-
摘要:
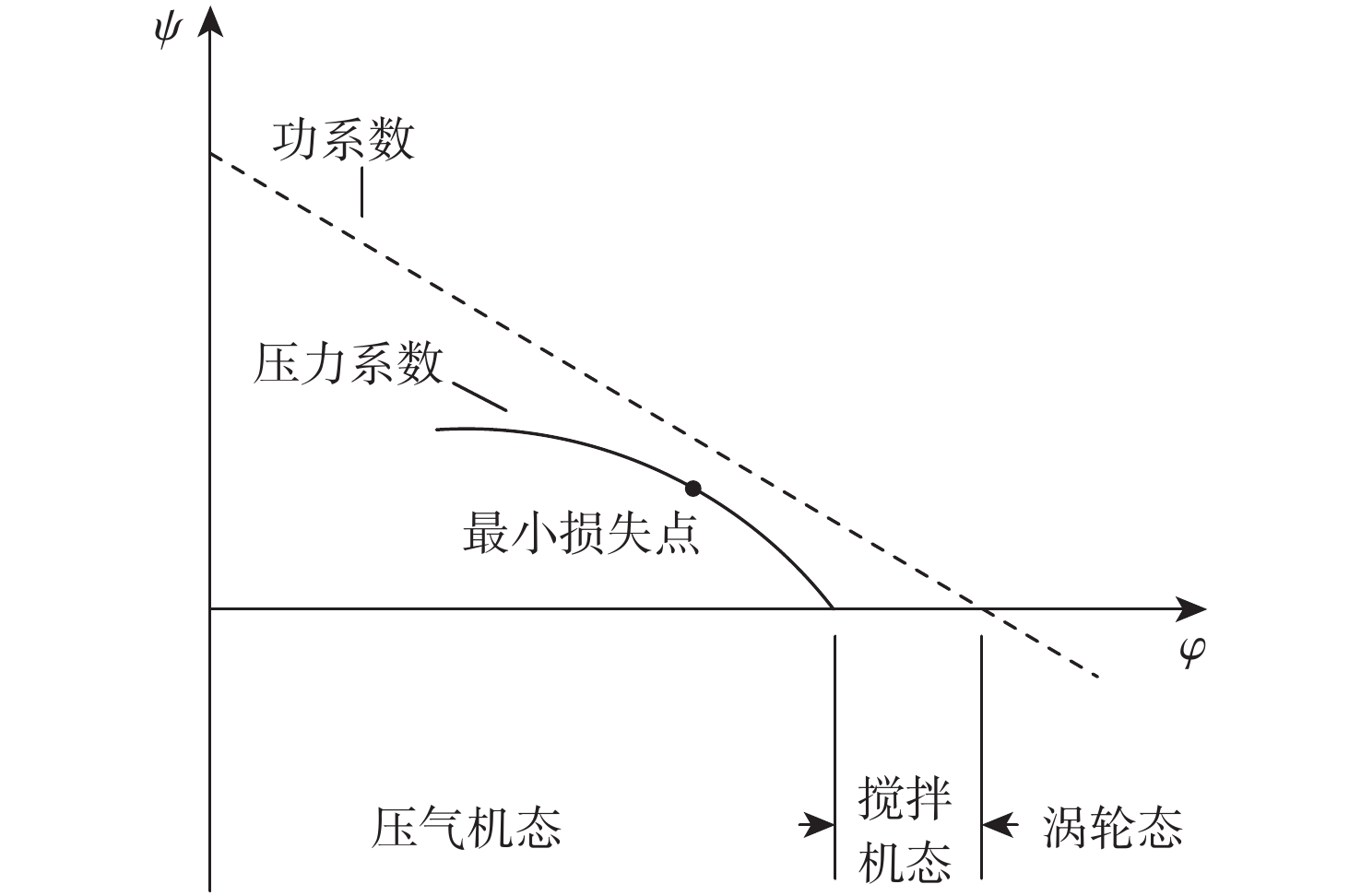
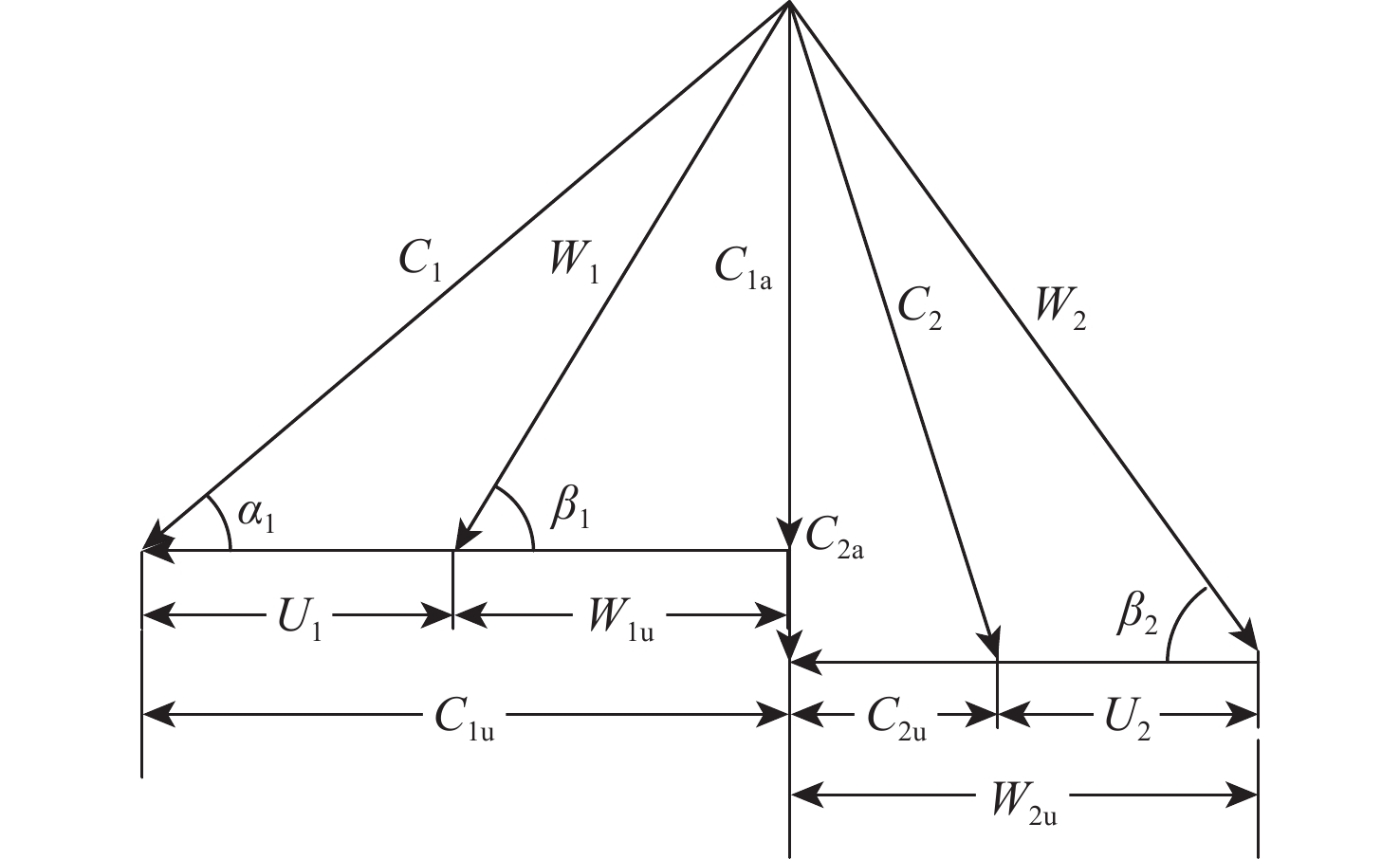
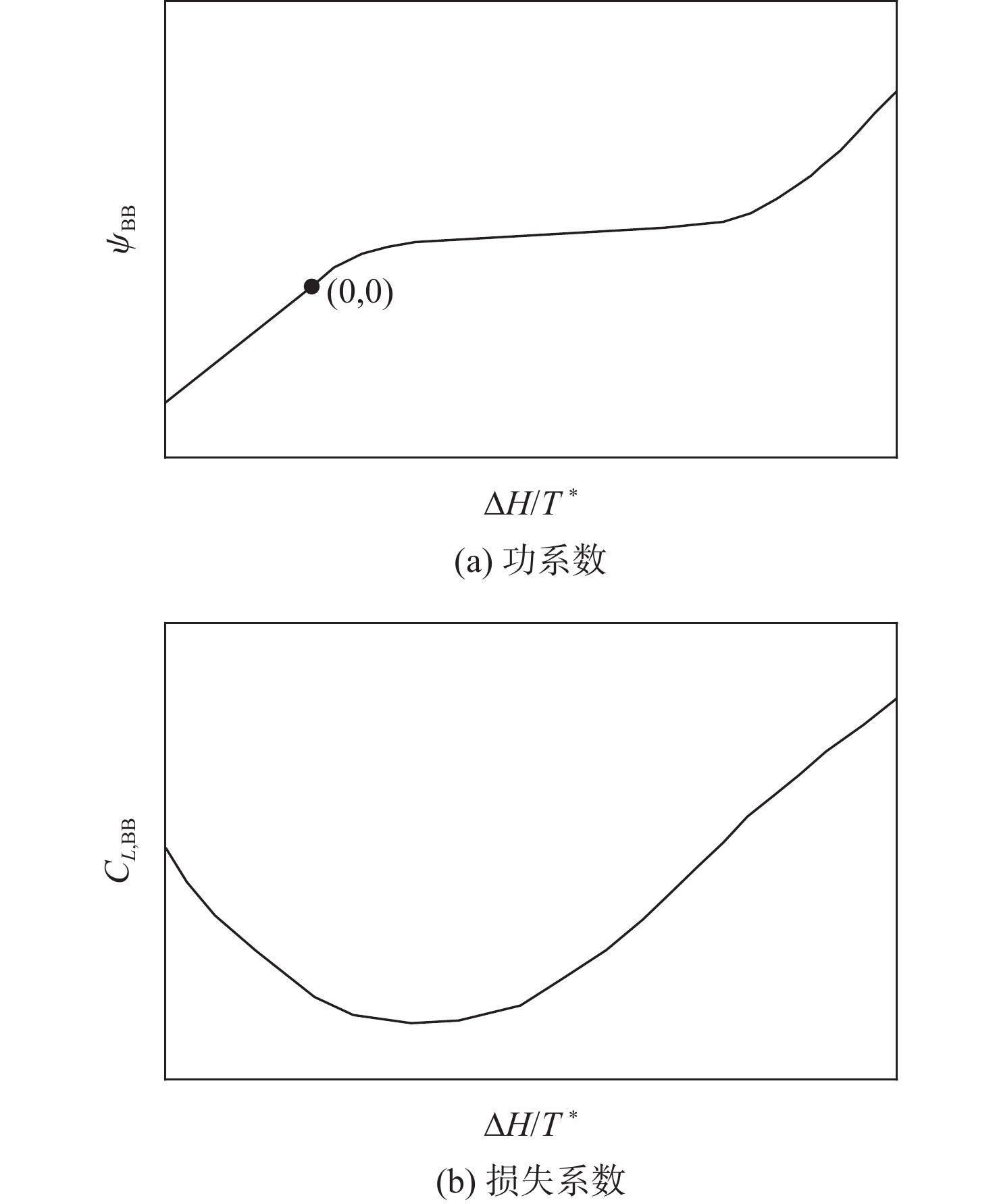
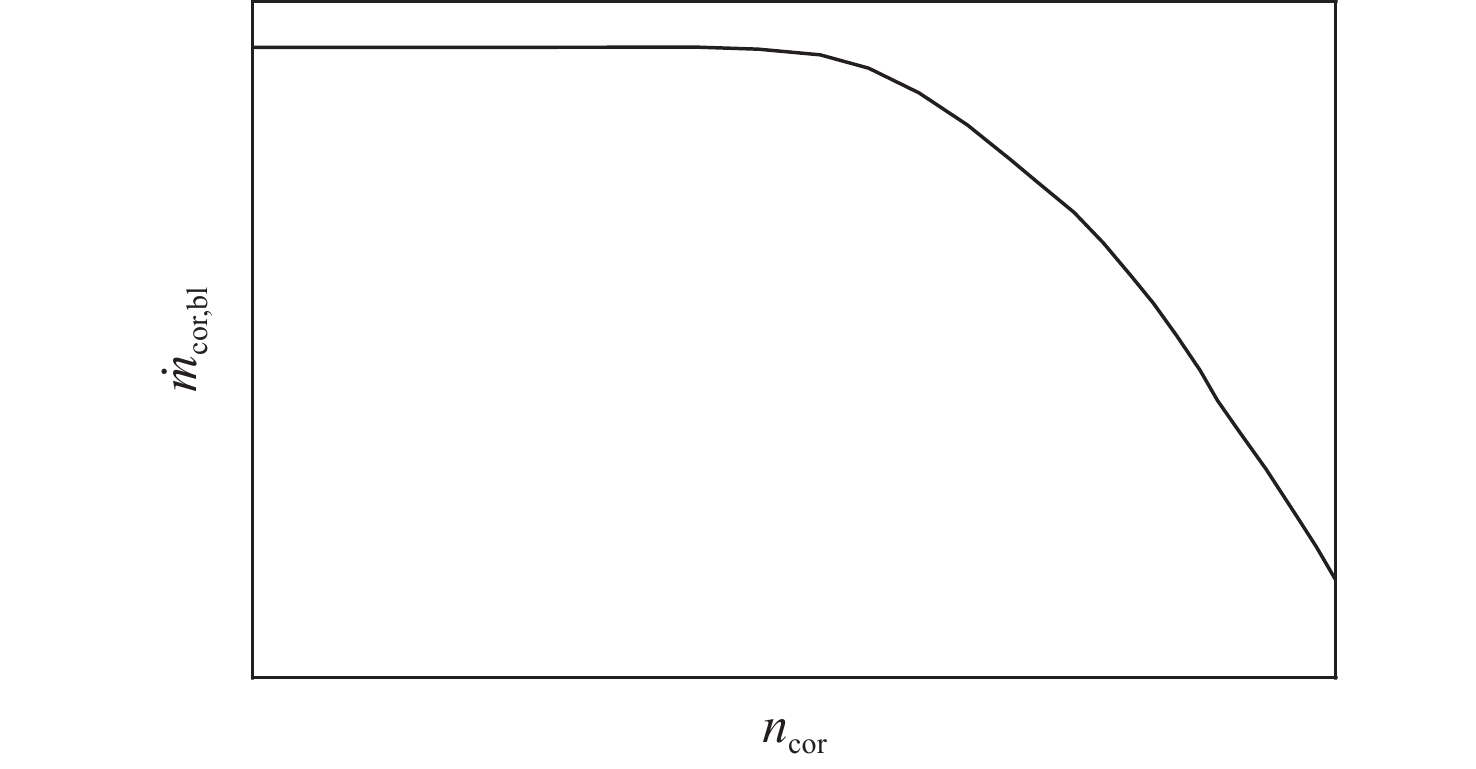
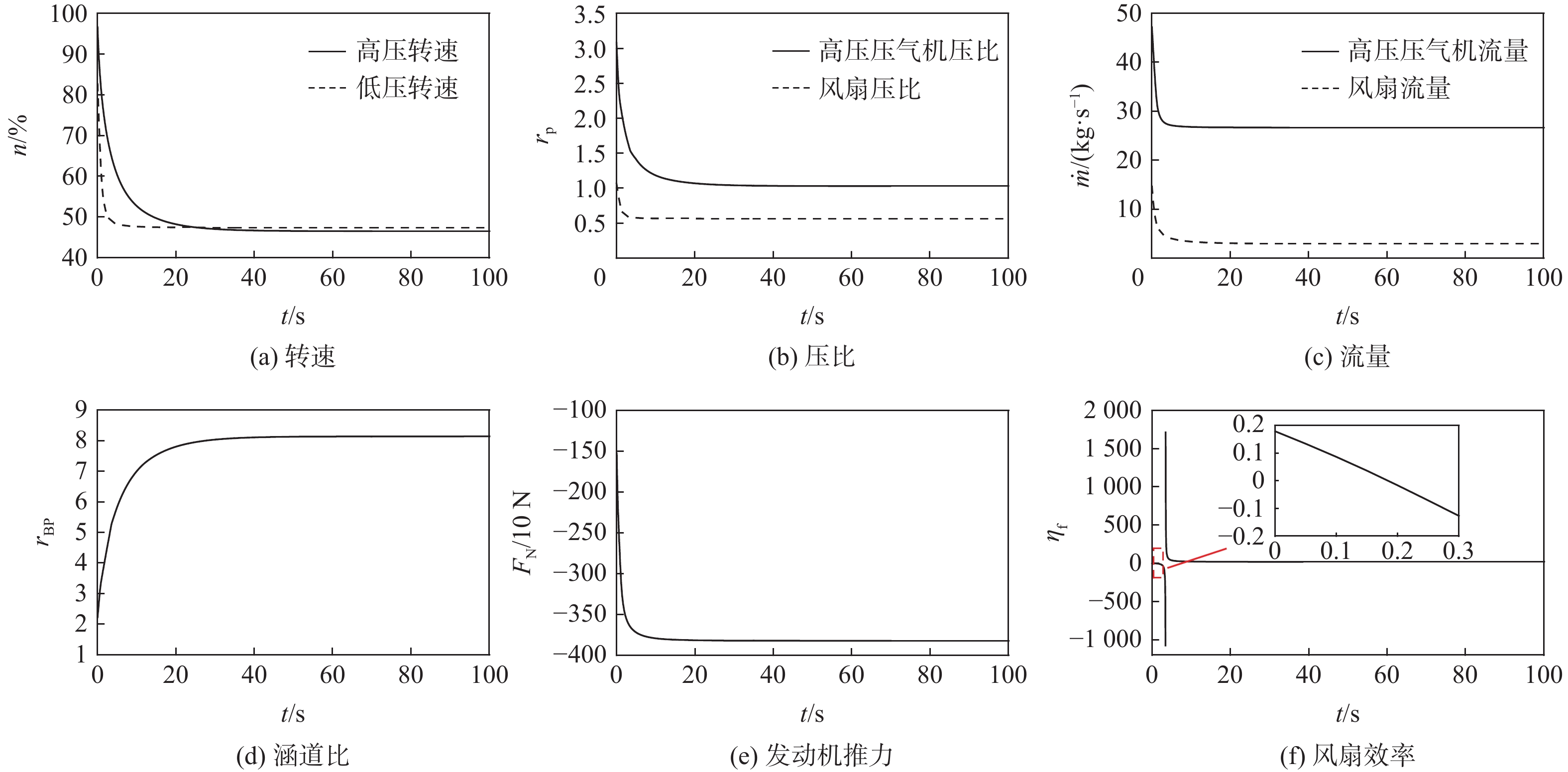
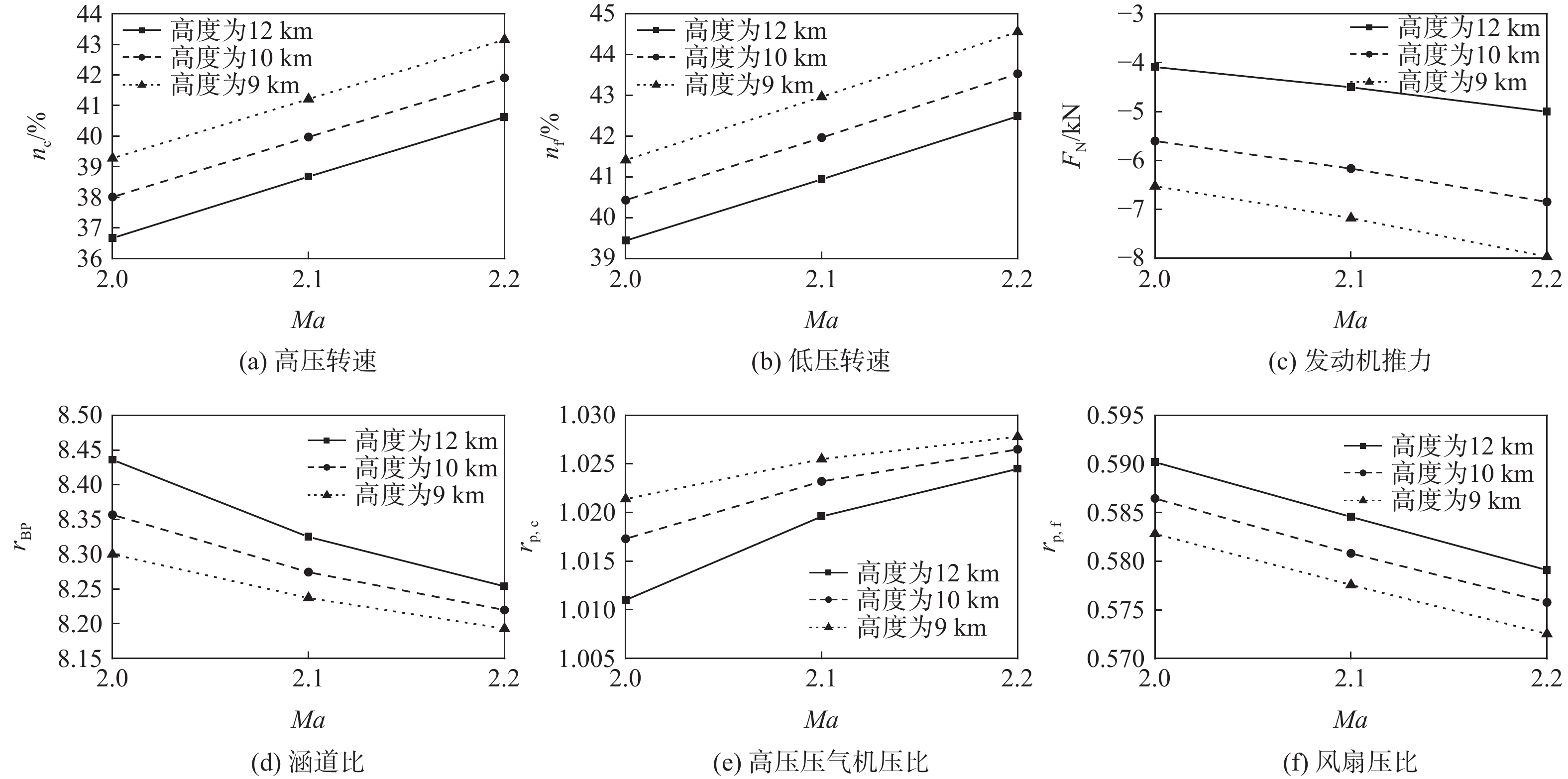
旋转部件在高空低转速时,其工作状态受来流的吹动作用可能会发生变化,此时压气机处在特殊的“搅拌机”或“涡轮”工作状态,使得发动机的动态计算中效率插值出现不连续的问题。为解决此问题,采用美国国家航空航天局(NASA)和通用电气公司(GE)联合开发的针对旋转部件特性转化的脊背特征方法,通过分析低转速下旋转部件脊背特征及非脊背特征的变化趋势,提出基于脊背特征的旋转部件低转速范围特性的扩展方法,并有效规避了效率特性在低转速下插值的失效。以某型军用涡扇发动机为例,计算其处于不同飞行条件下的发动机风车工作状况,结果表明:所提方法能够反映出低转速下压气机压比小于1的特殊工作状态,且不同飞行条件下的风车特性计算合理。
Abstract:The blowing action of the incoming flow may cause the functioning state of the rotating components to alter when they operate at high altitudes but low speeds. The compressor is in a special “mixer” or “turbine” working state at such a condition, which makes a discontinuous change of efficiency during the dynamic operation of the engine. In order to solve this problem, the method based on the backbone features developed by National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and General Electric Company (GE) was used to transform the characteristics of rotating parts. It is possible to expand the low-speed range characteristics of rotating parts and successfully prevent the invalidation of the interpolation of efficiency characteristics at low speeds by studying the changing trends of the backbone and off-backbone features at low speeds. Taking a military turbofan engine as an example, the windmilling characteristics under different flight conditions are calculated. The results show that this method can reflect the special working conditions of the compressor with a pressure ratio of less than 1 at low speeds, and the calculation of windmilling characteristics under different flight conditions is reasonable.
-
Key words:
- low speeds /
- efficiency /
- discontinuity /
- backbone /
- off-backbone /
- windmilling
-
-
[1] BRAIG W, SCHULTE H, RIEGLER C. Comparative analysis of the windmilling performance of turbojet and tbrbofan engines[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 1999, 15(2): 326-333. doi: 10.2514/2.5430 [2] WALKER C L, FENN D B. Investigation of power extraction characteristics and braking requirements of a windmilling turbojet engine[J]. Australian Veterinary Journal, 1952, 48(5): 258-62. [3] BINDER N, COURTY-AUDREN S K, DUPLAA S, et al. Theoretical analysis of the aerodynamics of low-speed fans in free and load-controlled windmilling operation[J]. Journal of Turbomachinery, 2015, 137(10): 101001. doi: 10.1115/1.4030308 [4] KURZKE J. How to get component maps for aircraft gas turbine performance calculations[C]//ASME 1996 International Gas Turbine and Aeroengine Congress and Exhibition. Birmingham: American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 1996. [5] XU S Y, ZHU Z L, LIU Z D, et al. Research on the starting characteristics and control law of two spool turbofan engine[J]. Energy Procedia, 2019, 158: 1765-1771. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2019.01.418 [6] 王松岭, 张学镭, 陈海平, 等. 基于相似定律外推压气机通用特性曲线的方法[J]. 动力工程, 2007, 27(2): 169-173.WANG S L, ZHANG X L, CHEN H P, et al. Method based on similarity laws for extrapolating generalized performance curves of compressors[J]. Journal of Power Engineering, 2007, 27(2): 169-173(in Chinese). [7] GAUDET S R, DONALD GAUTHIER J E. A simple sub-idle component map extrapolation method[C]//Proceedings of ASME Turbo Expo 2007: Power for Land, Sea, and Air. Montreal: ASME, 2009: 29-37. [8] JONES G, CURNOCK B. Compressor characteristics in gas turbine performance modelling: 2001-GT-0384 [R]. New Orleans : ASME , 2001. [9] 王占学, 王永杰, 乔渭阳, 等. 涡扇发动机低转速部件特性扩展和风车状态性能模拟[J]. 推进技术, 2006, 27(2): 146-149. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4055.2006.02.012WANG Z X, WANG Y J, QIAO W Y, et al. Extrapolating component maps into the low speed and simulation of windmilling performance of turbofan engine[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2006, 27(2): 146-149(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4055.2006.02.012 [10] HOWARD J. Sub-idle modelling of gas turbines: Altitude relight and windmilling[D]. Cranfield : Cranfield University, 2007. [11] ZACHOS P K, ASLANIDOU I, PACHIDIS V, et al. A sub-idle compressor characteristic generation method with enhanced physical background[J]. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 2011, 133(8): 1. [12] GOTO T, KATO D, OHTA Y, et al. Unsteady flow structure in an axial compressor at windmill condition[C]//Proceedings of ASME Turbo Expo 2014. Düsseldorf: ASME, 2014. [13] ZACHOS P K, PENGUE F, PACHIDIS V, et al. Flowfield investigation of a compressor cascade at high incidence—part 2: Numerical analysis[C]//Proceedings of ASME Turbo Expo 2009: Power for Land, Sea, and Air. Orlando : ASME, 2010: 355-362. [14] 饶高, 苏三买, 翟向博. 指数外推法和支持向量机相结合的压气机特性扩展方法[J]. 航空动力学报, 2017, 32(3): 749-755. doi: 10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.2017.03.029RAO G, SU S M, ZHAI X B. Method of compressor characteristic extension combining exponent extrapolation method with support vector machine[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2017, 32(3): 749-755(in Chinese). doi: 10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.2017.03.029 [15] CONVERSE G L, GIFFIN R. Extended parametric representation of compressor fans and turbines. Volume 1: CMGEN user’s manual: NASA-CR-174645 [R]. Washington D. C. : NASA, 1984. [16] RIEGLER C, BAUER M, KURZKE J. Some aspects of modelling compressor behavior in gas turbine performance calculations[C]// ASME Turbo Expo 2000: Power for Land, Sea, and Air. Munich: ASME, 2000. [17] 马文通, 苏明, 余南华. 变几何多级轴流式压气机特性估算[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2008, 28(11): 72-76. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2008.11.013MA W T, SU M, YU N H. Characteristic estimation method of variable geometry multistage axial-flow compressors[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2008, 28(11): 72-76(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2008.11.013 [18] SETHI V, DOULGERIS G, PILIDIS P, et al. The map fitting tool methodology: Gas turbine compressor off-design performance modeling[J]. Journal of Turbomachinery, 2013, 135(6): 061010. doi: 10.1115/1.4023903 [19] DIXON S L, HALL C A . Fluid mechanics and thermodynamics of turbomachinery[M]. Oxford : Pergamon Press, 1998. [20] FLAGG E E. Analytical procedure and computer program for determining the off-design performance of axial flow turbines: NASA-CR-710 [R]. Washington D. C. : NASA, 1967. [21] CONVERSE G L. Extended parametric representation of compressor fans and turbines volume Ⅱ- PART user’s manual: NASA-CR-174646 [R]. Washington D. C. : NASA, 1984. [22] 施洋. 民用大涵道比涡扇发动机全状态性能模型研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2017.SHI Y. A research on full states performance model for civil high bypass turbofan engine[D]. Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2017 (in Chinese). [23] 高扬, 田晓平, 李秋锋. 基于换算扭矩特性的混排涡扇发动机风车状态性能模拟[J]. 现代机械, 2017(6): 10-13. doi: 10.13667/j.cnki.52-1046/th.2017.06.003GAO Y, TIAN X P, LI Q F. Simulation of windmilling performance for mixed flow turbofan engine based on converted torque characteristics[J]. Modern Machinery, 2017(6): 10-13(in Chinese). doi: 10.13667/j.cnki.52-1046/th.2017.06.003 [24] PRASAD D, LORD W K. Internal losses and flow behavior of a turbofan stage at windmill[J]. Journal of Turbomachinery, 2010, 132(3): 1. -







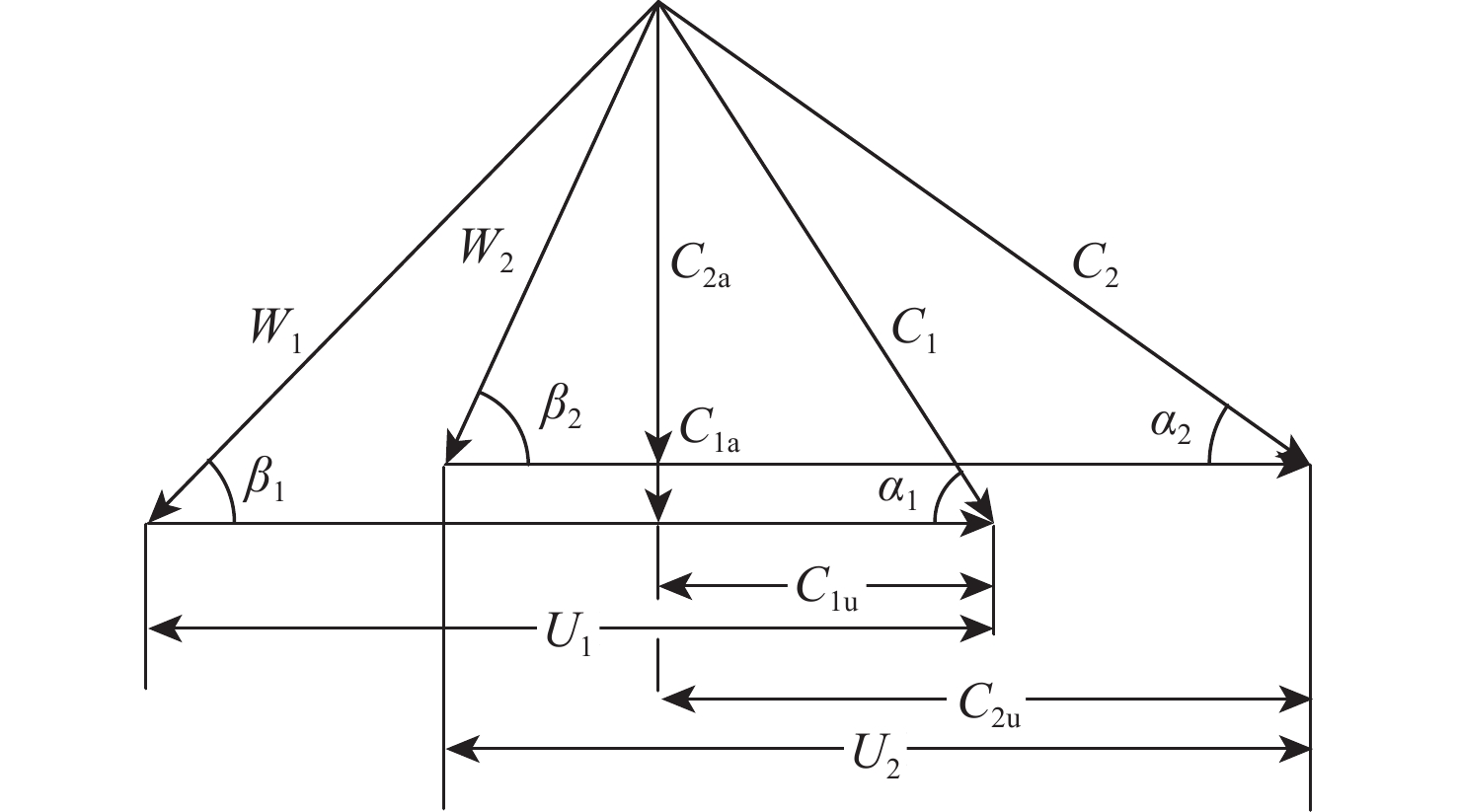
 下载:
下载: