-
摘要:
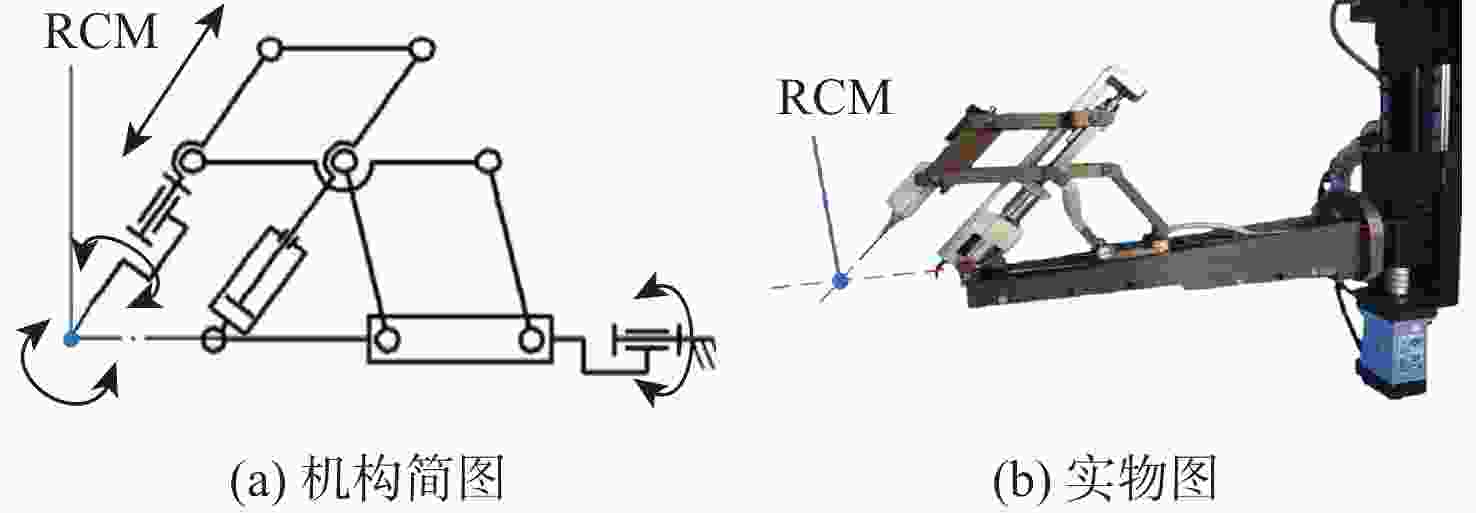
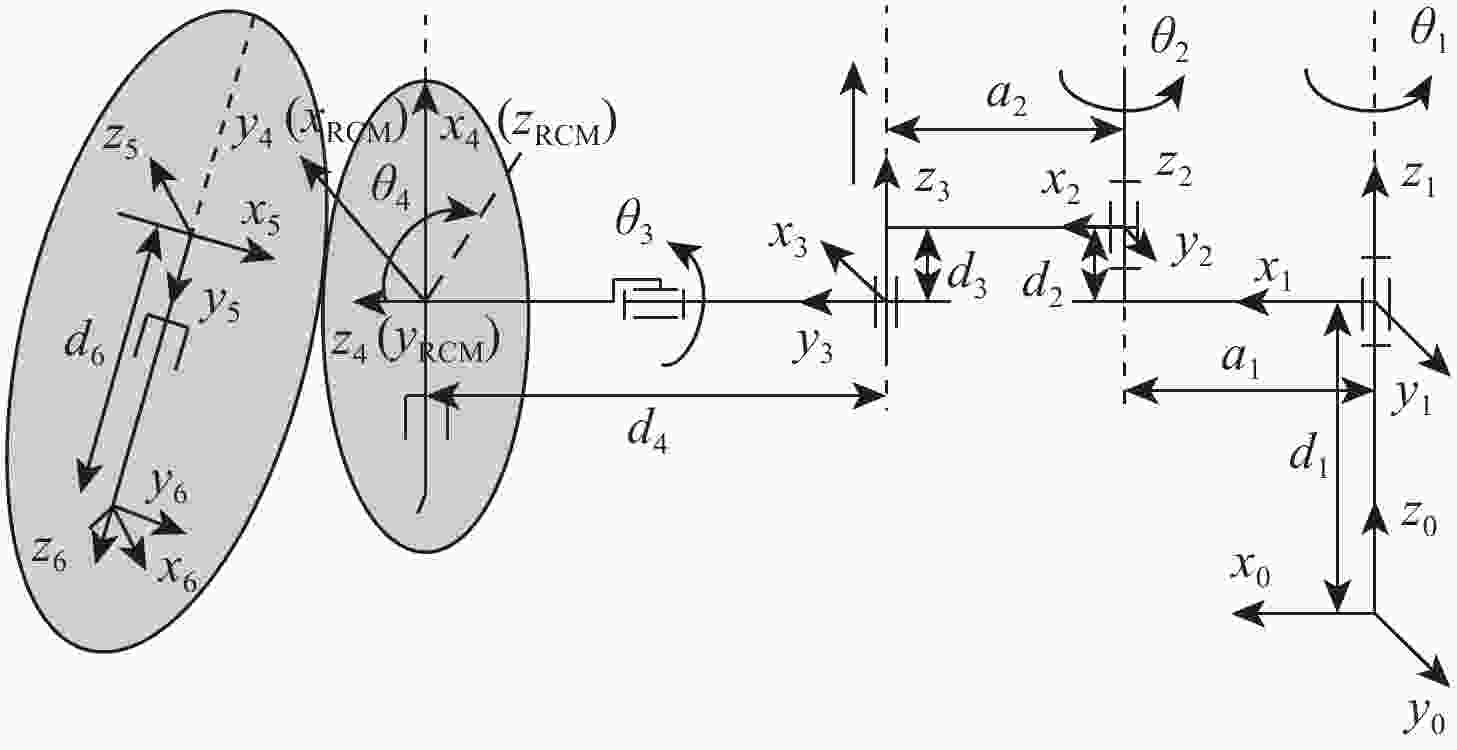
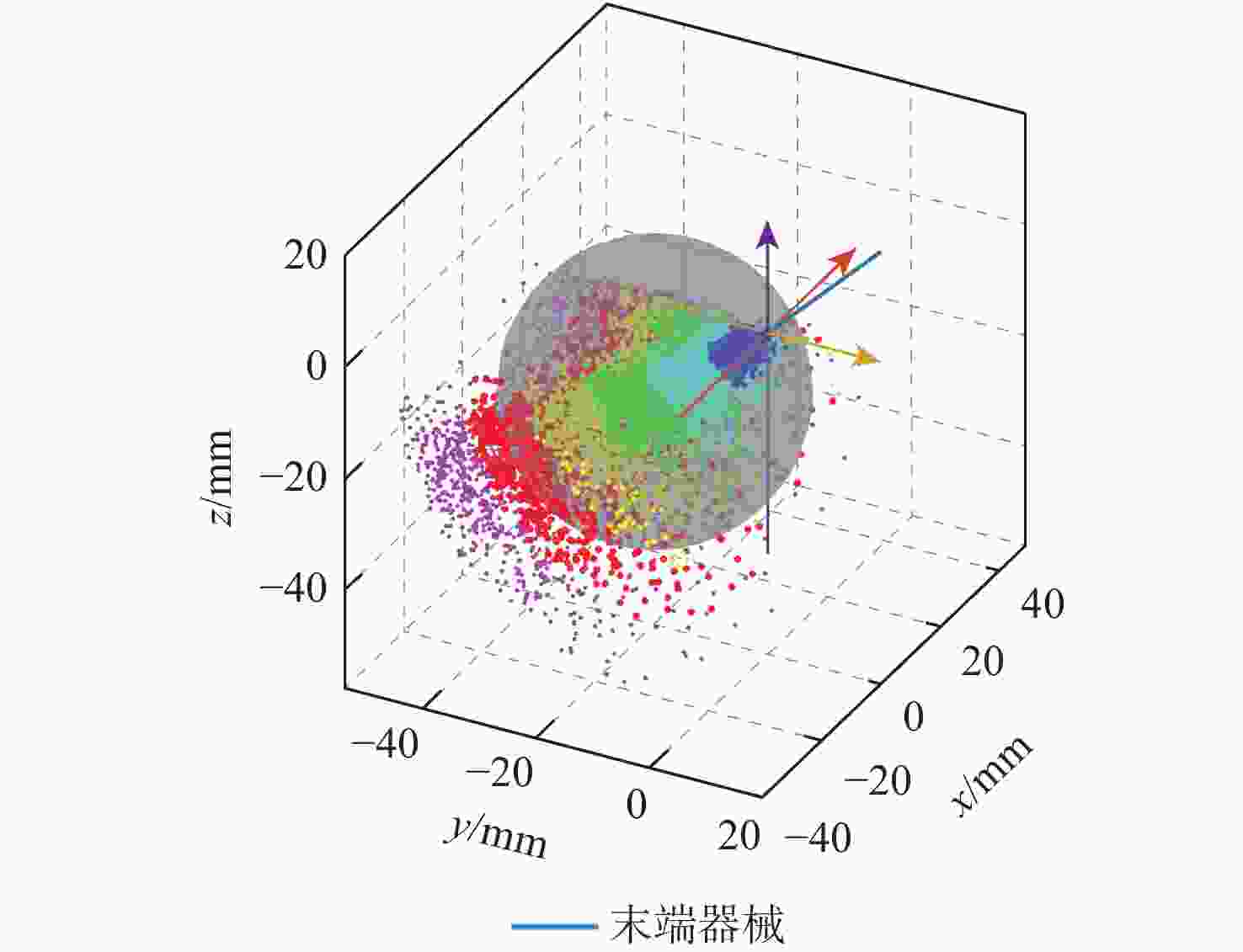
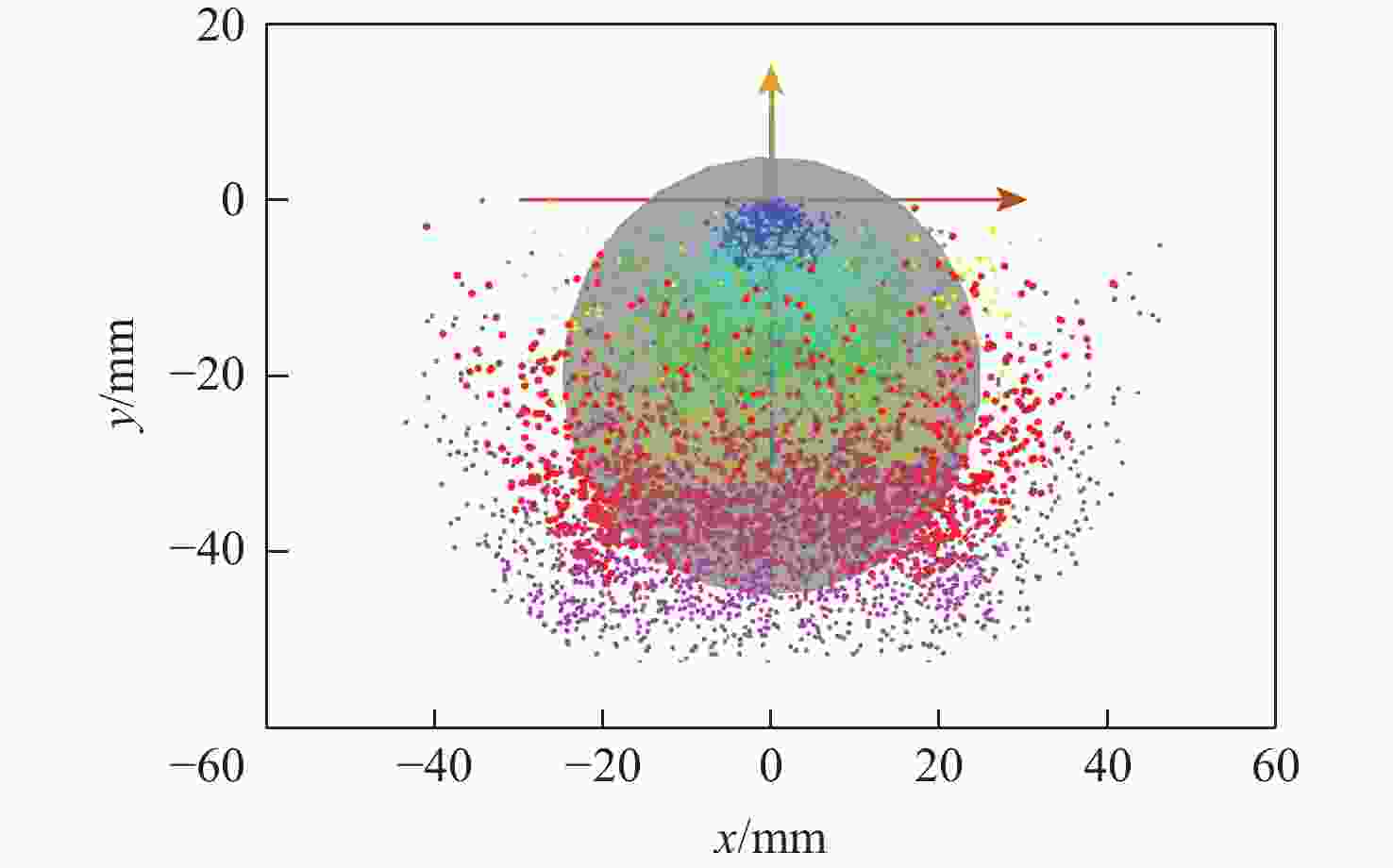
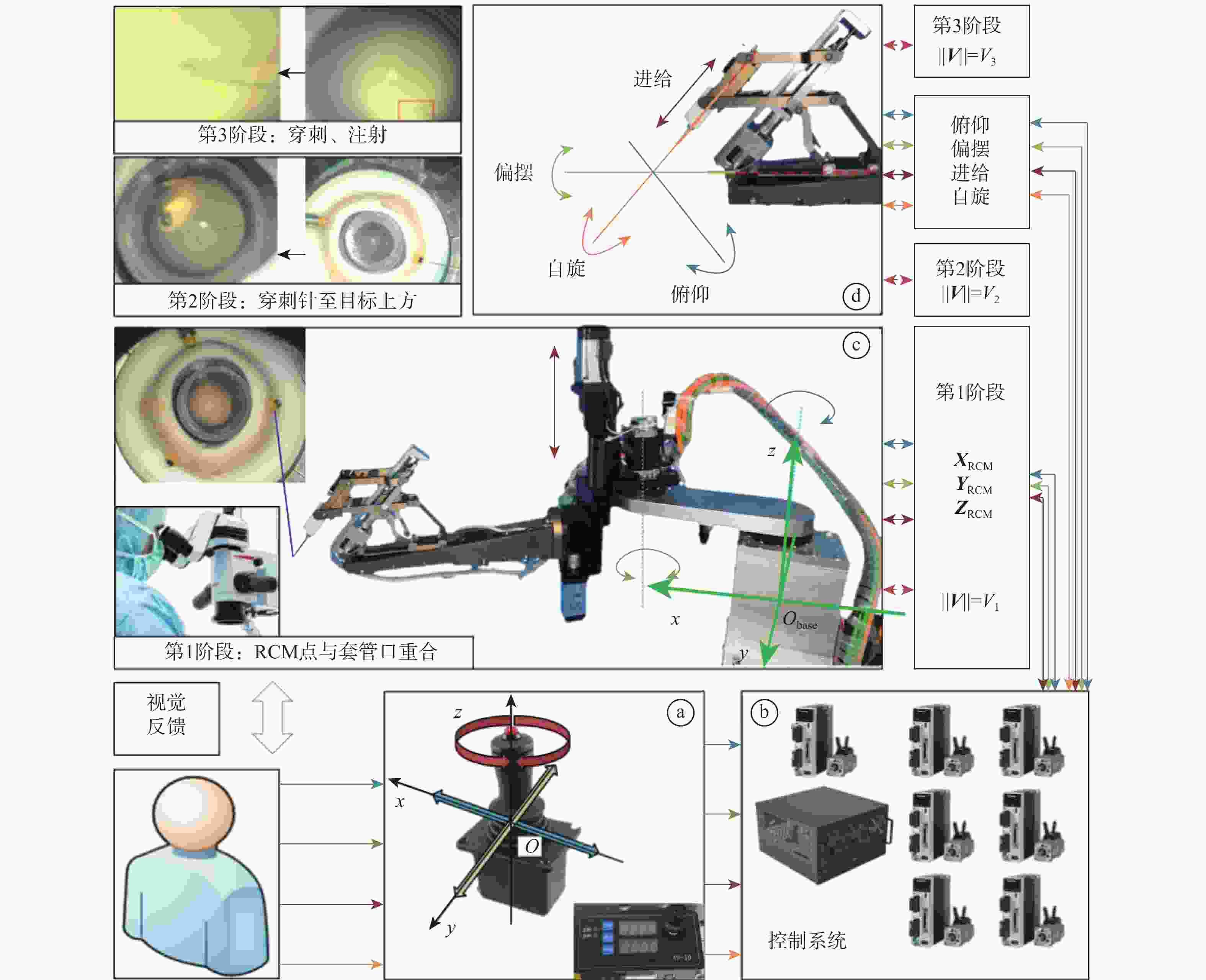
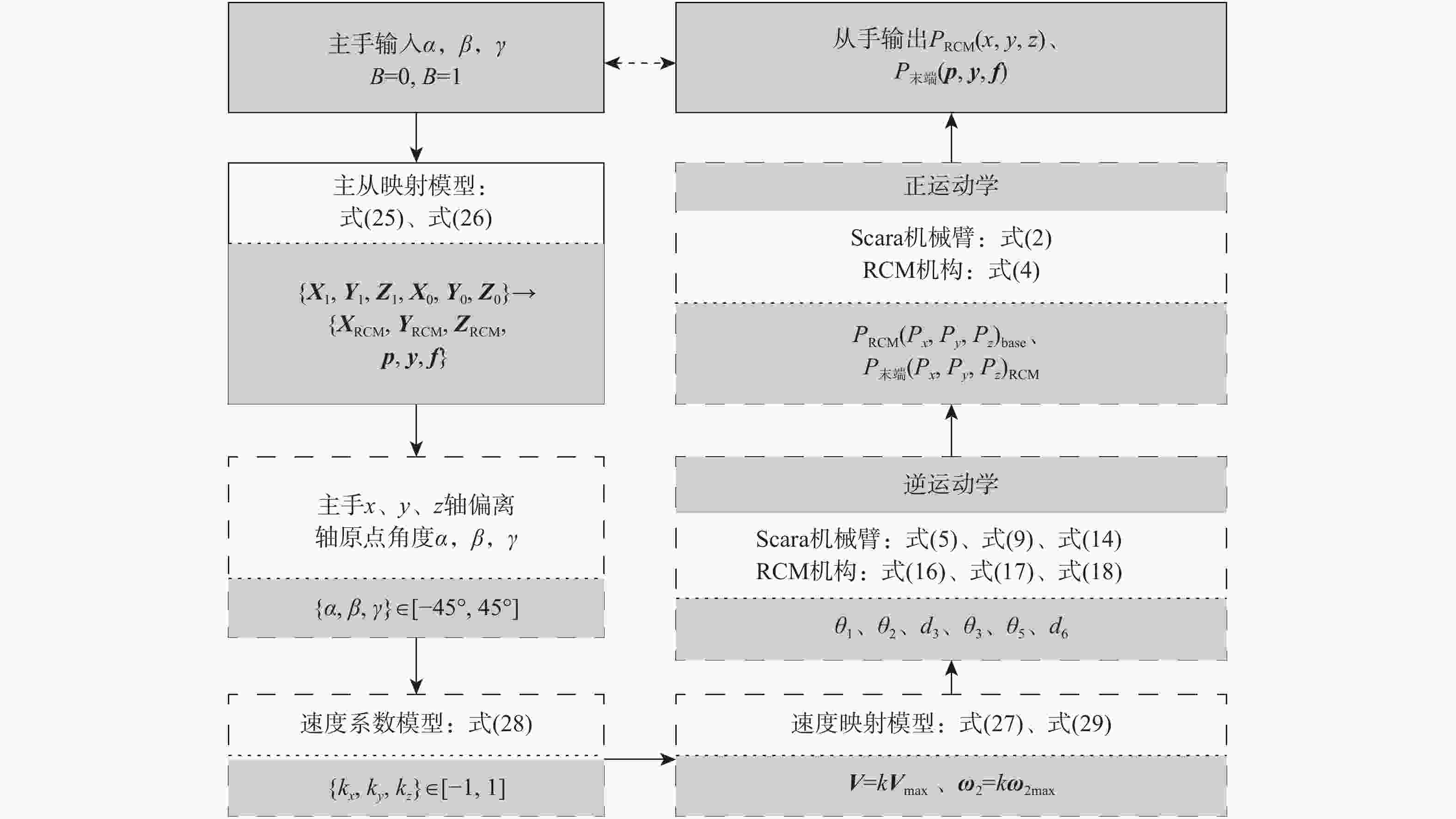
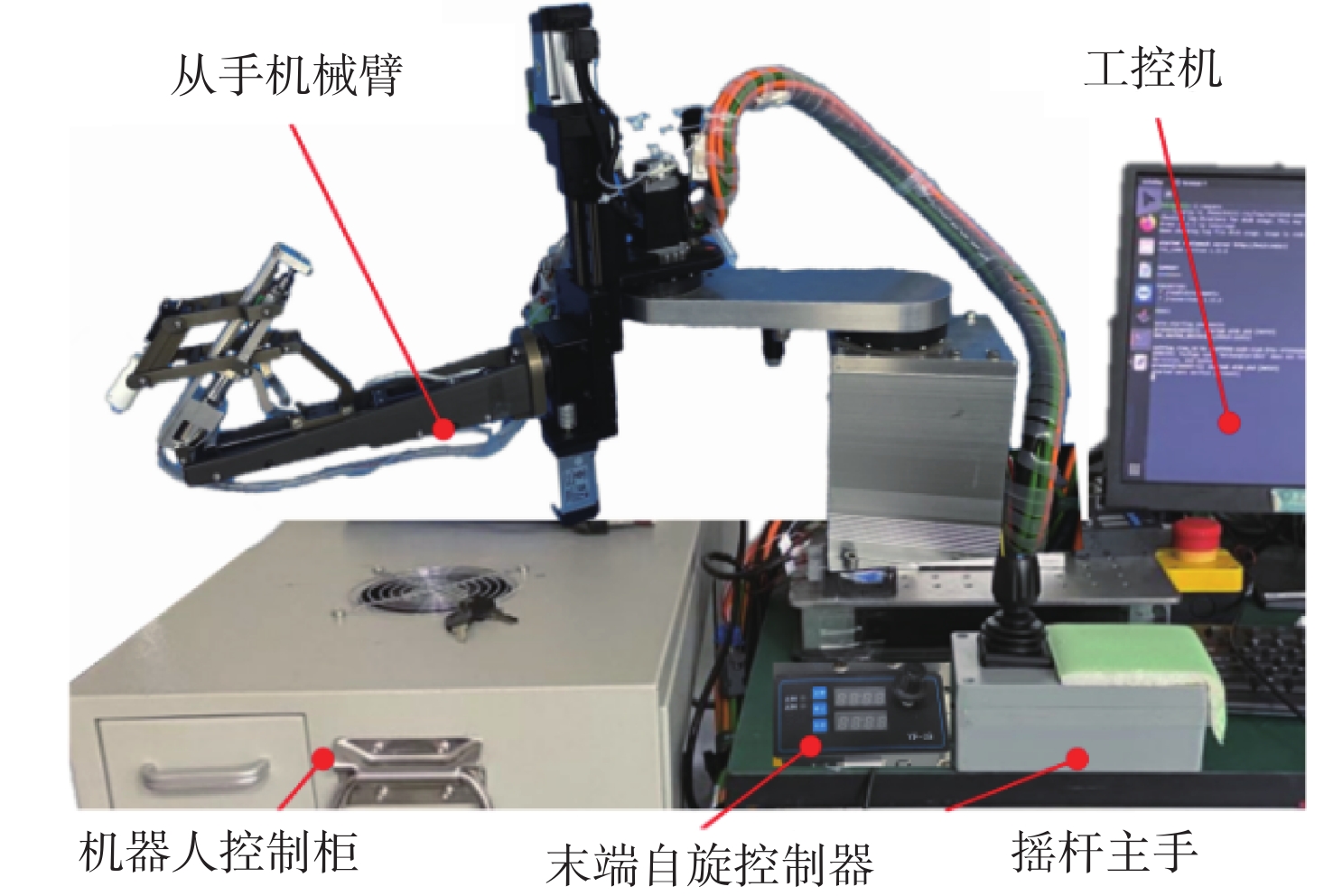
视网膜下注射人胚胎干细胞是治疗视网膜变性的一种有效术式,该术式对医生手术操作的精准性、稳定维持能力、安全性均提出了很高的要求。为此,提出一种基于主从式机器人的视网膜下注射系统,辅助医生完成视网膜下注射操作。构建从手机器人的正逆运动学模型,然后进行视网膜下注射手术运动分析,确定从手机器人的运动要求。建立主手和从手机器人之间的运动映射关系,依据运动映射关系推导建立远程运动中心(RCM)点位置调整运动、术中RCM运动的状态切换和分离过程的速度映射模型。通过离体猪眼球视网膜下穿刺注射实验对机器人的精确性和稳定维持能力进行验证,结果表明:机器人辅助操作系统末端注射针具有稳定维持能力和运动的精确性,机器人辅助操作比徒手操作对视网膜造成的创伤更小,注射更稳定。
-
关键词:
- 机器人辅助视网膜手术 /
- 主从控制 /
- 远程运动中心 /
- 眼内手术 /
- 显微手术
Abstract:Subretinal injection of human embryonic stem cells is an effective procedure for treating retinal degeneration, which imposes high demands on the precision, stability, and safety of the surgical procedure. To address these challenges, a robot-assisted retinal surgery system based on a master-slave control approach is proposed. The system utilizes a master robot to control a slave robot during the subretinal injection operation. By constructing the direct and inverse kinematic models of the slave robot, the precise motion requirements for the subretinal injection are determined. Additionally, the system incorporates the concept of the remote center of motion (RCM) to adjust the position of the surgical instruments during remote motion. A velocity mapping model is derived to facilitate the adjustment of the RCM point, state transitions, and separation process during the procedure.The validation of the system’s accuracy and stability is conducted through ex vivo porcine eyeball subretinal puncture injection experiments, simulating the conditions of intraocular surgery. The results demonstrate that the robot-assisted system exhibits stable needle maintenance and precise motion, indicating its superiority over manual procedures in terms of reducing trauma to the retina and achieving more stable injections. This technology represents a advancement in microsurgery techniques, enhancing the precision and safety of subretinal injection procedures for the treatment of retinal degeneration.
-
表 1 机器人性能指标
Table 1. Robot performance index
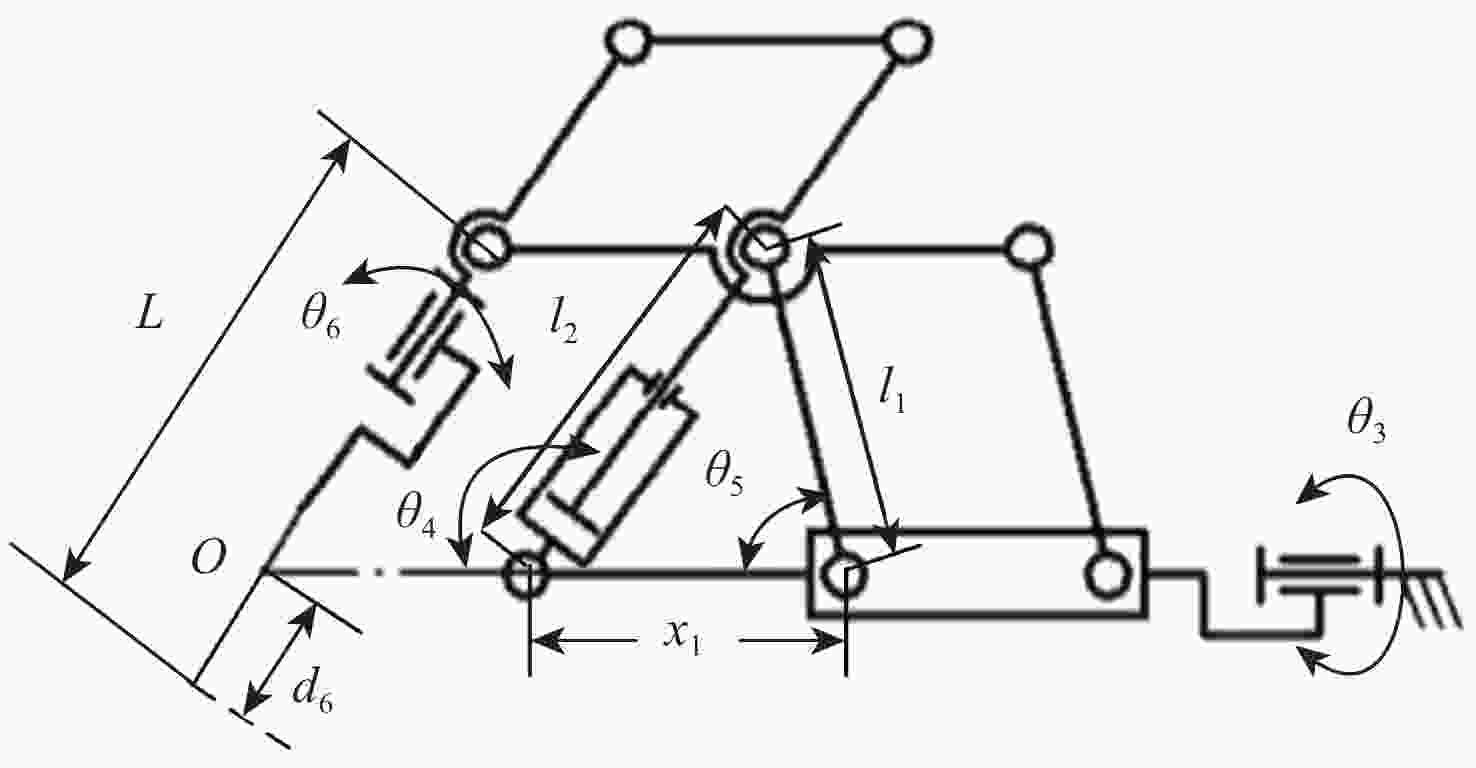
参数 数值 RCM点xyz运动范围/mm ±50 RCM点xyz运动精度/mm 0.01 俯仰运动范围/(°) ±30 翻滚运动范围/(°) ±90 俯仰/翻滚运动精度/rad 0.000 5 注射针自身轴向的旋转范围/(°) ±180 注射针自身轴向的旋转精度/(°) < 1 表 2 D-H参数表
Table 2. D-H parameter table
i zi-1到zi沿xi-1
距离ai-1zi-1到zi绕xi-1
角度αi-1/(°)xi-1到xi沿zi
距离dixi-1到xi绕zi
角度θi1 0 0 d1 θ1 2 a1 0 d2 θ2 3 a2 0 d3 −90° 4 0 −90 d4 −90°+θ3 5 0 −90 0 θ4 6 0 −90 d6 0 表 3 实验结果
Table 3. Experimental result
操作方式及编号 玻璃体腔漏液 视网膜创伤孔大小 眼球完整性 徒手操作1 +++ +++ 完整 徒手操作2 +++ ++ 完整 徒手操作3 + ++ 完整 徒手操作4 +++ +++ 完整 徒手操作5 + ++++ 完整 机器人辅助6 + + 完整 机器人辅助7 ++ ++ 完整 机器人辅助8 + + 完整 机器人辅助9 + + 完整 机器人辅助10 + + 完整 -
[1] MILLER J W, D’ANIERI L L, HUSAIN D, et al. Age-related macular degeneration (AMD): A view to the future[J]. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2021, 10(5): 1124. doi: 10.3390/jcm10051124 [2] HANDA J T, RICKMAN C B, DICK A D, et al. A systems biology approach towards understanding and treating non-neovascular age-related macular degeneration[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 106-116. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-08036-6 [3] ZHU J, LAMBA D A. Small molecule-based retinal differentiation of human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells[J]. Bio-Protocol, 2018, 8(12): e2882. [4] SHIRAI H, MANDAI M, MATSUSHITA K, et al. Transplantation of human embryonic stem cell-derived retinal tissue in two primate models of retinal degeneration[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(1): 81-90. [5] YE K, TAKEMOTO Y, ITO A, et al. Reproducible production and image-based quality evaluation of retinal pigment epithelium sheets from human induced pluripotent stem cells[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 1748-1760. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58656-6 [6] CHAO J R, LAMBA D A, KLESERT T R, et al. Transplantation of human embryonic stem cell-derived retinal cells into the subretinal space of a non-human primate[J]. Translational Vision Science & Technology, 2017, 6(3): 4. [7] HE C Y, YANG Y. Multipoint force-constrained admittance control for retinal surgical robot[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 57(9): 12-18. doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.09.012 [8] XIAO J J, YANG Y, SHEN L J, et al. A robotic system for retinal vascular bypass surgery[J]. Robot, 2014, 36(3): 293-299(in Chinese). [9] HE C Y, YANG Y, LIANG Q F, et al. Applications and research progress of robot assisted eye surgery[J]. Robot, 2019, 41(2): 265-275(in Chinese). [10] ÜNERI A, BALICKI M A, HANDA J, et al. New steady-hand eye robot with micro-force sensing for vitreoretinal surgery[C]//2010 3rd IEEE RAS & EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 814-819. [11] HE X C, ROPPENECKER D, GIERLACH D, et al. Toward clinically applicable steady-hand eye robot for vitreoretinal surgery[C]// Proceedings of ASME 2012 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition. New York: ASME, 2013: 145-153. [12] EDWARDS T L, XUE K, MEENINK H C M, et al. First-in-human study of the safety and viability of intraocular robotic surgery[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2018, 2(9): 649-656. doi: 10.1038/s41551-018-0248-4 [13] GIJBELS A, SMITS J, SCHOEVAERDTS L, et al. In-human robot-assisted retinal vein cannulation, D world first[J]. Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 2018, 46(10): 1676-1685. doi: 10.1007/s10439-018-2053-3 [14] GIJBELS A, WILLEKENS K, ESTEVENY L, et al. Towards a clinically applicable robotic assistance system for retinal vein cannulation[C]//2016 6th IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 284-291. [15] SU P, DENG S J, HUANG L, et al. Analysis and evaluation of a robotic trephination in penetrating keratoplasty[J]. Journal of Medical Devices, 2016, 10(2): 024503. doi: 10.1115/1.4032869 [16] XIAO J J, HUANG L, SHEN L J, et al. Design and research of a robotic aided system for retinal vascular bypass surgery[J]. Journal of Medical Devices, 2014, 8(4): 044501. doi: 10.1115/1.4027230 [17] HE C Y, HUANG L, YANG Y, et al. Research and realization of a master-slave robotic system for retinal vascular bypass surgery[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 31(1): 1-10. doi: 10.1186/s10033-018-0219-4 [18] HUANG L, YANG Y, SU P, et al. Type synthesis of 1R1T remote center of motion mechanisms[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 51(13): 131-136(in Chinese). doi: 10.3901/JME.2015.13.131 [19] SCRUGGS B A, JIAO C H, CRANSTON C M, et al. Optimizing donor cellular dissociation and subretinal injection parameters for stem cell-based treatments[J]. Stem Cells Translational Medicine, 2019, 8(8): 797-809. doi: 10.1002/sctm.18-0210 [20] SINGH S P N, RIVIERE C N. Physiological tremor amplitude during retinal microsurgery[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 28th Annual Northeast Bioengineering Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2002: 171-172. -







 下载:
下载: