Modeling and accuracy analysis of GNSS ionospheric error in EU-China based on GA-BP
-
摘要:
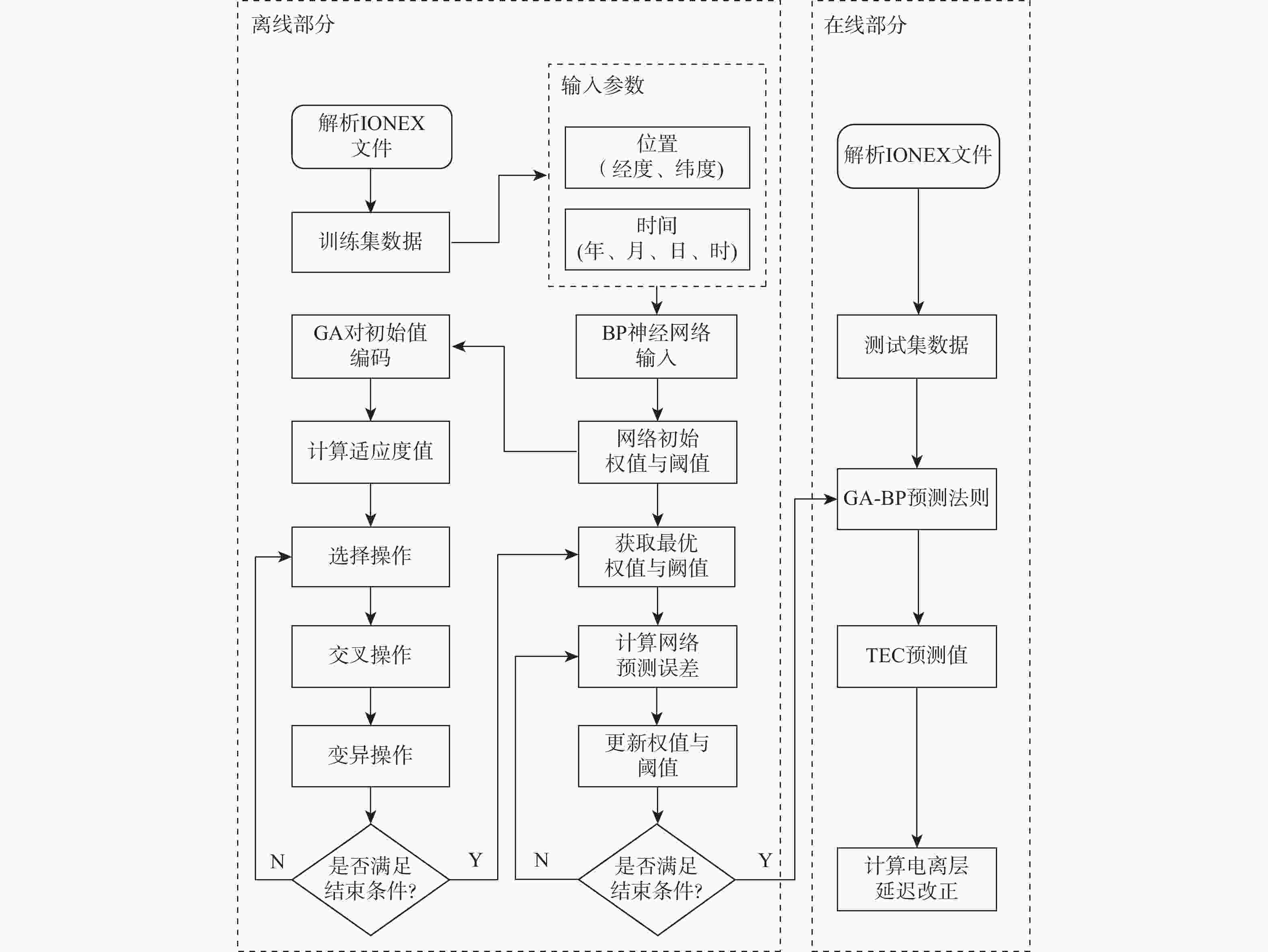
电离层误差是全球卫星导航系统 (GNSS)的主要误差来源之一,改正电离层误差的关键在于确定电离层的总电子含量(TEC)。针对现有电离层误差改正模型中存在的经验模型精度较低、球谐函数模型计算繁琐及其他模型存在的计算效率不足等问题,提出了基于遗传算法优化反向传播神经网络(GA-BP)的中欧GNSS电离层误差建模方法,并对模型精度进行了评估。通过国际GNSS服务组织(IGS)提供的TEC数据训练所提模型,挖掘了基于GA-BP模型的GNSS电离层TEC预测规则,并对不同时间和位置处的TEC值进行了短期、中期和长期预测。实验结果表明:基于GA-BP的电离层误差模型的短期预测均方根误差(RMSE)在不同纬度位置相比于自回归移动平均(ARIMA)模型分别提高了67.61%、36.33%、73.68%;在中期预测过程中的提升比例分别达到54.07%、22.36%、78.48%;在长期预测过程中的提升比例分别达到45.53%、43.78%、48.50%,能够更好地预测和拟合TEC随时间的变化情况。
Abstract:Ionospheric error is one of the main error sources of global navigation satellite system (GNSS). The key to correct ionospheric error is to determine the total electron content (TEC) of ionosphere. Aiming at the problems of low accuracy of empirical model, cumbersome calculation of spherical harmonic function model and insufficient calculation efficiency of other models in the existing ionospheric error correction model, an EU-China GNSS ionospheric error modeling method based on genetic algorithm optimized back propagation neural network (GA-BP) is proposed, and its model accuracy is evaluated. By training the model based on TEC data provided by International GNSS Service (IGS), the GNSS ionospheric TEC prediction rules based on GA-BP model are mined, and the short-term, medium-term and long-term prediction of TEC values at different time and locations are realized. The experimental results show that compared with other models, the root mean square error (RMSE) of short-term prediction of GA-BP model proposed in this paper are 67.61%, 36.33% and 73.68%, higher than that of autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) model in different latitudes. In the medium-term prediction, the improvement has reached 54.07%, 22.6% and 78.48% respectively; in the long-term prediction, the results have reached 45.53%, 43.78% and 48.50% respectively, which can better predict and fit the change of TEC with time.
-
表 1 各数据集样本数量
Table 1. Number of samples per dataset
数据集 样本数量 样本总数 低纬度 中纬度 高纬度 训练集 28 496 28 496 28 496 85 488 测试集 4745 4745 4745 14235 表 2 实验设计
Table 2. Experimental design
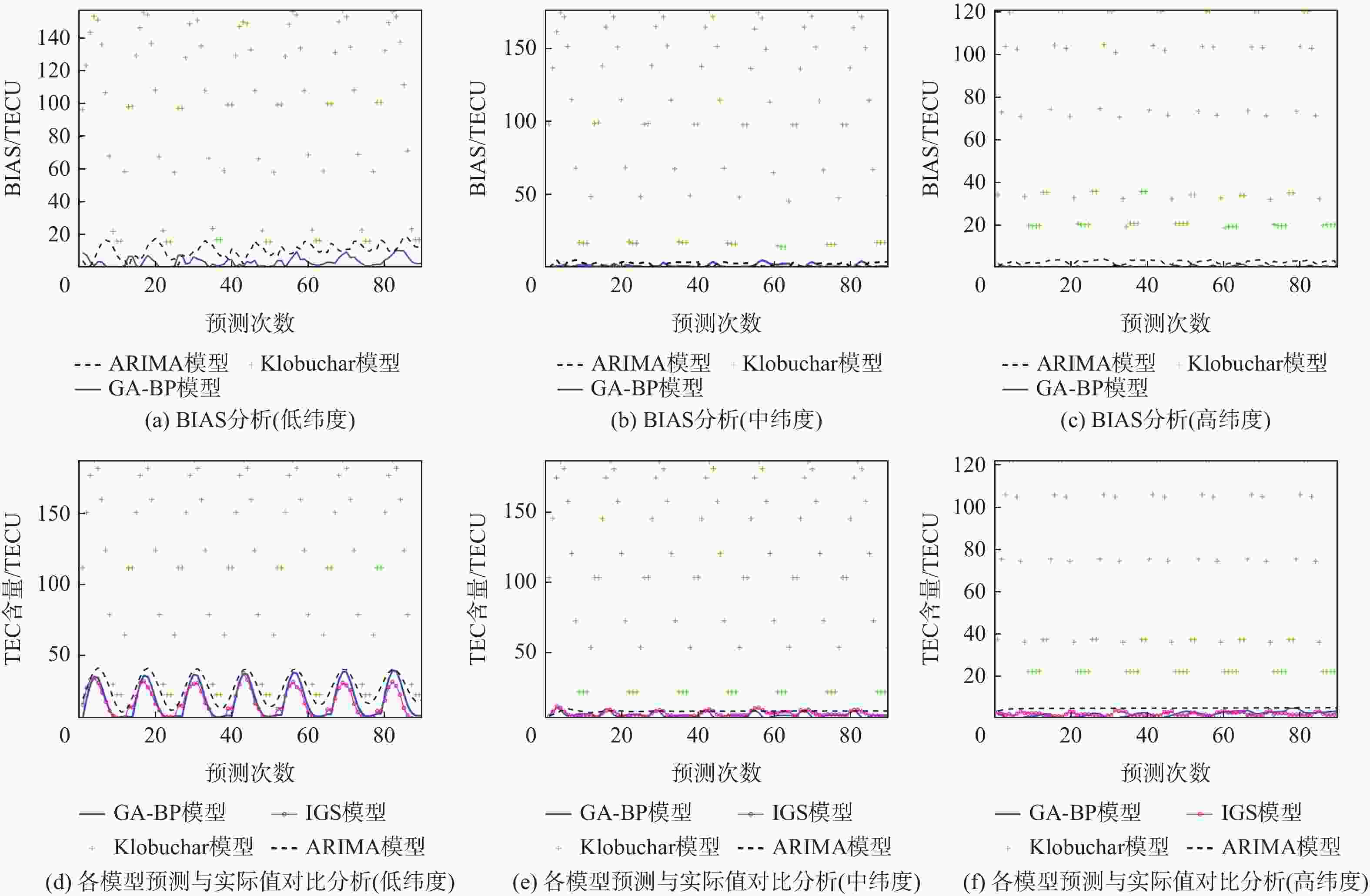
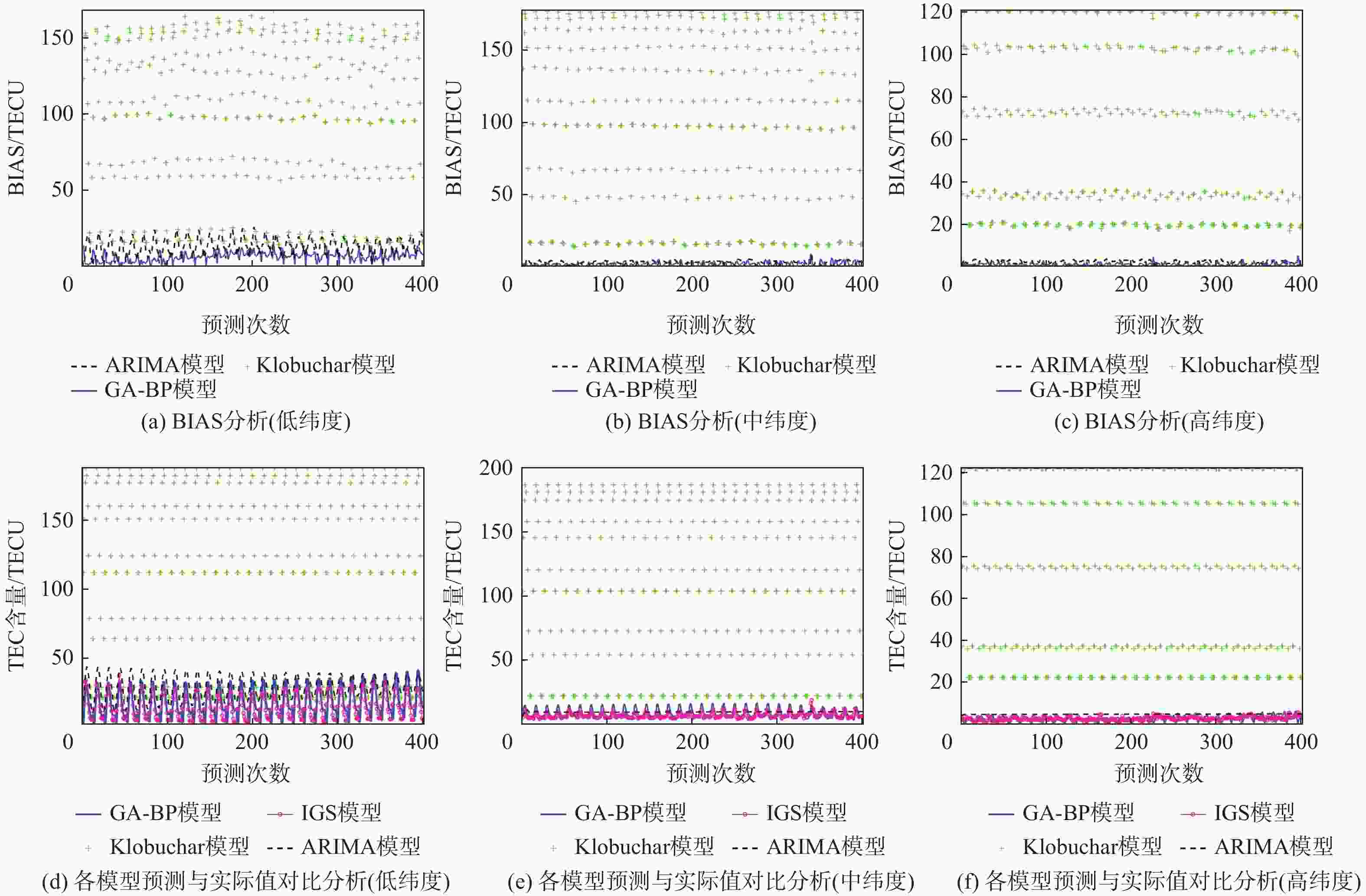
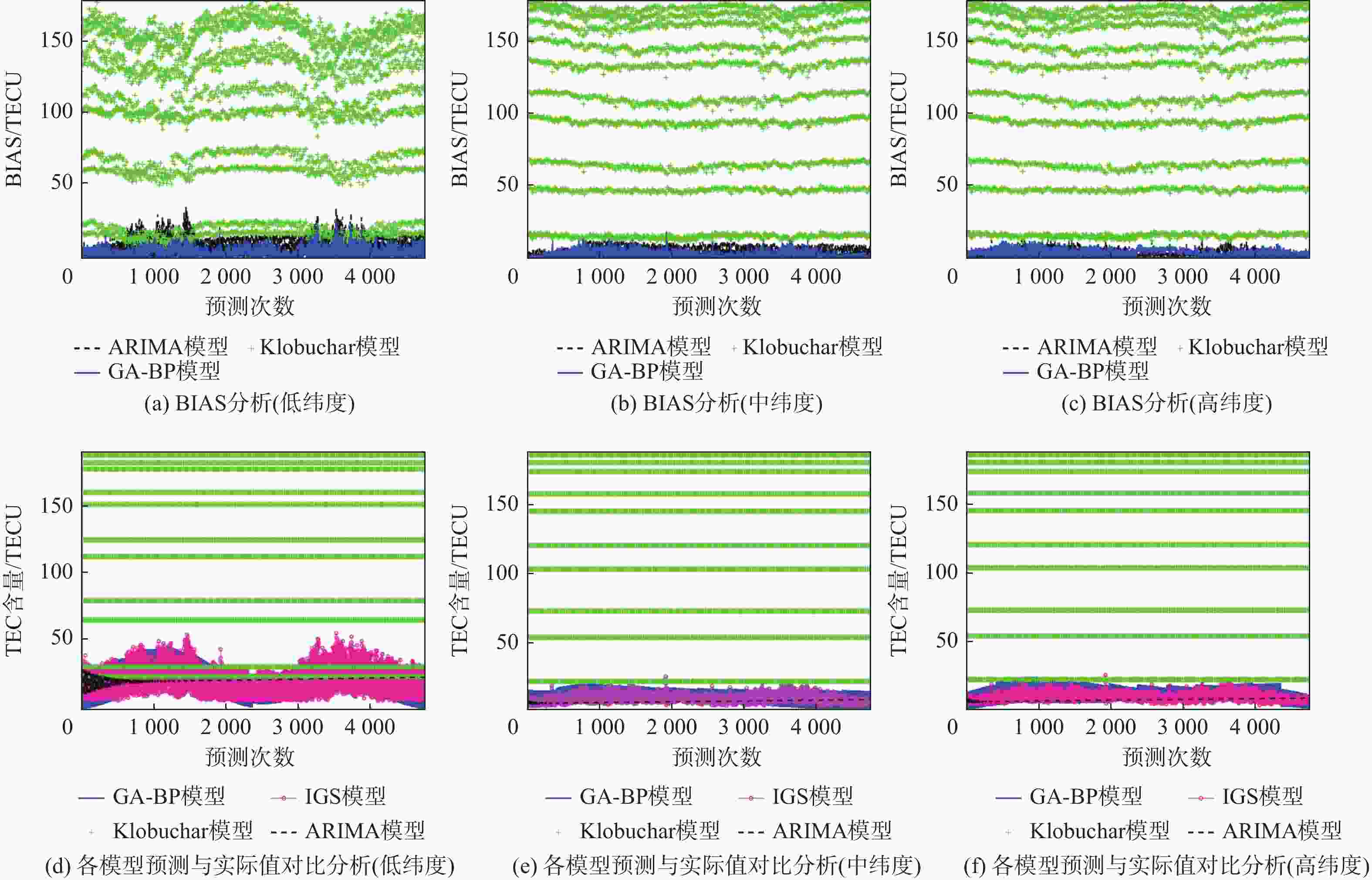
实验模型 实验1 实验2 实验3 Klobuchar 分别在3个不同纬度点处 分别在3个不同纬度点处 分别在3个不同纬度点处 ARIMA 利用各模型预测 利用各模型预测 利用各模型预报 GA-BP 未来1周的TEC变化 未来1月的TEC变化 未来1年的TEC变化 表 3 各模型短期(1周)预测精度对比
Table 3. Comparison of short-term (one week) prediction accuracy of each model
预测模型 RMSE/TECU 低纬度 中纬度 高纬度 Klobuchar 105.48 114.19 71.21 ARIMA 11.30 2.67 2.85 GA-BP 3.66 1.70 0.75 表 4 GA-BP模型短期(1周)预测精度提升率
Table 4. Improvement rate of short-term (one week) prediction accuracy of GA-BP model
% 类型 RMSE提升率 低纬度 中纬度 高纬度 相对Klobuchar模型的提升率 96.53 98.51 98.95 相对ARIMA模型的提升率 67.61 36.33 73.68 表 5 各模型中期(1月)预测精度对比
Table 5. Comparison of medium-term (one month) prediction accuracy of each model
预测模型 RMSE/TECU 低纬度 中纬度 高纬度 Klobuchar 105.07 113.76 70.92 ARIMA 14.50 3.31 3.95 GA-BP 6.66 2.57 0.85 表 6 GA-BP模型中期(1月)预测精度提升率
Table 6. Improvement rate of medium-term (one month) prediction accuracy of GA-BP model
% 类型 RMSE提升率 低纬度 中纬度 高纬度 相对Klobuchar模型的提升率 93.66 97.74 98.80 相对ARIMA模型的提升率 54.07 22.36 78.48 表 7 各模型长期(1年)预测精度对比
Table 7. Comparison of long-term (one year) prediction accuracy of each model
预测模型 RMSE/TECU 低纬度 中纬度 高纬度 Klobuchar 103.53 98.23 67.95 ARIMA 10.52 6.67 4.33 GA-BP 5.73 3.75 2.23 表 8 GA-BP模型长期(1年)预测精度提升率
Table 8. Improvement rate of long-term (one year) prediction accuracy of GA-BP model
% 类型 RMSE提升率 低纬度 中纬度 高纬度 相对Klobuchar模型的提升率 94.47 96.18 96.72 相对ARIMA模型的提升率 45.53 43.78 48.50 -
[1] 王松寒. 区域电离层延迟改正及预报模型研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2016.WANG S H. Research on the delay correction model and forecasting model of regional ionosphere[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2016(in Chinese). [2] 张小红, 李征航, 蔡昌盛. 用双频GPS观测值建立小区域电离层延迟模型研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2001, 26(2): 140-143.ZHANG X H, LI Z H, CAI C S. Study on regional ionospheric model using dual-frequency GPS measurements[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2001, 26(2): 140-143(in Chinese). [3] 魏传军. 基于地基GNSS观测数据的电离层延迟改正研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2014.WEI C J. Study of ionospheric delay correction based on ground-based GNSS observations[D]. Xi’an: Changan University, 2014(in Chinese). [4] 李涌涛, 赵昂, 李建文, 等. 单站区域电离层TEC建模及精度分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2022, 47(1): 69-78.LI Y T, ZHAO A, LI J W, et al. Regional ionospheric TEC modeling and accuracy analysis based on observations from a station[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2022, 47(1): 69-78(in Chinese). [5] 张小红, 任晓东, 吴风波, 等. 自回归移动平均模型的电离层总电子含量短期预报[J]. 测绘学报, 2014, 43(2): 118-124.ZHANG X H, REN X D, WU F B, et al. Short-term TEC prediction of ionosphere based on ARIMA model[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2014, 43(2): 118-124(in Chinese). [6] 唐宏, 唐诗华, 陈雨田, 等. Holt-Winters与ARIMA模型在电离层总电子含量预报中的比较[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2019, 39(4): 905-911.TANG H, TANG S H, CHEN Y T, et al. Comparison of Holt-Winters and ARIMA models for TEC forecasting[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2019, 39(4): 905-911(in Chinese). [7] 张禄. 基于时间序列、神经网络、灰色和组合预测对电离层TEC的预测研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2012.ZHANG L. Based on the time series, neural network, grey and combination forecasting of ionospheric tec forecast research[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, 2012(in Chinese). [8] 谢劭峰, 陈军, 黄良珂, 等. 基于Holt-Winters的电离层总电子含量预报[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2017, 37(1): 72-76.XIE S F, CHEN J, HUANG L K, et al. Ionospheric TEC prediction based on Holt-Winters models[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2017, 37(1): 72-76(in Chinese). [9] 陈鹏, 姚宜斌, 吴寒. 利用时间序列分析预报电离层TEC[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2011, 36(3): 267-270.CHEN P, YAO Y B, WU H. TEC prediction of ionosphere based on time series analysis[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2011, 36(3): 267-270(in Chinese). [10] 刘先冬, 宋力杰, 杨晓晖, 等. 基于小波神经网络的电离层TEC短期预报[J]. 海洋测绘, 2010, 30(5): 49-51.LIU X D, SONG L J, YANG X H, et al. Predicting shortdated ionospheric TEC based on wavelet neural network[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2010, 30(5): 49-51(in Chinese). [11] 李淑慧. 基于混沌理论的GPS电离层预测研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2010.LI S H. GPS ionospheric prediction research based on chaotic theory[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2010(in Chinese). [12] 张富彬, 周晨, 王成, 等. 基于深度学习的全球电离层TEC预测[J]. 电波科学学报, 2021, 36(4): 553-561.ZHANG F B, ZHOU C, WANG C, et al. Global ionospheric TEC prediction based on deep learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2021, 36(4): 553-561(in Chinese). [13] 袁天娇, 陈艳红, 刘四清, 等. 基于深度学习递归神经网络的电离层总电子含量经验预报模型[J]. 空间科学学报, 2018, 38(1): 48-57. doi: 10.11728/cjss2018.01.048YUAN T J, CHEN Y H, LIU S Q, et al. Prediction model for ionospheric total electron content based on deep learning recurrent neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2018, 38(1): 48-57(in Chinese). doi: 10.11728/cjss2018.01.048 [14] 李淑慧, 彭军还, 徐伟超, 等. 利用神经网络预报短期电离层TEC变化[J]. 测绘科学, 2013, 38(1): 8-9.LI S H, PENG J H, XU W C, et al. Short-term ionospheric TEC change prediction by neural network[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2013, 38(1): 8-9(in Chinese). [15] 李征航, 黄劲松. GPS测量与数据处理[M]. 武汉: 武汉大学出版社, 2005.LI Z H, HUANG J S. GPS surveying and data processing[M]. Wuhan: Wuhan University Press, 2005(in Chinese). [16] 李萍, 曾令可, 税安泽, 等. 基于MATLAB的BP神经网络预测系统的设计[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2008, 25(4): 149-150.LI P, ZENG L K, SHUI A Z, et al. Design of forecast of back propagation neural network based on MATLAB[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2008, 25(4): 149-150(in Chinese). [17] 边霞, 米良. 遗传算法理论及其应用研究进展[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2010, 27(7): 2425-2429.BIAN X, MI L. Development on genetic algorithm theory and its applications[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2010, 27(7): 2425-2429(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: