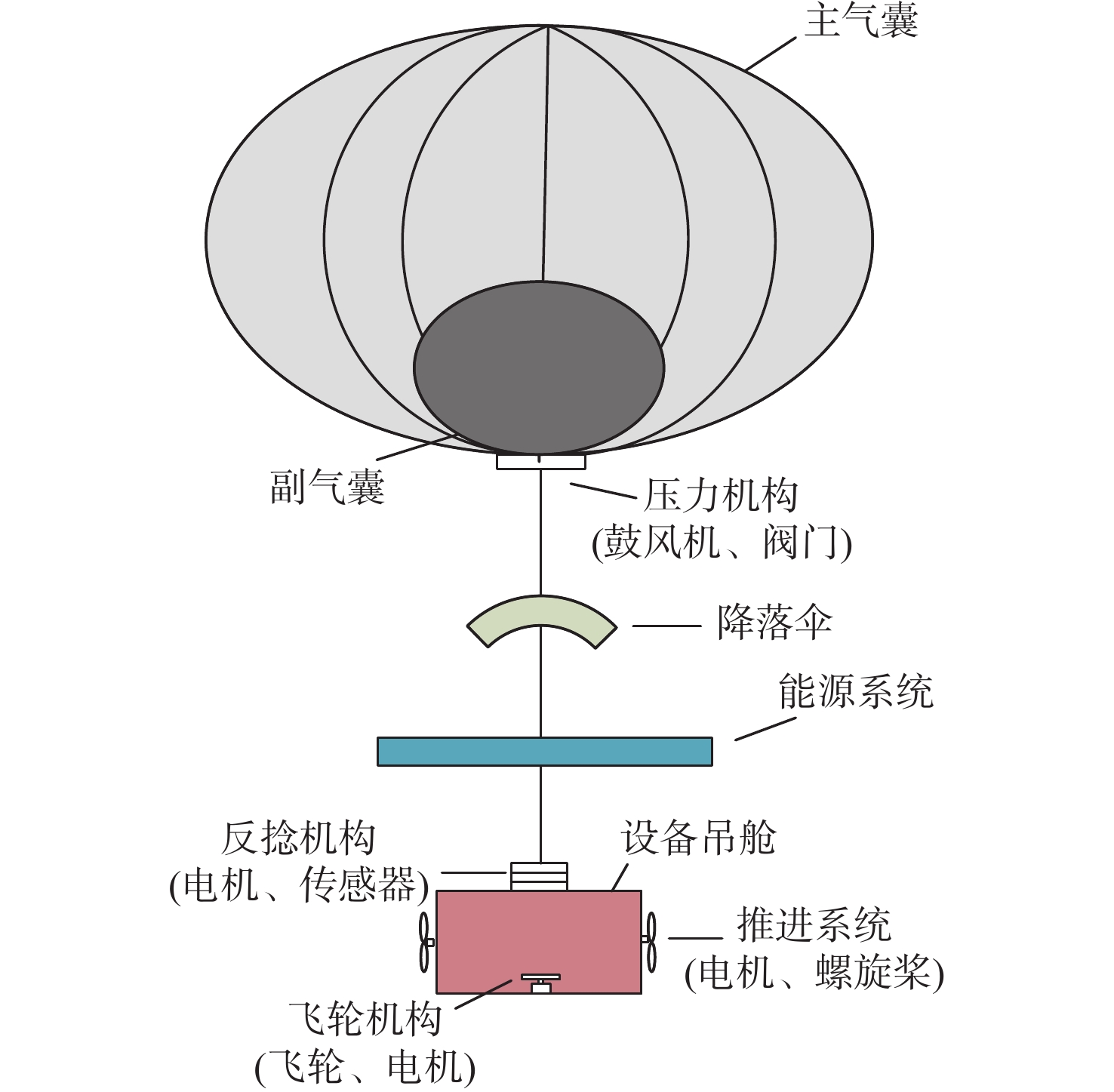
-
摘要:
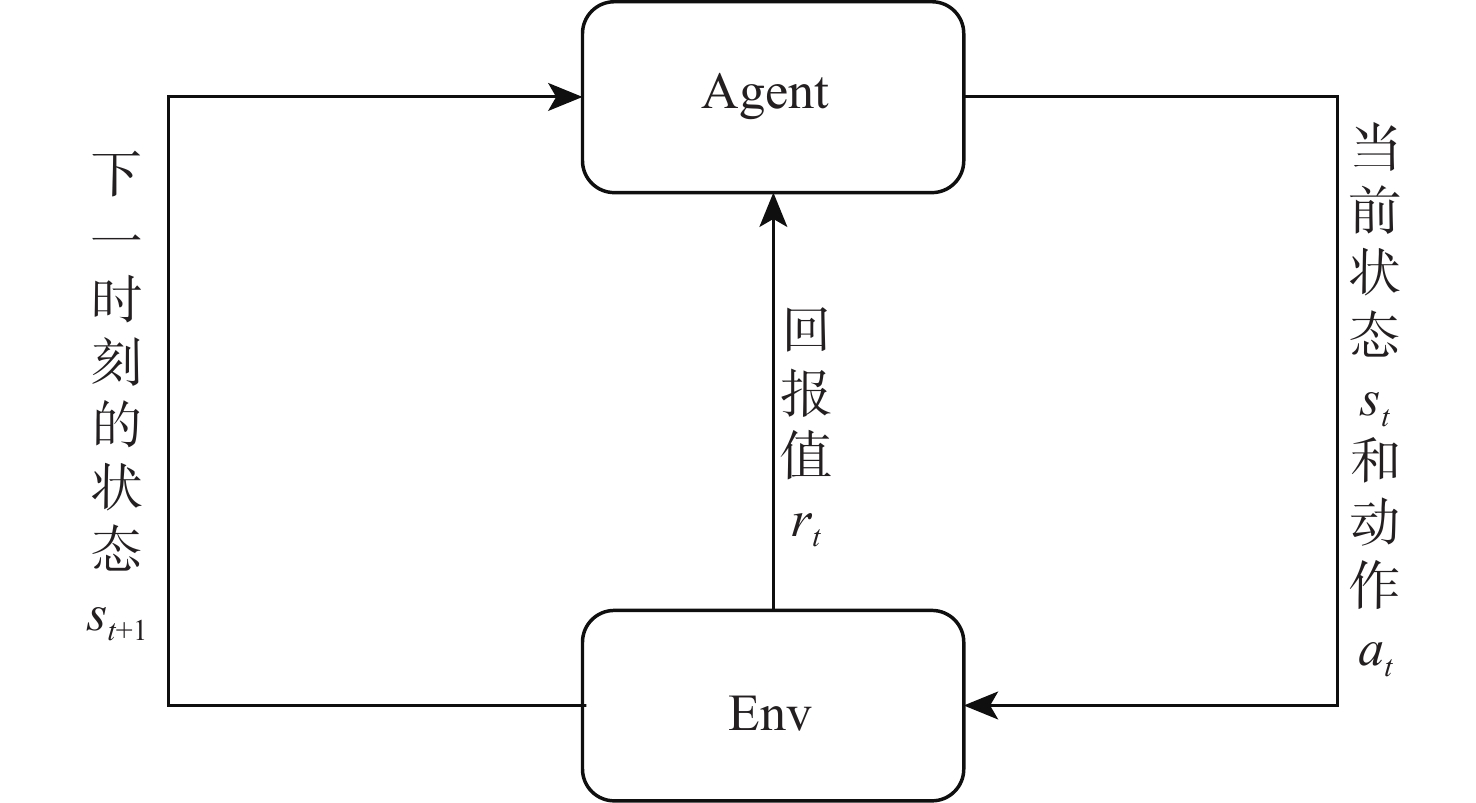
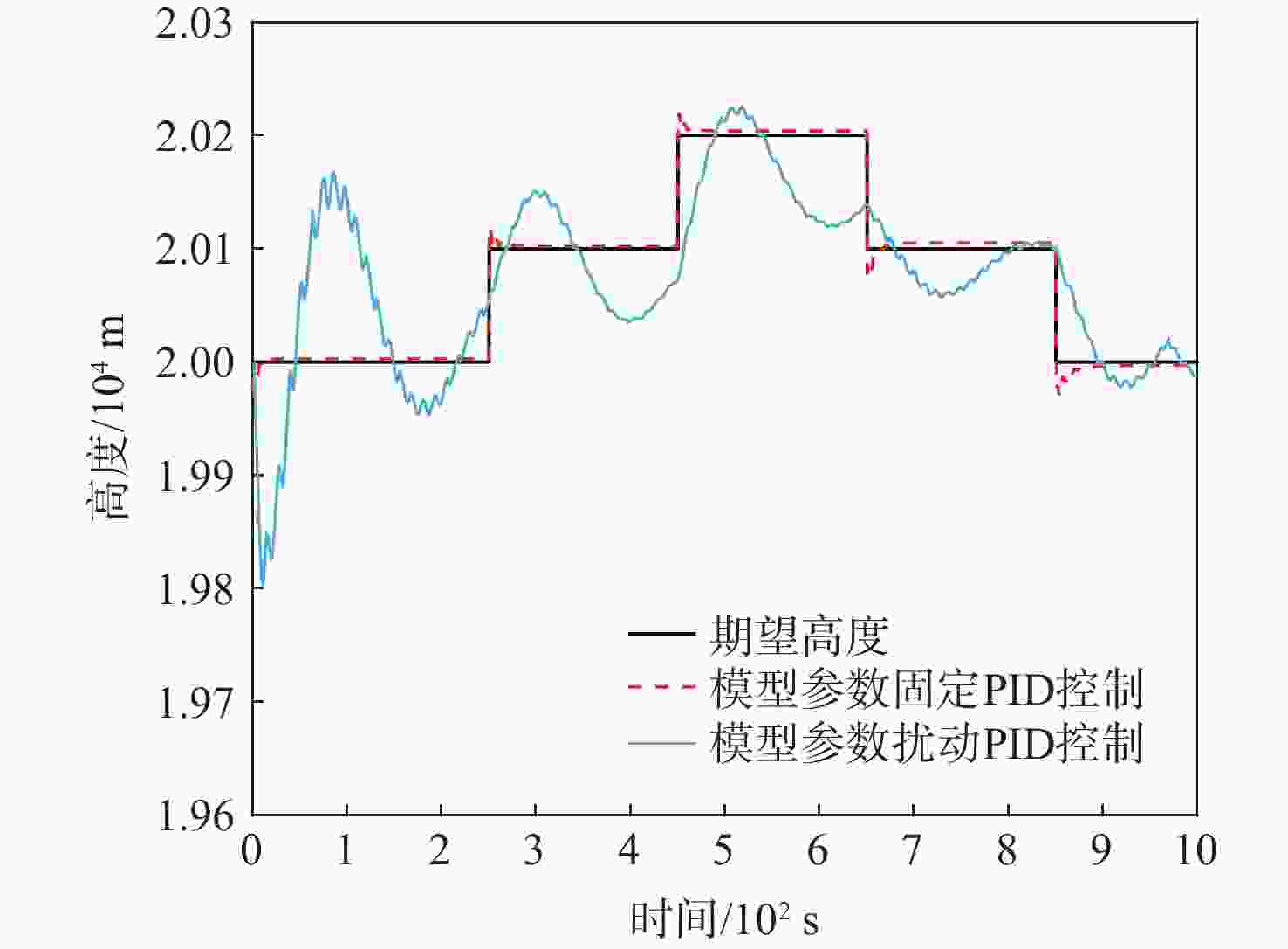
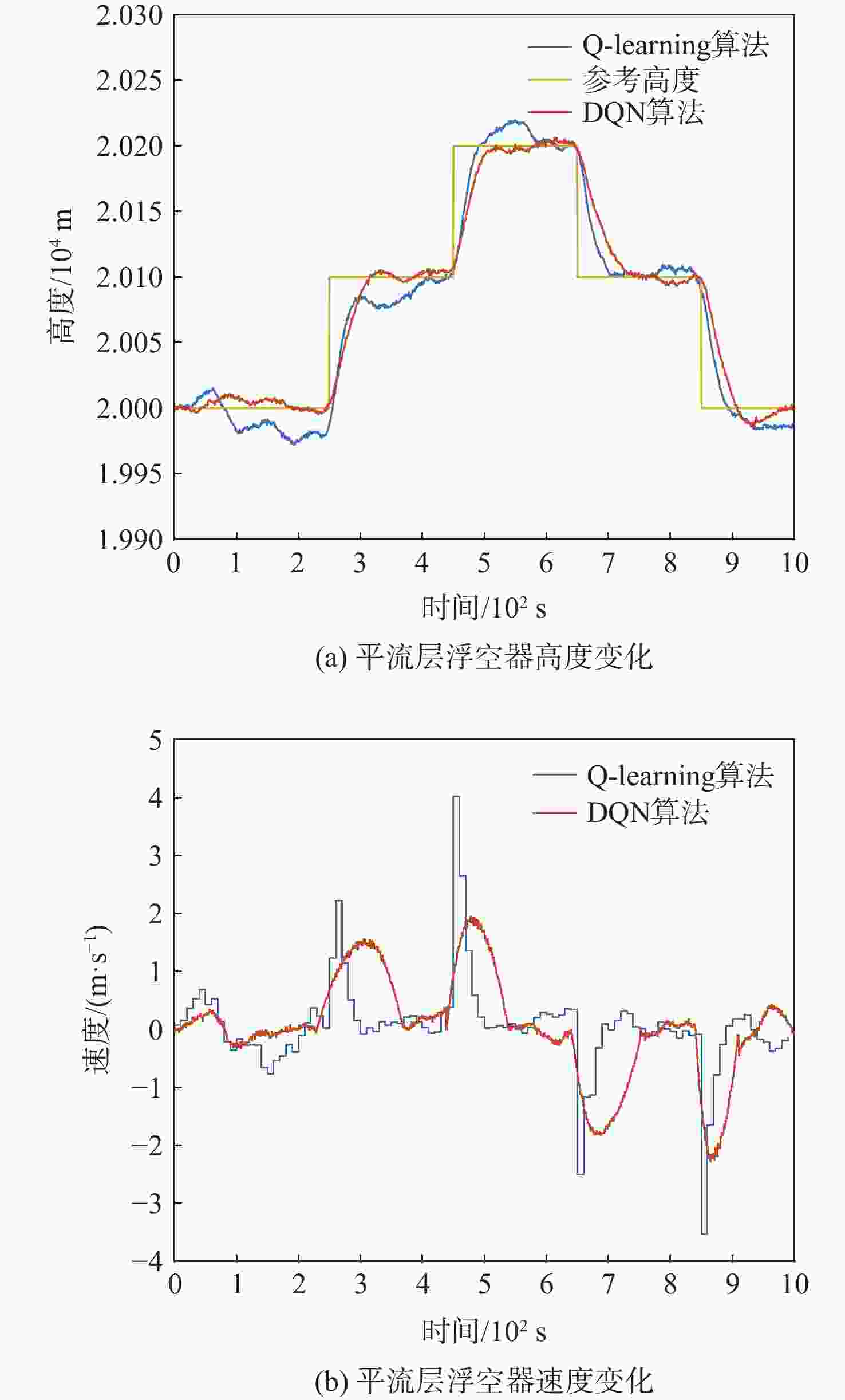
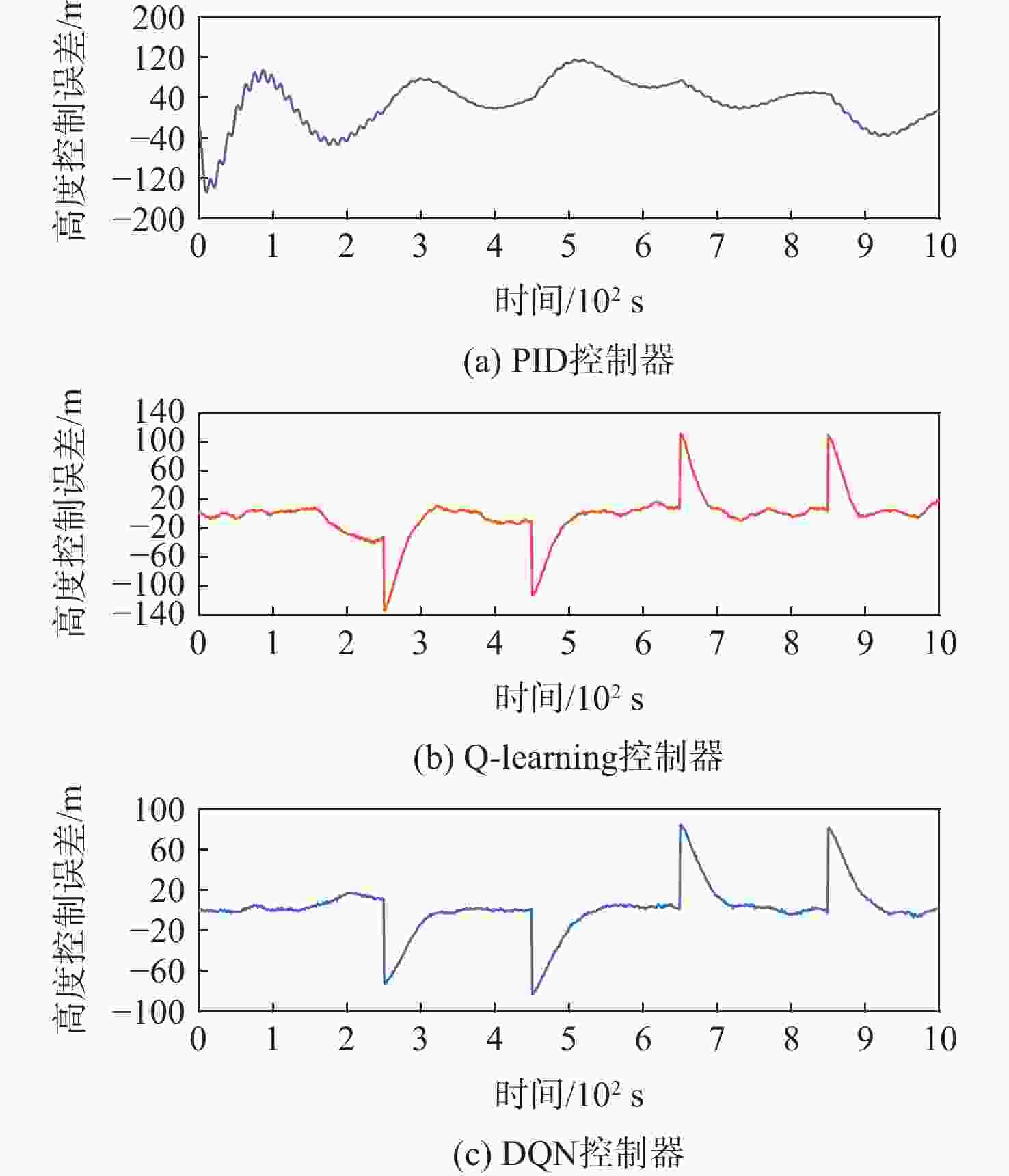
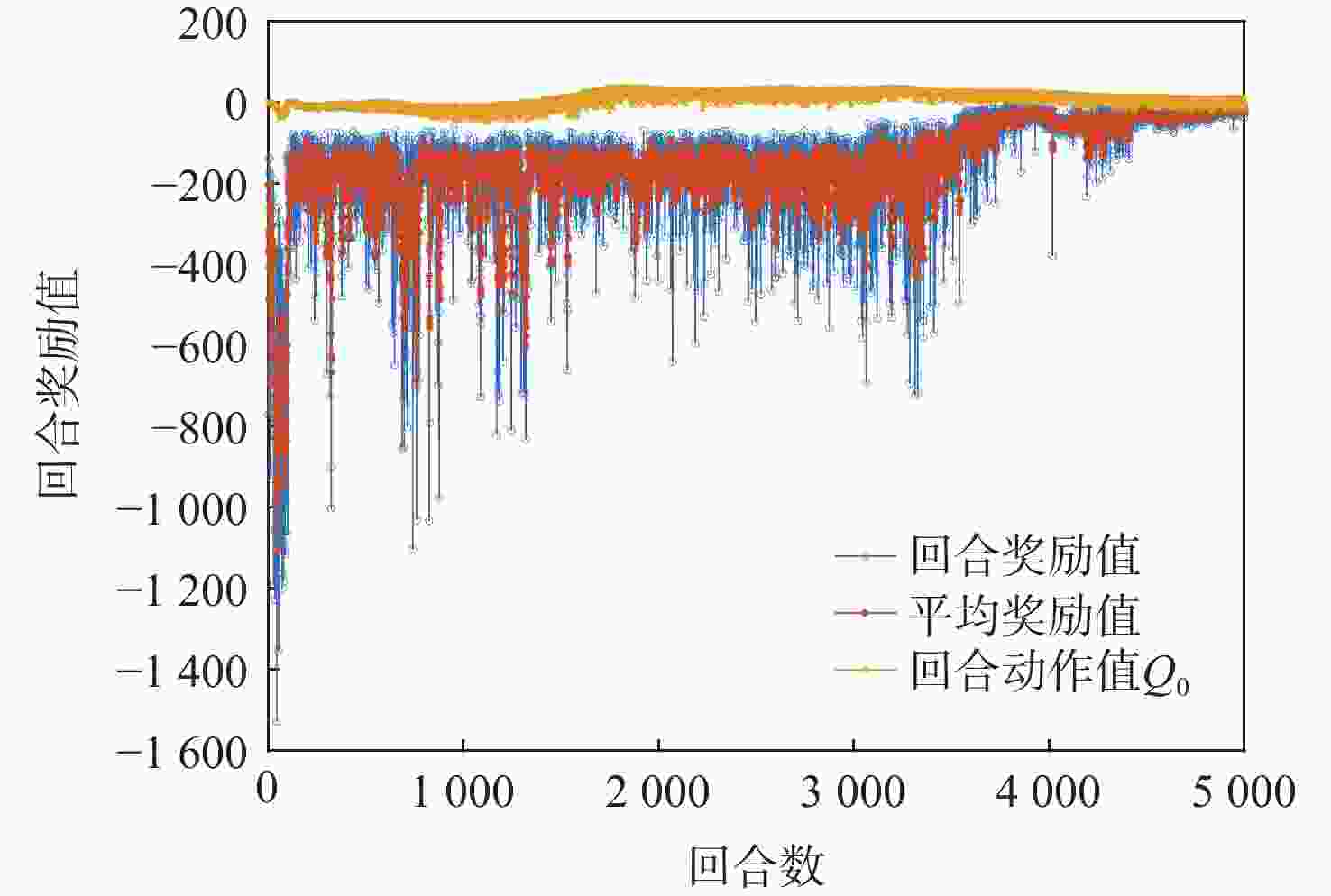
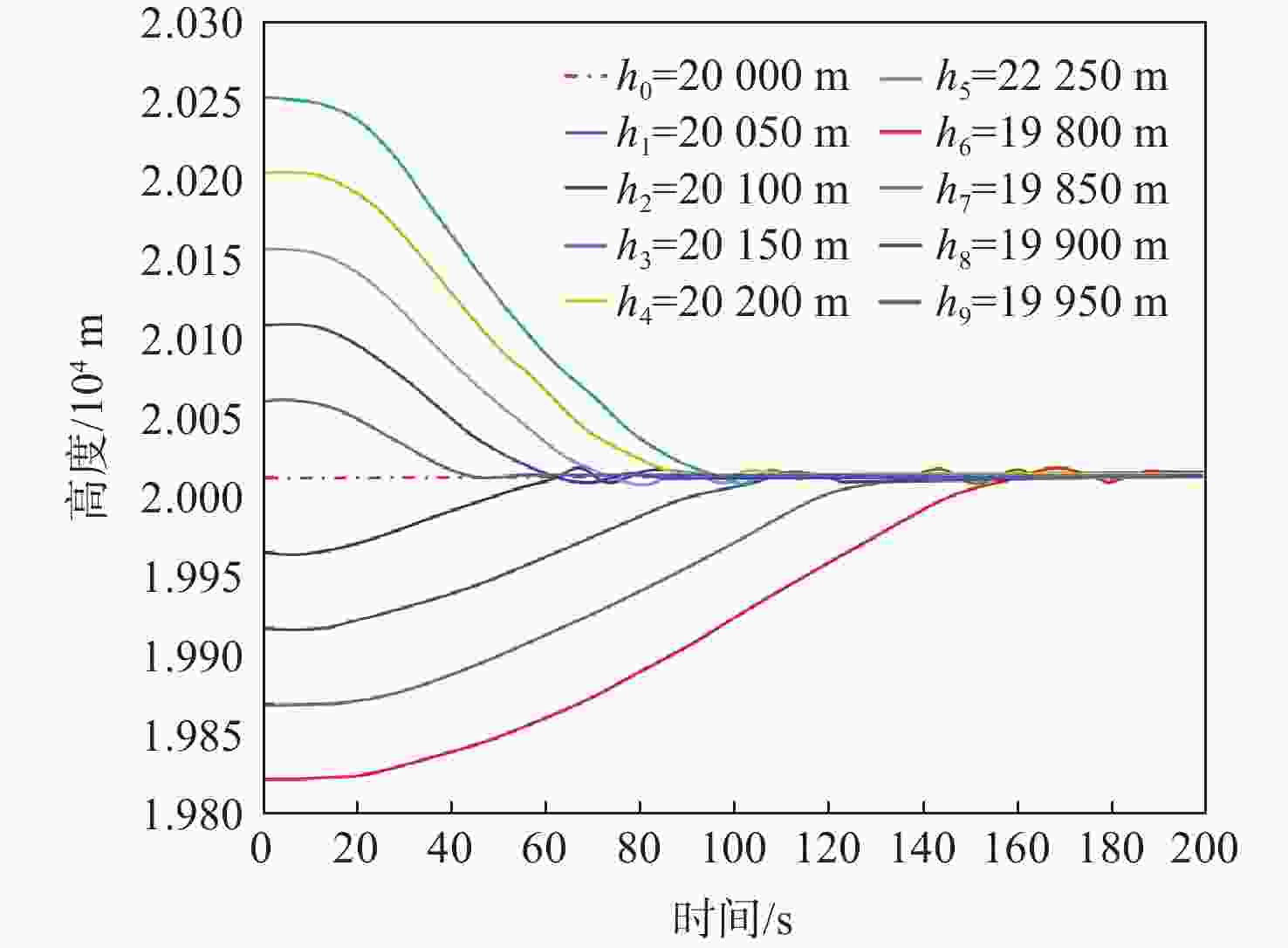
为研究基于深度强化学习的平流层浮空器高度控制问题。建立平流层浮空器动力学模型,提出一种基于深度 Q 网络(DQN)算法的平流层浮空器高度控制方法,以平流层浮空器当前速度、位置、高度差作为智能体的观察状态,副气囊鼓风机开合时间作为智能体的输出动作,平流层浮空器非线性动力学模型与扰动风场作为智能体的学习环境。所提方法将平流层浮空器的高度控制问题转换为未知转移概率下连续状态、连续动作的强化学习过程,兼顾随机风场扰动与速度变化约束,实现稳定的变高度控制。仿真结果表明:考虑风场环境对浮空器影响下,DQN算法控制器可以很好的实现变高度的跟踪控制,最大稳态误差约为10 m,与传统比例积分微分(PID)控制器对比,其控制效果和鲁棒性更优。
Abstract:A dynamic model of the stratospheric aerostat was built with the goal of controlling the aerostat's altitude while taking air temperature into consideration, and a method based on the deep Q-network (DQN) algorithm was developed. Due to the difficulty in predicting the stratospheric wind field and the physical model of the aerostat itself being unknown, most model-based control methods cannot solve the problem of long-term altitude control of the stratospheric aerostat. For this reason, the altitude control problem of the stratospheric aerostat is transformed into a continuous state and continuous action reinforcement learning process with unknown transition probability. The DQN algorithm combined with reinforcement learning and neural network can solve such problems well. The simulation results show that considering the influence of the wind field environment on the aerostat, the DQN algorithm controller can well realize the tracking control of variable altitude, and the maximum error is about 10 m. Compared with the traditional proportional inteyral derivative (PID) controller, the deep reinforcement learning algorithm proposed in this paper has a better control effect and robustness.
-
Key words:
- near space /
- stratospheric aerostat /
- altitude control /
- deep reinforcement learning /
- PID controller
-
表 1 智能体DQN算法控制结果
Table 1. Control results of agent DQN algorithm
飞行段/s 调节时间/s 超调量/m 稳态误差/m 0~250 10 9.6 250~450 100 11.2 450~650 68 4.5 650~850 76 6 850~1 000 61 10.5 表 2 智能体Q-learning算法控制结果
Table 2. Control results of agent Q-learning algorithm
飞行段/s 调节时间/s 超调量/m 稳态误差/m 0~250 49 250~450 450~65 153 650~850 53 13 10.8 850~1 000 97 14.3 -
[1] 洪延姬, 金星, 李小将. 临近空间飞行器技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2012: 20-34.HONG Y J, JIN X, LI X J. Near space vehicle technology[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2012: 20-34 (in Chinese). [2] LI J, LIAO J, LIAO Y X, et al. An approach for estimating perpetual endurance of the stratospheric solar-powered platform[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2018, 79: 118-130. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2018.05.035 [3] 邓小龙, 杨希祥, 麻震宇, 等. 基于风场环境利用的平流层浮空器区域驻留关键问题研究进展[J]. 航空学报, 2019, 40(8): 022941.DENG X L, YANG X X, MA Z Y, et al. Review of key technologies for station-keeping of stratospheric aerostats based on wind field utilization[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2019, 40(8): 022941(in Chinese). [4] LU L L, SONG H W, WANG Y W, et al. Deformation behavior of non-rigid airships in wind tunnel tests[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2019, 32(3): 611-618. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2018.12.016 [5] 张永栋, 翟嘉琪, 孟小君, 等. 基于行为逻辑的平流层飞艇试验自动测试方法[J]. 航空学报, 2018, 39(9): 322191.ZHANG Y D, ZHAI J Q, MENG X J, et al. Approach for automatic testing of stratospheric airship test based on behavior logic[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2018, 39(9): 322191(in Chinese). [6] 赵达, 刘东旭, 孙康文, 等. 平流层飞艇研制现状、技术难点及发展趋势[J]. 航空学报, 2016, 37(1): 45-56.ZHAO D, LIU D X, SUN K W, et al. Research status, technical difficulties and development trend of stratospheric airship[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2016, 37(1): 45-56(in Chinese). [7] 肖存英, 胡雄, 龚建村, 等. 中国上空平流层准零风层的特征分析[J]. 空间科学学报, 2008, 28(3): 230-235. doi: 10.11728/cjss2008.03.230XIAO C Y, HU X, GONG J C, et al. Analysis of the characteristics of the stratospheric quasi-zero wind layer over China[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2008, 28(3): 230-235(in Chinese). doi: 10.11728/cjss2008.03.230 [8] JIANG Y, LV M Y, QU Z P, et al. Performance evaluation for scientific balloon station-keeping strategies considering energy management strategy[J]. Renewable Energy, 2020, 156: 290-302. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2020.04.011 [9] 王益平, 周飞, 徐明. 临近空间浮空器区域驻留控制策略研究[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2018, 38(1): 63-69.WANG Y P, ZHOU F, XU M. Research on control strategy of territory-hovering aerostat in near space[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2018, 38(1): 63-69(in Chinese). [10] DU H F, LV M Y, ZHANG L C, et al. Energy management strategy design and station-keeping strategy optimization for high altitude balloon with altitude control system[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2019, 93: 105342. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2019.105342 [11] WAGHELA R, YODER C D, GOPALARATHNAM A, et al. Aerodynamic sails for passive guidance of high-altitude balloons: Static-stability and equilibrium performance[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2019, 56(5): 1849-1857. doi: 10.2514/1.C035353 [12] KAYHAN Ö, YÜCEL Ö, HASTAOĞLU M A. Simulation and control of serviceable stratospheric balloons traversing a region via transport phenomena and PID[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2016, 53: 232-240. [13] ZHENG Z W, CHEN T, XU M, et al. Modeling and path-following control of a vector-driven stratospheric satellite[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2016, 57(9): 1901-1913. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2016.02.004 [14] YANG X W, YANG X X, DENG X L. Horizontal trajectory control of stratospheric airships in wind field using Q-learning algorithm[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2020, 106: 106100. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2020.106100 [15] SÓBESTER A, CZERSKI H, ZAPPONI N, et al. High-altitude gas balloon trajectory prediction: A MonteCarlo model[J]. AIAA Journal, 2014, 52(4): 832-842. doi: 10.2514/1.J052900 [16] 李春霖, 罗蓉媛, 陈彤曦. 平流层通信新思路—谷歌气球计划[J]. 通信技术, 2015, 48(2): 125-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0802.2015.02.002LI C L, LUO R Y, CHEN T X. New idea for stratospheric comm-unications—Google Loon[J]. Communications Technology, 2015, 48(2): 125-129(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0802.2015.02.002 [17] BELLEMARE M G, CANDIDO S, CASTRO P S, et al. Autonomous navigation of stratospheric balloons using reinforcement learning[J]. Nature, 2020, 588(7836): 77-82. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2939-8 [18] YANG X X, ZHANG W H, HOU Z X. Improved thermal and vertical trajectory model for performance prediction of stratospheric balloons[J]. Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2015, 28(3): 04014075. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)AS.1943-5525.0000404 [19] WATKINS C J C H, DAYAN P. Q-learning[J]. Machine Learning, 1992, 8(3): 279-292. [20] MNIH V, KAVUKCUOGLU K, SILVER D, et al. Playing atari with deep reinforcement learning[J]. Computer Science, 2013, 1312: 5602. -






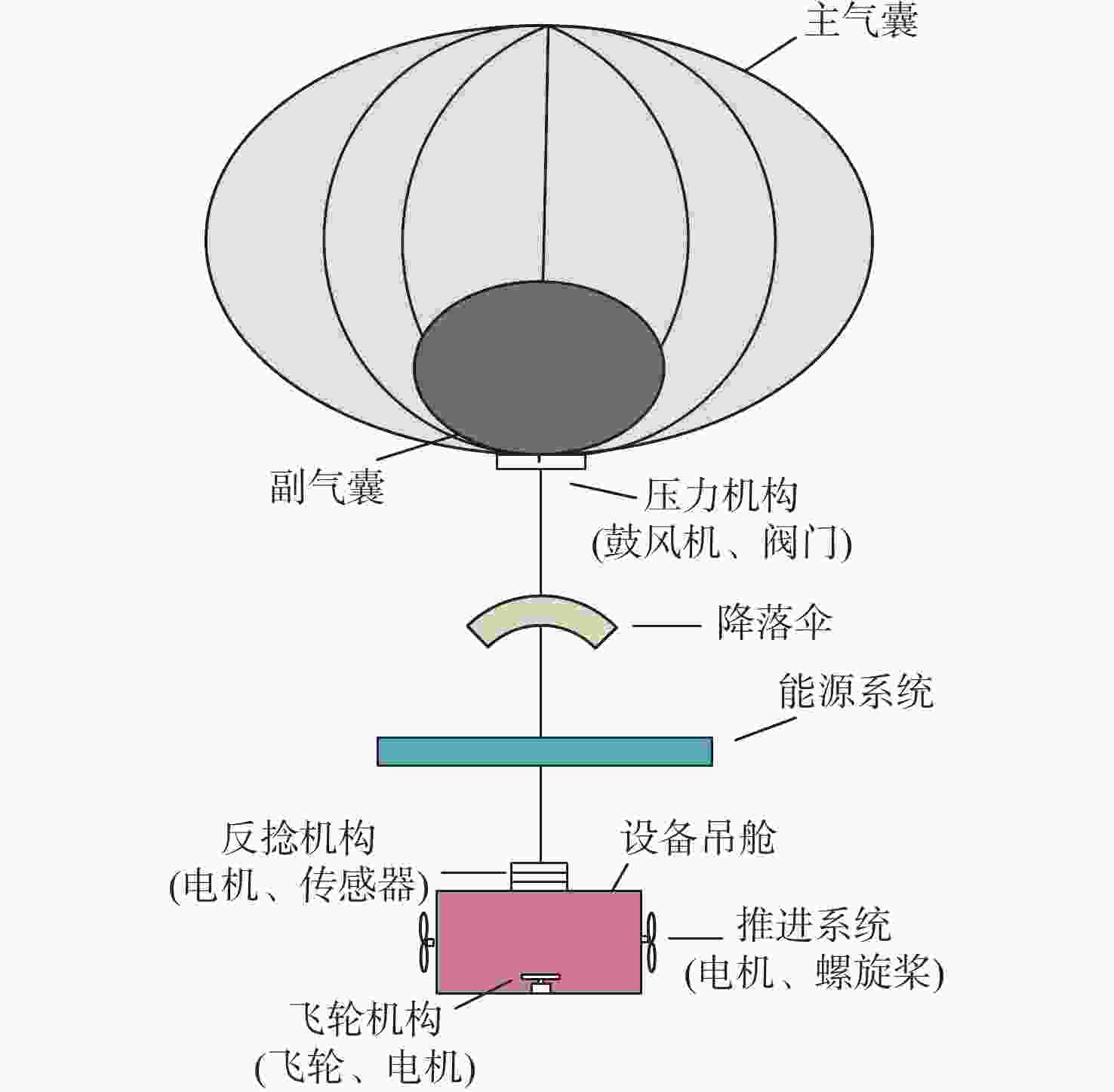
 下载:
下载: