-
摘要:
大型工件加工时执行机构伸展空间不足是目前航天制造业一个亟待解决的问题。为增大执行机构末端的工作空间,并为其提供稳定可靠的伸展基础,提出一类具备高刚度、大伸展特性的并联可伸展机构。重点针对并联可伸展机构展开设计与分析,基于图论进行可伸展机构构型综合,利用构型演化得到PRRR、PRRR-3R和PRRR-6R(P表示移动副,R表示转动副)这3种可伸展支链单元构型,在此基础上,对3种可伸展机构支链单元的伸展性能、刚度进行对比分析,最终优选出满足要求的PRRR支链单元配置成并联可伸展机构。该并联可伸展机构可应用于需要提供大伸展及大刚度的场合,实现对其他执行机构运动空间的拓展。
Abstract:In the process of large-scale workpiece machining, the insufficient extension space of the executive mechanism is an urgent problem to be solved in the aerospace manufacturing industry. To increase the working space at the end of the executive mechanism, and to provide the mechanism with a stable and reliable extension foundation, a parallel extendable mechanism with high stiffness and large extension is proposed. This paper focuses on the design and analysis of parallel extensible mechanisms. Based on graph theory, the configuration of the extendable mechanism was synthesized, and the three extendable branch unit configurations, PRRR, PRRR-3R and PRRR-6R (P represents prismatic pair, R represents rotation pair) were obtained by using the configuration evolution. On this basis, the extensibility and stiffness of the branch chain unit of the three extensible mechanisms were compared and analyzed. And finally, the PRRR branch chain unit that satisfies the requirements was configured as a parallel extensible mechanism. The parallel extendable mechanism can be applied to occasions that need to provide large extension and large stiffness and realize the expansion of the movement space of other actuators.
-
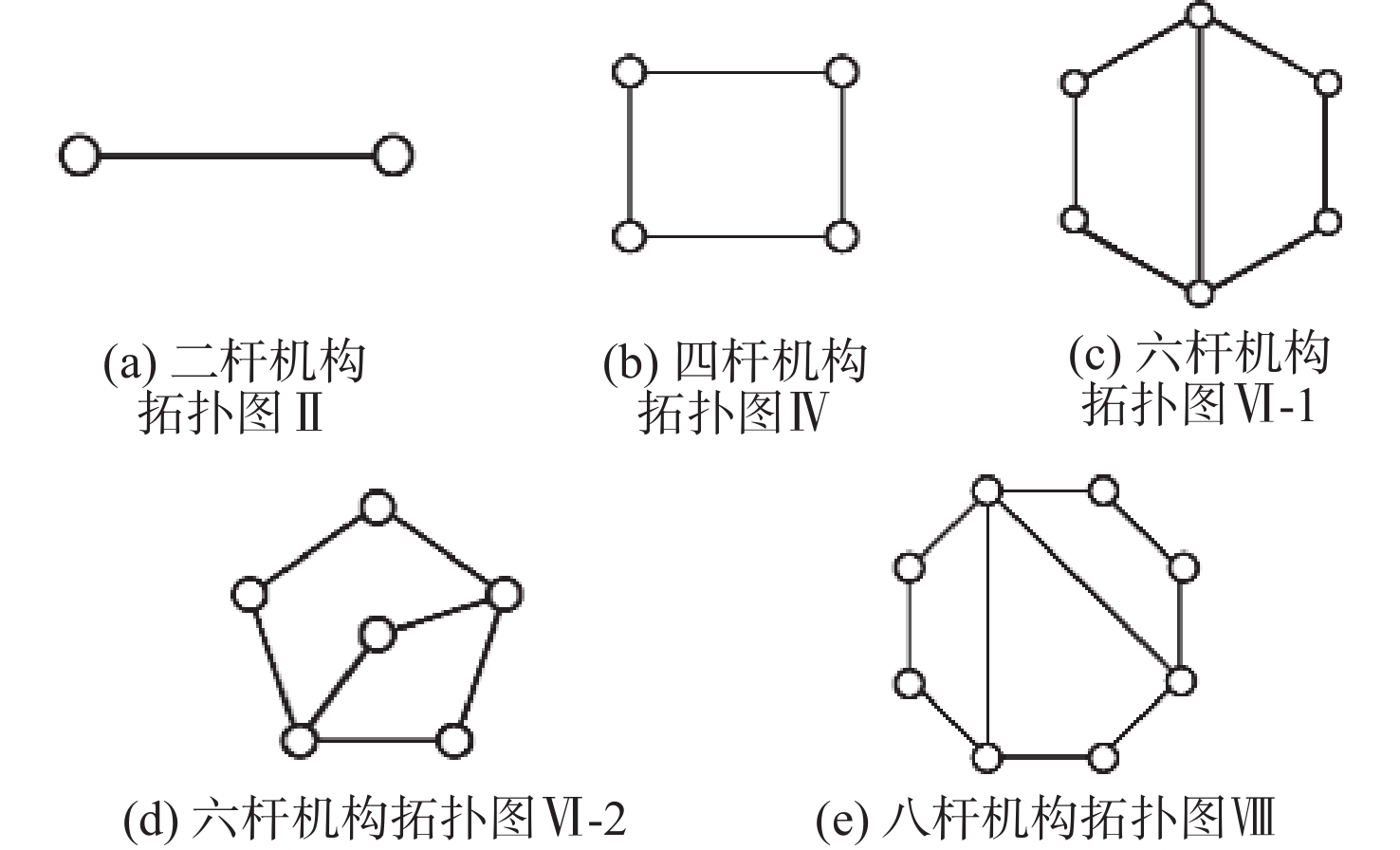
表 1 构件数N、运动副数M和运动链闭环数L的对应关系
Table 1. Corresponding relationship between components N,motion pairs M and closed loops L
构件数N 运动副数量M 运动链的闭环数L 2 1 0 4 4 1 6 7 2 8 10 3 $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ 表 2 四杆机构拓扑图Ⅳ与邻接矩阵的对应关系
Table 2. Correspondence between topological diagram Ⅳ of four-bar mechanism and adjacency matrix
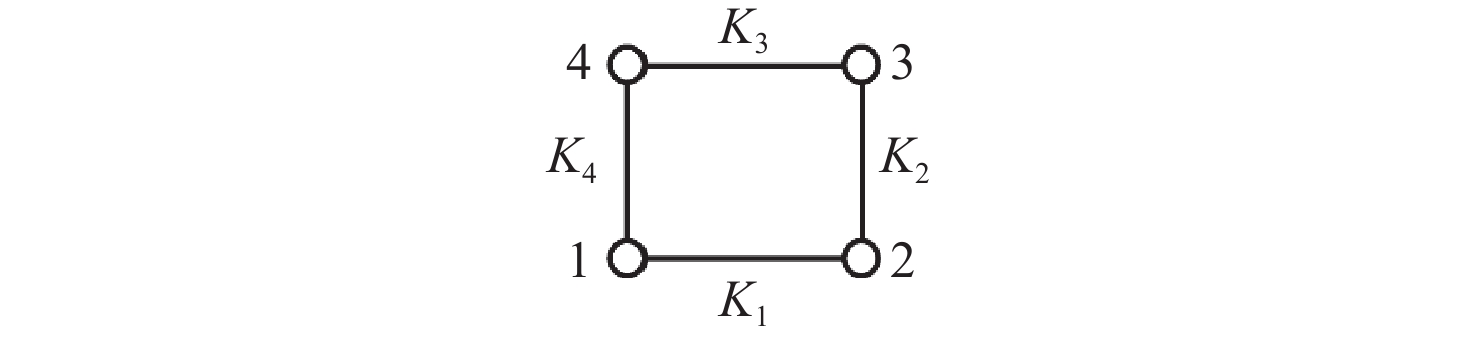
顶点 1 2 3 4 1 0 1 0 1 2 1 0 1 0 3 0 1 0 1 4 1 0 1 0 表 3 四杆机构拓扑图部分构型演化
Table 3. Partial configuration evolution of topological diagram for four-bar mechanism
运动副情况 拓扑图 演化构型 1个P副 

1个P副 

全R副 

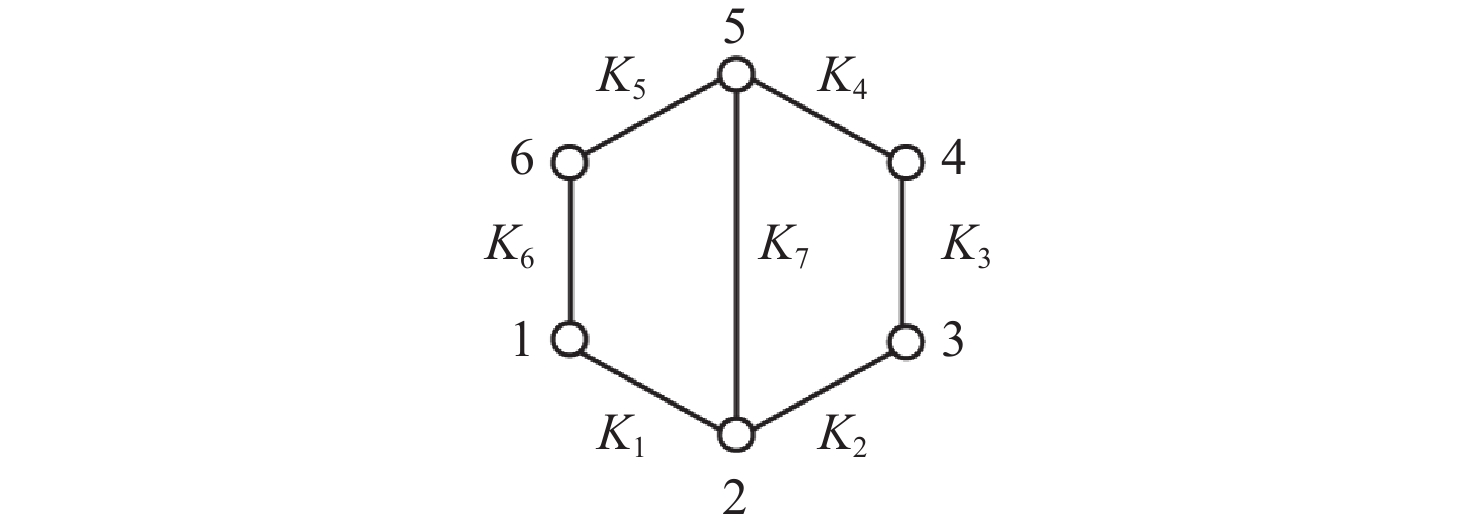
表 4 六杆机构拓扑VI-1的构型总数
Table 4. Total number of configurations of topological diagram for six-bar mechanism Ⅵ-1
机架 拓扑图 1个P副 2个P副 全R副 构型总数 构件1 
$ {}_1^1{M_6} = 7 $ $ {}_1^2{M_6} = 21 $ $ {}_1^0{M_6} = 1 $ 29 构件2 
$ {}_2^1{M_6} = 4 $ $ {}_2^2{M_6} = 12 $ $ {}_2^0{M_6} = 1 $ 17 表 5 六杆机构拓扑VI-2的构型总数
Table 5. Total number of configurations of topological diagram for six-bar mechanism Ⅵ-2
机架 拓扑图 1个P副 2个P副 全R副 构型总数 构件1 
$ {}_1^1{M_6} = 5 $ $ {}_1^2{M_6} = 13 $ $ {}_1^0{M_6} = 1 $ 19 构件2 
$ {}_2^1{M_6} = 4 $ $ {}_2^2{M_6} = 12 $ $ {}_2^0{M_6} = 1 $ 17 构件5 
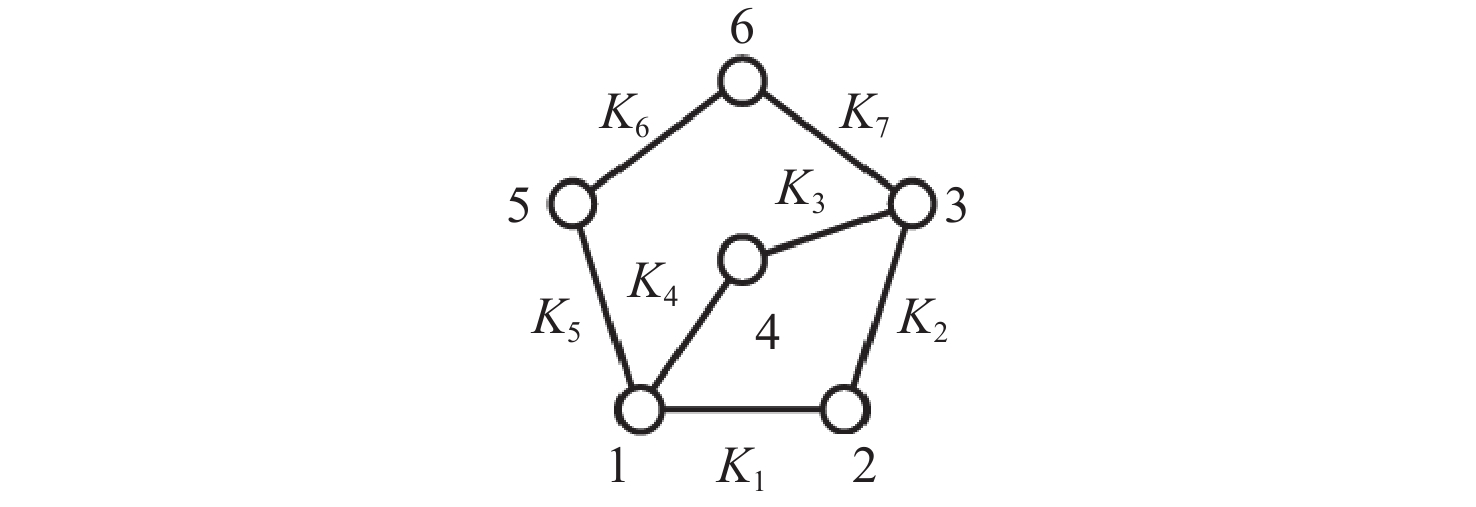
$ {}_5^1{M_6} = 5 $ $ {}_5^2{M_6} = 13 $ $ {}_5^0{M_6} = 1 $ 19 表 6 六杆机构拓扑图部分构型演化
Table 6. Partial configuration evolution of topological diagram for six-bar mechanism
序号 运动副情况 拓扑图 演化构型 1 1个P副 

2 1个P副 

3 1个P副 

4 1个P副 

5 全R副 

6 全R副 

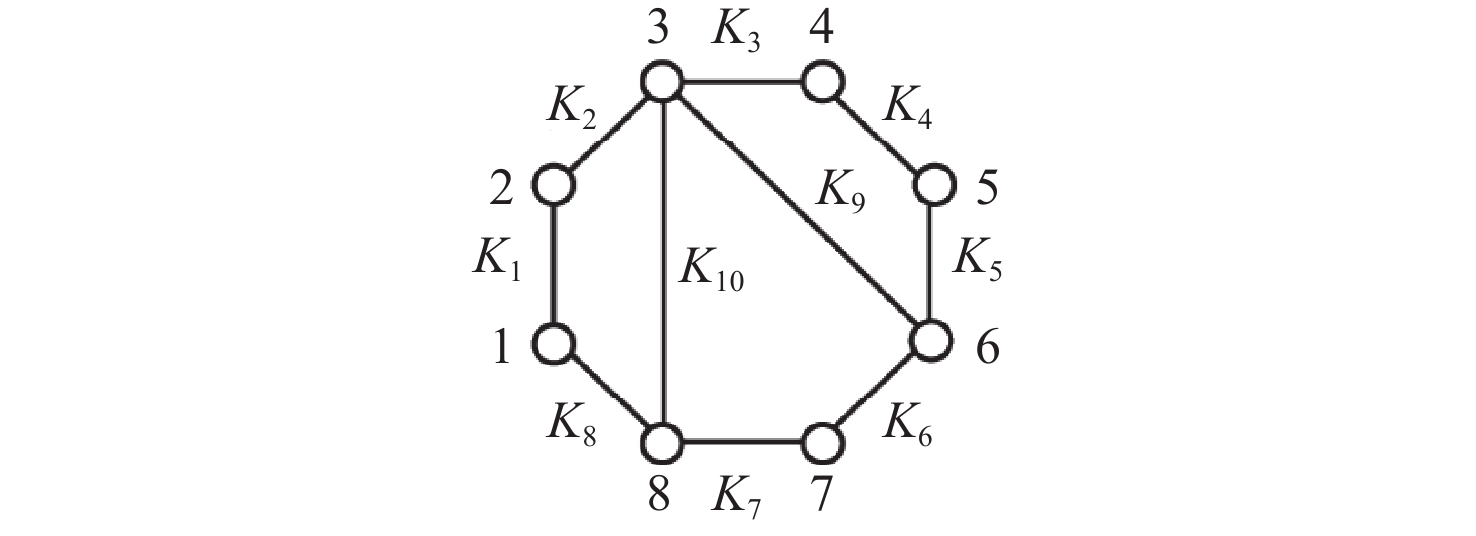
表 7 八杆机构拓扑图部分构型演化
Table 7. Partial configuration evolution of topological diagram of eight-bar mechanism
运动副情况 构型拓扑图 演化构型 1个P副 

全R副 

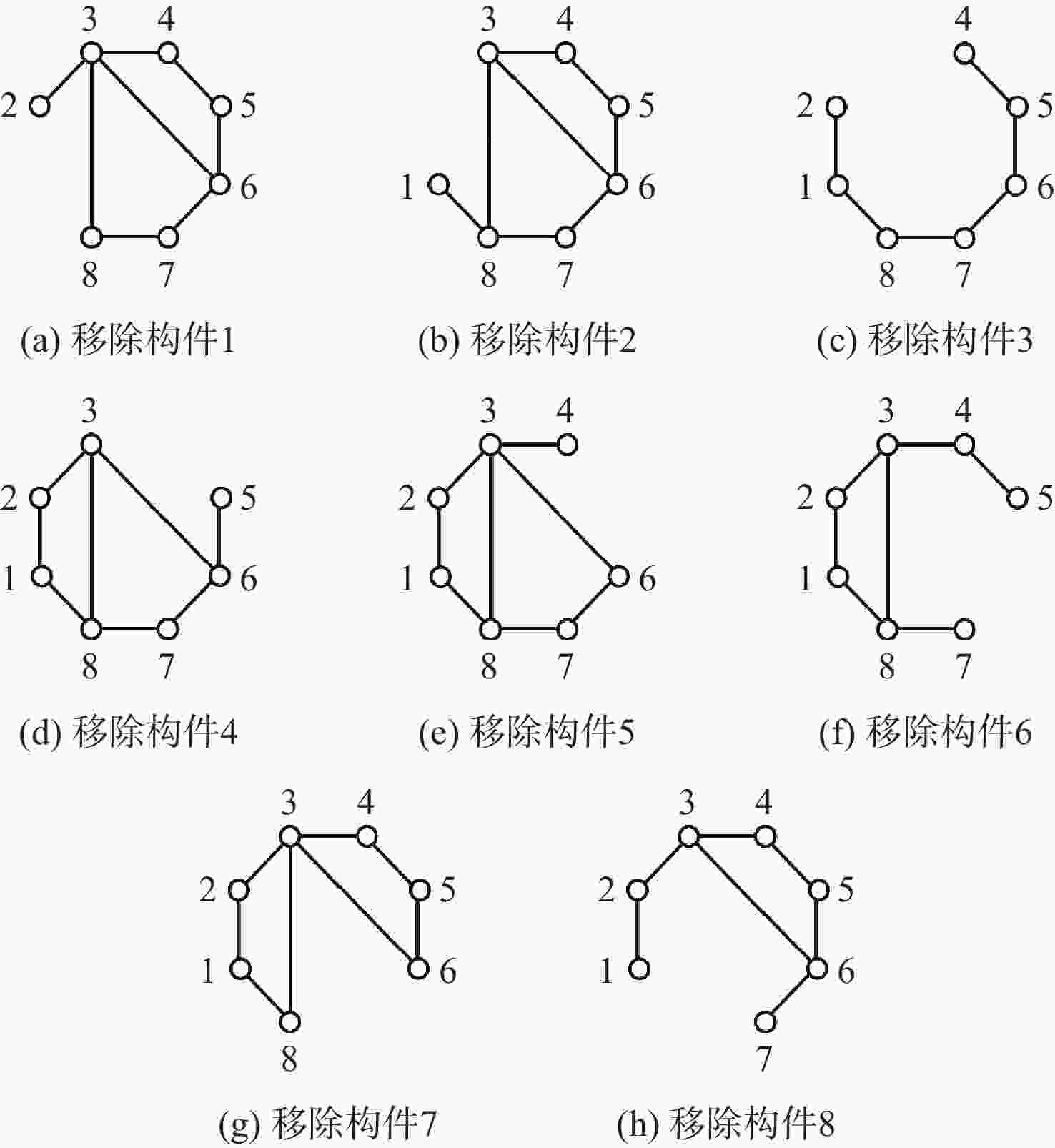
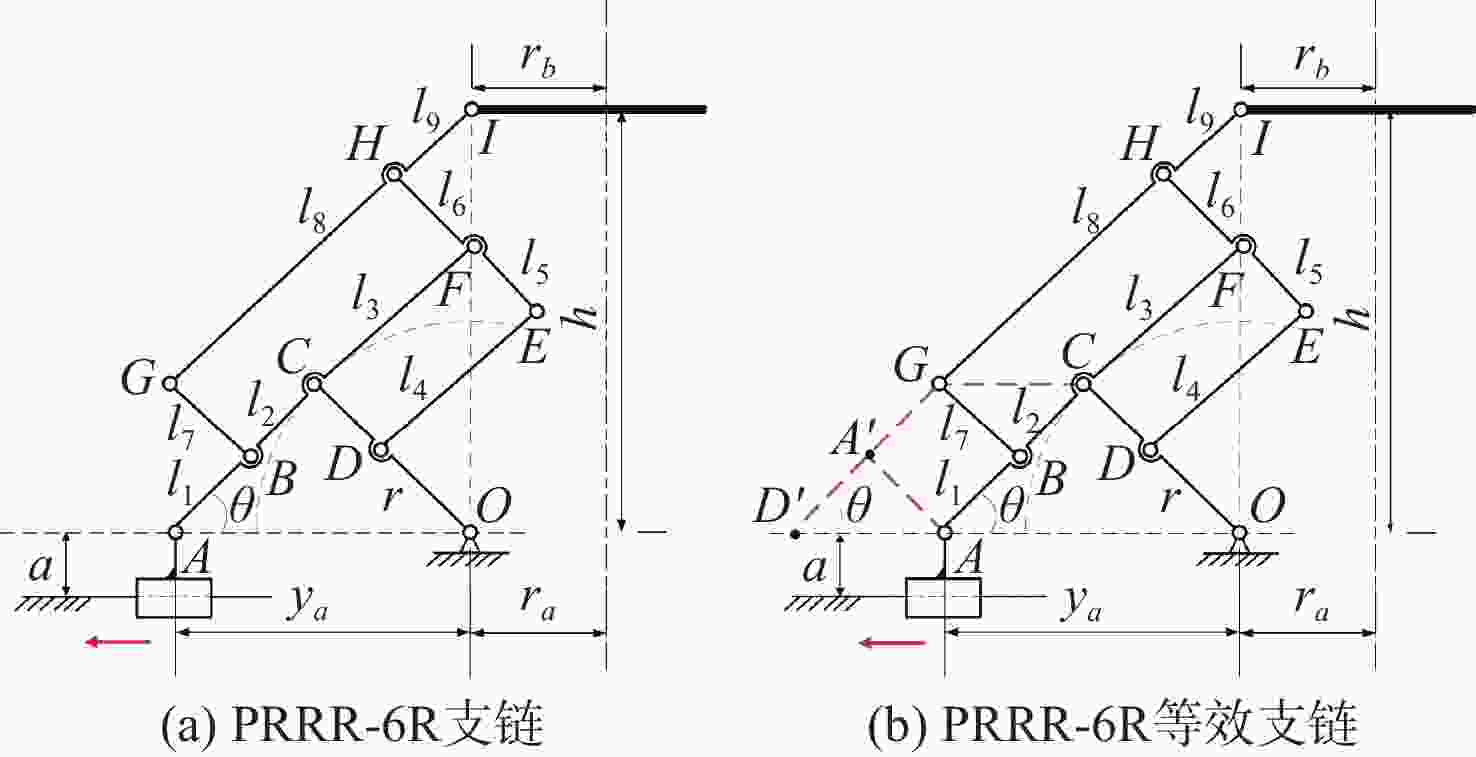
表 8 可伸展支链构型拓扑图及其演化构型
Table 8. Topological diagram of extendable branched chain configuration and its evolutionary configuration
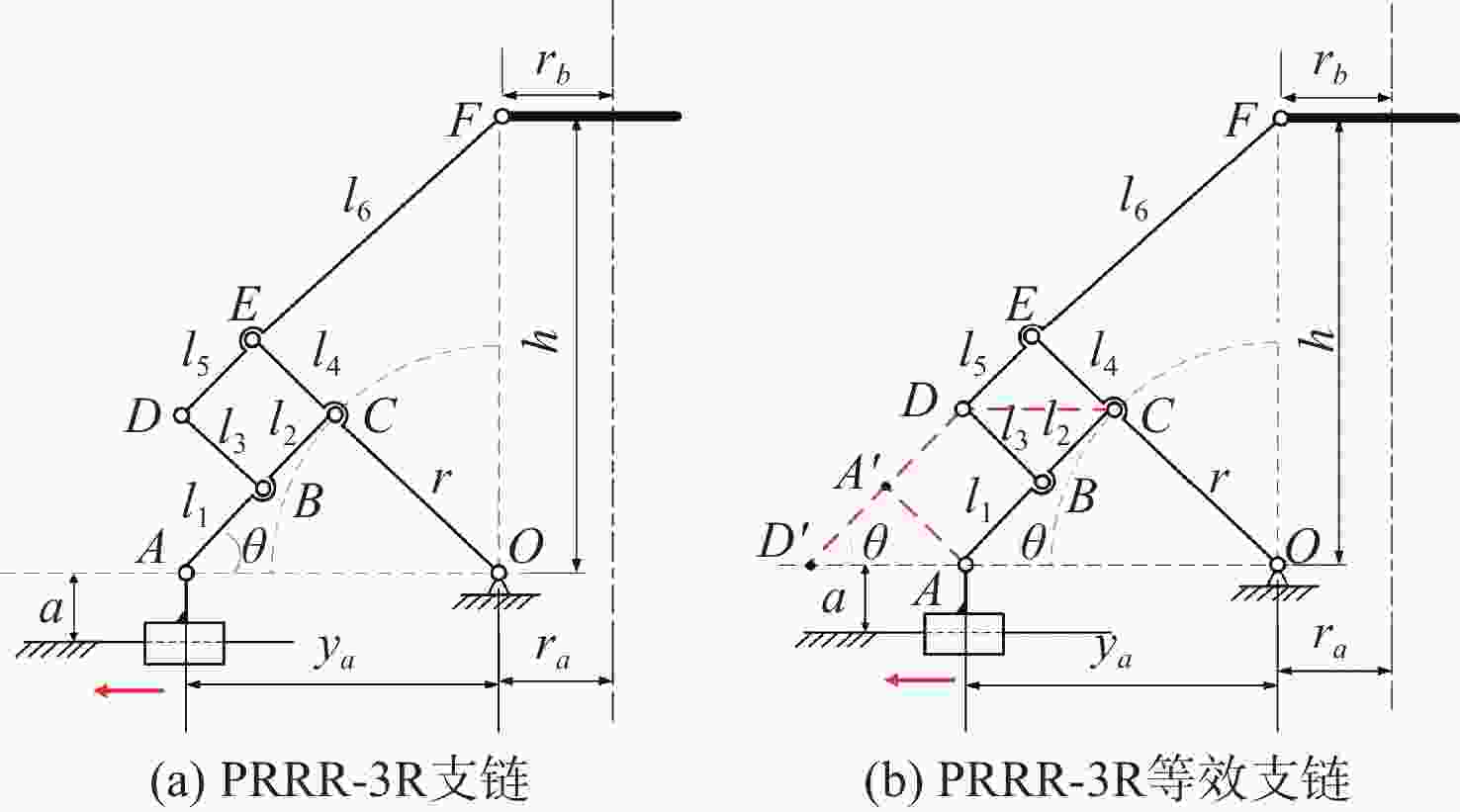
支链单元 机构 构型拓扑图 演化构型 PRRR
支链四杆机构 

PRRR-3R
支链六杆机构 

PRRR-6R
支链八杆机构 

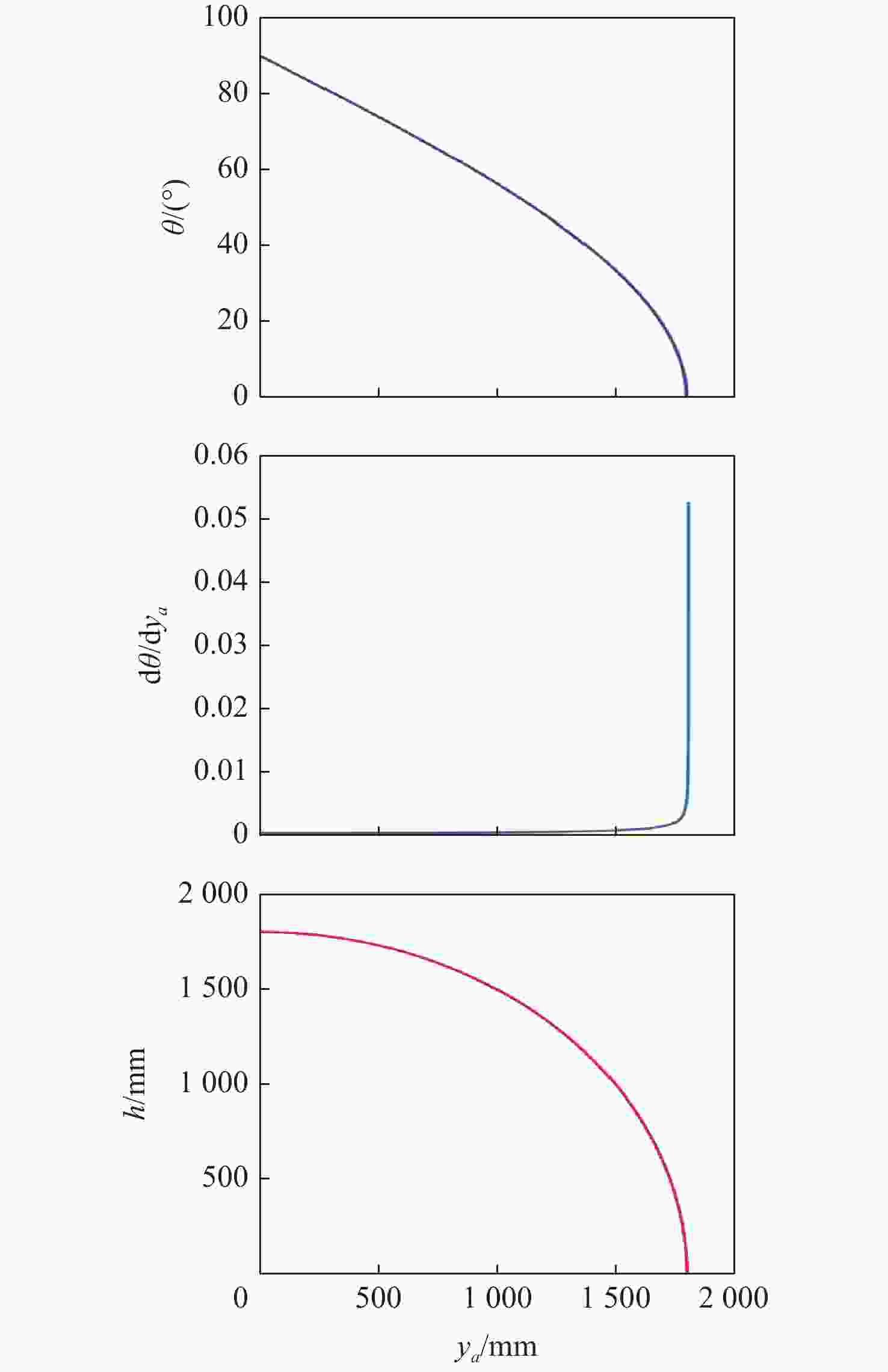
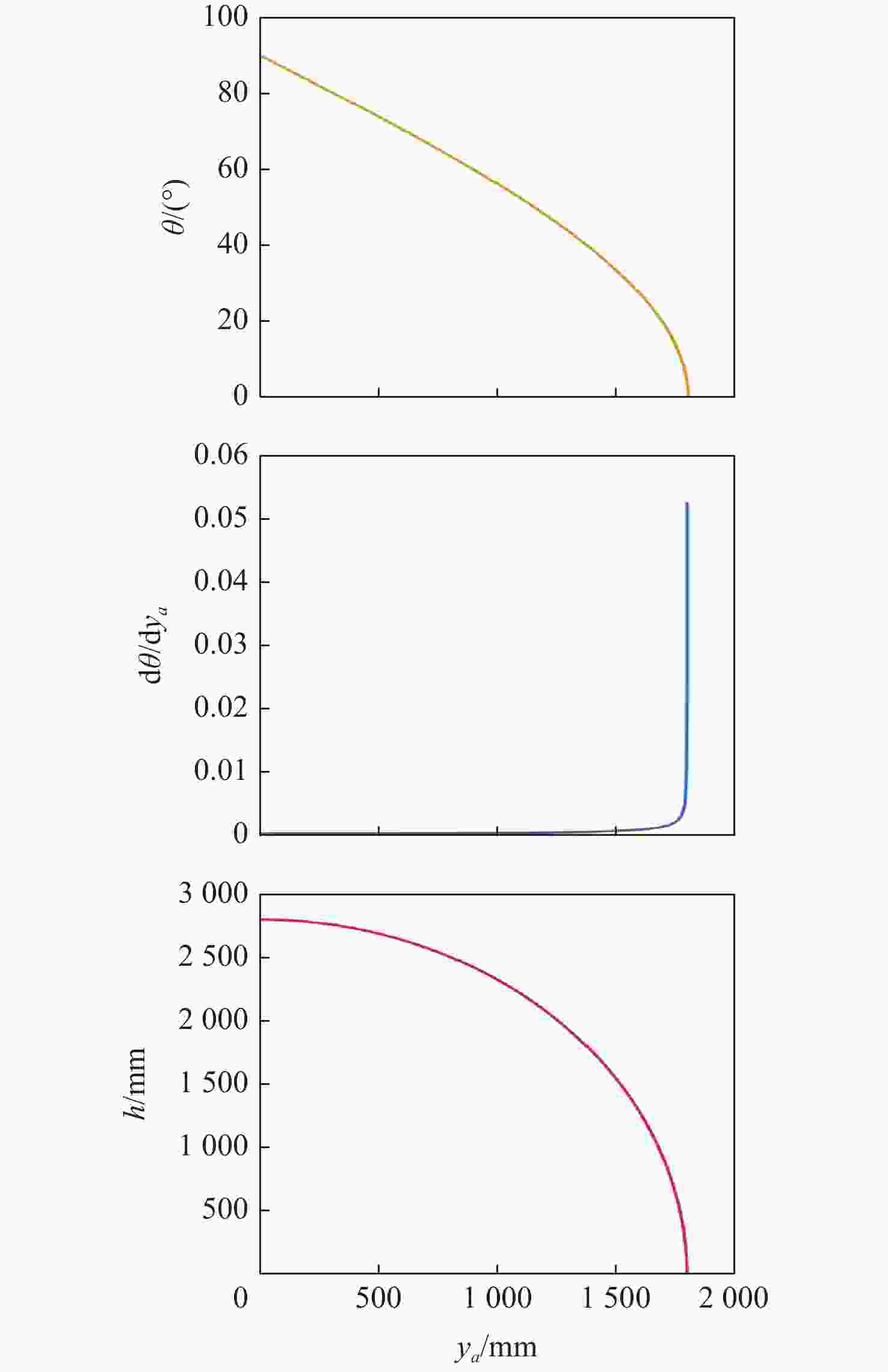
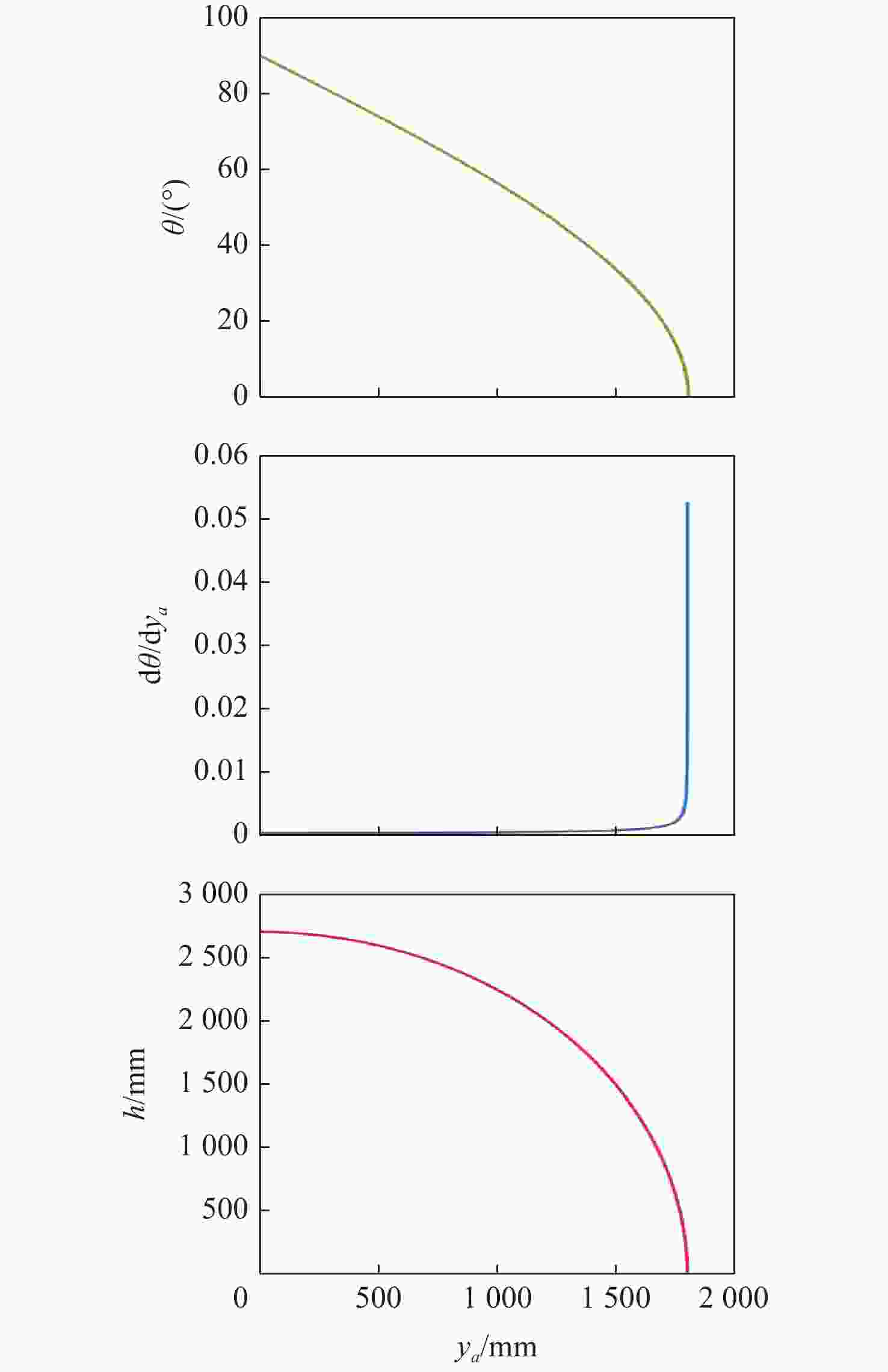
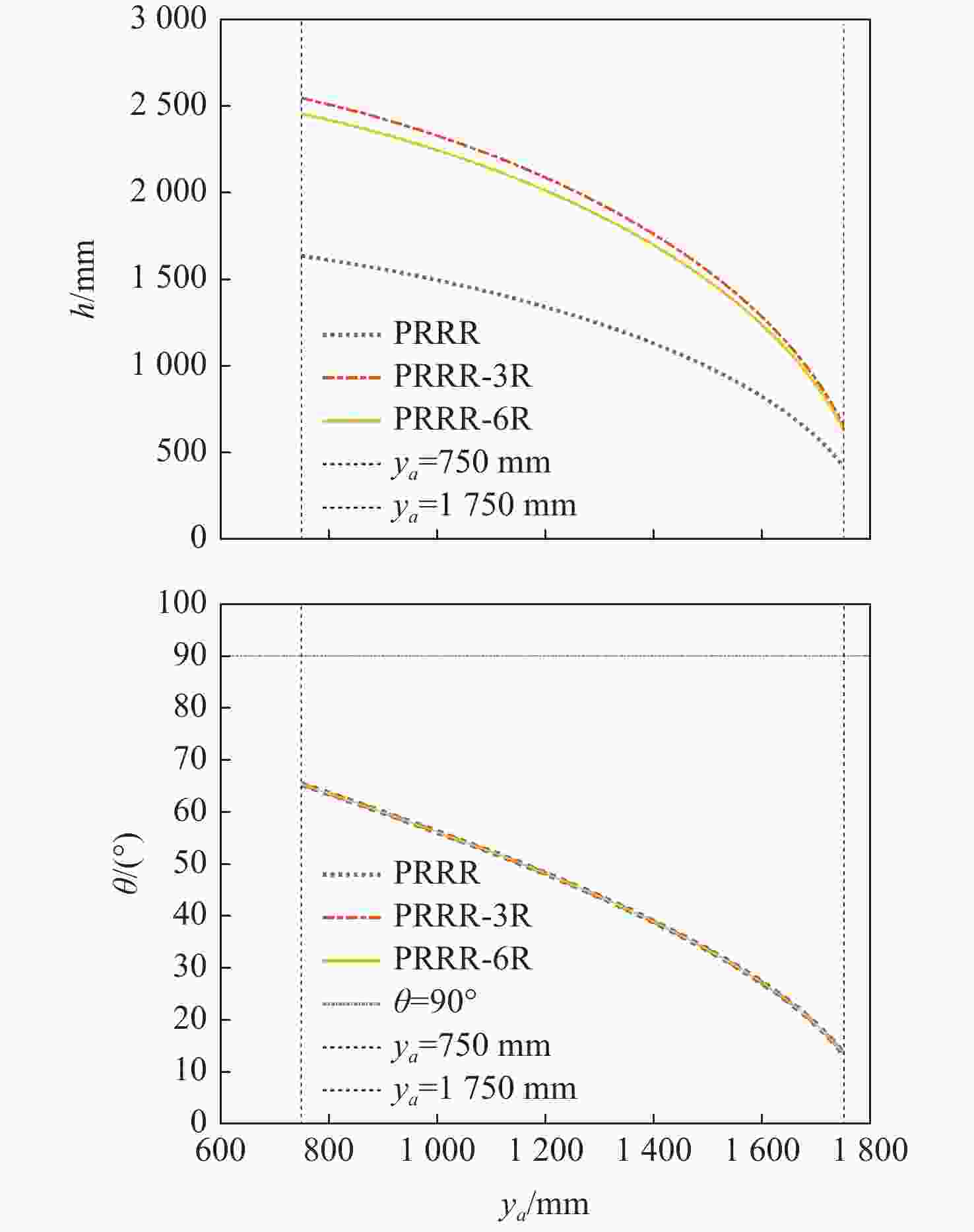
表 9 不同可伸展机构的伸展性能比较
Table 9. Comparison of stretching performance of different extendable mechanisms
序
号基本支
链单元移动距离
$\Delta y$/mm起始高度/
mm终止高度/
mm高度差
$\Delta h$/mm1 PRRR 支链 1000 1636.3068 421.3075 1214.9993 2 PRRR-3R
支链1000 2545.3662 655.3672 1889.9990 3 PRRR-6R
支链1000 2454.4602 631.9612 1822.4990 表 10 3种支链构型的线伸展比
Table 10. Linear extension ratio of three branched chain configurations
基本支链单元 支链尺寸参数 高度差$\Delta h$/mm 线伸展比 PRRR
支链
1214.9993 1.215 PRRR-3R
支链
1889.9990 1.890 PRRR-6R
支链
1822.4990 1.822 表 11 45号钢的相关性能参数
Table 11. Relevant performance parameters of 45# steel
材料名称 弹性模量/
(N·m−2)泊松比 质量密度/
(kg·m−3)屈服强度/
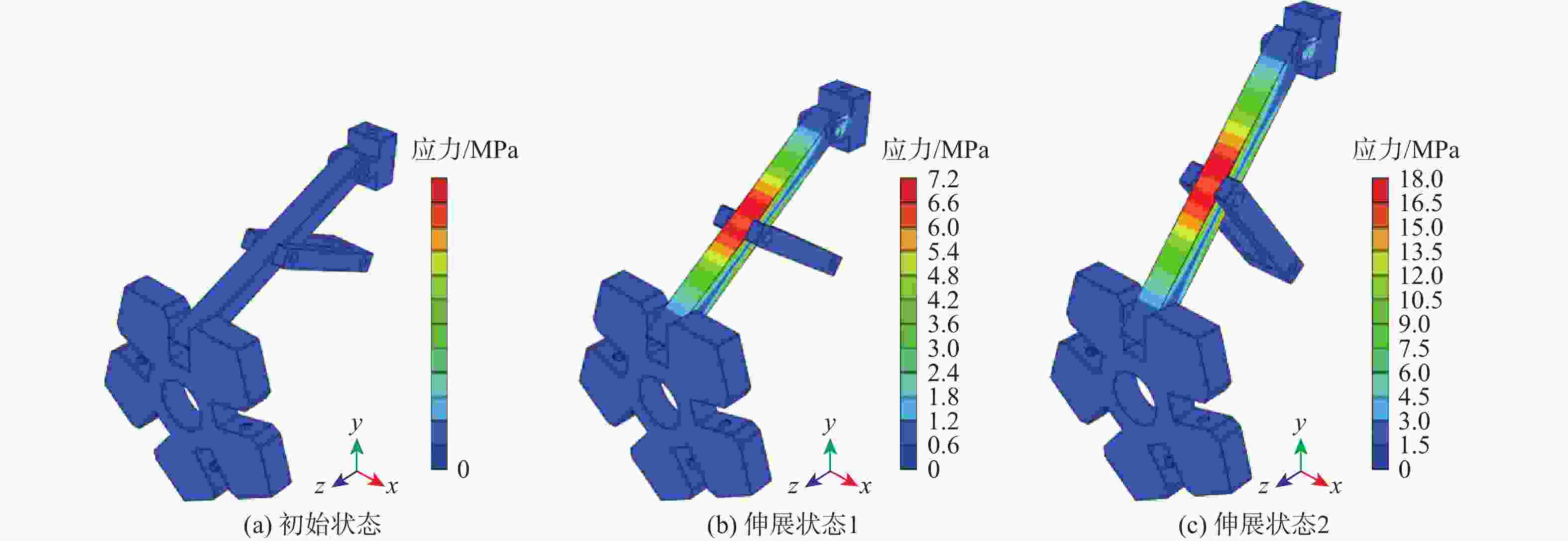
(N·m−2)45号钢 2.09×1011 0.269 7.89×103 3.55×108 表 12 3种可伸展支链构型的性能比较
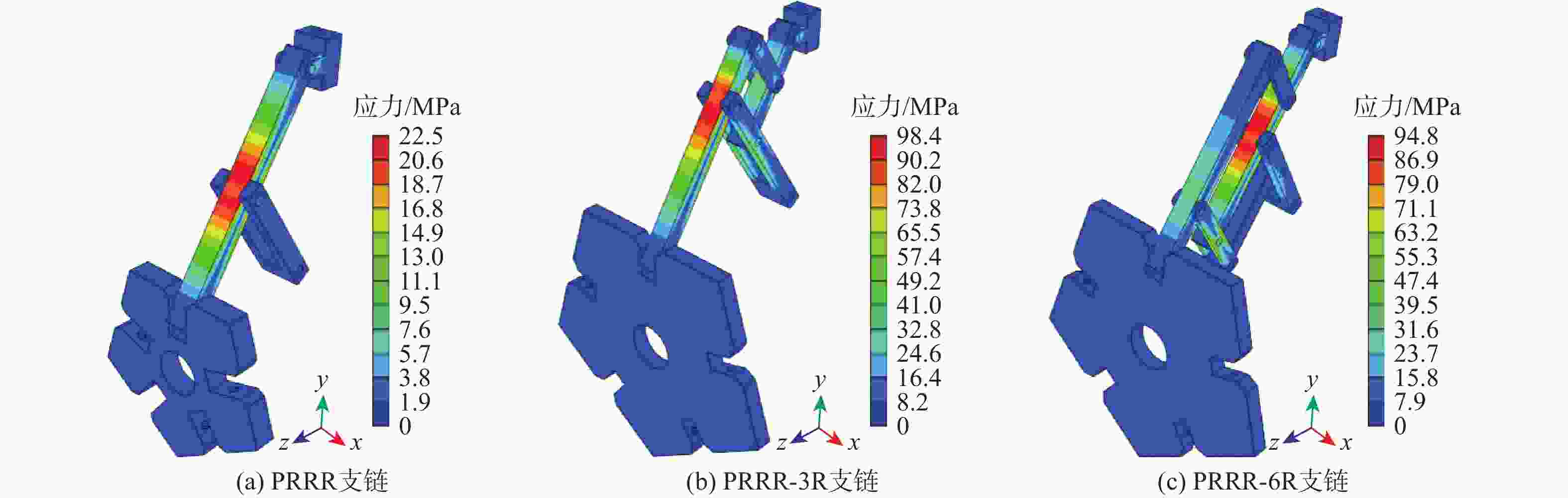
Table 12. Stiffness comparison of three extendable branched chain configurations
基本支链
单元可伸展支链
结构可伸展支链
应力云图最大应
力/ MPa占[σ]
百分比/%伸展
性能Θ并联可伸展机构 PRRR
支链

22.5 15.8 1.215 
PRRR-3R
支链

98.4 69.3 1.890 
PRRR-6R
支链

94.8 66.8 1.822 
-
[1] 刘欣, 王国庆, 李曙光, 等. 重型运载火箭关键制造技术发展展望[J]. 航天制造技术, 2013(1): 1-6.LIU X, WANG G Q, LI S G, et al. Forecasts on crucial manufacturing technology development of heavy lift launch vehicle[J]. Aerospace Manufacturing Technology, 2013(1): 1-6(in Chinese). [2] 周磊, 李新和, 俞大辉, 等. 球冠形薄壁封头在小减薄率工况下的失稳研究[J]. 锻压技术, 2016, 41(1): 25-31. doi: 10.13330/j.issn.1000-3940.2016.01.006ZHOU L, LI X H, YU D H, et al. Research on instabilities of thin-walled spherical head at low thinning rate[J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2016, 41(1): 25-31(in Chinese). doi: 10.13330/j.issn.1000-3940.2016.01.006 [3] 朱云平, 张帆. 贮箱绝热层打磨机器人系统设计[J]. 上海工程技术大学学报, 2017, 31(1): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-444X.2017.01.001ZHU Y P, ZHANG F. Design of grinding robot system for tank insulating layer[J]. Journal of Shanghai University of Engineering Science, 2017, 31(1): 1-4(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-444X.2017.01.001 [4] 黄顺舟, 王力, 祁佩, 等. 低温贮箱隔热层打磨机器人的动力学仿真分析[J]. 环球市场信息导报, 2016, 37: 137-139.HUANG S Z, WANG L, QI P, et al. Dynamic simulation analysis of low temperature tank insulation polishing robot[J]. Global Market Information Guide, 2016, 37: 137-139(in Chinese). [5] 党嘉强, 陶正瑞, 徐锦泱, 等. 聚氨酯泡沫绝热层高效精密打磨装置设计与建模[J]. 机床与液压, 2020, 48(2): 59-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2020.02.013DANG J Q, TAO Z R, XU J Y, et al. Design and modeling of high-efficiency and high-precision grinding device for polyurethane foam insulations[J]. Machine Tool & Hydraulics, 2020, 48(2): 59-62(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2020.02.013 [6] 陶波, 赵兴炜, 丁汉. 大型复杂构件机器人移动加工技术研究[J]. 中国科学(技术科学), 2018, 48(12): 1302-1312. doi: 10.1360/N092018-00192TAO B, ZHAO X W, DING H. Study on robotic mobile machining techniques for large complex components[J]. Scientia Sinica (Technologica), 2018, 48(12): 1302-1312(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/N092018-00192 [7] 李冰岩, 刘荣强, 从强, 等. 基于豆荚杆的三棱柱式可展开薄膜支撑臂设计与优化[J]. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56(7): 35-43. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.07.035LI B Y, LIU R Q, CONG Q, et al. Design and optimization of a tri-prism deployable membrane support arm using lenticular collapsible composite tubes[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(7): 35-43(in Chinese). doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.07.035 [8] 杨萍萍, 冯长凯. 可展开伸缩套管式伸展臂结构设计与分析[J]. 电子科技, 2008, 21(9): 8-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7820.2008.09.003YANG P P, FENG C K. The structural design and analysis of the deployable[J]. Electronic Science and Technology, 2008, 21(9): 8-11(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7820.2008.09.003 [9] SHAN M H, GUO H W, LIU R Q, et al. Design and analysis of a triangular prism modular deployable mast[C]//2013 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 1546-1551. [10] 高明星, 刘荣强, 李冰岩, 等. 空间可展开三棱柱伸展臂设计与优化[J]. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56(15): 129-137. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.15.129GAO M X, LIU R Q, LI B Y, et al. Design and optimization of space deployable tri-prism mast[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(15): 129-137(in Chinese). doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.15.129 [11] 马艳, 张群, 李锐明, 等. 可折展空间八转动副连杆捕获机构的设计[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2020, 54(3): 179-187. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb202003022MA Y, ZHANG Q, LI R M, et al. Design and analysis of foldable capture mechanism based on spatial 8-rotation linkages[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2020, 54(3): 179-187(in Chinese). doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb202003022 [12] 刘仁志, 宋志佳, 高文杰, 等. 正八面体空间伸展臂的八面体单元结构分析[J]. 机械设计, 2013, 30(6): 72-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2354.2013.06.018LIU R Z, SONG Z J, GAO W J, et al. Analysis of octahedron unit structure of regular octahedron space deployable arm[J]. Journal of Machine Design, 2013, 30(6): 72-75(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2354.2013.06.018 [13] 韩博, 许允斗, 姚建涛, 等. 双层环形桁架可展天线机构运动特性与动力学分析[J]. 兵工学报, 2020, 41(4): 810-821. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2020.04.020HAN B, XU Y D, YAO J T, et al. Kinematic characteristics and dynamics analysis of a double-ring truss deployable antenna mechanism[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2020, 41(4): 810-821(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2020.04.020 [14] ZHAO J S, CHU F L, FENG Z J. The mechanism theory and application of deployable structures based on SLE[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2009, 44(2): 324-335. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2008.03.014 [15] 史创, 郭宏伟, 刘荣强, 等. 双层环形可展开天线机构构型优选及结构设计[J]. 宇航学报, 2016, 37(7): 869-878.SHI C, GUO H W, LIU R Q, et al. Configuration optimization and structure design of the double-layer hoop deployable antenna mechanism[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2016, 37(7): 869-878(in Chinese). [16] ZHAO T S, WANG C, LIU X, et al. Stiffness and singularity analysis of foldable parallel mechanism for ship-based stabilized platform[J]. Robotica, 2016, 34(4): 913-924. doi: 10.1017/S0263574714001969 [17] 房海蓉, 陈江红. 一种新型四自由度并联机构设计与分析[J]. 北京交通大学学报, 2011, 35(4): 134-137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0291.2011.04.027FANG H R, CHEN J H. Structure synthesis and analysis of a novel four-degree-of-freedom parallel manipulator[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2011, 35(4): 134-137(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0291.2011.04.027 [18] LI D, GUO S, CHEN Y. Kinematic performance and task planning analysis of a parameter reconfigurable parallel mechanism[C]//2019 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 545-552. [19] 邹琦, 曲海波, 郭盛. 一种三自由度可重构并联机构优化设计及性能分析[J]. 中国机械工程, 2018, 29(10): 1172-1178. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2018.10.007ZOU Q, QU H B, GUO S. Optimal design and performance analysis of a 3-DOF reconfigurable parallel mechanism[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 29(10): 1172-1178(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2018.10.007 [20] HUANG G Y, GUO S, ZHANG D, et al. Kinematic analysis and multi-objective optimization of a new reconfigurable parallel mechanism with high stiffness[J]. Robotica, 2018, 36(2): 187-203. doi: 10.1017/S0263574717000236 [21] 杨廷力. 机器人机构拓扑结构学[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2004.YANG T L. Topology structure design of robot mechanisms[M]. Beijing: China Mechine Press, 2004 (in Chinese). [22] 丁华锋, 黄真. 基于环路特性的运动链拓扑图及特征描述的自动生成[J]. 机械工程学报, 2007, 43(11): 40-43. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6686.2007.11.006DING H F, HUANG Z. Automatic creation of topological graphs and the characteristic representations of kinematic chains based on the loop characteristics[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2007, 43(11): 40-43(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6686.2007.11.006 -







 下载:
下载: