-
摘要:
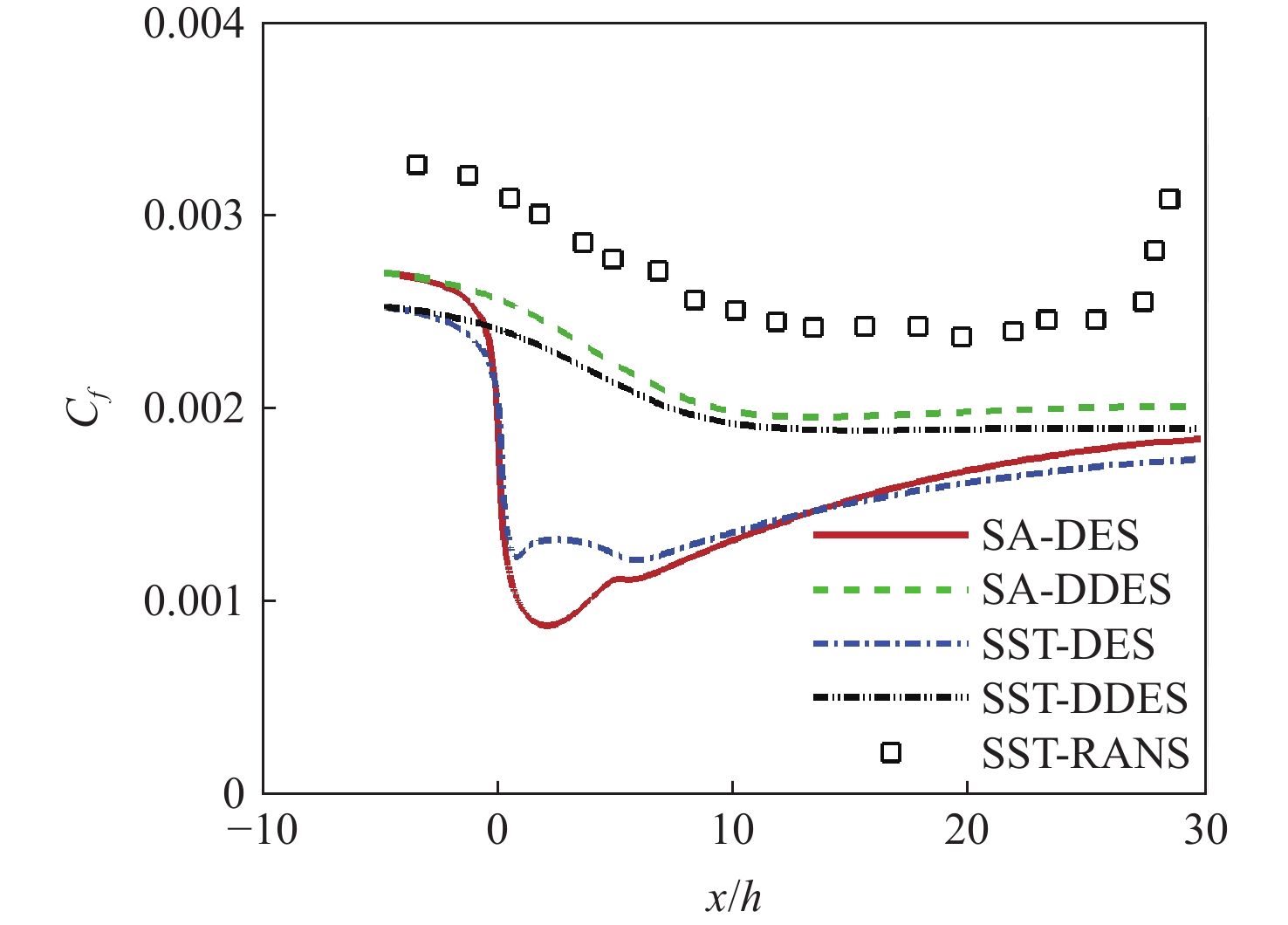
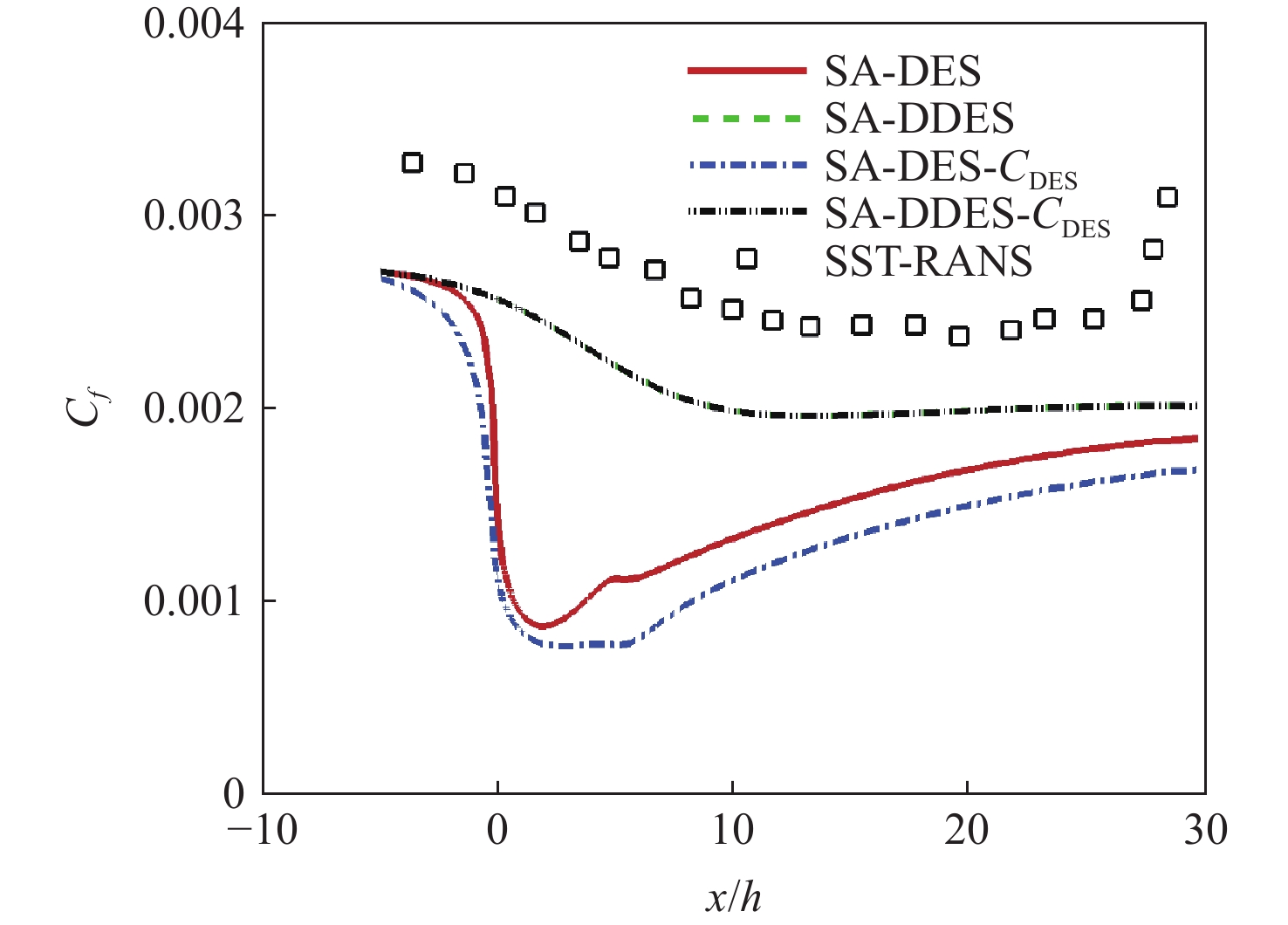
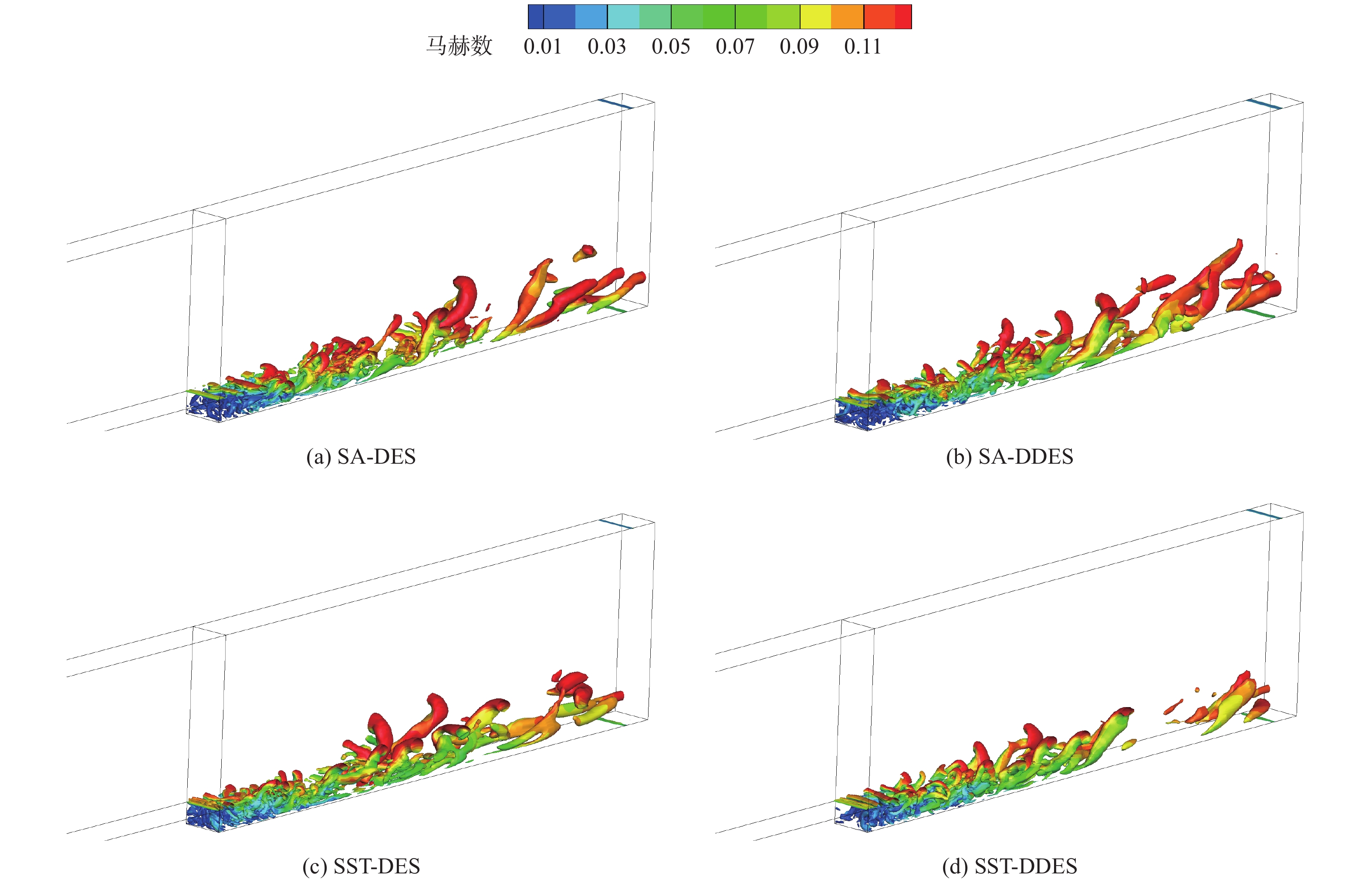
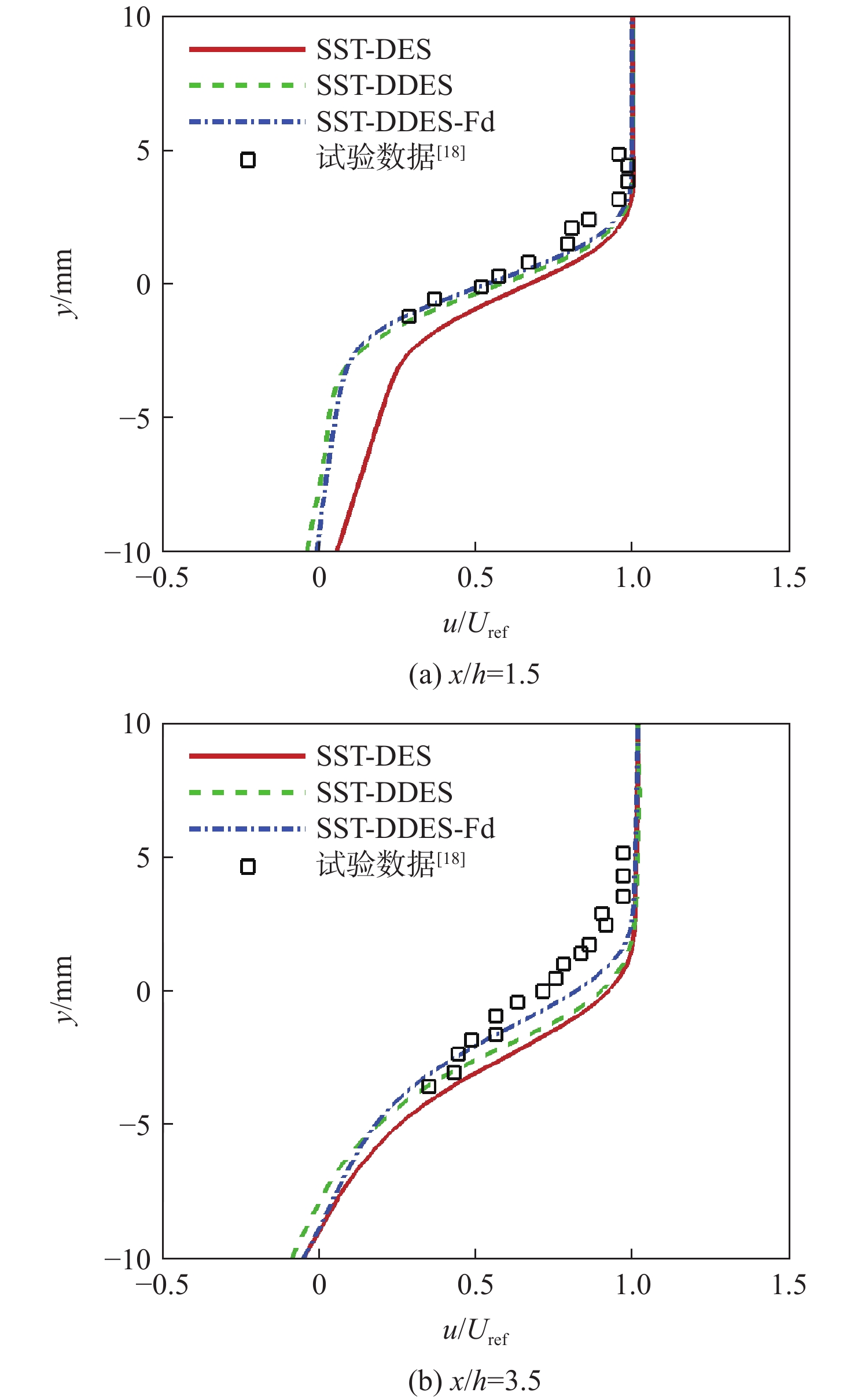
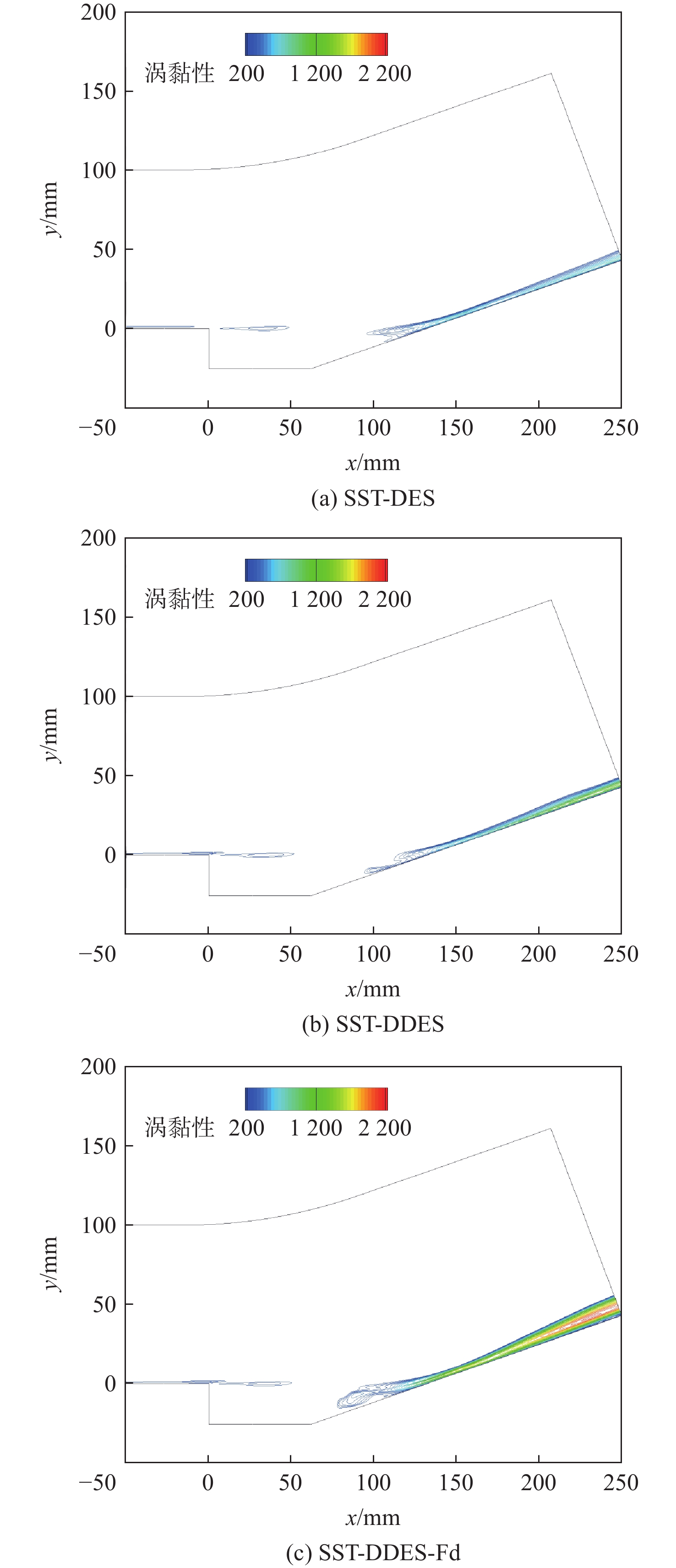
随着工程上流动结构的日益复杂,兼具雷诺平均Navier-Stokes(RANS)方法高效率与大涡模拟(LES)高精度的分离涡模拟(DES)类混合方法成为现阶段工程中最有效的湍流模拟方法之一。围绕DES类混合方法中的DES与延迟分离涡模拟(DDES)方法开展工作,分析二者开关函数构造上的不同,研究延迟因子作用机理,并考察DES与DDES方法的求解能力。研究表明:DES与DDES方法在模拟表现上存在一定差异,DDES方法通过引入延迟因子,保护RANS求解区域,改善模化应力不足,降低了DDES方法对交界面系数
C DES敏感程度; DDES方法在计算过程中容易出现过度保护,导致求解瞬时涡结构能力不如DES方法,分析与延迟因子引入比重及开关函数构造形式有关。Abstract:With the increasing complexity of flow structure in engineering, detached eddy simulation (DES) has become one of the most effective methods for turbulence simulation. DES is a hybrid method, combining Reynolds averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) and large eddy simulation (LES) and thus possessing the high efficiency of RANS and high prevision of DES. This research focuses on DES and delayed detached eddy simulation (DDES), analyzing the differences in the structure of shielding functions, and the action mechanism of delay factors. Backward step flow and supersonic cavity compression corner flow are selected to compare and analyze the solving ability of DES and DDES. The results show that DDES protects the RANS solution area by introducing the delay factor, improving modeled-stress depletion and reducing the sensitivity to
C DES. However, DDES is prone to over protection in the calculation process, resulting in lesser ability to solve the instantaneous vortex structure than DES method. The analysis is related to the introduction of delay factors and the construction form of shielding functions. -
-
[1] 阎超, 屈峰, 赵雅甜, 等. 航空航天CFD物理模型和计算方法的评述与挑战[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2020, 38(5): 829-857.YAN C, QU F, ZHAO Y T, et al. Review of development and challenges for physical modeling and numerical scheme of CFD in aeronautics and astronautics[J]. Acta Aerodynamic Sinica, 2020, 38(5): 829-857(in Chinese). [2] SLONTNICK J, KHODADOUST A, ALONSO J, et al. CFD vision 2030 study: A path to revolutionary computational aerosciences: NASA/CR-2014-218178 [R]. Washing ton, D. C. : NASA, 2014. [3] 张兆顺, 崔桂香, 许春晓. 湍流理论与模拟[M]. 第2版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2017: 173-174.ZHANG Z S, CUI G X, XU C X. Theory and modeling of turbulence[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2017: 173-174 (in Chinese). [4] 肖志祥, 罗堃宇, 刘健. 宽速域RANS-LES混合方法的发展及应用[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2017, 35(3): 338-353.XIAO Z X, LUO K Y, LIU J. Developments and applications of hybrid RANS-LES methods for wide-speed-range flows[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2017, 35(3): 338-353(in Chinese). [5] 杜若凡, 阎超, 韩政, 等. DDES延迟函数在超声速底部流动中的性能分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2017, 43(8): 1585-1593.DU R F, YAN C, HAN Z, et al. Performance of delayed functions in DDES for supersonic base flow[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017, 43(8): 1585-1593(in Chinese). [6] FRÖHLICH J, VON TERZI D. Hybrid LES/RANS methods for the simulation of turbulent flows[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2008, 44(5): 349-377. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2008.05.001 [7] SPALART P R, JOU W H, STRELETS M, et al. Comments on the feasibility of LES for wings and on a hybrid RANS/LES approach[C]//Proceedings of 1st AFOSR International Conference on DNS/LES, Advances in DNS/LES. Columbus: Greyden Press, 1997: 137-147. [8] STRELETS M. Detached eddy simulation of massively separated flows: AIAA-2001-0879 [R]. Reston: AIAA, 2001. [9] MENTER F R, KUNTZ M, LANGTRY R. Ten years of industrial experience with the SST turbulencemodel[C]//Heatand Mass Transfer 4. Redding: Begell House, 2003: 625-632. [10] SPALART P R, DECK S, SHUR M L, et al. A new version of detached-eddy simulation, resistant to ambiguous grid densities[J]. Theoretical and Computational Fluid Dynamics, 2006, 20(3): 181-195. doi: 10.1007/s00162-006-0015-0 [11] SPALART P, ALLMARAS S. A one-equation turbulence model for aerodynamic flows[C]// 30th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 1992. [12] MENTER F R. Two-equation eddy-viscosity turbulence models for engineering applications[J]. AIAA Journal, 1994, 32(8): 1598-1605. doi: 10.2514/3.12149 [13] DRIVER D M, SEEGMILLER H L. Features of a reattaching turbulent shear layer in divergent channelflow[J]. AIAA Journal, 1985, 23(2): 163-171. doi: 10.2514/3.8890 [14] 张露, 李杰, 牟永飞, 等. 基于DES类混合方法模拟后台阶分离流动[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2017, 35(6): 983-989.ZHANG L, LI J, MOU Y F, et al. Simulating unsteady flow over a backward facing step with advanced detached-eddy-simulation methods[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2017, 35(6): 983-989(in Chinese). [15] GRITSKEVICH M S, GARBARUK A V, SCHÜTZE J, et al. Development of DDES and IDDES formulations for the k-ω shear stress transport model[J]. Flow, Turbulence and Combustion, 2012, 88(3): 431-449. doi: 10.1007/s10494-011-9378-4 [16] GRITSKEVICH M S, GARBARUK A V, MENTER F R. Fine-tuning of DDES and IDDES formulations to the k–ω shear stress transport model[J]. Progress in Flight Physics, 2013, 5: 23-42. [17] ZHOU L, ZHAO R, YUAN W. An investigation of interface conditions inherent in detached-eddy simulation methods[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2018, 74(3): 46-55. [18] SETTLES G S, WILLIAMS D R, BACA B K, et al. Reattachment of a compressible turbulent free shear layer[J]. AIAA Journal, 1982, 20(1): 60-67. doi: 10.2514/3.51047 -







 下载:
下载: