Degradation-shock competing failure modeling considering randomness of failure threshold
-
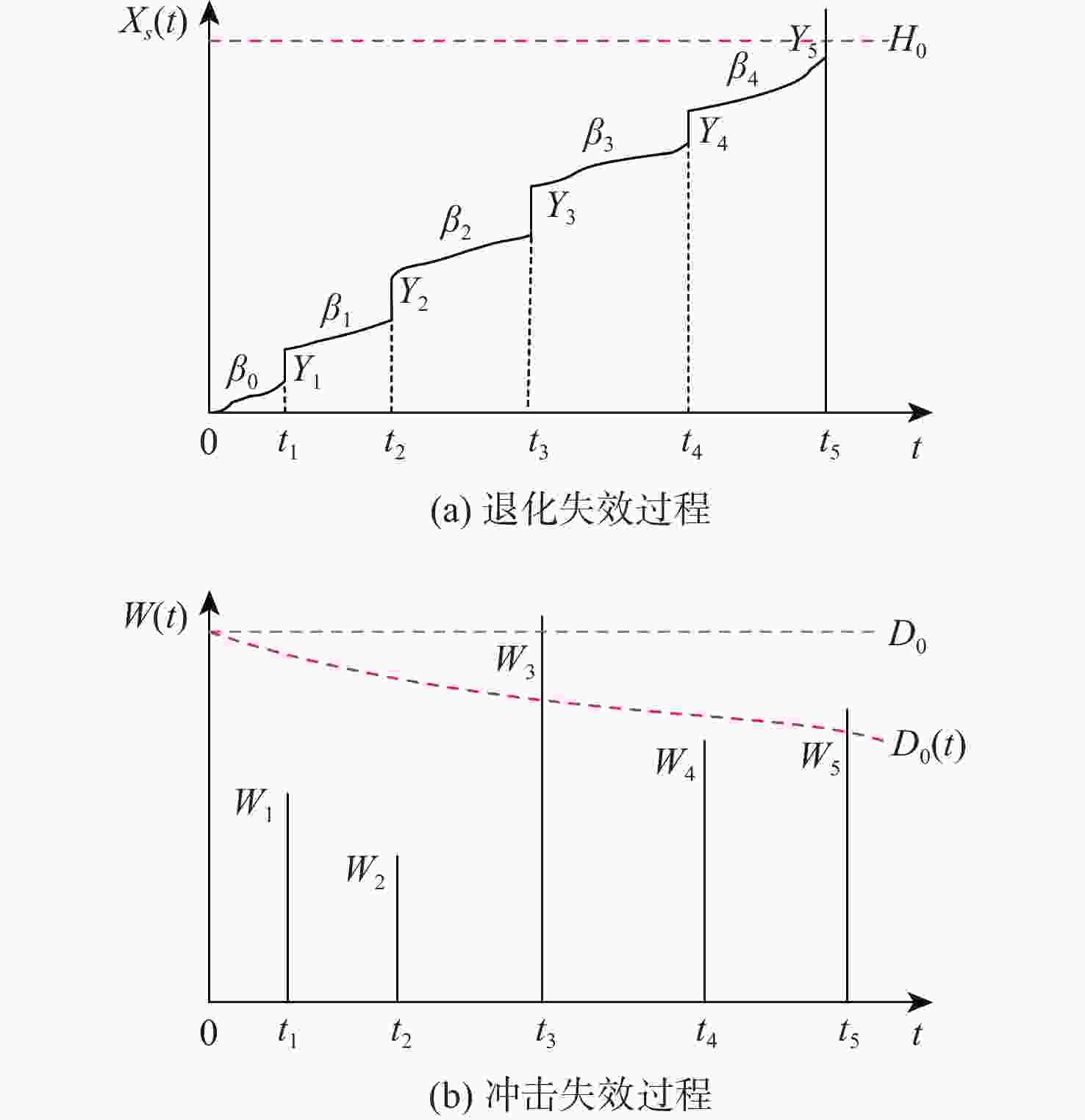
摘要:
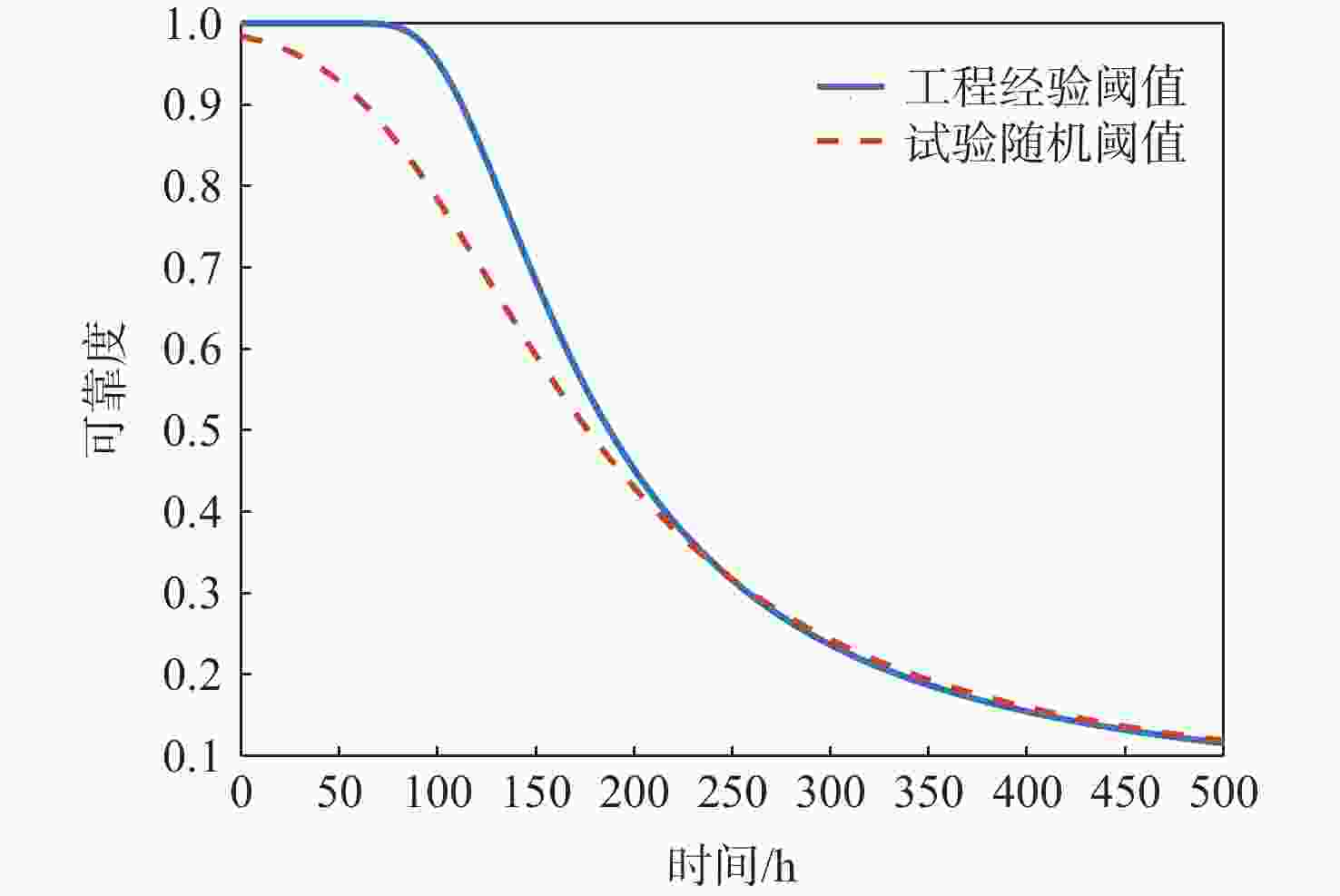
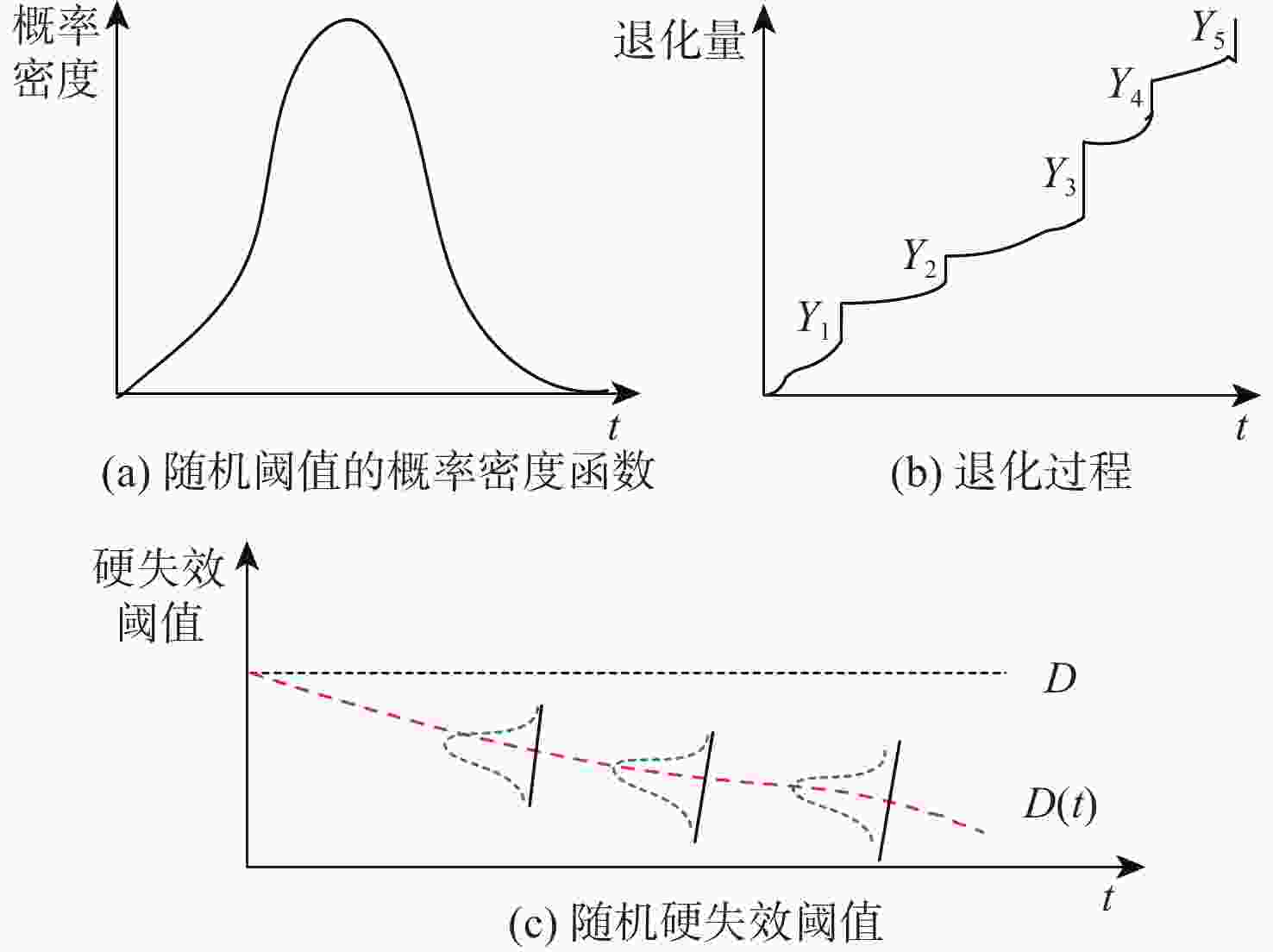
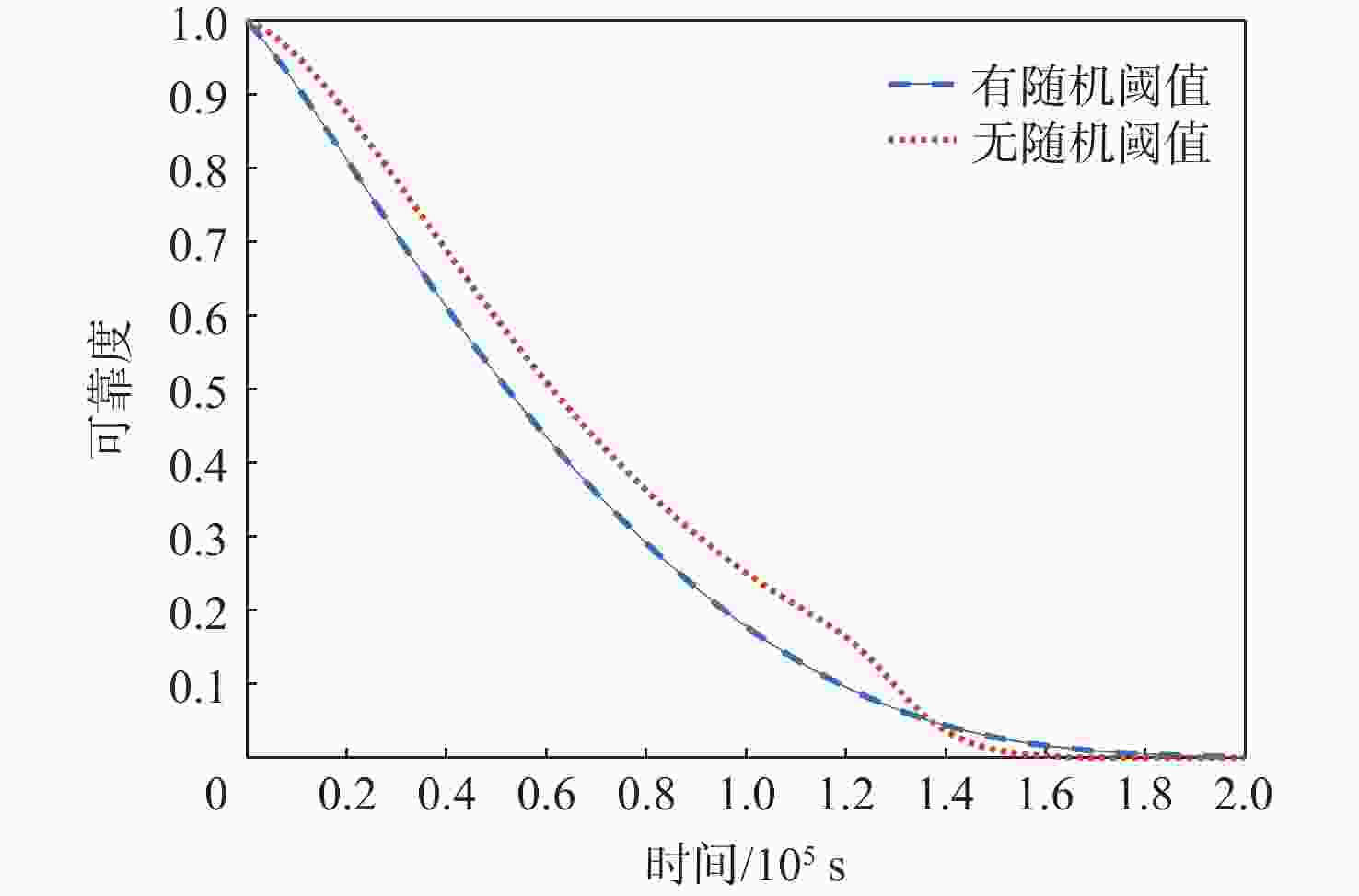
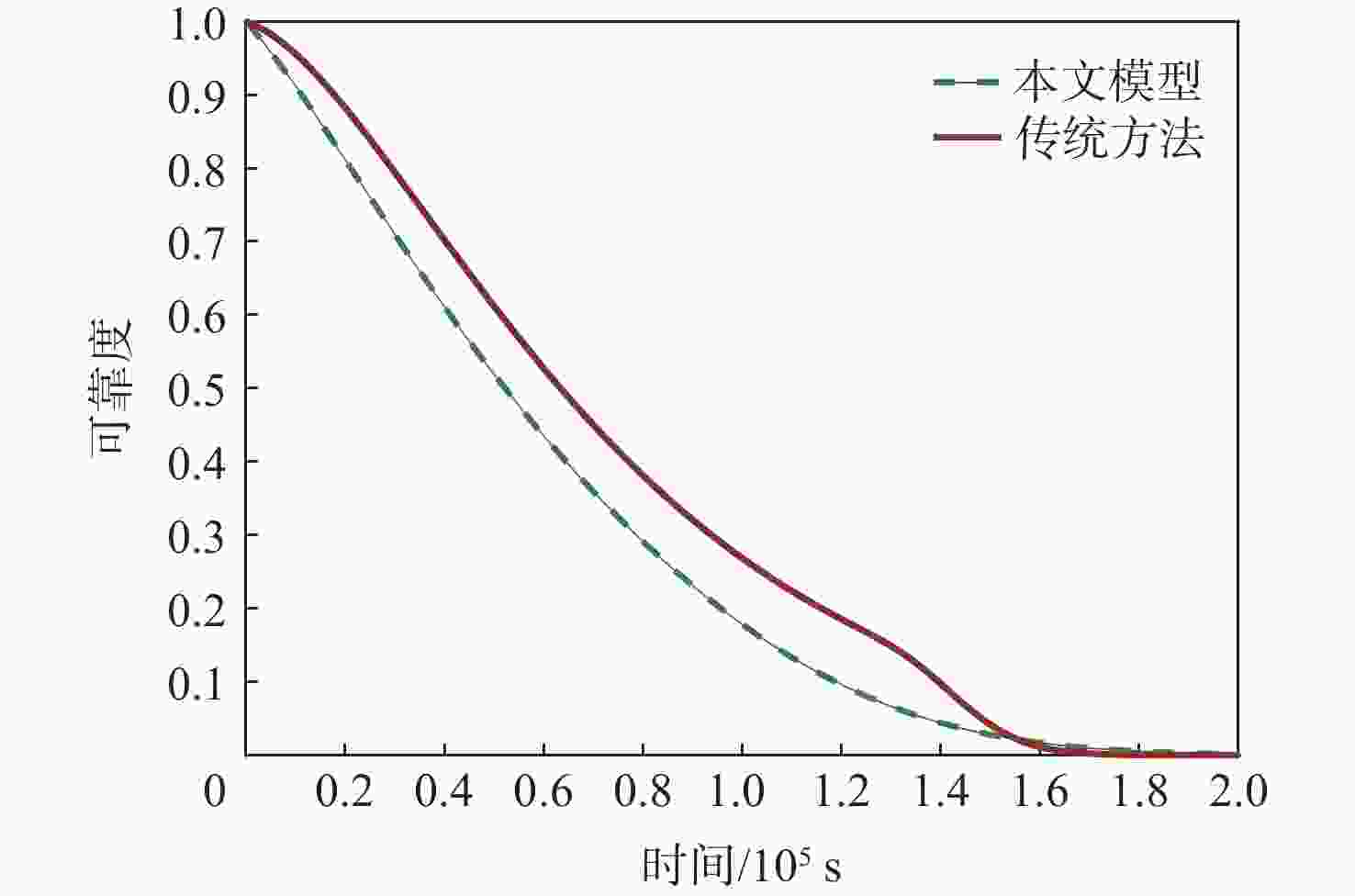
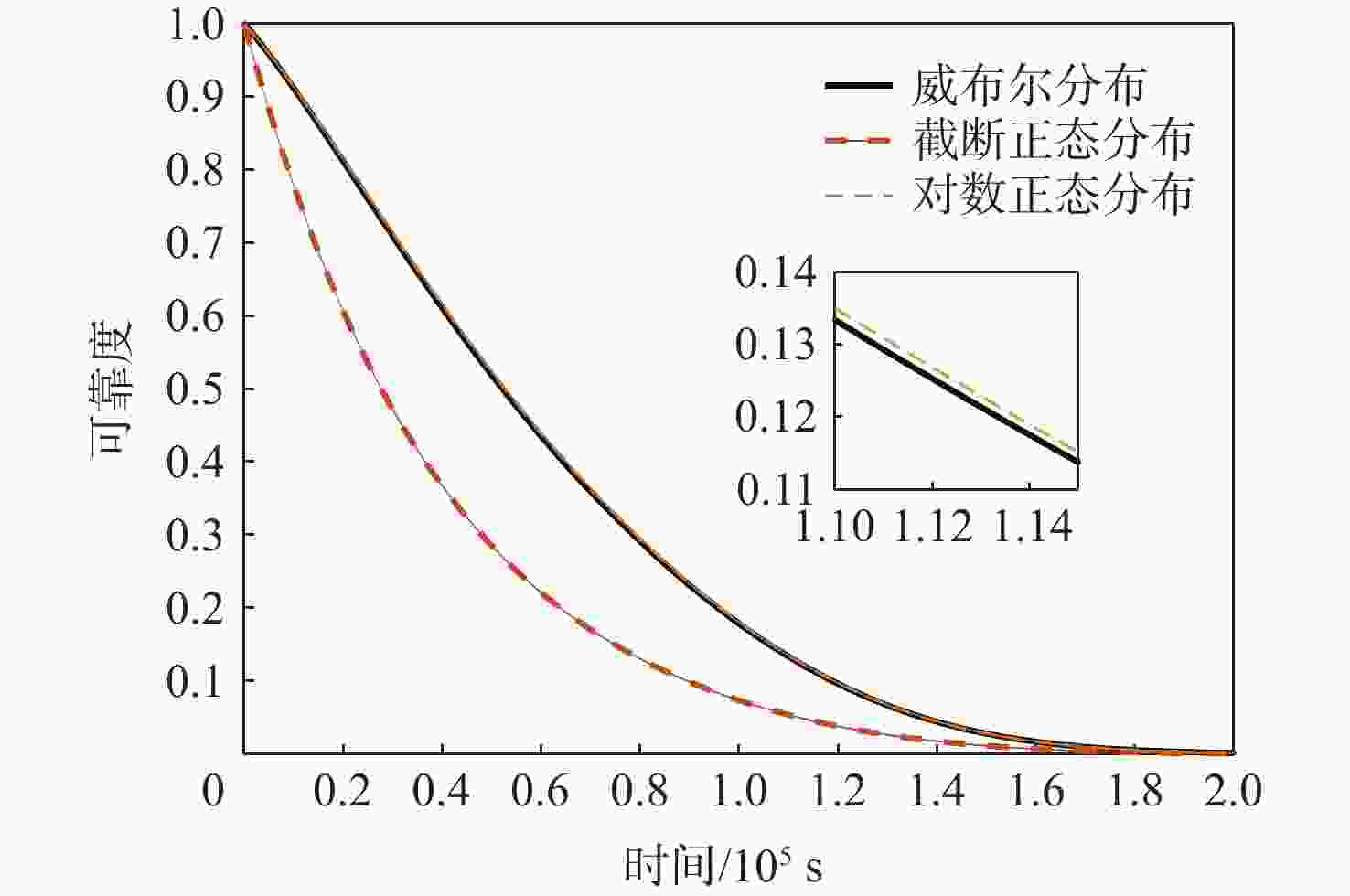
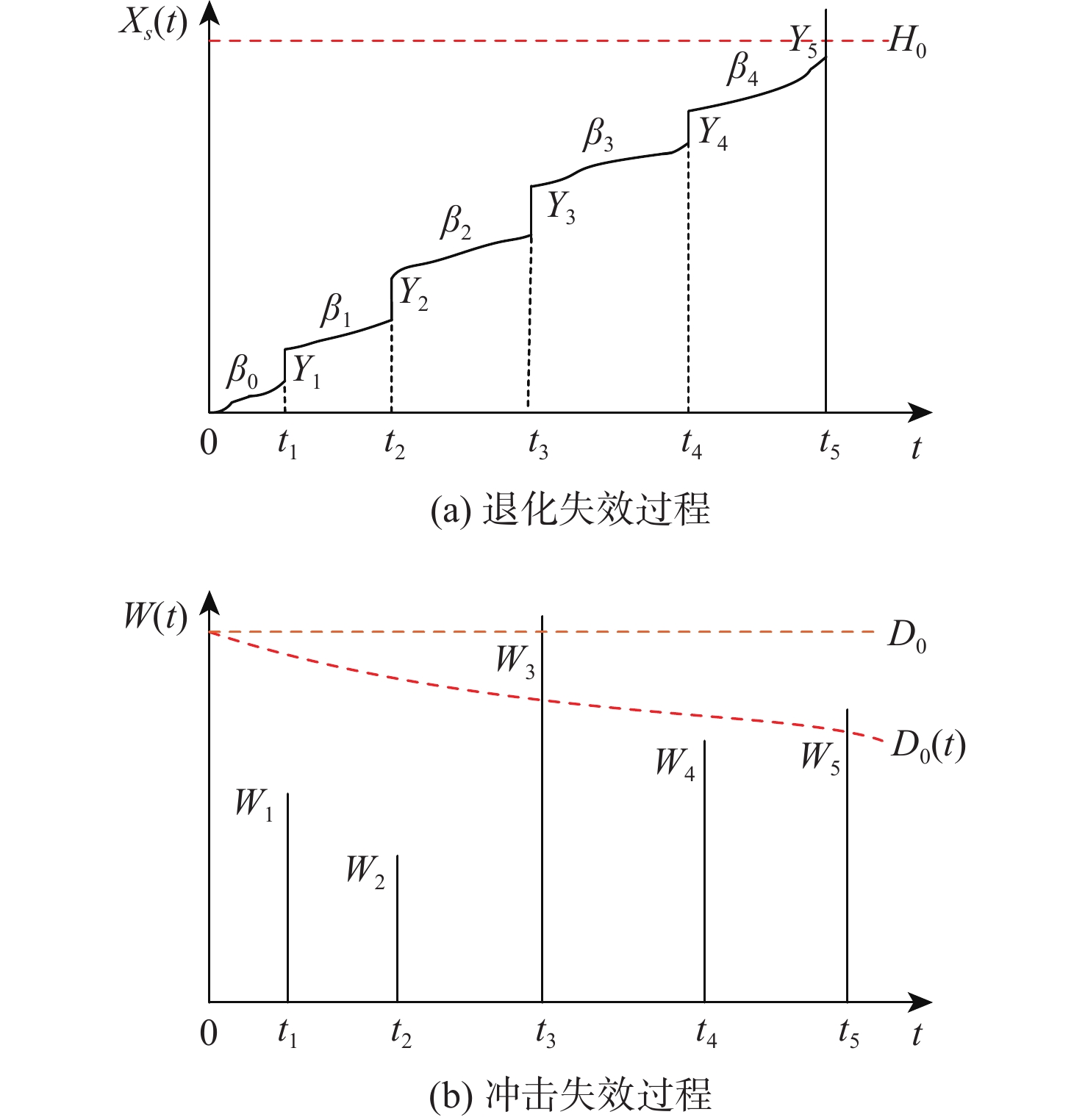
针对大多竞争失效可靠性研究未考虑失效阈值随机性的情况,提出一种随机失效阈值影响下的竞争失效系统可靠性评价模型。分析冲击影响下退化过程中退化量及退化率的变化,并在此基础上考虑阈值随机性。讨论累积退化影响下的冲击过程,以系统所能承受的强度分布描述冲击失效阈值,并结合累积退化量的期望水平建立随时间变化的冲击失效阈值,从而明确描述了冲击失效阈值与退化过程之间的依赖关系,给出竞争失效过程的可靠性函数。以微电机系统为例进行对比及敏感性分析,验证了随机失效阈值的引入更能反映系统真实运行状态。
Abstract:Since most research on competing failure reliability do not take the unpredictability of the failure threshold into account, a competing failure reliability model that takes the randomness of the failure threshold into account is devised. The variation of degradation quantity and degradation rate under shocks was analyzed, and the randomness of the threshold was considered on this basis. The cumulative degradation under the influence of the random shock process was analyzed. The shock failure threshold is described by the strength distribution that the system can withstand, and the shock failure threshold that changes with time is established based on the expected level of cumulative degradation, so the dependence between the shock failure threshold and the degradation process is clearly described, and the reliability function of the competing failure process is given. Last but not ultimately, a micromotor system is used as a comparison and sensitivity analysis example to confirm the logic and efficacy of the suggested concept.
-
表 1 参数取值
Table 1. Parameter values
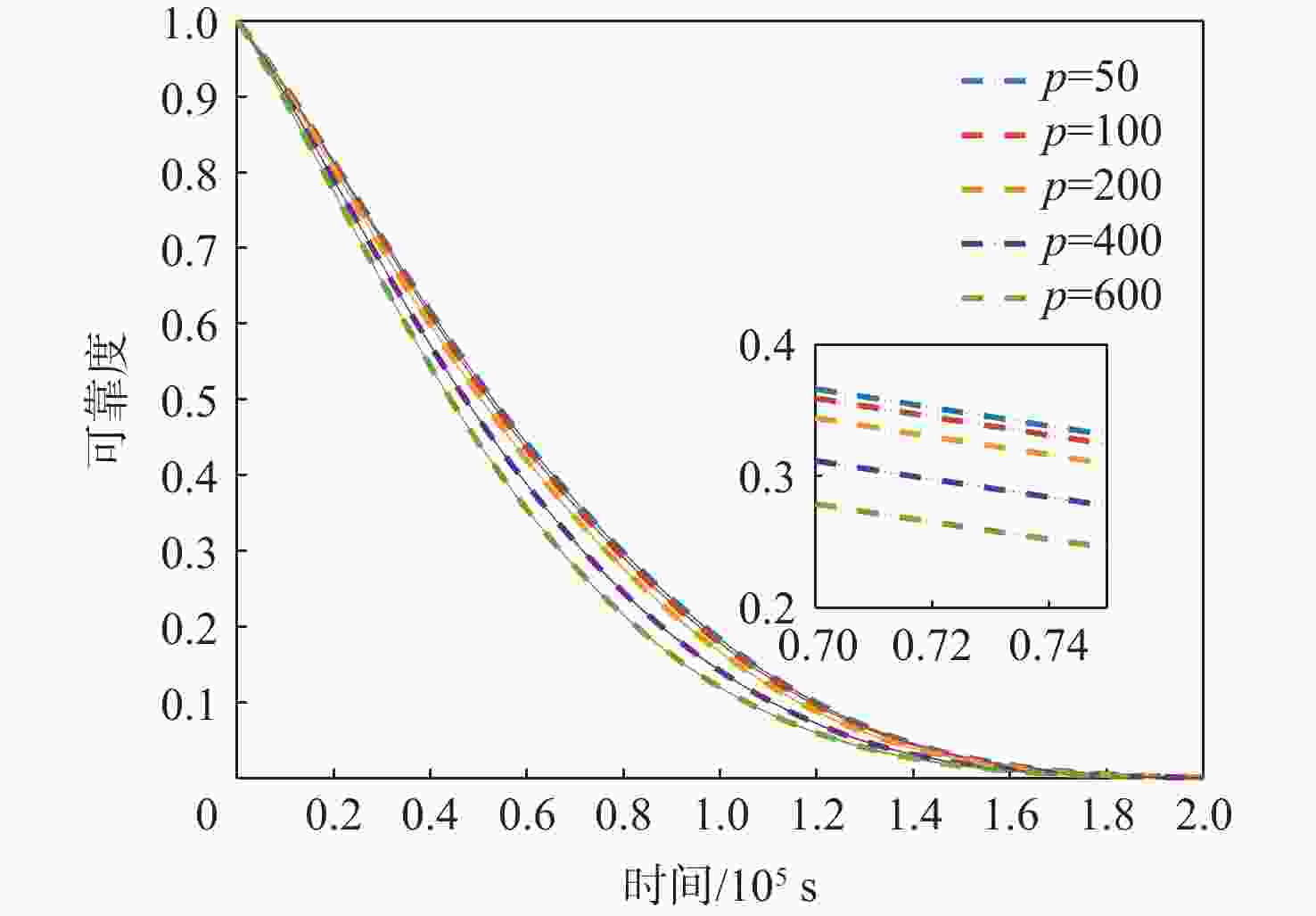
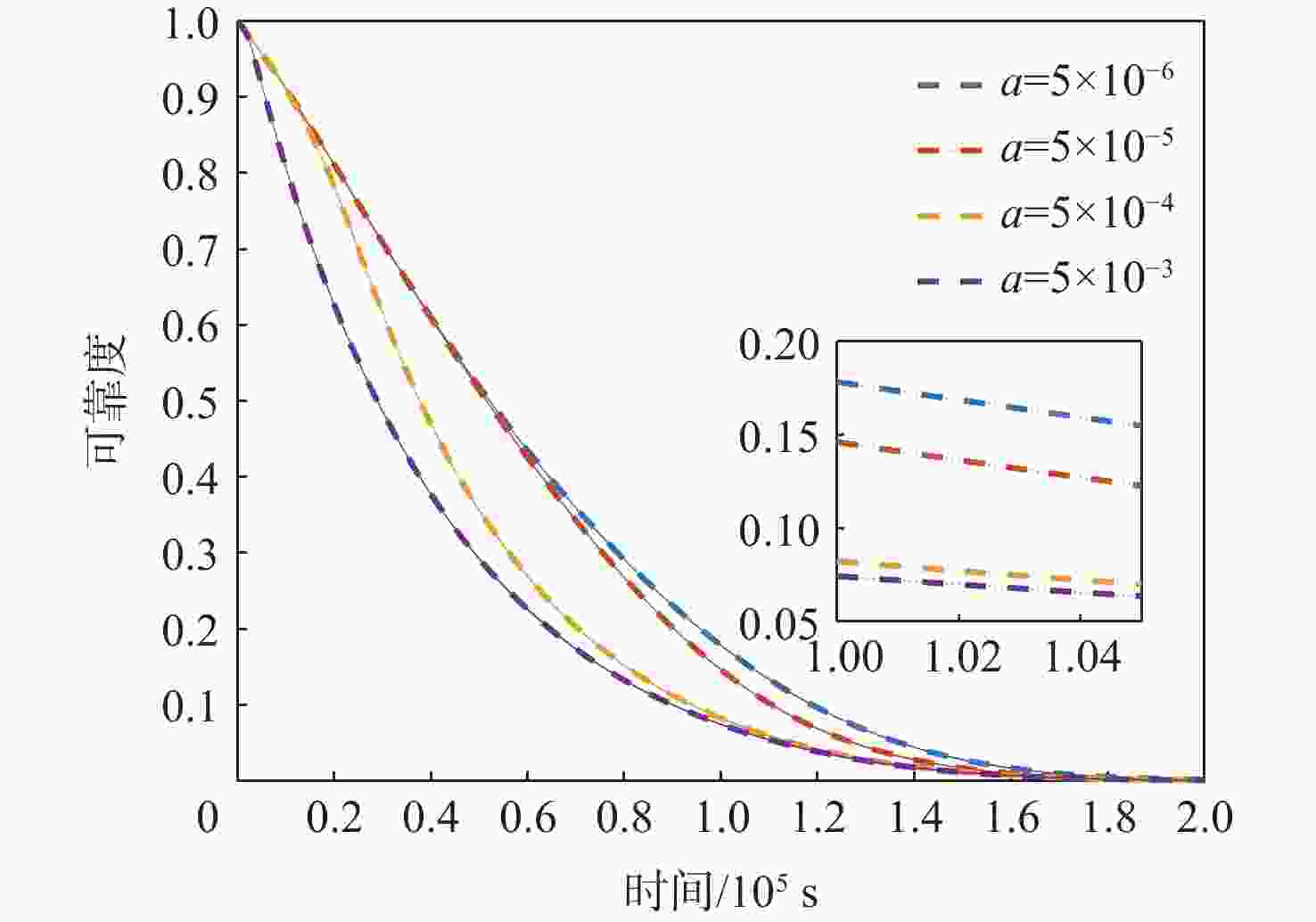
参数 数值 来源 ${\beta _0}\sim N({\mu _\beta },\sigma _\beta ^2)$ $\begin{gathered} {\mu _\beta } = 8.482\;3 \times {10^{ - 9} } \\ {\sigma _\beta } = 6.001\;6 \times {10^{ - 10} } \\ \end{gathered}$ 文献[6] $W\sim N({\mu _W},\sigma _W^2)$ $\begin{gathered} {\mu _W} = 1.2 \\ {\sigma _W} = 0.2 \\ \end{gathered} $ 文献[16] ${\mu _h}$ $1.25 \times {10^{ - 3}}$ 文献[16] $\lambda /{\rm{revolutions}}$ $2.5 \times {10^{ - 5} }$ 文献[6] $c/ ({ {\text{μm} }^3}\cdot{\text{GPa} }^{-1 })$ ${\text{8} }{\text{.333} } \times {\text{1} }{ {\text{0} }^{ - 5} }$ 文献[16] $\omega \sim W(\eta ,\gamma ,{\mu }_{\omega })$ $\begin{gathered} {\mu _\omega }{\text{ = } }0.85 \\ \eta = 0.685\;8 \\ \gamma = 1.569\;6 \\ \end{gathered}$ 假设 $\alpha $ 0 假设 $a$ $5 \times {10^{ - 6}}$ 假设 $p$ $100$ 假设 ${\sigma _\varepsilon }$ ${10^{ - 10}}$ 假设 $\sigma _h^2$ ${10^{ - 7}}$ 假设 注:revolutions表示发动机每一转。 -
[1] 毛业军, 赵胤淇, 张伟先, 等. 基于失效机理的超级电容加速退化研究[J]. 电源技术, 2021, 45(6): 778-780.MAO Y J, ZHAO Y Q, ZHANG W X, et al. Accelerated degradation of supercapacitor based on failure mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 45(6): 778-780(in Chinese). [2] ZHAO X, LV Z Y, HE Z D, et al. Reliability and opportunistic maintenance for a series system with multi-stage accelerated damage in shock environments[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2019, 137: 106029. [3] 孙富强, 李艳宏, 程圆圆. 考虑冲击韧性的退化-冲击相依竞争失效建模[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(12): 2195-2202. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0628SUN F Q, LI Y H, CHENG Y Y. Competing failure modeling for degradation-shock dependence systems with shock toughness[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(12): 2195-2202(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0628 [4] ZHU H Z, WANG X Q, XIAO M Q, et al. Reliability modeling for intermittent working system based on Wiener process[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2021, 160: 107599. [5] OUMOUNI M, SCHOEFS F, CASTANIER B. Modeling time and spatial variability of degradation through gamma processes for structural reliability assessment[J]. Structural Safety, 2019, 76: 162-173. doi: 10.1016/j.strusafe.2018.09.003 [6] WANG X G, LI L, CHANG M X, et al. Reliability modeling for competing failure processes with shifting failure thresholds under severe product working conditions[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2021, 89: 1747-1763. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2020.08.032 [7] YE Z S, TANG L C, XU H Y. A distribution-based systems reliability model under extreme shocks and natural degradation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2011, 60(1): 246-256. doi: 10.1109/TR.2010.2103710 [8] MONTORO-CAZORLA D, PÉREZ-OCÓN R. A reliability system under cumulative shocks governed by a BMAP[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2015, 39(23-24): 7620-7629. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2015.03.066 [9] GONG M, XIE M, YANG Y N. Reliability assessment of system under a generalized Run shock model[J]. Journal of Applied Probability, 2018, 55(4): 1249-1260. doi: 10.1017/jpr.2018.83 [10] ERYILMAZ S. δ-shock model based on Polya process and its optimal replacement policy[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2017, 263(2): 690-697. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2017.05.049 [11] PULCINI G. A model-driven approach for the failure data analysis of multiple repairable systems without information on individual sequences[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2013, 62(3): 700-713. doi: 10.1109/TR.2013.2273040 [12] FINKELSTEIN M, MARAIS F. On terminating Poisson processes in some shock models[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2010, 95(8): 874-879. [13] CAO Y S, LIU S F, FANG Z G, et al. Modeling ageing effects in the context of continuous degradation and random shock[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2020, 145: 106539. [14] SONG S L, COIT D W, FENG Q M. Reliability for systems of degrading components with distinct component shock sets[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2014, 132: 115-124. [15] RAFIEE K, FENG Q M, COIT D W. Reliability modeling for dependent competing failure processes with changing degradation rate[J]. IIE Transactions, 2014, 46(5): 483-496. doi: 10.1080/0740817X.2013.812270 [16] HAO S H, YANG J, MA X B, et al. Reliability modeling for mutually dependent competing failure processes due to degradation and random shocks[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2017, 51: 232-249. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2017.06.014 [17] LEI Y, ZHU W Q. Fatigue crack growth in degrading elastic components of nonlinear structural systems under random loading[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2000, 37(4): 649-667. doi: 10.1016/S0020-7683(99)00030-X [18] FAN M F, ZENG Z G, ZIO E, et al. Modeling dependent competing failure processes with degradation-shock dependence[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2017, 165: 422-430. [19] CHE H Y, ZENG S K, GUO J B, et al. Reliability modeling for dependent competing failure processes with mutually dependent degradation process and shock process[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2018, 180: 168-178. [20] JIANG L, FENG Q M, COIT D W. Reliability and maintenance modeling for dependent competing failure processes with shifting failure thresholds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2012, 61(4): 932-948. doi: 10.1109/TR.2012.2221016 [21] WANG X L, JIANG P, GUO B, et al. Real-time reliability evaluation based on damaged measurement degradation data[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2012, 19(11): 3162-3169. doi: 10.1007/s11771-012-1391-9 [22] WANG W B, CARR M, XU W J, et al. A model for residual life prediction based on Brownian motion with an adaptive drift[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2011, 51(2): 285-293. doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2010.09.013 [23] USYNIN A, HINES J W, URMANOV A. Uncertain failure thresholds in cumulative damage models[C]//2008 Annual Reliability and Maintainability Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2009: 334-340. [24] WANG P, COIT D W. Reliability and degradation modeling with random or uncertain failure threshold[C]//2007 Annual Reliability and Maintainability Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2007: 392-397. [25] WANG Z Z, CHEN Y X, CAI Z Y, et al. Methods for predicting the remaining useful life of equipment in consideration of the random failure threshold[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 31(2): 415-431. doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2020.000018 [26] TANNER D M, WALRAVEN J A, HELGESEN K, et al. MEMS reliability in shock environments[C]//2000 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium Proceedings. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2002: 129-138. [27] TANG S J, YU C Q, FENG Y B, et al. Remaining useful life estimation based on Wiener degradation processes with random failure threshold[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2016, 23(9): 2230-2241. doi: 10.1007/s11771-016-3281-z [28] 王泽洲, 陈云翔, 蔡忠义, 等. 考虑随机失效阈值的设备剩余寿命在线预测[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(5): 1162-1168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.05.32WANG Z Z, CHEN Y X, CAI Z Y, et al. Real-time prediction of remaining useful lifetime for equipment with random failure threshold[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(5): 1162-1168(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.05.32 [29] TANNER D M, DUGGER M T. Wear mechanisms in a reliability methodology[J]. Proceedings of Spie the International Society for Optical Engineering, 2003, 4980: 22-40. [30] PENG H, FENG Q M, COIT D W. Simultaneous quality and reliability optimization for microengines subject to degradation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2009, 58(1): 98-105. doi: 10.1109/TR.2008.2011672 [31] GAO H D, CUI L R, QIU Q G. Reliability modeling for degradation-shock dependence systems with multiple species of shocks[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2019, 185: 133-143. [32] 王俊昭. 基于竞争失效过程的产品可靠性评估[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2020: 6-20.WANG J Z. Product reliability evaluation based on competing failure process[D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2020: 6-20(in Chinese). [33] 陈琳. 材料强度的统计性质[J]. 国外石油机械, 1995(1): 71-76.CHEN L. Statistical properties of material strength[J]. Foreign Petroleum Machinery, 1995(1): 71-76(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: