-
摘要:
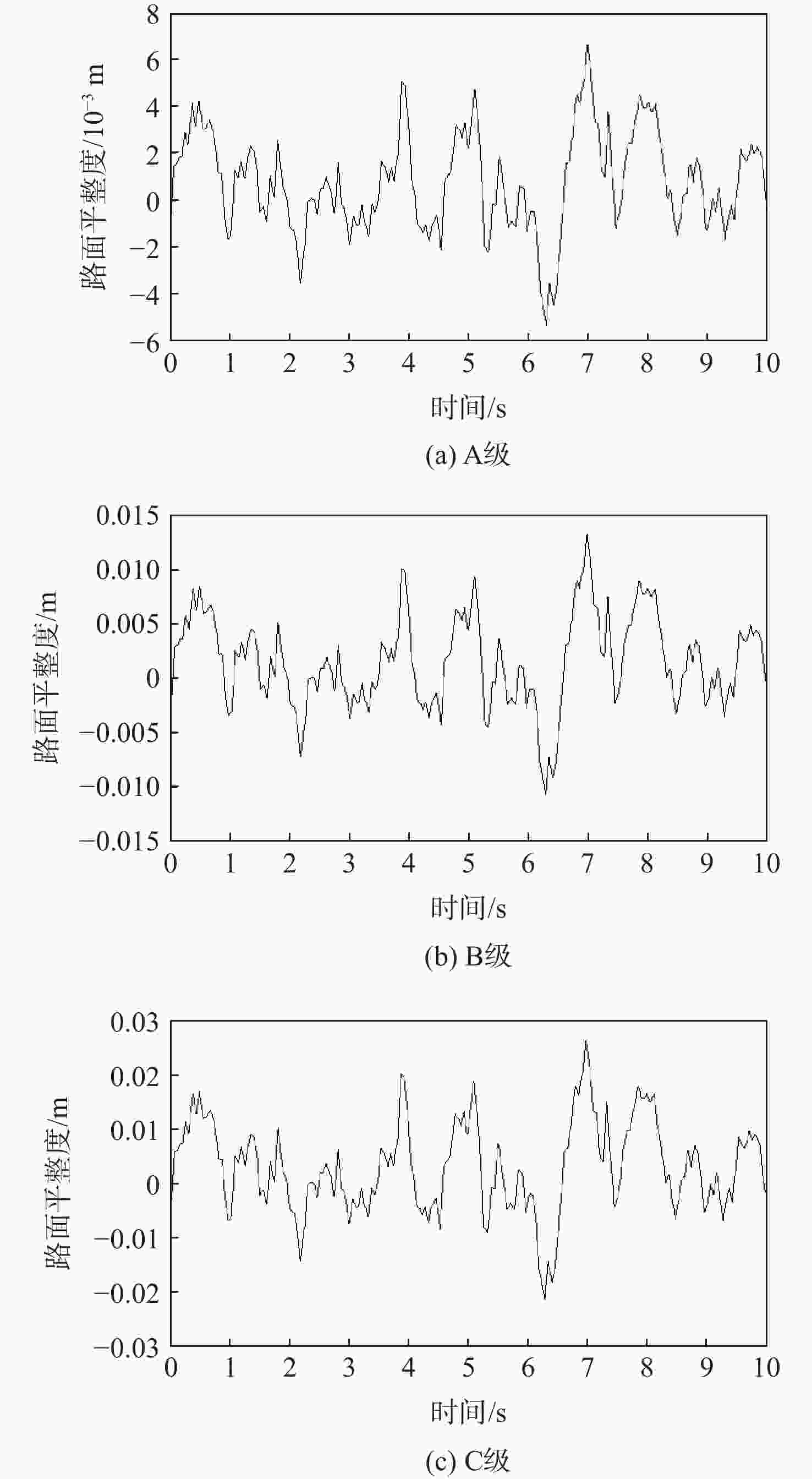
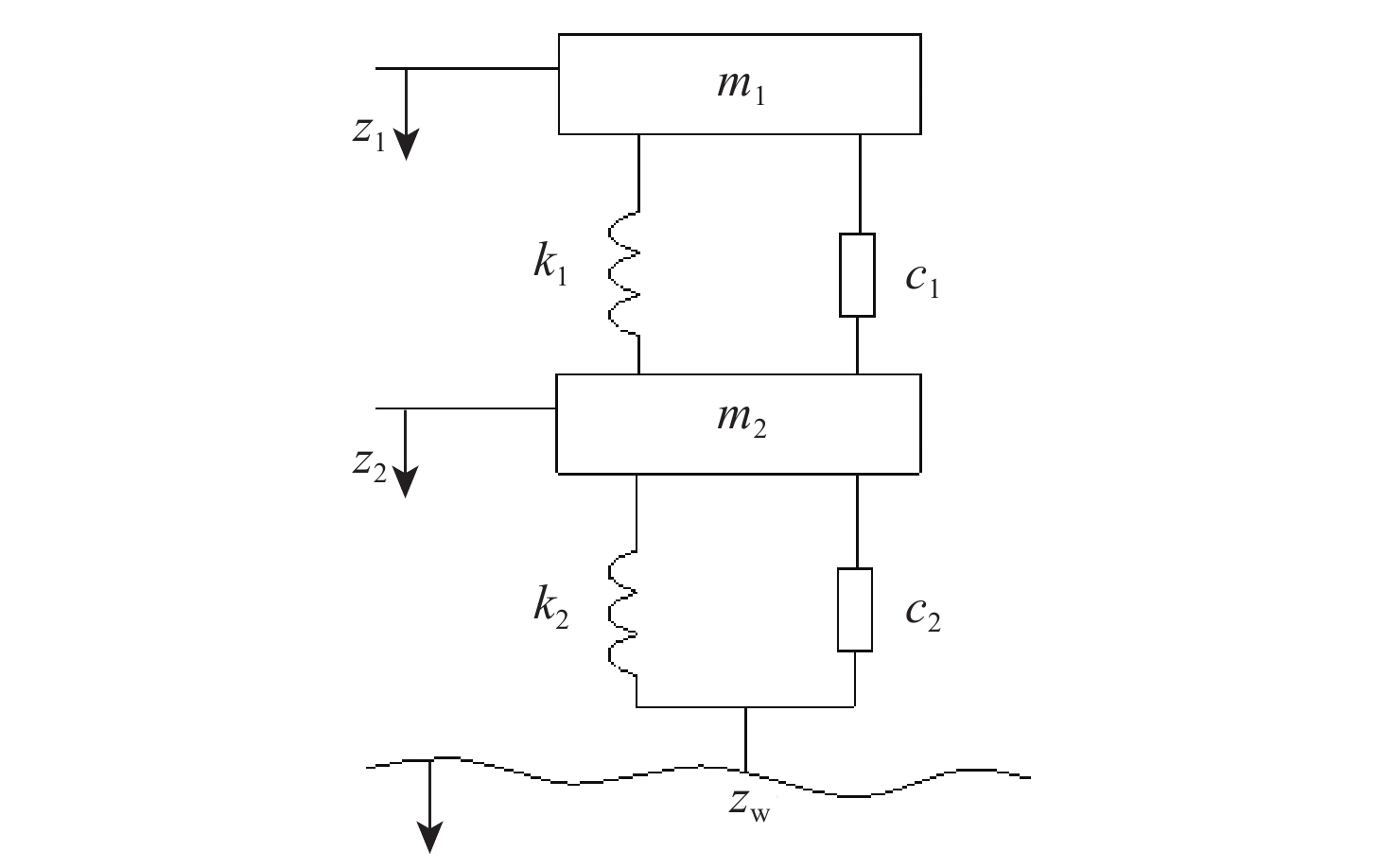
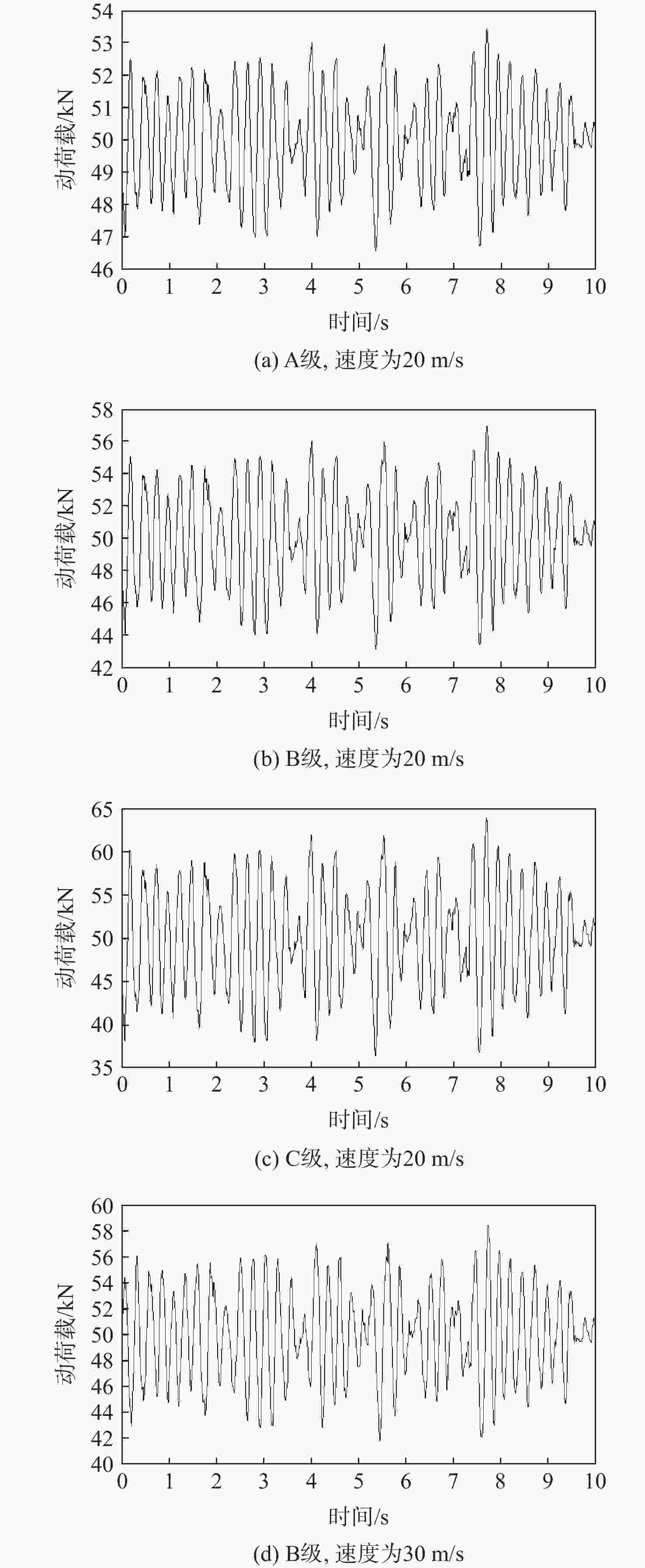
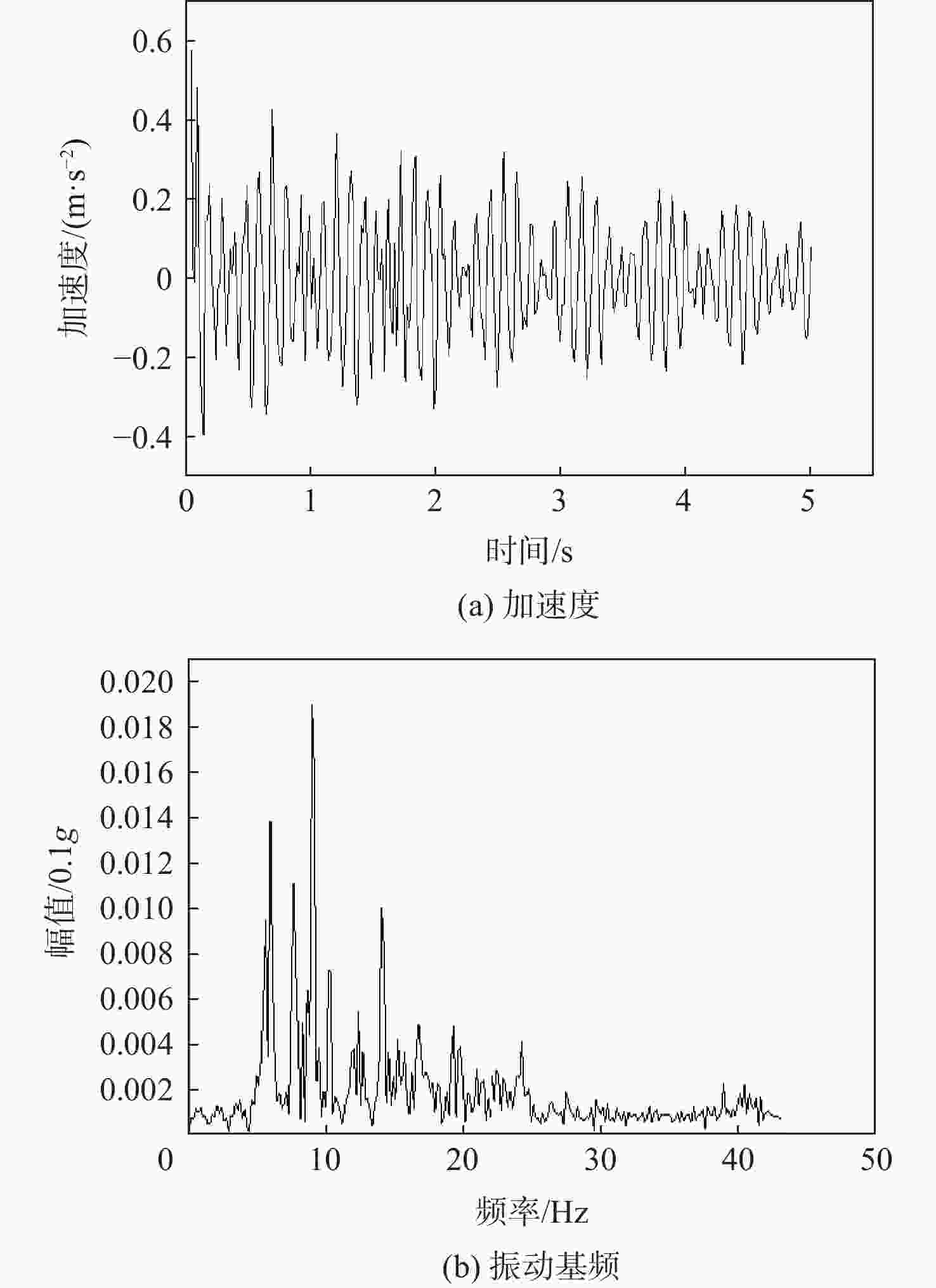
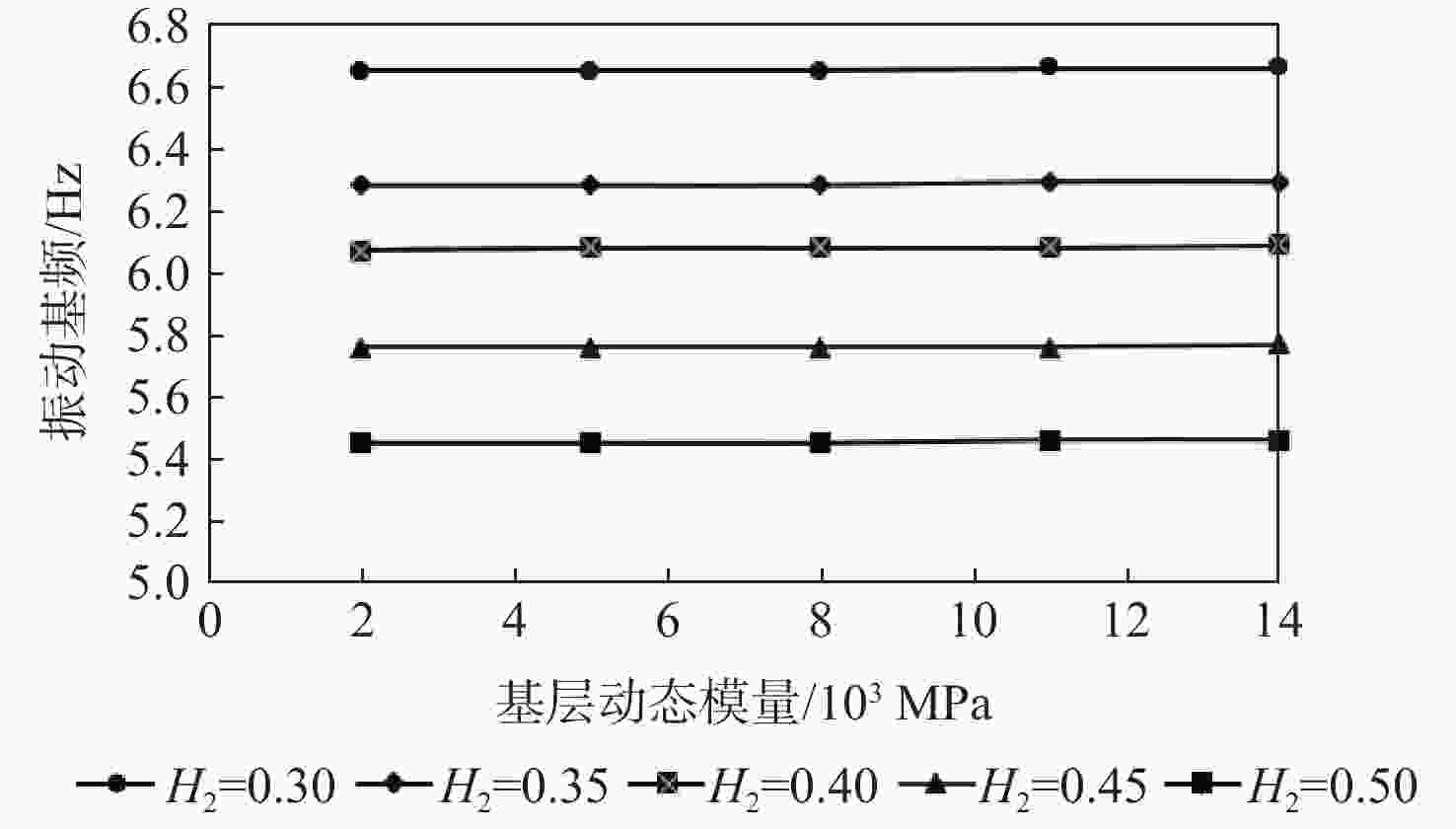
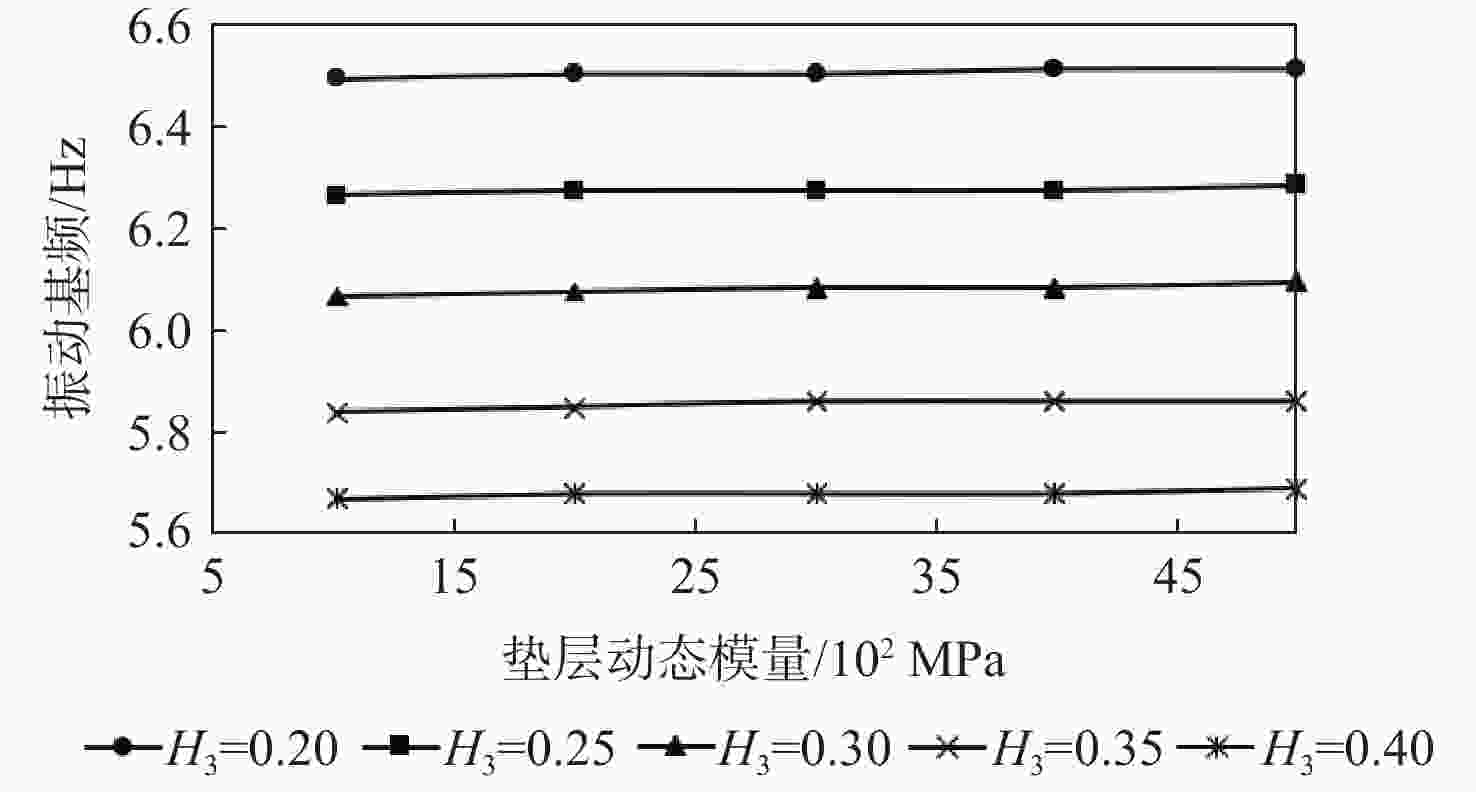
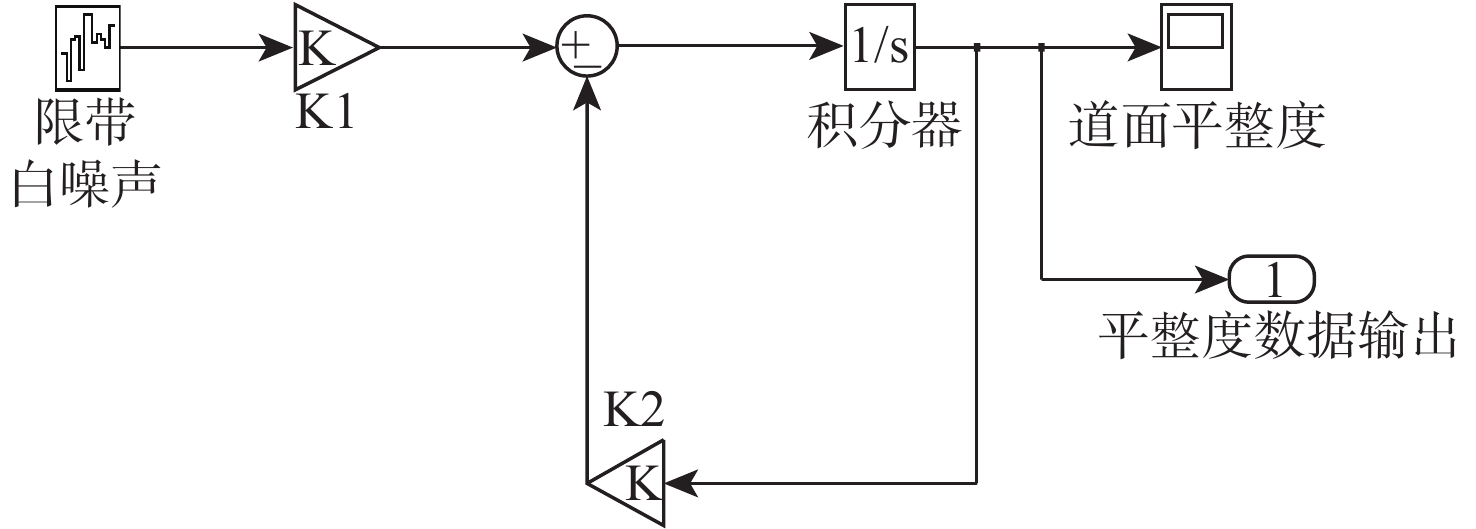
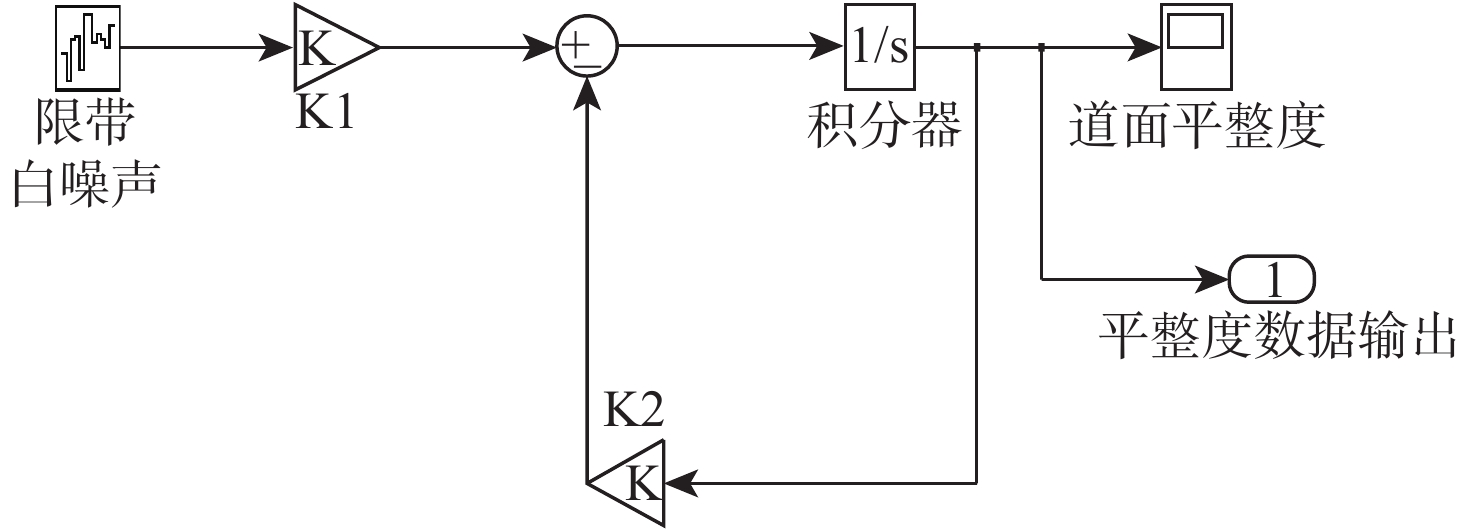
为研究沥青混凝土路面的振动特性,采用滤波白噪声法拟合出路面平整度时域模型,基于1/4车辆模型,考虑车辆–道路的耦合作用,分析不同车辆速度、不同路面平整度等级时,车辆对路面的实时动荷载;建立道路三维有限元模型,研究车辆随机动荷载作用下道路的振动响应,分析道路各结构层参数对道路表面中心振动基频的影响。结果表明:路面平整度等级、车辆行驶速度对车–路耦合系统影响显著,当路面平整度等级由A级变化至C级时,同一行驶速度下的车辆动荷载增大了20%;道路振动基频随土基动模量呈对数关系增加,土基动模量由60 MPa增大至260 MPa,道路振动基频由5.61 Hz增大至10.80 Hz,振动基频增幅高达48.06%;在常用动模量变化范围内,面层、基层、垫层的动模量对基频的影响较小;随着面层、基层与垫层厚度的增加,道路基频呈线性减小的趋势,面层厚度对振动频率影响的敏感性大于基层厚度,基层厚度对振动频率影响的敏感性大于垫层厚度;在常用结构层厚度变化范围内,振动基频分别减小9.28%、18.05%与12.75%。试验结果证明:振动基频计算较正确,计算结果可为道路承载力快速测试提供理论支持。
Abstract:To study the vibration characteristics of asphalt concrete pavement, the time domain model of road roughness was simulated by the white noise filtering method, the coupling effect of vehicle and road with different vehicle speeds and different road roughness levels was analyzed based on the quarter vehicle mode, and the real-time dynamic load of vehicle on the road surface was determined to study the vibration characteristics of Tarmac pavements. The three-dimensional finite element model of the road is established, the vibration response of the road under the action of the vehicle random dynamic load is analyzed, and the influence of the road structure-layer parameters on the fundamental vibrational frequency of the road surface center is analyzed. The results show that the pavement roughness level and vehicle speed have significant influence on the vehicle-road coupling system. When the pavement roughness level changes from class A to class C, the dynamic load of vehicles under the same speed increases by 20%; the fundamental vibrational frequency of the road increases with the logarithmic relation of dynamic subgrade modulus, the subgrade modulus increases from 60 MPa to 260 MPa, the fundamental vibrational frequency of the road increases from 5.61 Hz to 10.80 Hz, with an increase of 48.06%. The dynamic modulus of the surface layer, base layer and cushion have little influence on the fundamental frequency, which are almost negligible. As the thickness of surface layer, base layer and cushion increases, the fundamental frequency of road shows a linear decrease trend. Within the commonly used variation range of the thickness of structure layer, the fundamental vibrational frequency decreases by 9.28%, 18.05% and 12.75% respectively.
-
等级 下限值 几何平均值 上限值 A 8 16 32 B 32 64 128 C 128 256 512 D 512 1 024 2 048 E 2 048 4 096 8 192 F 8 192 16 384 32 768 G 32 768 65 536 131 072 H 131 072 262 144 524 288 表 2 10 t加载车辆参数
Table 2. Parameters of truck with 10 tons’ weight
参数 数值 簧载部分质量m1/kg 4450 非簧载部分质量m2/kg 550 簧载部分刚度系数k1/(N·m−1) 1000000 非簧载部分刚度系数k2/(N·m−1) 1750000 簧载部分阻尼系数c1/(N·s·m−1) 15000000 非簧载部分阻尼系数c2/(N·s·m−1) 2000000 表 3 路面结构和材料参数
Table 3. Structural and material parameters of road
结构层 厚度/m 动态模量/MPa 泊松比 密度/(kg.m−3) 沥青混凝土 0.20 4000 0.30 2400 水泥稳定碎石 0.40 8000 0.25 2200 二灰稳定碎石 0.30 2000 0.30 2000 土基 9 140 0.35 1900 表 4 不同深度处振动基频及幅值
Table 4. Fundamental frequencies and amplitudes at different depths
y/m 振动
基频
/Hz幅值/0.1g 9.9 6.08 0.014 9.7 6.08 0.013 9.3 6.08 0.013 9.0 6.08 0.013 7.0 6.08 0.010 5.0 6.08 0.009 3.0 6.08 0.007 1.0 6.08 0.004 表 5 不同道面参数时的振动基频
Table 5. Fundamental frequencies under different pavement parameters
面层
厚
度
/m面层
模
量
/MPa振动
基
频
/Hz面层
厚
度
/m面层
模
量
/MPa振动
基
频
/Hz0.14 3 500 6.57 0.20 3 500 6.08 4 000 6.58 4 000 6.08 4 500 6.58 4 500 6.08 5 000 6.58 5 000 6.09 5 500 6.59 5 500 6.09 0.16 3 500 6.40 0.22 3 500 5.96 4 000 6.40 4 000 5.96 4 500 6.40 4 500 5.97 5 000 6.40 5 000 5.98 5 500 6.41 5 500 5.98 0.18 3 500 6.26 4 000 6.26 4 500 6.27 5 000 6.27 5 500 6.27 表 6 不同土基动态模量下道路基频
Table 6. Fundamental frequency under different soil foundation dynamic moduli
土基动态模量/MPa 基频/Hz 土基动态模量/MPa 基频/Hz 60 5.61 180 9.10 100 7.01 220 9.88 140 8.19 260 10.80 表 7 道路结构及参数
Table 7. Structures and Parameters of road
结构层 静态模量
/MPa动态模量
/MPa厚度
/m密度
/
(kg·m−3)沥青混凝土面层 2000 4890 0.2 2400 水泥稳定碎石基层 5000 7893.03 0.4 2200 二灰稳定碎石底基层 800 1098 0.3 2000 土基 55 167 ∞ 1900 表 8 道路振动基频
Table 8. Fundamental frequencies of test road
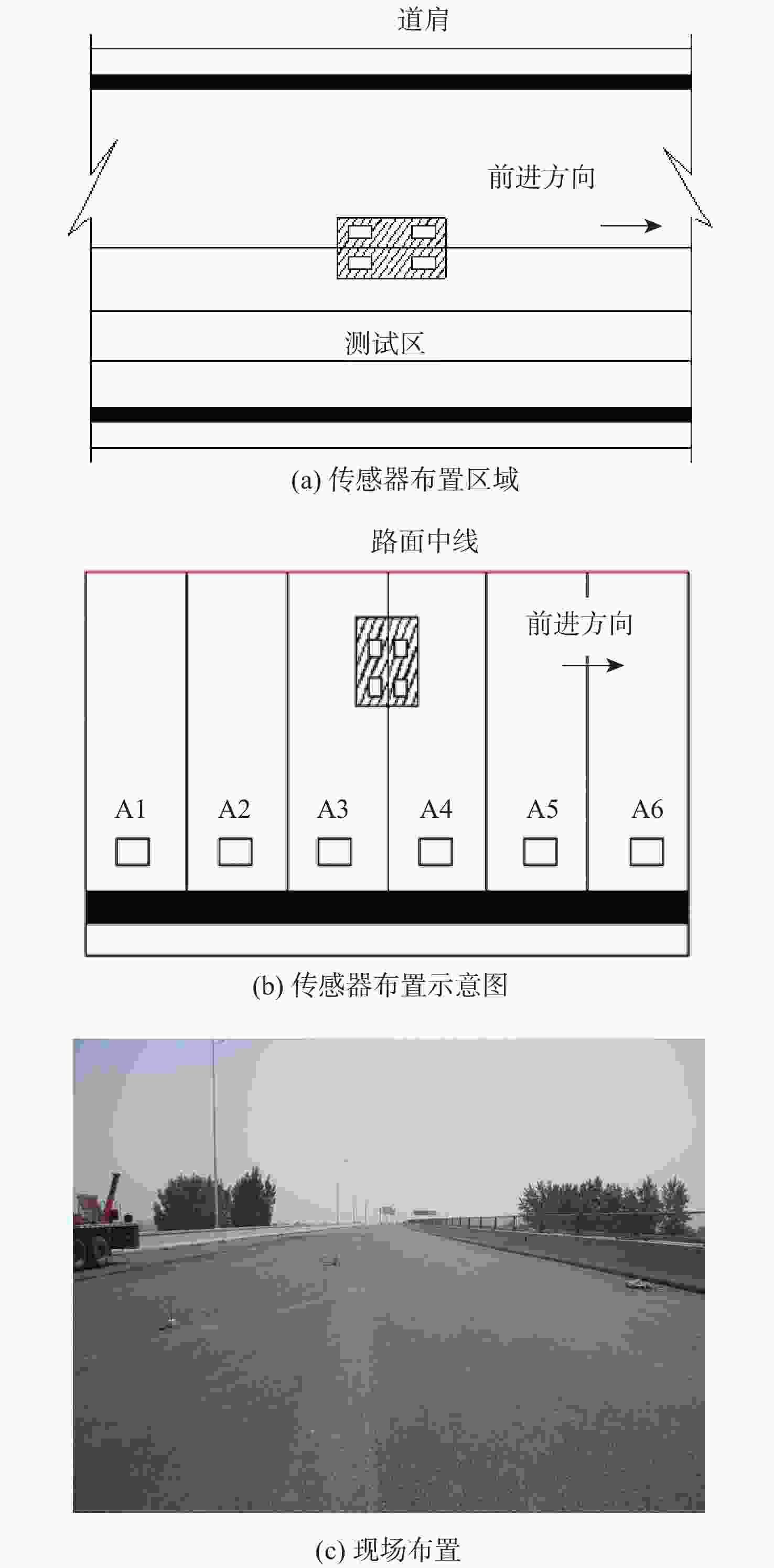
传感器 振动基频/Hz 传感器 振动基频/Hz A1 8.74 A4 8.64 A2 8.64 A5 8.64 A3 8.74 A6 8.74 -
[1] WANG H, XIE P Y, JI R, et al. Prediction of airfield pavement responses from surface deflections: Comparison between the traditional backcalculation approach and the ANN model[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2021, 22(9): 1930-1945. doi: 10.1080/14680629.2020.1733638 [2] TAREFDER R A, AHMED M U. Modeling of the FWD deflection basin to evaluate airport pavements[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2014, 14(2): 205-213. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0000305 [3] HAMIM A, YUSOFF N I M, CEYLAN H, et al. Comparative study on using static and dynamic finite element models to develop FWD measurement on flexible pavement structures[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 176: 583-592. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.05.082 [4] LI M Y, WANG H. Prediction of asphalt pavement responses from FWD surface deflections using soft computing methods[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering Part B-Pavements, 2018, 144(2): 04018014. doi: 10.1061/JPEODX.0000044 [5] LI M Y, WANG H. Development of ANN-GA program for backcalculation of pavement moduli under FWD testing with viscoelastic and nonlinear parameters[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2019, 20(4): 490-498. doi: 10.1080/10298436.2017.1309197 [6] LAJNEF N, RHIMI M, CHATTI K, et al. Toward an integrated smart sensing system and data interpretation techniques for pavement fatigue monitoring[J]. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 2011, 26(7): 513-523. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8667.2010.00712.x [7] SKAR A, KLAR A, LEVENBERG E. Load-independent characterization of plate foundation support using high-resolution distributed fiber-optic sensing[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(16): 3518. doi: 10.3390/s19163518 [8] NIELSEN J, LEVENBERG E, SKAR A. Inference of pavement properties with roadside accelerometers[C]//Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Maintenance and Rehabilitation of Pavements. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 719-728. [9] 董倩. 基于飞机滑行刚性道面位移场的跑道承载力研究[D]. 天津: 中国民航大学, 2013.DONG Q. Studies on carrying capacity of rigid pavement based on displacement field in conditions of aircraft taxing[D]. Tianjin: Civil Aviation University of China, 2013 (in Chinese). [10] RYYNÄNEN T, PELLINEN T, BELT J. The use of accelerometers in the pavement performance monitoring and analysis[J]. IOP Conference Series:Materials Science and Engineering, 2010, 10: 012110. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/10/1/012110 [11] ARRAIGADA M, PARTL M N, ANGELONE S M, et al. Evaluation of accelerometers to determine pavement deflections under traffic loads[J]. Materials and Structures, 2009, 42(6): 779-790. doi: 10.1617/s11527-008-9423-5 [12] 张存巍. 基于车辆和道路结构耦合振动的道路振动频率研究[D]. 天津: 中国民航大学, 2016.ZHANG C W. Studies on road surface vibration frequency based on vehicle-road coupling vibration system[D]. Tianjin: Civil Aviation University of China, 2016 (in Chinese). [13] 薛海, 李强. 地铁车辆天线梁振动加速度及动应力试验[J]. 北京交通大学学报, 2015, 39(4): 33-36.XUE H, LI Q. Test study on vibration and dynamic stress of subway vehicle’s antenna beam[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2015, 39(4): 33-36(in Chinese). [14] 张献民, 胡鹏. 随机荷载作用下刚性路面动态响应研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2015, 34(19): 126-130.ZHANG X M, HU P. Dynamic response of a rigid pavement under random loads[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2015, 34(19): 126-130(in Chinese). [15] 殷珺, 陈辛波, 吴利鑫, 等. 滤波白噪声路面时域模拟方法与悬架性能仿真[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 45(3): 398-407. doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2017.03.014YIN J, CHEN X B, WU L X, et al. Simulation method of road excitation in time domain using filtered white noise and dynamic analysis of suspension[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2017, 45(3): 398-407(in Chinese). doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2017.03.014 [16] 雷继超, 石鑫刚, 蔡良才, 等. 滤波白噪声法的单轮起落架滑跑模型[J]. 空军工程大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 21(3): 12-18.LEI J C, SHI X G, CAI L C, et al. A quarter landing gear taxiing model based on filtered white noise method[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 21(3): 12-18(in Chinese). [17] 中华人民共和国机械工业部. 机械振动 道路路面谱测量数据报告: GB/T 7031-2005[S]. 北京: 中国质检出版社, 1995.Ministry of Machine-Building and Electronics Industry. Mechanical vibration-road surface profiles-reporting of measured data: GB/T 7031-2005[S]. Beijing: China Quality Inspection Press, 1995(in Chinese). [18] 赵济海, 王哲人, 关朝雳. 路面不平度的测量分析与应用[M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2000.ZHAO J H, WANG Z R, GUAN C L. Measurement analysis and application of road roughness[M]. Beijing: Beijing Insititute of Technology Press, 2000(in Chinese). [19] 周玉民, 谈至明, 刘伯莹. 1/4车-路耦合动力学模型研究[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 40(3): 408-413.ZHOU Y M, TAN Z M, LIU B Y. Quarter vehicle-road coupling dynamics models[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2012, 40(3): 408-413(in Chinese). [20] 李倩, 刘俊卿. 基于车-路相互作用的沥青路面平整度劣化研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2018, 37(6): 76-81.LI Q, LIU J Q. Asphalt pavement evenness deterioration analysis based on the vehicle-pavement interaction[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2018, 37(6): 76-81(in Chinese). [21] 孔伟斌. 行车荷载作用下路面结构动态响应敏感性分析[J]. 北方交通, 2017(3): 87-90.KONG W B. The analysis on pavement structure dynamic response sensitivity under the action of vehicle load[J]. Northern Communications, 2017(3): 87-90(in Chinese). [22] 沙爱民, 胡力群. 半刚性基层材料的结构特征[J]. 中国公路学报, 2008, 21(4): 1-5.SHA A M, HU L Q. Structural characteristics of semi-rigid base course material[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2008, 21(4): 1-5(in Chinese). [23] 曾胜. 路面性能评价与分析方法研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2003.ZENG S. Research on the pavement performance evaluation and analyze methods[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2003(in Chinese). [24] 中华人民共和国交通运输部. 公路沥青路面设计规范: JTG D50—2017[S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2017.Ministry of Tran Sport of the People's Republic of China. Specifications for design of highway asphalt pavement: JTG D50—2017[S]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2017 (in Chinese). [25] 张献民, 张存巍, 张靖. 水泥混凝土面层结构的振动响应试验研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2016, 33(9): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2016.09.001ZHANG X M, ZHANG C W, ZHANG J. Experimental study on vibration response of cement concrete pavement surface course[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2016, 33(9): 1-6(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2016.09.001 [26] 程少锋. 基于道路振动频率快速检测道面承载能力的研究[D]. 天津: 中国民航大学, 2018.CHENG S F. Research on fast detection of pavement bearing capacity based on vibration frequency[D]. Tianjin: Civil Aviation University of China, 2018(in Chinese). [27] 卢正, 王长柏, 付建军, 等. 交通荷载作用下公路路基工作区深度研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2013, 34(2): 316-321.LU Z, WANG C B, FU J J, et al. Research on influence depth of road subgrade induced by vehicle loads[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(2): 316-321(in Chinese). [28] 付梓君. 车—路耦合作用下沥青路面振动规律及能量谱表征研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2018.FU Z J. Study on the vibration regularity and energy spectrum characterization of asphalt pavement under the coupling of vehicles and roads[D]. Xi’an: Changan University, 2018 (in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: