A real-time correlation algorithm for GEO targets based on radar ranging and velocity measurement
-
摘要:
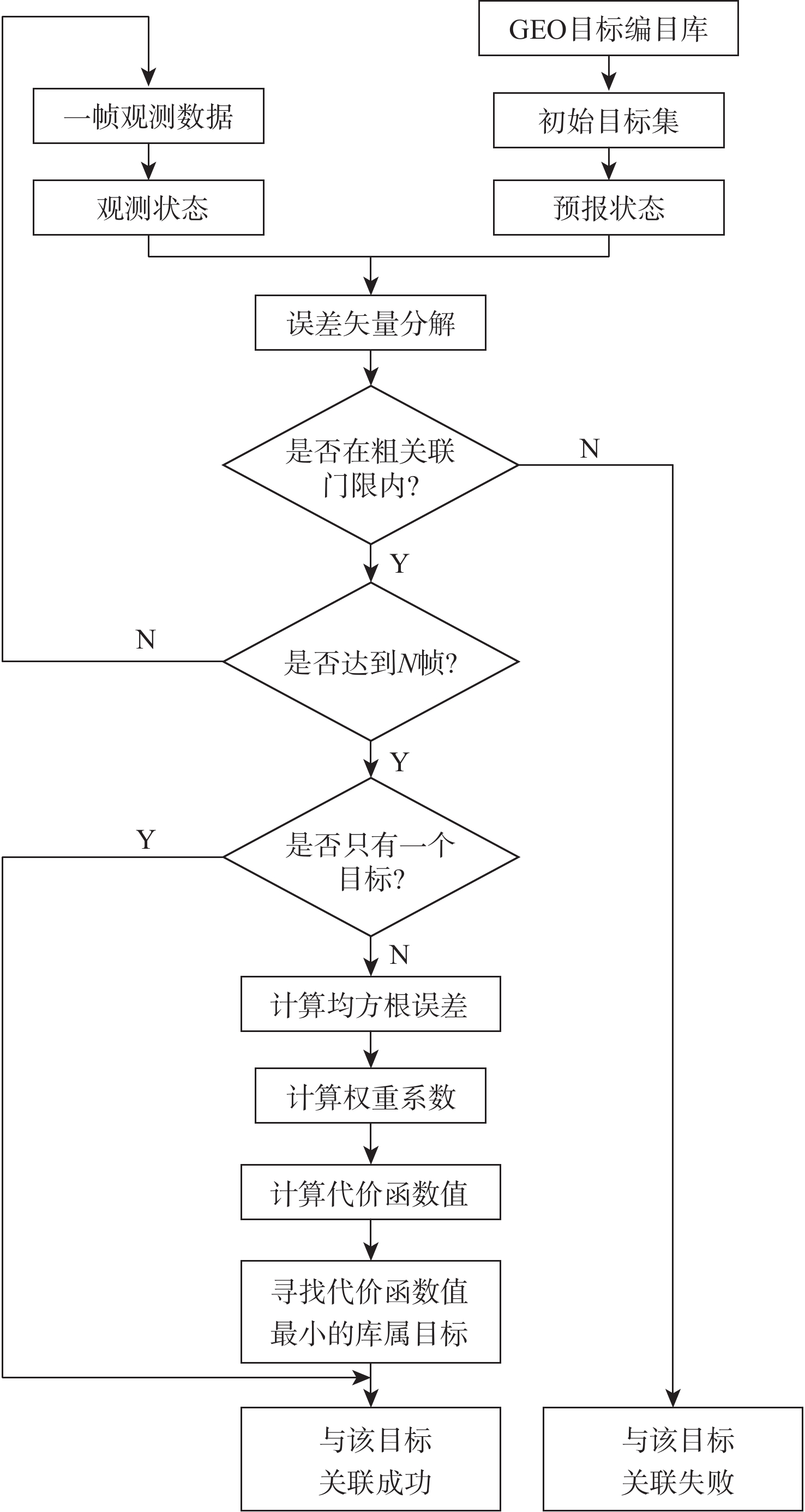
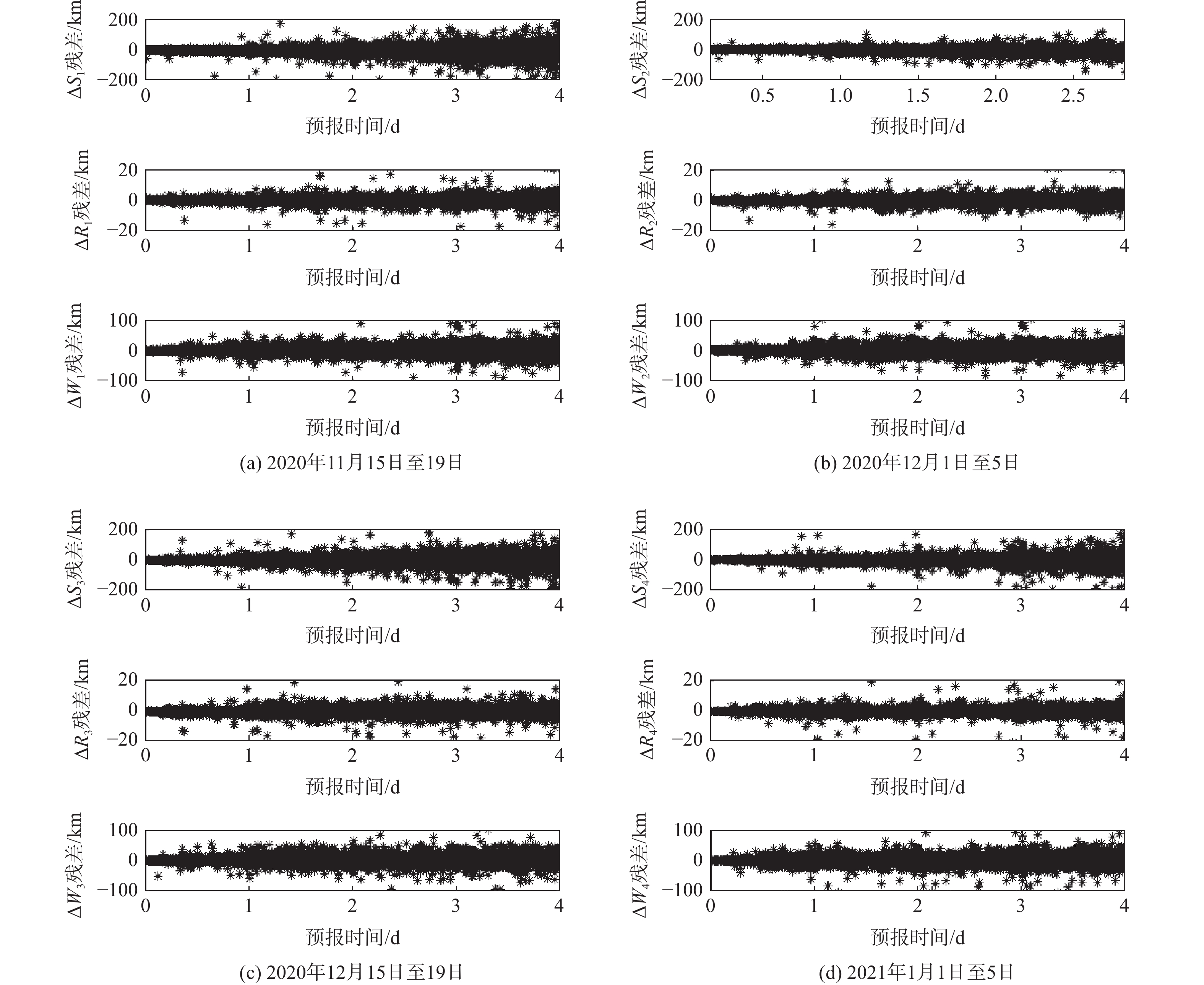
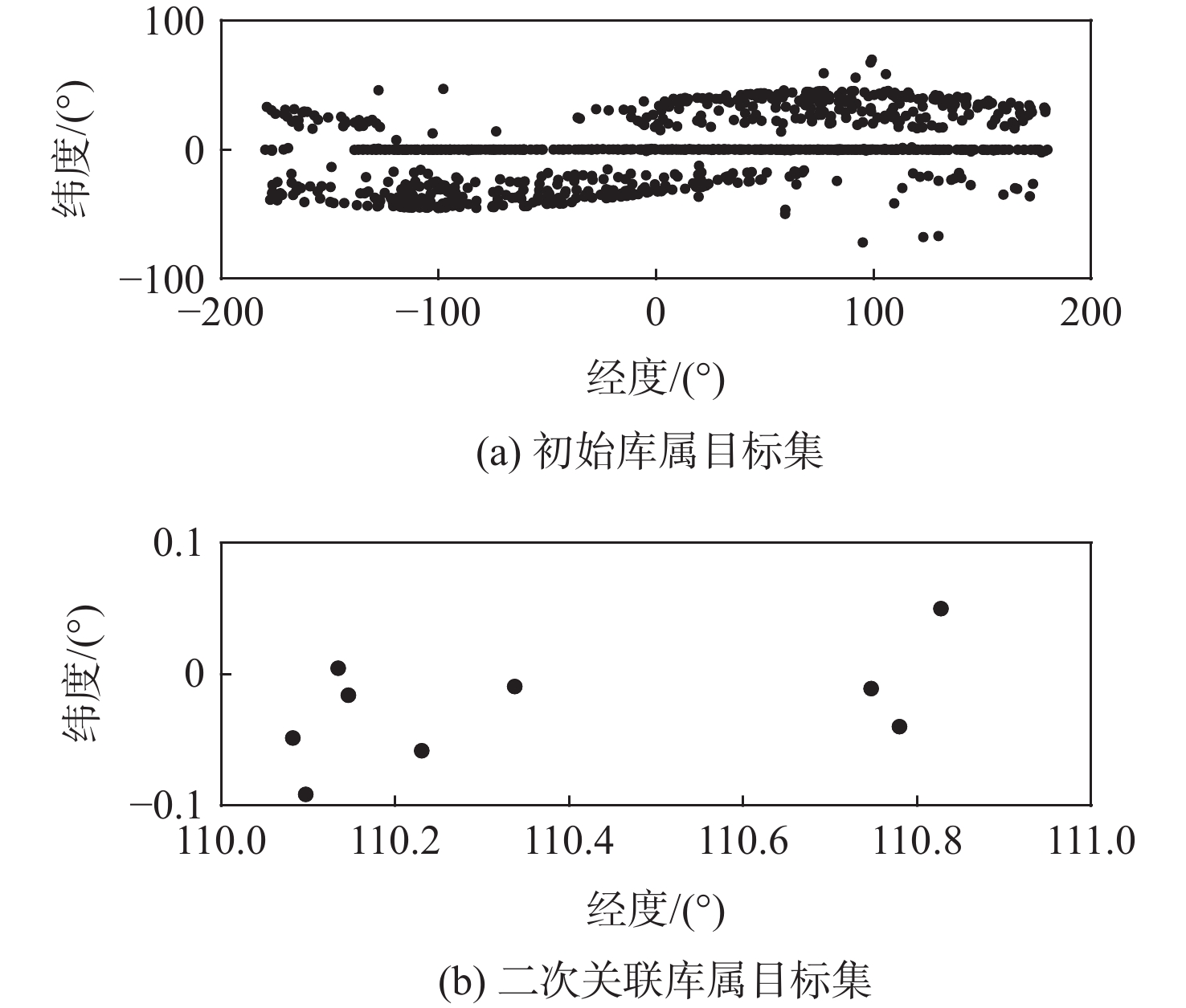
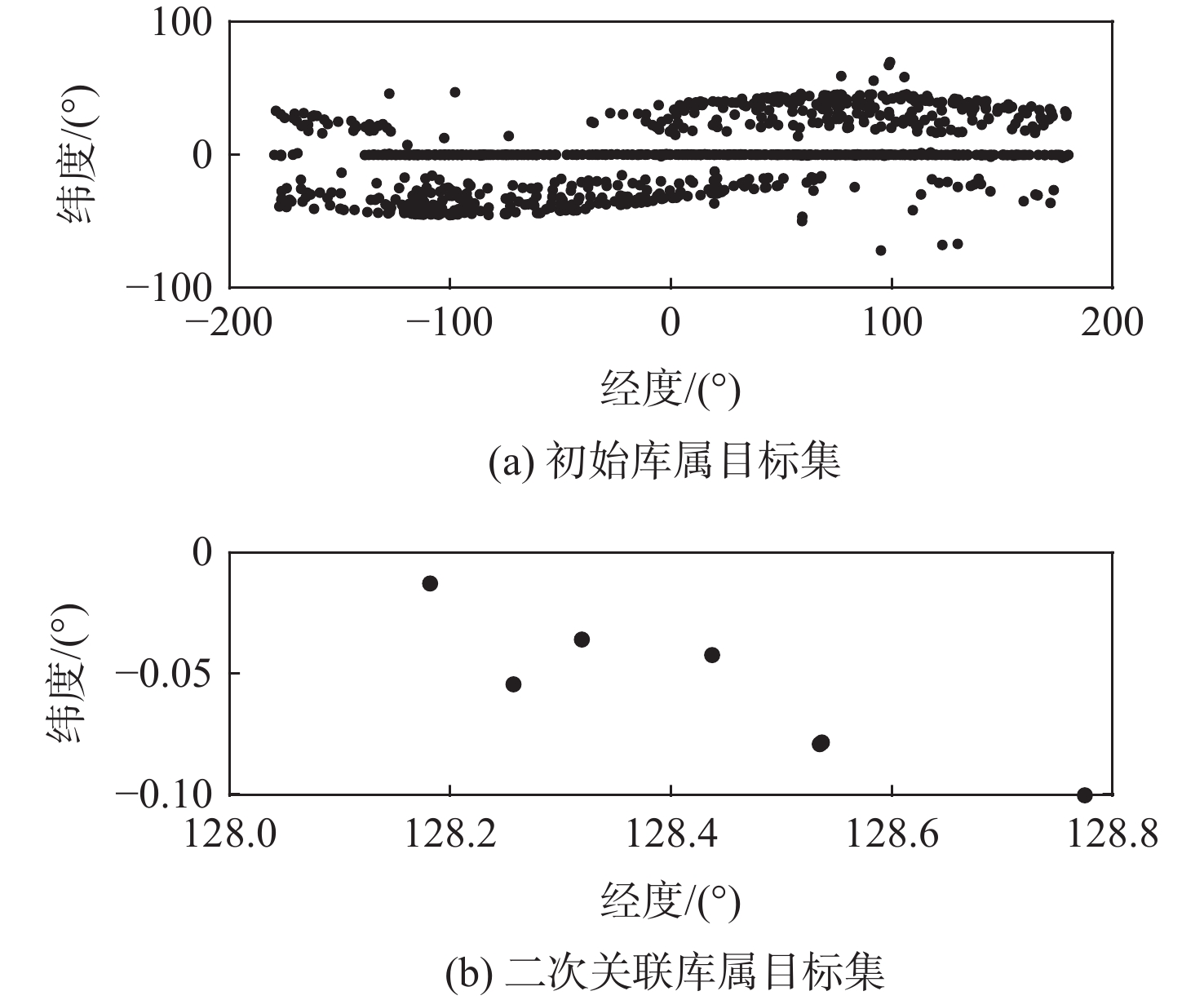
针对航迹密集情况下地球同步轨道(GEO)目标容易关联错误的问题,提出了一种基于雷达测距和测速二维判决的GEO目标实时关联算法。利用空间目标两行轨道根数(TLE)建立待关联初始库属目标集;根据空间目标轨道预报误差扩散规律设置粗关联门限,得到二次关联库属目标集;利用雷达测距和测速精度高的特点构建二次关联代价函数,根据归一化加权均方根误差最小原则得到关联结果。仿真结果表明:该算法在目标航迹密集的情况下取得了较好的关联效果,具有较高的关联正确率。
Abstract:In order to address the issue of error correction of the geosynchronous orbit (GEO) targets under the dense track, a real-time correlation algorithm for the GEO targets based on the two-dimensional of radar range and velocity measurement was developed. Firstly, the initial target set is established by using two lines elements (TLE). Then, the rough-correlation threshold is set according to the diffusion law of orbit prediction error of the space targets, and the secondary correlation target set is obtained. Finally, the correlation result is obtained using the idea of the minimal normalized weighted root mean square error, and the secondary correlation cost function is built based on the characteristics of high-accuracy radar range and velocity measurement. The simulation results show that the algorithm achieves a better correlation effect under the condition of dense target tracks, and has a higher correlation accuracy.
-
Key words:
- radar /
- two-dimensional judgment /
- dense track /
- geosynchronous orbit /
- real-time correlation
-
表 1 跟踪雷达参数信息
Table 1. Tracking-radar parameter information
工作
频段信号带宽/
MHz天线波束
宽度/(°)脉冲重复
间隔/ms脉冲宽度/
msS 5 0.15 5~20 1~4 表 2 测量信息中添加的高斯噪声(标准差)
Table 2. Gaussian noise (standard deviation) added to measurement information
距离维/m 方位维/mrad 俯仰维/mrad 速度维/(m·s−1) 10 0.2 0.2 0.01 表 3 TLE目标集中目标更新周期分布
Table 3. Update period distribution of targets in TLE
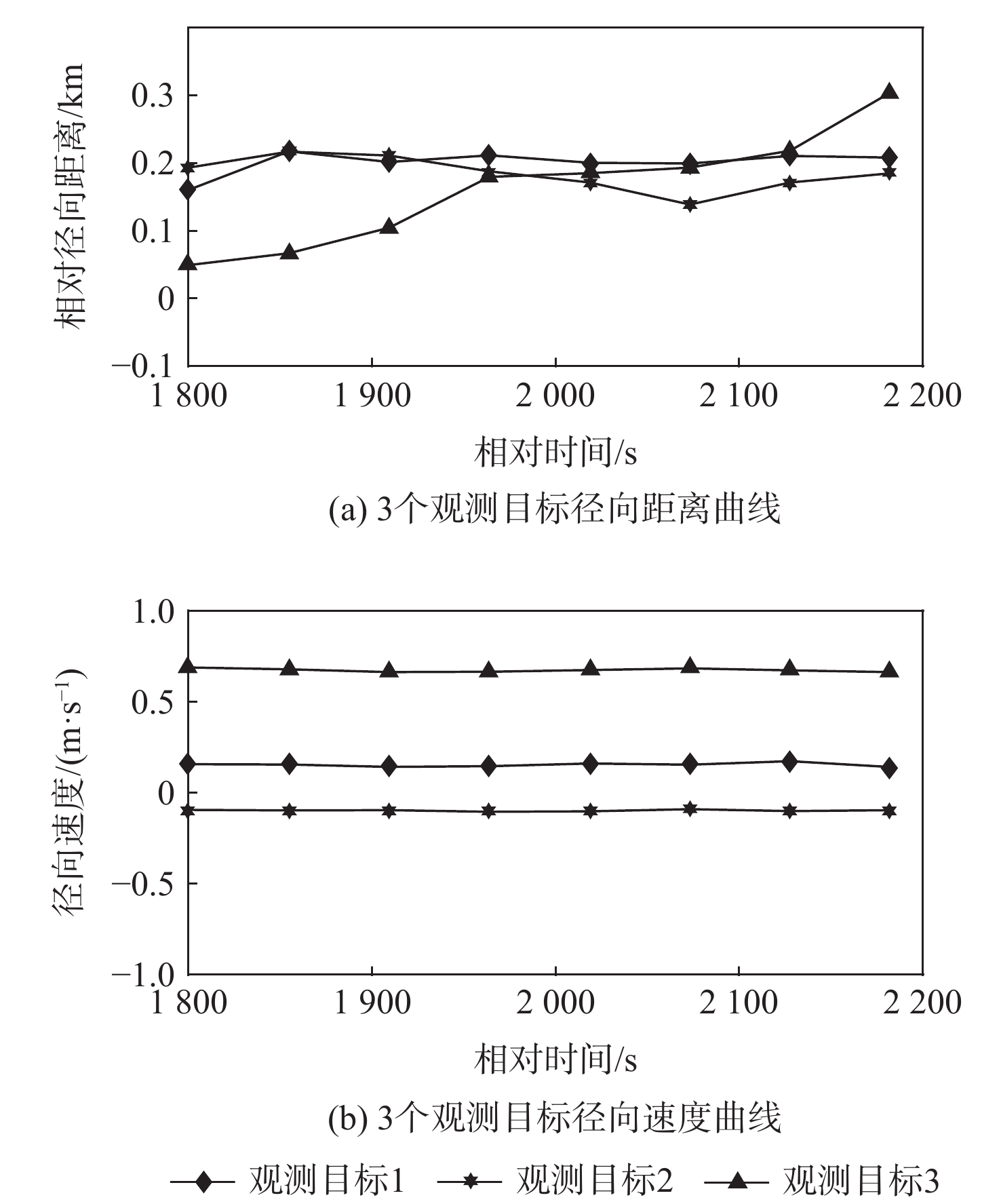
更新周期/d 目标数量/个 数量占比/% 1 1576 96.75 2 31 1.90 3 5 0.31 4 7 0.43 其他 10 0.61 注:其他为更新周期大于等于5 d的目标个数。 表 4 观测目标1二次关联情况
Table 4. Secondary correlation of observation target No.1
真实目标 二次关联库属目标 距离RMSE/km 速度RMSE/(m·s−1) 代价函
数值关联
结果37776 32019 202.359 0.249 36.481 37776 37207 235.142 0.402 42.483 37677 131.702 1.490 24.832 37776 0.870 0.002 0.158 41903 4.542 0.082 0.881 42662 8.661 3.126 4.118 42951 0.695 0.346 0.409 45807 624.462 258.579 324.170 46112 3.099 0.348 0.841 表 5 观测目标4二次关联情况
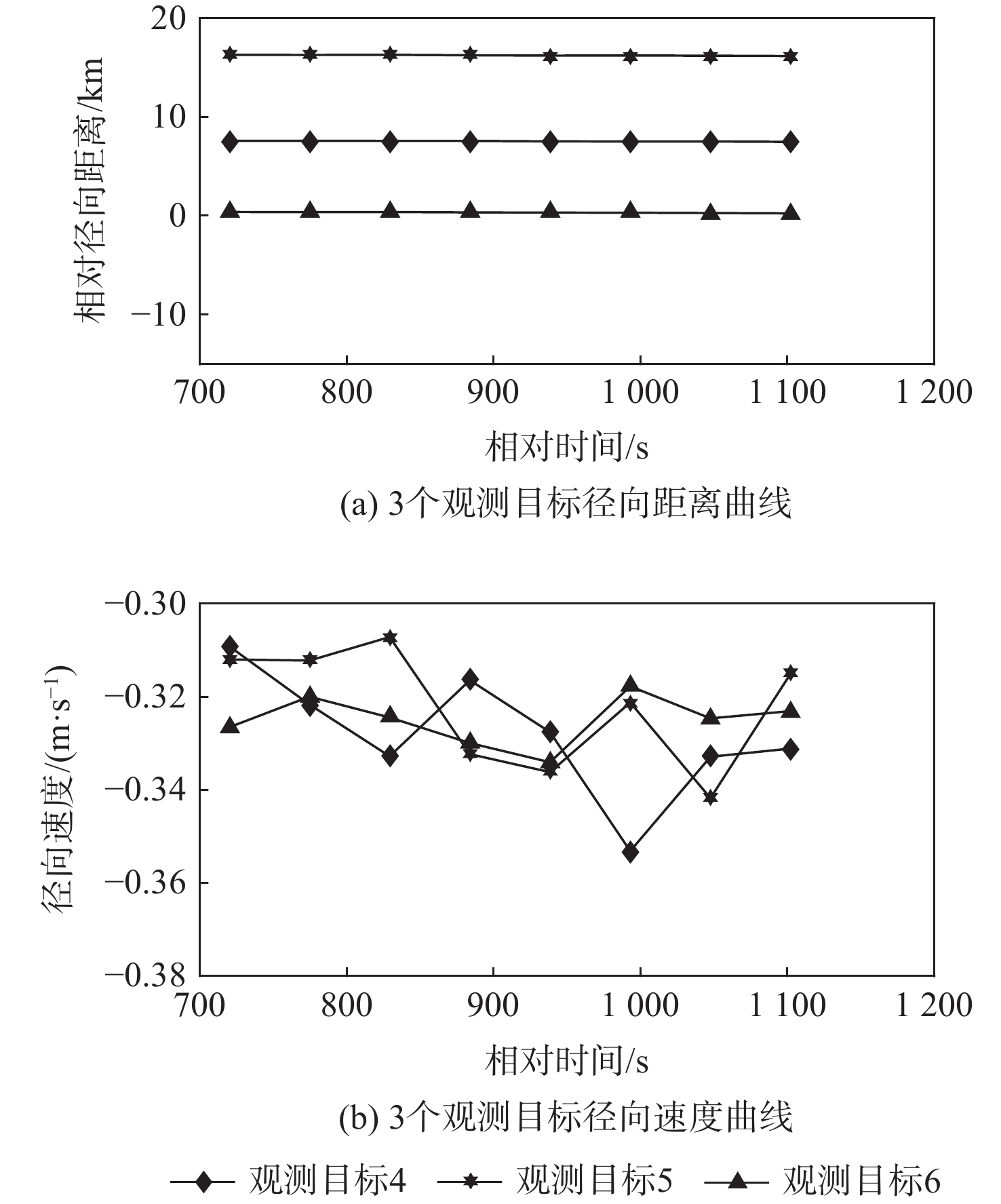
Table 5. Secondary correlation of observation target No.4
真实目标 二次关联库属目标 距离RMSE/km 速度RMSE/(m·s−1) 代价函数值 关联结果 36744 29272 18.4363 0.0661 0.0831 36744 36744 0.0098 2.7727×10−4 0.0003 41034 84.4975 0.0101 0.0882 41729 54.0964 2.3420×10−4 0.0503 43432 3.3355 0.0155 0.0185 43823 74.8245 1.024×10−4 0.0693 45246 0.6103 0.1260 0.1265 表 6 目标关联实验结果
Table 6. Results of target correlation experiments
序号 样本总数/条 关联成功概率/% 基于协方差理论的关联算法 基于距离辅助的关联算法 本文算法 1 432 90.51 96.33 99.54 2 425 88.94 95.69 99.04 3 453 90.28 96.07 99.13 4 435 90.34 94.63 99.02 5 437 89.70 97.02 99.08 6 458 91.70 97.54 99.11 7 419 89.50 96.06 99.12 -
[1] 刘二江. GEO目标接近轨迹规划与控制方法研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2016.LIU E J. Research on trajectory planning and control method of GEO target approaching[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2016(in Chinese). [2] 黄晓斌, 张燕, 肖锐, 等. 空间目标的雷达定轨实时识别问题研究[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2021, 19(1): 63-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2021.01.010HUANG X B, ZHANG Y, XIAO R, et al. Research on radar orbit determination real-time recognition of space target[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2021, 19(1): 63-68(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2021.01.010 [3] YAO Y, ZHAO J H, WU L N. Doppler data association scheme for multi-target tracking in an active sonar system[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(9): 2003. doi: 10.3390/s19092003 [4] 陶勇, 胡卫东, 徐劲. 基于轨道匹配和改进的空间目标识别方法[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2006, 4(3): 10-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2006.03.002TAO Y, HU W D, XU J. A method of space object identification based on orbit matching and improving[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2006, 4(3): 10-15(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2006.03.002 [5] REIHS B. Orbit determination for space surveillance[D]. Luleå: Luleå University of Technology, 2016. [6] LEE K C, HUANG C W, FANG M C. Radar target recognition by projected features of frequency-diversity RCS[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research, 2008, 81: 121-133. doi: 10.2528/PIER08010206 [7] WANG T, BI W J, ZHAO Y L, et al. Radar target recognition algorithm based on RCS observation sequence—Set-valued identification method[J]. Journal of Systems Science and Complexity, 2016, 29(3): 573-588. [8] LI H J, YANG S H. Using range profiles as feature vectors to identify aerospace objects[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1993, 41(3): 261-268. doi: 10.1109/8.233138 [9] LI Y, CHENG M M, PENG X J, et al. Ship detection and recognition combing one-dimensional range profile with SAR image[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 2019(19): 6252-6254. doi: 10.1049/joe.2019.0191 [10] MCCARTHY. IERS conventions (1996)[R]. Washington, D.C.: U. S. Naval Observatory, 1996. [11] 程昊文. 航天器轨道理论在空间目标编目管理中的应用[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2012.CHENG H W. The application of satellite orbit theory in maintaining the space object catalog[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2012(in Chinese). [12] FLOHRER T, SCHILDKNECHT T, MUSCI R, et al. Performance estimation for GEO space surveillance[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2005, 35(7): 1226-1235. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2005.03.101 [13] 闫瑞东, 王荣兰, 刘四清, 等. 基于协方差理论的非关联轨道动态关联算法[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2018, 38(6): 36-44. doi: 10.16708/j.cnki.1000-758X.2018.0062YAN R D, WANG R L, LIU S Q, et al. Uncorrelated tracks dynamic association based on orbital covariance[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2018, 38(6): 36-44(in Chinese). doi: 10.16708/j.cnki.1000-758X.2018.0062 [14] 董思远. 同步轨道目标雷达快速批量监视技术研究[D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2019.DONG S Y. Study on radar rapid batch surveillance technology for geosynchronous orbit objects[D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2019(in Chinese). [15] 焦润之. 地面侦察雷达多目标跟踪技术研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2018.JIAO R Z. Research on multi-target tracking technology of ground surveillance radar[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2018(in Chinese). [16] DAVID A V. Fundamentals of astrodynamics and applications[M]. 2nd Ed. El Segundo: Microcosm Press, 2004. [17] 白显宗. 空间目标轨道预报误差与碰撞概率问题研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2013.BAI X Z. Research on orbital prediction error and collision probability of space objects[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2013(in Chinese). [18] 钟芳宇. 雷达探测空间目标跟踪与数据关联方法研究[D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2016.ZHONG F Y. Study on tracking and data association for radar detecting space target[D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2016(in Chinese). [19] 张永红. 脉冲雷达凝视模式探测空间碎片技术研究[D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2016.ZHANG Y H. The technology study of space debris in staring mode detection of the pulse radar[D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2016(in Chinese). [20] XU X L, XIONG Y Q. Study on the orbit prediction errors of space objects based on historical TLE data[J]. Chinese Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2019, 43(4): 563-578. doi: 10.1016/j.chinastron.2019.11.007 [21] 陈磊, 韩蕾, 白显宗, 等. 空间目标轨道力学与误差分析[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2010.CHEN L, HAN L, BAI X Z., et al Orbital dynamics and error analysis of space object[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2010(in Chinese). [22] 李浩, 张杉, 曹斌, 等. 基于城市道路卡口数据的交通流量预测[J]. 重庆大学学报, 2020, 43(11): 29-40. doi: 10.11835/j.issn.1000-582X.2020.11.004LI H, ZHANG S, CAO B, et al. Prediction traffic flow based on teaffic data of urban road check points[J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 2020, 43(11): 29-40(in Chinese). doi: 10.11835/j.issn.1000-582X.2020.11.004 [23] CURRY G R. Radar system performance modeling [M]. 2nd ed. Boston: Artech House, 2005. -







 下载:
下载: