-
摘要:
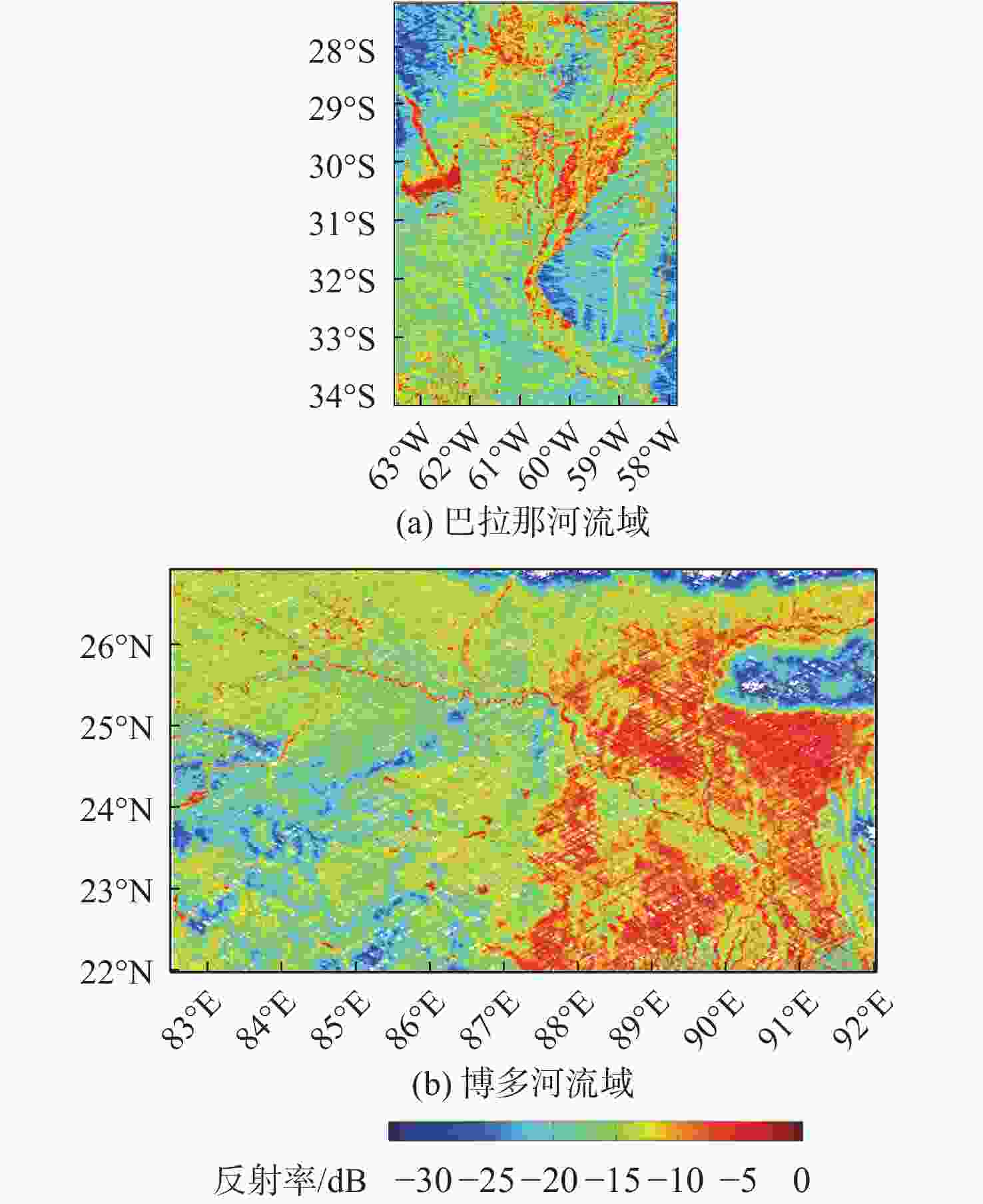
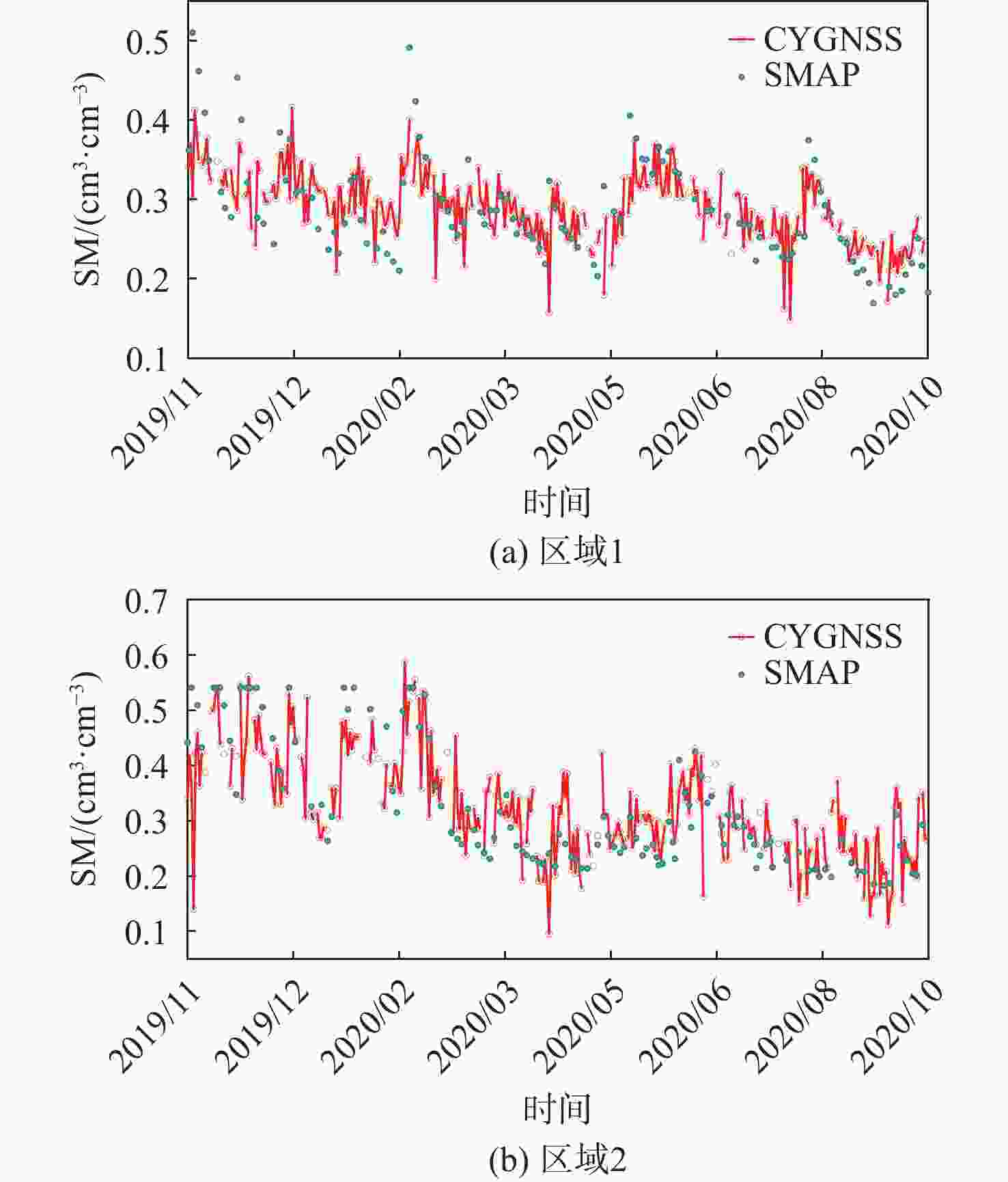
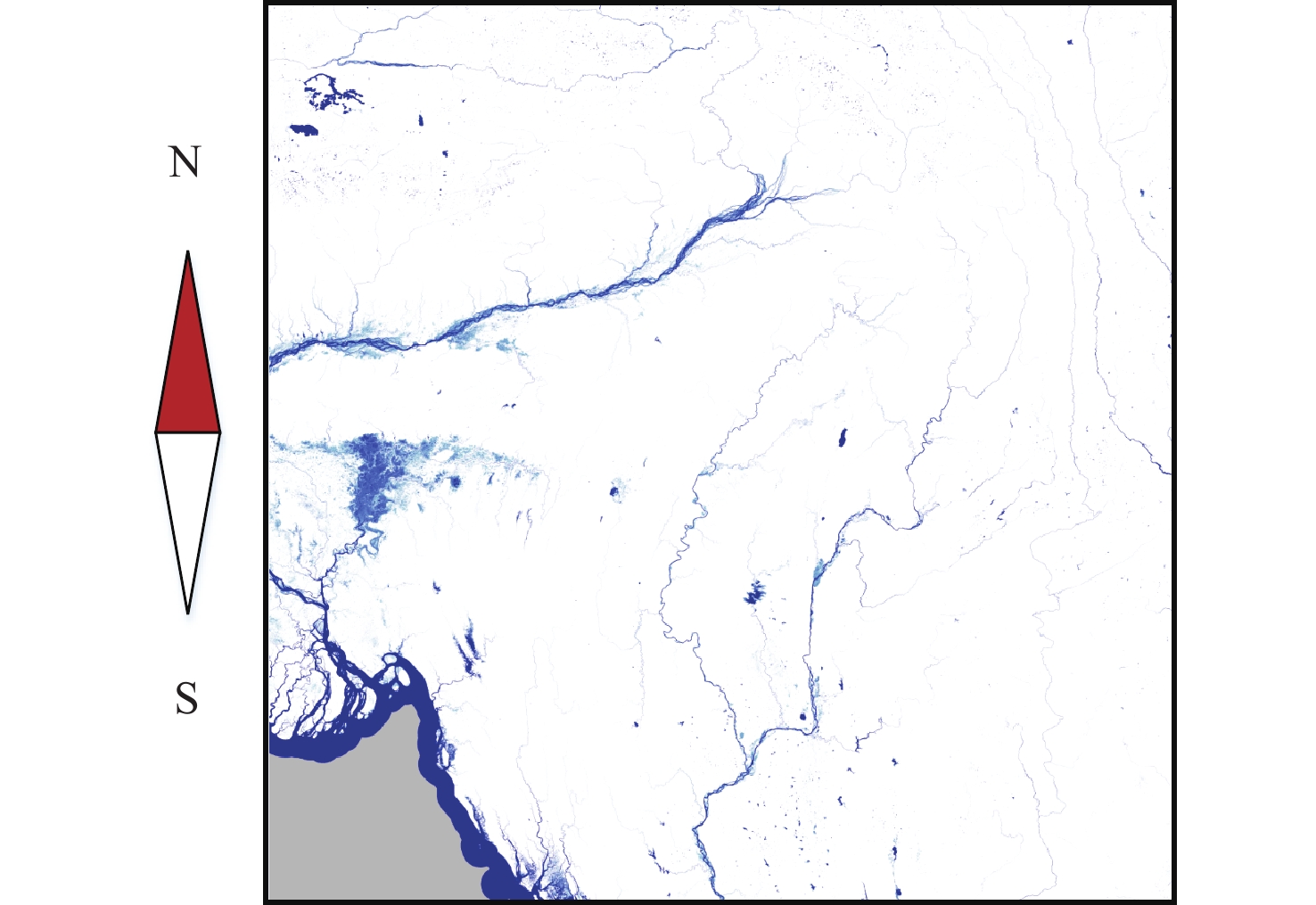
通过星载全球导航卫星系统-反射测量(GNSS-R)技术可以获取高时空分辨率的土壤湿度(SM)信息,但开放水域会影响反演结果的精度。针对此问题,提出一种开放水域剔除的改进方法。校正其模拟功率得出反射率,结合掩膜数据精确剔除开放水域。为验证改进方法的可行性,处理了2个开放水域比较密集的试验区内为期一年的飓风全球导航卫星系统(CYGNSS) 1级数据。反演结果与主被动土壤湿度(SMAP)3级土壤湿度产品进行对比分析,其均方根误差为0.052 1 cm3/cm3,相关性为0.654。与开放水域剔除前的结果相比分别提升6.2%和9%;与CYGNSS官方发布的产品相比分别提升32%和24%。反演结果可以作为SMAP的SM补充,提供高时间分辨率的SM值。
-
关键词:
- 全球导航卫星系统-反射测量 /
- 土壤湿度 /
- 开放水域 /
- 飓风全球导航卫星系统 /
- 主被动土壤湿度
Abstract:Soil moisture(SM) information can be obtained through the high spatial and temporal resolution spaceborne GNSS-R technology, however, open water will affect the accuracy of the retrieval results. To solve this problem, this paper proposes an improved method of removing open water. Prior to precisely removing the open water region based on the mask data, the simulated power must first be corrected to achieve the reflectivity.In order to verify the feasibility of the improved method, a one-year CYGNSS level 1 data was processed in two test areas with dense open water. The retrieval result was compared and analyzed with the soil moisture active passive (SMAP) level 3 soil moisture product. The root mean square error was 0.052 1 cm3/cm3, and the correlation was 0.654. Compared with the results before removing open water, it increased by 6.2% and 9%, respectively; Compared with the products officially released by CYGNSS, it increased by 32% and 24%. As a result, the retrieval results can be utilized to complement SMAP of SM measurements by providing highly time-resolved SM values.
-
表 1 式(4)中变量和所对应的CYGNSS数据集参数
Table 1. Variables in Eq. (4) and corresponding CYGNSS dataset parameters
变量 CYGNSS数据集参数 $ {P}_{\mathrm{r}}^{\mathrm{t}}{G}^{\mathrm{t}} $ gps_eirp $ {G}^{\mathrm{r}} $ sp_rx_gain $ {R}_{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{s}} $ tx_to_sp_range $ {R}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{r}} $ rx_to_sp_range 表 2 开放水域剔除后的CYGNSS的SM反演结果
Table 2. CYGNSS of SM retrieval results after removing open water
区域 R RMSE/ (cm3·cm−3) 巴拉那河流域 0.616 7 0.045 8 博多河流域 0.673 4 0.056 2 2个区域总计 0.653 7 0.052 1 表 3 未考虑开放水域CYGNSS的SM反演结果
Table 3. CYGNSS of SM inversion results without considering open water
区域 R RMSE/ (cm3·cm−3) 巴拉那河流域 0.5700 0.0477 博多河流域 0.6313 0.0589 2个区域总计 0.6019 0.0553 表 4 UCAR\CU的SM反演结果
Table 4. Retrieval results of SM from UCAR\CU
区域 R RMSE/ (cm3·cm−3) 巴拉那河流域 0.522 1 0.085 0 博多河流域 0.529 6 0.073 6 2个区域总计 0.527 6 0.076 8 -
[1] ENTEKHABI D, RODRIGUEZ-ITURBE I, CASTELLI F. Mutual interaction of soil moisture state and atmospheric processes[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1996, 184(1-2): 3-17. doi: 10.1016/0022-1694(95)02965-6 [2] KUENZER C, GUO H D, HUTH J, et al. Flood mapping and flood dynamics of the Mekong delta: ENVISAT-ASAR-WSM based time series analyses[J]. Remote Sensing, 2013, 5(2): 687-715. doi: 10.3390/rs5020687 [3] 杨东凯, 张其善. GNSS反射信号处理基础与实践[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2012.YANG D K, ZHANG Q S. GNSS reflected signal processing: Fundamentals and applications[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2012 (in Chinese). [4] 李黄, 夏青, 尹聪, 等. 我国GNSS-R遥感技术的研究现状与未来发展趋势[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(4): 389-399.LI H, XIA Q, YIN C, et al. The Current status of research on GNSS-R remote sensing technology in China and future development[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(4): 389-399(in Chinese). [5] 汉牟田, 张波, 杨东凯, 等. 利用GNSS干涉信号振荡幅度反演土壤湿度[J]. 测绘学报, 2016, 45(11): 1293-1300. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2016.20160145HAN M T, ZHANG B, YANG D K, et al. Soil moisture retrieval utilizing GNSS interference signal amplitude[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2016, 45(11): 1293-1300(in Chinese). doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2016.20160145 [6] 严颂华, 龚健雅, 张训械, 等. GNSS-R测量地表土壤湿度的地基实验[J]. 地球物理学报, 2011, 54(11): 2735-2744. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.11.003YAN S H, GONG J Y, ZHANG X X, et al. Ground based GNSS-R observations for soil moisture[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2011, 54(11): 2735-2744(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.11.003 [7] FOTI G, GOMMENGINGER C, JALES P, et al. Spaceborne GNSS reflectometry for ocean winds: First results from the UK TechDemoSat-1 mission[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(13): 5435-5441. doi: 10.1002/2015GL064204 [8] CHEW C, SHAH R, ZUFFADA C, et al. Demonstrating soil moisture remote sensing with observations from the UK TechDemoSat-1 satellite mission[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43(7): 3317-3324. doi: 10.1002/2016GL068189 [9] CAMPS A, PARK H, PABLOS M, et al. Sensitivity of GNSS-R spaceborne observations to soil moisture and vegetation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(10): 4730-4742. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2588467 [10] YAN Q Y, HUANG W M, JIN S G, et al. Pan-tropical soil moisture mapping based on a three-layer model from CYGNSS GNSS-R data[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2020, 247: 111944. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2020.111944 [11] CHEW C C, SMALL E E. Soil moisture sensing using spaceborne GNSS reflections: Comparison of CYGNSS reflectivity to SMAP soil moisture[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(9): 4049-4057. doi: 10.1029/2018GL077905 [12] KIM H, LAKSHMI V. Use of cyclone global navigation satellite system (CyGNSS) observations for estimation of soil moisture[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(16): 8272-8282. doi: 10.1029/2018GL078923 [13] CLARIZIA M P, PIERDICCA N, COSTANTINI F, et al. Analysis of CYGNSS data for soil moisture retrieval[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12(7): 2227-2235. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2895510 [14] DONG Z N, JIN S G. Evaluation of the land GNSS-reflected DDM coherence on soil moisture estimation from CYGNSS data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(4): 570. doi: 10.3390/rs13040570 [15] YANG T, WAN W, SUN Z G, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of using TechDemoSat-1 and CYGNSS data to estimate soil moisture over mainland China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(11): 1699. doi: 10.3390/rs12111699 [16] CHEW C, SMALL E. Description of the UCAR/CU soil moisture product[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(10): 1558. doi: 10.3390/rs12101558 [17] RUF C S, ATLAS R, CHANG P S, et al. New Ocean winds satellite mission to probe hurricanes and tropical convection[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2016, 97(3): 385-395. doi: 10.1175/BAMS-D-14-00218.1 [18] RUF C, ASHARAF S, BALASUBRAMANIAM R, et al. In-orbit performance of the constellation of CYGNSS hurricane satellites[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2019, 100(10): 2009-2023. doi: 10.1175/BAMS-D-18-0337.1 [19] PEKEL J F, COTTAM A, GORELICK N, et al. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes[J]. Nature, 2016, 540(7633): 418-422. doi: 10.1038/nature20584 [20] ENTEKHABI D, NJOKU E G, O'NEILL P E, et al. The soil moisture active passive (SMAP) mission[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2010, 98(5): 704-716. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2010.2043918 [21] NGHIEM S V, ZUFFADA C, SHAH R, et al. Wetland monitoring with global navigation satellite system reflectometry[J]. Earth and Space Science, 2017, 4(1): 16-39. doi: 10.1002/2016EA000194 [22] ZAVOROTNY V U, VORONOVICH A G. Scattering of GPS signals from the ocean with wind remote sensing application[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(2): 951-964. doi: 10.1109/36.841977 [23] VORONOVICH A G, ZAVOROTNY V U. Bistatic radar equation for signals of opportunity revisited[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 56(4): 1959-1968. [24] DE ROO R D, ULABY F T. Bistatic specular scattering from rough dielectric surfaces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1994, 42(2): 220-231. doi: 10.1109/8.277216 [25] ULABY F T, LONG D G, BLACKWELL W, et al. Microwave radar and radiometric remote sensing[M]. Norwood: Artech House, 2013. [26] WANG T L, RUF C S, BLOCK B, et al. Design and performance of a GPS constellation power monitor system for improved CYGNSS L1B calibration[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 12(1): 26-36. [27] RODRIGUEZ-ALVAREZ N, PODEST E, JENSEN K, et al. Classifying inundation in a tropical wetlands complex with GNSS-R[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(9): 1053. doi: 10.3390/rs11091053 [28] YANG W T, XU T H, WANG N Z, et al. Research on the method of precisely removing open water in the retrieval of soil moisture by spaceborne GNSS-R[C]//Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering. Singapore: Springer Singapore, 2021: 22-32. [29] CAMPS A, PARK H, CASTELLVÍ J, et al. Single-pass soil moisture retrievals using GNSS-R: Lessons learned[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(12): 2064. doi: 10.3390/rs12122064 -






 下载:
下载: