-
摘要:
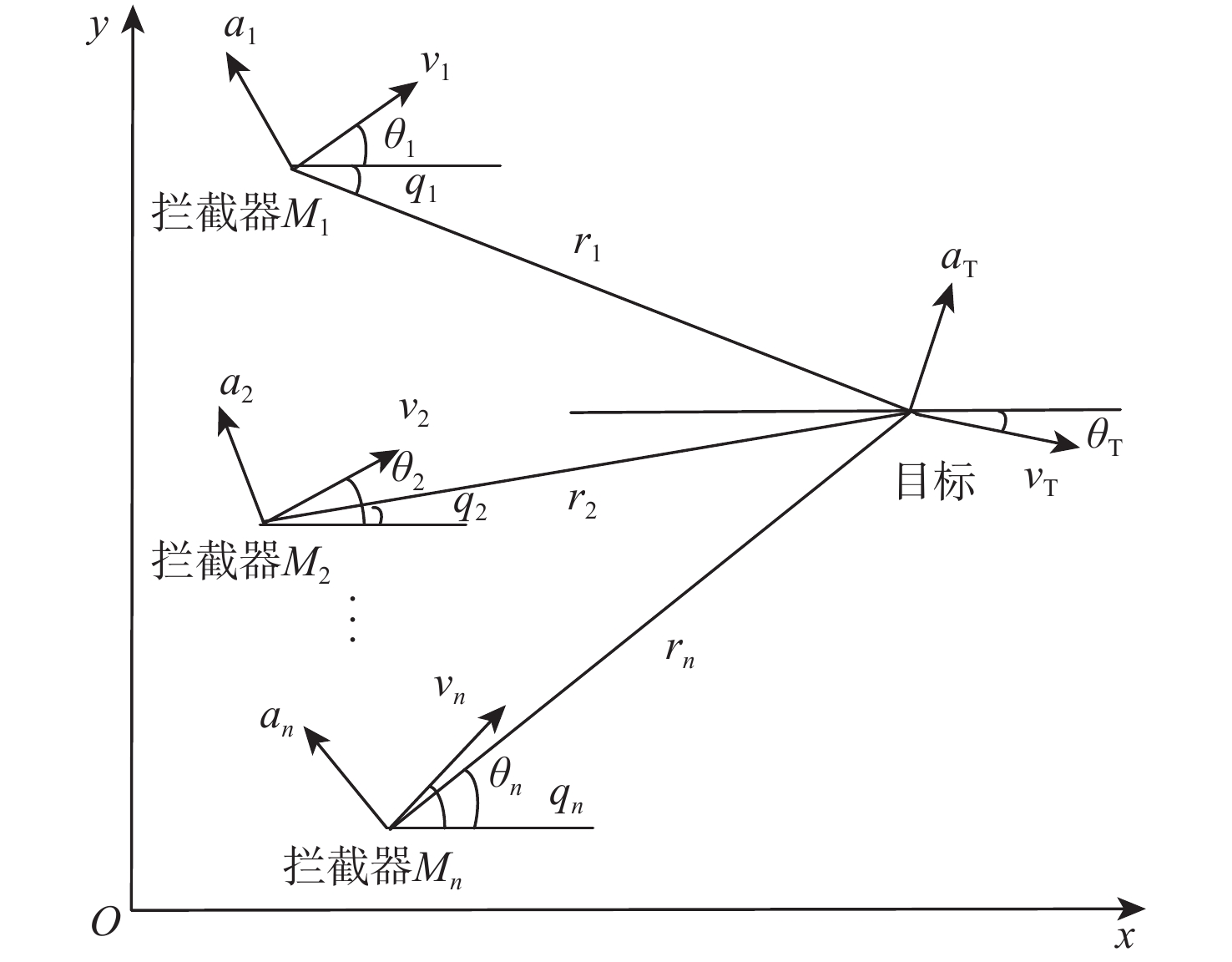
针对多飞行器协同拦截机动目标问题,基于有限时间滑模控制方法和一致性理论提出一种考虑拦截时间约束的协同制导方法。基于相对运动学和动力学关系,建立考虑拦截时间和角度约束的协同拦截模型;基于滑模控制理论和超螺旋控制算法分别设计了视线方向和视线法向协同制导律以保证各飞行器拦截时间在有限时间内一致收敛且拦截角度收敛到期望值;基于一致性理论证明了所提方法有限时间一致收敛性能。仿真结果表明:所提方法能够保证各飞行器以期望拦截角同时拦截目标,验证了所提方法的有效性。
Abstract:To address the problem of multi-aircraft cooperative interception of maneuvering targets, a cooperative guidance method considering interception time constraints is proposed based on the finite-time sliding mode control method and consistency theory. Based on the relative kinematics and dynamics, a cooperative interception model considering interception time and angle constraints is established. Based on the sliding mode control theory and super-twisting control algorithm, the coordinate guidance laws in line-of-sight direction and line-of-sight normal direction are designed to ensure that the interception time of each aircraft converges uniformly within the finite time and that the interception angle converges to the expected value. Based on the consistency theory, the finite-time consistent convergence performance of the proposed guidance method is demonstrated. The simulation results show that all the aircrafts can intercept targets simultaneously at the desired intercept angle, which verifies the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
Key words:
- cooperative guidance /
- multi-axis aircraft /
- interception time /
- interception angle /
- consistency
-
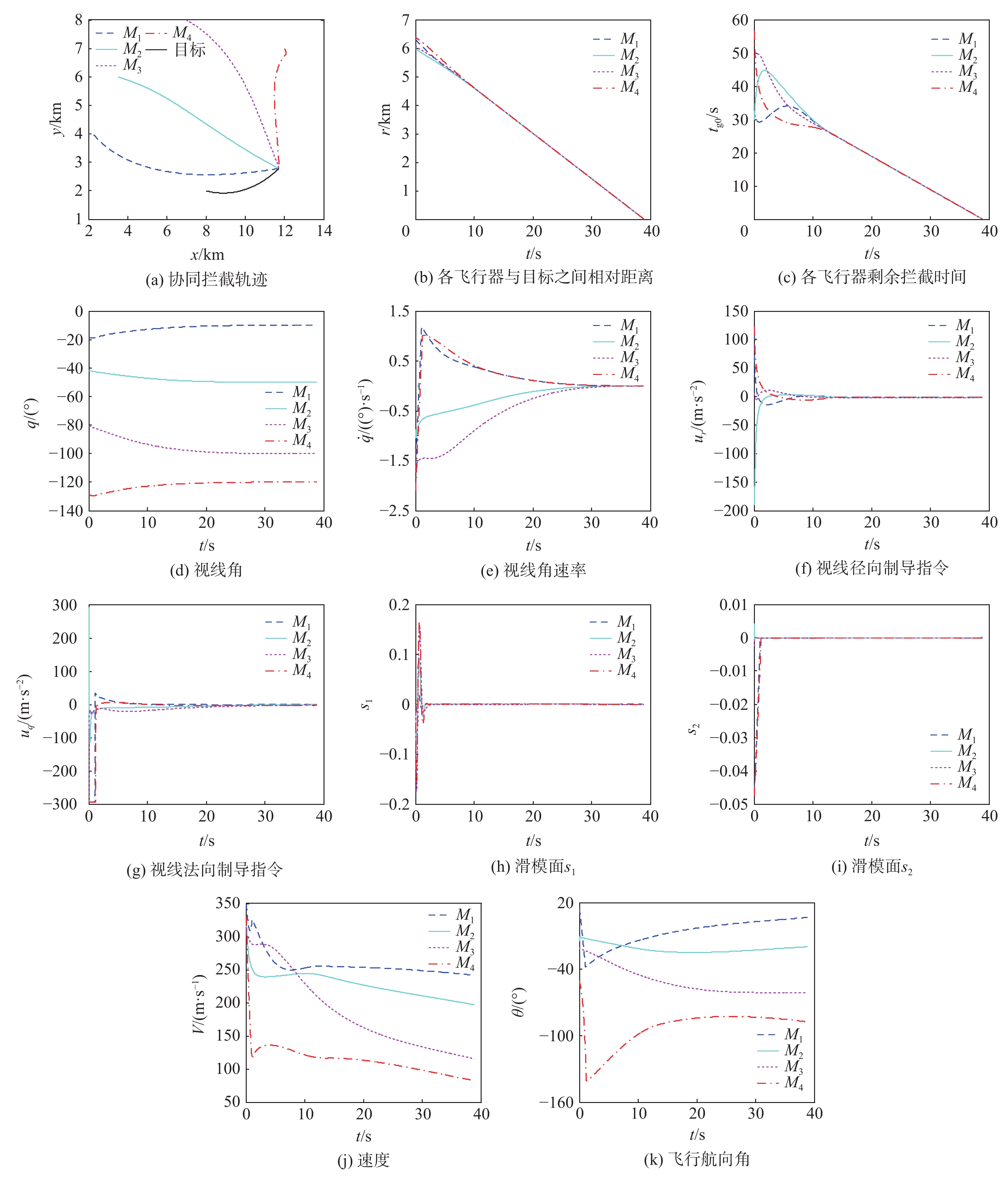
表 1 目标和各飞行器初始状态设置
Table 1. Initial states of each aircraft and target
飞行器 初始位置/km 初始速度/( m·s−1) 初始
航向角/(°)期望落角/(°) 目标 (8,2) 100 −10 M1 (2,4) 350 15 −10 M2 (3.5,6) 320 −15 −50 M3 (7,8) 320 −20 −100 M4 (12,7) 330 −50 −120 表 2 协同拦截结果
Table 2. Results of cooperative interception
飞行器 脱靶量/m 拦截耗时/s 拦截角误差/(°) M1 0.85 38.76 0.06 M2 0.76 38.76 0.12 M3 0.94 38.76 0.16 M4 0.73 38.76 0.10 -
[1] JEON I S, LEE J I, TAHK M J. Impact-time-control guidance law for anti-ship missiles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2006, 14(2): 260-266. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2005.863655 [2] JEON I S, LEE J I, TAHK M J. Guidance law to control impact time and angle[C]// 2005 International Conference on Control and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2005: 852-857. [3] HU Q L, HAN T, XIN M. New impact time and angle guidance strategy via virtual target approach[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2018, 41(8): 1755-1765. doi: 10.2514/1.G003436 [4] HU Q L, HAN T, XIN M. Sliding-mode impact time guidance law design for various target motions[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2019, 42(1): 136-148. doi: 10.2514/1.G003620 [5] KIM M, JUNG B, HAN B, et al. Lyapunov-based impact time control guidance laws against stationary targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(2): 1111-1122. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.130717 [6] ZHANG Y A, WANG X L, WU H L. A distributed cooperative guidance law for salvo attack of multiple anti-ship missiles[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2015, 28(5): 1438-1450. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2015.08.009 [7] JEON I S, LEE J I, TAHK M J. Impact-time-control guidance with generalized proportional navigation based on nonlinear formulation[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2016, 39(8): 1885-1890. doi: 10.2514/1.G001681 [8] ZHOU J L, YANG J Y. Distributed guidance law design for cooperative simultaneous attacks with multiple missiles[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2016, 39(10): 2439-2447. doi: 10.2514/1.G001609 [9] WANG X L, ZHANG Y A, WU H L. Distributed cooperative guidance of multiple anti-ship missiles with arbitrary impact angle constraint[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2015, 46: 299-311. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2015.08.002 [10] WANG B H, WANG J C, ZHANG B, et al. Leader-follower consensus for multi-agent systems with three-layer network framework and dynamic interaction jointly connected topology[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 207: 231-239. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.03.073 [11] 孙雪娇, 周锐, 吴江, 等. 多导弹分布式协同制导与控制方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2014, 40(1): 120-124. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2014.01.014SUN X J, ZHOU R, WU J, et al. Distributed cooperative guidance and control for multiple missiles[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2014, 40(1): 120-124(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2014.01.014 [12] 马国欣, 张友安. 多导弹时间协同分布式导引律设计[J]. 控制与决策, 2014, 29(5): 843-847.MA G X, ZHANG Y A. Time-cooperative distributed guidance law design for multi-missiles[J]. Control and Decision, 2014, 29(5): 843-847(in Chinese). [13] GUTMAN S. Impact-time vector guidance[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2017, 40(8): 2110-2114. doi: 10.2514/1.G002556 [14] 吕腾, 吕跃勇, 李传江, 等. 带视线角约束的多导弹有限时间协同制导律[J]. 兵工学报, 2018, 39(2): 305-314.LYU T, LYU Y Y, LI C J, et al. Finite time cooperative guidance law for multiple missiles with line-of-sight angle constraint[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2018, 39(2): 305-314(in Chinese). [15] 张春妍, 宋建梅, 侯博, 等. 带落角和时间约束的网络化导弹协同制导律[J]. 兵工学报, 2016, 37(3): 431-438.ZHANG C Y, SONG J M, HOU B, et al. Cooperative guidance law with impact angle and impact time constraints for networked missiles[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2016, 37(3): 431-438(in Chinese). [16] SONG J H, SONG S M, ZHOU H B. Adaptive nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode guidance law with impact angle constraints[J]. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2016, 14(1): 99-114. doi: 10.1007/s12555-014-0155-8 [17] IDAN M, GOLAN O M, GUELMAN M. Optimal planar interception with terminal constraints[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 1995, 18(6): 1273-1279. doi: 10.2514/3.21541 [18] RATNOO A, GHOSE D. Impact angle constrained interception of stationary targets[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2008, 31(6): 1817-1822. doi: 10.2514/1.37864 [19] KIM M, GRIDER K V. Terminal guidance for impact attitude angle constrained flight trajectories[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1973, 9(6): 852-859. [20] ERER K S, MERTTOPÇUOGLU O. Indirect impact-angle-control against stationary targets using biased pure proportional navigation[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2012, 35(2): 700-704. doi: 10.2514/1.52105 [21] GHOSH S, GHOSE D, RAHA S. Composite guidance for impact angle control against higher speed targets[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2016, 39(1): 98-117. doi: 10.2514/1.G001232 [22] PARK B G, KWON H H, KIM Y H, et al. Composite guidance scheme for impact angle control against a nonmaneuvering moving target[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2016, 39(5): 1132-1139. doi: 10.2514/1.G001547 [23] PARK B G, KIM T H, TAHK M J. Biased PNG with terminal-angle constraint for intercepting nonmaneuvering targets under physical constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(3): 1562-1572. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2667518 [24] KUMAR S R, RAO S, GHOSE D. Sliding-mode guidance and control for all-aspect interceptors with terminal angle constraints[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2012, 35(4): 1230-1246. doi: 10.2514/1.55242 [25] ZHANG Y X, SUN M W, CHEN Z Q. Finite-time convergent guidance law with impact angle constraint based on sliding-mode control[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2012, 70: 619-625. doi: 10.1007/s11071-012-0482-3 [26] KUMAR S R, RAO S, GHOSE D. Nonsingular terminal sliding mode guidance with impact angle constraints[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2014, 37(4): 1114-1130. doi: 10.2514/1.62737 [27] HARL N, BALAKRISHNAN S N. Impact time and angle guidance with sliding mode control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2012, 20(6): 1436-1449. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2011.2169795 [28] HE S M, LIN D F. Adaptive nonsingular sliding mode based guidance law with terminal angular constraint[J]. International Journal of Aeronautical and Space Sciences, 2014, 15(2): 146-152. doi: 10.5139/IJASS.2014.15.2.146 [29] ZHANG Y J, YANG Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Distributed finite-time tracking control for nonlinear multi-agent systems subject to external disturbances[J]. International Journal of Control, 2013, 86(1): 29-40. [30] WANG Z. Adaptive smooth second-order sliding mode control method with application to missile guidance[J]. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, 2017, 39(6): 848-860. doi: 10.1177/0142331215621616 [31] 张帅, 郭杨, 王仕成. 带有引诱角色的有限时间协同制导方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2018, 39(3): 308-317.ZHANG S, GUO Y, WANG S C. Finite time cooperative guidance method with a lure role[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2018, 39(3): 308-317(in Chinese). [32] 张帅, 郭杨, 王仕成. 考虑探测构形的多飞行器协同探测与制导一体化设计[J]. 宇航学报, 2018, 39(4): 401-410.ZHANG S, GUO Y, WANG S C. Integrated design of multi-aircraft cooperative detection and guidance considering the detection configuration[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2018, 39(4): 401-410(in Chinese). [33] SONG J H, SONG S M. Three-dimensional guidance law based on adaptive integral sliding mode control[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2016, 29(1): 202-214. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2015.12.012 [34] 宋俊红, 宋申民, 徐胜利. 一种拦截机动目标的多导弹协同制导律[J]. 宇航学报, 2016, 37(12): 1306-1314.SONG J H, SONG S M, XU S L. A cooperative guidance law for multiple missiles to intercept maneuvering target[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2016, 37(12): 1306-1314(in Chinese). [35] 吕腾, 吕跃勇, 李传江, 等. 带空间协同的多导弹时间协同制导律[J]. 航空学报, 2018, 39(10): 322115.LYU T, LYU Y Y, LI C J, et al. Time-cooperative guidance law for multiple missiles with spatial cooperation[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2018, 39(10): 322115(in Chinese). [36] SONG J H, SONG S M, XU S L. Three-dimensional cooperative guidance law for multiple missiles with finite-time convergence[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2017, 67: 193-205. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2017.04.007 [37] 周慧波, 宋申民, 宋俊红. 基于观测器的有限时间收敛的滑模导引律设计[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 47(1): 91-99.ZHOU H B, SONG S M, SONG J H. Design of an observer-based sliding mode guidance law with finite time convergence[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2016, 47(1): 91-99(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: