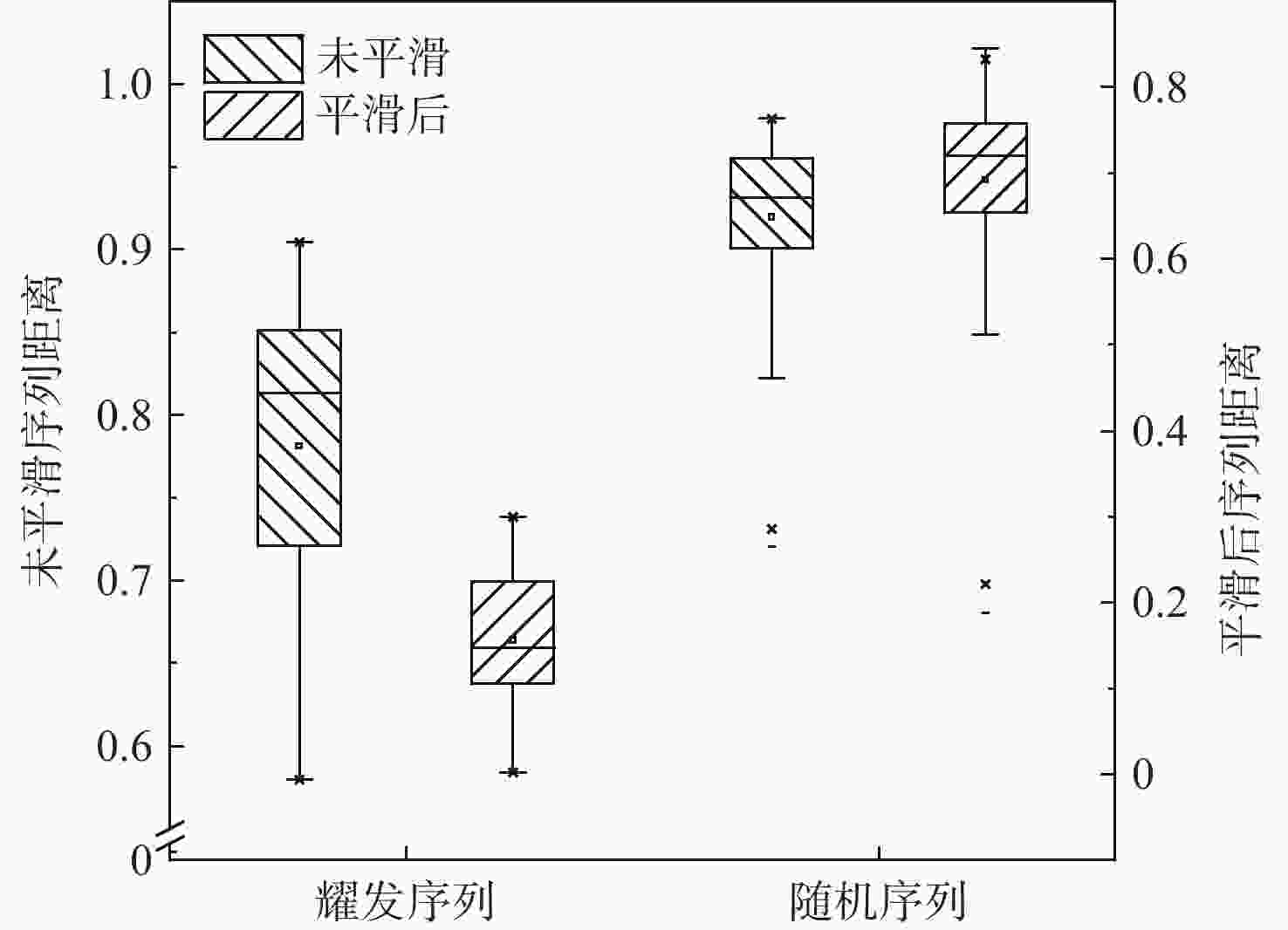
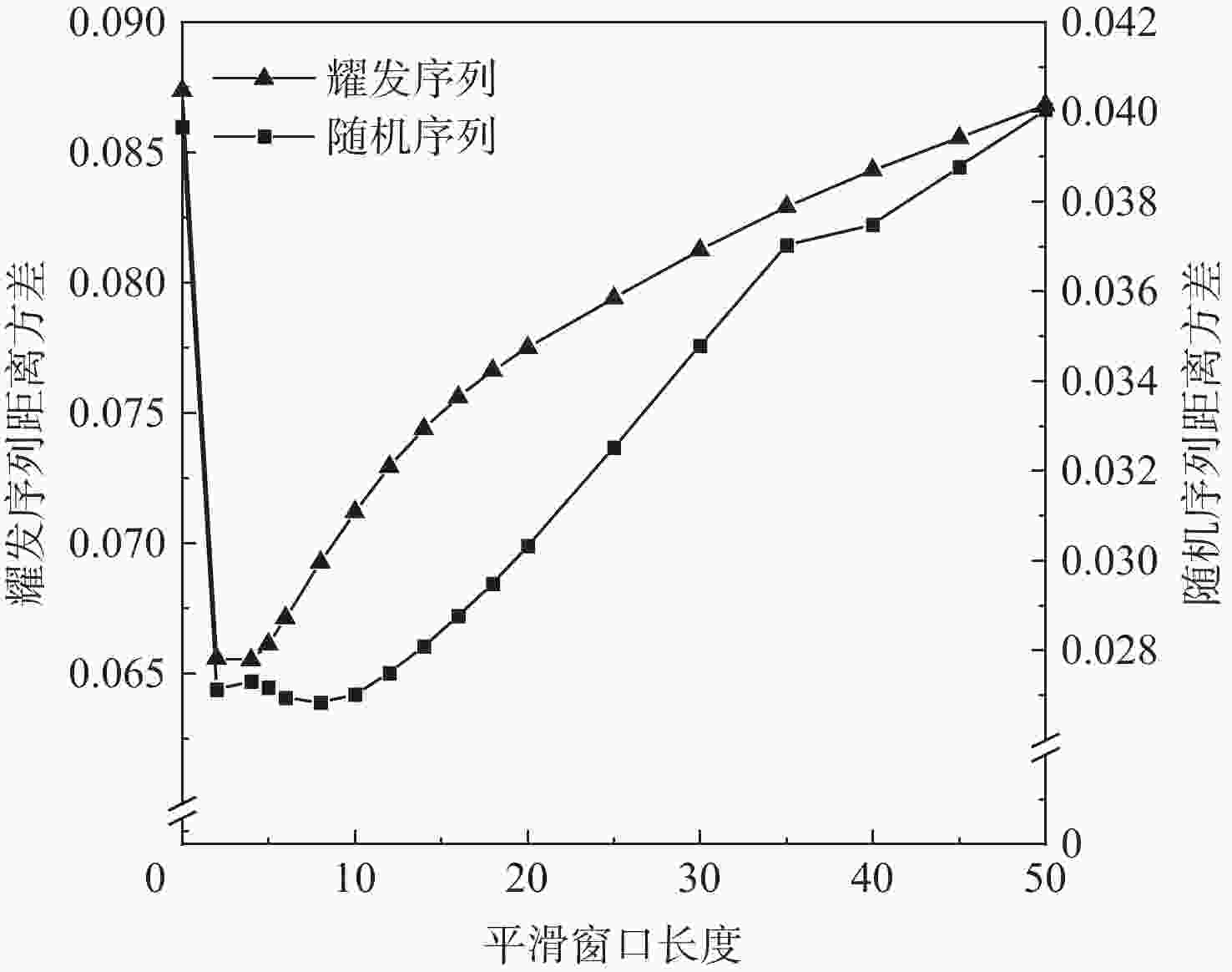
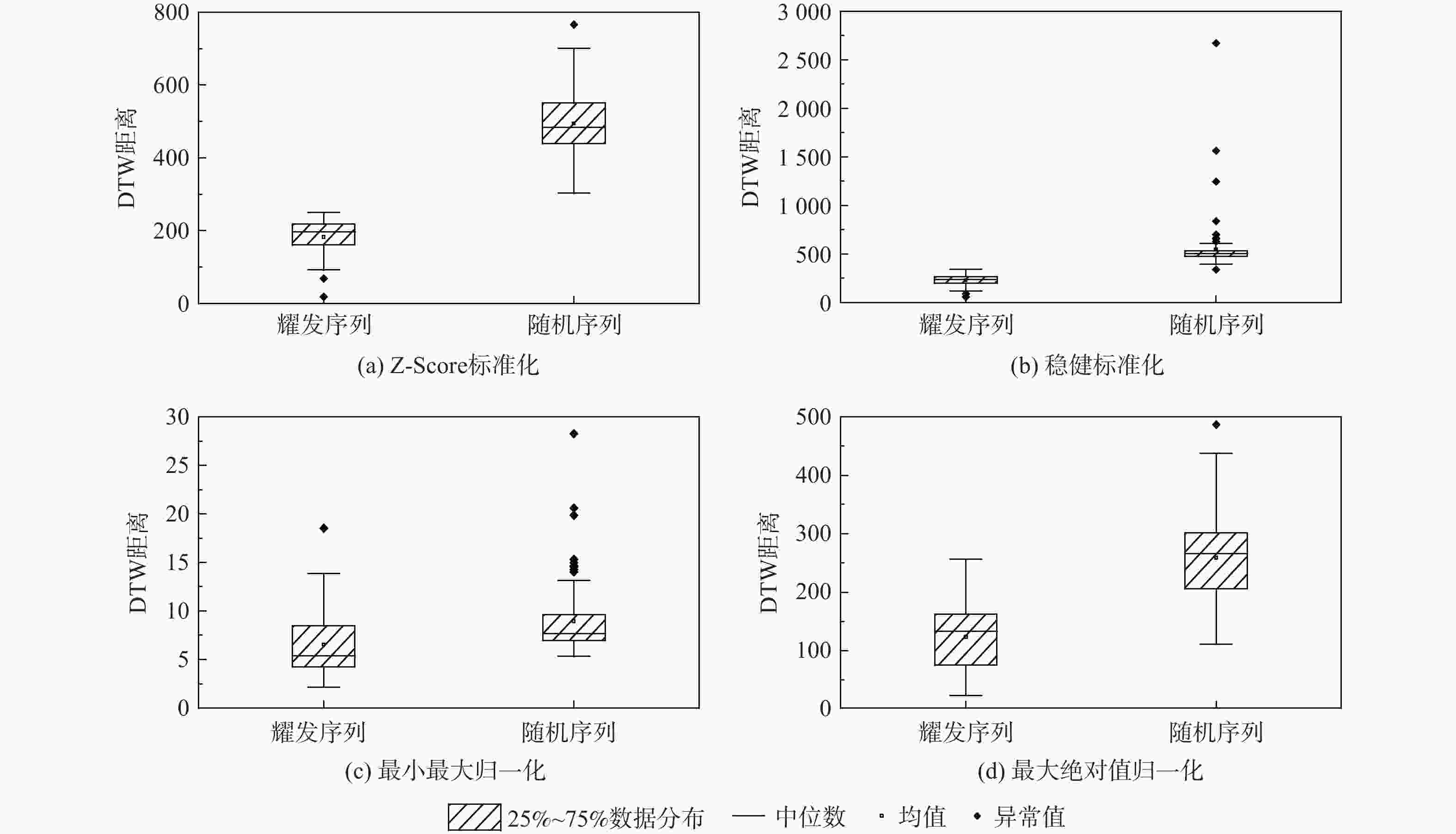
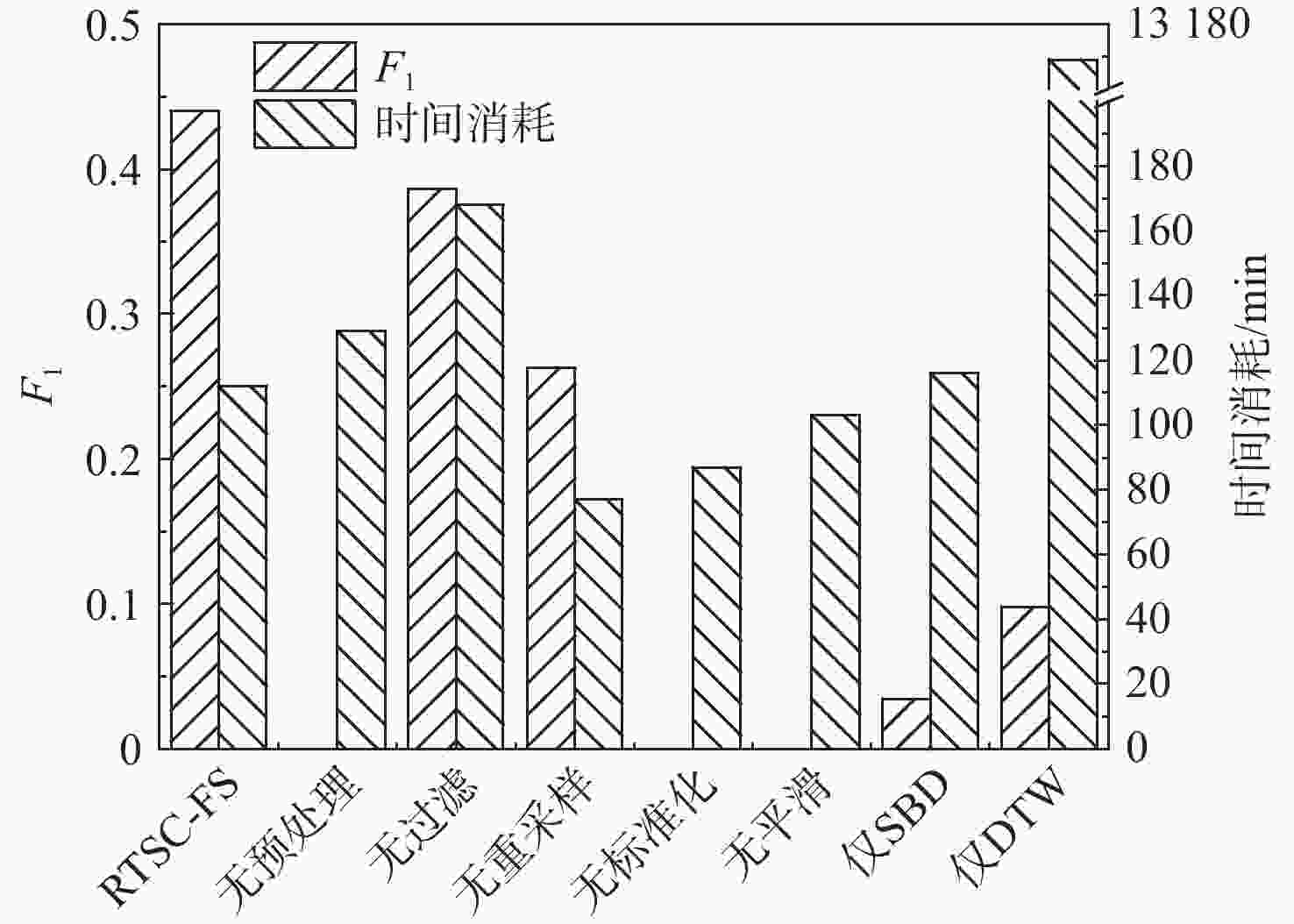
-
摘要:
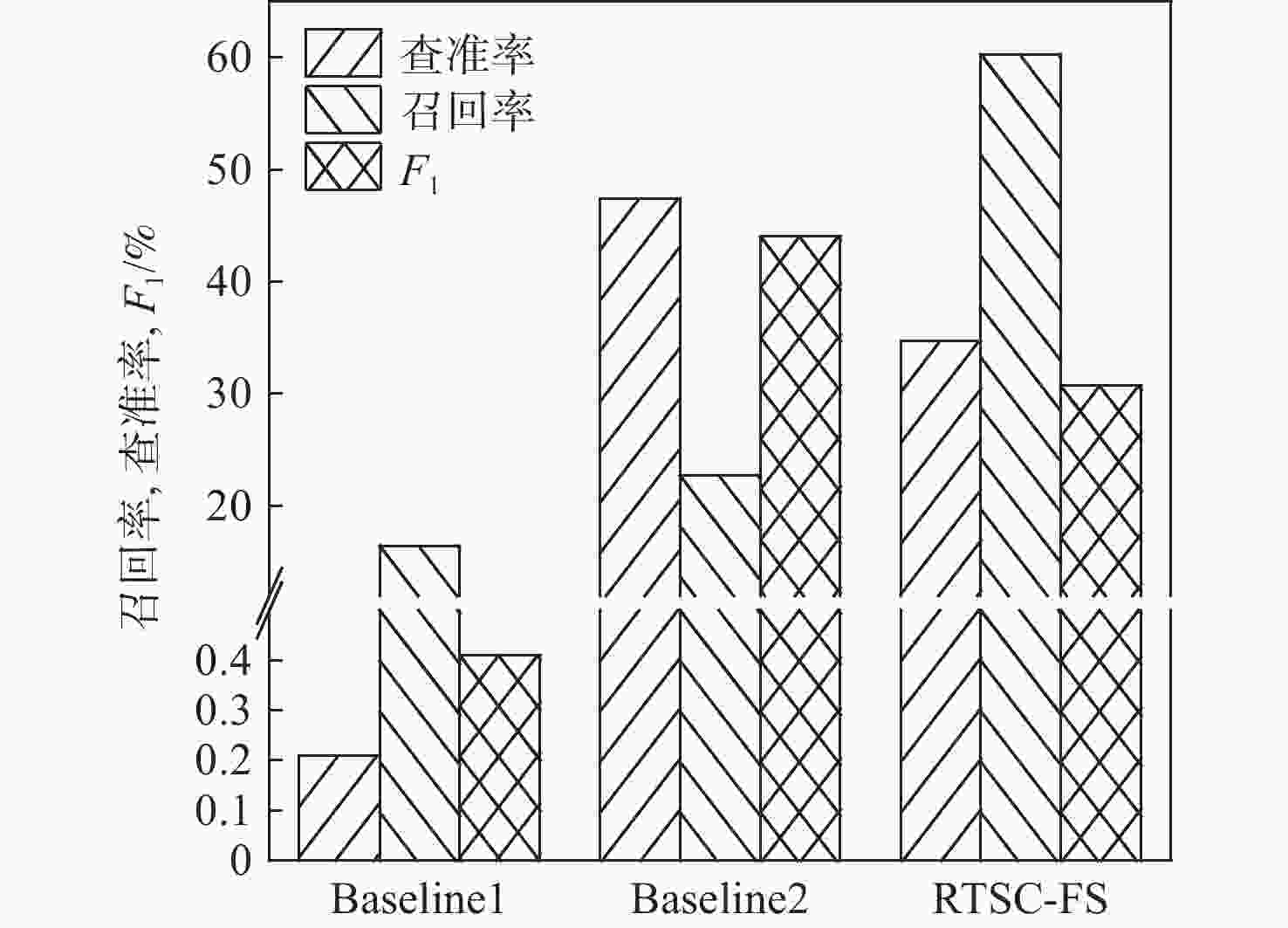
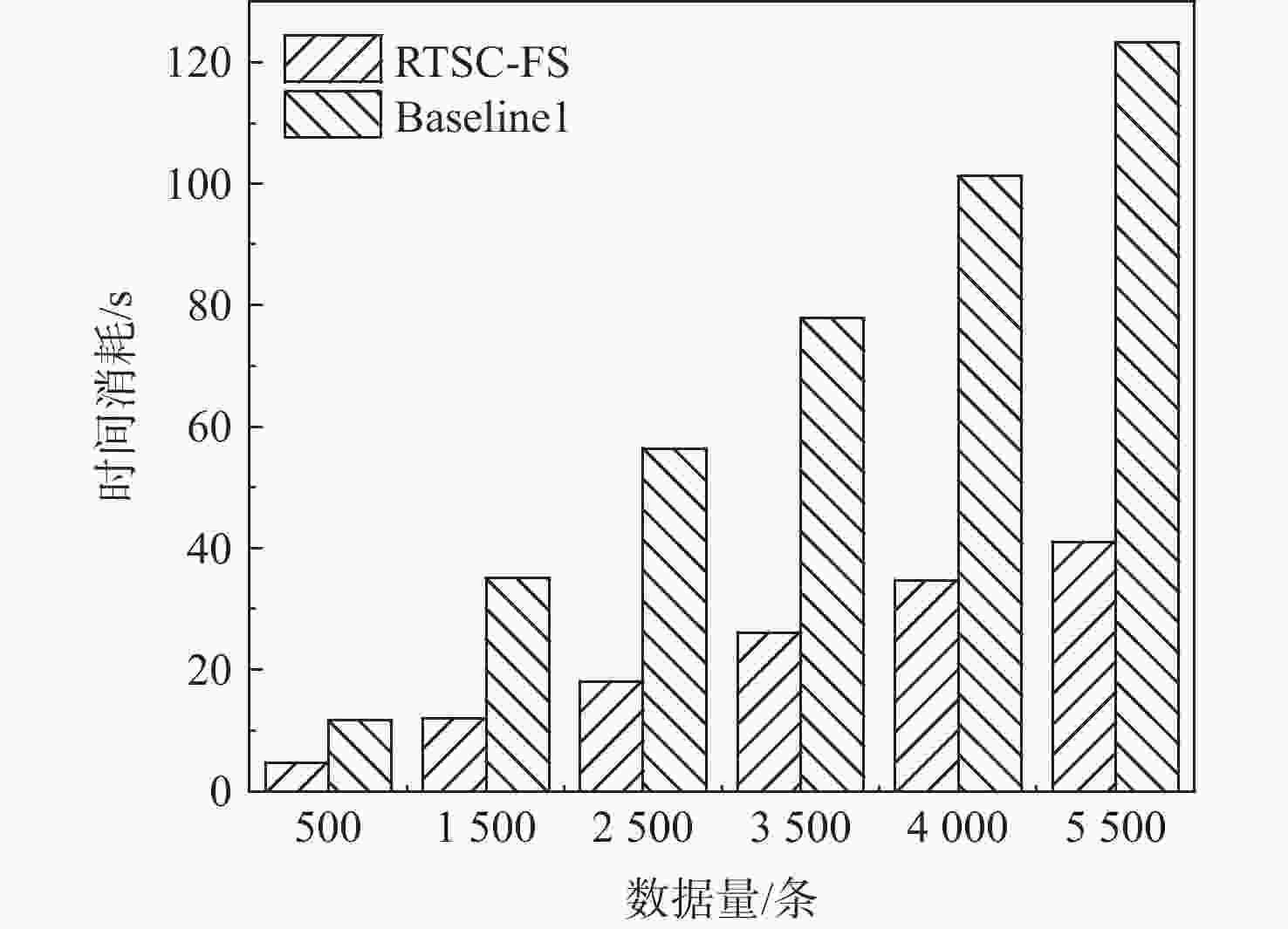
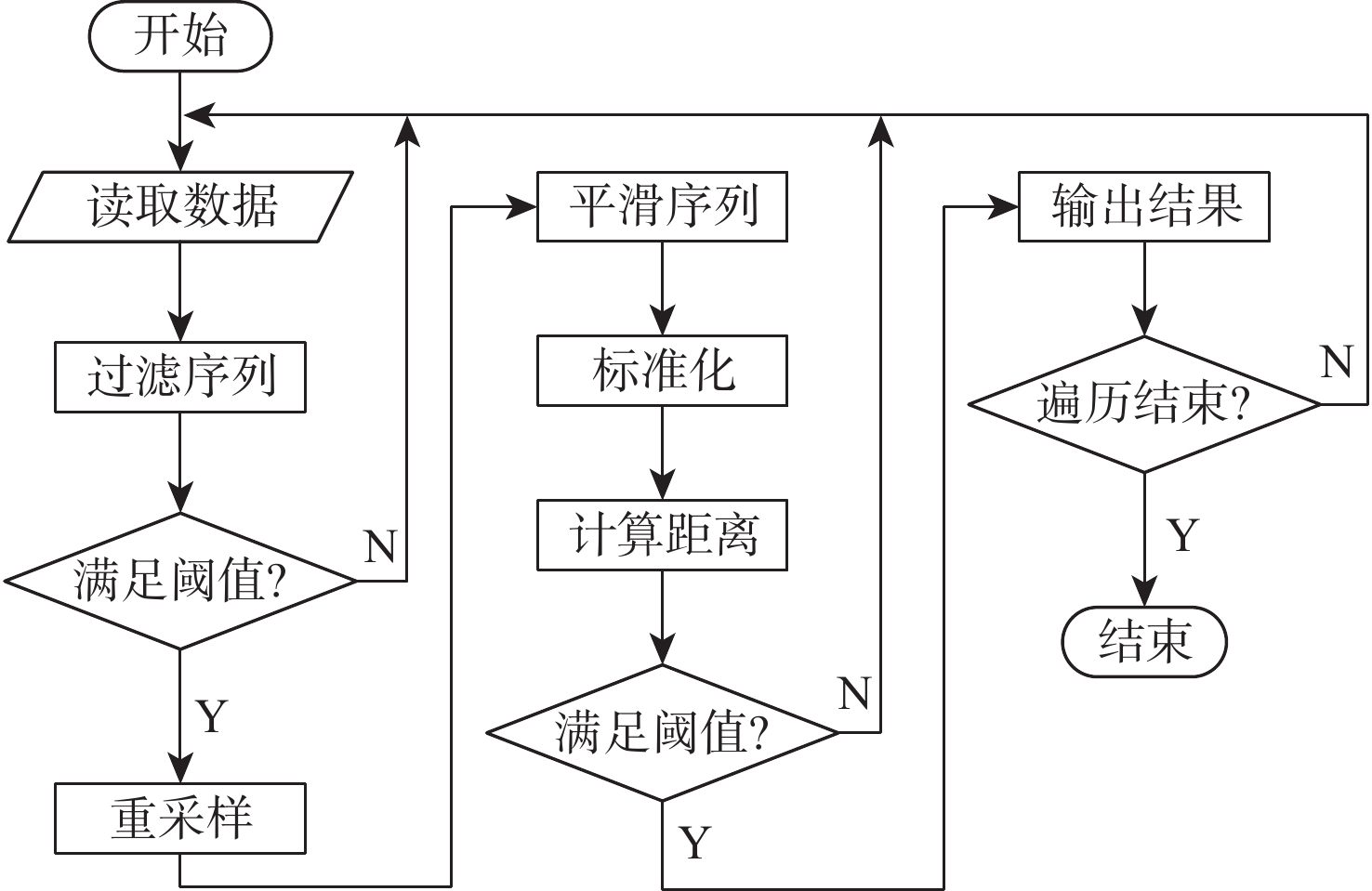
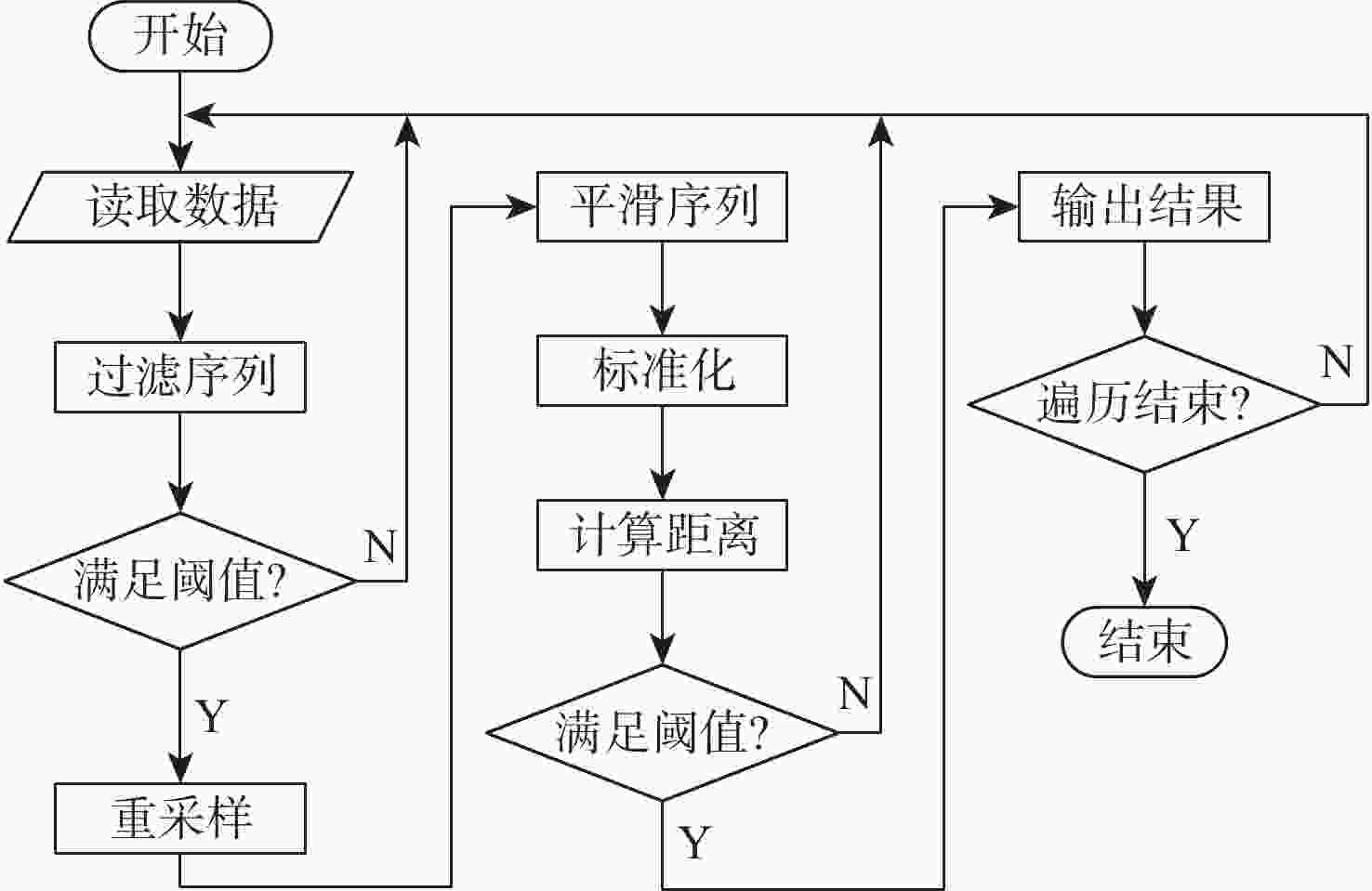
稀有时间序列分类(RTSC)在天文观测等领域有广泛应用。针对目前稀有时间序列方法处理大规模数据集存在准确率低和时间成本高的问题,以天文观测中的短时标稀有天体光变事件——耀发现象为研究对象,提出改进的稀有时间序列分类方法RTSC-FS。该方法融合动态时间弯曲(DTW)的改进FastDTW和SBD度量序列距离,同时具有FastDTW计算复杂度低、衡量精度高和SBD计算速度快的特点,采用滑动窗口过滤、重采样、窗函数平滑、标准化数据等数据预处理技术进一步降低时间成本。在由地基广角相机阵(GWAC)记录到的星等变化的时间序列数据集上,所提方法从约791万天次的光变数据中发现具有耀发特征的曲线44条,召回率60.27%,查准率达34.65%,相比Baseline发现数量更多,召回率、查准率有所提升。
Abstract:Rare time series classification (RTSC) is widely used in astronomical observation and other fields. Aiming at the problems of low accuracy and high time cost in the current rare time series classification methods for large-scale data, RTSC-FS is proposed, which takes the short-time scale rare celestial body light change events in astronomical observations as the research object. The dynamic time wrapping (DTW) enhancement FastDTW and SBD are combined in RTSC-FS to estimate sequence distance. The former has low computational complexity, excellent measurement accuracy, while the latter has fast computational speed. Utilizing additional time-saving data preprocessing methods such as resampling, window function smoothing, standardized data, and sliding window filtering. On the time series data set of magnitude changes recorded by the ground-based wide-angle camera (GWAC), RTSC-FS found 44 curves with flare characteristics from approximately 7.91 million days of light change data. The recall rate is 60.27%, and the precision rate is 34.65%. Compared with the Baseline, the number of discoveries is larger, and the recall rate and accuracy rate have been improved.
-
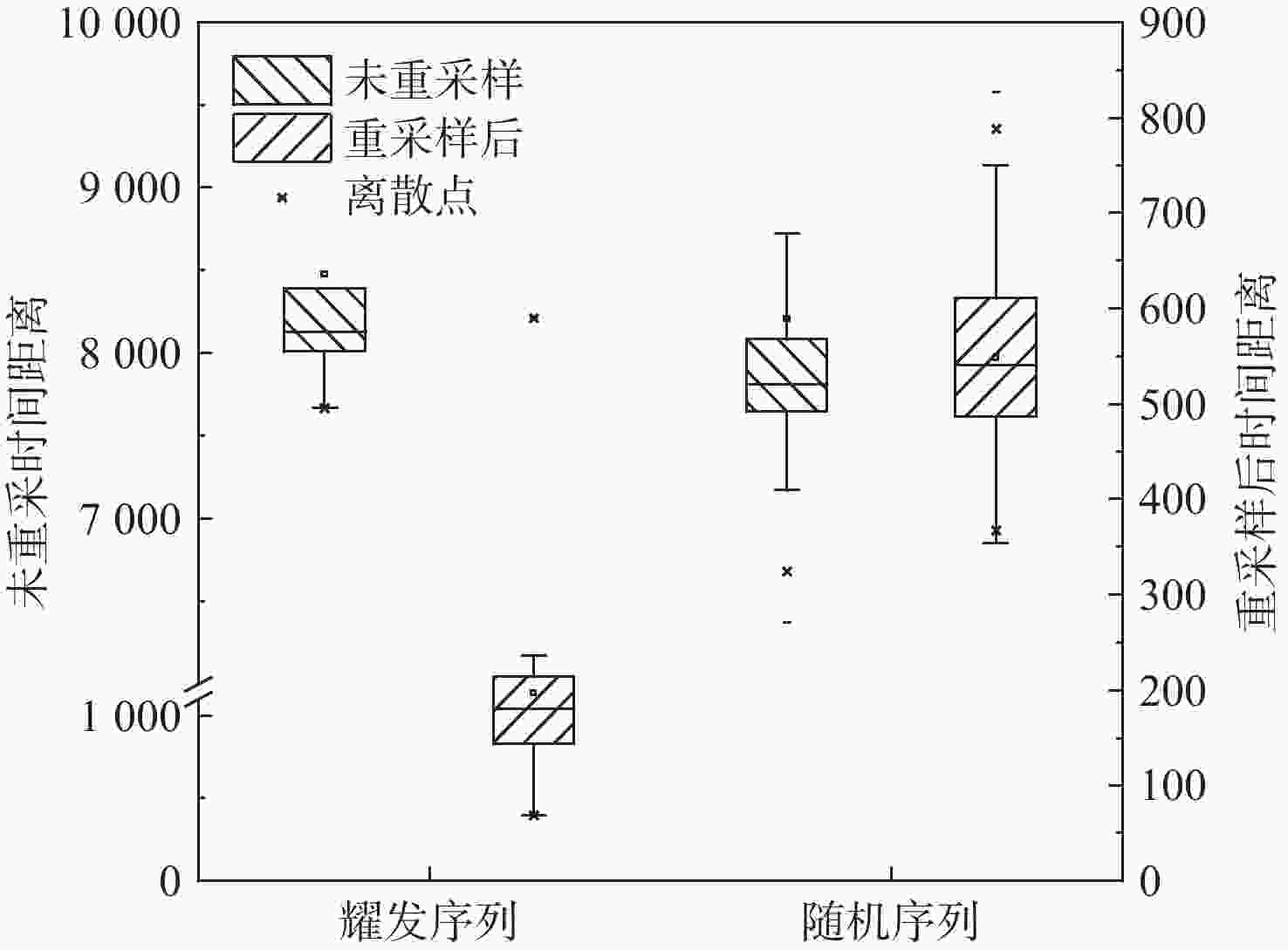
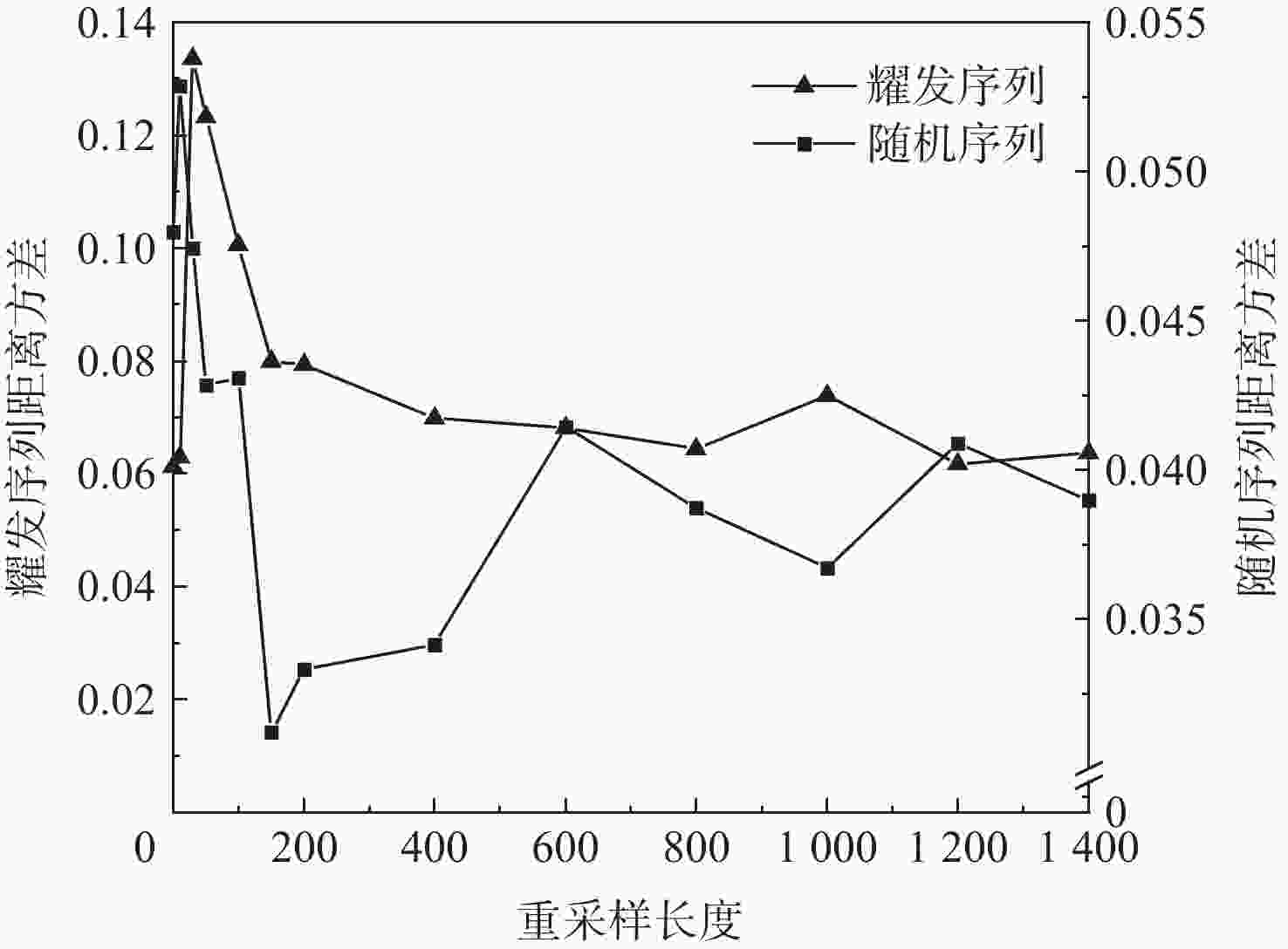
表 1 不同窗函数计算距离均值的差值
Table 1. Difference of distance mean calculated by different window functions
窗函数 DTW1 DTW2 SBD1 SBD2 Blackman 283.287 6 306.278 6 0.286 6 0.475 4 Bartlett 276.359 0 301.501 0 0.278 2 0.471 4 Hanning 279.461 0 303.506 0 0.282 1 0.473 4 Hamming 275.730 0 301.512 6 0.277 4 0.471 1 注:DTW1代表耀发序列和随机序列分别与模板1的DTW距离均值的差值,DTW2代表耀发序列和随机序列分别与模板2的DTW距离均值的差值。SBD1、SBD2同理。 -
[1] MINOR A C, DU Z, SUN Y, et al. GPU accelerated anomaly detection of large scale light curves[C]//2020 IEEE High Performance Extreme Computing Conference (HPEC). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 1-7. [2] CORDIER B, WEI J, ATTEIA J L, et al. The SVOM gamma-ray burst mission[EB/OL]. (2015-11-10)[2021-08-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03323. [3] BI J, FENG T Z, YUAN H T. Real-time and short-term anomaly detection for GWAC light curves[J]. Computers in Industry, 2018, 97: 76-84. doi: 10.1016/j.compind.2018.01.021 [4] 付夏楠, 黄垒, 魏建彦. Mini-GWAC控制系统的故障诊断专家系统[J]. 天文研究与技术, 2016, 13(3): 366-372.FU X N, HUANG L, WEI J Y. The fault diagnosis expert system of Mini-GWAC[J]. Astronomical Research & Technology, 2016, 13(3): 366-372(in Chinese). [5] BERNDT D J, CLIFFORD J. Using dynamic time warping to find patterns in time series[C]//Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 1994: 359-370. [6] SALVADOR S, CHAN P. Toward accurate dynamic time warping in linear time and space[J]. Intelligent Data Analysis, 2007, 11(5): 561-580. doi: 10.3233/IDA-2007-11508 [7] LAHRECHE A, BOUCHEHAM B. A fast and accurate similarity measure for long time series classification based on local extrema and dynamic time warping[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 168: 114374. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2020.114374 [8] CHANG X, TUNG F, MORI G. Learning discriminative prototypes with dynamic time warping[C]//IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 8391-8400. [9] PAPARRIZOS J, GRAVANO L. K-Shape: Efficient and accurate clustering of time series[J]. ACM SIGMOD Record, 2016, 45(1): 69-76. doi: 10.1145/2949741.2949758 [10] CHEN H, SHU L C, XIA J, et al. Mining frequent patterns in a varying-size sliding window of online transactional data streams[J]. Information Sciences, 2012, 215: 15-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2012.05.007 [11] SCHÄFER P, LESER U. Fast and accurate time series classification with WEASEL[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 ACM on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. New York: ACM, 2017: 637-646. [12] XU F. Algorithm to remove spectral leakage, close-in noise, and its application to converter test[C]//IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2007: 1038-1042. [13] CLAEYS T, VANOOST D, PEUTEMAN J, et al. Removing the spectral leakage in time-domain based near-field scanning measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2015, 57(6): 1329-1337. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2015.2447051 [14] ABANDA A, MORI U, LOZANO J A. A review on distance based time series classification[J]. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2019, 33(2): 378-412. doi: 10.1007/s10618-018-0596-4 [15] RAKTHANMANON T, KEOGH E. Fast shapelets: A scalable algorithm for discovering time series shapelets[C]//Proceedings of the 2013 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining. Philadelphia: SIAM, 2013: 668-676. [16] LI G Z, CHOI B, XU J L, et al. Efficient shapelet discovery for time series classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2022, 34(3): 1149-1163. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2020.2995870 [17] GRABOCKA J, SCHILLING N, WISTUBA M, et al. Learning time-series shapelets[C]//Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2014: 392-401. [18] YE L, KEOGH E. Time series shapelets: A novel technique that allows accurate, interpretable and fast classification[J]. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2011, 22(1-2): 149-182. doi: 10.1007/s10618-010-0179-5 [19] JEONG Y S, JEONG M K, OMITAOMU O A. Weighted dynamic time warping for time series classification[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2011, 44(9): 2231-2240. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2010.09.022 [20] REBBAPRAGADA U, PROTOPAPAS P, BRODLEY C E, et al. Finding anomalous periodic time series[J]. Machine Learning, 2009, 74(3): 281-313. doi: 10.1007/s10994-008-5093-3 [21] HYNDMAN R J, WANG E, LAPTEV N. Large-scale unusual time series detection[C]//IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshop(ICDMW). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1616-1619. [22] IMANI S, ABDOLI A, KEOGH E. Time2Cluster: Clustering time series using neighbor information[C]//Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning(ICML). [S.l.]: [s.n.], 2021: 1-5. [23] MBOUOPDA M F. Uncertain time series classification[C]//Proceedings of the 30th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. [S.l.]: [s.n.], 2021: 4903-4904. [24] DOUZAS G, BACAO F, LAST F. Improving imbalanced learning through a heuristic oversampling method based on k-means and SMOTE[J]. Information Sciences, 2018, 465: 1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.06.056 [25] MA Q L, ZHENG Z J, ZHENG J W, et al. Joint-label learning by dual augmentation for time series classification[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2021, 35: 8847-8855. [26] KANG Q, CHEN X S, LI S S, et al. A noise-filtered under-sampling scheme for imbalanced classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(12): 4263-4274. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2016.2606104 [27] GÜNNEMANN N, PFEFFER J. Cost matters: A new example-dependent cost-sensitive logistic regression model[C]//Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Berlin: Springer, 2017: 210-222. [28] BO S. Research on the classification of high dimensional imbalanced data based on the optimizational of random forest algorithm[C]//2017 9th International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation (ICMTMA). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 228-231. [29] LEE D, LEE S, YU H. Learnable dynamic temporal pooling for time series classification[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2021, 35: 8288-8296. [30] YAMAGUCHI A, NISHIKAWA T. One-class learning time-series shapelets[C]//2018 IEEE International Conference on Big Data. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 2365-2372. [31] TAVENARD R, FAOUZI J, VANDEWIELE G, et al. Tslearn, a machine learning toolkit for time series data[J]. Journal of Machince Learning Research, 2020, 21(118): 1-6. [32] TESTA A, GALLO D, LANGELLA R. On the processing of harmonics and interharmonics: Using Hanning window in standard framework[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2004, 19(1): 28-34. doi: 10.1109/TPWRD.2003.820437 [33] GARG M, BANSAL R K, BANSAL S. Reducing power dissipation in FIR filter: An analysis[J]. Signal Processing:An International Journal (SPIJ), 2010, 4(1): 62-67. [34] CHAKRABORTY S. Advantages of Blackman window over Hamming window method for designing FIR filter[J]. International Journal of Computer Science and Engineering Technology, 2013, 4(8): 1181-1189. [35] SULISTYANINGSIH S, PUTRANTO P, QURRACHMAN T, et al. Performance comparison of Blackman, Bartlett, Hanning and Kaiser window for radar digital signal processing[C]//2019 4th International Conference on Information Technology, Information Systems and Electrical Engineering (ICITISEE). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 391-394. -






 下载:
下载: