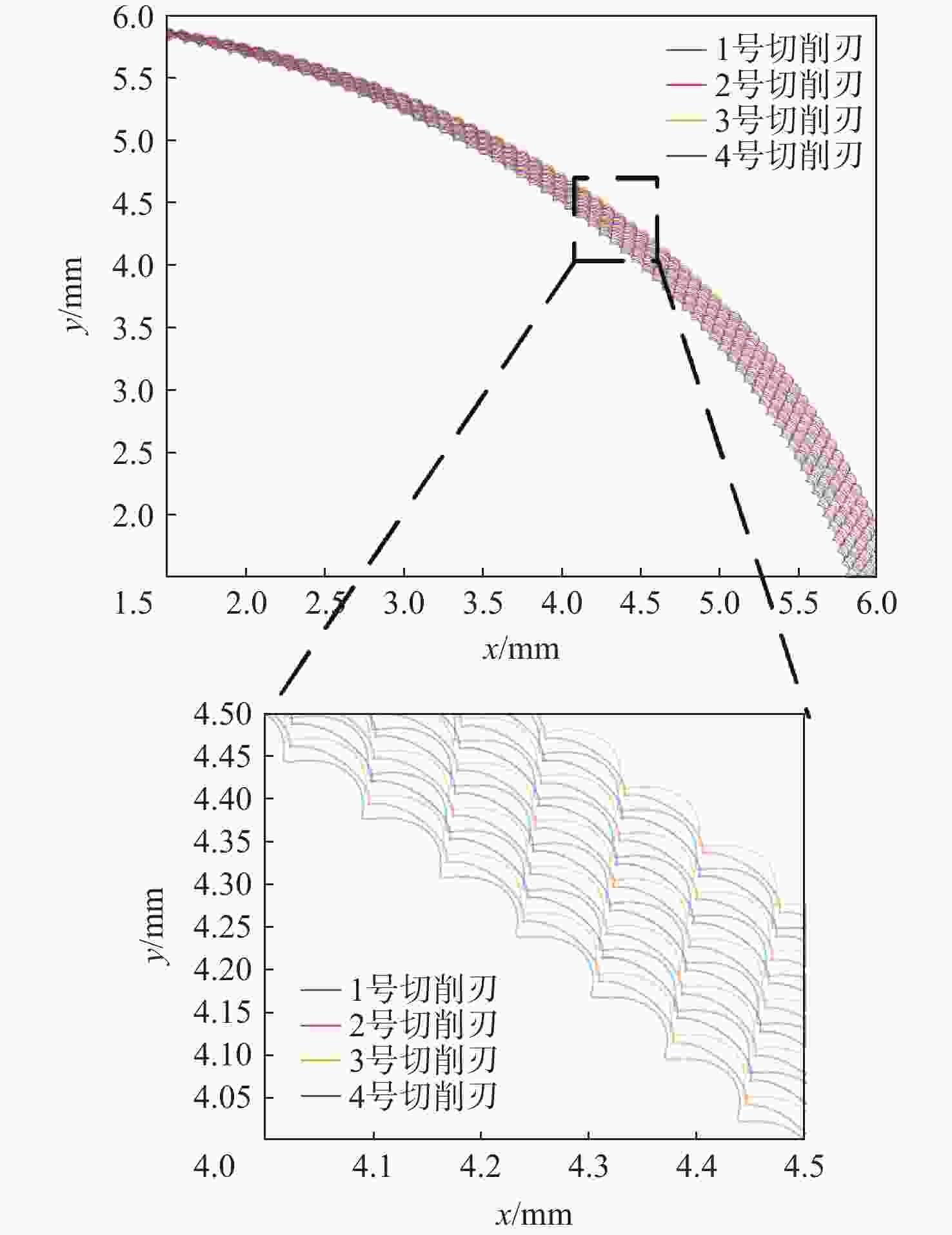
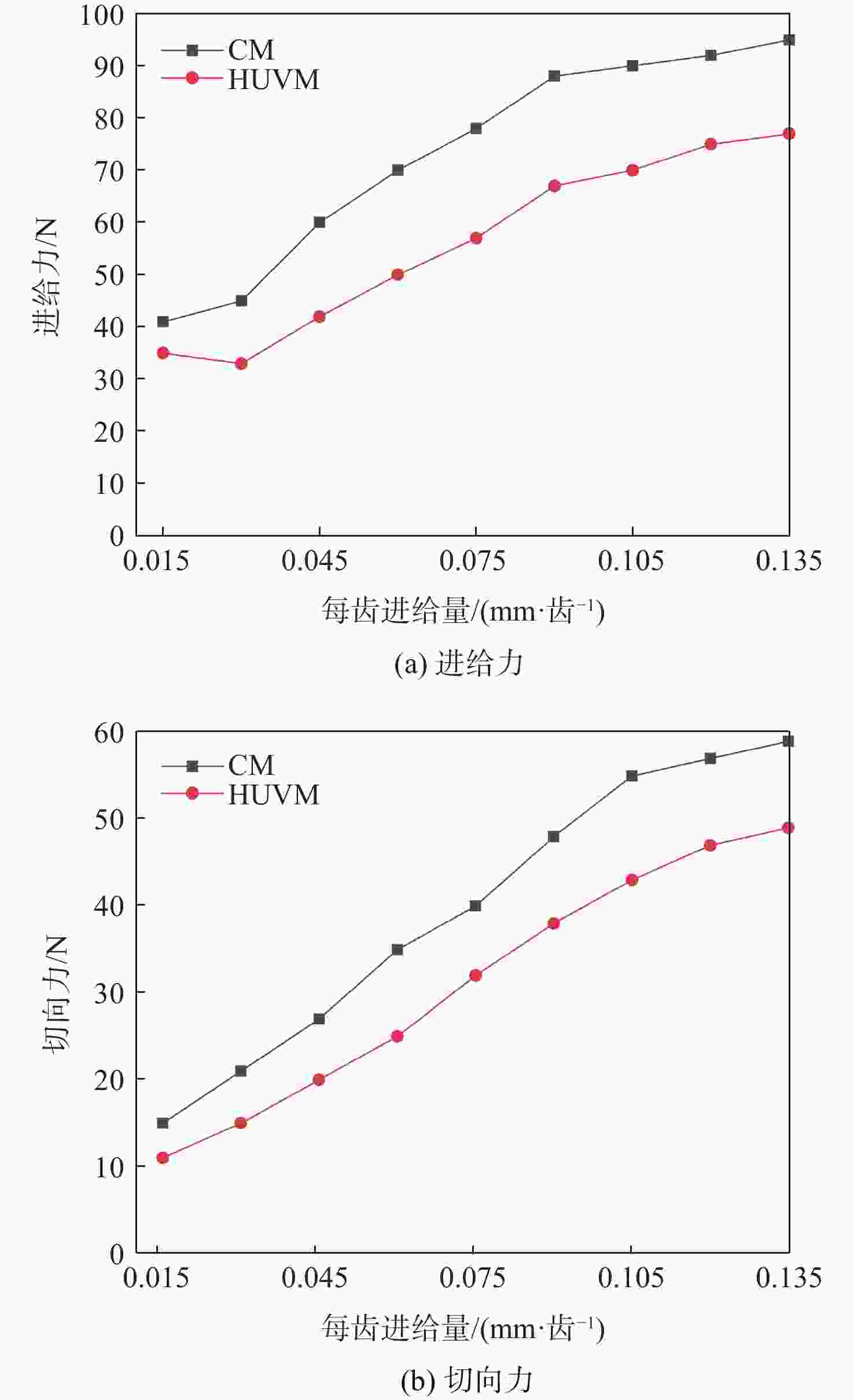
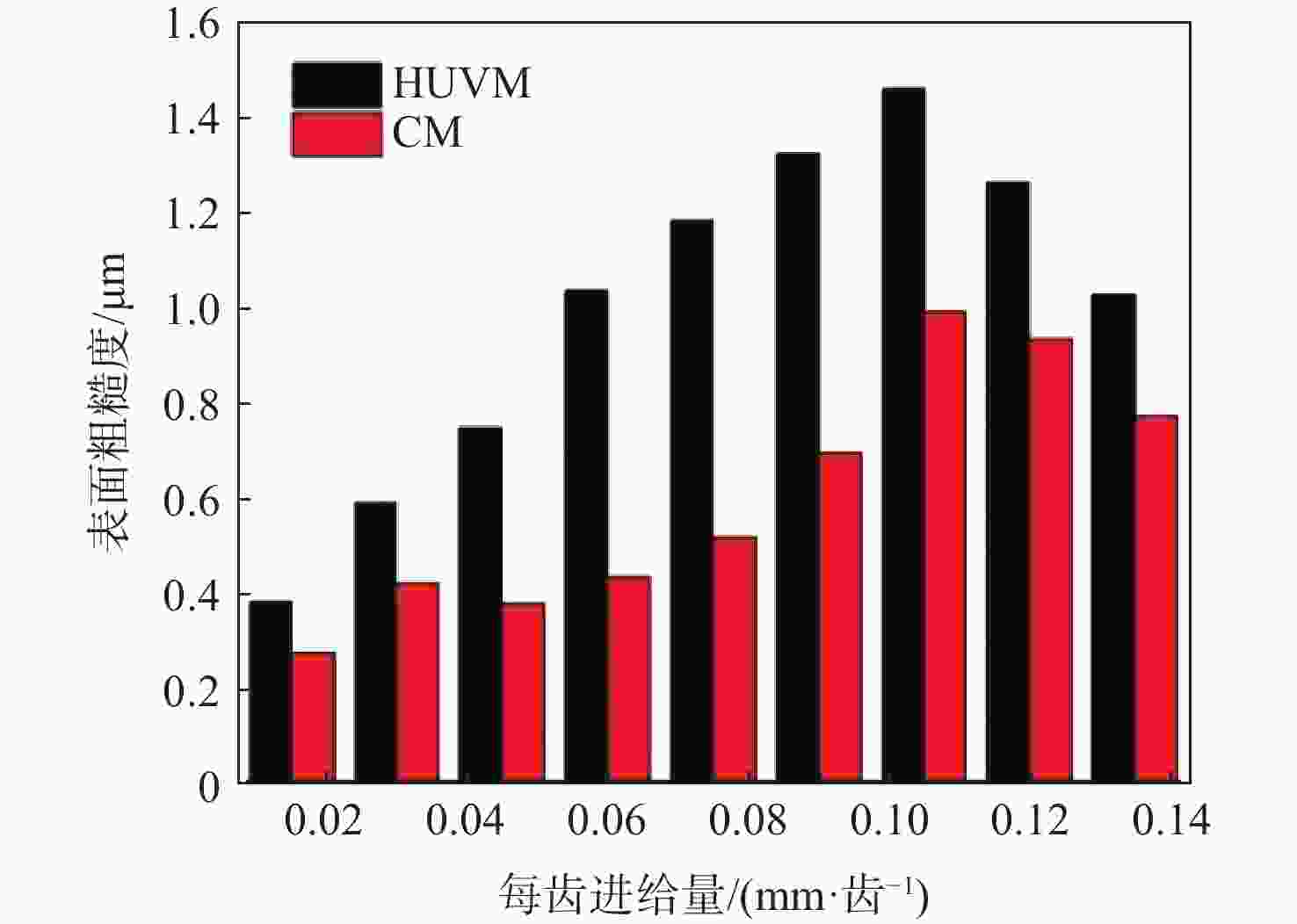
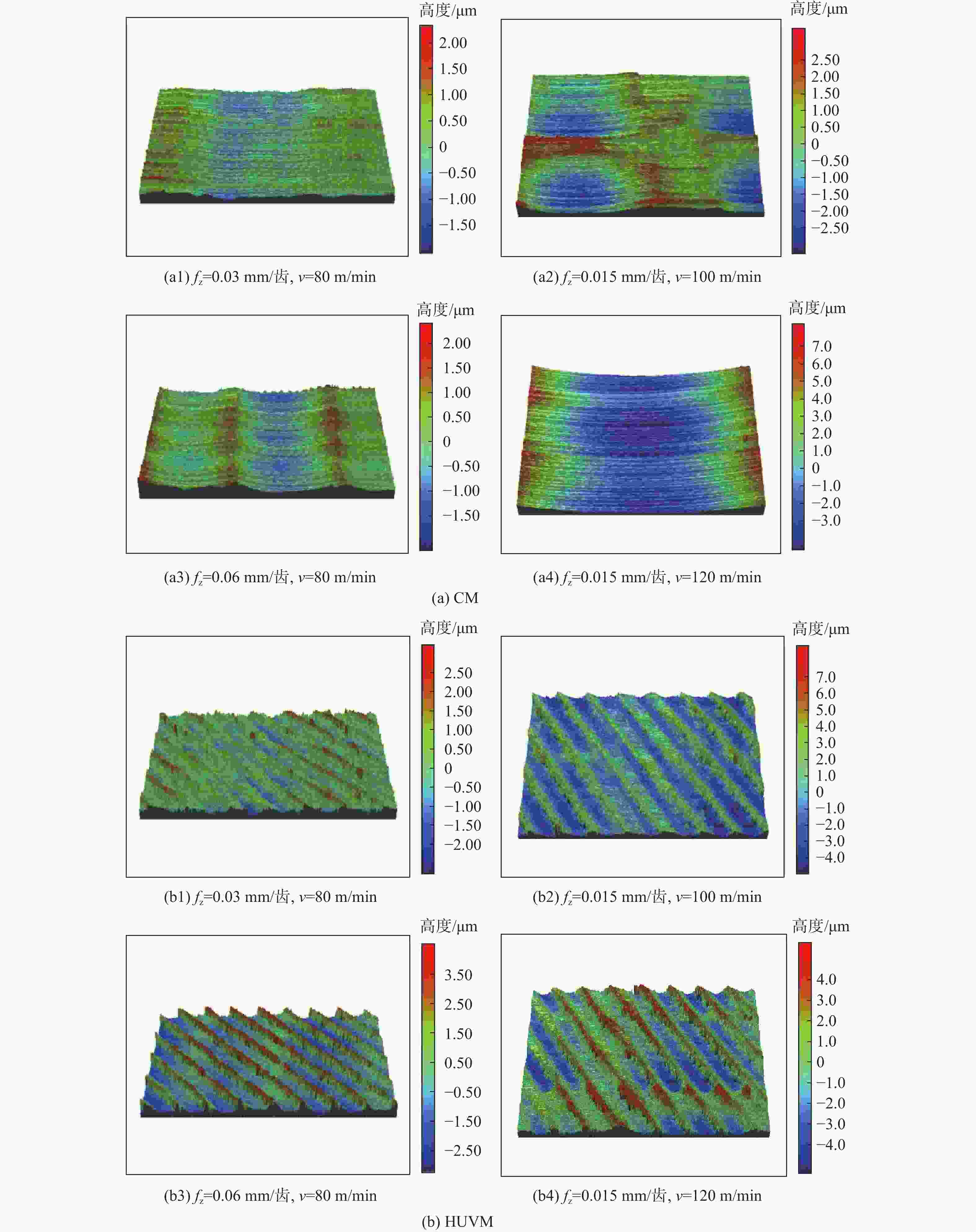
-
摘要:
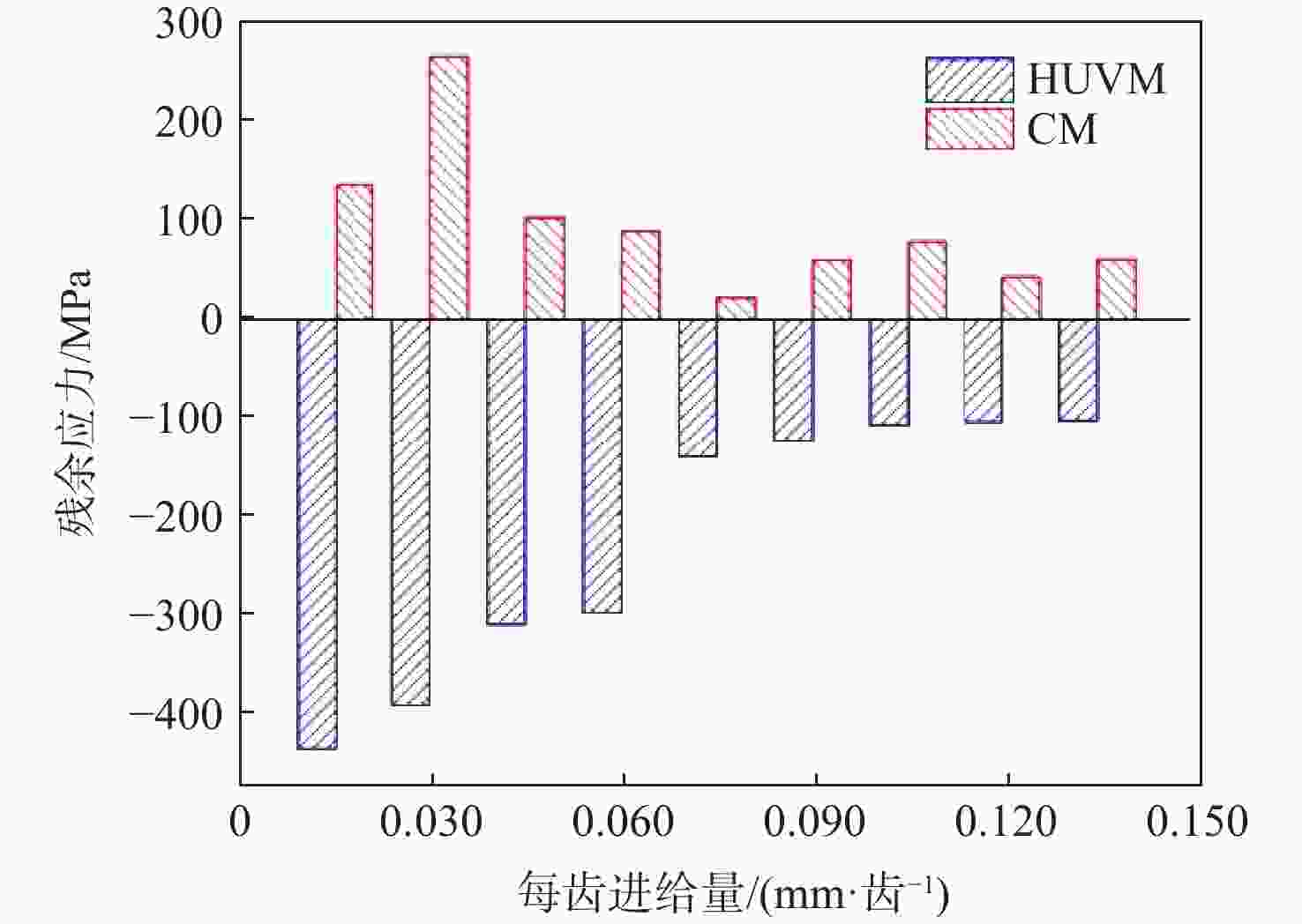
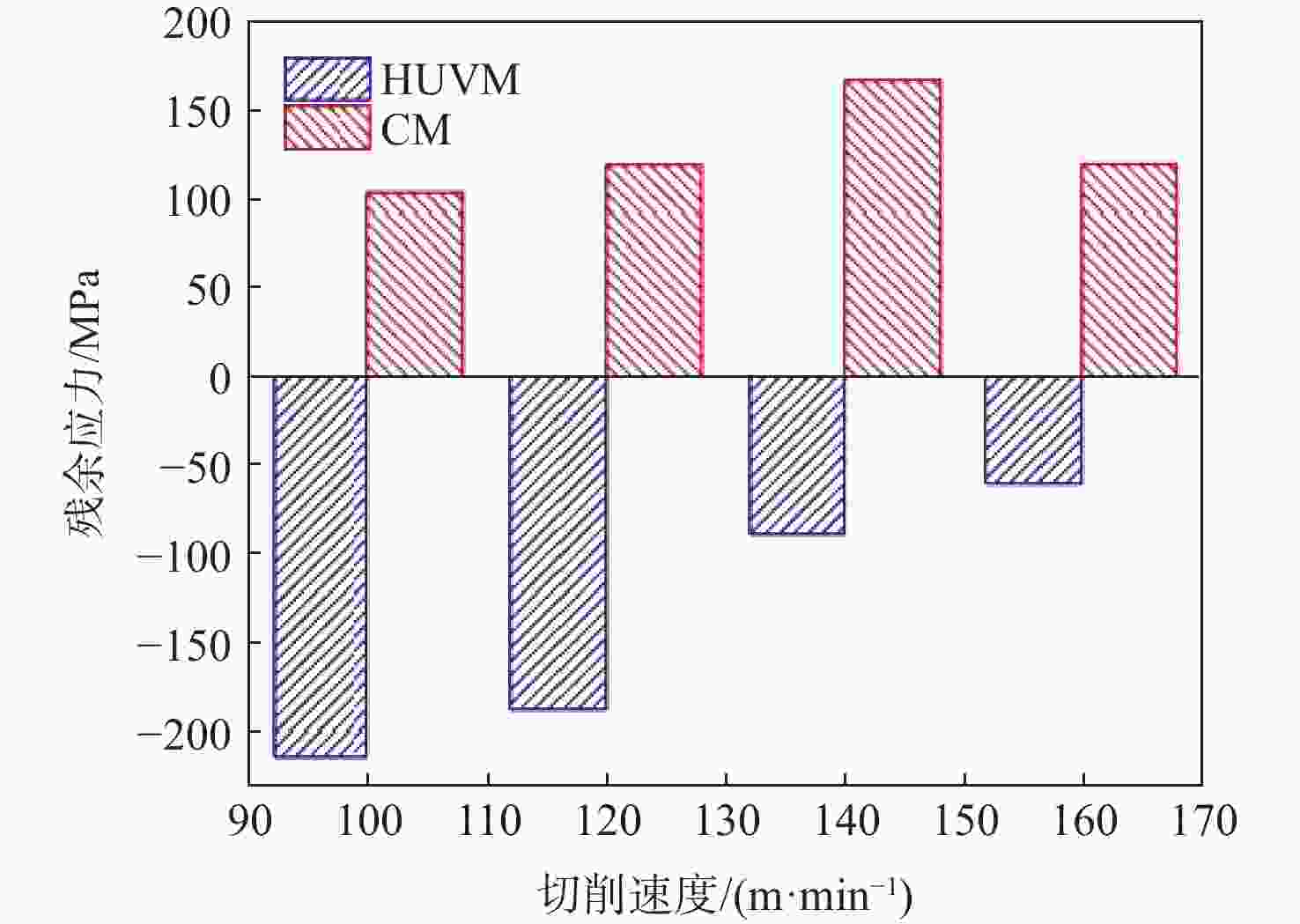
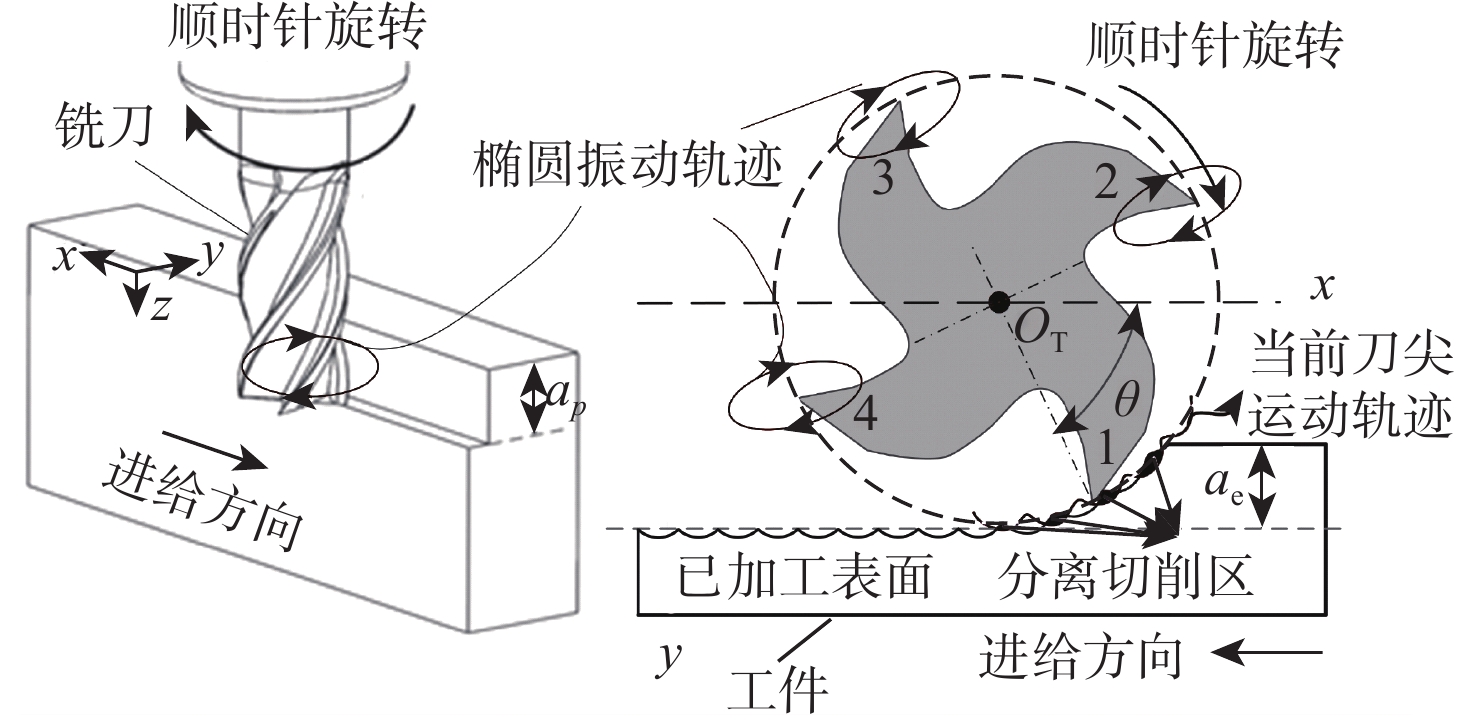
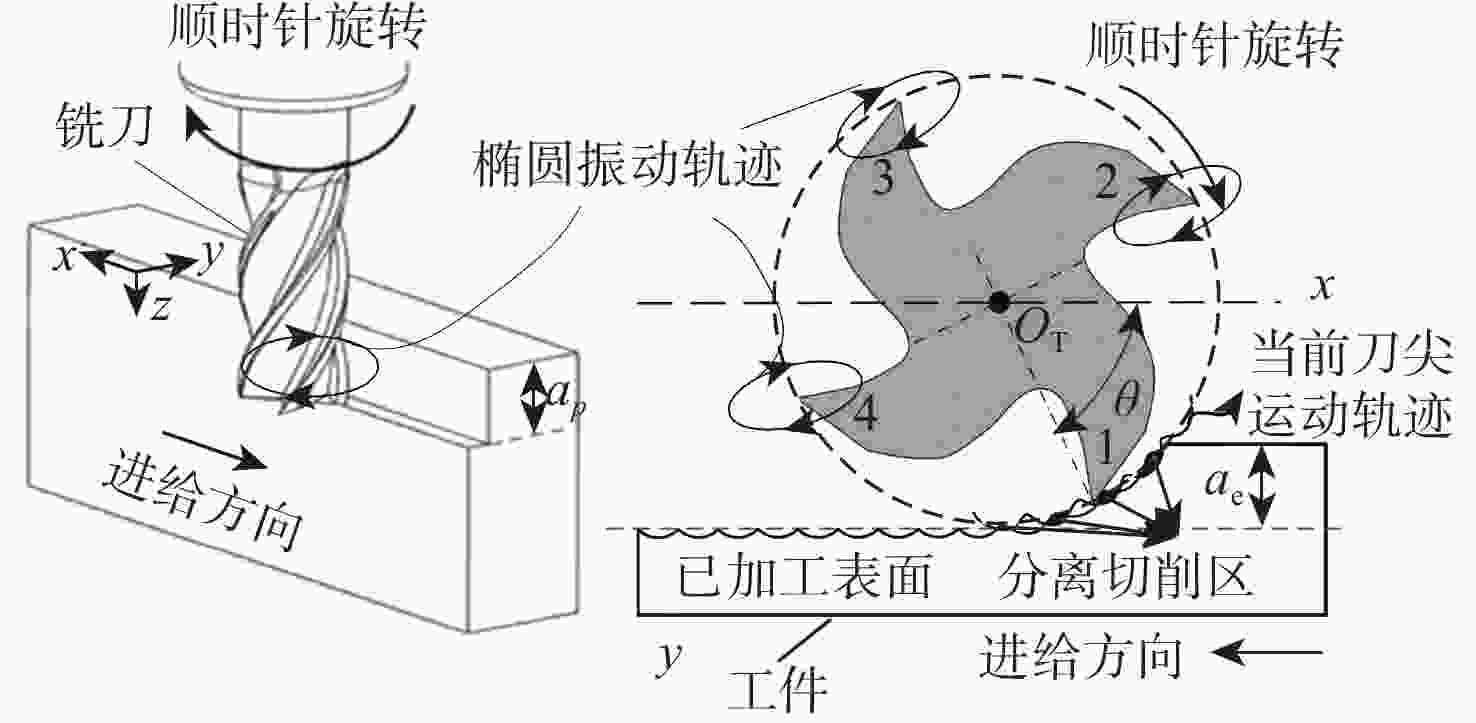
针对钛合金在普通铣削(CM)时因切削速度低而面临的切削力大、薄壁工件变形大、加工效率低、刀具磨损严重等问题,采用高速超声振动铣削(HUVM)方法加工钛合金,实验研究其加工表面质量和切削力。从运动学角度出发对HUVM方法进行运动学分析。搭建包括超声振动系统、加工系统及测量系统在内的高速超声振动铣削实验平台。采用单因素实验对比CM和HUVM这2种方法对钛合金加工切削力和表面质量的影响规律。研究结果表明:与CM加工相比,HUVM加工可以使切削力降低32.6%~35.3%。并且HUVM加工表面粗糙度虽略有增加,但是表面结构可以更加均匀;此外,HUVM加工表面残余应力均为压应力,其绝对值随着每齿进给量和切削速度的增大而降低,而CM加工表面残余应力为拉应力。
Abstract:Conventional milling (CM) causes problems for titanium alloys, such as high cutting forces, large deformation of thin-walled workpieces, low processing efficiency, and severe tool wear due to low cutting speeds. To address these problems, a new method of high-speed ultrasonic vibration milling (HUVM) is adopted to machine titanium alloys. Their surface quality and the cutting force are also examined through experiments. The kinematic equation of HUVM is constructed. An HUVM experimental platform including ultrasonic vibration system, machining system and measurement system is built. Single factor experiments are carried out to explore the effects of CM and HUVM on the surface quality and cutting force. The experimental results show that compared with CM, HUVM could generate more uniform surface structure with increased surface roughness. Unlike CM with residual tensile stress of the machined surfaces, HUVM has residual compressive stress with its value decreasing with the increase of feed per tooth and cutting speed. Moreover, HUVM could reduce cutting force by 32.6%~35.3% compared to CM.
-
Key words:
- ultrasonic vibration /
- milling /
- surface roughness /
- residual stress /
- cutting force
-
元素 Al V Fe C N H O Ti 占比/% 5.5~
6.753.5~
4.5<0.25 <0.08 <0.05 <0.01 <0.2 余量 表 2 实验参数设置
Table 2. Experimental parameter settings
参数 数值 每齿进给量fz/(mm·齿−1) 0.015,0.03,0.045,0.06,0.075,0.09,
0.105,0.12,0.135切削速度v/(m·min−1) 80,100,120,140,160 径向切宽/mm 0.2 轴向切深/mm 8 铣削类型 CM, HUVM 振动频率/Hz 17880 振动幅值/μm A=15.8, B=13.6 -
[1] ZHANG M, ZHANG D, GUO H, et al. High-speed rotary ultrasonic elliptical milling of Ti-6Al-4V using high-pressure coolant[J]. Metals, 2020, 10(4): 500. doi: 10.3390/met10040500 [2] LI A H, ZHAO J, LUO H B, et al. Progressive tool failure in high-speed dry milling of Ti-6Al-4V alloy with coated carbide tools[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2012, 58(5): 465-478. [3] WU Y, NIU J Z, FUJIMOTO M, et al. Fundamental machining characteristics of ultrasonic assisted turning of titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2013, 797: 344-349. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.797.344 [4] 路冬, 蔡力钢, 程强, 等. 钛合金超声椭圆振动辅助车削实验研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2015, 34(6): 151-154. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2015.06.029LU D, CAI L G, CHENG Q, et al. Tests for ultrasonic elliptical vibration-assisted turning of titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2015, 34(6): 151-154(in Chinese). doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2015.06.029 [5] 张明亮, 张德远, 刘佳佳, 等. 钛合金薄壁件高速超声椭圆振动铣削机理和试验[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(8): 1606-1612. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0712ZHANG M L, ZHANG D Y, LIU J J, et al. Mechanism and experiment of high-speed ultrasonic elliptical vibration milling of thin-walled titanium alloy parts[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(8): 1606-1612(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0712 [6] 王明海, 李世永, 郑耀辉. 超声铣削钛合金材料表面粗糙度研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2014, 45(6): 341-346. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2014.06.052WANG M H, LI S Y, ZHENG Y H. Surface roughness of titanium alloy under ultrasonic vibration milling[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(6): 341-346(in Chinese). doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2014.06.052 [7] TAO G C, MA C, SHEN X H, et al. Experimental and modeling study on cutting forces of feed direction ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2017, 90(1): 709-715. [8] CAKIR F H, GURGEN S, SOFUOGLU M A, et al. Finite element modeling of ultrasonic assisted turning of Ti6Al4V alloy[J]. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 2015, 195: 2839-2848. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.06.404 [9] 张翔宇, 隋翯, 张德远, 等. 高速超声振动切削钛合金可行性研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2017, 53(19): 120-127. doi: 10.3901/JME.2017.19.120ZHANG X Y, SUI H, ZHANG D Y, et al. Feasibility study of high-speed ultrasonic vibration cutting titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 53(19): 120-127(in Chinese). doi: 10.3901/JME.2017.19.120 [10] ZHENG K, LIAO W H, DONG Q, et al. Friction and wear on titanium alloy surface machined by ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling[J]. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 2018, 40(9): 411. doi: 10.1007/s40430-018-1336-9 [11] 武民. 不同振动方式下的钛合金振动辅助铣削工艺效果研究[D]. 新乡: 河南科技学院, 2018.WU M. Study on the technological effect of vibration-assisted milling of titanium alloy under different vibration modes[D]. Xinxiang: Henan Institute of Science and Technology, 2018 (in Chinese). [12] 李世永. 超声扭转振动辅助铣削钛合金的加工技术研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳航空航天大学, 2014.LI S Y. Research on machining technology of ultrasonic torsional vibration assisted milling of titanium alloy[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Aerospace University, 2014 (in Chinese). [13] ZHU Z J, SUN J, LI J F, et al. Investigation on the influence of tool wear upon chip morphology in end milling titanium alloy Ti6Al4V[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2016, 83(9): 1477-1485. [14] LIU J J, JIANG X G, HAN X, et al. Effects of rotary ultrasonic elliptical machining for side milling on the surface integrity of Ti-6Al-4V[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2019, 101(5): 1451-1465. [15] CHEN G, REN C Z, ZOU Y H, et al. Mechanism for material removal in ultrasonic vibration helical milling of Ti6Al4V alloy[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2019, 138: 1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2018.11.001 [16] 于浩, 赵军, 盖少磊, 等. 42CrMo钢车削表面完整性研究[J]. 组合机床与自动化加工技术, 2021(7): 137-140. doi: 10.13462/j.cnki.mmtamt.2021.07.032YU H, ZHAO J, GAI S L, et al. Research on surface integrity in turning of 42CrMo steel[J]. Modular Machine Tool & Automatic Manufacturing Technique, 2021(7): 137-140(in Chinese). doi: 10.13462/j.cnki.mmtamt.2021.07.032 [17] 陈建岭, 李剑峰, 孙杰, 等. 钛合金铣削加工表面残余应力研究[J]. 机械强度, 2010, 32(1): 53-57. doi: 10.16579/j.issn.1001.9669.2010.01.011CHEN J L, LI J F, SUN J, et al. Surface residual stress of titanium alloy induced by milling[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2010, 32(1): 53-57(in Chinese). doi: 10.16579/j.issn.1001.9669.2010.01.011 -






 下载:
下载: