Mural inpainting progressive generative adversarial networks based on structure guided
-
摘要:
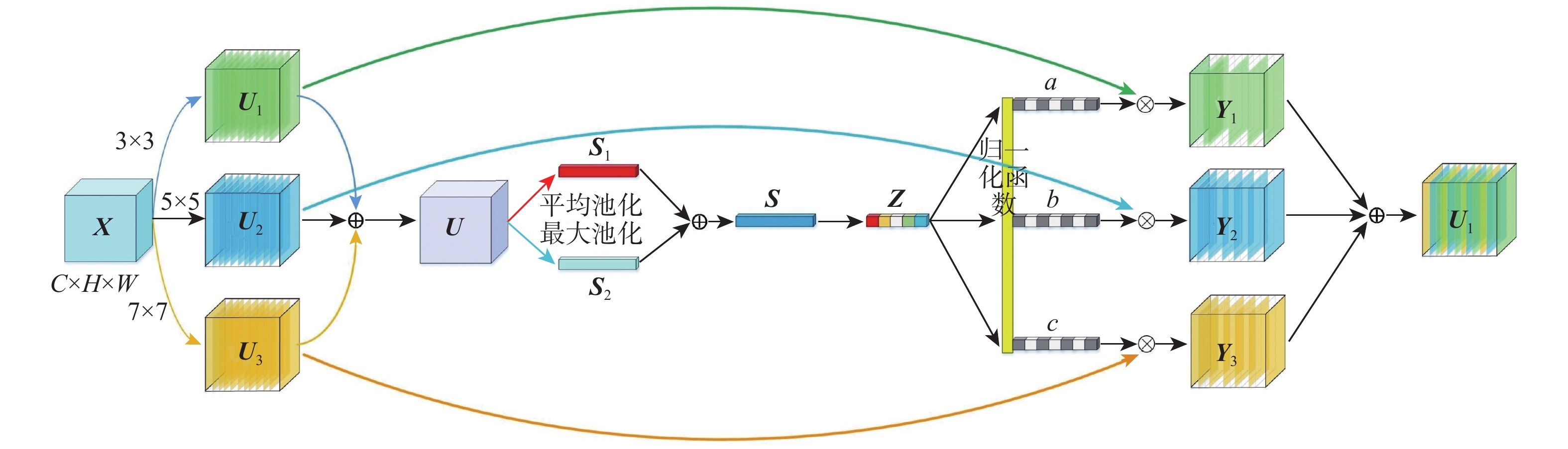
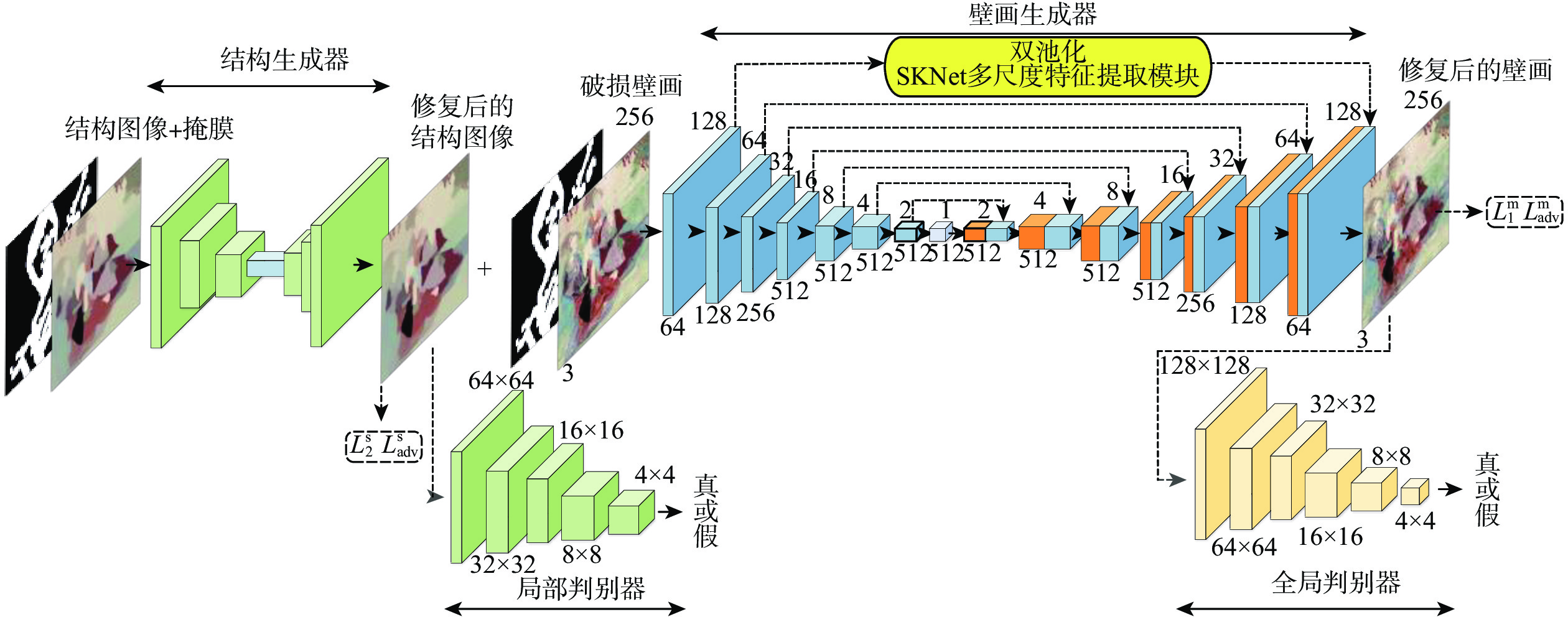
针对破损壁画图像修复过程中存在的结构修复不当及修复后壁画细节重构丢失等问题,提出了一种基于结构引导的渐进式生成对抗壁画修复深度学习模型。设计结构生成器对壁画缺失结构内容进行修复,得到修复的壁画结构图像。通过壁画生成器生成对抗学习,结合改进的双池化SKNet多尺度特征提取模块,利用修复后的结构图像引导破损壁画实现渐进式修复,以提高壁画的细节特征学习能力。通过局部判别器和全局判别器,完成对结构图像和壁画图像的重构判别,增强壁画修复效果的全局一致性。通过对真实敦煌壁画数字化修复的实验表明:所提方法能够有效修复破损的敦煌壁画,修复后的壁画具有更好的结构及细节信息,在主客观评价指标上均优于比较方法。
Abstract:Aiming at the problems of improper structural repair and loss of mural detail reconstruction after repairing during the process of damaged mural image inpainting, mural inpainting progressive generative adversarial networks based on structure guided is proposed. Firstly, a structure generator is designed to generate the missing structure content of the mural. Secondly, the mural generator is used to generate adversarial learning, and combined with the improved double pooling SKNet multi-scale feature extraction modular, the repaired structure image is used to guide the damaged mural to achieve progressive repair, which improves the detailed feature learning ability of the mural. Lastly, the reconstruction of the structural picture and the mural image is finished using the local discriminator and the global discriminator, which improves the overall consistency of the mural restoration result. Experiments on digital restoration of real Dunhuang murals show that the proposed method can effectively repair damaged Dunhuang murals, and the restored murals have a stronger structure and high-quality texture details than other comparison algorithms. Meanwhile, the proposed has better both subjective and objective evaluation.
-
表 1 中心掩膜修复结果PSNR和SSIM对比
Table 1. Comparison of PSNR and SSIM of center mask inpainting results
表 2 随机掩膜修复结果PSNR和SSIM对比
Table 2. Comparison of PSNR and SSIM of random mask inpainting results
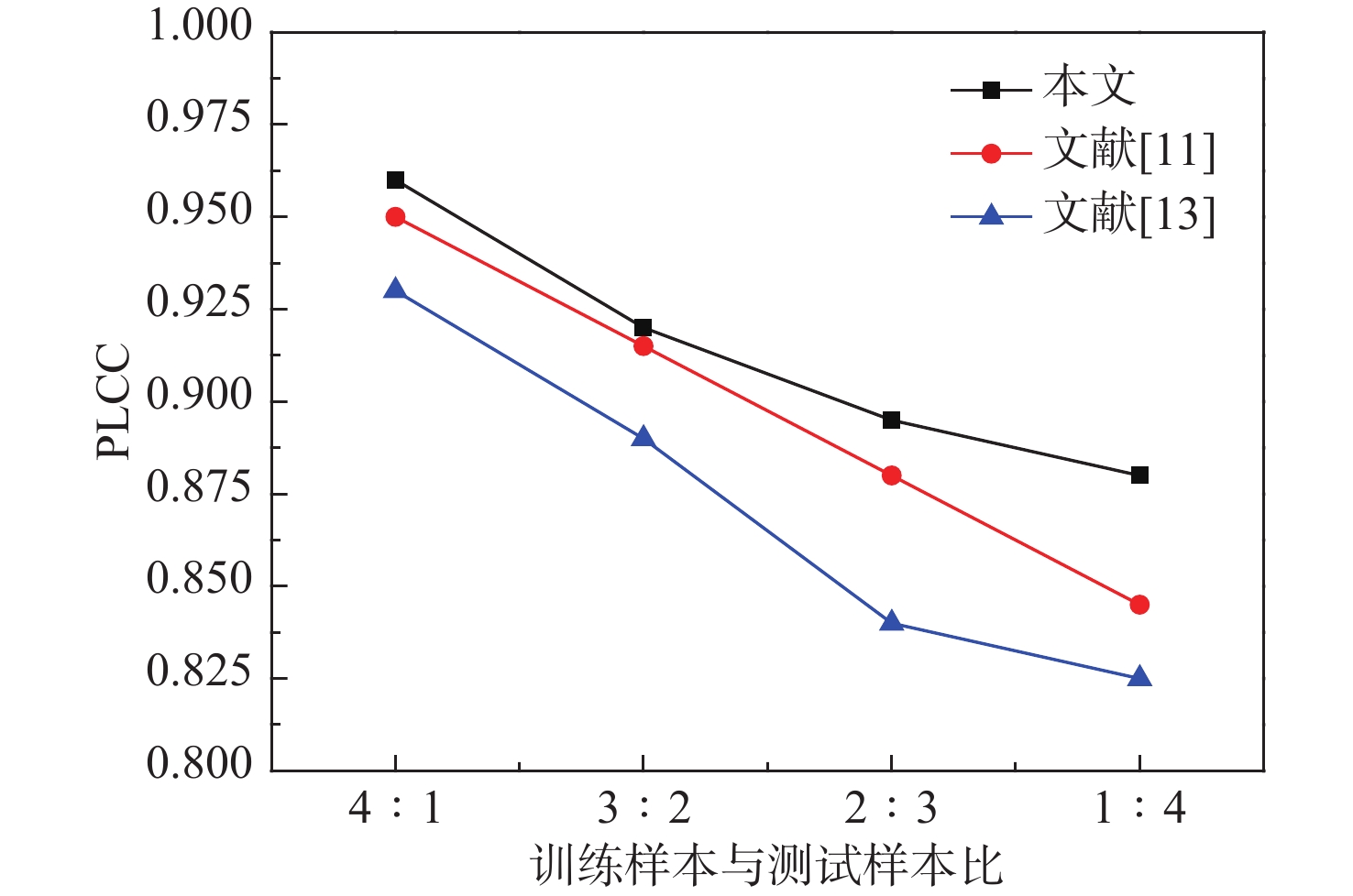
表 3 不同方法模型平均准确率比较
Table 3. Comparison of average accuracy of different algorithm models
-
[1] WANG H, LI Q Q, JIA S. A global and local feature weighted method for ancient murals inpainting[J]. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2020, 11(6): 1197-1216. doi: 10.1007/s13042-019-01032-2 [2] SHAO H, WANG Y X. Generative image inpainting with salient prior and relative total variation[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2021, 79: 103231. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2021.103231 [3] BRKIC A L, MITROVIC D, NOVAK A. On the image inpainting problem from the viewpoint of a nonlocal Cahn-Hilliard type equation[J]. Journal of Advanced Research, 2020, 25: 67-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.04.015 [4] YANG X H, GUO B L, XIAO Z L, et al. Improved structure tensor for fine-grained texture inpainting[J]. Signal Processing:Image Communication, 2019, 73: 84-95. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2018.02.006 [5] FAN Y. Damaged region filling by improved criminisi image inpainting algorithm for thangka[J]. Cluster Computing, 2019, 22(6): 13683-13691. [6] LI P, CHEN W G, NG M K. Compressive total variation for image reconstruction and restoration[J]. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 2020, 80(5): 874-893. doi: 10.1016/j.camwa.2020.05.006 [7] BINI A A. Image restoration via DOST and total variation regularisation[J]. IET Image Processing, 2019, 13(3): 458-468. doi: 10.1049/iet-ipr.2018.5504 [8] WAN W, HUANG H Y, LIU J. Local block operators and TV regularization based image inpainting[J]. Inverse Problems & Imaging, 2018, 12(6): 1389-1410. [9] 陈永, 艾亚鹏, 郭红光. 改进曲率驱动模型的敦煌壁画修复算法[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2020, 32(5): 787-796.CHEN Y, AI Y P, GUO H G. Improved curvature-driven model of Dunhuang mural restoration algorithm[J]. Journal of Computer Aided Design and Graphics, 2020, 32(5): 787-796(in Chinese). [10] QIN J, BAI H H, ZHAO Y. Multi-scale attention network for image inpainting[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2021, 204: 103155. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2020.103155 [11] XIE C H, LIU S H, LI C, et al. Image inpainting with learnable bidirectional attention maps[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 8858-8867. [12] DU W C, CHEN H, YANG H. Learning invariant representation for unsupervised image restoration[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 11224-11233. [13] DEMIR U, UNAL G. Patch-based image inpainting with generative adversarial networks[EB/OL]. (2018-03-20)[2021-08-01]. [14] FANG Y C, LI Y F, TU X K, et al. Face completion with hybrid dilated convolution[J]. Signal Processing:Image Communication, 2020, 80: 115664. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2019.115664 [15] HE X, YIN Y. Non-local and multi-scale mechanisms for image inpainting[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(9): 3281. doi: 10.3390/s21093281 [16] SHI Y, FAN Y, ZHANG N. A generative image inpainting network based on the attention transfer network across layer mechanism[J]. Optik, 2021, 242: 167101. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.167101 [17] 胡凯, 赵健, 刘昱, 等. 结构引导的图像修复[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(7): 1269-1277. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2021.0004HU K, ZHAO J, LIU Y, et al. Structure-guided image restoration[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(7): 1269-1277(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2021.0004 [18] 李清泉, 王欢, 邹勤. 一种基于稀疏表示模型的壁画修复算法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2018, 43(12): 1847-1853.LI Q Q, WANG H, ZOU Q. A mural restoration algorithm based on sparse representation model[J]. Journal of Wuhan University (Information Science Edition), 2018, 43(12): 1847-1853(in Chinese). [19] REN Y R, YU X M, ZHANG R N, et al. StructureFlow: Image inpainting via structure-aware appearance flow[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 181-190. [20] LIU H Y, JIANG B, SONG Y B, et al. Rethinking image inpainting via a mutual encoder-decoder with feature equalizations[C]//Computer Vision-ECCV 2020. Berlin: Springer, 2020, 12347: 725-741. [21] LI X, WANG W H, HU X L, et al . Selective kernel networks[C]// Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 510-519. [22] HOU Q B, ZHANG L, CHENG M M, et al. Strip pooling: Rethinking spatial pooling for scene parsing[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 4002- 4011. -







 下载:
下载: