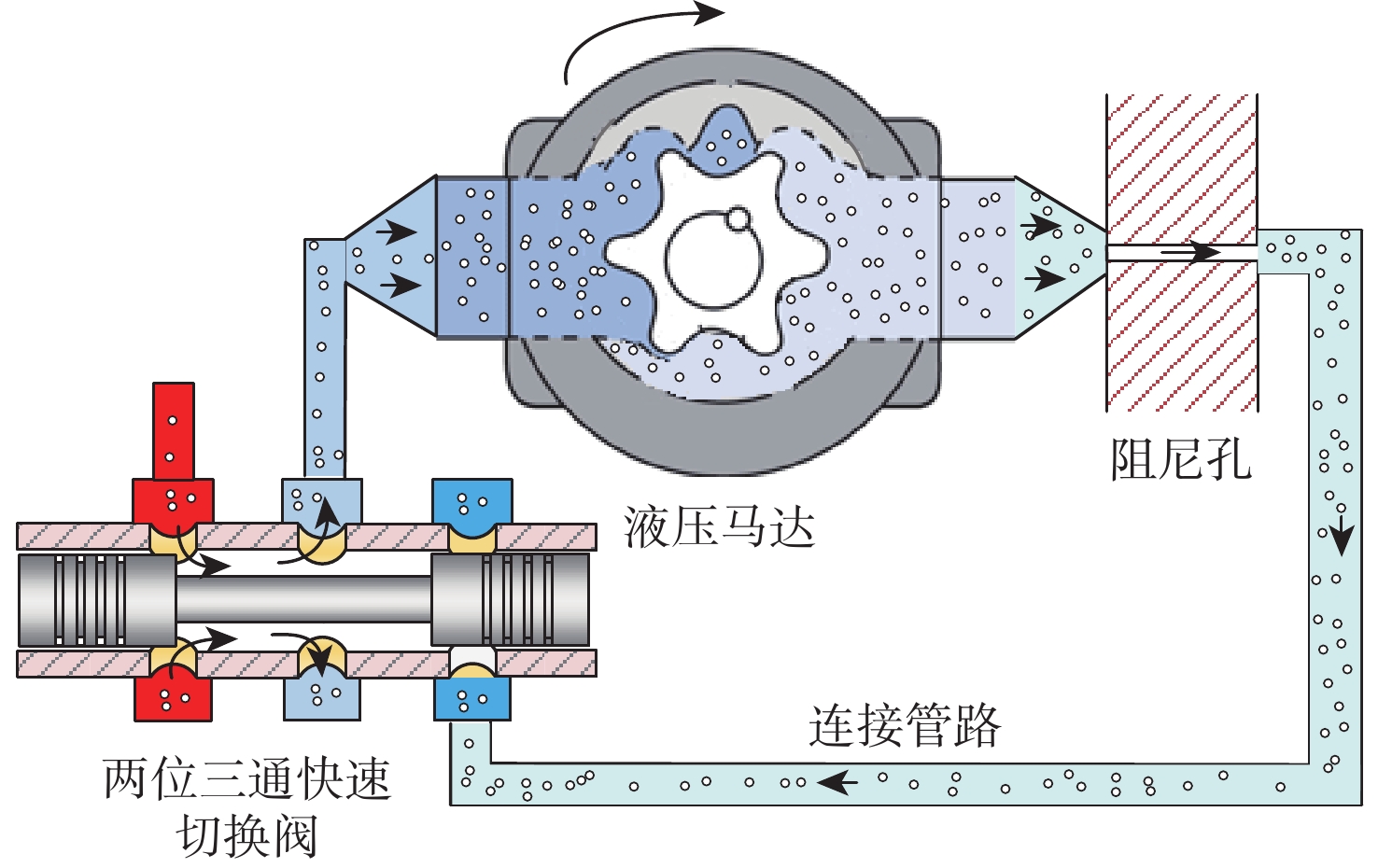
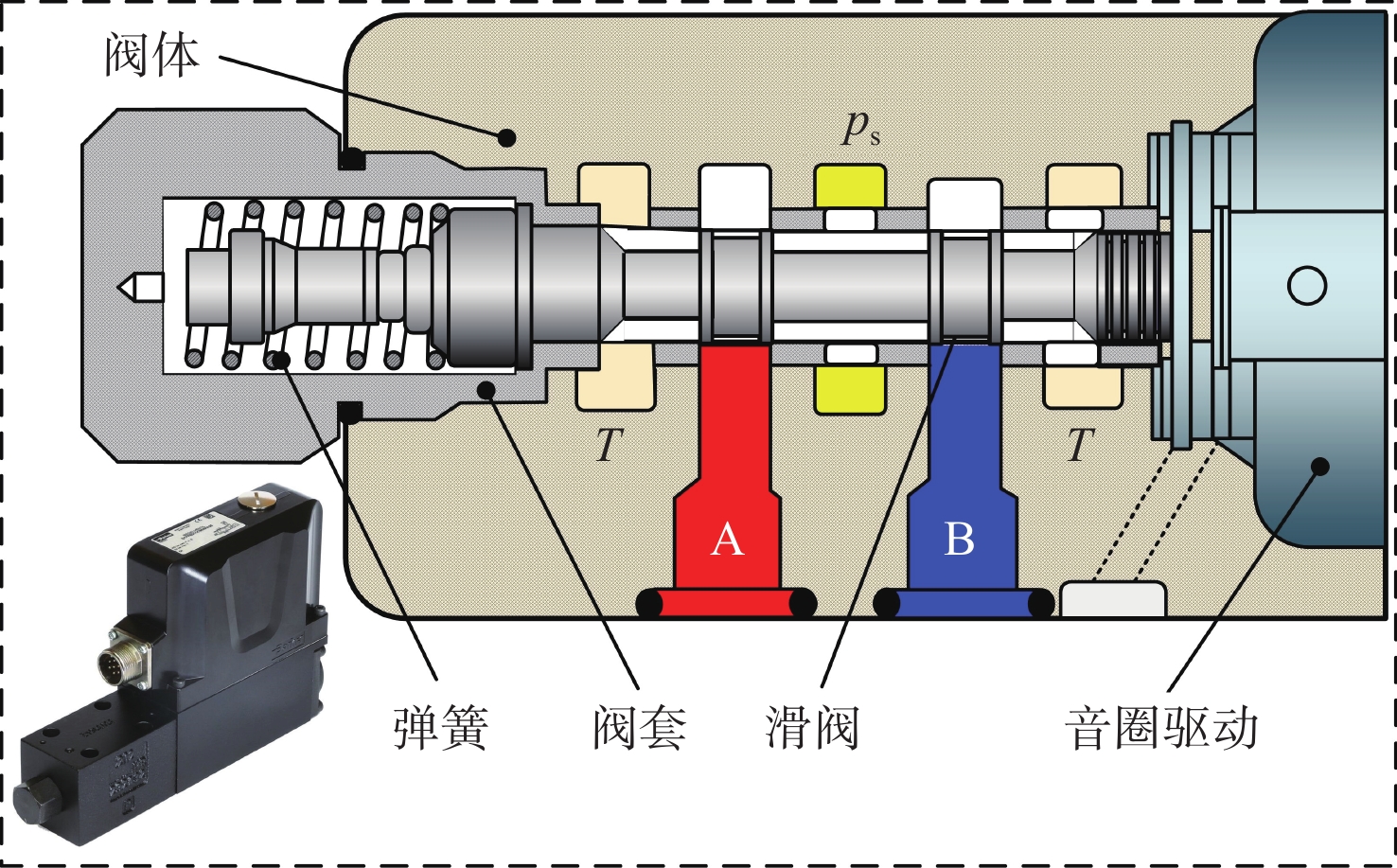
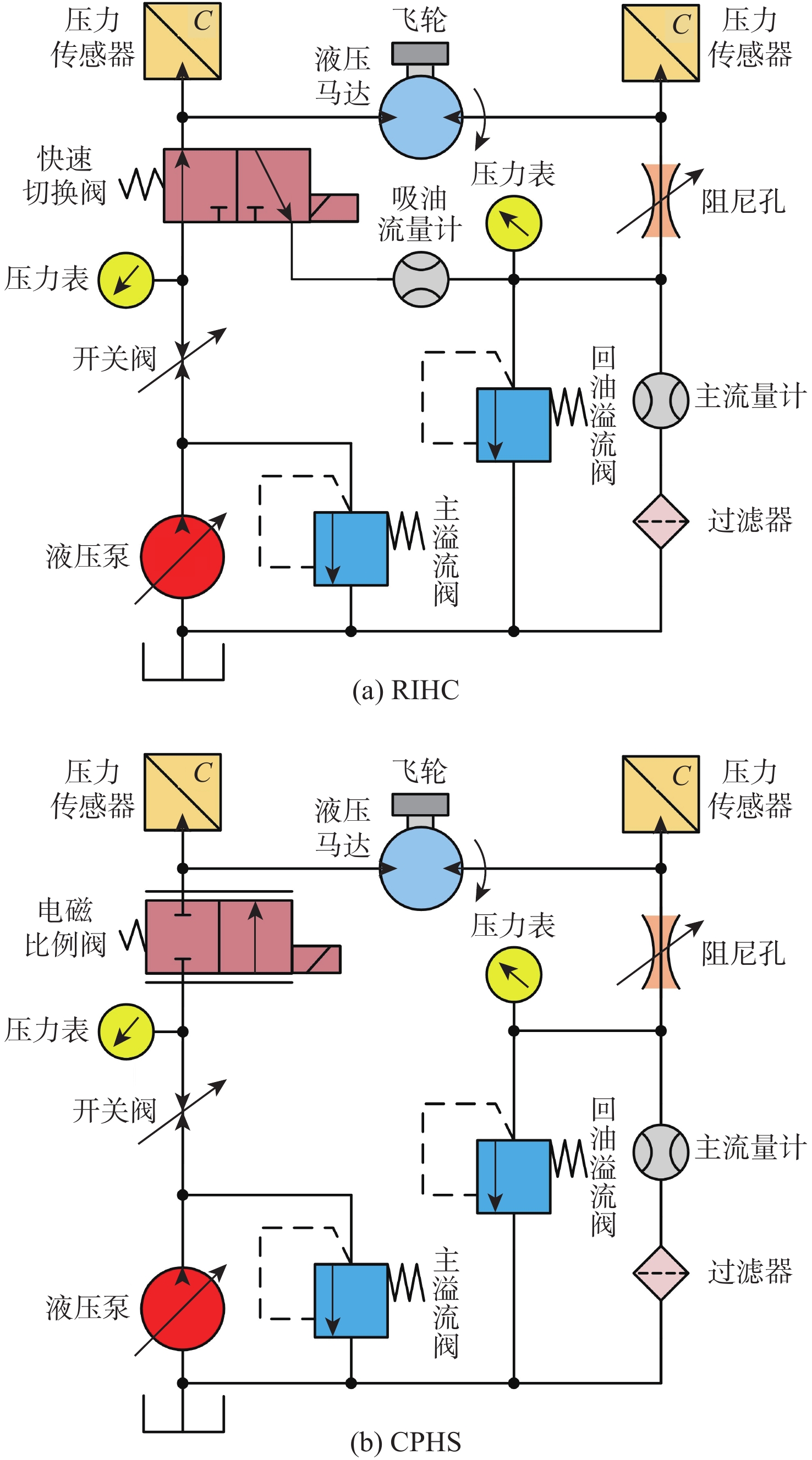
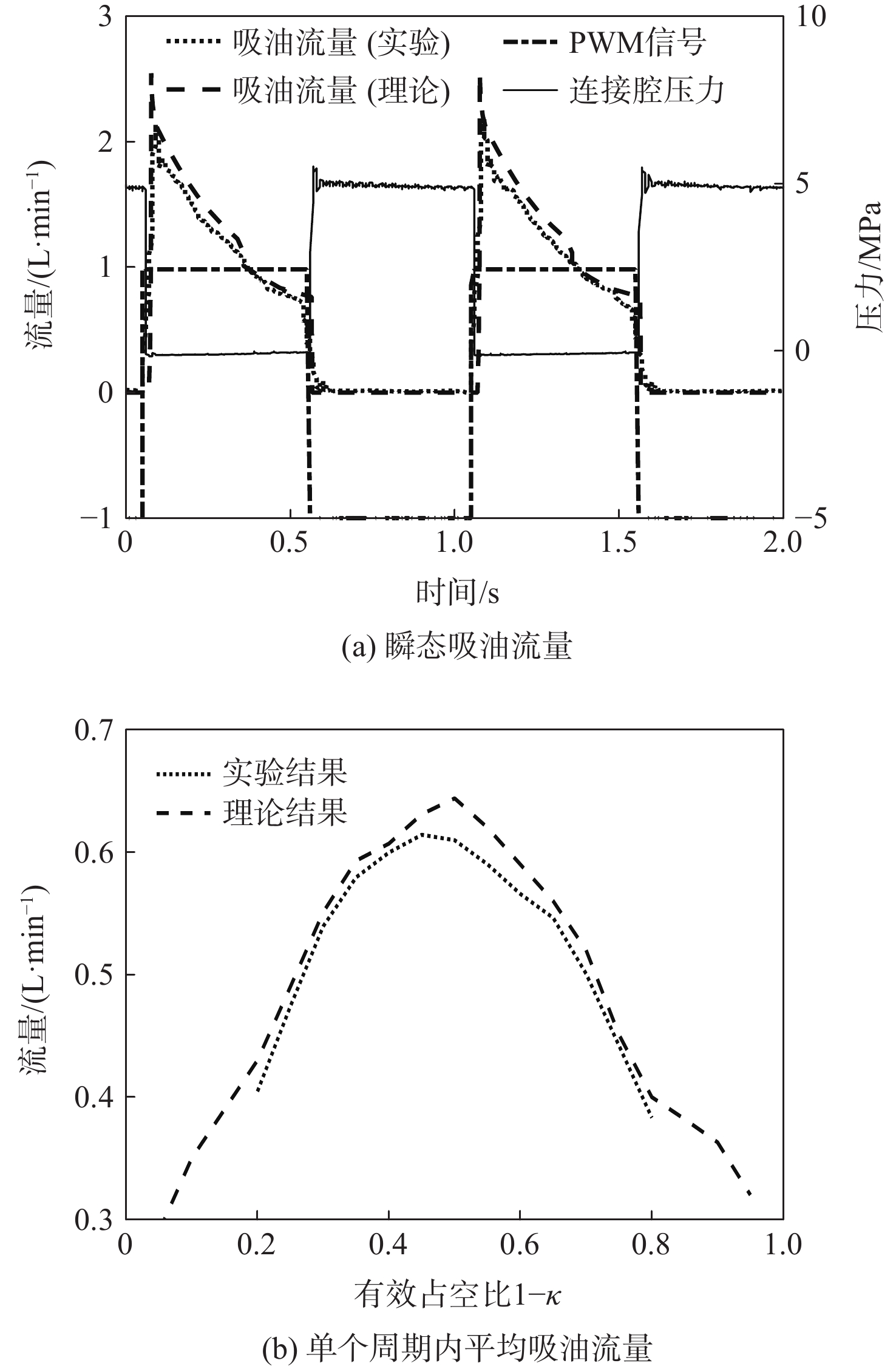
Energy-efficiency characteristic investigation of rotational inertia hydraulic converter
-
摘要:
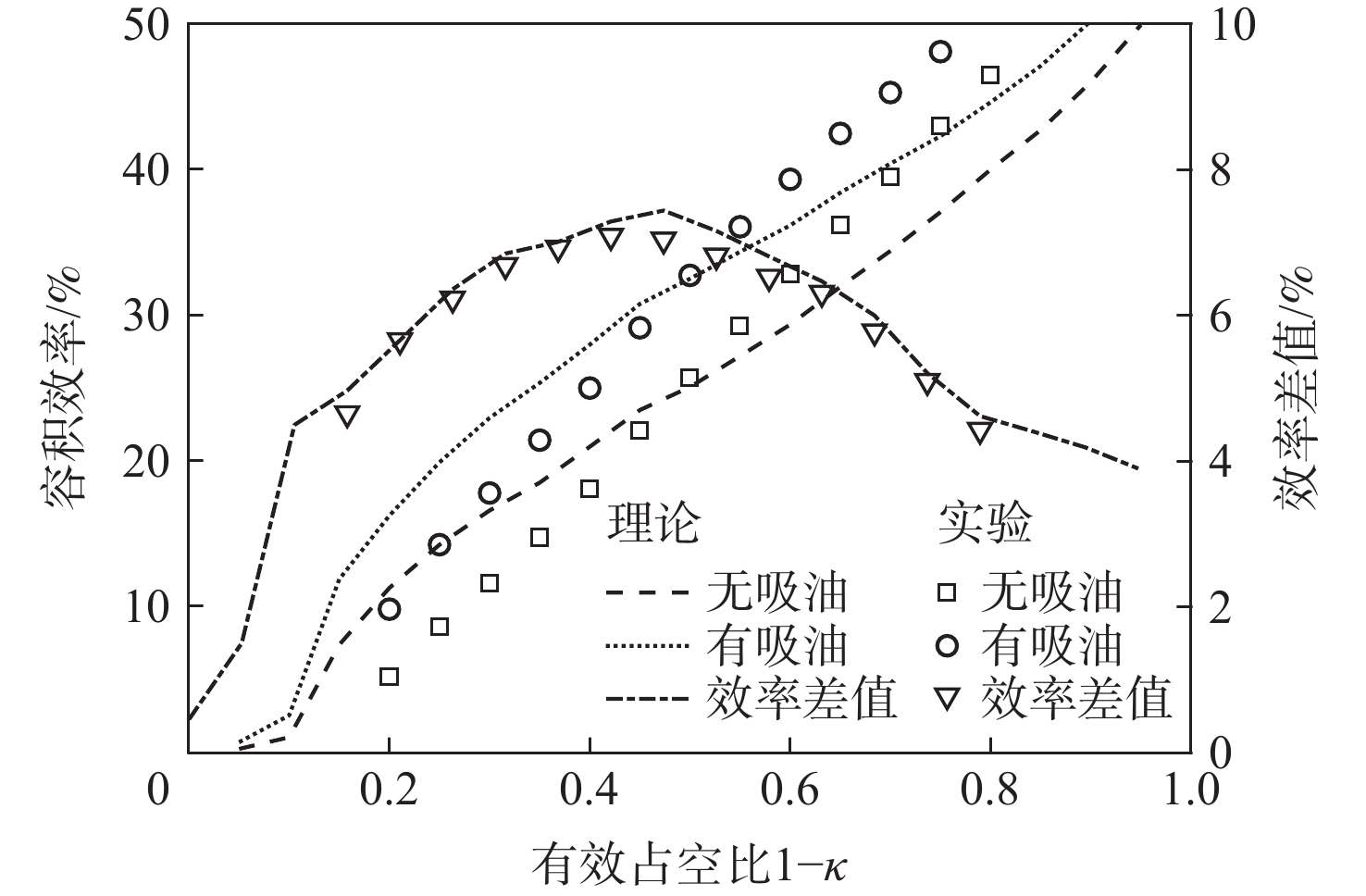
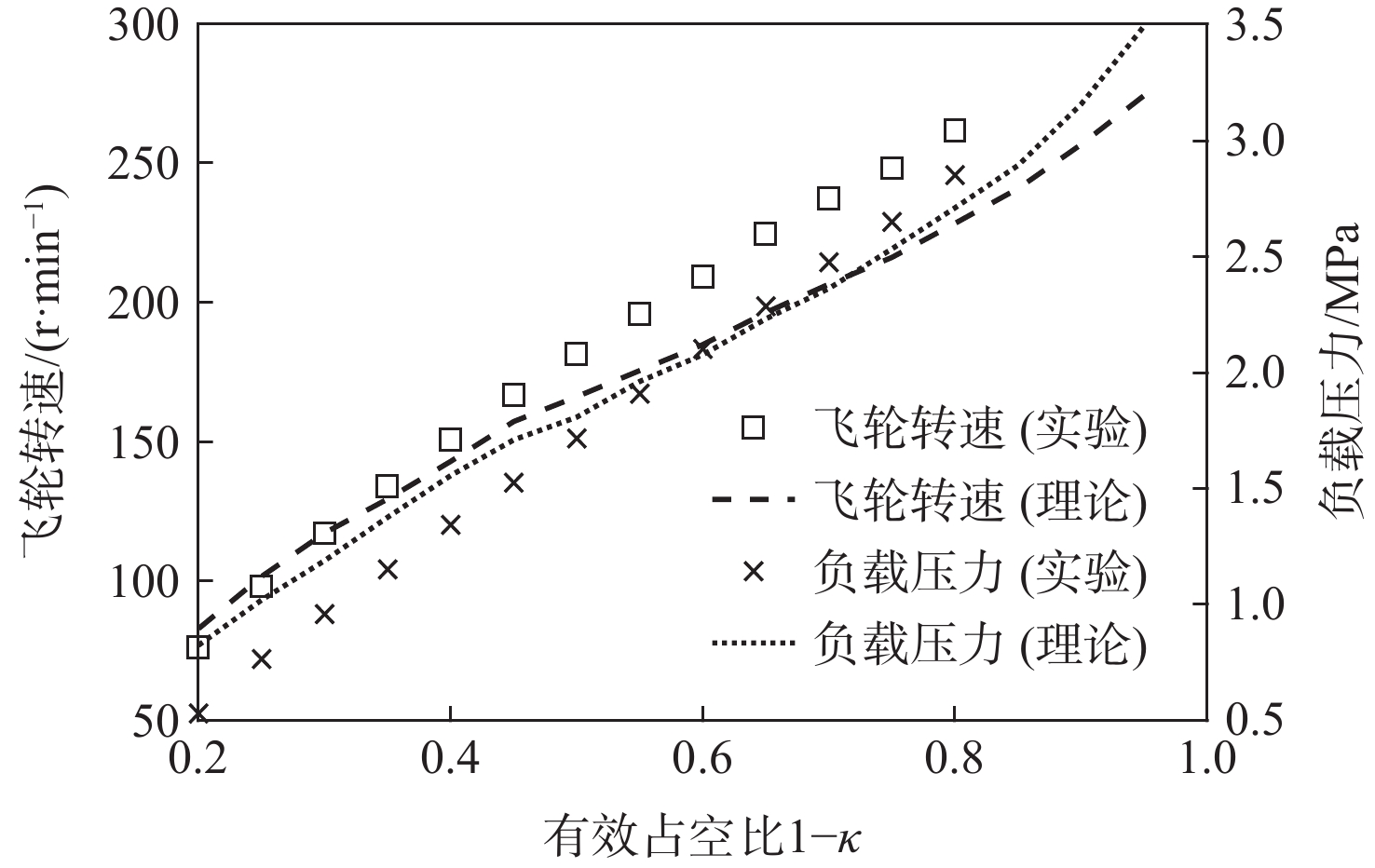
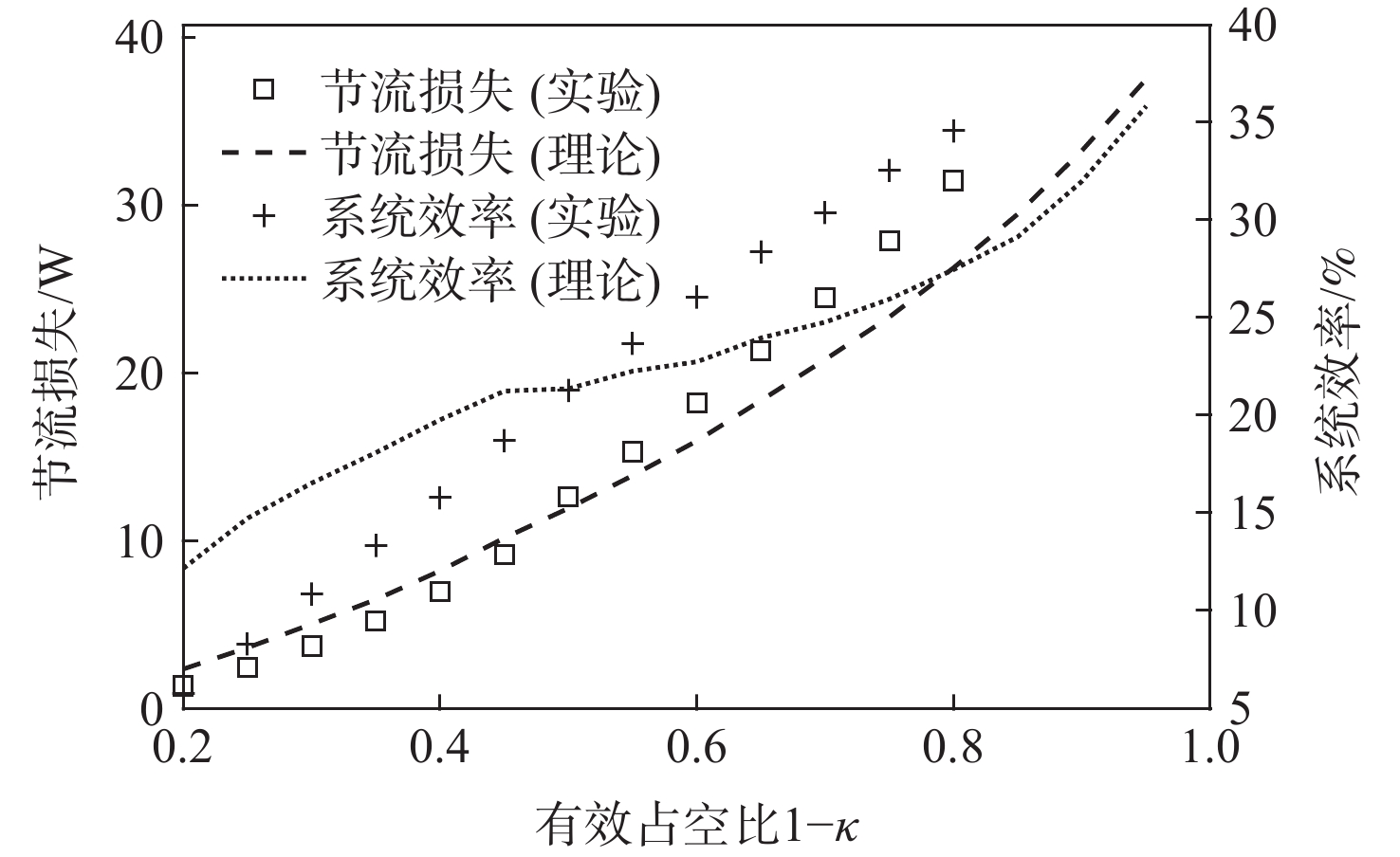
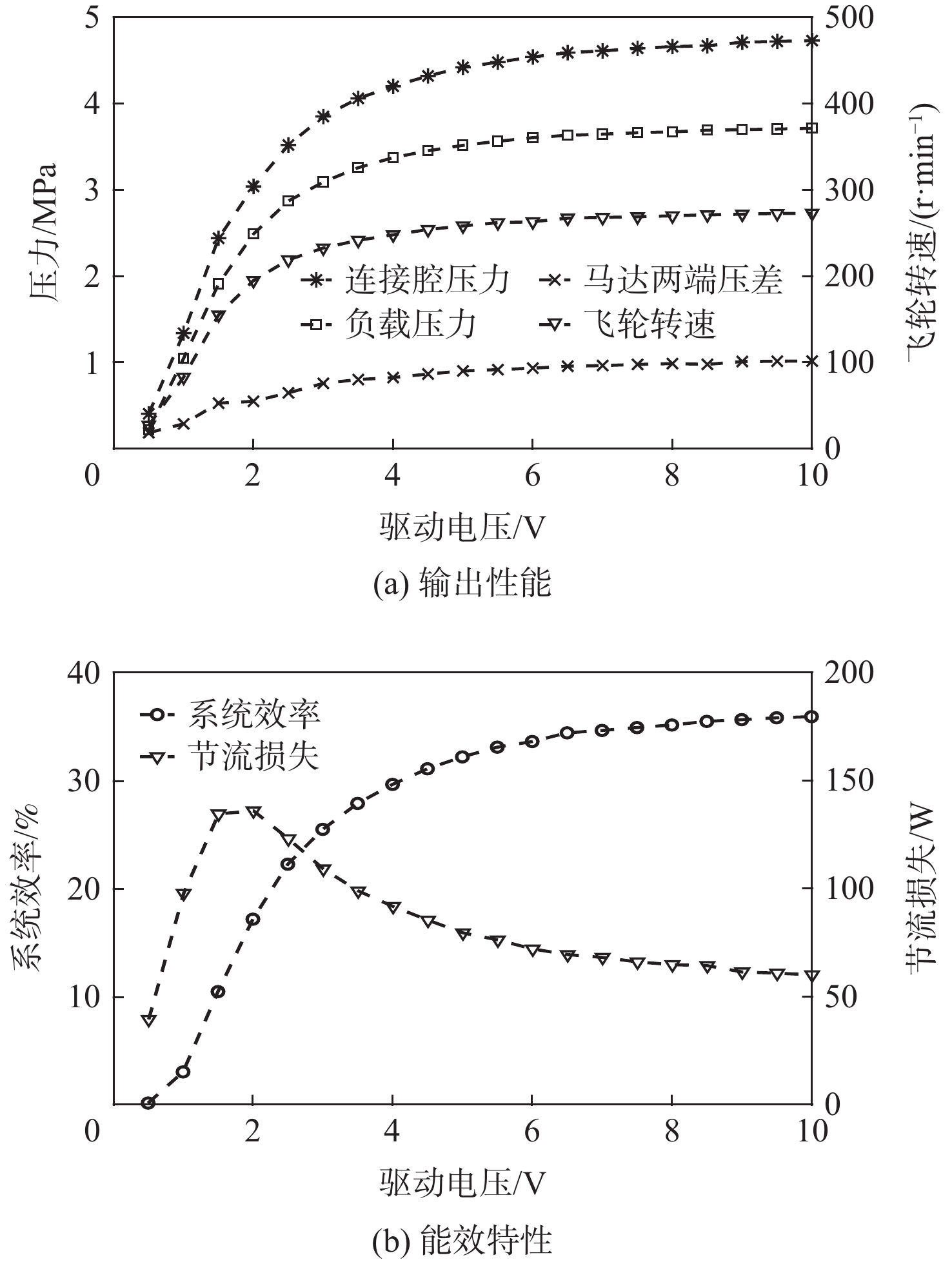
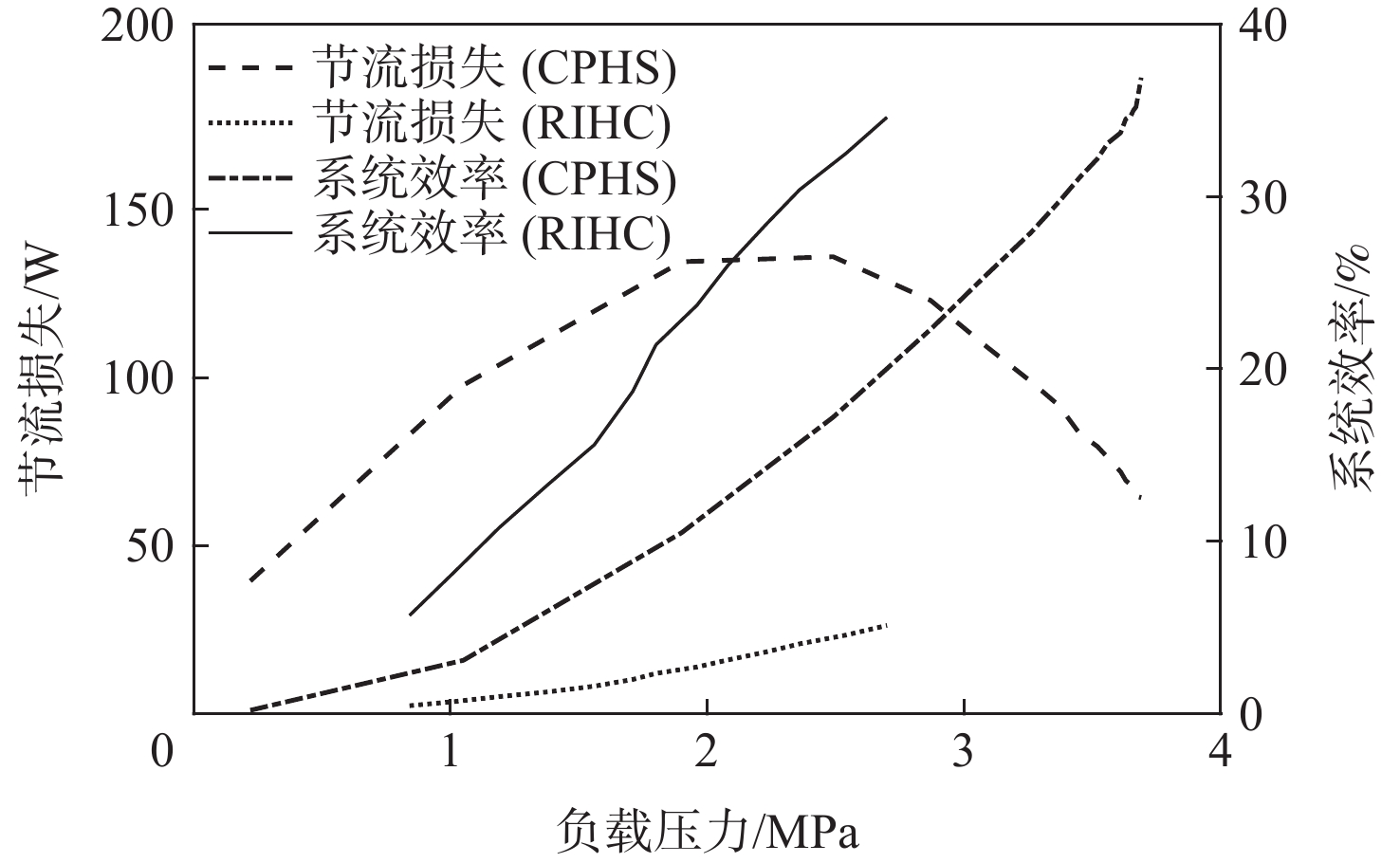
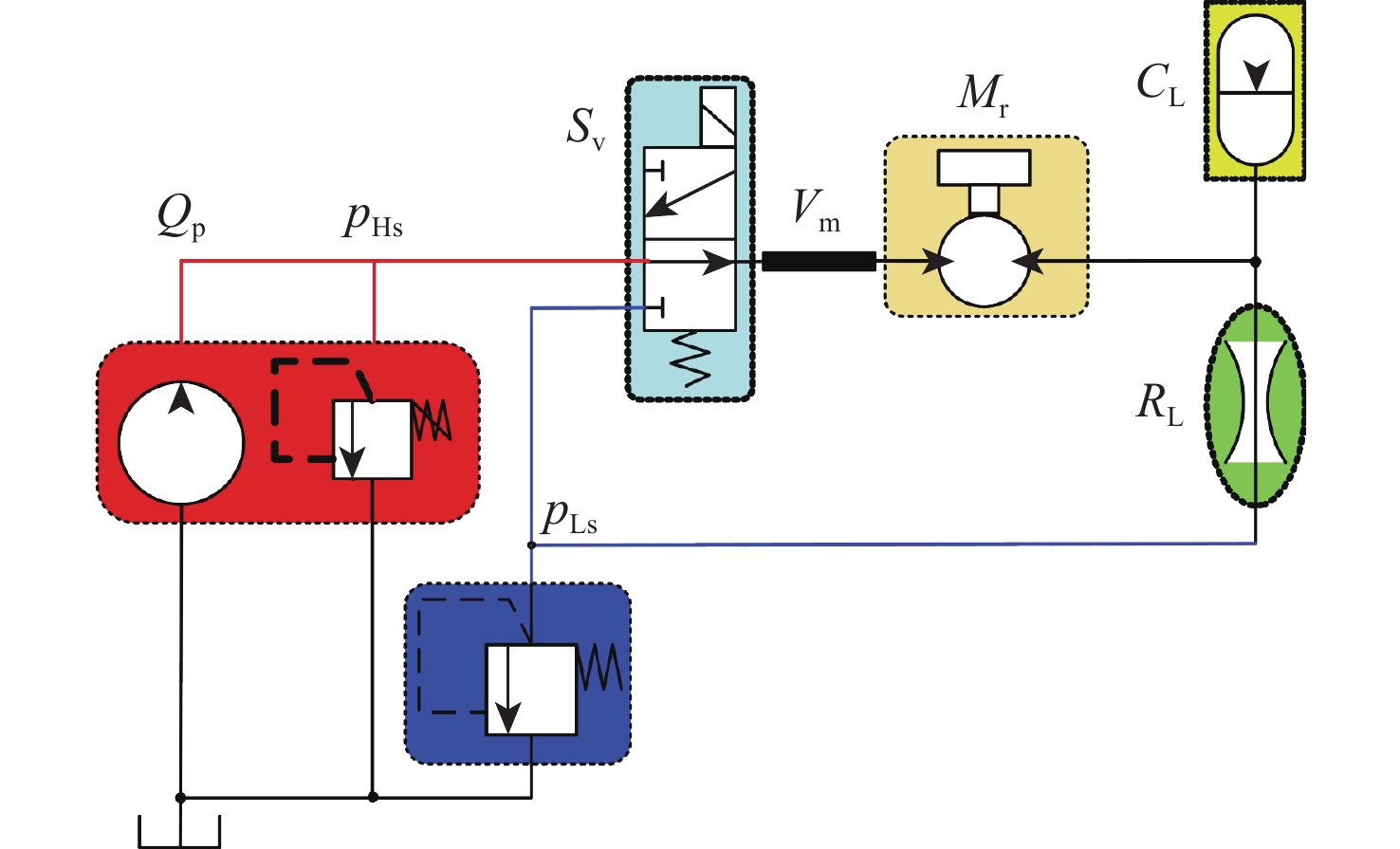
为探究旋转惯性液压变换器(RIHC)的主要性能及其能量转化机制,针对由等效两位三通快速切换阀驱动的旋转惯性液压变换器构型建立其理论分析模型。通过与传统比例液压系统(CHPS)对比实验,验证所建理论模型并给出两者能效差异。结果表明:所建理论模型可有效预测RIHC的主要性能,可通过系统吸油流量量化旋转惯性效应的大小,稳态吸油流量在有效占空比0.5时达到峰值。脉宽调制信号有效占空比控制模式下,随着飞轮转速、负载压力的增加,测得阀口节流损失与系统效率线性化增加。实验表明:负载压力在0~4 MPa范围内,RIHC相较于CHPS最高可减少89%的阀口节流损失,系统效率提升15.7%。
Abstract:To explore the main characteristics and energy conversion mechanism of rotational inertia hydraulic converter (RIHC). Using a rotating inertia hydraulic converter configuration powered by an analogous rapid switching valve, the overall theoretical model was developed to investigate the key features and energy conversion mechanism of the device. The results indicated that the main characteristics can be basically predicted by the theoretical model, and the rotational inertia can be effectively quantified by the suction flow rate, whose mean value reach to the peak value at the duty cycle of 0.5. In the effective duty cycle control mode of PWM signal, with the growth of the flywheel rotation speed and load pressure, the positively correlated throttling power loss and system efficiency are acquired. When the load pressure is between 0 and 4 MPa, experimental comparison showed that the RIHC may reduce throttling power loss by up to 89% and achieve an increase in system efficiency of 15.7% while compared to CPHS.
-
表 1 DFplus阀主要参数
Table 1. Main parameters of DFplus valve
参数 数值 公称流量Qn/ (L·min−1) 25 阶跃响应/ ms <3.5 迟滞 <0.05 频响±5%信号/ Hz 350 驱动电压Vt/ V 10 表 2 RIHC理论模型主要参数
Table 2. Main parameters of RIHC theoretical model
参数 数值 电机转速vp/( r·min−1) 1750 液压泵排量Dp/( m3·rad−1) 1.68×10−6 供油压力pHs/MPa 5.5 供油压力pLs/MPa 1.1 马达排量Dm/(m3·rad−1) 2.67×10−6 阻尼系数Bm/(N·m·s·rad−1) 0.0292 飞轮惯量Im/(N·m·s2·rad−1) 0.162 电磁力Fm/N 200 流量系数Cds/CdL 0.65 初始位置xs0/mm 0.05 阀芯质量ms/kg 0.1 弹簧刚度ks/(N·m−1) 20000 黏性阻尼系数bs/(N·s·m−1) 0.8 有效过流面积AL/mm 0.785 圆孔数z 4 孔径dn/mm 2.8 管路内径dh/mm 12.5 空气含量γ 0.05 油液密度ρ/(kg·m−3) 878 油液动力黏度μ/(Pa·s) 0.04025 纯油弹性模量K/Pa 8×109 -
[1] YANG H Y, PAN M. Engineering research in fluid power: A review[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE A, 2015, 16(6): 427-442. doi: 10.1631/jzus.A1500042 [2] VACCA A. Energy efficiency and controllability of fluid power systems[J]. Energies, 2018, 11(5): 1169. doi: 10.3390/en11051169 [3] 杨华勇, 王双, 张斌, 等. 数字液压阀及其阀控系统发展和展望[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(5): 1494-1505. doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb201605017YANG H Y, WANG S, ZHANG B, et al. Development and prospect of digital hydraulic valve and valve control system[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46(5): 1494-1505(in Chinese). doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb201605017 [4] LINJAMA M. Digital fluid power: State of the art[C]//Proceedings of the 12th Scandinavian International Conference on Fluid Power. Tampere: Tampere University of Technology, 2011. [5] BROWN F T. Switched reactance hydraulics: a new way to control fluid power[C]//Proceedings of the National Conference on Fluid Power. Chicago: National Fluid Power Association, 1987: 25-34. [6] YUAN C G, PAN M, PLUMMER A. A review of switched inertance hydraulic converter Technology[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 2020, 142(5): 050801. doi: 10.1115/1.4046103 [7] KOGLER H, SCHEIDL R. Energy efficient linear drive axis using a hydraulic switching converter[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 2016, 138(9): 091010. doi: 10.1115/1.4033412 [8] 陈晓明, 朱玉川, 高强, 等. 数字开关液压系统中流体惯性效应分析与实验[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 48(6): 70-76. doi: 10.13245/j.hust.200612CHEN X M, ZHU Y C, GAO Q, et al. Analysis and experiment of fluid inertia in digital switched hydraulic system[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(6): 70-76(in Chinese). doi: 10.13245/j.hust.200612 [9] PAN M, PLUMMER A, EL AGHA A. Theoretical and experimental studies of a switched inertance hydraulic system in a four-port high-speed switching valve configuration[J]. Energies, 2017, 10(6): 780. doi: 10.3390/en10060780 [10] SELL N P, JOHNSTON D N, PLUMMER A R, et al. Control of a fast switching valve for digital hydraulics[C]//Proceedings from the 13th Scandinavian International Conference on Fluid Power. Linköping: Linköping University Electronic Press, 2013: 497-503. [11] WINKLER B, PLOECKINGER A, SCHEIDL R. A novel piloted fast switching multi poppet valve[J]. International Journal of Fluid Power, 2010, 11(3): 7-14. doi: 10.1080/14399776.2010.10781010 [12] VAN DE VEN JAMES D. On fluid compressibility in switch-mode hydraulic circuits, part II: Experimental results[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 2013, 135(2): 021014. doi: 10.1115/1.4023063 [13] WIENS T K. Analysis and mitigation of valve switching losses in switched inertance converters[C]//Proceedings of ASME/BATH 2015 Symposium on Fluid Power and Motion Control. New York: ASME, 2016 [14] WIENS T. Improving performance of a switched inertance buck converter via positioning of reservoir flow valve[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 2016, 138(12): 124502. doi: 10.1115/1.4034045 [15] BATDORFF M A, LUMKES J H. Virtually variable displacement hydraulic pump including compressability and switching losses[C]//Proceedings of ASME 2006 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition. New York: ASME, 2007: 57-66. [16] PAN M, JOHNSTON N, PLUMMER A, et al. Theoretical and experimental studies of a switched inertance hydraulic system including switching transition dynamics, non-linearity and leakage[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part I:Journal of Systems and Control Engineering, 2014, 228(10): 802-815. doi: 10.1177/0959651814548299 [17] 陈晓明, 朱玉川, 吴昌文, 等. 数字开关液压系统管路压力波传播建模与分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(7): 1335-1344. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0478CHEN X M, ZHU Y C, WU C W, et al. Modeling and analysis of pressure wave propagation inside pipeline of digital switched hydraulic system[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(7): 1335-1344(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0478 [18] DANTLGRABER J. Hydro-transformer: European patent application (PCT) international publication, No. 6499295[P]. 2002-12-31. [19] 顾临怡, 邱敏秀, 金波, 等. 由液压总线和开关液压源构成的新原理液压系统[J]. 机械工程学报, 2003, 39(1): 84-88. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6686.2003.01.018GU L Y, QIU M X, JIN B, et al. New hydraulic systems made up of hydraulic power bus and switch- mode hydraulic power supplies[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2003, 39(1): 84-88(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6686.2003.01.018 [20] WANG F, GU L Y, CHEN Y. A continuously variable hydraulic pressure converter based on high-speed on-off valves[J]. Mechatronics, 2011, 21(8): 1298-1308. doi: 10.1016/j.mechatronics.2011.09.002 [21] CHEN X M, ZHU Y C, WIENS T, et al. Investigation of suction flow characteristic in the inertance hydraulic converters for efficiency improvement[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part I:Journal of Systems and Control Engineering, 2022, 236(1): 3-25. doi: 10.1177/09596518211024878 [22] CHEN X M, ZHU Y C, WIENS T, et al. Characteristic investigation of a flow-dependent inertia hydraulic converter driven by an equivalent fast switching valve[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C:Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 2022, 236(7): 3354-3374. doi: 10.1177/09544062211038983 [23] LAU K K, EDGE K A, JOHNSTON D N. Impedance characteristics of hydraulic orifices[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part I:Journal of Systems and Control Engineering, 1995, 209(4): 241-253. doi: 10.1243/PIME_PROC_1995_209_392_02 [24] TAMBURRANO P, AMIRANTE R, DISTASO E, et al. Full simulation of a piezoelectric double nozzle flapper pilot valve coupled with a main stage spool valve[J]. Energy Procedia, 2018, 148: 487-494. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2018.08.124 -







 下载:
下载: