Rapid detection analysis method of thermal runaway gas composition and risk of lithium ion battery
-
摘要:
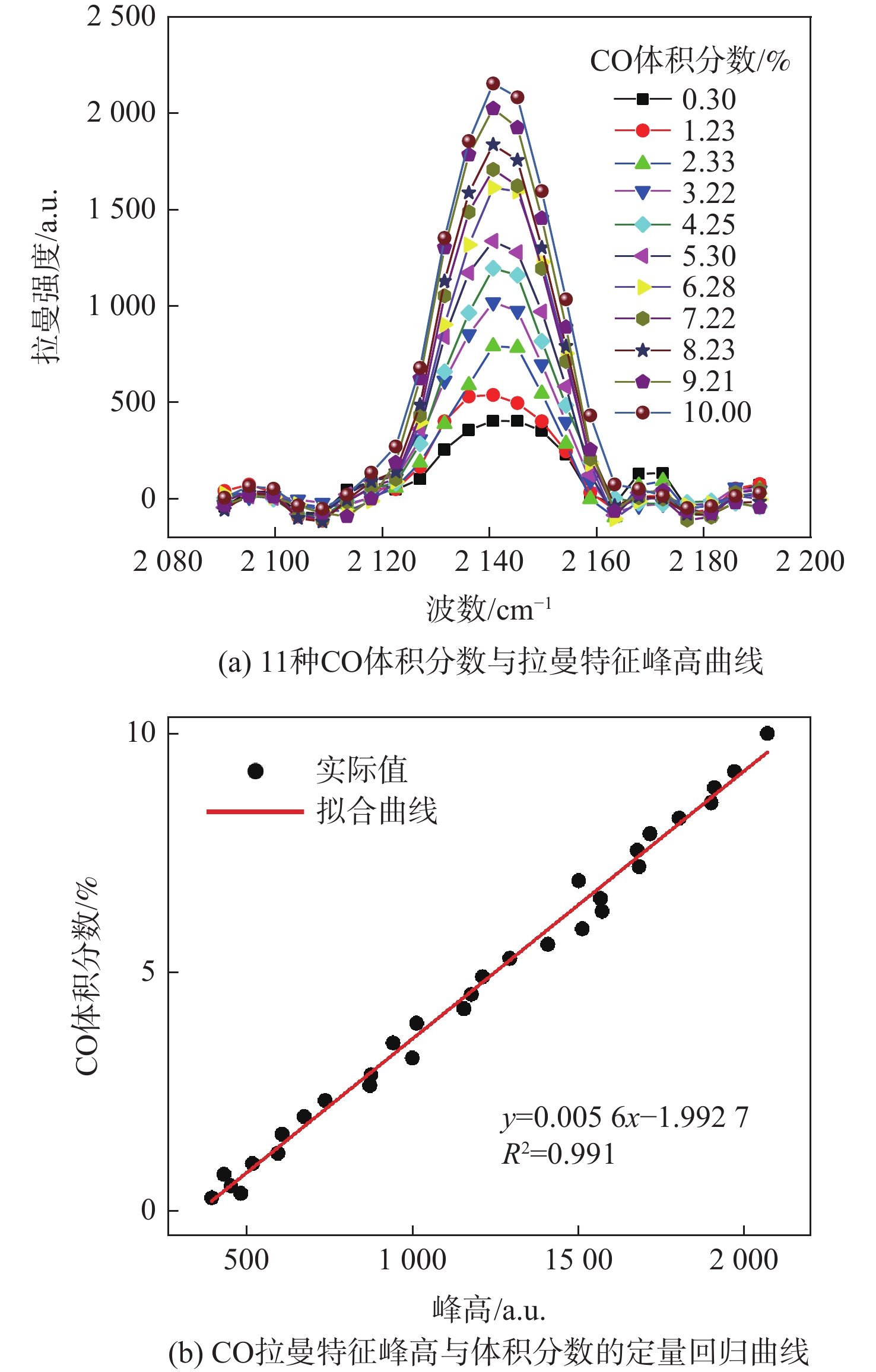
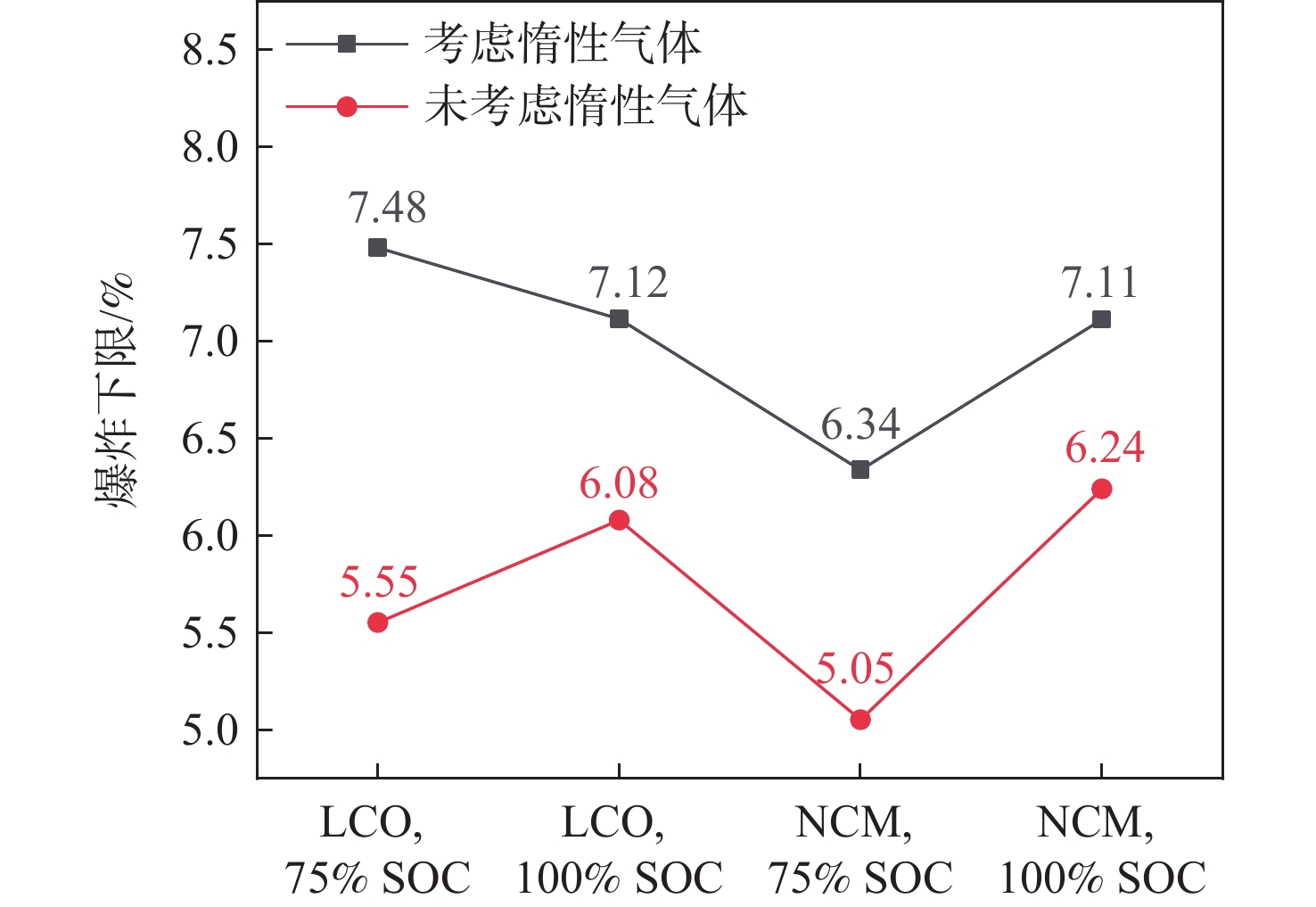
为实现对锂离子电池热失控气体成分及危险性进行快速分析,提出了一种基于激光拉曼光谱气体检测技术结合经验公式的分析方法。利用自主设计搭建的锂离子电池气体检测平台,使用不同荷电状态(75%、100%)和不同正极材料(LCO、NCM)的18650型锂离子电池对热失控气体成分及爆炸危险性分析方法进行验证。结果表明:相同荷电状态(SOC)下,NCM电池比LCO电池在热失控后释放的可燃气体量更多,100%荷电状态的NCM电池在热失控后容器内部CO占比高达22.02%,随着荷电状态的增加,锂离子电池热失控生成的可燃气体量增加。不同实验工况下,锂离子电池热失控后的气体仍具有较高的爆炸风险。研究结果证明了激光拉曼光谱气体检测技术检测锂离子电池热失控气体的可行性,为热失控气体成分和爆炸危险性的快速检测及分析提供了理论依据和技术支撑。
Abstract:In order to quickly analyze the composition and risk of thermal runaway gas in lithium ion batteries, an analysis method based on laser Raman spectroscopy and the empirical formula is proposed. Using the independently designed gas detection platform of the lithium ion battery, the composition and explosion risk of runaway gas released by a 18650 lithium ion battery with different charge states (75%,100%) and different cathode materials (LCO,NCM) were studied. According to the experimental findings, the NCM battery releases more flammable gas following thermal runaway than the LCO battery under the same state of charge (SOC). After thermal runaway, the proportion of CO in the container of NCM battery with 100% SOC is as high as 22.02%. With the increase of SOC, the amount of combustible gas generated by the thermal runaway of lithium ion batteries increases. Under different experimental conditions, the gas after the thermal runaway of the lithium-ion battery still had a high explosion risk. The findings demonstrate the viability of using laser Raman spectroscopy to identify lithium-ion battery thermal runaway gas, and they offer a theoretical foundation and technical backing for the quick identification and evaluation of the composition of thermal runaway gas and explosion danger.
-
Key words:
- lithium ion battery /
- thermal runaway /
- Raman spectroscopy /
- gas detection /
- explosion limit
-
表 1 实验电池参数
Table 1. Experimental battery parameters
正极材料 容量/(mA·h) 额定电压/V 截止电压/V 充电电压/V LCO 2200 3.6 2.65 4.2 NCM 2600 3.635 2.5 4.2 表 2 锂离子电池在不同实验条件下的实验数据
Table 2. Experimental data of lithium ion battery under various experimental conditions
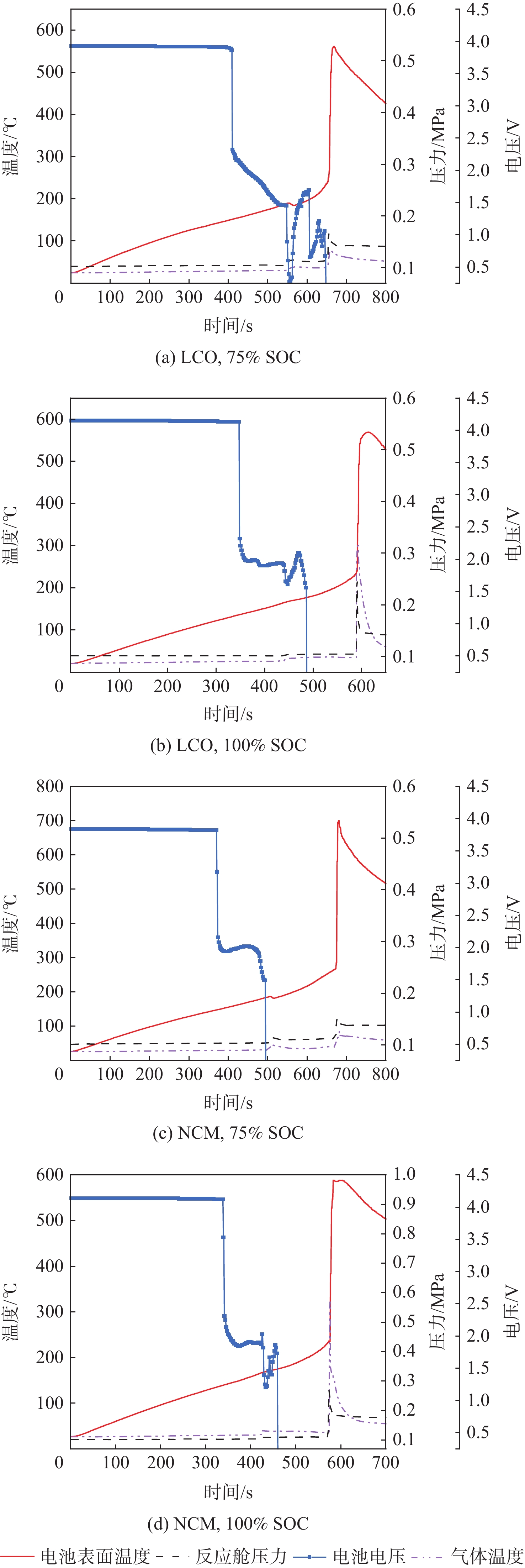
正极材料 T1/℃ T2/℃ ΔP/MPa Tgmax/℃ Tmax/℃ 75%SOC 100%SOC 75%SOC 100%SOC 75%SOC 100%SOC 75%SOC 100%SOC 75%SOC 100%SOC LCO 189.03 164.77 266.43 233.82 0.0386 0.1418 77.9 300.03 561.65 569.24 NCM 186.24 162.59 264.95 232.98 0.0515 0.1656 85.69 321.26 699.95 588.3 表 3 锂离子电池热失控气体分析结果
Table 3. Analysis results of thermal runaway gas of lithium ion battery
正极材料 N2体积分数/% O2体积分数/% H2体积分数/% CO2体积分数/% CO体积分数/% CxHy体积分数/% 75%SOC 100%SOC 75%SOC 100%SOC 75%SOC 100%SOC 75%SOC 100%SOC 75%SOC 100%SOC 75%SOC 100%SOC LCO 67.89 54.54 14.31 11.26 5.92 8.81 4.86 5.30 3.58 11.95 3.44 8.14 NCM 59.75 39.89 14.57 4.71 5.66 11.56 5.21 7.25 4.21 22.02 9.31 14.57 -
[1] 华政, 梁风, 姚耀春, 等. 电动汽车电池的发展现状与趋势[J]. 化工进展, 2017, 36(8): 2874-2881. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2017-0007HUA Z, LIANG F, YAO Y C, et al. Status and development trend for battery of electric vehicles[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2017, 36(8): 2874-2881(in Chinese). doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2017-0007 [2] 芮新宇, 冯旭宁, 韩雪冰, 等. 锂离子电池热失控蔓延问题研究综述[J]. 电池工业, 2020, 24(4): 193-201. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7923.2020.04.005RUI X Y, FENG X N, HAN X B, et al. Review on the thermal runaway propagation of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Chinese Battery Industry, 2020, 24(4): 193-201(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7923.2020.04.005 [3] 张青松, 罗星娜, 程相静, 等. 基于锂离子电池温降指数的细水雾添加剂筛选方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(6): 1073-1079. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0362ZHANG Q S, LUO X N, CHENG X J, et al. Method for screening fine water mist additive based on temperature drop index of lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(6): 1073-1079(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0362 [4] 许辉勇, 范亚飞, 张志萍, 等. 针刺和挤压作用下动力电池热失控特性与机理综述[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9(4): 1113-1126. doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2020.0028XU H Y, FAN Y F, ZHANG Z P, et al. Thermal runaway characteristics and mechanisms of Li-ion batteries for electric vehicles under nail penetration and crush[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(4): 1113-1126(in Chinese). doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2020.0028 [5] 张青松, 赵启臣. 过充循环对锂离子电池老化及安全性影响[J]. 高电压技术, 2020, 46(10): 3390-3397. doi: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20200361ZHANG Q S, ZHAO Q C. Effects of overcharge cycling on the aging and safety of lithium ion batteries[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2020, 46(10): 3390-3397(in Chinese). doi: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20200361 [6] 贺元骅, 郭君, 王海斌, 等. 振动环境对锂离子电池热失控危险性的影响[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(29): 12242-12246. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.29.061HE Y H, GUO J, WANG H B, et al. Impact of vibration on thermal runaway risk of lithium-ion battery[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(29): 12242-12246(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.29.061 [7] 郭志慧, 崔潇丹, 赵林双, 等. 高镍三元锂离子电池火灾及气体爆炸危险性实验[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(1): 193-200.GUO Z H, CUI X D, ZHAO L S, et al. Experimental research on fire and gas explosion hazards of high nickel lithium-ion battery[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(1): 193-200(in Chinese). [8] 张青松, 刘添添, 赵洋. 受限空间环境压力对三元锂离子电池热失控影响[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2021, 17(6): 36-40.ZHANG Q S, LIU T T, ZHAO Y. Effect of environmental pressure in confined space on thermal runaway of ternary lithium ion battery[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2021, 17(6): 36-40(in Chinese). [9] FERNANDES Y, BRY A, DE-PERSISI S. Identification and quantification of gases emitted during abuse tests by overcharge of a commercial Li-ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 389: 106-119. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.03.034 [10] YUAN L M, DUBANIEWICZ T, ZLOCHOWER I, et al. Experimental study on thermal runaway and vented gases of lithium-ion cells[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2020, 144: 186-192. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2020.07.028 [11] GOLUBKOV A W, FUCHS D, WAGNER J, et al. Thermal-runaway experiments on consumer Li-ion batteries with metal-oxide and olivine-type cathodes[J]. RSC Advances, 2014, 4: 3633-3642. doi: 10.1039/C3RA45748F [12] SUN J, LI J, ZHOU T, et al. Toxicity, a serious concern of thermal runaway from commercial Li-ion battery[J]. Nano Energy, 2016, 27: 313-319. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2016.06.031 [13] SAID A O, LEE C, STOLIAROV S I. Experimental investigation of cascading failure in 18650 lithium ion cell arrays: Impact of cathode chemistry[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 446: 227347. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.227347 [14] BULDAKOV M A, KOROLKOV V A, MATROSOV I I, et al. Analyzing natural gas by spontaneous Raman scattering spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Optical Technology, 2013, 80(7): 426-430. doi: 10.1364/JOT.80.000426 [15] SOMANDEPALLI V, MARR K, HORN Q. Quantification of combustion hazards of thermal runaway failures in lithium-ion batteries[J]. SAE International Journal of Alternative Powertrains, 2014, 3(1): 98-104. doi: 10.4271/2014-01-1857 [16] PENG Y, YANG L Z, JU X Y, et al. A comprehensive investigation on the thermal and toxic hazards of large format lithium-ion batteries with LiFePO4 cathode[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 381: 120916. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120916 [17] BAK S M, HU E Y, ZHOU Y N, et al. Structural changes and thermal stability of charged LiNixMnyCozO2 cathode materials studied by combined in situ time-resolved XRD and mass spectroscopy[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(24): 22594-22601. [18] PASQUIER A D, DISMA F, BOWMER T, et al. Differential scanning calorimetry study of the reactivity of carbon anodes in plastic Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1998, 145(4): 472-477. [19] YOSHIDA H, FUKUNAGA T, HAZAMA T, et al. Degradation mechanism of alkyl carbonate solvents used in lithium-ion cells during initial charging[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 1997, 68(2): 311-315. doi: 10.1016/S0378-7753(97)02635-9 [20] KIM G H, PESARAN A, SPOTNITZ R. A three-dimensional thermal abuse model for lithium-ion cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 170(2): 476-489. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2007.04.018 [21] DIAZ F, WANG Y F N, WEYHE R, et al. Gas generation measurement and evaluation during mechanical processing and thermal treatment of spent Li-ion batteries[J]. Waste Management, 2019, 84: 102-111. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2018.11.029 -








 下载:
下载: