-
摘要:
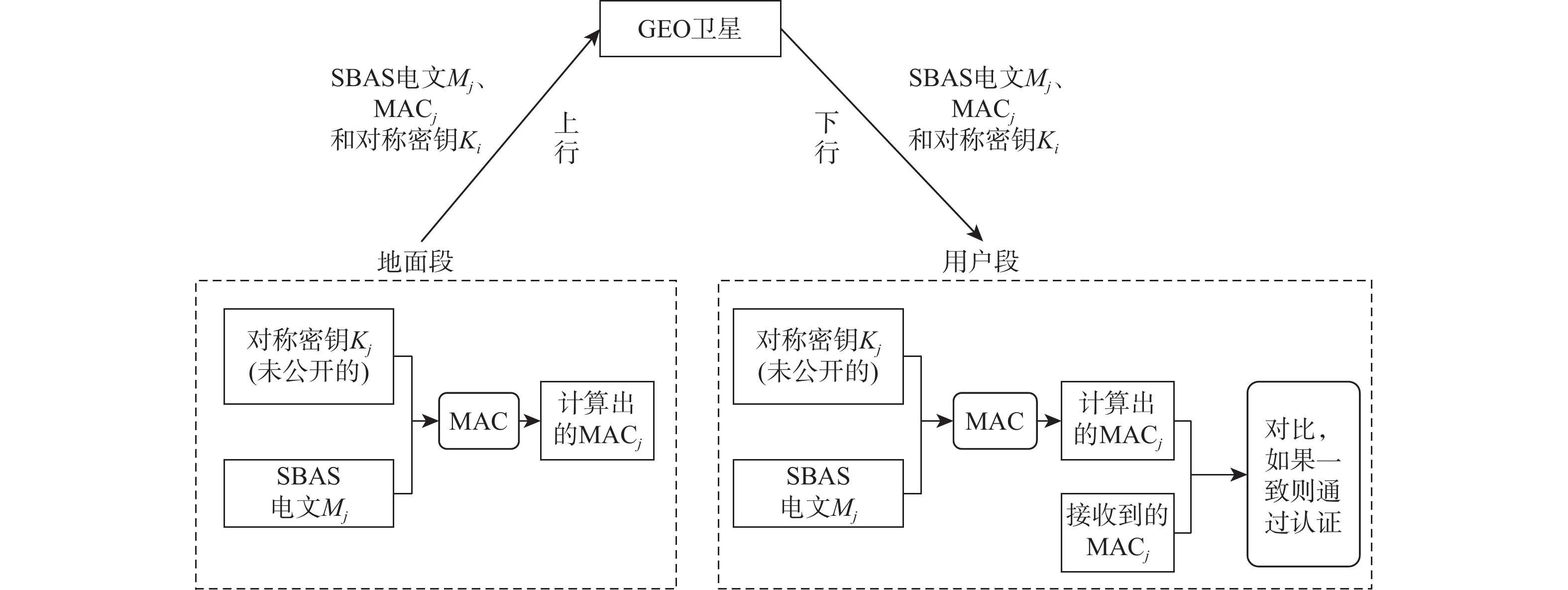
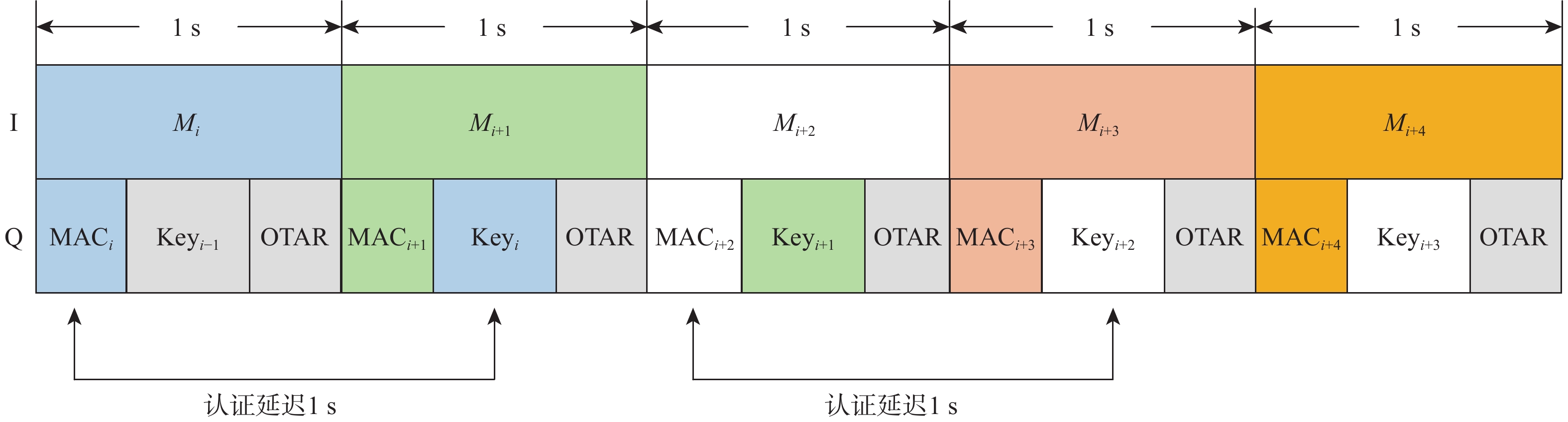
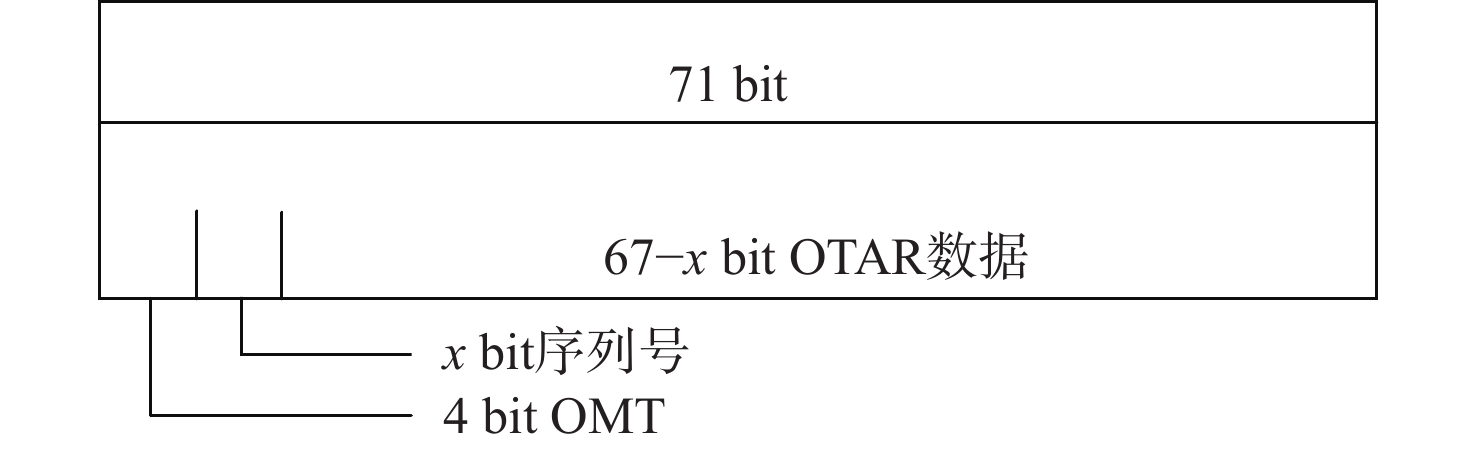
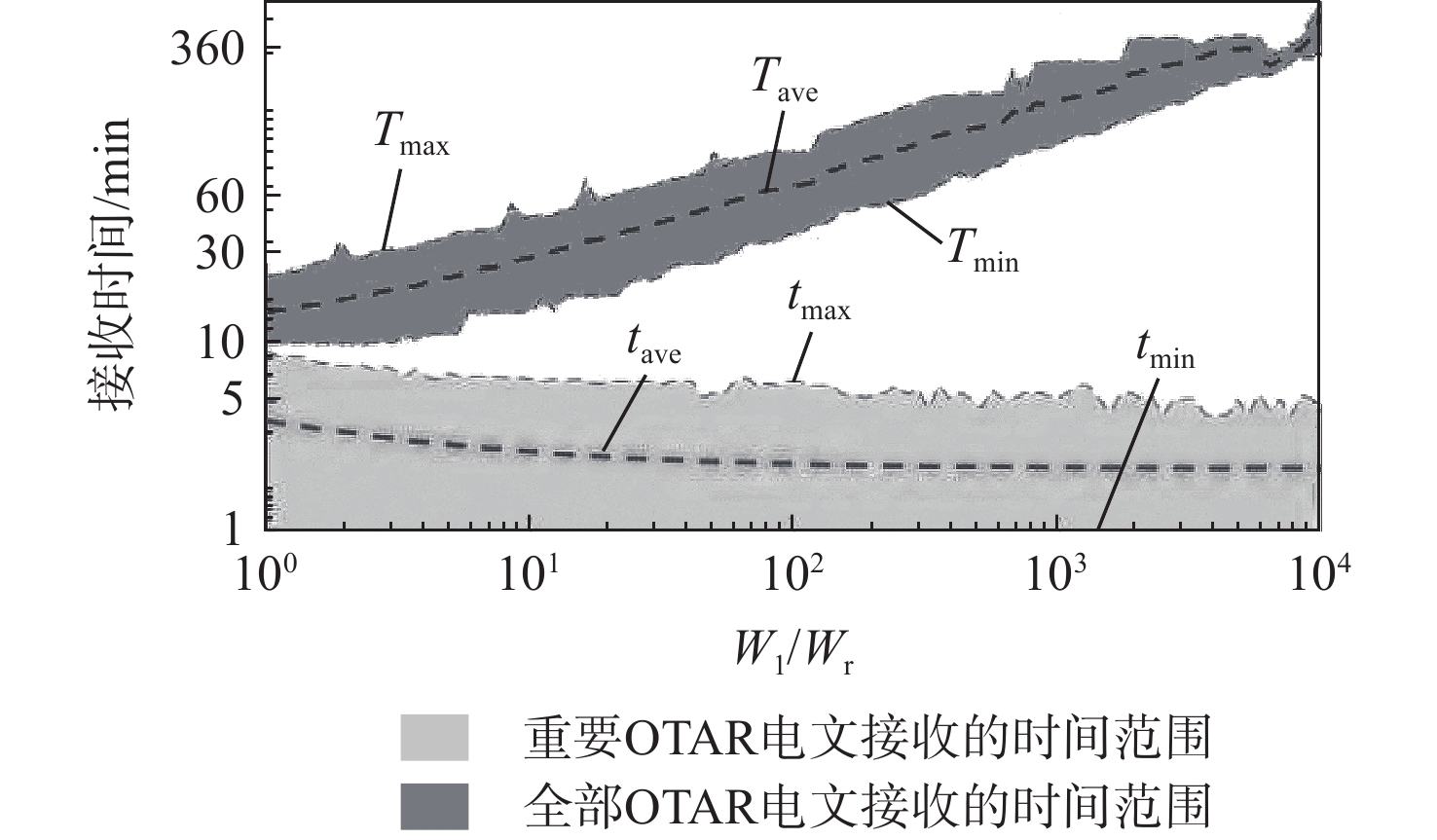
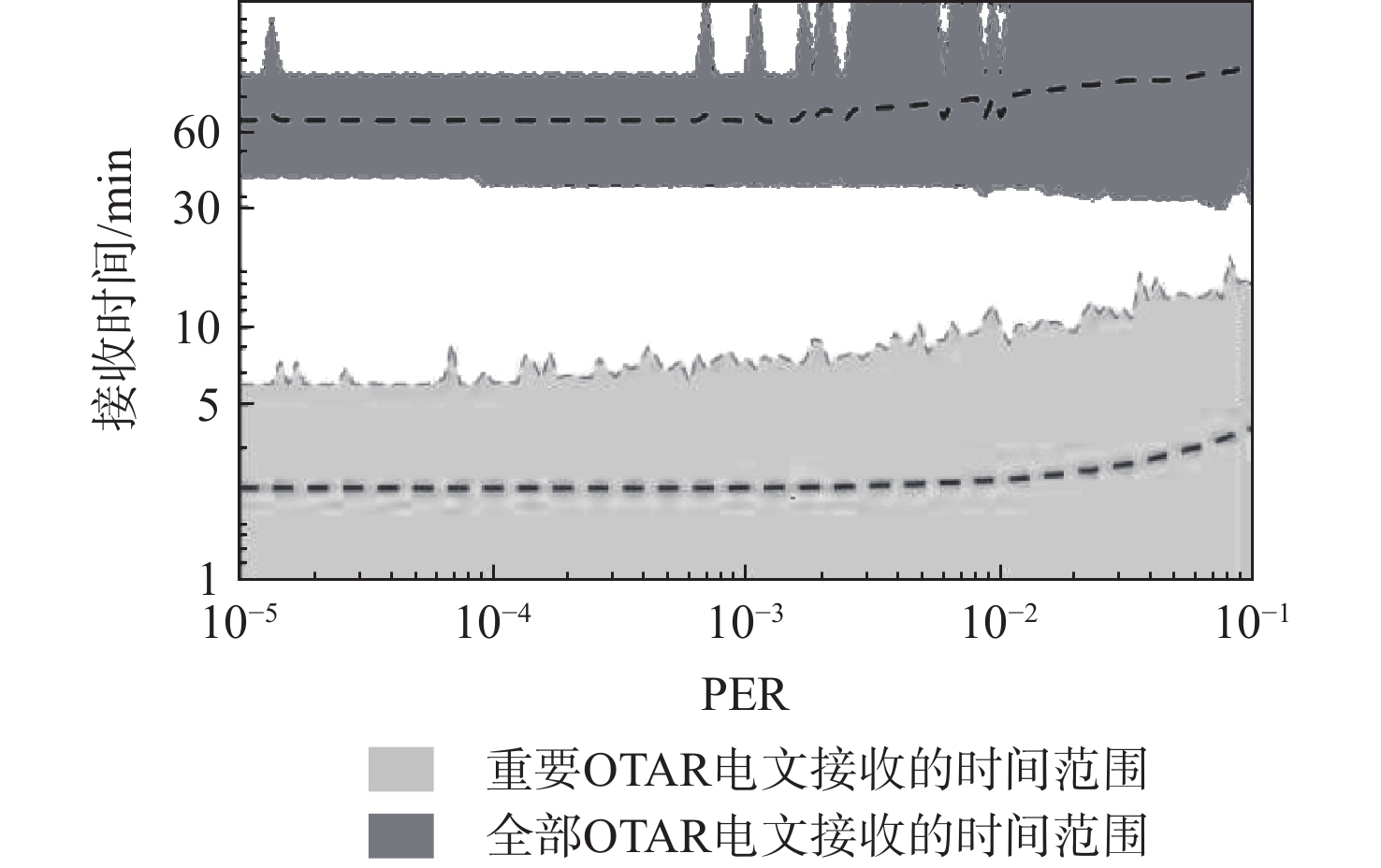
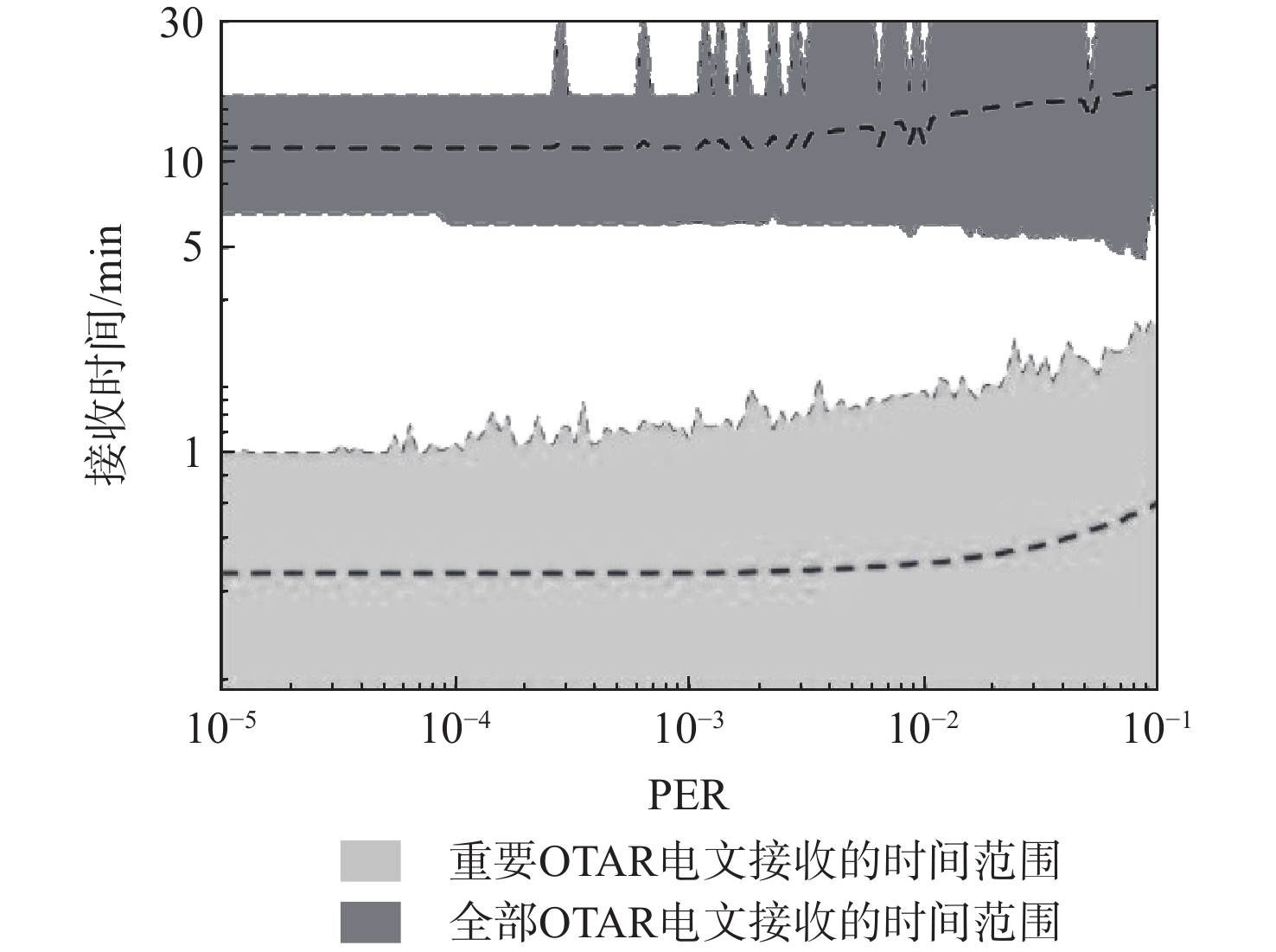
星基增强系统(SBAS)能为航空、航海等生命安全领域提供完好性增强服务,针对SBAS服务的欺骗风险,面向北斗星基增强系统(BDSBAS)发展,提出基于中国商用密码标准算法的时间效应流丢失容错认证机制(TESLA)电文认证方案。阐述SBAS电文认证架构与TESLA认证原理,开展基于中国商用密码标准算法的BDSABS认证电文编排及空中密钥更新(OTAR)的电文播发设计,针对L5I与L5Q开展认证时间间隔和最大认证延迟等指标的理论分析,进一步从OTAR信息权重和解调错误率2方面仿真首次认证时间指标。仿真结果能为基于TESLA协议的BDSBAS电文认证提供一定的理论支持。
-
关键词:
- 北斗星基增强系统 /
- 电文认证 /
- 消息认证码 /
- 时间效应流丢失容错认证机制 /
- 空中密钥更新
Abstract:Aviation, navigation, and other life safety areas can benefit from the integrity augmentation services offered by SBAS. In response to the deception risk of SBAS services and the development of the BeiDou satellite-based augmentation system (BDSBAS), this paper proposes a message authentication method based on the timed efficient streaming loss-tolerant authentication (TESLA) protocol. Firstly, this article introduces SBAS service security risks and the concept of message authentication and then explains the principle of TESLA, key chain generation, and operation process. The Over the Air Rekeying (OTAR) message broadcast design and authentication message format are created in accordance with the domestic commercial cryptographic standard hash algorithm. Finally, a simulation test is carried out for the L5I channel and the L5Q channel. The simulation results can provide theoretical support for the BDSBAS authentication based on the TESLA scheme.
-
表 1 TESLA OTAR播发电文类型
Table 1. TESLA OTAR message type
OTAR播发电文类型 定义 长度/bit OMT1 当前盐值、密钥链的根
密钥或中间密钥30+115 OMT2 当前盐值和根密钥的数字签名 512 OMT3 当前系统公钥 512 OMT4 当前系统公钥的CA数字签名 512 OMT5 当前盐值/密钥链/系统公钥/
认证机构公钥到期声明48 OMT6 到期声明的CA数字签名 512 OMT7 下一个盐值、密钥链的
根密钥或中间密钥30+115 OMT8 下一个盐值和根密钥或
者中间密钥的数字签名512 OMT9 下一个系统公钥 512 OMT10 下一个系统公钥的CA数字签名 512 OMT11 下一个认证机构公钥的3项签名证书 512*3 表 2 TESLA-I权重比对比结果
Table 2. Comparison results of weight ratio for TESLA-I
W1/Wr tave/s tmax/s tmin/s Tave/s 100 235.5 552 54 873.4 101 161.2 384 54 1688.2 102 138.3 378 54 3973.5 103 132.7 330 54 11505.7 104 131.5 252 54 32457.2 表 3 TESLA-Q权重比对比结果
Table 3. Comparison results of weight ratio for TESLA-Q
W1/Wr tave/s tmax/s tmin/s Tave/s 100 39.2 92 9 145.6 101 26.9 64 9 281.3 102 23.1 63 9 662.2 103 22.1 55 9 1917.6 104 21.9 42 9 5409.5 表 4 TESLA-I帧错误率对比结果
Table 4. Comparison results of TESLA-I PER
PER tave/s tmax/s tmin/s Tave/s 10−1 239.7 1056 54 6553.5 10−2 150.7 594 54 5004.1 10−3 139.5 498 54 3986.3 10−4 139.0 384 54 3985.6 10−5 139.2 360 54 3979.3 表 5 TESLA-Q帧错误率对比结果
Table 5. Comparison results of TESLA-Q PER
PER tave/s tmax/s tmin/s Tave/s 10−1 40.6 164 9 1087.3 10−2 25.1 98 9 828.1 10−3 23.3 74 9 663.3 10−4 23.2 65 9 663.4 10−5 23.2 60 9 663.8 表 6 基于ECDSA和TESLA方案的TBA和MAL指标
Table 6. TBA and MAL indicators based ECDSA and TESLA soulution
表 7 首次认证时间性能指标
Table 7. TTFA performance indicators
s 方案 不接收OTAR
电文时间tmax tmin tave Tave Tmin Tave TESLA-I 6~12 360 54 139.2 6000 2406 3979.3 TESLA-Q 1~2 60 9 23.2 1000 401 663.9 TESLA-I 6~12 264 66 134.2 6000 3858 4989.4 -
[1] 谭述森. 北斗卫星导航系统的发展与思考[J]. 宇航学报, 2008, 29(2): 391-396. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2008.02.001TAN S S. Development and thought of compass navigation satellite system[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2008, 29(2): 391-396(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2008.02.001 [2] PSIAKI M L, HUMPHREYS T E. GNSS spoofing and detection[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2016, 104(6): 1258-1270. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2016.2526658 [3] CHEN Y, GAO W G, CHEN X, et al. Advances of SBAS authentication technologies[J]. Satellite Navigation, 2021, 2(1): 1-7. doi: 10.1186/s43020-020-00033-9 [4] DALLA CHIARA A, DA BROI G, POZZOBON O, et al. Authentication concepts for satellite-based augmentation systems[C]//Proceedings of the 29th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation. Manassas: Institute of Navigation, 2016: 3208-3221. [5] ENGE P, WALTER T. Digital message authentication for SBAS and APNT[C]//Proceedings of the 27th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation. Manassas: Institute of Navigation , 2014: 1328-1336. [6] SCOTT L. Anti-spoofing & authenticated signal architectures for civil navigation systems[C]//Proceedings of the 16th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation. Manassas: Institute of Navigation, 2003: 1543-1552. [7] FERNáNDEZ-HERNáNDEZ I. GNSS authentication: Design parameters and service concepts[C]//Proceedings of the European Navigation Conference. Alphen aan den Rijn: EUGIN, 2014. [8] NEISH A, WALTER T, POWELL J D. SBAS data authentication: a concept of operations[C]//Proceedings of the 32nd International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation. Manassas: Institute of Navigation, 2019: 1812-1823. [9] DALLA CHIARA A, DA BROI G, POZZOBON O, et al. SBAS authentication proposals and performance assessment[C]//Proceedings of the 30th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation. Manassas: Institute of Navigation, 2017: 2106-2116. [10] FERNÁNDEZ-HERNÁNDEZ I, WALTER T, NEISH A M, et al. SBAS message authentication: A review of protocols, figures of merit and standardization plans[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 International Technical Meeting of the Institute of Navigation. Manassas: Institute of Navigation, 2021: 111-124. [11] 穆盛林, 陈颖, 刘婷, 等. 面向BDSBAS电文认证的OTAR播发策略设计[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(7): 1453-1461. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2020.0222MU S L, CHEN Y, LIU T, et al. Design of message authentication and OTAR broadcast strategy for BDSBAS[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(7): 1453-1461(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2020.0222 [12] NEISH A, WALTER T, ENGE P. Parameter selection for the TESLA keychain[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation. Manassas: Institute of Navigation, 2018: 2155-2171. [13] NEISH A, WALTER T, ENGE P. Quantum-resistant authentication algorithms for satellite-based augmentation systems[J]. Navigation, 2019, 66(1): 199-209. doi: 10.1002/navi.287 [14] NEISH A, WALTER T, POWELL J D. Design and analysis of a public key infrastructure for SBAS data authentication[C]//Proceedings of the ION 2019 Pacific PNT Meeting. Manassas: Institute of Navigation, 2019: 964-988. [15] PERRIG A, CANETTI R, TYGAR J D, et al. Efficient authentication and signing of multicast streams over lossy channels[C]//Proceeding 2000 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2002: 56-73. [16] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检查检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. SM3密码杂凑算法: GB/T 32905—2016. [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Information security techniques—SM3 cryptographic hash algorithm: GB/T 32905—2016 [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017(in Chinese) [17] Satellite Based Augmentation System Interoperability Working Group. SBAS L5 DFMC interface control document [S]. Montreal: SBAS IWG, 2015 [18] FERNÁNDEZ-HERNÁNDEZ I, CHÂTRE E, DALLA CHIARA A, et al. Impact analysis of SBAS authentication[J]. Navigation, 2018, 65(4): 517-532. doi: 10.1002/navi.267 [19] 结城浩著. 图解密码技术[M]. 周自恒译. 第3版. 北京: 人民邮电出版社, 2016.HIROSHI Y K. Graphic cryptography technology[M]. ZHOU Z H translated. 3rd ed. Beijing: Posts & Telecom Press, 2016 (in Chinese). [20] NEISH A. Establishing trust through authentication in satellite based augmentation systems[D]. Stanford: Stanford University, 2020. -








 下载:
下载: