Semantic segmentation of remote sensing images based on U-shaped network combined with spatial enhance attention
-
摘要:
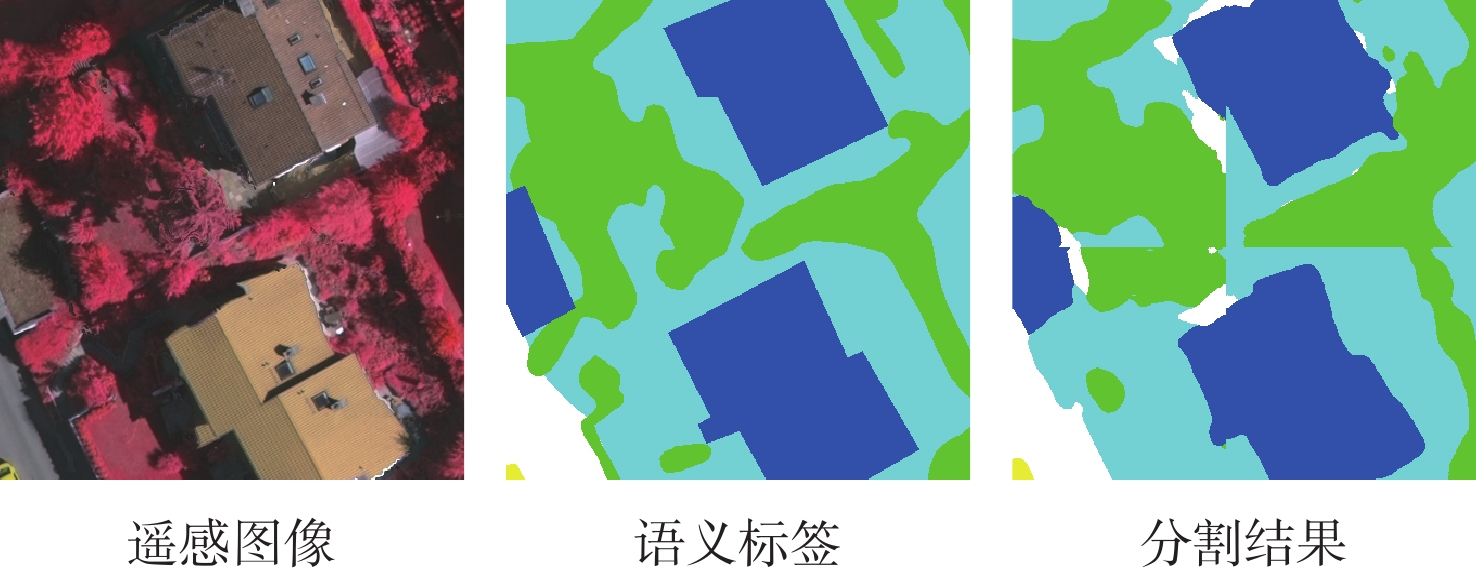
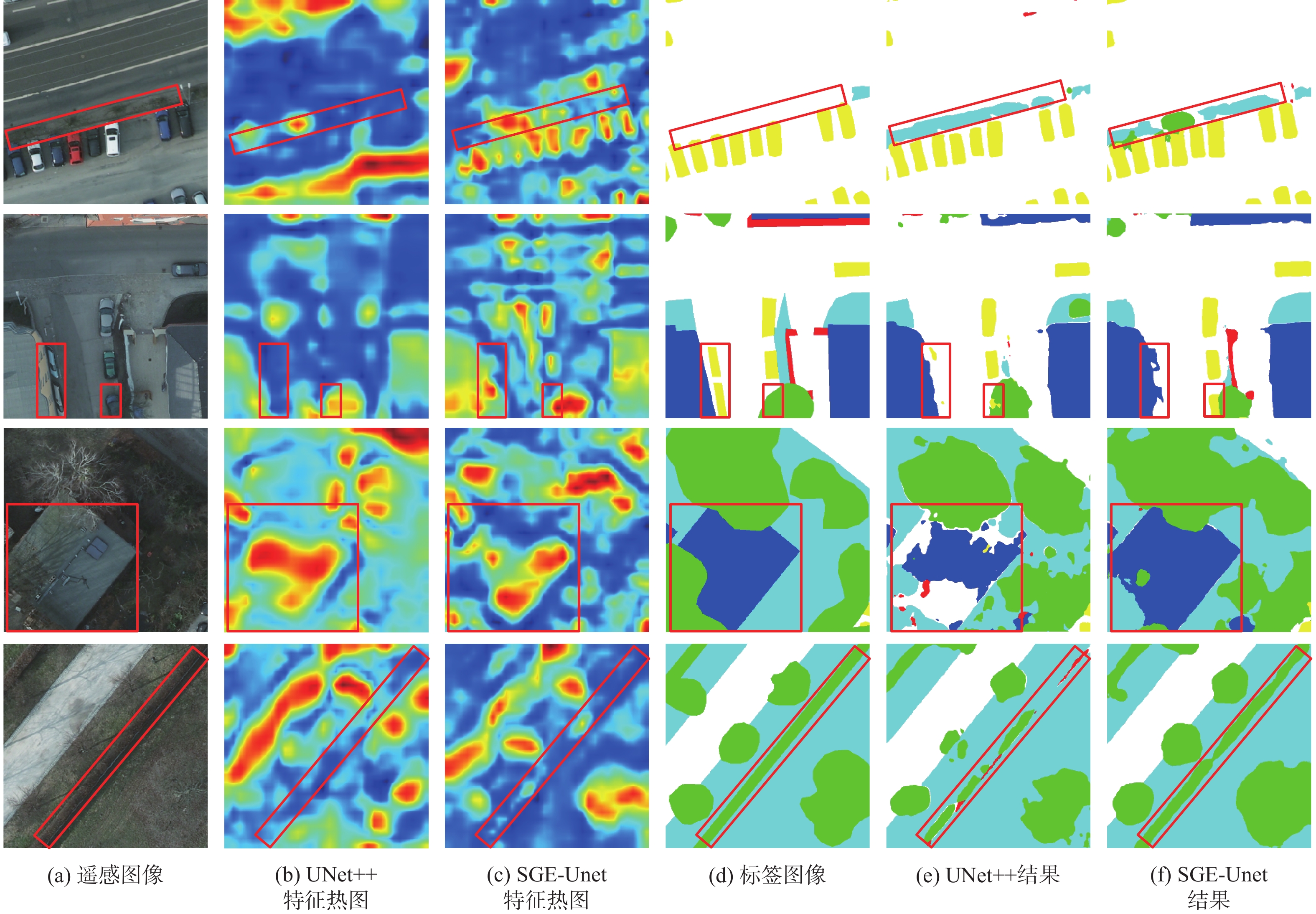
针对基于深度学习的语义分割模型在解析遥感图像时,小尺寸目标和目标边界存在分割不准确的问题,提出一种U型网络模型SGE-Unet。该模型通过优化网络结构加强模型的特征提取能力;融合空间组增强注意力,提升模型对上下文语义信息的解析能力;采用中值频率平衡交叉熵损失函数抑制类别分布不均衡的影响。在2个数据集上进行实验,SGE-Unet的整体准确率、平均交并比、¯F1分数和Kappa系数均高于主流模型,Vaihingen数据集中小尺寸目标车的交并比和F1分数分别为0.719和0.901,比次优模型提升了16%和11%,实验结果表明所提模型能更精准地分割小尺寸目标及目标边界。
Abstract:The performance of semantic segmentation based on deep learning still need to be improved when analyzing small-sized objects and object boundaries in remote sensing images. Aiming at this problem, we propose a U-shaped network (SGE-Unet). Firstly, the structure of the model is optimized to enhance the representation of feature. Secondly, we add the attention module of spatial group enhance to extract semantic information. Finally, the median frequency balance cross-entropy loss function is used to suppress the unbalanced distribution of classes. The experiment was conducted on two datasets and shows that the overall accuracy,mean interaction over union, ¯F1, and Kappa of SGE-Unet are better than mainstream models. In experiments of the Vaihingen dataset, the interaction over union and
F 1 of the car reached 0.719 and 0.901, which were 16% and 11% higher than those of the model with the second-highest performance. The experimental results show that the proposed module greatly improves the segmentation of easily confused objects, small-sized objects, and object boundaries.-
Key words:
- remote sensing image /
- semantics segmentation /
- deep learning /
- attention /
- loss function
-
表 1 数据集分配
Table 1. Allocation of dataset
类别 Vaihingen Potsdam 训练集 1, 3, 11, 13, 15, 17, 21, 26, 28, 32, 34, 37 2_12, 3_10, 3_11, 3_12, 4_11, 4_12, 5_10, 5_12, 6_7,
6_8, 6_9, 6_10, 6_12, 7_7, 7_9, 7_10, 7_11, 7_12验证集 5, 7, 23, 30 2_11, 4_10, 5_11, 7_8 测试集 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 20, 22, 24, 27, 29, 31, 33, 35, 38 2_10, 2_13, 2_14, 3_13, 3_14, 4_13, 4_14, 4_15,
5_13, 5_14, 5_15, 6_13, 6_14, 6_15, 7_13表 2 Vaihingen数据集上的语义分割结果
Table 2. Semantic segmentation result on Vaihingen dataset
模型 IOU F1 OA mIoU ¯F1 Kappa 不透水表面 建筑 低植被 树 车 不透水表面 建筑 低植被 树 车 FCN[5] 0.669 0.761 0.506 0.697 0.634 0.801 0.864 0.687 0.822 0.768 0.823 0.653 0.788 0.783 SegNet[21] 0.753 0.805 0.656 0.705 0.458 0.859 0.892 0.792 0.827 0.629 0.845 0.675 0.800 0.791 DeepLabV3[26] 0.822 0.912 0.711 0.770 0.568 0.902 0.954 0.831 0.870 0.724 0.858 0.757 0.856 0.809 SCAttNetV2[27] 0.804 0.823 0.667 0.671 0.544 0.891 0.903 0.801 0.803 0.705 0.855 0.702 0.821 0.788 UNet++[17] 0.783 0.878 0.614 0.716 0.619 0.952 0.952 0.817 0.931 0.809 0.854 0.722 0.892 0.808 SGE-Unet 0.803 0.890 0.706 0.830 0.719 0.935 0.966 0.934 0.941 0.901 0.866 0.790 0.935 0.824 表 3 Potsdam数据集上的语义分割结果
Table 3. Semantic segmentation result on Potsdam dataset
模型 IOU F1 OA mIoU ¯F1 Kappa 不透水表面 建筑 低植被 树 车 不透水表面 建筑 低植被 树 车 FCN[5] 0.776 0.799 0.720 0.670 0.797 0.874 0.889 0.837 0.820 0.887 0.808 0.752 0.861 0.781 SegNet[21] 0.854 0.912 0.786 0.757 0.881 0.921 0.954 0.880 0.862 0.937 0.811 0.838 0.911 0.782 DeepLabV3[26] 0.882 0.944 0.789 0.745 0.871 0.938 0.971 0.882 0.854 0.931 0.835 0.846 0.915 0.799 SCAttNetV2[27] 0.818 0.888 0.707 0.663 0.803 0.901 0.941 0.829 0.797 0.891 0.879 0.776 0.872 0.805 UNet++[17] 0.864 0.923 0.781 0.767 0.865 0.941 0.974 0.895 0.883 0.933 0.872 0.840 0.925 0.828 SGE-Unet 0.879 0.940 0.815 0.795 0.891 0.955 0.982 0.905 0.957 0.969 0.883 0.864 0.954 0.843 表 4 Vaihingen数据集上的消融实验
Table 4. Ablation experiments result on Vaihingen dataset
模型 IOU F1 OA mIoU ¯F1 Kappa 不透水表面 建筑 低植被 树 车 不透水表面 建筑 低植被 树 车 UNet++ 0.783 0.877 0.613 0.716 0.619 0.973 0.952 0.817 0.930 0.809 0.853 0.722 0.896 0.808 UNet++&EfficientNet 0.815 0.911 0.627 0.721 0.655 0.976 0.967 0.823 0.937 0.832 0.866 0.746 0.907 0.825 UNet++&EfficientNet&SGE 0.813 0.901 0.626 0.722 0.714 0.971 0.963 0.826 0.938 0.894 0.867 0.755 0.918 0.824 表 5 Potsdam数据集上的消融实验
Table 5. Ablation experiments result on Potsdam dataset
模型 IOU F1 OA mIoU ¯F1 Kappa 不透水表面 建筑 低植被 树 车 不透水表面 建筑 低植被 树 车 UNet++ 0.811 0.905 0.695 0.666 0.804 0.965 0.974 0.895 0.883 0.931 0.872 0776 0.930 0.828 UNet++&EfficientNet 0.829 0.918 0.711 0.691 0.810 0.960 0.986 0.892 0.909 0.943 0.879 0.792 0.938 0.839 UNet++&EfficientNet&SGE 0.826 0.915 0.709 0.694 0.823 0.955 0.982 0.898 0.913 0.970 0.883 0.793 0.944 0.843 表 6 各模型的参数量和计算复杂度对比
Table 6. Comparison of parameters and computational complexity of different modes
-
[1] YUAN X H, SHI J F, GU L C. A review of deep learning methods for semantic segmentation of remote sensing imagery[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 169: 114417. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2020.114417 [2] XING S, XIE Q, WANG M. Semantic segmentation for remote sensing images based on adaptive feature selection network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 8006705. [3] 蒋晨琛, 霍宏涛, 冯琦. 一种基于PCA的面向对象多尺度分割优化算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(6): 1192-1203.JIANG C C, HUO H T, FENG Q. An object-oriented multi-scale segmentation optimization algorithm based on PCA[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(6): 1192-1203(in Chinese). [4] KAMPFFMEYER M, SALBERG A B, JENSSEN R. Semantic segmentation of small objects and modeling of uncertainty in urban remote sensing images using deep convolutional neural networks[C]// IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 680-688. [5] SHELHAMER E, LONG J, DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(4): 640-651. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2572683 [6] GUO R, LIU J B, LI N, et al. Pixel-wise classification method for high resolution remote sensing imagery using deep neural networks[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2018, 7(3): 110. doi: 10.3390/ijgi7030110 [7] LI R, DUAN C X, ZHENG S Y, et al. MACU-Net for semantic segmentation of fine-resolution remotely sensed images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 8007205. [8] ALAM M, WANG J F, CONG G P, et al. Convolutional neural network for the semantic segmentation of remote sensing images[J]. Mobile Networks and Applications, 2021, 26(1): 200-215. doi: 10.1007/s11036-020-01703-3 [9] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]// International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Berlin: Springer, 2015: 234-241. [10] 张小娟, 汪西莉. 完全残差连接与多尺度特征融合遥感图像分割[J]. 遥感学报, 2020, 24(9): 1120-1133.ZHANG X J, WANG X L. Image segmentation models of remote sensing using full residual connection and multiscale feature fusion[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2020, 24(9): 1120-1133(in Chinese). [11] FENG Y, DIAO W, SUN X, et al. NPALoss: Neighboring pixel affinity loss for semantic segmentation in high-resolution aerial imagery[J]. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2020, V-2-2020(I-3): 475-482. doi: 10.5194/isprs-annals-V-2-2020-475-2020 [12] 肖春姣, 李宇, 张洪群, 等. 深度融合网结合条件随机场的遥感图像语义分割[J]. 遥感学报, 2020, 24(3): 254-264. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20208298XIAO C J, LI Y, ZHANG H Q, et al. Semantic segmentation of remote sensing image based on deep fusion networks and conditional random field[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2020, 24(3): 254-264(in Chinese). doi: 10.11834/jrs.20208298 [13] 翟鹏博, 杨浩, 宋婷婷, 等. 结合注意力机制的双路径语义分割[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2020, 25(8): 1627-1636. doi: 10.11834/jig.190533ZHAI P B, YANG H, SONG T T, et al. Two-path semantic segmentation algorithm combining attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2020, 25(8): 1627-1636(in Chinese). doi: 10.11834/jig.190533 [14] 杨军, 于茜子. 结合Atrous卷积的FuseNet变体网络高分遥感影响语义分割[J]. 武汉大学学报 (信息科学版), 2022, 47(7): 1071-1080. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20200305YANG J, YU X Z. Semantic segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing images based on improved FuseNet combined with the Atrous convolution[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2022, 47(7): 1071-1080(in Chinese). doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20200305 [15] WANG X Y, CUI Z Y, CAO Z J, et al. Dense docked ship detection via spatial group-wise enhance attention in SAR images[C]// IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 1244-1247. [16] TAN M X, LE Q V. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks[C]// IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML).Piscataway: IEEE press, 2019: 6105-6114. [17] ZHOU Z W, SIDDIQUEE M M R, TAJBAKHSH N, et al. UNet++: A nested U-net architecture for medical image segmentation[C]// International Workshop on Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis, International Workshop on Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 3-11. [18] 李道纪, 郭海涛, 卢俊, 等. 遥感影像地物分类多注意力融和U型网络法[J]. 测绘学报, 2020, 49(8): 1051-1064. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2020.20190407LI D J, GUA H T, LU J, et al. A remote sensing image classification procedure based on multilevel attention fusion U-Net[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2020, 49(8): 1051-1064(in Chinese). doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2020.20190407 [19] 言有三. 深度学习之图像识别: 核心技术与案例实战[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2019: 231-232.YAN Y S. Image recognition by deep learning: Core technologies and practices[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2019: 231-232(in Chinese). [20] ROTTENSTEINER F, SOHN G, JUNG J, et al. The ISPRS benchmark on urban object classification and 3d building reconstruction[J]. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2012(I-3): 293-298. [21] BADRINARAYANAN V, KENDALL A, CIPOLLA R. SegNet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12): 2481-2495. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615 [22] CHAI D F, NEWSAM S, HUANG J F. Aerial image semantic segmentation using DCNN predicted distance maps[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 161: 309-322. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.01.023 [23] XU Z Y, SU C, ZHANG X C. A semantic segmentation method with category boundary for land use and land cover (LULC) mapping of very-high resolution (VHR) remote sensing image[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2021, 42(8): 3146-3165. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2020.1871100 [24] 胡伟, 高博川, 黄振航, 等. 树形结构卷积神经网络优化的城区遥感图像语义分割[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2020, 25(5): 1043-1052. doi: 10.11834/jig.190324HU W, GAO B C, HUANG Z H, et al. Semantic segmentation of urban remote sensing image based on optimized tree structure convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2020, 25(5): 1043-1052(in Chinese). doi: 10.11834/jig.190324 [25] KINGMA D, BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[C]// International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). [S.1.]: ICLR, 2015. [26] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. DeepLab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4): 834-848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184 [27] LI H F, QIU K J, CHEN L, et al. SCAttNet: Semantic segmentation network with spatial and channel attention mechanism for high-resolution remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(5): 905-909. -







 下载:
下载: