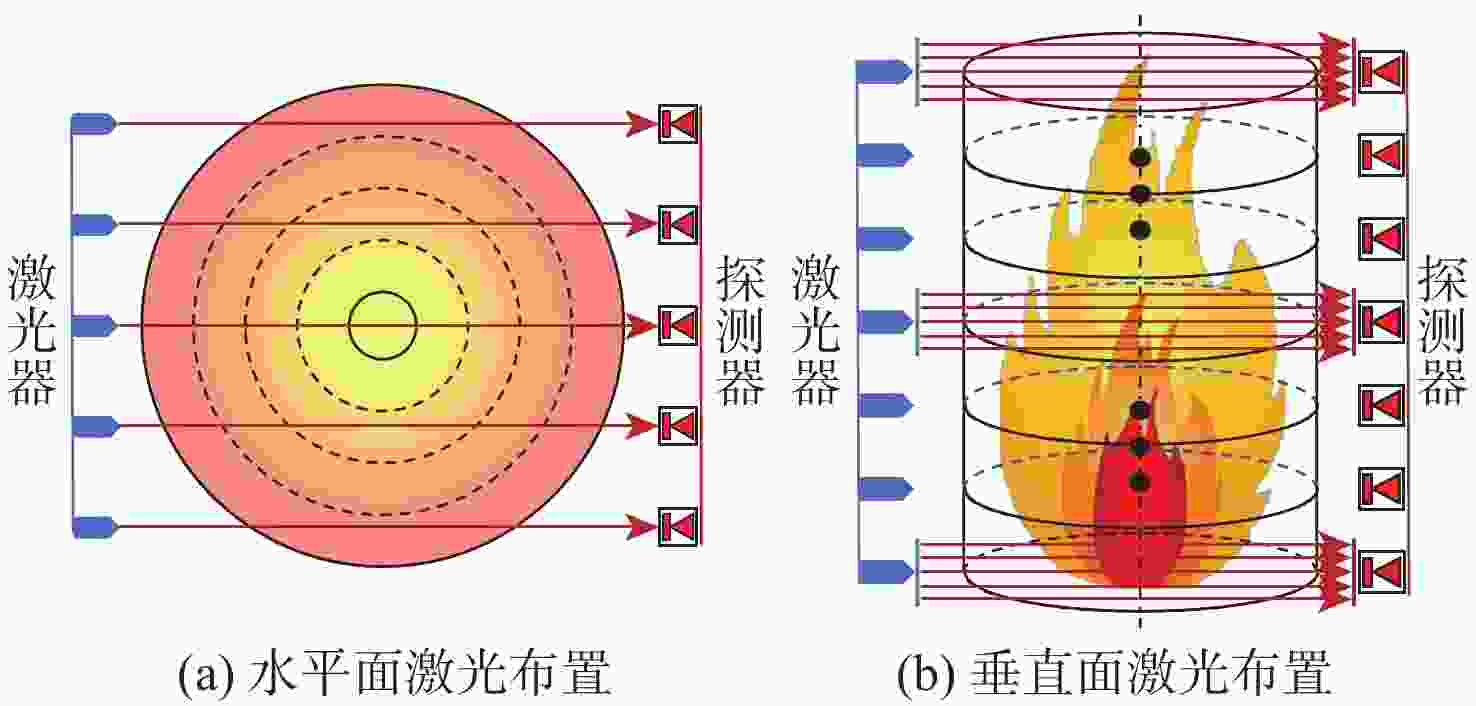
Multi-parameter reconstruction of soot flame based on active and passive tomography
-
摘要:
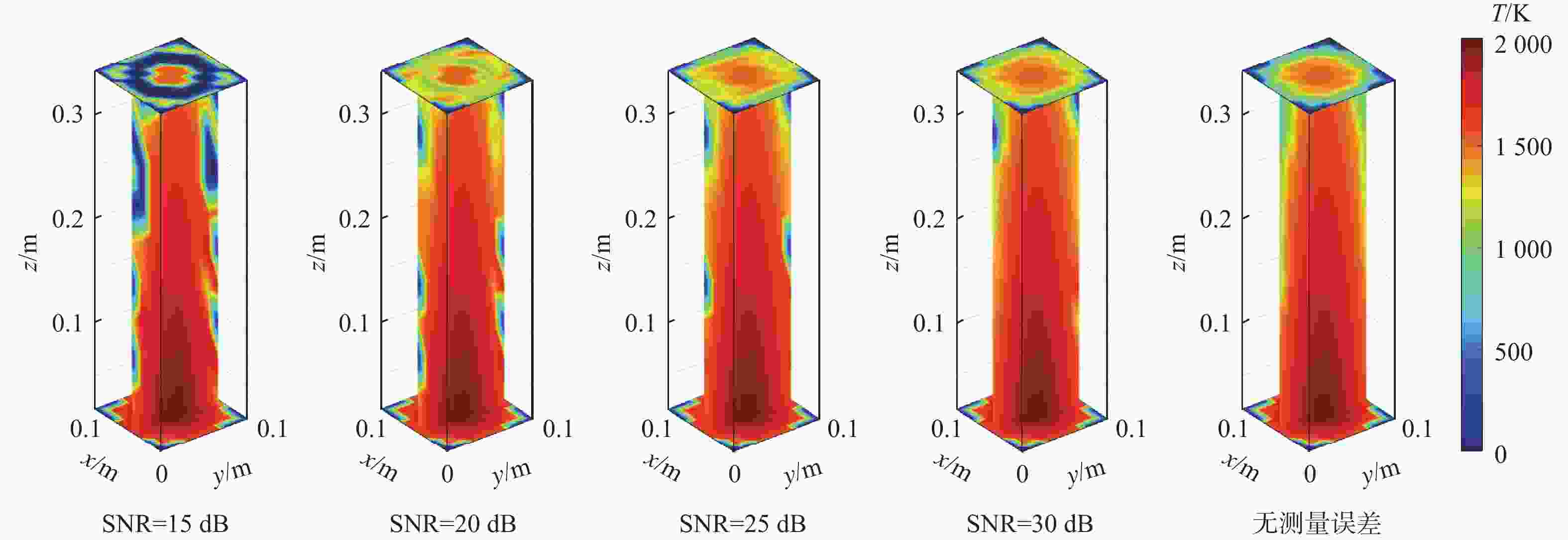
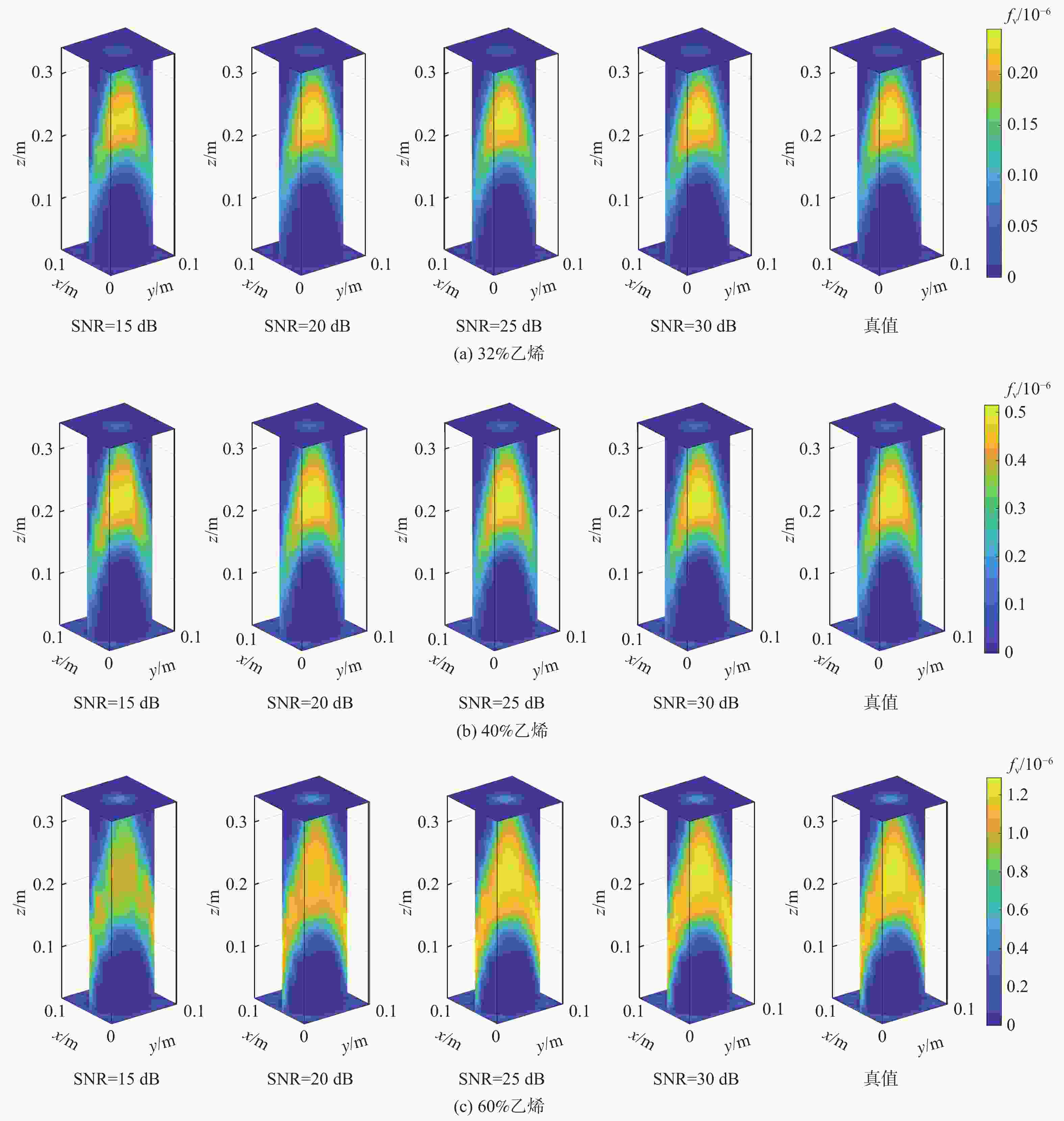
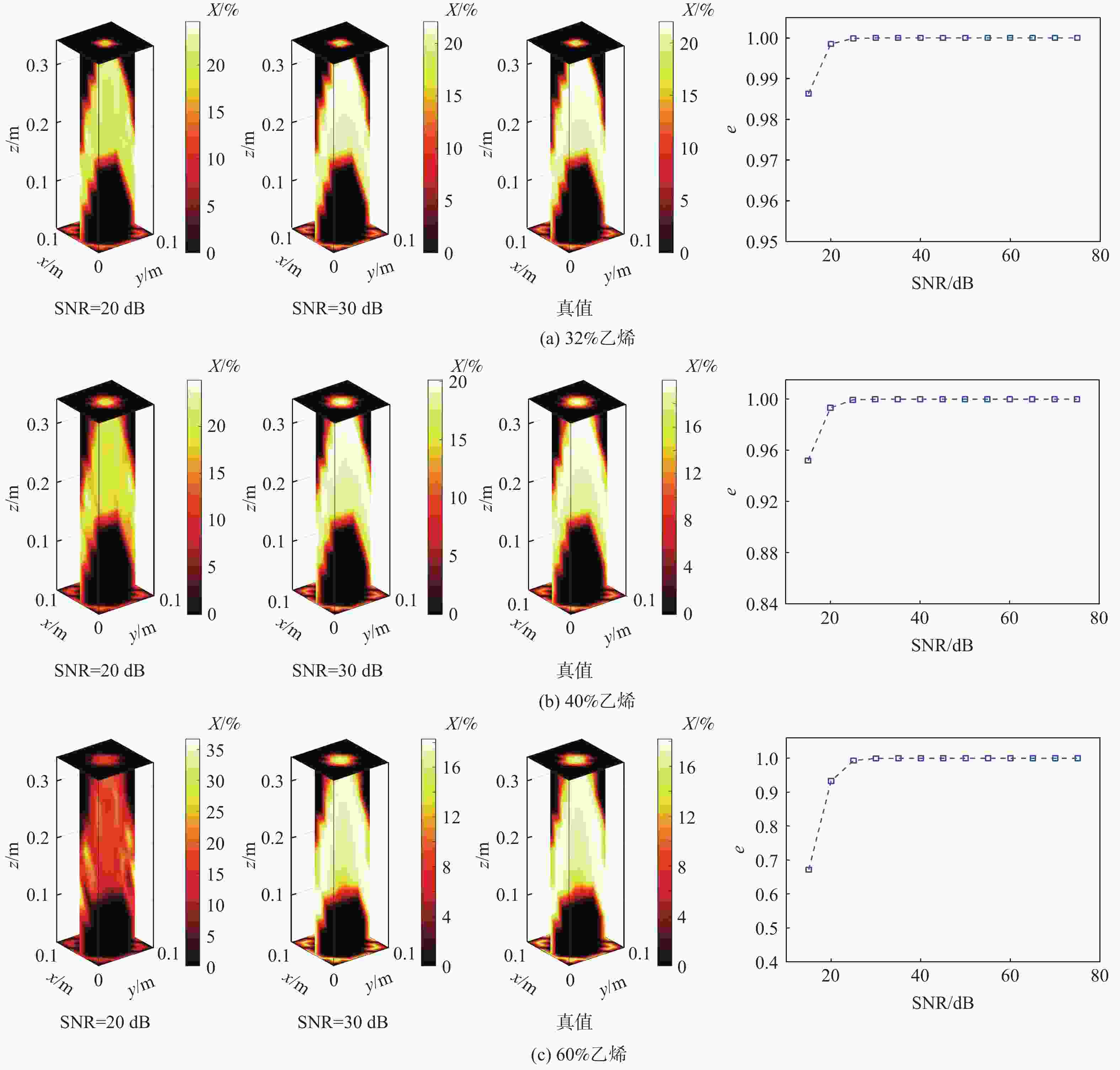
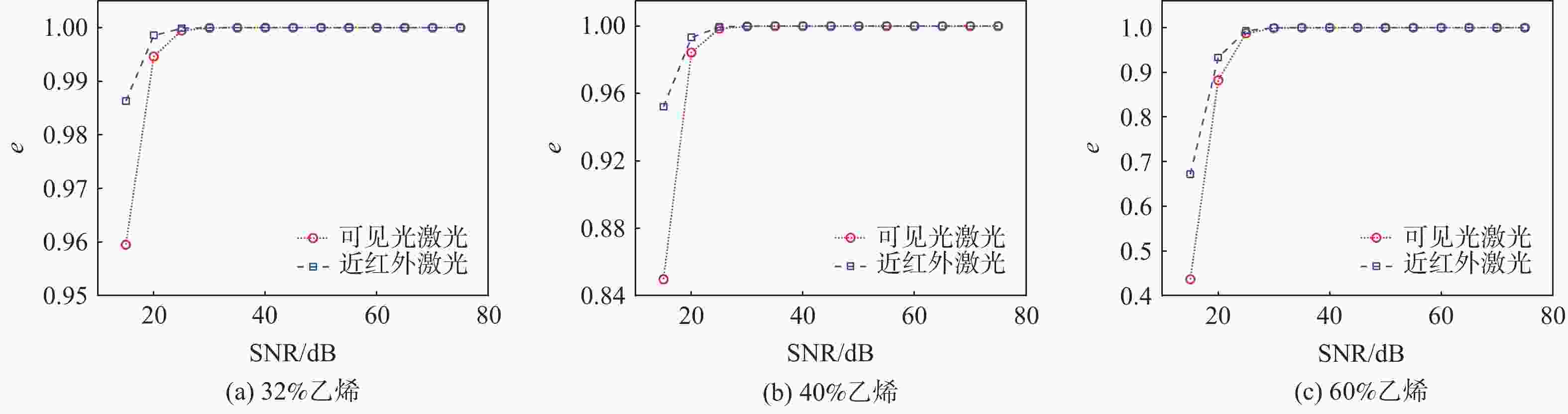
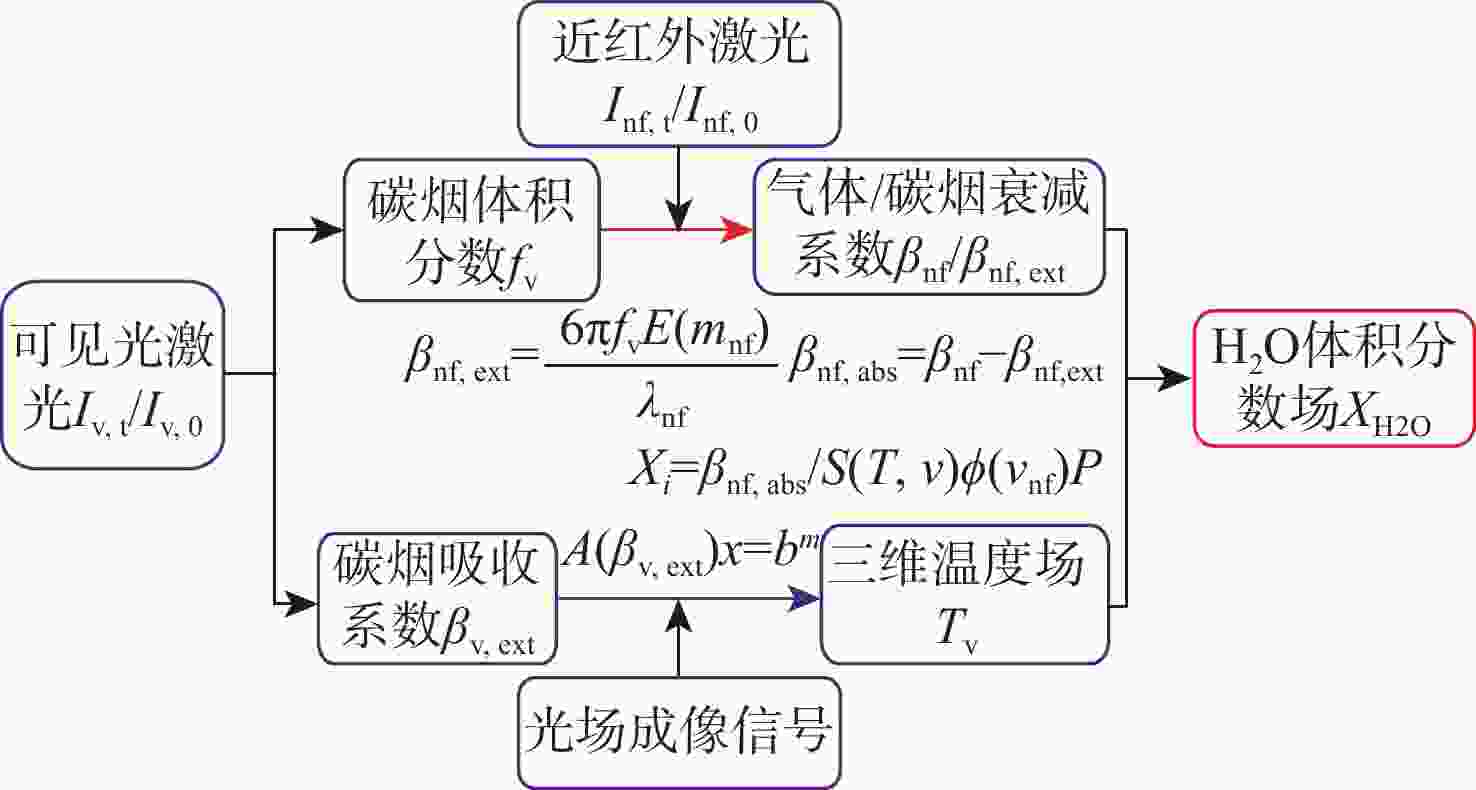
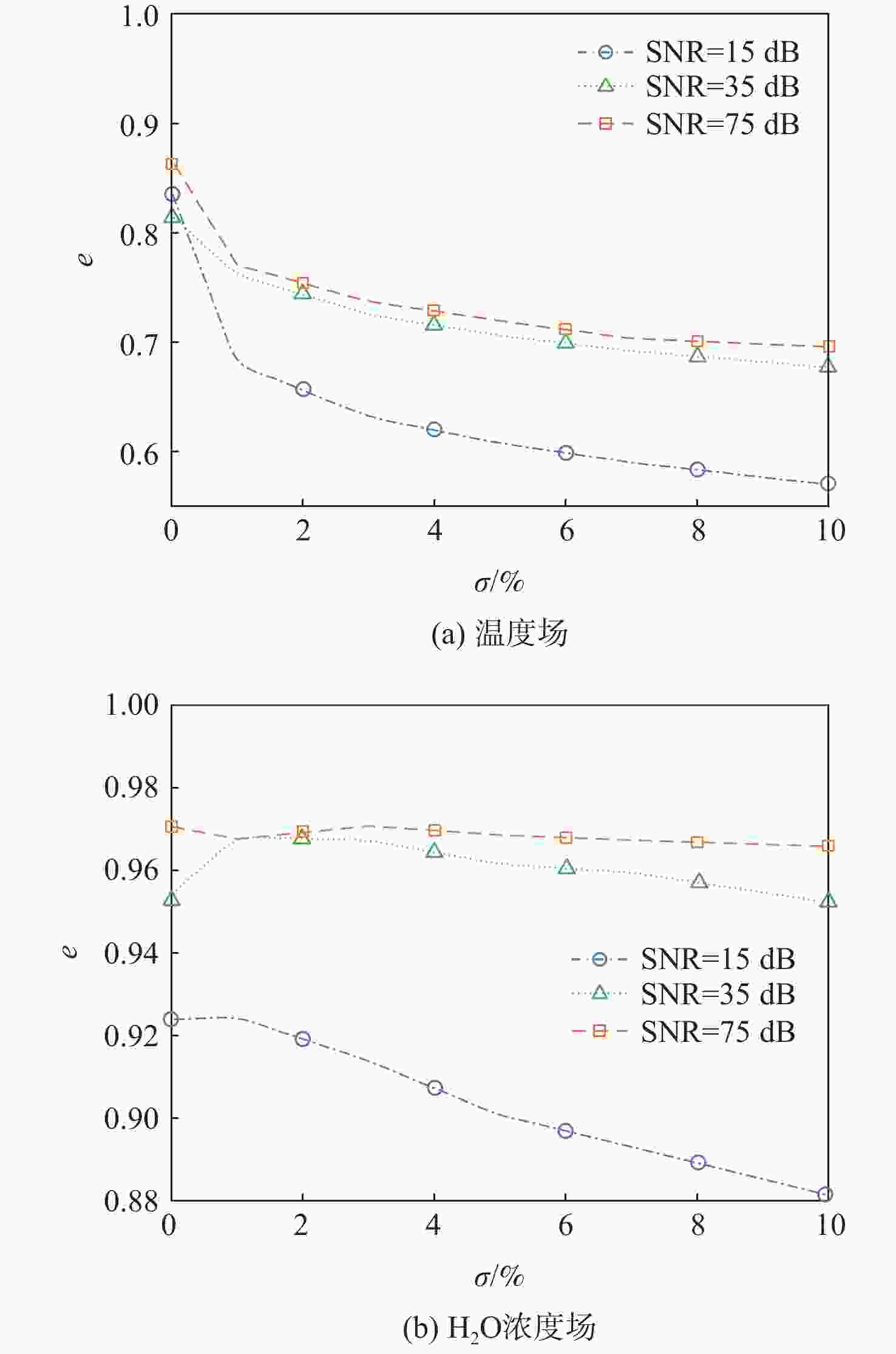
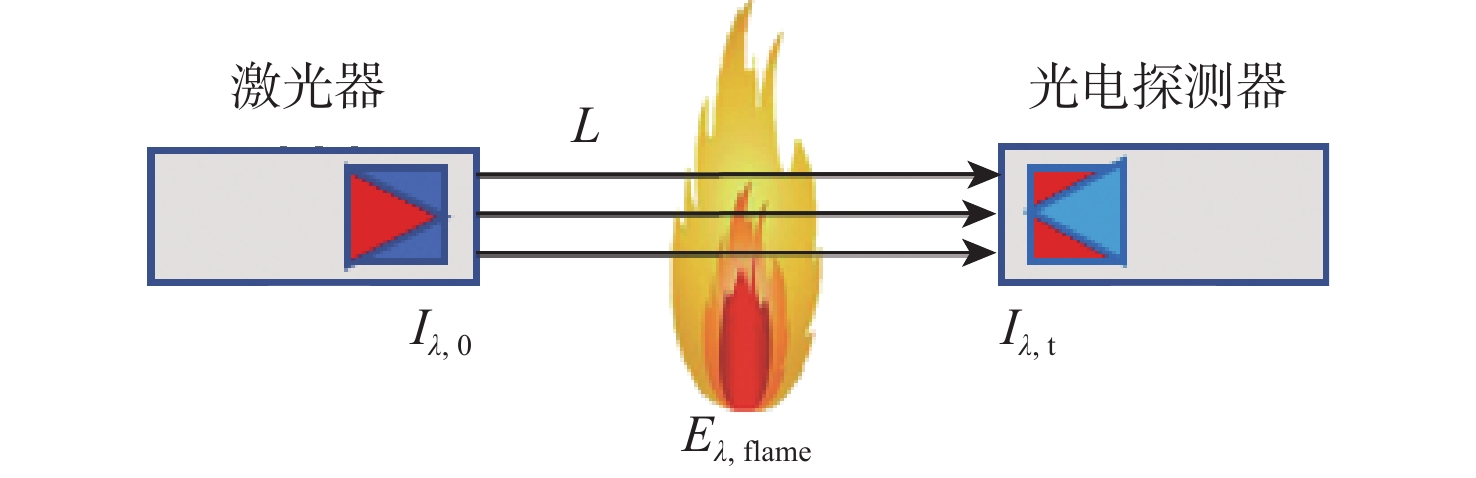
为克服实际工程应用中火焰辐射特性未知导致对火焰温度和辐射特性协同重建的低效率和低精度难题,结合主动激光层析吸收光谱和被动辐射成像技术,提出一种基于主被动层析融合的高温碳烟火焰多物理场协同重建的新方法。结合多谱段下激光层析透射测量信号和火焰自发辐射光场测量信号,根据火焰弥散介质辐射传输机理建立主被动层析的多场协同重建模型,对数值模拟高温碳烟火焰和耶鲁大学实验燃烧火焰的三维辐射物性场、温度场及气固两相燃烧产物组分浓度场的协同重建进行模拟研究,并对多种测量信号的随机误差进行误差传递分析。结果表明:当激光信噪比大于25 dB时,模拟火焰衰减系数场重建的相关系数接近1,重建的温度场与真值吻合较好;当激光信噪比大于30 dB时,实验火焰碳烟颗粒浓度场重建的相关系数接近1,温度场重建相关系数约为0.83;光场信号测量噪声对温度重建精度的影响比激光测量噪声显著,应尽可能保证激光与光场测量系统的标定精度。
Abstract:A new combustion diagnosis and measurement technology should be developed in order to realize the collaborative reconstruction of multiple physical parameter fields, such as the three-dimensional temperature field, the radiation physical property field, and the component concentration field of the gas-solid combustion products of the high-temperature soot flame. In order to overcome the problem of low efficiency and low accuracy in the coordinated reconstruction of flame temperature and radiation property caused by unknown radiation characteristics in practical engineering applications, a new method of collaborative reconstruction of multi-physical parameter fields of high temperature soot flame based on active and passive tomography fusion is proposed by combining active laser tomography absorption spectroscopy and passive radiation imaging technology. Based on the radiation transmission mechanism of the flame dispersion medium, a multi-parameter collaborative reconstruction model of active and passive tomography is established by combining the transmission measurement signal of laser tomography and spontaneous emission light field measurement signal of flame in the multi-spectral range. According to the numerical simulation flame and the combustion experiment data of Yale University, the cooperative reconstruction of three dimensional radiation physical property, temperature and the gas-solid two-phase combustion product component concentration field of the high-temperature soot flame was simulated and studied, and the error transfer analysis is carried out on the measurement noise of various signals. The results show that when the laser signal-to-noise ratio is greater than 25, the correlation coefficient of the reconstructed extinction coefficient field of the simulated flame is close to 1, and the reconstruction results of temperature field is in good agreement with the true value; When the laser signal-to-noise ratio is greater than 30, the correlation coefficient of reconstructed soot concentration field of the experimental flame is close to 1, and the correlation coefficient of the reconstructed temperature field is about 0.83; The influence of light-field signal measurement noise on temperature reconstruction accuracy is more significant than that of laser measurement noise, and the calibration accuracy of laser and light-field measurement system should be ensured in the measurement process to improve the accuracy of parameter reconstruction.
-
表 1 不同激光噪声下衰减系数场重建质量
Table 1. Reconstruction quality of extinction coefficient under different laser noise
SNR / dB e 15 0.9726 20 0.9971 25 0.9998 30 1 35 1 表 2 不同激光噪声下火焰碳烟颗粒体积分数场重建质量
Table 2. Reconstruction quality of soot flame particle concentration under different laser noise
工况 SNR / dB e 工况 SNR / dB e 工况1 15 0.9893 工况2 30 1 工况1 20 0.9988 工况2 35 1 工况1 25 0.9999 工况2 40 1 工况1 30 1 工况3 15 0.9834 工况1 35 1 工况3 20 0.9983 工况1 40 1 工况3 25 0.9998 工况2 15 0.9901 工况3 30 1 工况2 20 0.9987 工况3 35 1 工况2 25 0.9999 工况3 40 1 表 3 不同激光噪声下火焰温度场重建质量
Table 3. Reconstruction quality of flame temperature under different laser noise
工况 SNR / dB e 工况 SNR / dB e 工况1 15 0.7929 工况2 30 0.8260 工况1 20 0.8121 工况2 35 0.8412 工况1 25 0.8161 工况2 40 0.8957 工况1 30 0.8289 工况3 15 0.7440 工况1 35 0.8396 工况3 20 0.7704 工况1 40 0.8677 工况3 25 0.8004 工况2 15 0.7565 工况3 30 0.8166 工况2 20 0.8058 工况3 35 0.8344 工况2 25 0.8189 工况3 40 0.9078 表 4 可见光激光信号噪声的误差传递
Table 4. Error propagation of visible laser signal noise
参数场 SNR/dB e 碳烟浓度 15 0.9893 碳烟浓度 20 0.9988 碳烟浓度 25 0.9999 碳烟浓度 30 1 碳烟浓度 35 1 温度 15 0.7929 温度 20 0.8121 温度 25 0.8161 温度 30 0.8289 温度 35 0.8396 H2O浓度 15 0.924 H2O浓度 20 0.9407 H2O浓度 25 0.9443 H2O浓度 30 0.9484 H2O浓度 35 0.954 -
[1] EL-MAHALLAWY F, HABIK S E D. Fundamentals and technology of combustion[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2002: 1-75. [2] JAROSINSKI J, VEYSSIERE B. Combustion phenomena: Selected mechanisms of flame formation, propagation and extinctions[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2009: 1-12. [3] NI M J, ZHANG H D, WANG F, et al. Study on the detection of three-dimensional soot temperature and volume fraction fields of a laminar flame by multispectral imaging system[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016, 96: 421-431. [4] 周怀春. 炉内火焰可视化检测原理与技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005: 1-7.ZHOU H C. The principle and technology of visual inspection of flames in furnaces[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005: 1-7(in Chinese). [5] WEI Z, YAN L, LI Z, et al. 3-D reconstruction algorithm of flame based on inversion calculation of thermal radiation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2016, 65(12): 2808-2815. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2016.2611382 [6] TEICHERT H, FERNHOLZ T, EBERT V. Simultaneous in situ measurement of CO, H2O, and gas temperatures in a full-sized coal-fired power plant by near-infrared diode lasers[J]. Applied Optics, 2003, 42(12): 2043-2051. doi: 10.1364/AO.42.002043 [7] 黄兴. 基于主被动光学探测的发光火焰多物理量场重建[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019.HUANG X. Reconstruction of the multi-physical fields in luminous flame based on active and passive optical detection[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019(in Chinese). [8] 李可. 基于吸收光谱技术的燃烧场温度与浓度层析成像方法研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2016.LI K. Study on tomography of temperature and concentration in combustion based on absorption spectrum technology[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2016(in Chinese). [9] 周怀春, 炉内火焰可视化检测原理与技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005: 1-12.ZHOU H C. Principle and technology of flame visualization detection in furnace[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005: 1-12(in Chinese). [10] CHILDS P, GREENWOOD J R, LONG C A. Review of temperature measurement[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2000, 71(8): 2959-2978. doi: 10.1063/1.1305516 [11] EHN A, ZHU J, LI X, et al. Advanced laser-based techniques for gas-phase diagnostics in combustion and aerospace engineering[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2017, 71(3): 341-366. doi: 10.1177/0003702817690161 [12] LI T, LI S, YUAN Y, et al. Light field imaging analysis of flame radiative properties based on Monte Carlo method[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 119: 303-311. [13] NIU C Y, QI H, HUANG X, et al. Efficient and robust method for simultaneous reconstruction of the temperature distribution and radiative properties in absorbing, emitting, and scattering media[J]. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 2016, 184: 44-57. [14] LI J, LIU G, YING Y, et al. On the treatment of lens optical center uncertainty in simultaneous reconstruction of flame temperature and soot volume fraction distributions by a CCD camera[J]. Optik, 2021, 241: 167238. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.167238 [15] KOHSE-HÖINGHAUS K, BARLOW R S, ALDÉN M, et al. Combustion at the focus: Laser diagnostics and control[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2005, 30(1): 89-123. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2004.08.274 [16] CHENG Q, ZHANG X Y, WANG Z C, et al. Simultaneous measurement of three-dimensional temperature distributions and radiative properties based on radiation image processing technology in a gas-fired pilot tubular furnace[J]. Heat Transfer Engineering, 2013, 35(6-8): 770-779. [17] HANSON R K, FALCONE P K. Temperature measurement technique for high-temperature gases using a tunable diode laser[J]. Applied Optics, 1978, 17(16): 2477-2480. [18] DENNIS C N, SLABAUGH C D, BOXX I G, et al. 5 kHz thermometry in a swirl-stabilized gas turbine model combustor using chirped probe pulse femtosecond CARS. Part 1: Temporally resolved swirl-flame thermometry[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2016, 173: 441-453. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2016.02.033 [19] CAI W, LI X, LI F, et al. Numerical and experimental validation of a three-dimensional combustion diagnostic based on tomographic chemiluminescence[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(6): 7050-7064. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.007050 [20] WORTH N A, DAWSON J R. Tomographic reconstruction of OH* chemiluminescence in two interacting turbulent flames[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2013, 24(2): 024013. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/24/2/024013 [21] HOSSAIN M, LU G, YAN Y. Optical fiber imaging based tomographic reconstruction of burner flames[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2012, 61(5): 1417-1425. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2012.2186477 [22] ZHOU H C, LOU C, CHENG Q, et al. Experimental investigations on visualization of three-dimensional temperature distributions in a large-scale pulverized-coal-fired boiler furnace[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2005, 30(1): 1699-1706. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2004.08.090 [23] WANG H J, HUANG Z F, WANG D D, et al. Measurements on flame temperature and its 3D distribution in a 660 MWe arch-fired coal combustion furnace by visible image processing and verification by using an infrared pyrometer[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2009, 20(11): 114006. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/20/11/114006 [24] 张海丹. 基于高光谱成像系统的火焰三维温度场和烟黑浓度场重建研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2016.ZHANG H D. Three dimensional reconstruction of temperature and soot volume fraction distribution in flames based on hyperspectral imaging system[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2016(in Chinese). [25] 谢正超. 基于高光谱成像的火焰三维温度场、烟黑浓度场和气体浓度场重建研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018.XIE Z C. Three dimensional reconstruction of temperature, soot volume fraction distribution and gas volume fraction distribution in flames based on hyperspectral imaging system[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018(in Chinese). [26] 柳华蔚. 基于高光谱成像技术的扩散火焰温度和颗粒物特性研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2017.LIU H W. Research on the temperature and particle characteristic in diffusion flames using hyperspectral imaging technique[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2017(in Chinese). [27] LIU H, ZHOU H, XU C. A decomposition method for the simultaneous reconstruction of temperature and soot volume fraction distributions in axisymmetric flames[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2020, 31(11): 115202. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/ab9dbf [28] CAI W W, WANG X L, YU T. Spatial-frequency encoded imaging of multangular and multispectral images[J]. The Review of Scientific Instruments, 2021, 92(1): 015111. doi: 10.1063/5.0025112 [29] KELLY D L, PHILLIPS M A, THUROW B S, et al. A novel multi-band plenoptic pyrometer used for temperature measurements of strand burner plumes[C]//AIAA Scitech 2020 Forum. Reston: AIAA, 2020: 1-9. [30] JUN S, HOSSAIN M, CHUAN X, et al. A novel calibration method of focused light field camera for 3-D reconstruction of flame temperature[J]. Optics Communications, 2017, 390: 7-15. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2016.12.056 [31] SUN J, HOSSAIN M M, XU C L, et al. Investigation of flame radiation sampling and temperature measurement through light field camera[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 121: 1281-1296. [32] HUANG X, QI H, ZHANG X L, et al. Application of landweber method for three dimensional temperature field reconstruction based on the light-field imaging technique[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 2018, 140(8): 082701-082711. doi: 10.1115/1.4039305 [33] SHI J W, QI H, YU Z Q, et al. Three-dimensional temperature reconstruction of diffusion flame from the light-field convolution imaging by the focused plenoptic camera[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2022, 65(2): 302-323. [34] Harvard University. The HITRAN database[DB/OL]. (2023-03-01)[2023-03-21].https://hitran.org/. [35] LIU H W, ZHENG S, ZHOU H C. Measurement of soot temperature and volume fraction of axisymmetric ethylene laminar flames using hyperspectral tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2017, 66(2): 315-324. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2016.2631798 [36] QI H, SHI J W, SU Y X, et al. Soot temperature measurement within 3D flame by light-field imaging based on wave optics theory[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2020, 138: 106419. [37] SHI J W, QI H, ZHANG J Y, et al. Simultaneous measurement of flame temperature and species concentration distribution from nonlinear tomographic absorption spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 2020, 241: 106693. [38] Yale University. Yale doflow diffusion flames[DB/OL]. (2016-08-16) [2023-03-21]. http://guilford.eng.yale.edu/yalecoflowflames/. -






 下载:
下载: