-
摘要:
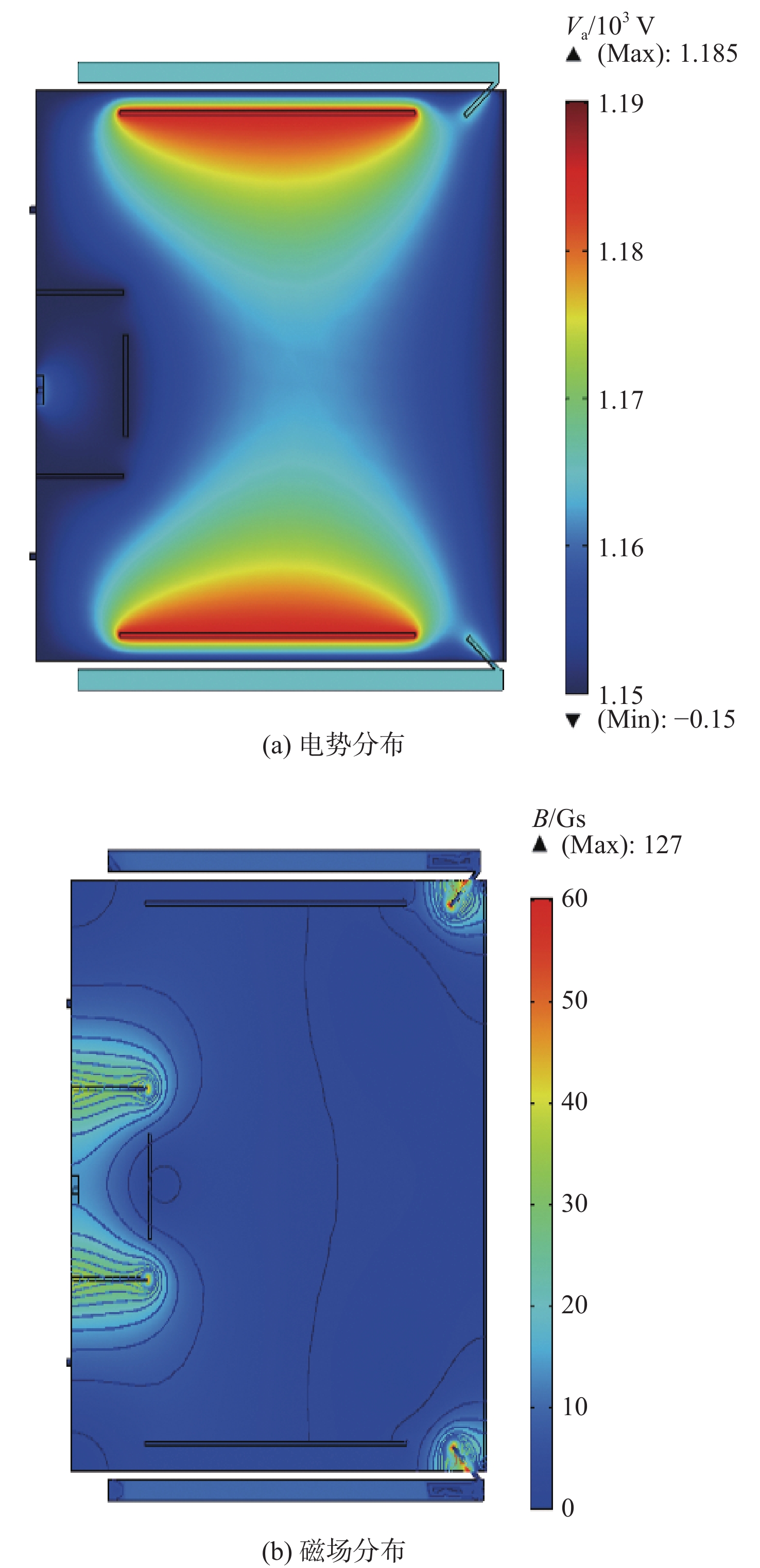
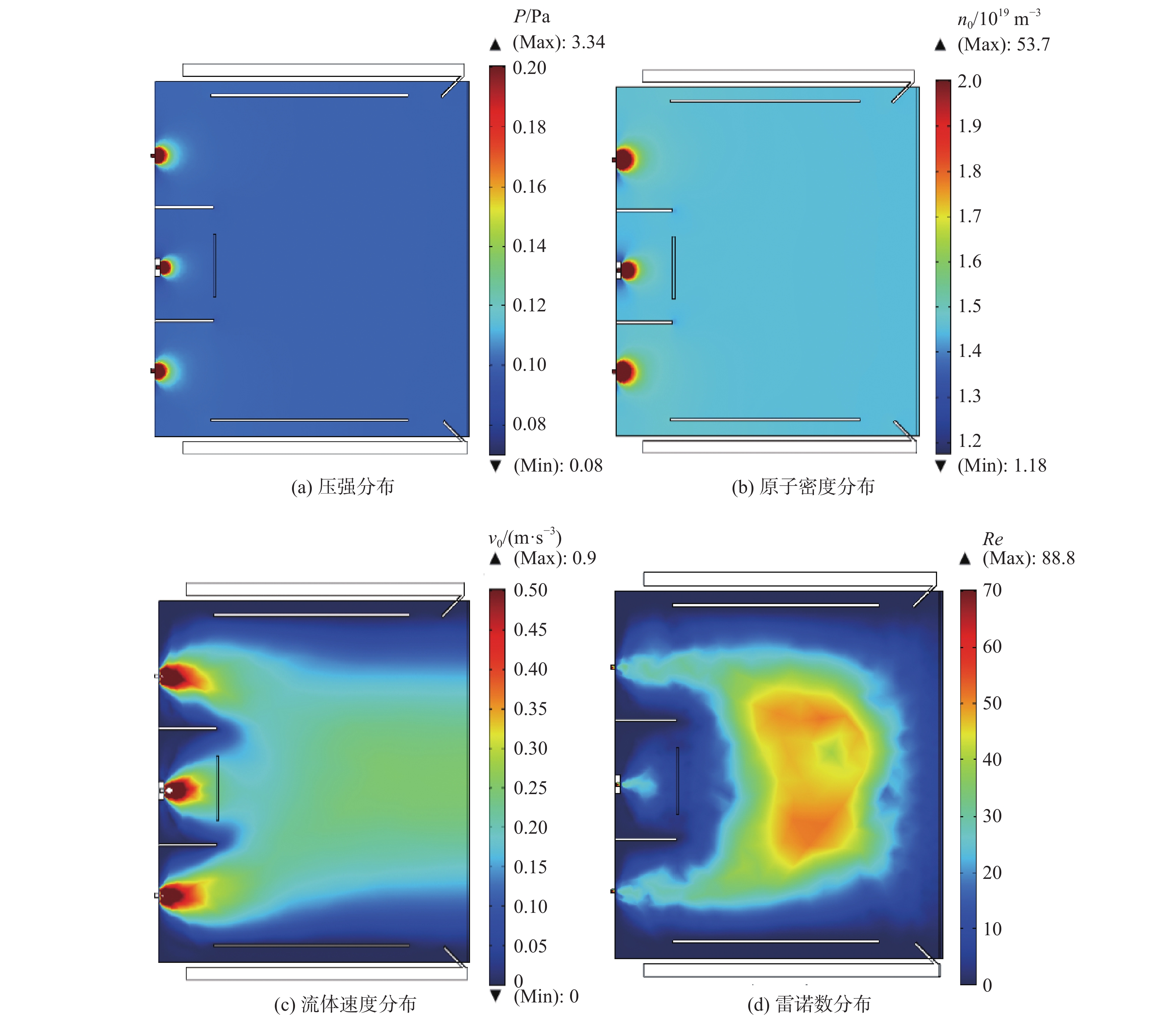
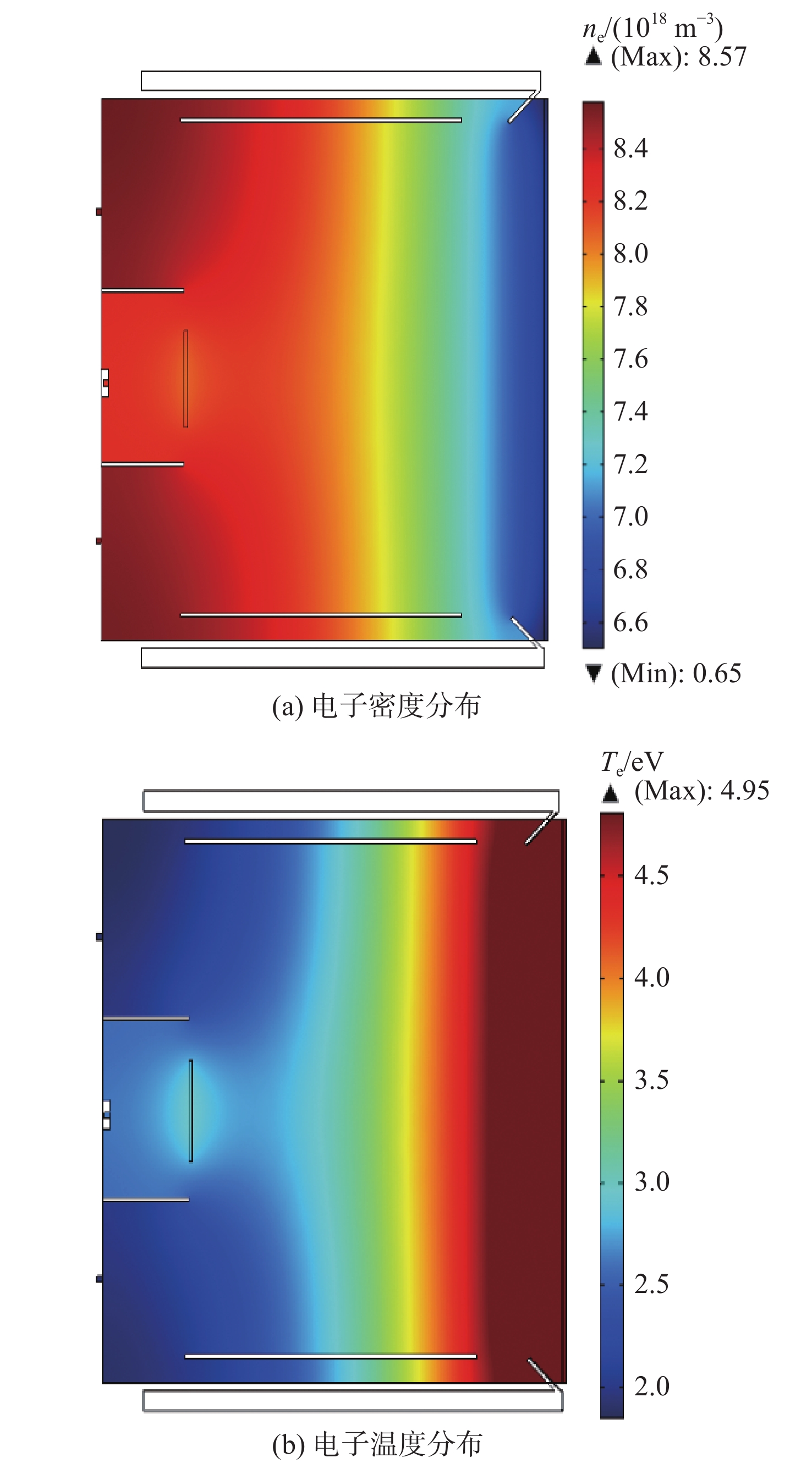
为研究10 cm口径发散磁场离子推力器内部的放电过程并对后续工程改进提供参考,采用COMSOL多物理场耦合软件建立推力器放电模型,获得关键放电参数,并根据试验结果进行验证。模拟结果表明:放电室内部上游磁极和下游磁极之间形成具有强烈发散特性的磁场,并在正交电场的影响下,使电子发生以磁力线为导向中心的霍尔漂移运动;放电室内部气体压强分布均匀且基本在0.1~0.11 Pa范围内,大部分区域的中性原子密度约为1.5×1019 m−3,流体速度在0.2~0.9 m/s的范围内且呈现明显的黏滞流特性;电子密度峰值出现在阴极出口区域,约为8.57×1018 m−3,阳极壁面附近及栅极上游区域的等离子密度约为6.8×1017 m−3。试验结果显示:采用E×B探针测量得到双核离子占总束流离子比为14.1%,根据COMSOL计算值得到的0.353 mA束流理论值与0.323 mA的束流实测值比对误差为9%,误差主要来自于仿真条件设置及试验测量。研究结果可为离子推力器工程化改进提供快速的放电参数分析及优化设计参考。
Abstract:A discharge model of the divergent magnetic field ion thruster (Kaufman thruster) of 10 cm diameter is established with COMSOL multi-physical field coupling software to study the internal discharge process of the thruster and to provide reference for subsequent engineering improvement. The key discharge parameters are obtained and verified through experiments. The calculation results show a magnetic field formed between the upstream and downstream magnetic poles in the discharge chamber with strong divergent characteristics. Due to the orthogonal electric field, the Hall drift of the electrons occur with the magnetic field line as the guiding center. The gas pressure in the discharge chamber is uniformly distributed in the range of 0.1−0.11 Pa, with the neutral atom density in most areas about 1.5×1019 m−3, and the fluid velocity in the range of 0.2−0.9 m/s. The fluid shows obvious characteristics of viscous flow. The peak electron density appears in the cathode outlet region, which is about 8.57×1018 m−3, while the plasma density near the anode wall and the upstream of the screen grid is about 6.8×1017 m−3. The results measured by E×B probe show that the proportion of divalent ions in the total beam ions is 14.1%. The comparison error between the theoretical beam current value of 0.353 mA and the measured beam current value of 0.323 mA is 9%, which is mainly due to the simulation setting and the measurement error. The discharge model established in this paper can provide rapid discharge parameter analysis and reference for optimal design of the thruster.
-
Key words:
- divergent magnetic field /
- ion thruster /
- discharge model /
- plasma density /
- electron temperature
-
表 1 10 cm口径发散磁场离子推力器20 mN主工况点的工作参数
Table 1. Parameters of 10 cm diameter divergent magnetic field ion thruster with 20 mN main work point
参数 数值 阴极流量/(mg·s−1) 0.08 阳极流量/(mg·s−1) 0.5 中和器流量/(mg·s−1) 0.08 屏栅电势/V 1150 加速栅电势/V −150 触持电势/V 1162 励磁电流/A 0.56 励磁电势/V 1150 挡板电势/V 1150 上磁极电势/V 1150 下磁极电势/V 1150 阳极电势/V 1185 表 2 迁移扩散模块的参数设置
Table 2. Parameter setting of drift diffusion module
参数 表达式 k1 1.99−14T0.93ee−0.41/Te k2 1.93−19e−11.6/Te/[T0.5e(8eTe/π/me)0.5] k3 10−20(3.97+0.643Te−0.0368T2e)e−12.127/Te(8eTe/π/me)0.5 r1 k1n0ne r2 k2n0ne r3 k3n0ne μe e/[me(νen+νei)] Re r2+r3 Sen −e(r1de1+r2de2+r3de3) σen 6.6−19(Te/4−0.1)/[1+(Te/4)1.6] lnΛ 230.5ln(10−6ne/T3e) ven σenn0(8kTe/π/me)0.5 vei 2.9−12nelnΛ/T1.5e de1 0 de2 8.31 de3 12.13 -
[1] GRAY H, SMITH P, FERN D. Design and development of the UK-10 ion propulsion system: AIAA-1996-3084[R]. Reston: AIAA, 1996. [2] BASSNER H, KILLINGER R, MARX M, et al. Ion propulsion for drag compensation of GOCE: AIAA-2000-3417[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2000. [3] CORBETT M, EDWARDS C. Thrust control algorithms for the GOCE ion propulsion assembly: IEPC-2007-228[R]. Florence: IEPC, 2007. [4] TIGHE G, CHIEN R, SOLIS E, et a1. Performance evaluation of the XIPS-25 cm thruster for application to NASA discovery missions: AIAA-2006-4666[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2006. [5] 赵以德, 吴宗海, 张天平, 等. 离子推力器多模式化研究[J]. 推进技术, 2020, 41(1): 187-193. doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.190357ZHAO Y D, WU Z H, ZHANG T P, et al. Research on multi-mode realization of ion thruster[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2020, 41(1): 187-193(in Chinese). doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.190357 [6] MILDER N. A survey and evaluation of research on the discharge chamber plasma of a Kaufman thruster: AIAA-1969-494[R]. Reston: AIAA, 1969. [7] GOEBEL D. Ion source discharge performance and stability[J]. Physics of Fluids, 1982, 25(6): 1093-1102. doi: 10.1063/1.863842 [8] BROPHY R, WILBUR P. Calculation of plasma properties in ion sources: AIAA-1985-2006[R]. Reston: AIAA, 1985. [9] JAMES A. Particle based plasma simulation for an ion engine discharge chamber[D]. Dayton: Wright State Niversity, 2007: 87-88. [10] MILLIGAN D, GABRIEL S. Generation of experimental plasma parameter maps around the baffle aperture of a Kaufman (UK-25) ion thruster[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2009, 64(2): 952-968. [11] OZAKI T, KASAI Y, NAKAGAWA T, et al. In-orbit operation of 20 mN class xenon ion engine for ETS-Ⅷ: IEPC-2007-084[R]. Florence: IEPC, 2007. [12] OZAKI T, NISHIDA E, KASAI Y, et al. Development status of xenon ion engine subsystem for ETS-Ⅷ: AIAA-2003-2215[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2003. [13] 杨福全, 王成飞, 胡竟, 等. 超低轨道卫星应用离子电推进技术方案[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2021, 1(3): 1-8. doi: 10.16708/j.cnki.1000-758X.2021.0038YANG F Q, WANG C F, HU J, et al. Ion-electric propulsion technology scheme for ultra-low orbit satellites[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2021, 1(3): 1-8(in Chinese). doi: 10.16708/j.cnki.1000-758X.2021.0038 [14] 杨福全, 胡竟, 郭德洲, 等. LIPS-100离子推力器挡板通道面积优化研究[J]. 真空与低温, 2021, 2(5): 395-399. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7086.2021.04.013YANG F Q, HU J, GUO D Z, et al. Study on optimization of baffle channel area of LIPS-100 ion thruster[J]. Vacuum and Cryogenics, 2021, 2(5): 395-399(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7086.2021.04.013 [15] 吴辰宸, 顾左. Kaufman型离子推力器束流调节理论与试验研究[J]. 真空科学与技术学报, 2015, 35(11): 1368-1373. doi: 10.13922/j.cnki.cjovst.2015.11.16WU C C, GU Z. Theoretical and experimental studies of beam current regulation of Kaufman-type ion thruster[J]. Chinese Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 2015, 35(11): 1368-1373(in Chinese). doi: 10.13922/j.cnki.cjovst.2015.11.16 [16] 陈娟娟, 张天平, 刘明正, 等. LIPS-200离子推力器放电室原初电子动力学行为的数值模拟研究[J]. 推进技术, 2015, 36(1): 155-160.CHEN J J, ZHANG T P, LIU M Z, et al. Investigation on dynamical behavior of primary electrons in LIPS-200 ion thruster discharge chamber[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2015, 36(1): 155-160(in Chinese). [17] 龙建飞, 张天平, 杨威, 等. 离子推力器推力密度特性[J]. 物理学报, 2018, 67(2): 022901. doi: 10.7498/aps.67.20171507LONG J F, ZHANG T P, YANG W, et al. Thrust density characteristics of ion thruster[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2018, 67(2): 022901(in Chinese). doi: 10.7498/aps.67.20171507 [18] GOEBEL D, KATZ I. Fundamentals of electric propulsion: Ion and hall thrusters[M]. New York: Wiley, 2005: 142-145. [19] CLAUSING P. The flow of highly rarefied gases through tubes of arbitrary length[J]. Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 1971, 8(2): 636-646. [20] SUM M M, ZHANG T P, WEN X D, et al. Plasma characteristics in the discharge region of a 20 A emission current hollow cathode[J]. Plasma Science and Technology, 2018, 20(1): 025503. [21] 孙明明, 张天平, 吴先明. 20 cm离子推力器放电室流场计算模拟[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2015, 27(5): 054003. doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.054003SUM M M, ZHANG T P, WU X M. Flow field simulation of 20 cm diameter ion thruster discharge chamber[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2015, 27(5): 054003(in Chinese). doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.054003 [22] WIRZ R, KATZ I. Plasma processes of DC ion thruster discharge chambers: AIAA-2005-3690[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2005. [23] MILLER J, PULLINS S, LEVANDIER D, et al. Xenon charge exchange cross sections for electrostatic thruster models[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2002, 91(3): 984-991. doi: 10.1063/1.1426246 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 赵志伟,张天平,冉文亮,李璇. 离子推力器中空心阴极耦合放电的试验研究. 真空与低温. 2022(06): 650-659 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(1)
-








 下载:
下载:

 百度学术
百度学术

