Automatic modulation recognition method based on improved weight AdaBoost.M2 algorithm
-
摘要:
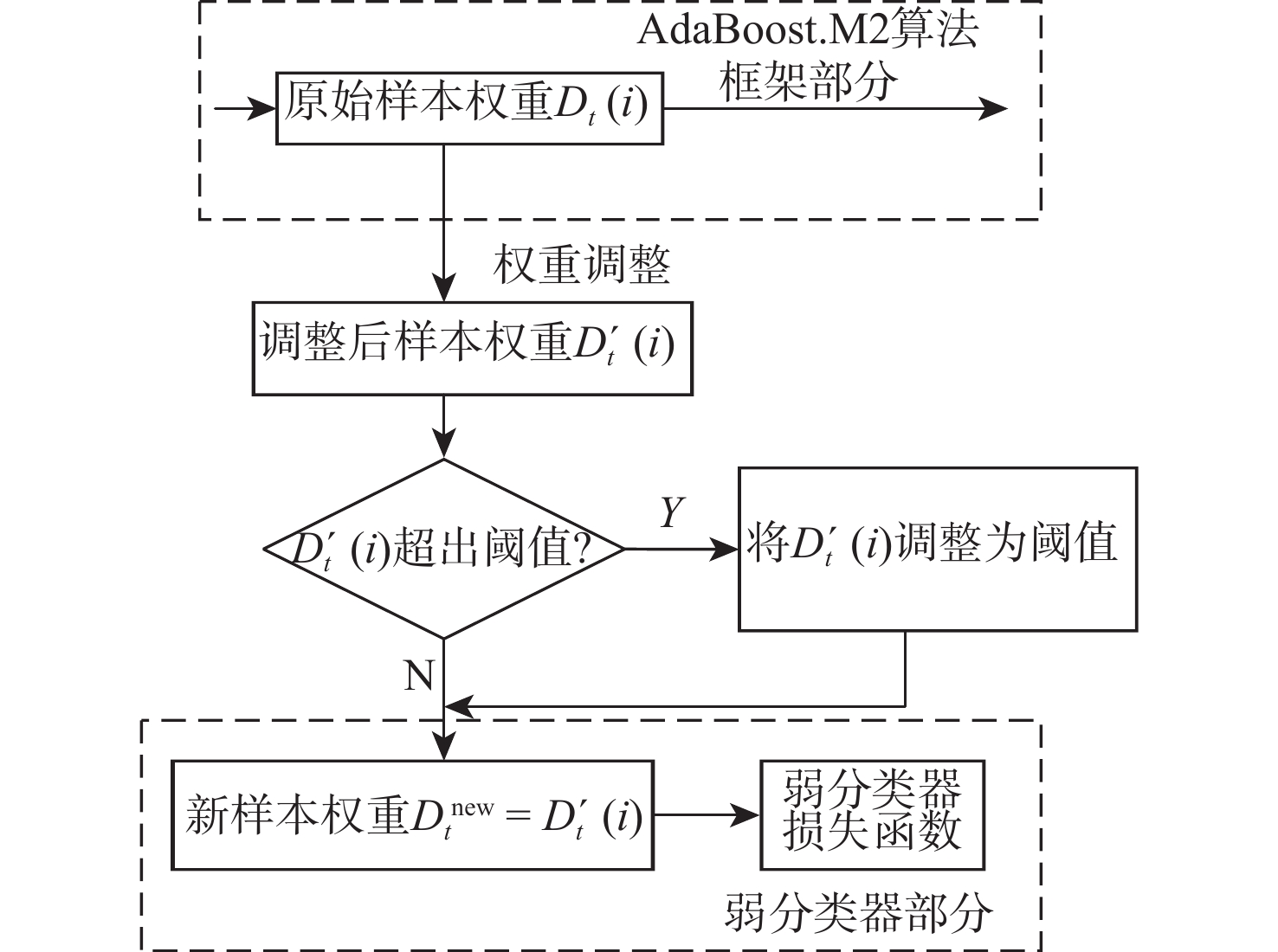
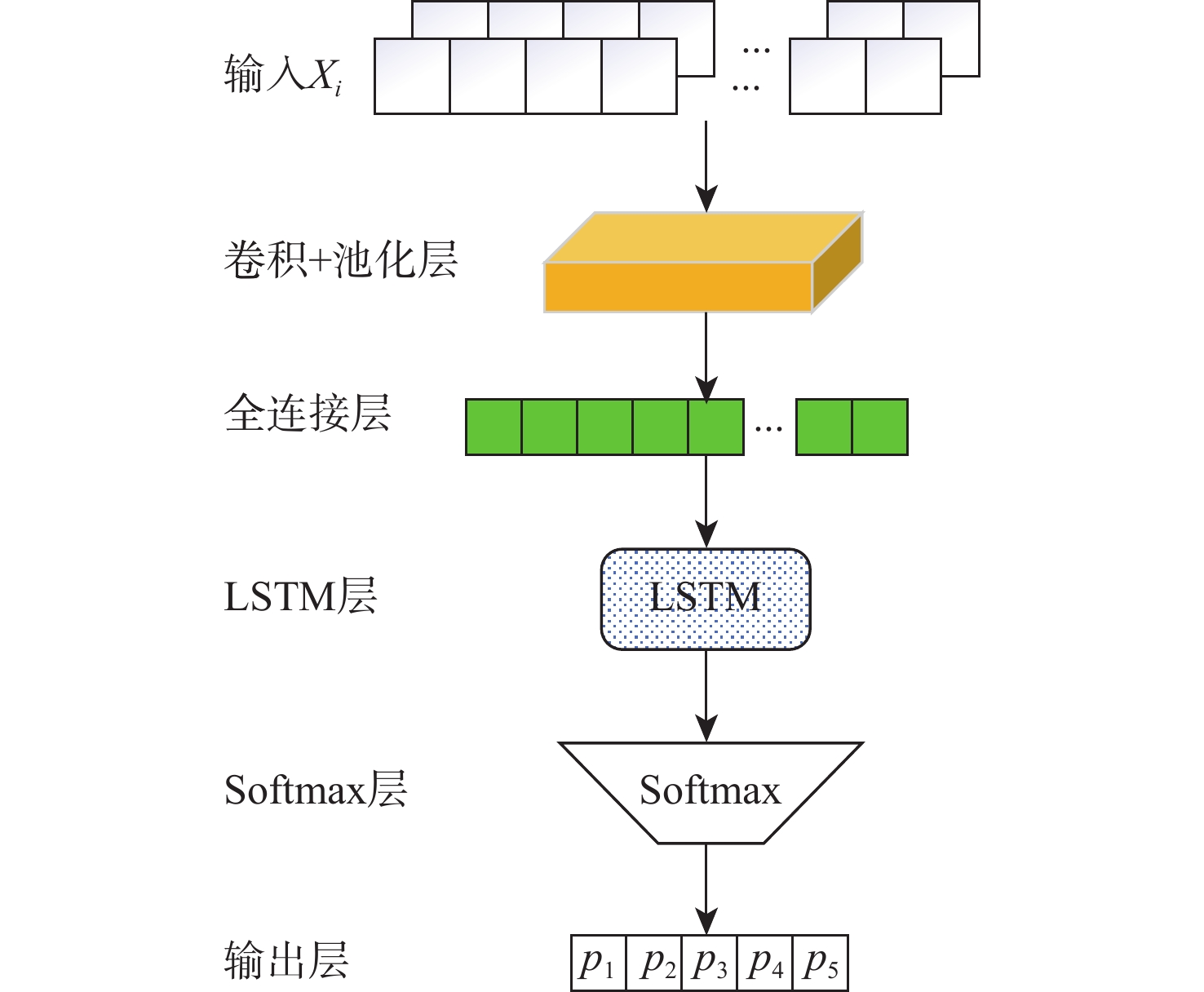
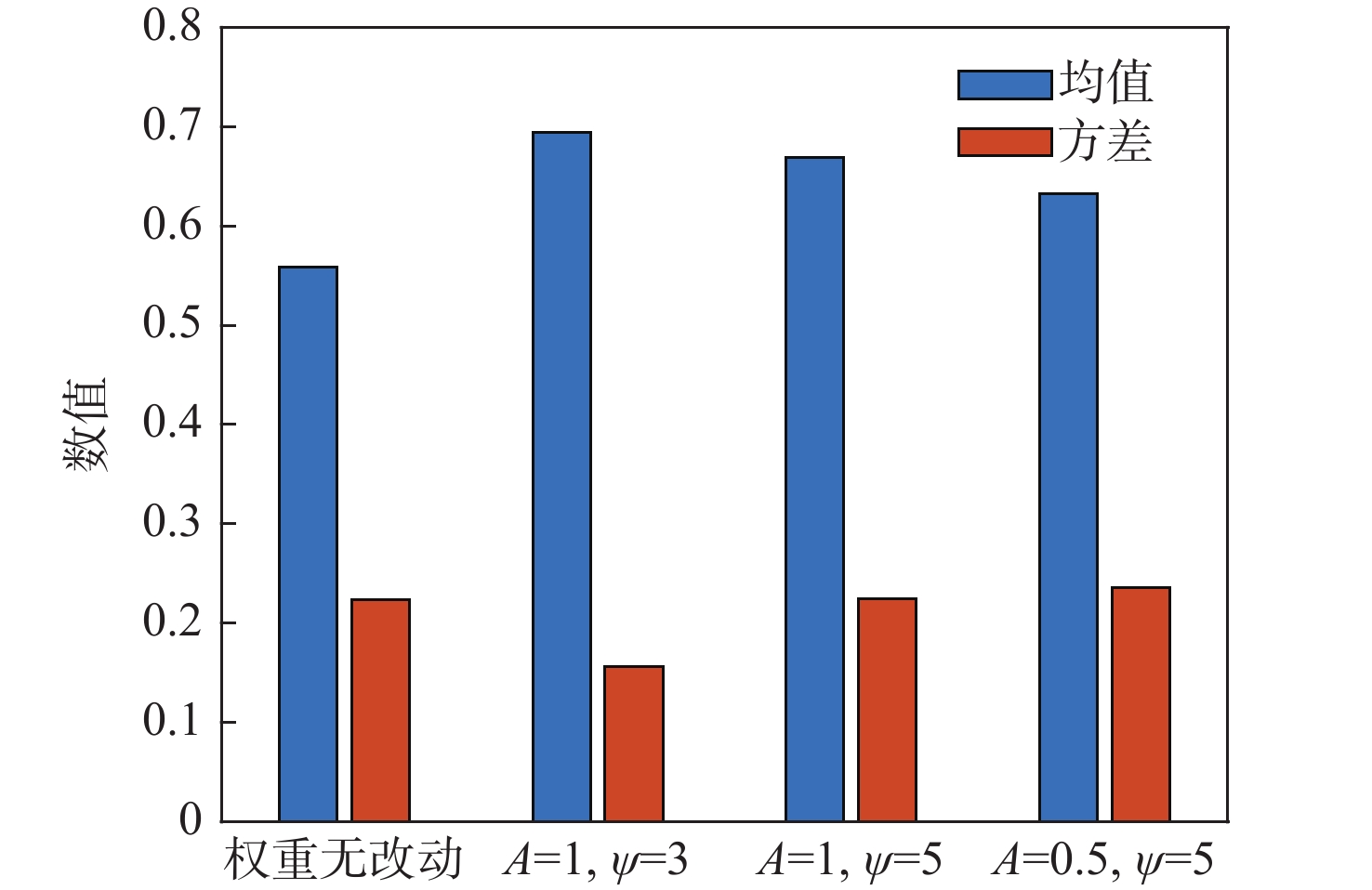
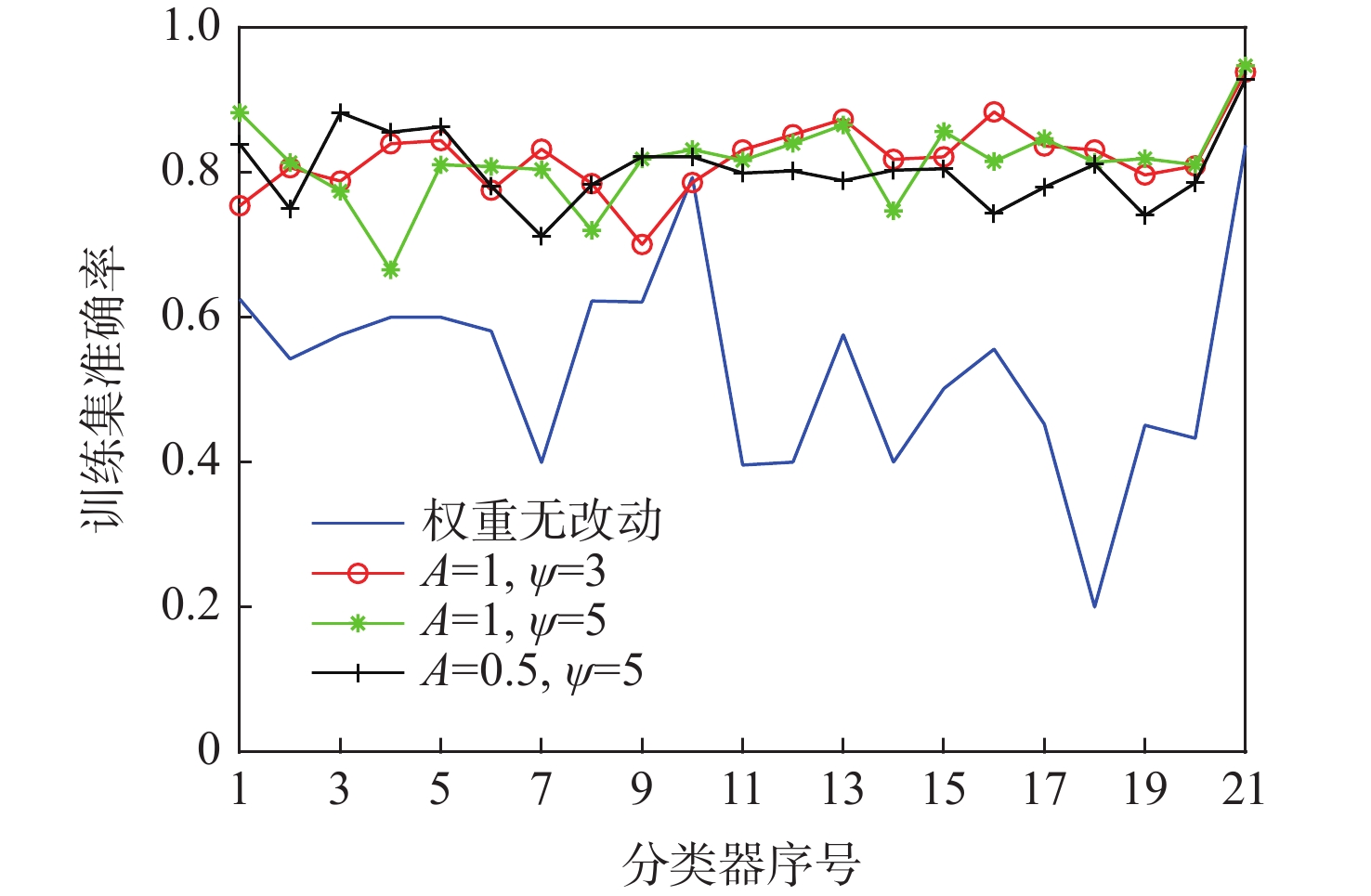
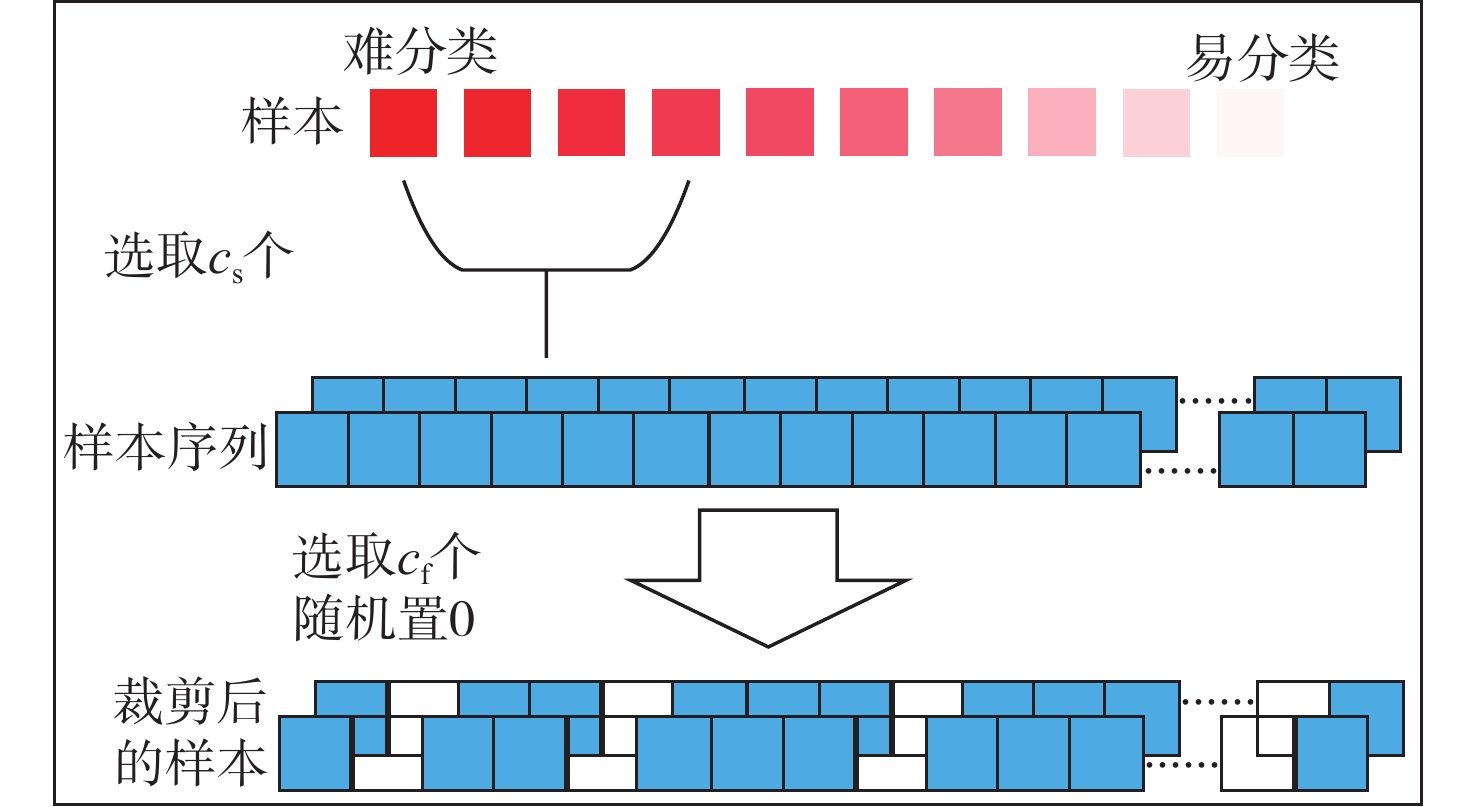
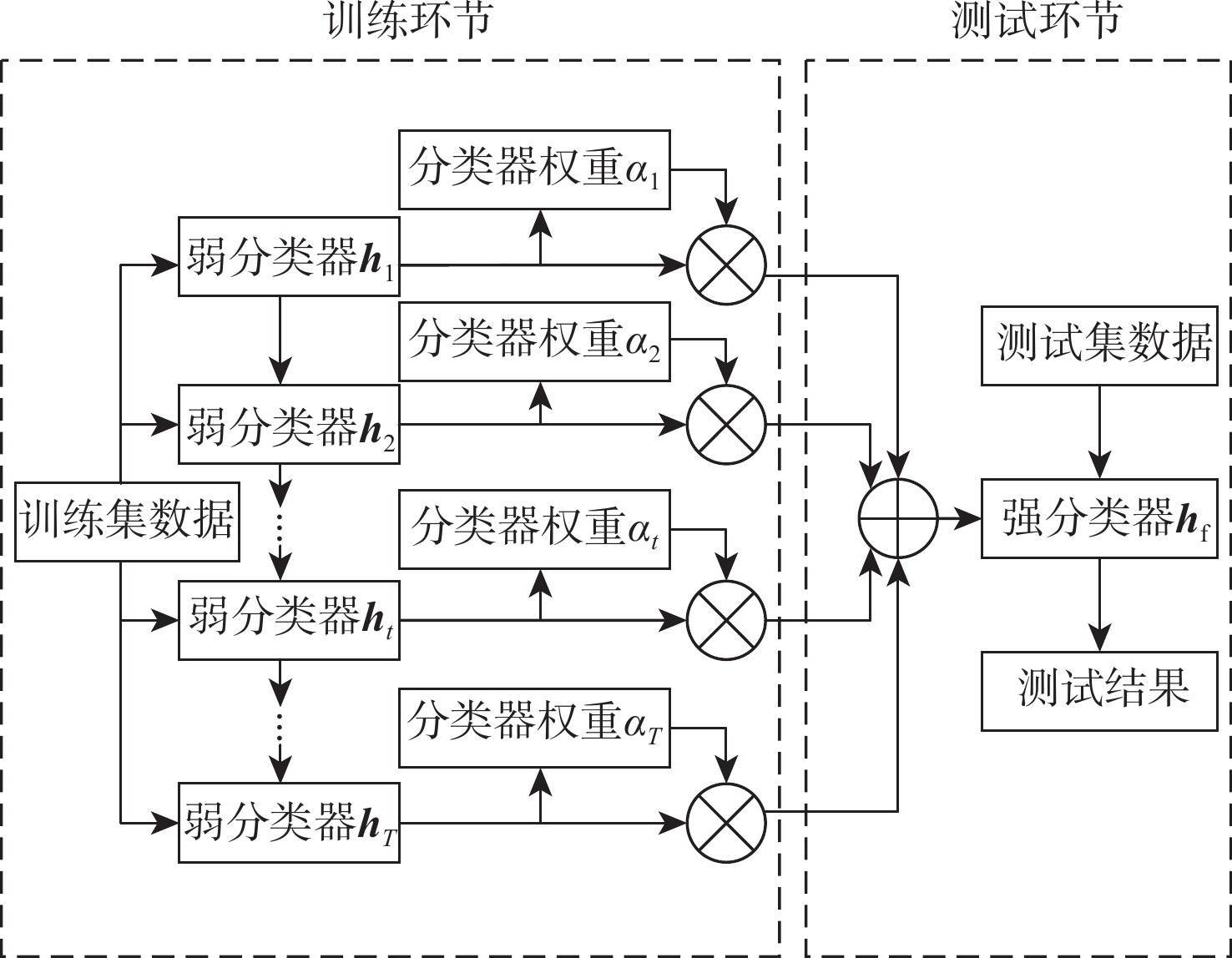
针对同族调制类型通信信号识别难度大、深度学习模型普遍存在泛化能力弱的问题,基于经典AdaBoost.M2算法,提出改进样本权重的AdaBoost.M2算法,用于解决大样本情况下学习率与加权后样本数据难以相适应的问题。改进后的新样本权重确保训练样本数据的数量级在加权后不变,并使算法更迅速地关注到难分类样本,提高了弱分类器综合性能,降低了加权投票模型中弱分类器重要性之间的差异。针对部分样本的统计特性易淹没于噪声中造成难分类问题,提出随机特征裁剪方法,使算法避免过度关注异常特征,降低了极难分类样本对AdaBoost.M2算法性能的负面影响,提升了算法的泛化能力,并以低信噪比数据进行实验验证。针对调制类型同族信号难分类的问题,选取同族调制类型的通信信号开展模型训练和测试。实验结果表明:相比于单一卷积长短时记忆全连接深度网络(CLDNN)算法,改进AdaBoost.M2算法对低信噪比PSK族类和QAM族类通信信号的测试集准确率分别提高了8.5%和11.25%,相比于直接集成CLDNN的经典AdaBoost.M2算法,测试集准确率分别提高了8.25%和6.5%。
-
关键词:
- AdaBoost.M2算法 /
- 深度学习 /
- 调制分类 /
- 样本权重 /
- 过拟合
Abstract:A signal modulation recognition method is proposed based on AdaBoost.M2 algorithm to address difficult identification of signals from the same family of modulation types and the poor generalization of the deep learning model. An improved method of sample weight is proposed to solve the problem that the learning rate of the weak learning algorithm is difficult to adapt to the weighted sample data in the case of large samples. The improved sample weight ensures that the order of magnitude of the training sample data remains unchanged after weighting, so that the algorithm pays more attention to the difficult classification samples, improving the comprehensive performance of the weak classifier. In addition, in view of the difficult classification problem caused by the statistical characteristics of some samples easily submerged in noise, a random feature clipping method is proposed to avoid much attention given to abnormal features. This method reduces the negative impact of extremely difficult classification samples on the performance of AdaBoost.M2 algorithm, improving the generalization ability of the algorithm. Experimental verification with low signal-to-noise ratio data is conducted. Finally, given the fact that the signals of the same family of modulation types are difficult to classify, the signals of the same family are selected for model training and testing. Results show that the improved AdaBoost.M2 algorithm increases the test set accuracy of PSK family and QAM family by 8.5 and 11.25% respectively compared with the single CLDNN algorithm, and by 8.25 and 6.5% respectively compared with the classical AdaBoost.M2 algorithm.
-
Key words:
- AdaBoost.M2 algorithm /
- deep learning /
- modulation classification /
- sample weight /
- over fitting
-
表 1 信号族类及调制类型
Table 1. Signal family and modulation type
族类 调制类型 PSK 8PSK、16PSK、32PSK、16APSK、32APSK QAM 16QAM、32QAM、64QAM、128QAM、256QAM 表 2 完整的参数组合及强分类器性能对比
Table 2. Complete parameter combination and comparison of strong classifier performance
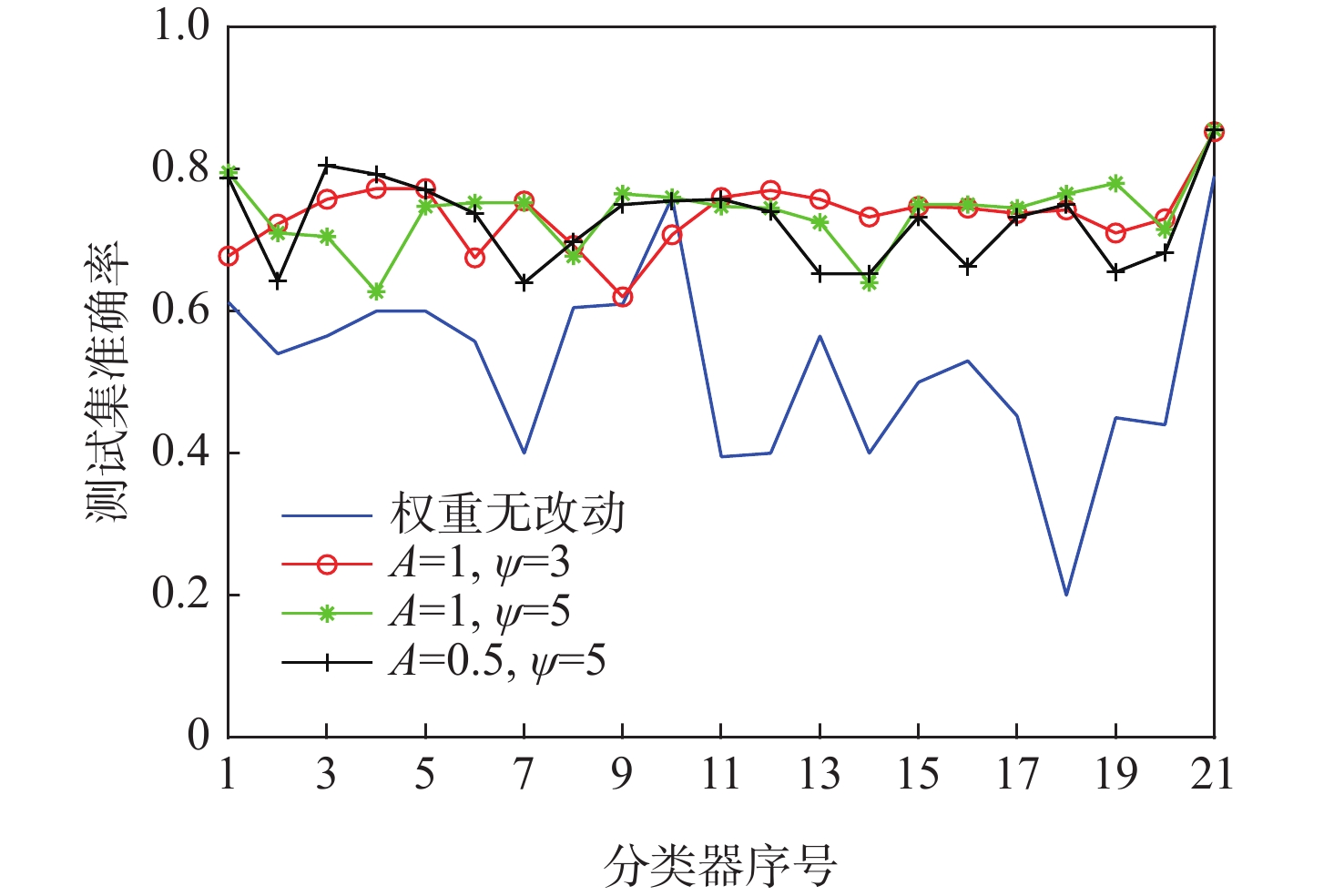
% 算法 训练集准确率 测试集准确率 无参数组合 A $\psi $ 无参数组合 A $\psi $ 2 3 5 10 2 3 5 10 CLDNN 88.85 79.75 经典AdaBoost.M2 85.45 80.00 改进样本权重的
AdaBoost.M20.5 92.80 93.60 92.85 94.85 0.5 84.75 84.00 85.50 84.50 1 94.45 93.85 94.70 94.25 1 84.50 85.25 85.50 84.25 2 94.65 95.40 95.60 96.10 2 82.75 81.75 81.50 83.50 表 3 不同特征裁剪方法参数下性能对比
Table 3. Performance comparison of different feature clipping methods with different parameters
% cs 训练集准确率 测试集准确率 cf=64 cf=128 cf=256 cf=512 cf=64 cf=128 cf=256 cf=512 125 92.45 93.10 93.70 93.60 80.50 78.25 83.25 80.50 62 95.30 95.50 95.50 95.80 84.50 84.50 84.25 86.75 30 91.50 91.60 91.60 89.15 85.50 85.50 85.25 84.25 20 90.00 92.20 91.25 91.10 86.00 85.25 83.25 86.25 10 92.60 92.80 92.75 93.85 84.75 87.25 88.25 84.25 表 4 算法复杂度对比
Table 4. Complexity comparison of algorithm
算法 训练2 000个
样本用时/min单样本测试
平均用时/msCLDNN 1.35 17.45 经典AdaBoost.M2 26.31 349.50 改进样本权重的AdaBoost.M2 27.85 390.13 本文算法 30.66 398.63 表 5 各算法对不同族类信号分类结果对比
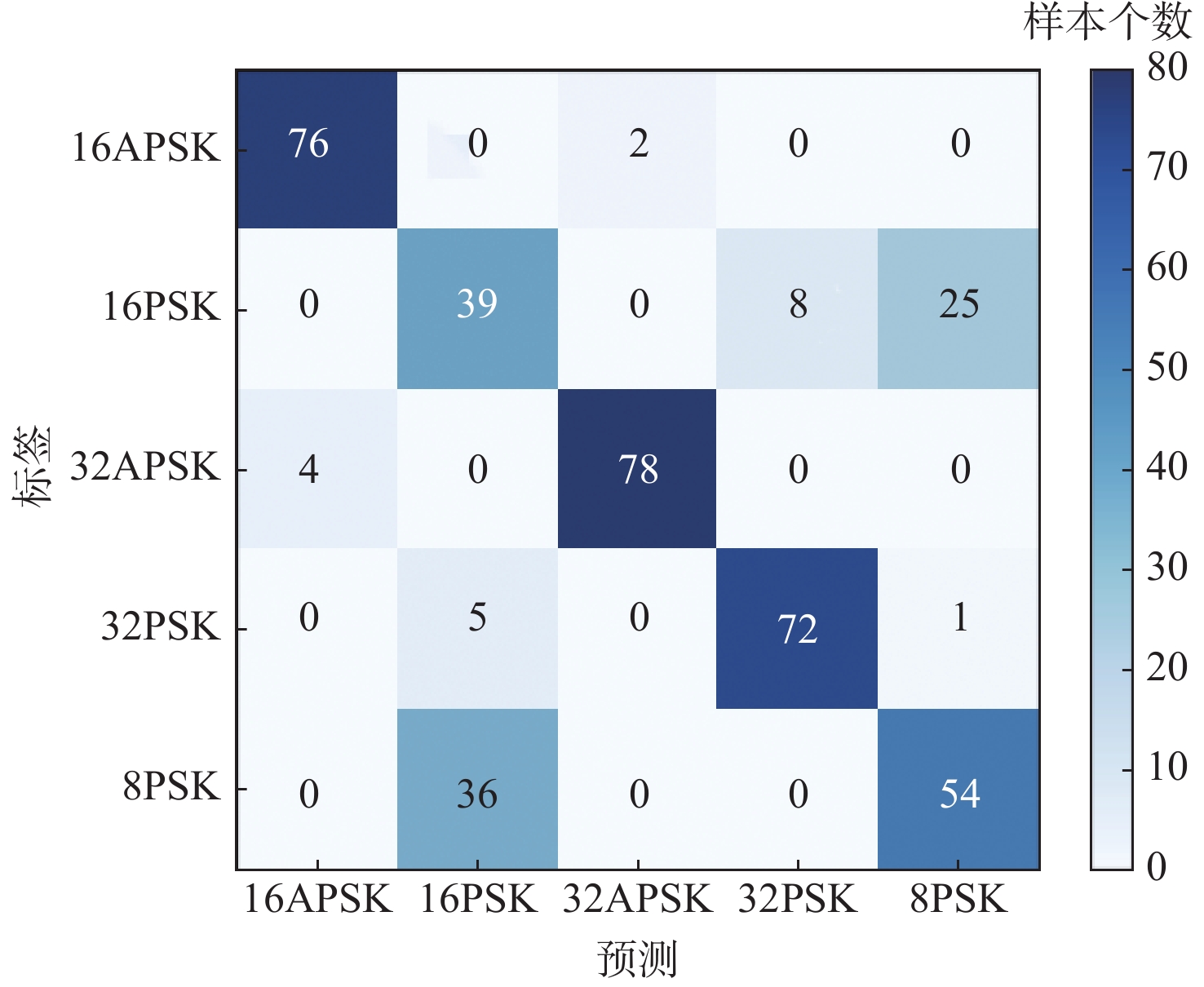
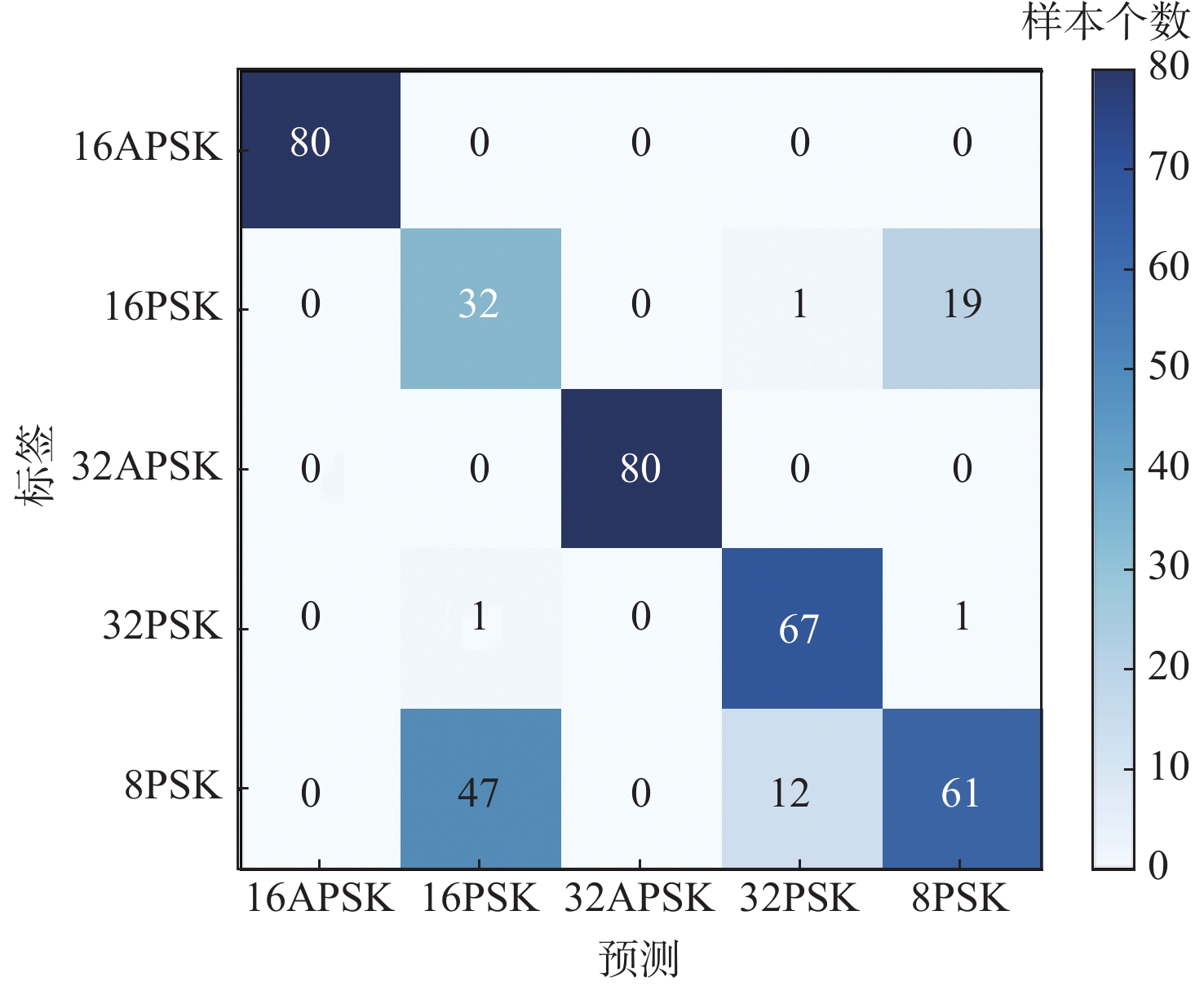
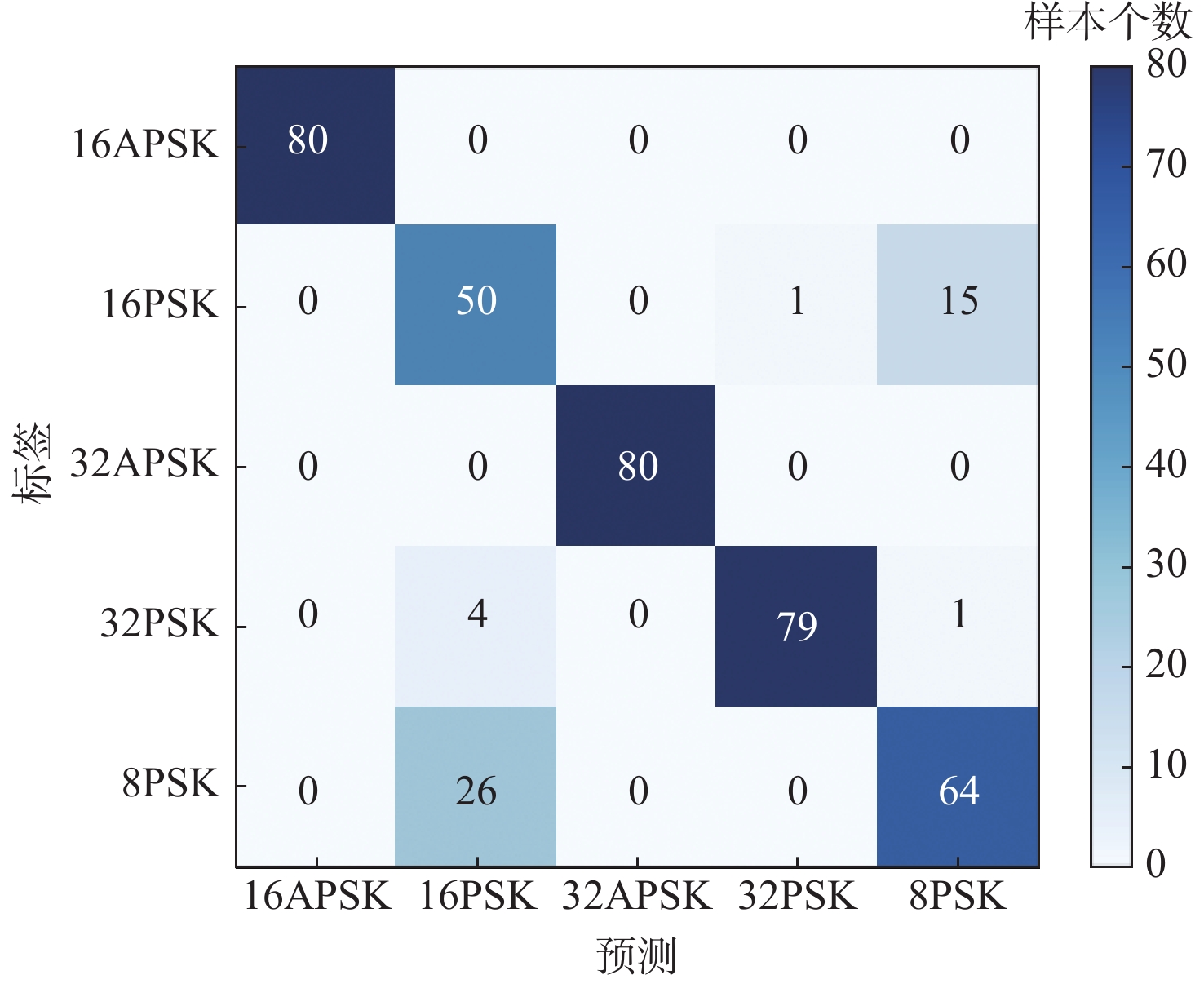
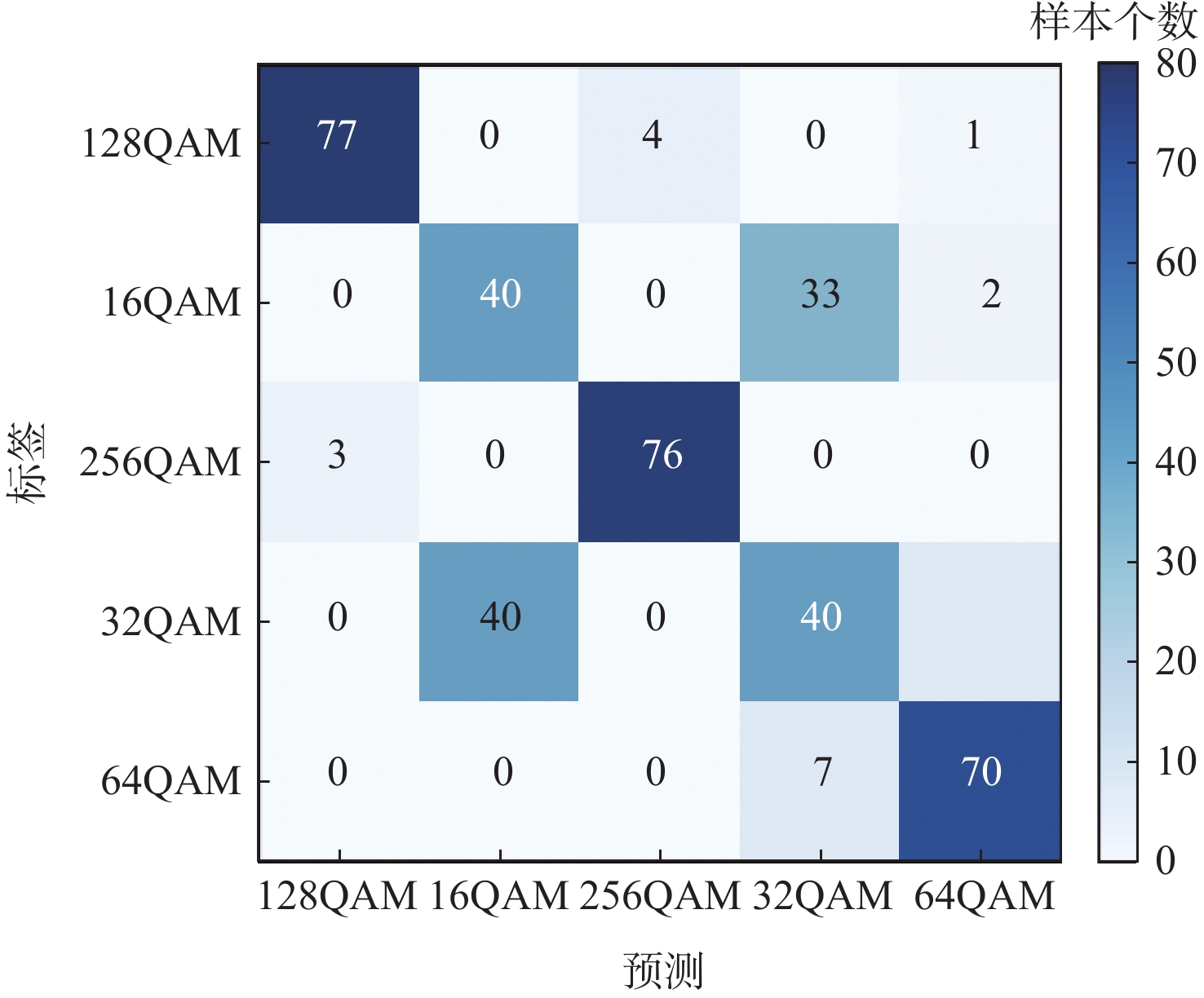
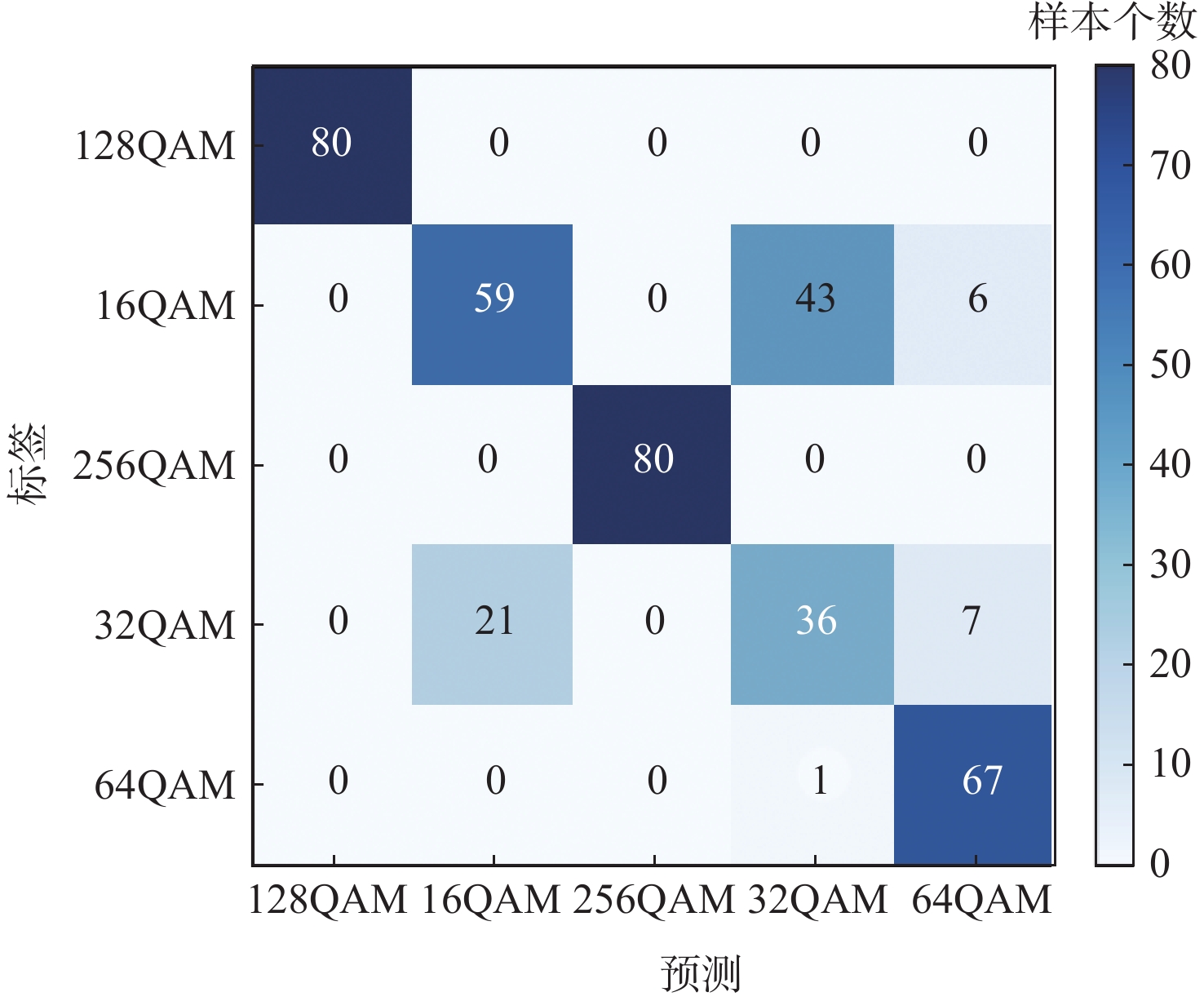
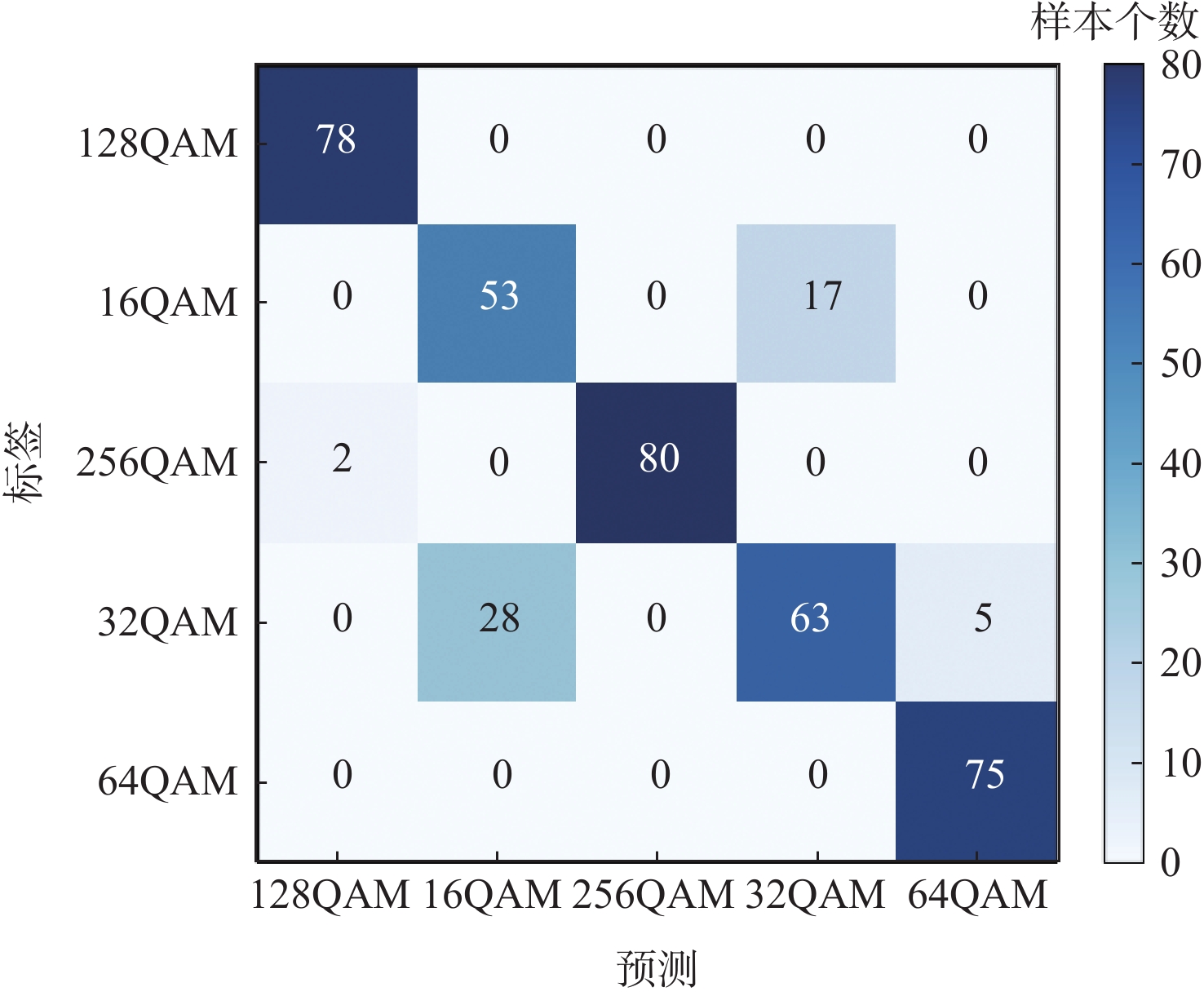
Table 5. Comparison of classification results of different signals by each algorithm
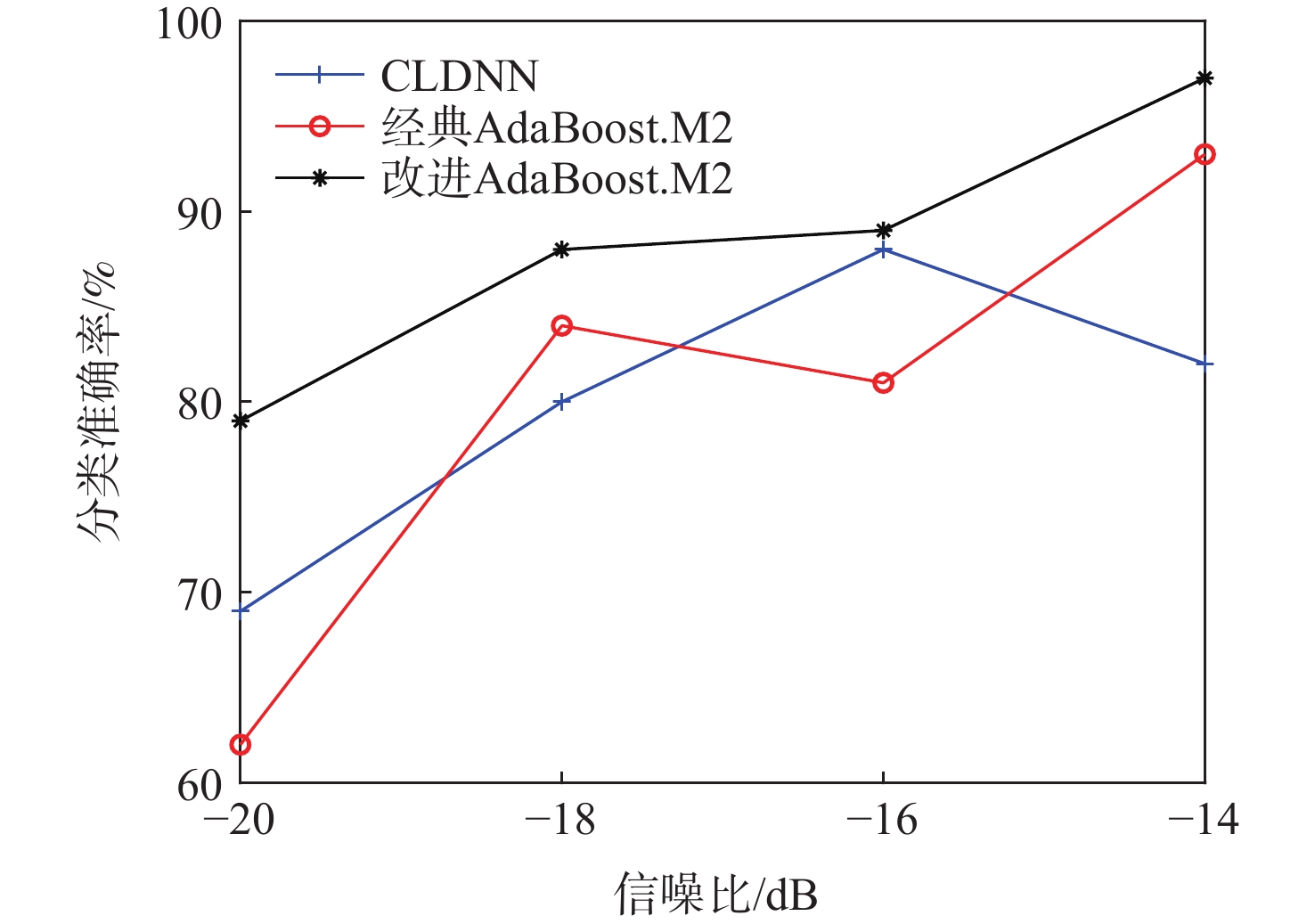
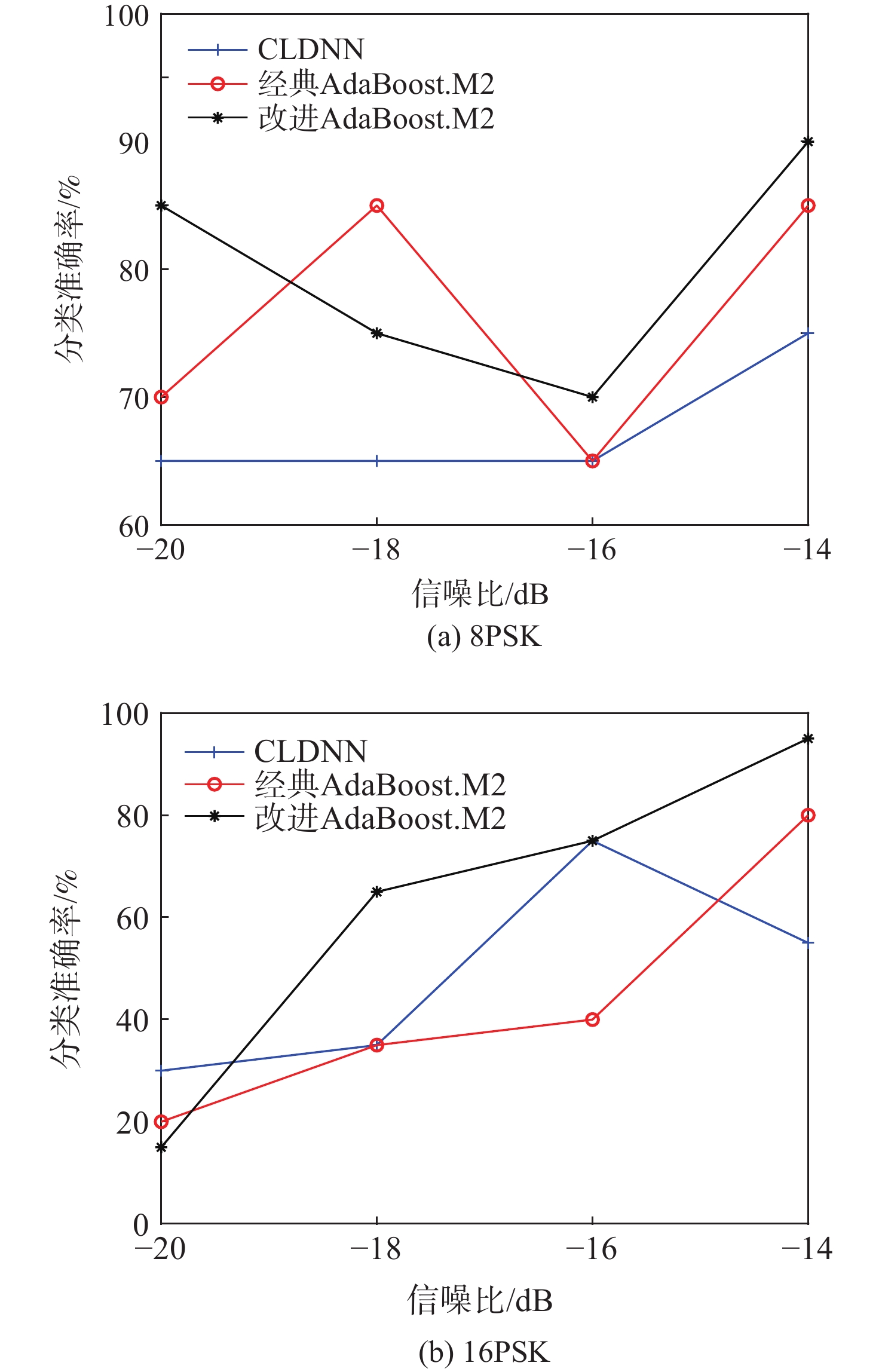
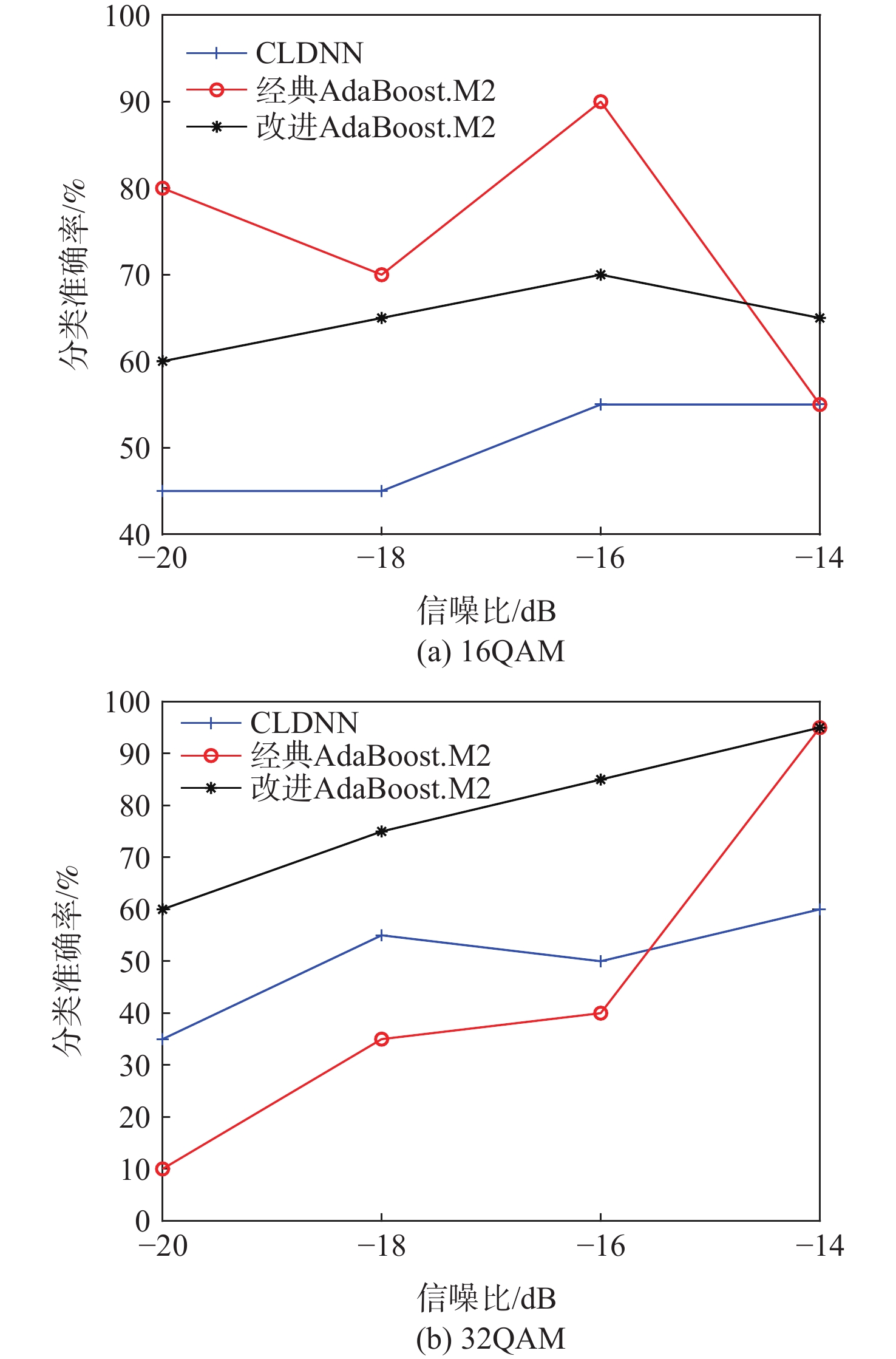
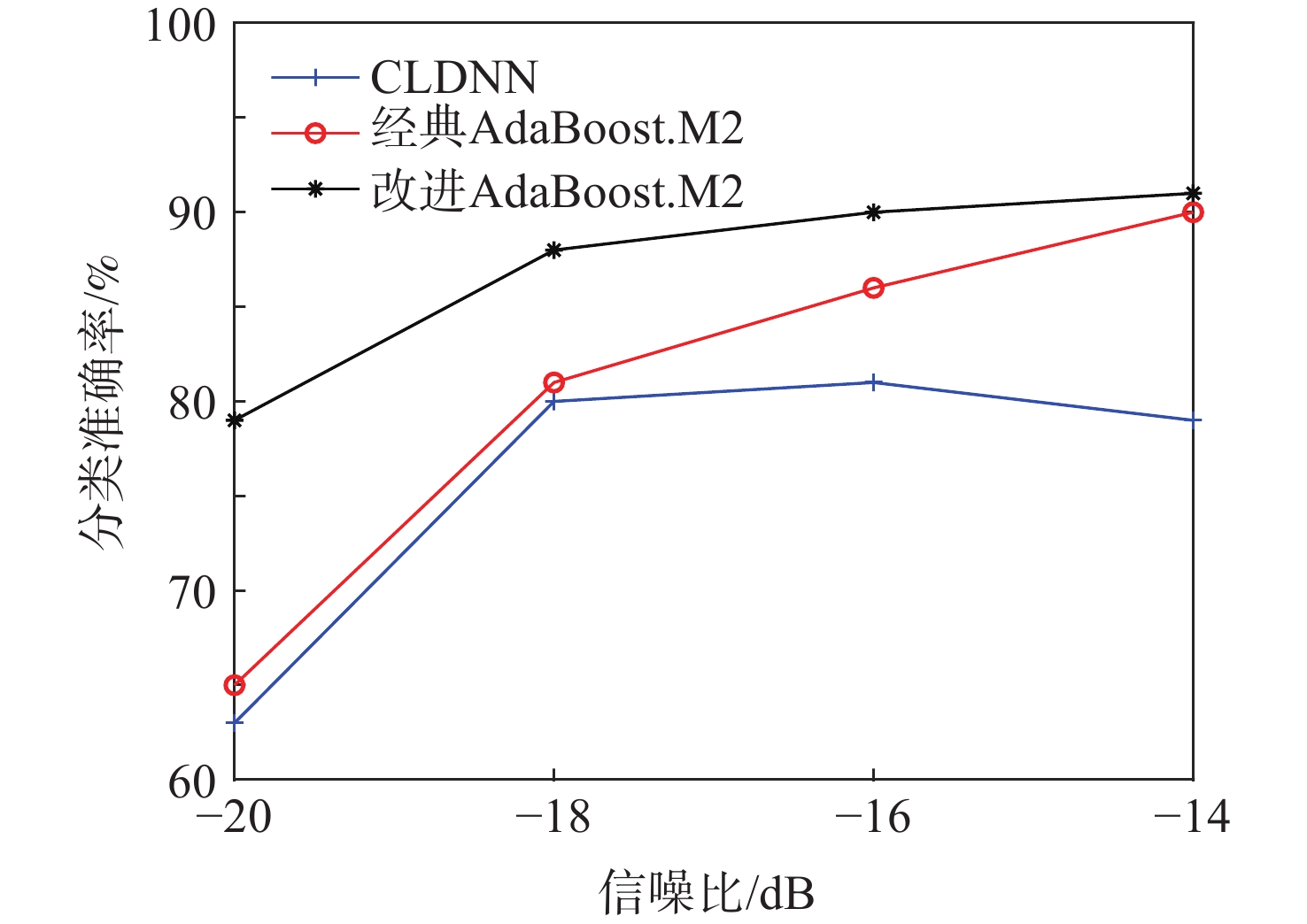
% 算法 训练集准确率 测试集准确率 PSK QAM PSK QAM CLDNN 88.85 93.40 79.75 75.75 经典AdaBoost.M2 85.45 87.95 80.00 80.50 本文算法 92.75 95.70 88.25 87.00 -
[1] 李晓峰, 周宁, 周亮. 通信原理[M]. 2版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2014: 1-10.LI X F, ZHOU N, ZHOU L. Communication principle[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2014: 1-10(in Chinese). [2] 高文欢. 浅析无线电信号通用解调和调制识别技术[J]. 中国无线电, 2015(3): 61-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7797.2015.03.037GAO W H. Analysis on general demodulation and modulation identification technology of radio signals[J]. China Radio, 2015(3): 61-62(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7797.2015.03.037 [3] 程汉文, 朱雷, 吴乐南. 基于累计量的干扰信号调制识别算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2009, 31(7): 1741-1745.CHENG H W, ZHU L, WU L N. Modulation classification algorithm for jamming signal based on cumulant[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2009, 31(7): 1741-1745(in Chinese). [4] 屈明, 张效义. 基于频域处理的信号检测和自动调制识别算法[J]. 数据采集与处理, 2006, 21(S1): 19-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2006.z1.005QU M, ZHANG X Y. Signal detection and classification algorithm based on frequency region processing[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition & Processing, 2006, 21(S1): 19-21(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2006.z1.005 [5] 潘宝凤. 通信侦察系统总体设计技术[J]. 电讯技术, 2011, 51(6): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2011.06.001PAN B F. Overall design of communication reconnaissance system[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2011, 51(6): 1-5(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2011.06.001 [6] WU H C, SAQUIB M, YUN Z F. Novel automatic modulation classification using cumulant features for communications via multipath channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2008, 7(8): 3098-3105. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2008.070015 [7] 张天骐, 范聪聪, 葛宛营, 等. 基于ICA和特征提取的MIMO信号调制识别算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(9): 2208-2215. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190320ZHANG T Q, FAN C C, GE W Y, et al. MIMO signal modulation recognition algorithm based on ICA and feature extraction[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2020, 42(9): 2208-2215(in Chinese). doi: 10.11999/JEIT190320 [8] NANDI A K, AZZOUZ E E. Modulation recognition using artificial neural networks[J]. Signal Processing, 1997, 56(2): 165-175. doi: 10.1016/S0165-1684(96)00165-X [9] MUSTAFA H, DOROSLOVACKI M. Digital modulation recognition using support vector machine classifier[C]//Conference Record of the Thirty-Eighth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2005: 2238-2242. [10] FEHSKE A, GAEDDERT J, REED J H. A new approach to signal classification using spectral correlation and neural networks[C]//First IEEE International Symposium on New Frontiers in Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2005: 144-150. [11] HEADLEY W C, REED J D, DA SILVA C R C M. Distributed cyclic spectrum feature-based modulation classification[C]//2008 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2008: 1200-1204. [12] O’SHEA T J, HOYDIS J. An introduction to deep learning for the physical layer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2017, 3(4): 563-575. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2017.2758370 [13] KARRA K, KUZDEBA S, PETERSEN J. Modulation recognition using hierarchical deep neural networks[C]//2017 IEEE International Symposium on Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks (DySPAN). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1-3. [14] 陈曦. 基于深度学习的数字信号调制方式识别方法研究[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2018: 9-67.CHEN X. Research on digital signal modulation recognition method based on deep learning[D]. Xi'an: Xidian University, 2018: 9-67 (in Chinese). [15] 张劭. 基于深度学习的未知调制类型的信号识别[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2018: 7-54.ZHANG S. Signal recognition of unknown modulation type based on deep learning[D]. Xi'an: Xidian University, 2018: 7-54(in Chinese). [16] O’SHEA T J, CORGAN J, CLANCY T C. Convolutional radio modulation recognition networks[C]//International Conference on Engineering Applications of Neural Networks. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 213-226. [17] ZHANG D N, DING W R, ZHANG B C, et al. Automatic modulation classification based on deep learning for unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(3): 924. doi: 10.3390/s18030924 [18] RAJENDRAN S, MEERT W, GIUSTINIANO D, et al. Deep learning models for wireless signal classification with distributed low-cost spectrum sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2018, 4(3): 433-445. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2018.2835460 [19] O’SHEA T J, ROY T, CLANCY T C. Over-the-air deep learning based radio signal classification[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2018, 12(1): 168-179. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2018.2797022 [20] LIU X Y, YANG D Y, EL GAMAL A. Deep neural network architectures for modulation classification[C]// 2017 51st Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 915-919. [21] 张宇. 基于深度学习的通信信号调制识别算法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2019: 7-59.ZHANG Y. Research on modulation recognition algorithm of communication signal based on deep learning[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2019: 7-59(in Chinese). [22] 陶桂平, 韩立岩. 最大熵原理在不完全信息博弈中的应用[J]. 首都经济贸易大学学报, 2011, 13(3): 67-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2700.2011.03.010TAO G P, HAN L Y. The application of the maximum entropy principle in the incomplete information game[J]. Journal of Capital University of Economics and Business, 2011, 13(3): 67-71(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2700.2011.03.010 [23] 廖红文, 周德龙. AdaBoost及其改进算法综述[J]. 计算机系统应用, 2012, 21(5): 240-244. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3254.2012.05.056LIAO H W, ZHOU D L. Review of AdaBoost and its improvement[J]. Computer Systems & Applications, 2012, 21(5): 240-244(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3254.2012.05.056 -







 下载:
下载: