-
摘要:
基于深度学习的目标检测是计算机视觉领域的研究热点,目前主流的目标检测模型大多通过增加网络深度和宽度以获得更好的检测效果,但容易导致参数量增加、检测速度降低的问题。为兼顾检测精度与速度,借鉴Ghost卷积和分组卷积的轻量化思想,提出了一种高效的轻量级Ghost卷积(LGC)模型,以采用更少的参数获得更多的特征图。在该卷积模型的基础上引入反残差结构重新设计了CSPDarkNet53,生成了一种基于LGC的反残差特征提取网络,以提高网络对全局特征信息的提取能力。使用反残差特征提取网络替换YOLOv4的骨干网络,辅以深度可分离卷积进一步减少参数,提出了一种反残差目标检测算法,以提升目标检测的整体性能。实验结果表明:相比于主流的目标检测算法,所提算法在检测精度相当的前提下,模型参数量和检测速度具有明显的优势。
Abstract:Target detection based on deep learning is a research hotspot in computer vision. Although existing mainstream detection models usually increase the depth and width of the network to acquire better detection results, it is unamiable to suffer from parameters increasing and detection rate decreasing. To address this problem, an efficient lightweight Ghost convolution (LGC) model, which aims to balance the detection accuracy and speed, and obtain more feature maps with fewer parameters, was proposed by referring to the lightweight idea of Ghost convolution and group convolution. CSPDarkNet53 that was redesigned with the above convolution and an inverted residual structure was introduced to generate an inverted residual feature extraction network to improve the global feature information extraction capability of the model. On this basis, the inverted residual feature extraction network was used as the backbone network of YOLOv4, and depthwise separable convolution was used to reduce the parameters. To improve the overall performance of the algorithm, an inverted residual target detection algorithm was proposed. Experimental results show that compared with the current mainstream target detection algorithm, the proposed algorithm has prominent advantages in the number of model parameters and detection speed under the premise of similar detection accuracy.
-
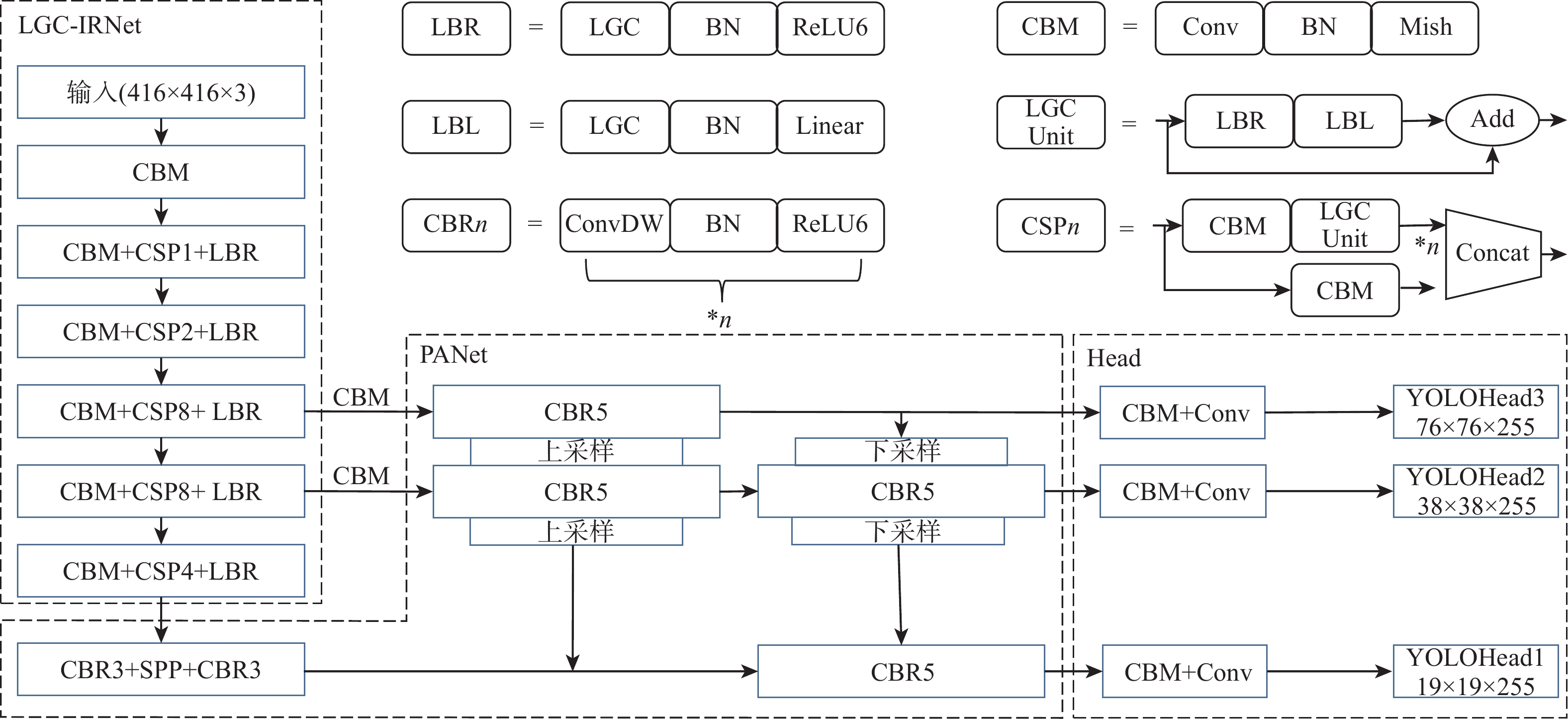
表 1 LGC-IRNet网络结构
Table 1. LGC-IRNet network structure
网络层次 通道数 尺寸/步长 输出 Conv2D 32 3×3/1 416×416×32 Conv2D 64 3×3/2 208×208×64 1× LGC 32 LGC 64 残差块 208×208×64 Conv2D 128 3×3/2 104×104×128 2× LGC 64 LGC 128 残差块 104×104×128 Conv2D 256 3×3/2 52×52×256 8× LGC 128 LGC 256 残差块 52×52×256 Conv2D 512 3×3/2 26×26×512 8× LGC 256 LGC 512 残差块 26×26×512 Conv2D 1024 3×3/2 13×13×1024 4× LGC 512 LGC 1024 残差块 13×13×1024 表 2 不同算法性能比较
Table 2. Performance comparison of different algorithms
表 3 不同骨干网络的网络模型性能比较
Table 3. Performance comparison of different backbone network models
主干网络 平均精度/% 模型体积/MB Conv2D Ghost LGC Conv2D Ghost LGC CSPDarkNet53 83.32 80.08 80.68 246 186 152 GhostNet 78.73 78.18 43 39 IRNet 84.08 85.06 172 149 -
[1] 赵永强, 饶元, 董世鹏, 等. 深度学习目标检测方法综述[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2020, 25(4): 629-654. doi: 10.11834/jig.190307ZHAO Y Q, RAO Y, DONG S P, et al. Survey on deep learning object detection[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2020, 25(4): 629-654(in Chinese). doi: 10.11834/jig.190307 [2] REDMON J, FARHADI A. YOLOv3: An incremental improve- ment [EB/OL]. (2018-04-08) [2021-08-01]. [3] BOCHKOVSKIY A, WANG C Y, LIAO H Y M. YOLOv4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection [EB/OL]. (2020-04-23) [2021-08-01]. [4] LIU W, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 21-37. [5] LI X Y, LV Z G, WANG P, et al. Combination weighted clustering algorithms in cognitive radio networks[J]. Concurrency and Computation:Practice and Experience, 2020, 32(23): e5516. [6] 张云佐, 杨攀亮, 李汶轩. 基于改进SSD算法的铁路隧道漏缆卡具检测[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2021, 58(22): 2215005.ZHANG Y Z, YANG P L, LI W X. Leaky coaxial cable fixture detection based on improved SSD algorithm[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 58(22): 2215005(in Chinese). [7] ZHOU Q, ZHONG B, ZHANG Y, et al. Deep alignment network based multi-person tracking with occlusion and motion reasoning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2018, 21(5): 1183-1194. [8] 崔家礼, 曹衡, 张亚明, 等. 一种复杂场景下的人眼检测算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(1): 38-44. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0641CUI J L, CAO H, ZHANG Y M, et al. A human eye detection algorithm in complex scenarios[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(1): 38-44(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0641 [9] 符惠桐, 王鹏, 李晓艳, 等. 面向移动目标识别的轻量化网络模型[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2021, 55(7): 1-9. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb202107014FU H T, WANG P, LI X Y, et al. Lightweight network model for moving object recognition[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2021, 55(7): 1-9(in Chinese). doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb202107014 [10] HOWARD A G, ZHU M, CHEN B, et al. MobileNets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications [EB/OL]. (2017-04-17) [2021-08-01]. [11] MA N, ZHANG X, ZHENG H T, et al. ShuffleNet V2: Practical guidelines for efficient CNN architecture design[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 116-131. [12] TAN M, LE Q V. MixConv: Mixed depthwise convolutional kernels[EB/OL]. (2019-12-01) [2021-08-01]. [13] HAN K, WANG Y, TIAN Q, et al. GhostNet: More features from cheap operations[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 1580-1589. [14] SU Z, FANG L, KANG W, et al. Dynamic group convolution for accelerating convolutional neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 138-155. [15] WEI H, WANG Z, HUA G. Dynamically mixed group convolution to lighten convolution operation[C]//2021 4th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Big Data. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 203-206. [16] CHOLLET F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 17355762. [17] XIE S, GIRSHICK R, DOLLAR P, et al. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1492-1500. [18] 孙琪翔, 何宁, 张聪聪, 等. 轻量级图卷积人体骨架动作识别方法[J]. 计算机工程, 2022, 48(5): 306-313.SUN Q X, HE N, ZHANG C C, et al. A lightweight graph convolution human skeleton action recognition method[J]. Computer Engineering, 2022, 48(5): 306-313(in Chinese). [19] 罗禹杰, 张剑, 陈亮, 等. 基于自适应空间特征融合的轻量化目标检测算法设计[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2022, 59(4): 302-312.LUO Y J, ZHANG J, CHEN L, et al. Design of lightweight target detection algorithm based on adaptive spatial feature fusion[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(4): 302-312(in Chinese). [20] WANG C Y, LIAO H Y M, WU Y H, et al. CSPNet: A new backbone that can enhance learning capability of CNN[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 390-391. [21] SANDLER M, HOWARD A, ZHU M, et al. MobileNetV2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 4510-4520. [22] LIU S, QI L, QIN H, et al. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Comp- uter Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 8759-8768. [23] 曹远杰, 高瑜翔. 基于GhostNet残差结构的轻量化饮料识别网络[J]. 计算机工程, 2022, 48(3): 310-314. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0059966CAO Y J, GAO Y X. A lightweight beverage recognition network based on GhostNet residual structure[J]. Computer Engineering, 2022, 48(3): 310-314(in Chinese). doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0059966 -







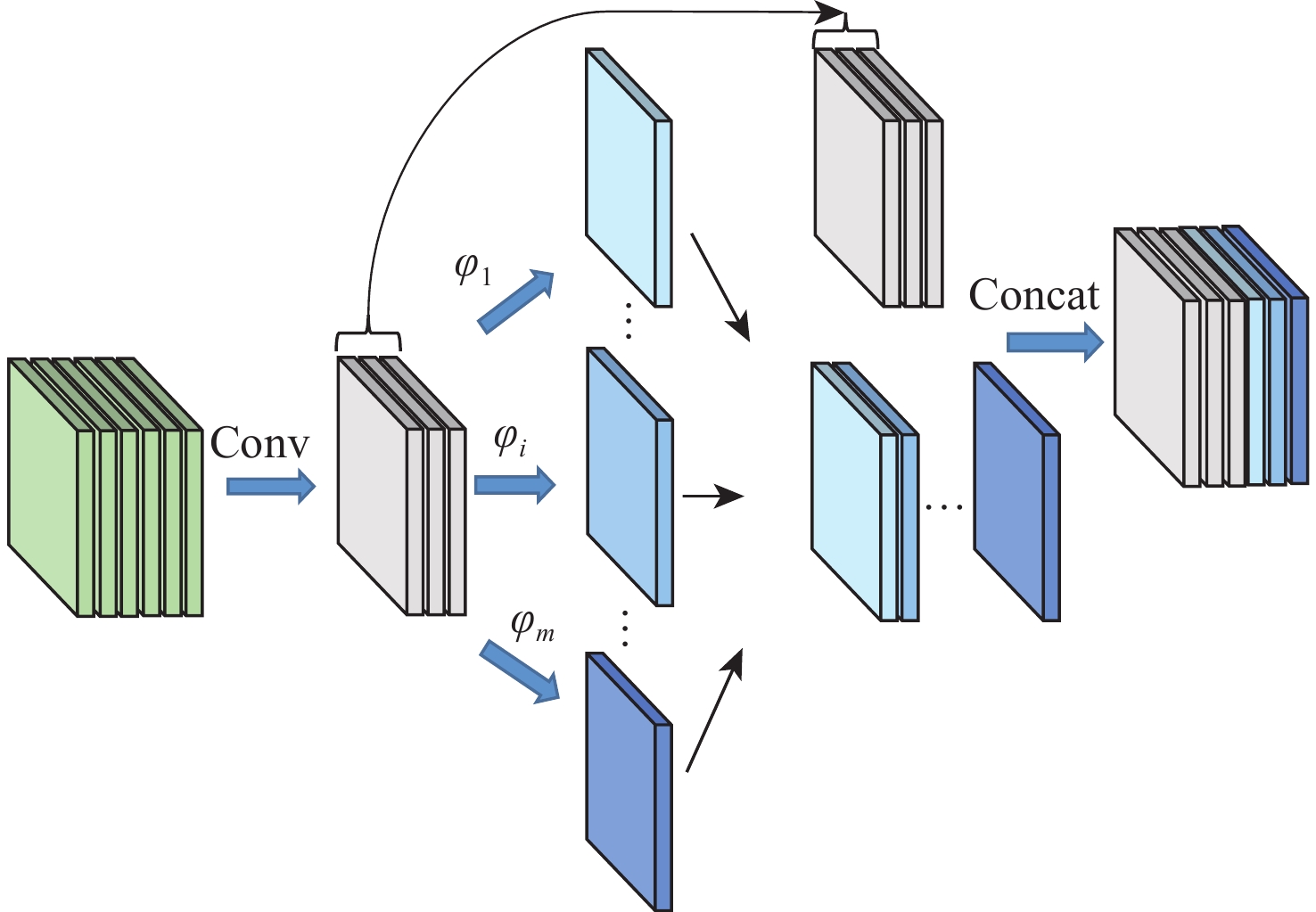
 下载:
下载: