-
摘要:
常用的时间序列模式匹配方法难以平衡计算复杂度与匹配精度,针对该问题,提出了一种特征点分段提取的时间序列模式匹配方法。提取时间序列每个变量维度上的特征点,降低序列长度;将特征点序列转化为分位点矩阵,利用欧氏距离对分位点矩阵进行相似性度量;在几组时间序列数据集上对所提方法进行分类实验。结果表明:所提方法在降低计算复杂度的同时,获得了较高的匹配精度。
Abstract:It is difficult for the common time series pattern matching methods to balance the computational complexity and matching accuracy. To solve this problem, a time series matching method based on segmented extraction of feature points is proposed. Firstly, the feature points on each variable dimension of the time series are extracted and the sequence length is compressed. Then, the quantile matrix is calculated according to the feature sequence, and the similarity of the quantile matrix is measured by Euclidean distance. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed method is verified on the application data set. Experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively reduce the computational complexity and ensure high matching accuracy.
-
Key words:
- time series /
- pattern matching /
- feature extraction /
- quantile matrix /
- computational complexity
-
表 1 实验数据集
Table 1. Detail of experimental datasets
数据集 长度 均长 变量个数 样本量 类别 ASL 47~95 59 22 216 8 LP1 15 15 6 88 4 JV 7~29 16 12 640 9 EEG 256 256 64 22 2 WR 128~1918 368 62 44 2 Trace 275 275 1 200 4 表 2 ASL数据集上的匹配精度
Table 2. Matching accuracy on ASL dataset
k SVD DTW ACM-DTW TD PD SFP-ED 1 0.718 0.977 0.926 0.972 0.579 0.986 5 0.639 0.929 0.870 0.958 0.570 0.947 10 0.570 0.929 0.856 0.906 0.557 0.944 表 3 6种模式匹配方法在不同准确率下的匹配次数
Table 3. Matching times of 6 pattern matching methods under different accuracy rates
e/% SVD DTW ACM-DTW TD PD SFP-ED N=1 N=5 N=10 N=1 N=5 N=10 N=1 N=5 N=10 N=1 N=5 N=10 N=1 N=5 N=10 N=1 N=5 N=10 0 61 20 12 5 0 0 16 9 0 6 0 0 91 33 14 3 0 0 10 19 0 3 0 13 0 20 27 15 0 0 4 0 0 0 25 17 2 0 30 19 1 2 2 28 3 40 34 19 13 0 10 5 4 3 36 18 9 4 50 25 6 5 9 26 1 60 29 26 12 5 10 13 9 8 34 17 6 3 70 7 15 15 7 13 10 80 22 7 14 11 29 17 15 22 23 6 10 7 90 7 30 25 30 12 15 100 155 84 60 211 177 148 200 154 125 210 188 135 125 65 52 213 189 173 表 4 6组数据集上的匹配精度
Table 4. Accuracy on 6 datasets
数据集 SVD DTW ACM-DTW TD PD SFP-ED ASL 0.718 0.977 0.926 0.972 0.578 0.986 LP1 0.477 0.886 0.909 0.636 0.830 0.921 JV 0.489 0.963 0.759 0.548 0.581 0.958 EEG 0.909 0.727 0.727 1 0.591 0.864 WR 0.977 0.977 0.955 1 1 0.977 Trace 0.995 1 0.930 0.995 表 5 9个分位点提取结果
Table 5. Nine quantile results
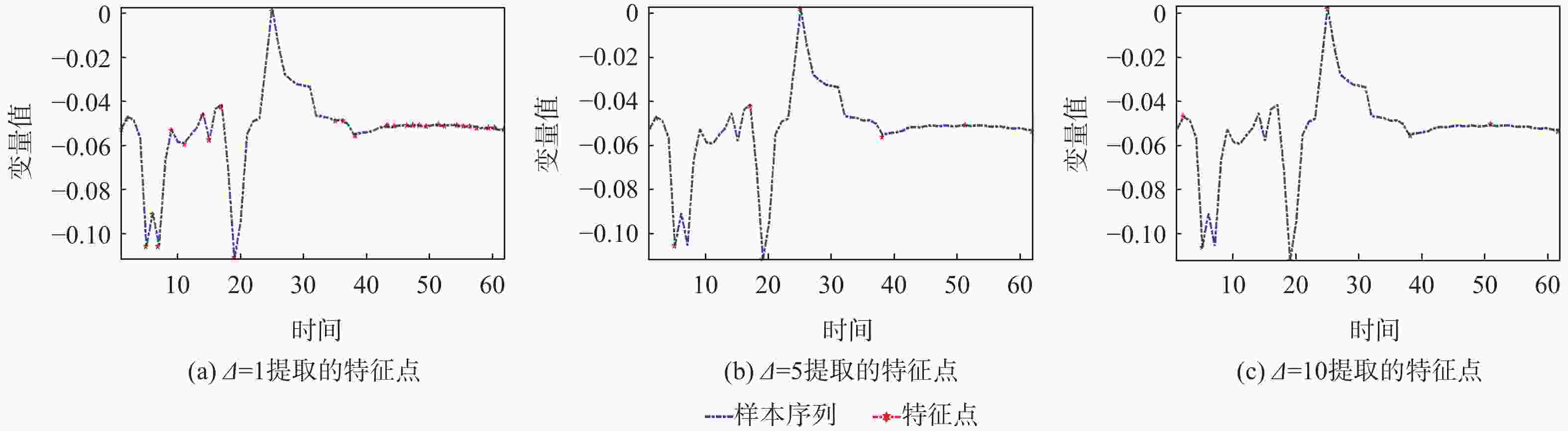
Δ 最小值点 5% 10% 25% 50% 75% 90% 95% 最大值点 1 −0.1111 −0.1052 −0.0975 −0.0528 −0.0512 −0.0506 −0.0460 −0.0414 0.0024 5 −0.1111 −0.1111 −0.1093 −0.0800 −0.0516 −0.0441 −0.0108 0.0024 0.0024 10 −0.1111 −0.1111 −0.1099 −0.0926 −0.0528 −0.0477 −0.0075 0.0024 0.0024 -
[1] BOHANNON A W, LAWHERN V J, WAYTOWICH N R, et al. The autoregressive linear mixture model: A time-series model for an instantaneous mixture of network processes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 4481-4496. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3012946 [2] WANG F, LI C, ZENG Z, et al. Cornerstone network with feature extractor: A metric-based few-shot model for Chinese natural sign language[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2021, 51(5): 1-12. [3] PAN H, ZHOU H. Study on convolutional neural network and its application in data mining and sales forecasting for E-commerce[J]. Electronic Commerce Research, 2020, 20(2): 297-320. doi: 10.1007/s10660-020-09409-0 [4] JIANG X Q, ZHANG L C. Stock price fluctuation prediction method based on time series analysis[J]. Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems, 2018, 12(4): 915-927. [5] WEN S C, YANG C H. Time series analysis and prediction of nonlinear systems with ensemble learning framework applied to deep learning neural networks[J]. Information Sciences, 2021, 572: 167-181. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2021.04.094 [6] CABRERA D, SANCHO F, CERRADA M, et al. Knowledge extraction from deep convolutional neural networks applied to cyclo-stationary time-series classification[J]. Information Sciences, 2020, 524: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.03.039 [7] MA Q, CHEN Z, TIAN S, et al. Difference-guided representation learning network for multivariate time series classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 3: 1-11. [8] 李正欣, 张凤鸣, 李克武, 等. 一种支持DTW距离的多元时间序列索引结构[J]. 软件学报, 2014, 25(3): 560-575.LI Z X, ZHANG F M, LI K W, et al. Index structure for multivariate time series under DTW distance metric[J]. Journal of Software, 2014, 25(3): 560-575(in Chinese). [9] SOLEIMANI G, ABESSI M. DLCSS: A new similarity measure for time series data mining[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 92: 103664. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2020.103664 [10] ZHU H, WANG X, CHEN X, et al. Similarity search and performance prediction of shield tunnels in operation through time series data mining[J]. Automation in Construction, 2020, 114: 103178. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2020.103178 [11] LI H. Time works well: Dynamic time warping based on time weighting for time series data mining[J]. Information Sciences, 2021, 547: 592-608. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.08.089 [12] OKAWA M. Time-series averaging and local stability-weighted dynamic time warping for online signature verification[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2021, 112: 107699. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107699 [13] NIE C X. Nonlinear correlation analysis of time series based on complex network similarity[J]. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 2020, 14(4): 736-749. [14] WANG B Q, JIANG T H, ZHOU X, et al. Time-series classification based on fusion features of sequence and visualization[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(12): 4124. doi: 10.3390/app10124124 [15] LI H H, LIU J X, YANG Z L, et al. Adaptively constrained dynamic time warping for time series classification and clustering[J]. Information Sciences, 2020, 534: 97-116. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.04.009 [16] NISHINO T, HOKUGO A. A stochastic model for time series prediction of the number of post-earthquake fire ignitions in buildings based on the ignition record for the 2011 Tohoku Earthquake[J]. Earthquake Spectra, 2020, 36(1): 232-249. doi: 10.1177/8755293019878184 [17] WAN Y Q, SI Y W. A hidden semi-Markov model for chart pattern matching in financial time series[J]. Soft Computing, 2018, 22: 6525-6544. doi: 10.1007/s00500-017-2703-7 [18] SUN J, YANG Y, LIU Y, et al. Univariate time series classification using information geometry[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 95: 832-843. [19] HUANG W, YUE B, CHI Q, et al. Integrating data-driven segmentation, local feature extraction and fisher kernel encoding to improve time series classification[J]. Neural Processing Letters, 2019, 49(1): 43-66. doi: 10.1007/s11063-018-9798-4 [20] YOU D G, LIN W W, SHI F, et al. A novel approach for CPU load prediction of cloud server combining denoising and error correction[J]. Computing, 2023, 105(3): 577-594. doi: 10.1007/s00607-020-00865-y [21] IOKIBE T, KOYAMA M, TANIGUCHI M. A study for complexity of chaotic time series and prediction accuracy[C]//IEEE International Fuzzy Systems Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1999: 6430833. [22] MONTAGNON C E. Forecasting by splitting a time series using singular value decomposition then using both ARMA and a Fokker Planck equation[J]. Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2020, 567(3): 536-545. [23] THUY H, ANH D T, CHAU V. Efficient segmentation-based methods for anomaly detection in static and streaming time series under dynamic time warping[J]. Journal of Intelligent Information Systems, 2021, 56(3): 373-386. [24] 孟晓静, 万源. 自适应代价动态时间弯曲的多元时间序列相似性度量[J]. 统计与决策, 2020, 14(2): 25-29.MENG X J, WAN Y. Multivariate time series similarity measure for dynamic time warping of adaptive cost[J]. Statistics and Decision, 2020, 14(2): 25-29(in Chinese). [25] 李正欣, 张凤鸣, 李克武. 多元时间序列模式匹配方法研究[J]. 控制与决策, 2011, 24(4): 565-570.LI Z X, ZHANG F M, LI K W. Research on pattern matching method of multivariate time series[J]. Control and Decision, 2011, 24(4): 565-570(in Chinese). [26] GUIGOU F, COLLET P, PARREND P. SCHEDA: Lightweight euclidean-like heuristics for anomaly detection in periodic time series[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2019, 82(3): 1432-1443. [27] 管河山, 姜青山, 王声瑞. 基于点分布特征的多元时间序列模式匹配方法[J]. 软件学报, 2009, 20(1): 67-69. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1001.2009.00067GUAN H S, JIANG Q S, WANG S R. Pattern matching method based on point distribution for multivariate time series[J]. Journal of Software, 2009, 20(1): 67-69(in Chinese). doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1001.2009.00067 [28] GUO X G, HONG P Y, LALEG-KIRATI T M. Calibration and validation for a real-time membrane bioreactor: A sliding window approach[J]. Journal of Process Control, 2021, 98(6): 92-105. [29] JILANI T A, BURNEY A S, ARDIL C. A new quantile based fuzzy time series forecasting model[J]. Proceedings of World Academy of Science Engineering & Technology, 2008, 23(1): 32-41. [30] 刘畅, 李正欣, 张晓丰, 等. 基于特征点界标过滤的时间序列模式匹配方法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2022, 39(4): 1008-1012. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2021.09.0396LIU C, LI Z X, ZHANG X F, et al. Time series pattern matching method based on feature point landmark filtering[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2022, 39(4): 1008-1012(in Chinese). doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2021.09.0396 -







 下载:
下载: