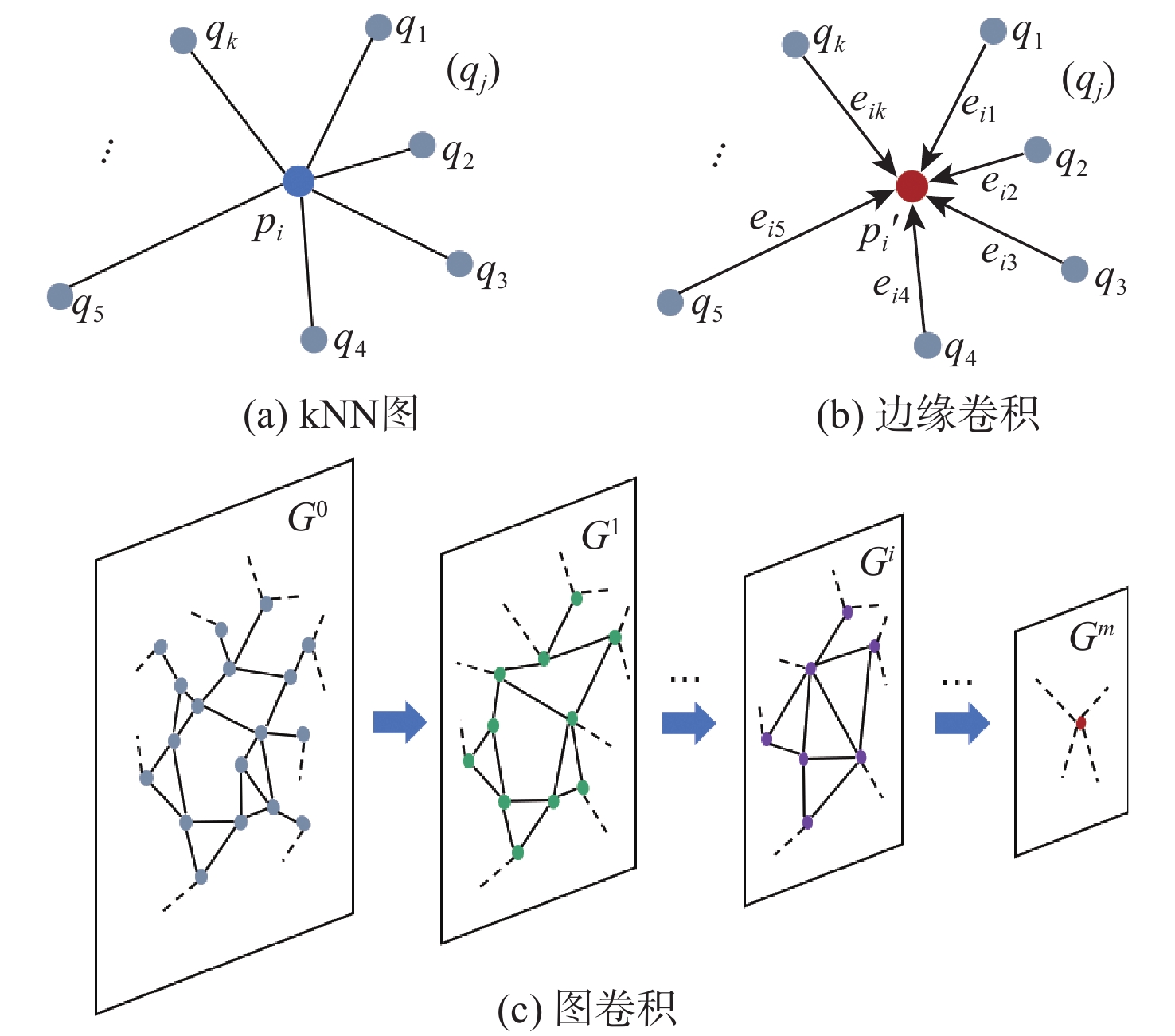
Ground object classification based on height-aware multi-scale graph convolution network
-
摘要:
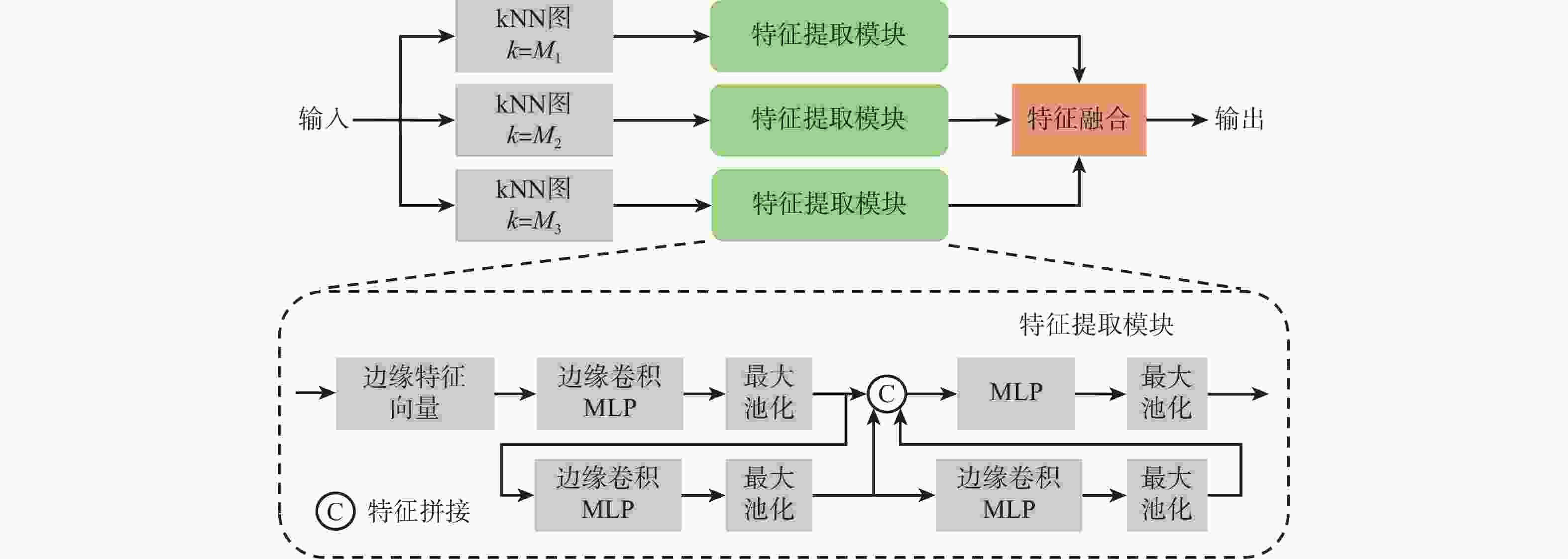
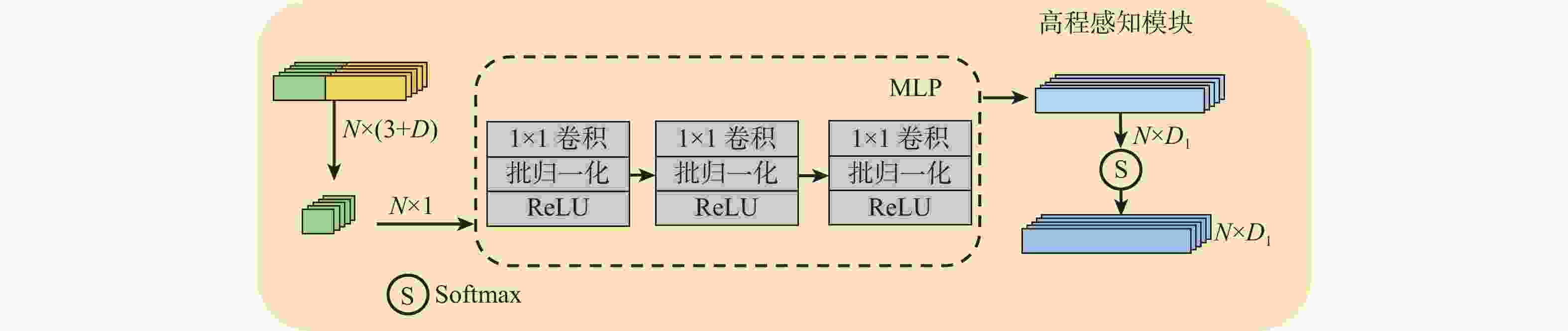
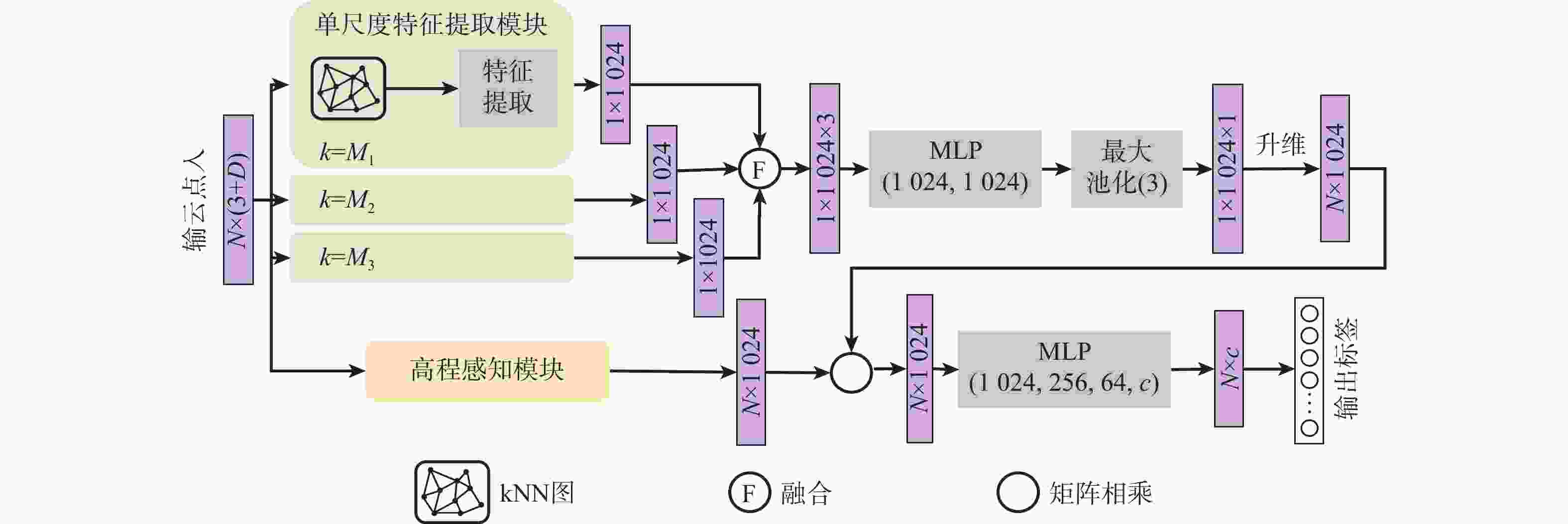
机载激光雷达获取的点云具有类别分布不均匀、样本高程差异大的复杂特点,现有方法难以充分识别其细粒度的局部结构。针对该问题,堆叠使用多层边缘卷积算子同时提取局部信息和全局信息,并引入高程注意力权重作为特征提取的补充,设计了一种用于机载激光雷达点云地物分类的端到端网络,提出基于高程感知多尺度图卷积网络的地物分类方法。对原始点云划分子块并采样到固定点数;采用多尺度边缘卷积算子提取多尺度局部-全局特征并进行融合,同时采用高程感知模块生成注意力权重并应用于特征提取网络;利用改进的焦点损失函数进一步解决类别分布不均问题,完成分类。采用国际摄影测量与遥感学会(ISPRS)提供的标准测试数据集对所提方法进行验证,所提方法的总体分类精度达到0.859,单类别分类精度特别是对建筑物的提取精度较ISPRS竞赛中公开的最好结果提高了4.6%。研究结果对实际应用和网络设计优化具有借鉴意义。
Abstract:The point cloud acquired by airborne LiDAR has the complex characteristics of uneven distribution of categories and large differences in sample elevation. Existing methods are difficult to fully identify fine-grained local structures. This paper proposes an end-to-end network for airborne LiDAR point cloud classification after employing stacked multi-layer edge convolution operators to simultaneously extract local and global information. It also introduces elevation attention weights as a supplement to feature extraction. First, the original point cloud is divided into sub-blocks and sampled to a fixed number of points. Then the multi-scale edge convolution operator is used to extract multi-scale local-global features which are merged thereafter, at the same time, the height-aware module is used to generate attention weights and applied to the feature extraction network. Finally, the improved focus loss function is used to further solve the problem of uneven distribution of categories and complete the classification. The standard test data set provided by the International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing (ISPRS) was used to verify the proposed method. Overall, 85.9% of the classifications were accurate. The single-category classification accuracy, especially the roof, was increased by 4.6% than the best result published in the ISPRS competition. The research results have reference significance for practical applications and network design optimization.
-
Key words:
- image processing /
- graph convolution /
- deep learning /
- height-aware /
- point cloud classification
-
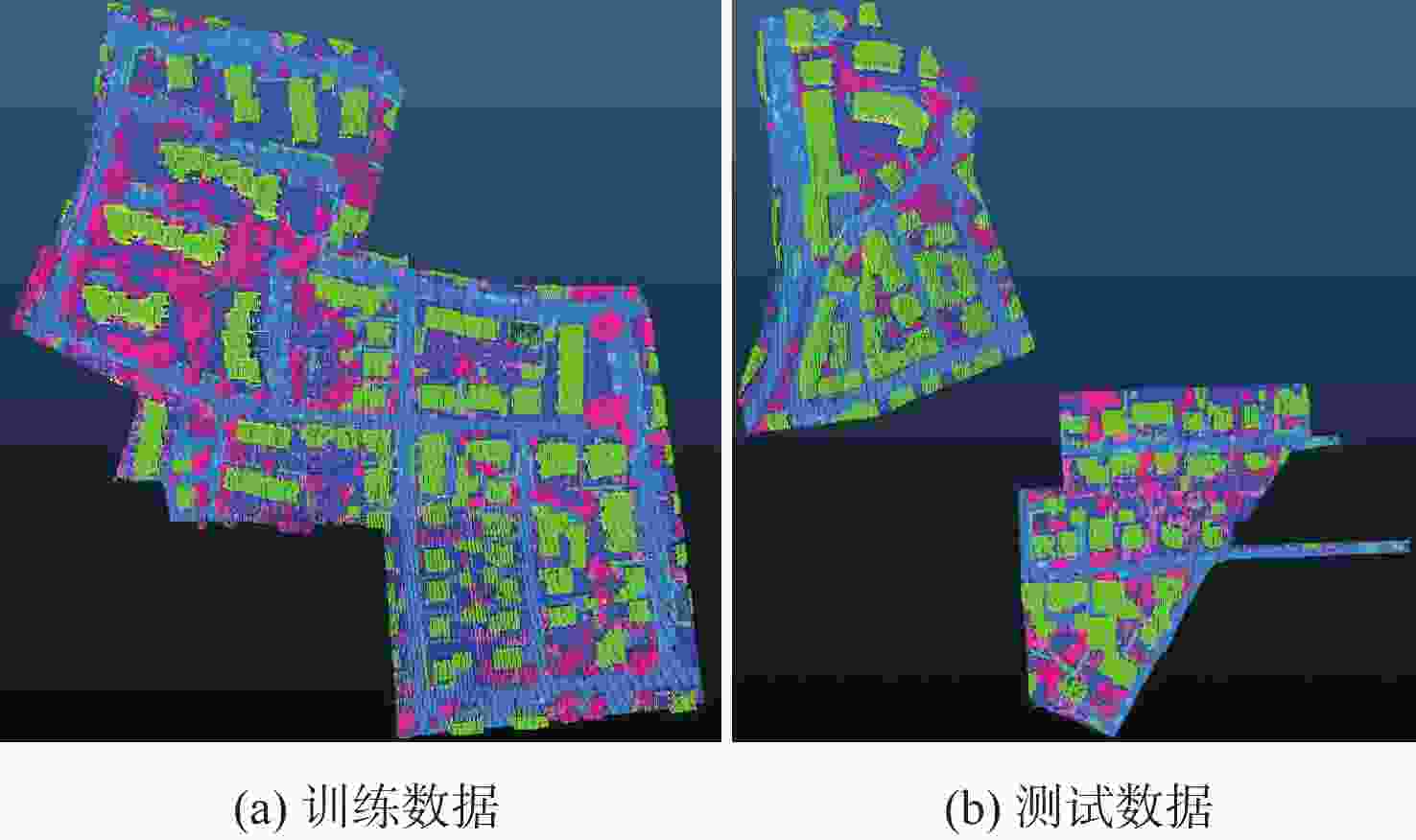
表 1 实验数据集中不同类别的百分比
Table 1. The percent of different categories in the experimental dataset
% 类别 训练集 测试集 电力线 0.07 0.15 低矮植被 23.99 23.97 不透水表面 25.70 14.77 车辆 0.61 0.90 篱笆/栅栏 1.60 1.80 屋顶 20.17 26.48 外墙立面 3.61 2.72 灌木 6.31 6.03 树木 17.94 13.17 表 2 本文方法与其他模型在ISPRS数据集上的结果对比
Table 2. Comparisons between the proposed method and other models on the ISPRS dataset
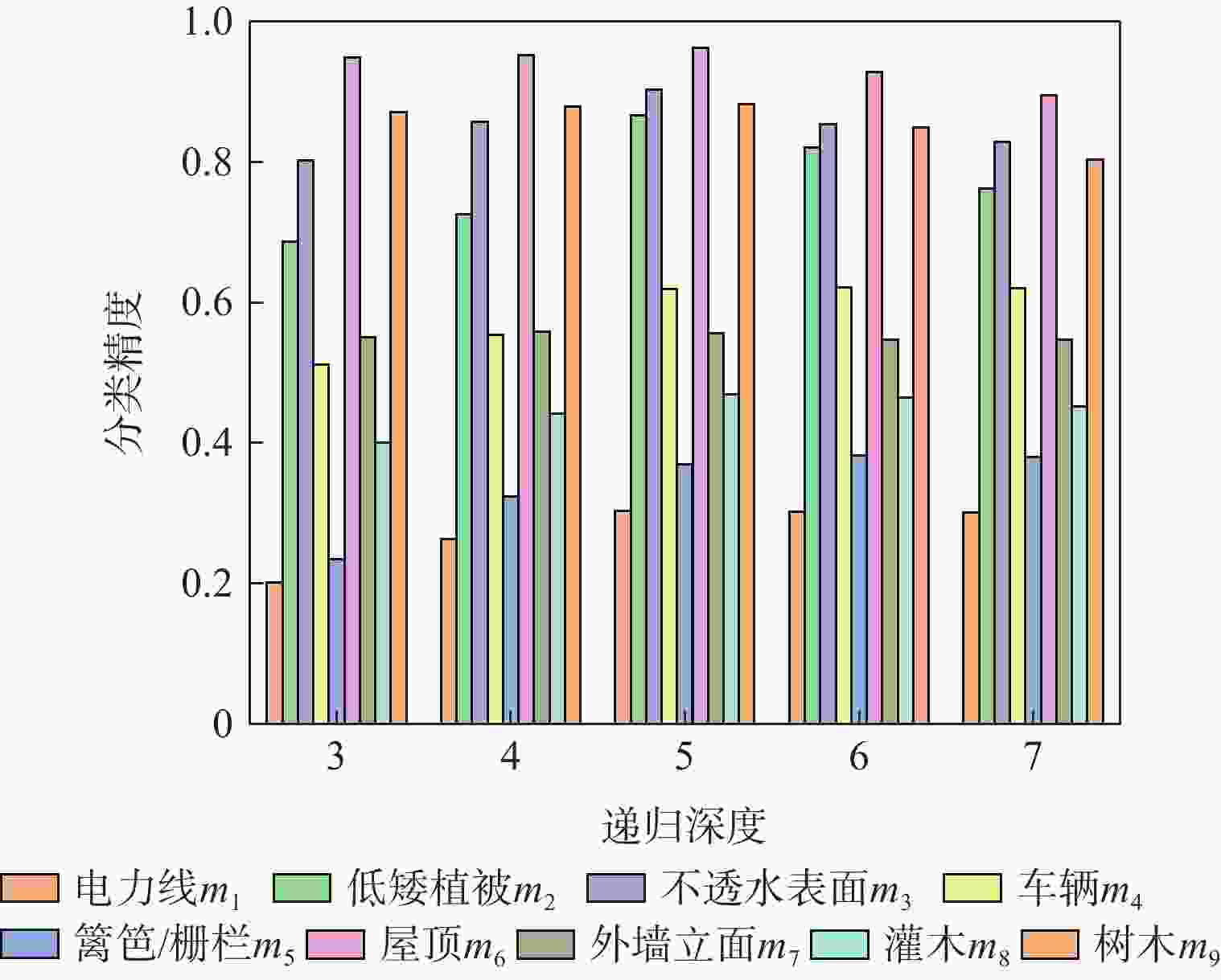
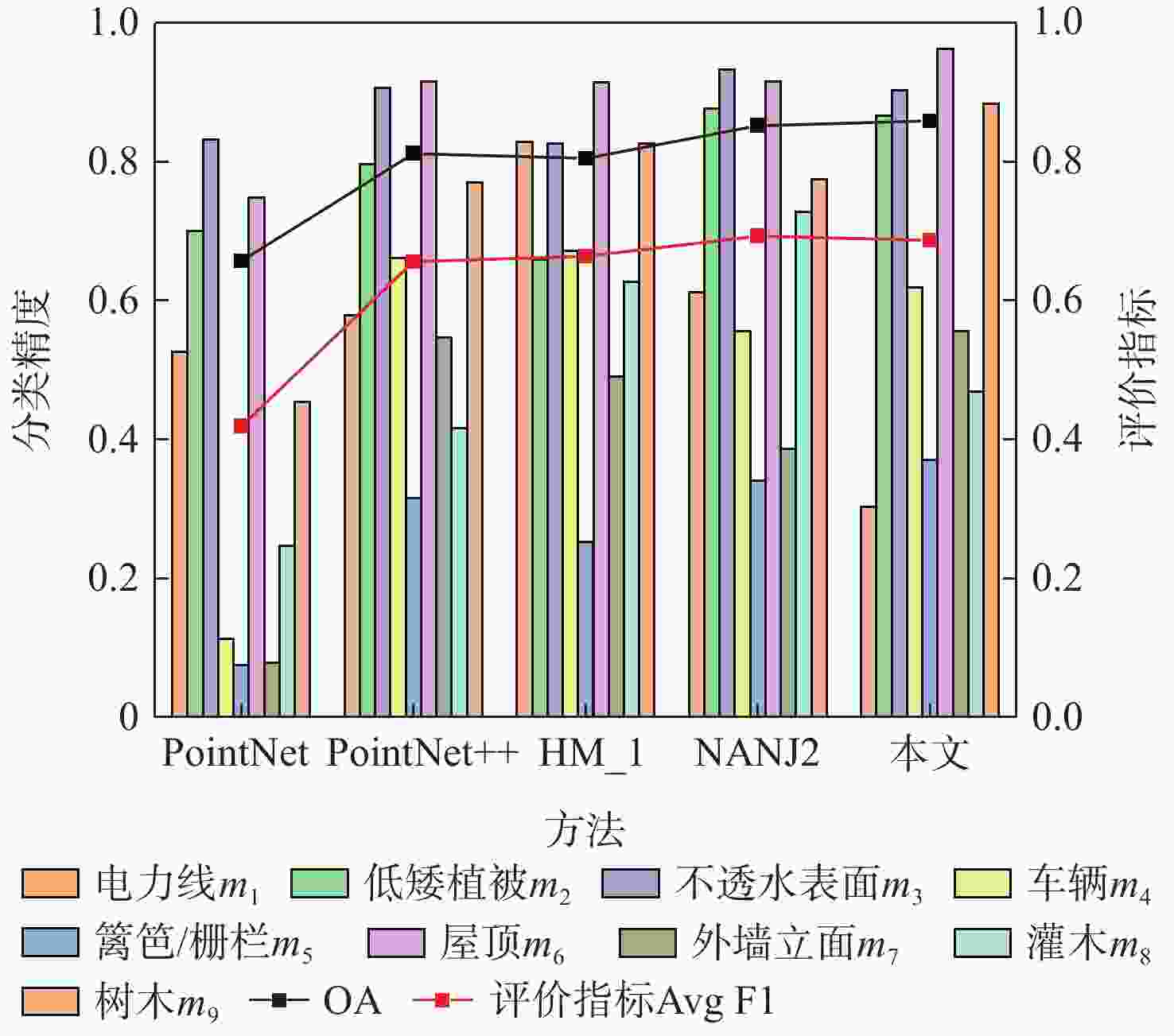
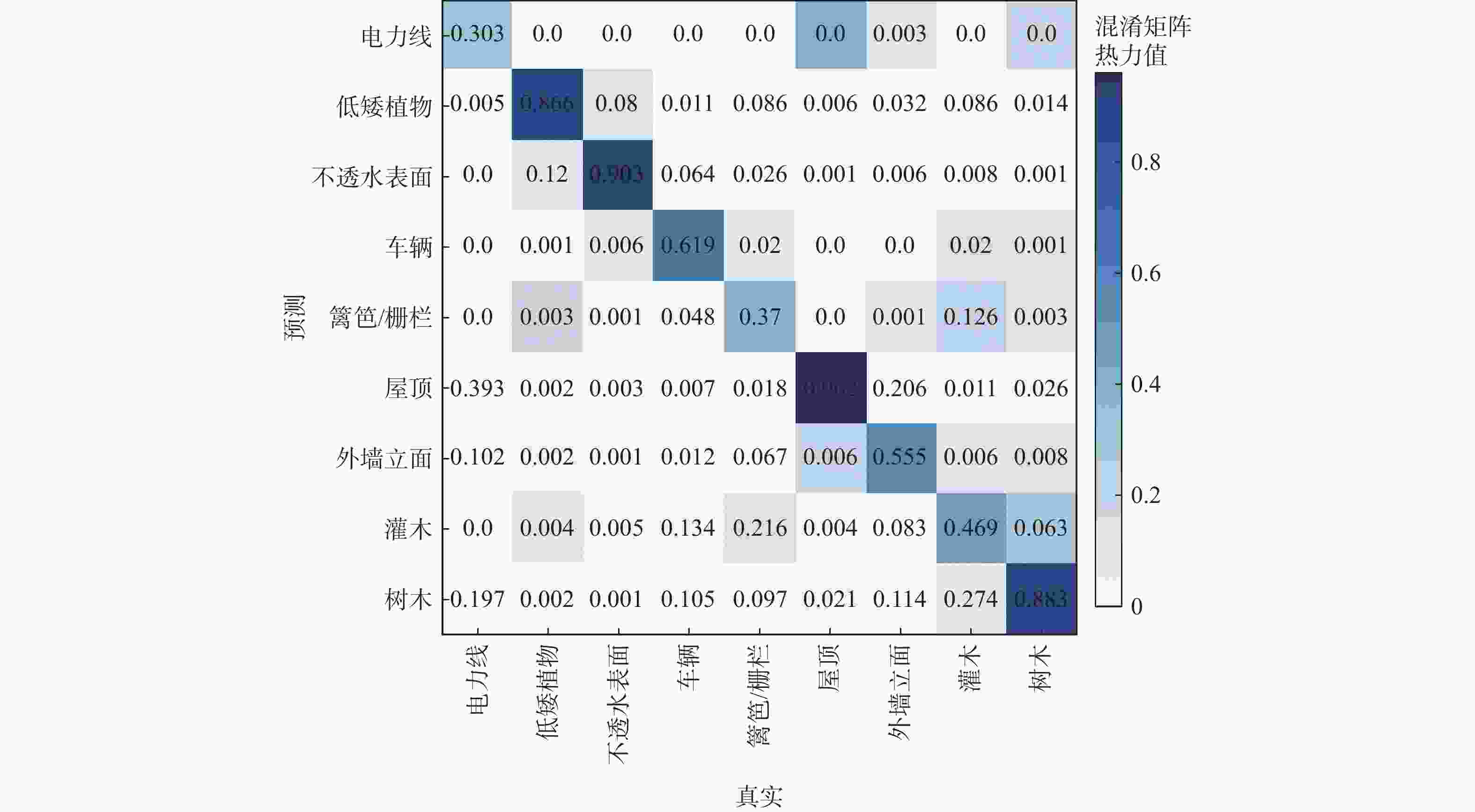
方法 m1 m2 m3 m4 m5 m6 m7 m8 m9 OA Avg F1 PointNet 0.526 0.700 0.832 0.112 0.075 0.748 0.078 0.246 0.454 0.657 0.419 PointNet++ 0.579 0.796 0.906 0.661 0.315 0.916 0.546 0.416 0.770 0.812 0.656 文献 [20] 0.828 0.659 0.942 0.671 0.252 0.915 0.490 0.627 0.826 0.805 0.664 文献 [21] 0.612 0.877 0.933 0.556 0.619 0.916 0.386 0.727 0.775 0.852 0.693 本文 0.303 0.866 0.903 0.340 0.370 0.962 0.555 0.469 0.883 0.859 0.687 表 3 不同模块对实验结果的影响
Table 3. Effects of different modules for the proposed method on the Vaihingen dataset
边缘卷积 多尺度 高程感知 OA Avg F1 √ 0.815 0.662 √ √ 0.826 0.671 √ √ 0.834 0.674 √ √ √ 0.859 0.687 注:“√”表示测试网络集成了该模块。 -
[1] ZERMAS D, IZZAT I, PAPANIKOLOPOULOS N. Fast segmentation of 3D point clouds: A paradigm on LiDAR data for autonomous vehicle applications[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 5067-5073. [2] YANG B S, HUANG R G, LI J P, et al. Automated reconstruction of building LoDs from airborne LiDAR point clouds using an improved morphological scale space[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(1): 14-27. doi: 10.3390/rs9010014 [3] POLEWSKI P, YAO W, HEURICH M, et al. Detection of fallen trees in ALS point clouds using a Normalized Cut approach trained by simulation[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2015, 105: 252-271. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2015.01.010 [4] ENE L T, NÆSSET E, GOBAKKEN T, et al. Large-scale estimation of change in aboveground biomass in miombo woodlands using airborne laser scanning and national forest inventory data[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2017, 188: 106-117. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2016.10.046 [5] TCHAPMI L, CHOY C, ARMENI I, et al. SEGCloud: Semantic segmentation of 3D point clouds[C]//2017 International Conference on 3D Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 537-547. [6] HU Q, YANG B, XIE L, et al. RandLA-Net: Efficient semantic segmentation of large-scale point clouds[C]//2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020. [7] LI Y Y, BU R, SUN M, et al. PointCNN: Convolution on χ-transformed points[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. San Francisco: Curran Associates Inc, 2018: 820-830. [8] COLGAN M, BALDECK C, FÉRET J B, et al. Mapping savanna tree species at ecosystem scales using support vector machine classification and BRDF correction on airborne hyperspectral and LiDAR data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2012, 4(11): 3462-3480. doi: 10.3390/rs4113462 [9] WANG C S, SHU Q Q, WANG X Y, et al. A random forest classifier based on pixel comparison features for urban LiDAR data[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2019, 148: 75-86. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2018.12.009 [10] NIEMEYER J, ROTTENSTEINER F, SOERGEL U. Contextual classification of LIDAR data and building object detection in urban areas[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2014, 87: 152-165. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2013.11.001 [11] SU H, MAJI S, KALOGERAKIS E, et al. Multi-view convolutional neural networks for 3D shape recognition[C]//2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 945-953. [12] WANG L, HUANG Y C, SHAN J, et al. MSNet: Multi-scale convolutional network for point cloud classification[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(4): 612. doi: 10.3390/rs10040612 [13] CHARLES R Q, HAO S, MO K C, et al. PointNet: Deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation[C]// 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 77-85. [14] QI C R, YI L, SU H, et al. PointNet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space[C]// Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: ACM, 2017: 5105–5114. [15] WANG Y, SUN Y B, LIU Z W, et al. Dynamic graph CNN for learning on point clouds[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2019, 38(5): 1-12. [16] HSU P H, ZHUANG Z Y. Incorporating handcrafted features into deep learning for point cloud classification[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(22): 3713. doi: 10.3390/rs12223713 [17] LI W Z, WANG F D, XIA G S. A geometry-attentional network for ALS point cloud classification[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 164: 26-40. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.03.016 [18] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(2): 318-327. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2858826 [19] CHEN Y, LIU G L, XU Y M, et al. PointNet++ network architecture with individual point level and global features on centroid for ALS point cloud classification[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(3): 472. doi: 10.3390/rs13030472 [20] YANG Z S, TAN B, PEI H K, et al. Segmentation and multi-scale convolutional neural network-based classification of airborne laser scanner data[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(10): 3347-3357. doi: 10.3390/s18103347 [21] ZHAO R B, PANG M Y, WANG J D. Classifying airborne LiDAR point clouds via deep features learned by a multi-scale convolutional neural network[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2018, 32(5): 960-979. doi: 10.1080/13658816.2018.1431840 -






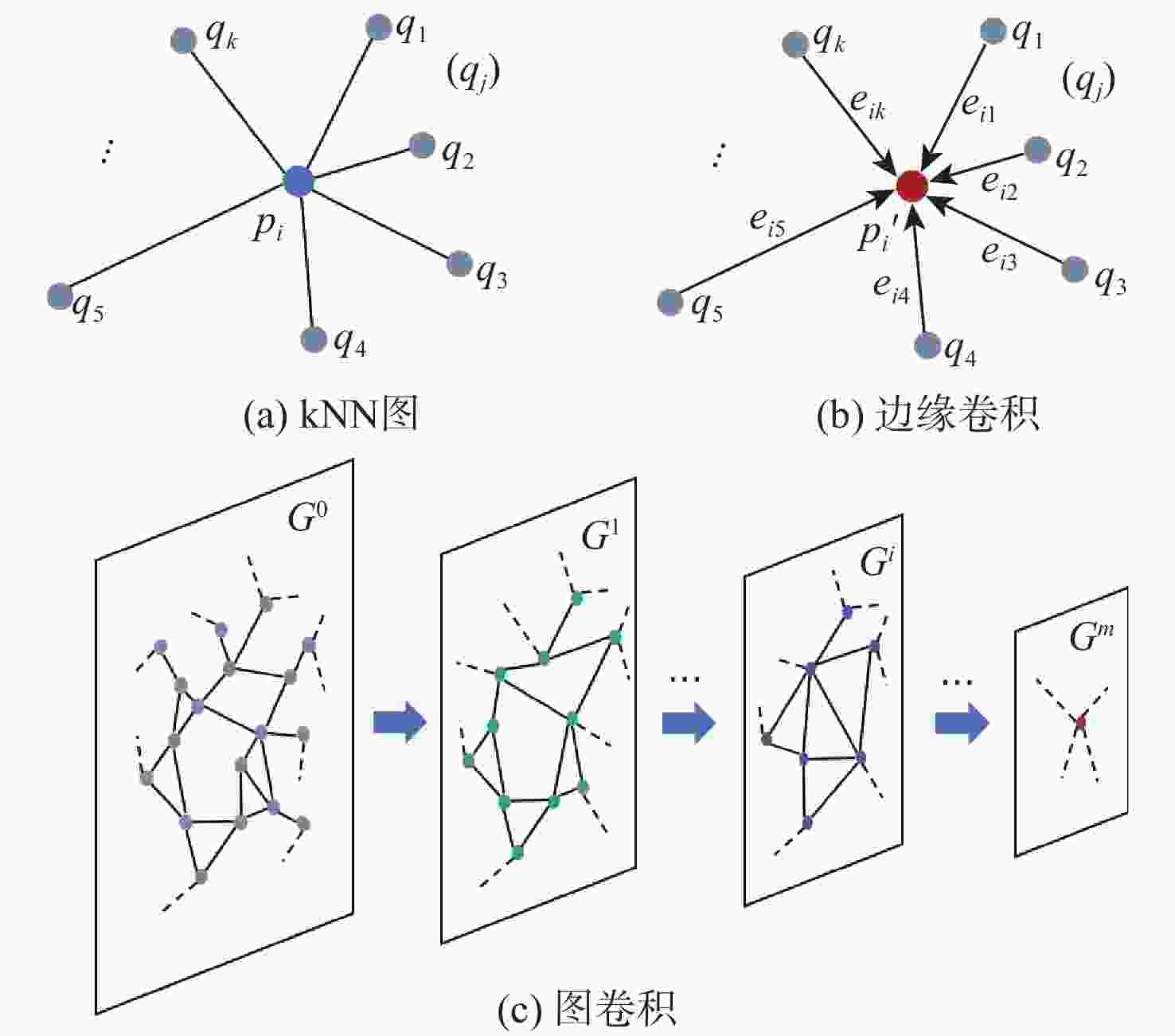
 下载:
下载: