Process control net modelling and analyzing for satellite test and evaluation in launch site
-
摘要:
发射场卫星试验鉴定流程控制联合考虑试验鉴定过程模型和试验科目,实现对试验鉴定的流程控制。目前发射场卫星技术流程以文字和图片描述,在节点状态和约束迁移方面存在量化问题,无法构建形式化模型以嵌入自动化试验鉴定评估系统。以网模型为基础,构造发射场卫星试验鉴定流程控制网模型,并提出配套结构分析和性能分析方法,实现量化的可达性、作业不确定性和资源竞争性等分析内容,支持并行多星多任务的评估分析,从而支撑发射场卫星试验鉴定流程管理中试验鉴定方案设计及卫星流程模型优化设计等工作。
Abstract:During the prelaunch phase, the process control combines test models with subjects to enable the design and modification of satellite test and evaluation procedures. Since non-structural words and images are mostly used to describe and build the technical process of the satellite at the launch site, it is difficult to quantify state transportation and constraint issues and prohibits formalization in the automation mission system. This paper proposes the process control net model and the related analysis method for satellite test and evaluation at the launch site. The provided model and methodology enable accessibility, work uncertainty, and resource competition quantitative scheduling analysis for satellites' many and parallel jobs. These quantification abilities are helpful to support the scheme design and process optimization of satellite tests and evaluations.
-
Key words:
- launch site /
- satellite /
- test evaluation /
- Petri net /
- process control net
-
表 1 发射场卫星流程控制模型状态示例
Table 1. States example of satellite process control net model in launch site
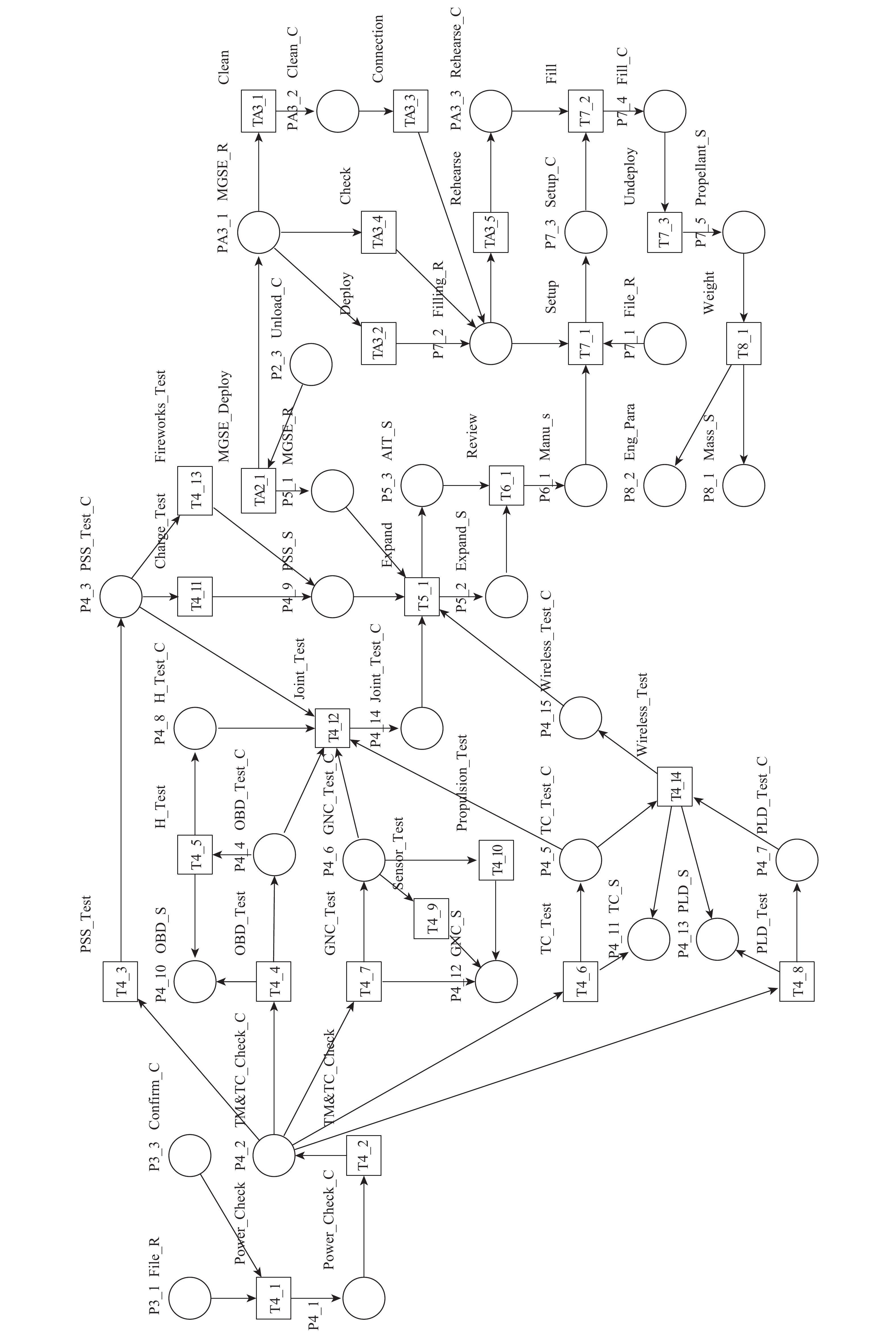
过程 业务内容 状态 发射场技术区测试 卫星加电正常 P4_1 卫星遥测遥控正常 P4_2 供配电分系统试验完成 P4_3 数管分系统试验完成 P4_4 ⋮ ⋮ 发射场太阳翼/天线
安装及展开试验太阳翼/天线等
展开架工装到位P5_1 ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ 表 2 发射场卫星流程控制模型变迁示例
Table 2. Transition example of satellite process control net model in launch site
过程 业务内容 变迁 平均作业时间/d 发射场技术区测试 供电检查 T4_1 0.1 遥测遥控检查 T4_2 0.1 供配电分系统试验 T4_3 4 数管分系统试验 T4_4 4 ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ 表 3 结构分析初始状态
Table 3. Initial values for structure analysis
序号 变量 1 Δt=[0.2,0.2,2,3,1,2,2,4,1,0.5,1,1,0.5,2] 2 M(1)S,I=[1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0] 3 M(1)S,O=[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0] 4 M(1)T,I=[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0] 5 M(1)T,O=[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0] 表 4 变迁和状态激活记录
Table 4. Transition and state activation records
迭代次数 激活时间/d MT,O变迁激活 MS,I状态激活 1 0 T4_1 P3_1 2 0.2 T4_2 P4_1 3 0.4 T4_3,T4_6,T4_7 P4_2 4 2.4 T4_10 P4_3,P4_5,P4_6 5 2.9 T4_4,T4_9,T4_11,T4_13 6 3.4 T4_5,T4_8 P4_4,P4_9,P4_12 7 4.4 T4_12 P4_7,P4_8 8 5.4 T4_14 P4_14 9 6.4 P4_11,P4_15 表 5 性能分析初始状态
Table 5. Initial values for performance analysis
序号 变量 1 ΔtE=[0.5,1,1,0.5,1,1,0.5,1,1,0.5,1,1]T 2 ΔtS=[0.3,0.8,0.8,0.3,0.8,0.8,0.3,0.8,0.8,0.3,0.8,0.8]T 3 ΔtL=[0.7,1.2,1.2,0.7,1.2,1.2,0.7,1.2,1.2,0.7,1.2,1.2]T 4 Δs=[3,4]T 5 r=[1,2,2,1,2,2,1,2,2,1,2,21,2,1,1,2,1,1,2,1,1,2,1] 6 M(1)S,I=[1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0]T 7 M(1)S,O=[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]T 8 M(1)T,I=[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]T 9 M(1)T,O=[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]T 表 6 变迁激活记录
Table 6. Transition activation records
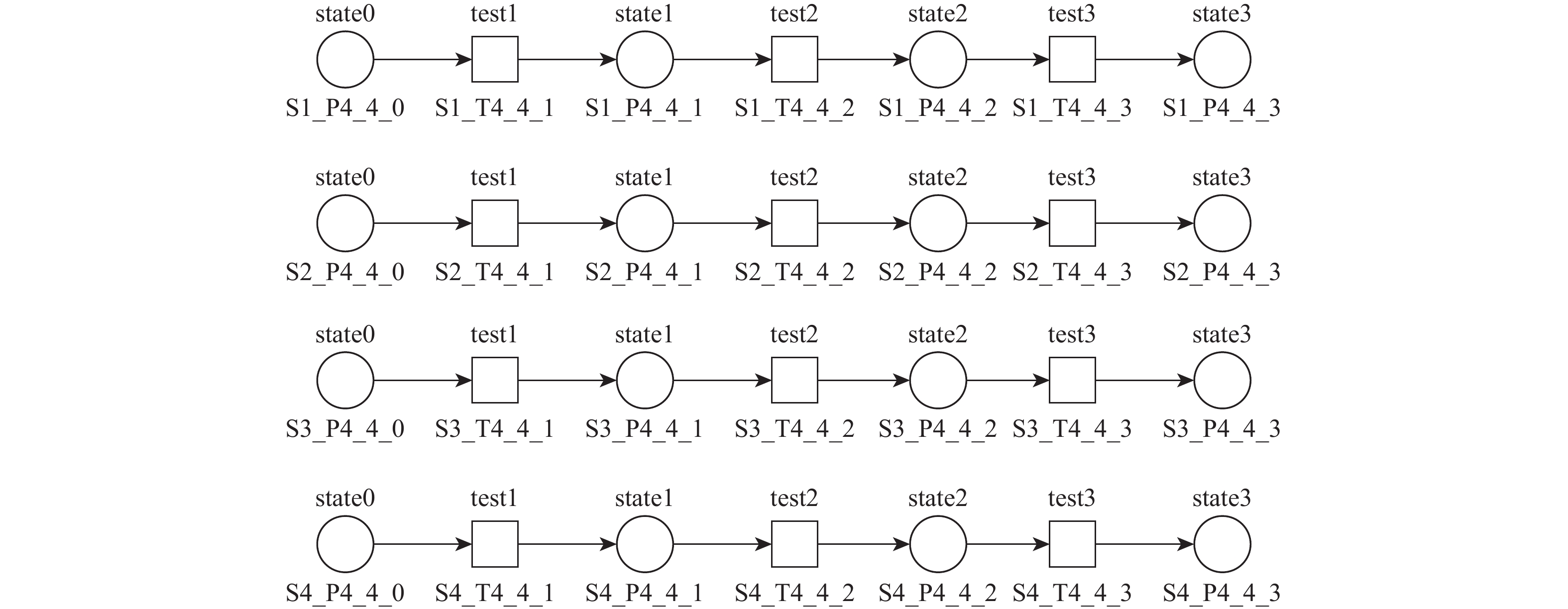
迭代次数 激活时间/天 变迁激活 MT,I MT,I_X MT,O 1 0 S1_T4_4_1
S2_T4_4_1
S3_T4_4_1
S4_T4_4_1S1_T4_4_1
S2_T4_4_1
S3_T4_4_1S1_T4_4_1
S2_T4_4_1
S3_T4_4_12 0.5 S1_T4_4_2
S2_T4_4_2
S3_T4_4_2S4_T4_4_1
S1_T4_4_2S4_T4_4_1 3 1 S4_T4_4_2 S1_T4_4_2 4 1.5 S1_T4_4_3 S1_T4_4_3 S1_T4_4_3 5 2.5 S2_T4_4_2 S2_T4_4_2 6 3.5 S2_T4_4_3 S2_T4_4_3 S2_T4_4_3 7 4.5 S3_T4_4_2 S3_T4_4_2 8 5.5 S3_T4_4_3 S3_T4_4_3 S3_T4_4_3 9 6.5 S4_T4_4_2 S4_T4_4_2 10 7.5 S4_T4_4_3 S4_T4_4_3 S4_T4_4_3 表 7 作业时间
Table 7. Work time
d 平均激活
时间最早开始
时间最晚开始
时间冗余激活
时间0 0 0 0 0.5 0.3 0.7 0.566 7 1 0.6 1.4 1.133 3 1.5 1.1 1.9 1.633 3 2.5 1.9 3.1 2.7 3.5 2.7 4.3 3.766 7 4.5 3.5 5.5 4.833 3 5.5 4.3 6.7 5.9 6.5 5.1 7.9 6.966 7 7.5 5.9 9.1 8.033 3 8.5 6.7 10.3 9.1 -
[1] 郭凯, 胡旖旎. 航天装备试验鉴定案例分析: 天基红外系统[J]. 航天返回与遥感, 2021, 42(2): 79-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2021.02.009GUO K, HU Y N. Case analysis of space equipment test and evaluation—a space-based infrared system[J]. Spacecraft Recovery & Remote Sensing, 2021, 42(2): 79-84(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2021.02.009 [2] 周思卓, 刘宝平, 彭洪江, 等. 美军航天装备试验鉴定体系发展现状研究[J]. 装备学院学报, 2016, 27(6): 65-68.ZHOU S Z, LIU B P, PENG H J, et al. Research on development of U.S. army space system test and evaluation[J]. Journal of Equipment Academy, 2016, 27(6): 65-68(in Chinese). [3] 姜盛鑫, 韩天龙, 陆宏伟. 美军航天装备 COTS 试验鉴定工作透视及思考[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2021, 38(5): 599-603.JIANG S X, HAN T L, LU H W. Critical analysis of test and evaluation for COTS products used as USSF space equipment[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2021, 38(5): 599-603(in Chinese). [4] 杨俊岭, 曹金霞, 梁晋平, 等. 美军空间系统在轨试验问题综合研究[J]. 飞行器测控学报, 2011, 30(4): 1-5.YANG J L, CAO J X, LIANG J P, et al. An investigation into in-orbit test of US military space systems[J]. Journal of Spacecraft TT&C Technology, 2011, 30(4): 1-5(in Chinese). [5] 吴凌九, 胡亚军, 陈谨飞, 等. 卫星平台试验鉴定实践现状与思考[J]. 国防科技, 2022, 43(1): 32-37.WU L J, HU Y J, CHEN J F, et al. Current situation of the implementation of satellite platform test and evaluation[J]. National Defense Technology, 2022, 43(1): 32-37(in Chinese). [6] 何洋, 林屹立, 周思卓. 美军航天装备作战试验鉴定策略研究及案例分析[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2020, 37(4): 408-413. doi: 10.12126/see.2020.04.015HE Y, LIN Y L, ZHOU S Z. Analysis of operational test and case evaluation of USAF space equipment[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2020, 37(4): 408-413(in Chinese). doi: 10.12126/see.2020.04.015 [7] KLEPPER J, KNAPKE R, SIRBAUGH J, et al. Computational modeling and simulation applications to support integrated test and evaluation (IT&E) at AEDC[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 Aerodynamic Measurement Technology and Ground Testing Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2018. [8] PARKINSON D, VANLERBERGHE W M, RAHMAN S A. JANNAF test and evaluation guideline for liquid rocket engines: Status and application[C]//Proceedings of the 53rd AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2017. [9] NOMAGUCHI Y, SAITO M, FUJITA K. Multi-domain DSM method for design process management of complex system[J]. Journal of Industrial and Production Engineering, 2015, 32(7): 465-472. doi: 10.1080/21681015.2015.1083487 [10] SON M J, KIM T W. Implementation of an executable business process management model for the ship hull production design process[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Technology, 2014, 19(2): 170-184. doi: 10.1007/s00773-013-0238-x [11] 熊志勇, 刘梦玉, 庞婉婷. 基于Petri网的工业设计过程管理工作流建模研究[J]. 图学学报, 2018, 39(4): 611-615.XIONG Z Y, LIU M Y, PANG W T. Workflow modeling of industrial design process management based on petri net[J]. Journal of Graphics, 2018, 39(4): 611-615(in Chinese). [12] 梅磊, 刘鸿飞, 董文通. 基于测试过程管理的航天软件质量评价[J]. 西华大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 38(6): 67-72.MEI L, LIU H F, DONG W T. Aerospace software quality evaluation based on test process management[J]. Journal of Xihua University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 38(6): 67-72(in Chinese). [13] 袁崇义. Petri网原理与应用[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005: 58-62.YUAN C Y. Principle and application of Petri net[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2005: 58-62 (in Chinese). [14] YU W Y, JIA M H, LIU C, et al. Task preemption based on petri nets[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 11512-11519. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2964382 [15] IDEL M Y, NAIT-SIDI-MOH A, CHAKIR EL A E, et al. Petri nets conflicts resolution for performance evaluation and control of urban bus networks: A (max, +)-based approach[J]. Transportmetrica A:Transport Science, 2020, 16(2): 164-193. doi: 10.1080/23249935.2018.1527864 -







 下载:
下载: