-
摘要:
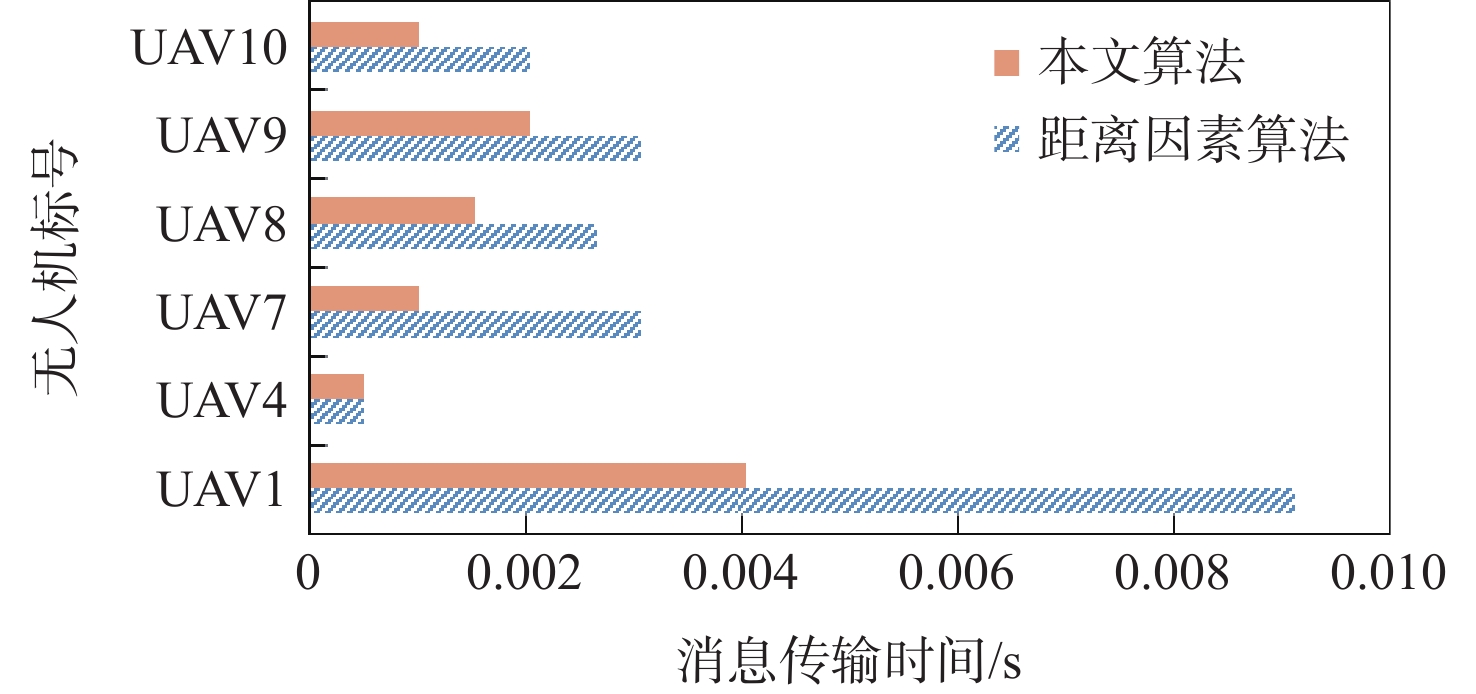
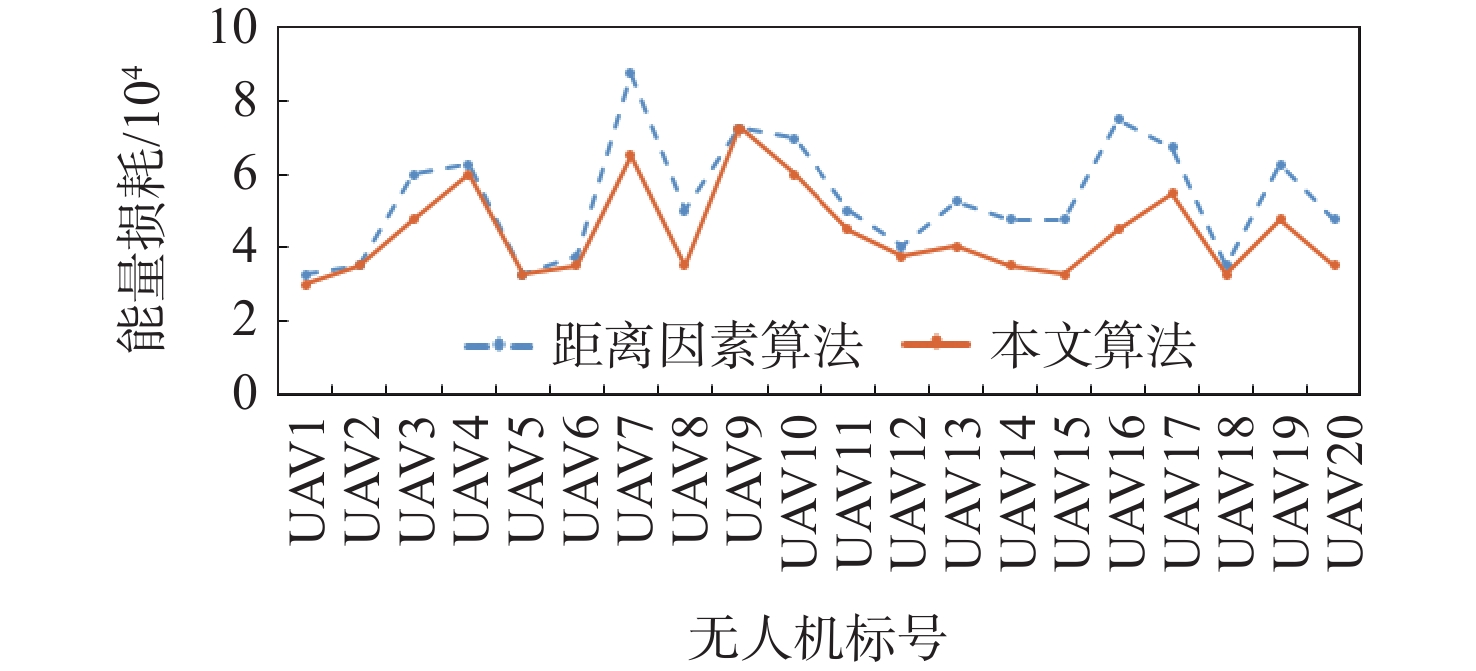
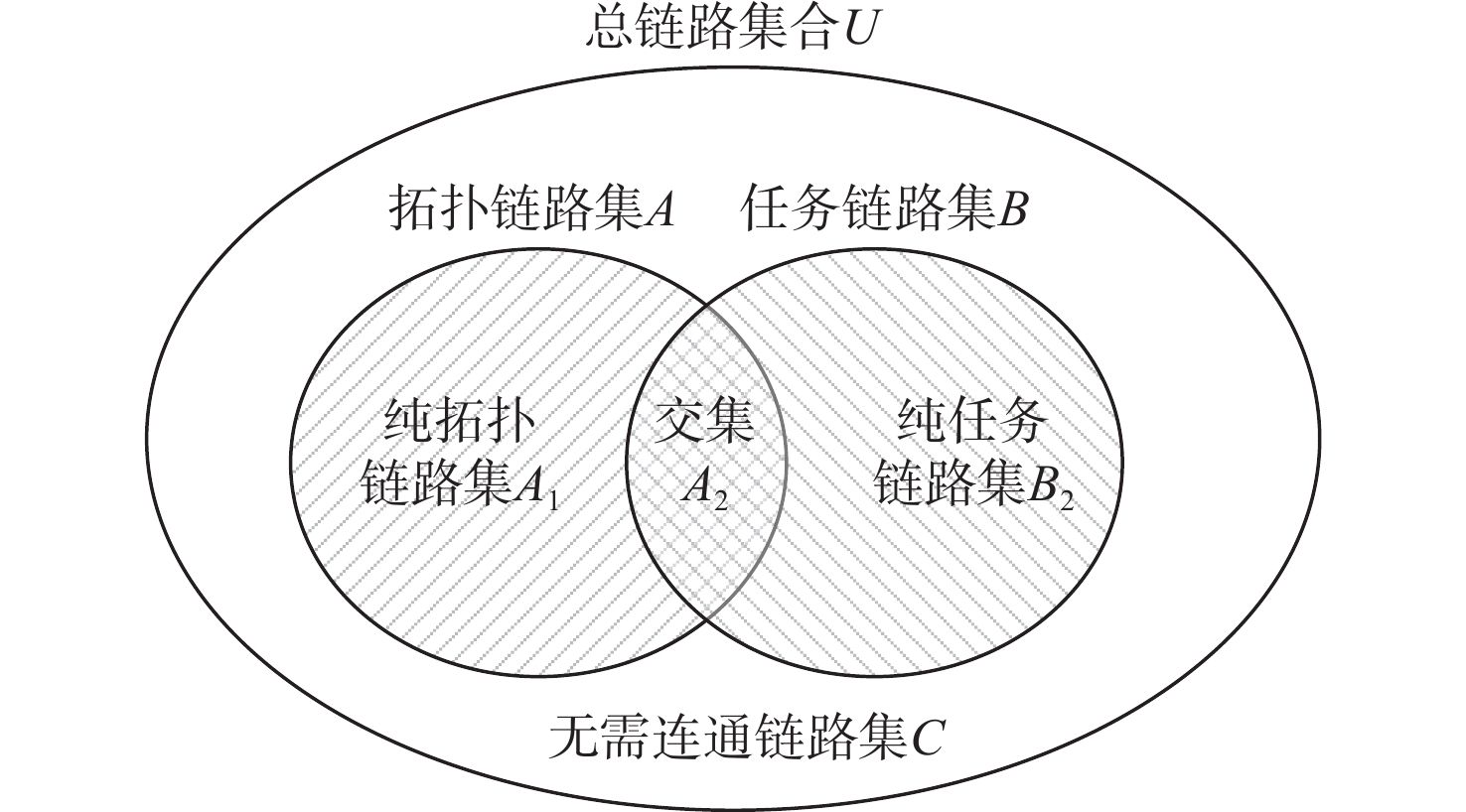
无人机(UAV)持久编队信息交互拓扑的优化是保证UAV编队结构稳定性和任务执行时效性的重要基础。现有的编队生成算法针对距离因素进行权重赋值和拓扑生成,由于未考虑任务分配因素,可能会引起整体任务执行时间过长甚至任务失败的问题,对UAV的能量也造成了不必要的损耗。以任务消息传输时间和能量损耗为关键优化目标,在保证UAV编队结构稳定的前提下,提出考虑任务分配因素的信息交互拓扑生成算法,优先连接承载实时性要求较高通信任务的关键汇聚链路,对剩余链路通过引入惩罚项,在权重上进一步将任务消息传输量因素考虑在内,生成最终的信息交互拓扑。使用OMNet++进行仿真验证,相比于只考虑距离因素的信息交互拓扑生成算法,所提算法在20架UAVs编队场景下,消息传输时间方面最高降低57.3%,最低降低28.1%,关键任务消息的到达时延降低了45.2%~51.6%,而任务执行过程单UAV的能量损耗总体减少了17.5%,平均每个节点减少损耗16.1%。
Abstract:The optimization of information interaction topology for persistent unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) formation is an important basis for the stability of UAV formation structure and the timeliness of task execution. The existing formation generation algorithms assign weights and generate topologies based on the factor of distance rather than task allocation; therefore, the overall task execution may be too long or even fail, causing unnecessary loss of UAV energy. This study proposes an information interaction topology optimization algorithm considering the factor of task allocation, with the task message transmission time and energy loss being the key optimization objectives, and with the premise of ensuring the stability of UAV formation structure. The key aggregation links performing high real-time communication tasks are preferentially connected, and the penalty term is introduced for the remaining links. Furthermore, the weight factor of task message transmission is taken into account to generate the final information interaction topology. OMNet++ is used for simulation verification. Compared with the information interaction topology generation algorithm considering only the distance factor, the algorithm considering the task factor can reduce the message transmission time by 57.3% and 28.1% at the highest and lowest levels in the formation scenario of 20 UAVs, respectively. The arrival delay of mission-critical messages is reduced by 45.2% to 51.6%. During the mission execution, the energy loss of a single UAV is reduced by 17.5% overall, and the loss per node is reduced by 16.1% on average.
-
表 1 任务列表
Table 1. Task list
任务组 任务 时间/s 耗费资源 后继任务 目标侦测 TD1 20 3 TD3 TD2 16 4 TD3 TD3 20 8 TP1 搜索锁定 TT1 13 7 TT2 TT2 20 10 TP1 综合导航 TN1 10 4 TN5 TN2 17 4 TN5 TN3 14 4 TN5 TN4 13 5 TN5 TN5 20 9 信息融合 TP1 20 3 TP3,TF1,TF2 TP2 16 1 TP3,TF1,TF2 TP3 20 6 TN5 火力攻击 TF1 14 10 TF3 TF2 13 10 TF3 TF3 18 10 表 2 任务分配方案
Table 2. Task assignment scheme
编号 任务 对应无人机 后继任务 1 TD1 UAV1 TD3 2 TD2 UAV2 TD3 3 TD3 UAV1 TP1 4 TT1 UAV3 TT2 5 TT2 UAV4 TP1 6 TN1 UAV2 TN5 7 TN2 UAV3 TN5 8 TN3 UAV6 TN5 9 TN4 UAV5 TN5 10 TN5 UAV1 11 TP1 UAV8 TP3,TF1,TF2 12 TP2 UAV7 TP3,TF1,TF2 13 TP3 UAV8 TN5 14 TF1 UAV9 TF3 15 TF2 UAV10 TF3 16 TF3 UAV7 -
[1] LUO F, JIANG C X, DU J, et al. A distributed gateway selection algorithm for UAV networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 2014, 3(1): 22-33. [2] DUTTA R, SUN L, PACK D. A decentralized formation and network connectivity tracking controller for multiple unmanned systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2018, 26(6): 2206-2213. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2017.2740837 [3] HE B, ZHANG X Y, LI Q Y. Effectiveness measurement of UAV combat in uncertain environment[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2018, 1069(1): 012048. [4] 董文奇, 何锋. 大规模UAV编队信息交互拓扑的分级分布式生成[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(6): 324380.DONG W Q, HE F. Hierarchical and distributed generation of information interaction topology for large scale UAV formation[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(6): 324380(in Chinese). [5] LI W, WANG L, LI H B. Design of distributed time-cooperative guidance of multiple flight vehicles with un-controllable velocity[C]//2019 Chinese Control and Decision Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 2419-2425. [6] 王国强. 面向队形保持的无人机编队信息交互拓扑优化问题的研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2016: 19.WANG G Q. Research on information exchange topology optimization problem of UAV formation during formation keeping[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2016: 19 (in Chinese) . [7] PRIOLO A, WILLIAMS R K, GASPARRI A, et al. Decentralized algorithms for optimally rigid network constructions[C]//2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 5010-5015. [8] HENDRICKX J M, ANDERSON B D O, DELVENNE J C, et al. Directed graphs for the analysis of rigidity and persistence in autonomous agent systems[J]. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2007, 17(10-11): 960-981. doi: 10.1002/rnc.1145 [9] 赵诗雪, 赵太飞, 刘昆, 等. 基于无线紫外光MIMO通信的优化持久编队算法[J]. 激光杂志, 2020, 41(10): 8-13. doi: 10.14016/j.cnki.jgzz.2020.10.008ZHAO S X, ZHAO T F, LIU K, et al. Algorithm on optimal persistent formation based on wireless ultraviolet MIMO communication[J]. Laser Journal, 2020, 41(10): 8-13(in Chinese). doi: 10.14016/j.cnki.jgzz.2020.10.008 [10] 罗贺, 李晓多, 王国强. 能耗均衡的三维最优持久编队通信拓扑生成[J]. 航空学报, 2022, 43(1): 324922.LUO H, LI X D, WANG G Q. Generation of three dimensional optimal persistent formation communication topology with energy consumption equilibrium[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(1): 324922(in Chinese). [11] 王金然, 罗小元, 杨帆, 等. 三维最优持久编队拓扑生成策略[J]. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(6): 1123-1130. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2015.c140474WANG J R, LUO X Y, YANG F, et al. Generation strategy of optimal persistent formation topology in 3D space[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(6): 1123-1130(in Chinese). doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2015.c140474 [12] REN W. Consensus strategies for cooperative control of vehicle formations[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2007, 1(2): 505-512. [13] LUO X Y, SHAO S K, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Generation of minimally persistent circle formation for a multi-agent system[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2014, 23(2): 614-622. [14] EREN T, ANDERSON B, MORSE A S, et al. Operations on rigid formations of autonomous agents[J]. Communications in Information and Systems, 2003, 3(4): 223-258. doi: 10.4310/CIS.2003.v3.n4.a2 [15] LUO X Y, LI S B, GUAN X P. Automatic generation of Min-weighted persistent formations[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2009, 18(8): 3104-3114. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/18/8/002 [16] 罗小元, 杨帆, 李绍宝, 等. 多智能体系统的最优持久编队生成策略[J]. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(7): 1311-1319.LUO X Y, YANG F, LI S B, et al. Generation of optimally persistent formation for multi-agent systems[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(7): 1311-1319(in Chinese). [17] 邵士凯. 多智能体系统最优持久编队生成与圆形编队控制[D]. 秦皇岛: 燕山大学, 2013: 1-66.SHAO S K. Optimally persistent formation generation and circle formation control for multi-agent syetems[D]. Qinhuangdao: Yanshan University, 2013: 1-66 (in Chinese). [18] 刘伟, 周绍磊, 祁亚辉, 等. 有向切换通信拓扑下多无人机分布式编队控制[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2015, 32(10): 1422-1427. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2015.50478LIU W, ZHOU S L, QI Y H, et al. Distributed formation control for multiple unmanned aerial vehicles with directed switching communication topologies[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2015, 32(10): 1422-1427(in Chinese). doi: 10.7641/CTA.2015.50478 [19] 程潇. 无人机编队组网技术研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2019: 25-38.CHENG X. Research on networking techniques of unmanned aerial vehicle formation[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2019: 25-38 (in Chinese). [20] 张小庆, 胡亚捷. 基于优先级与关键路径的工作流任务调度算法研究[J]. 武汉轻工大学学报, 2021, 40(2): 59-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-7386.2021.02.011ZHANG X Q, HU Y J. Research on workflow tasks scheduling algorithm based on priority and critical path[J]. Journal of Wuhan Polytechnic University, 2021, 40(2): 59-67(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-7386.2021.02.011 [21] 邓启波. 多无人机协同任务规划技术研究[D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2014: 28-55.DENG Q B. Cooperative task planning of multiple unmanned aerial vehicles[D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2014: 28-55 (in Chinese) . [22] 马霓, 孙礼, 贾群力, 等. 无线通信网络中点到点对等通信无线链接建立和保持的方法与装置: 中国, CN1527623A[P]. 2004-09-08.MA N, SUN L, JIA Q L, et al. Method and apparatus for establishing and retaining point-to-point communication radio chaining in radio communication network: China, CN1527623A[P]. 2004-09-08 (in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: