Design optimization of tow-steered composite structure targeting on manufacturing cost
-
摘要:
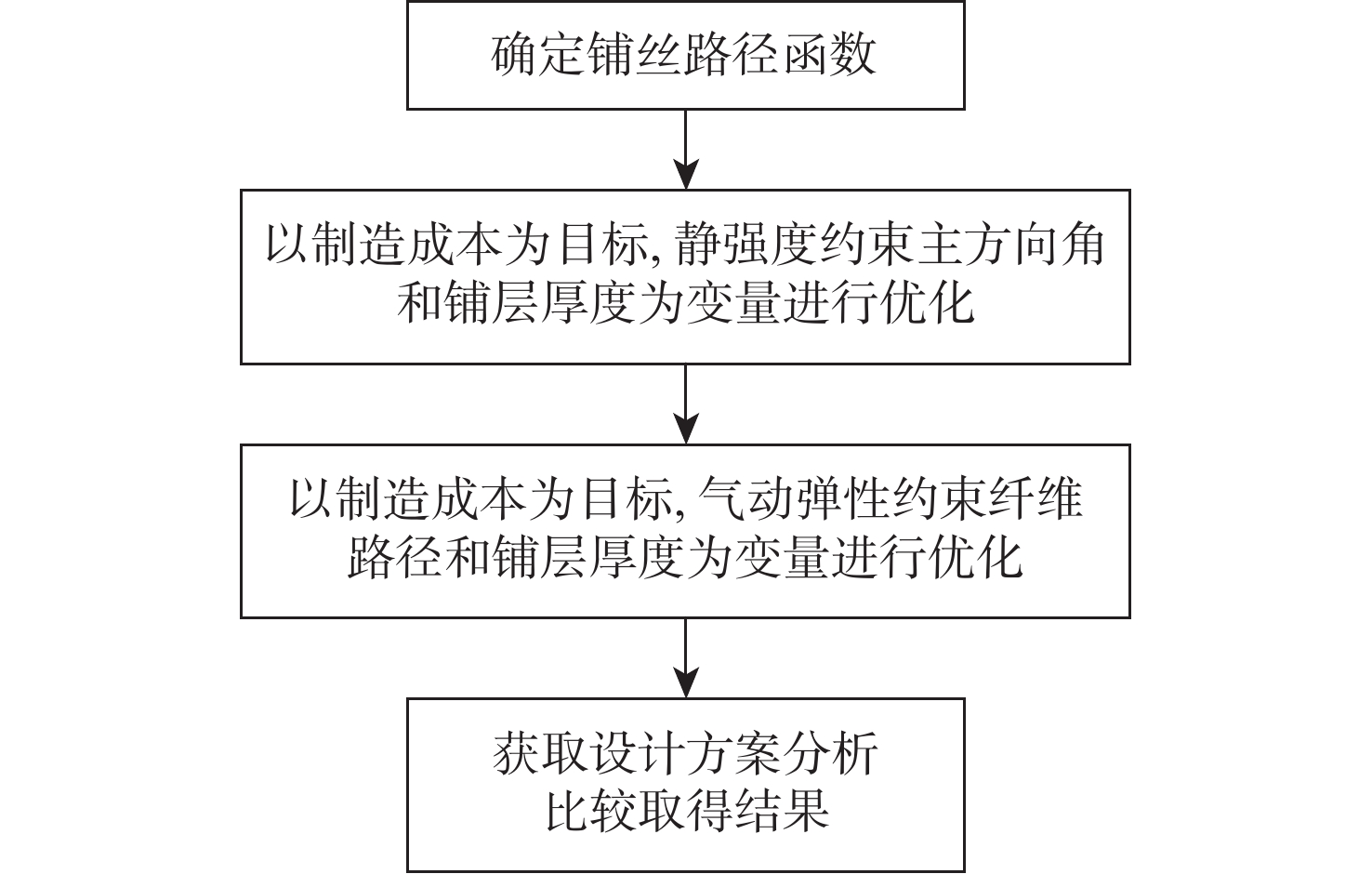
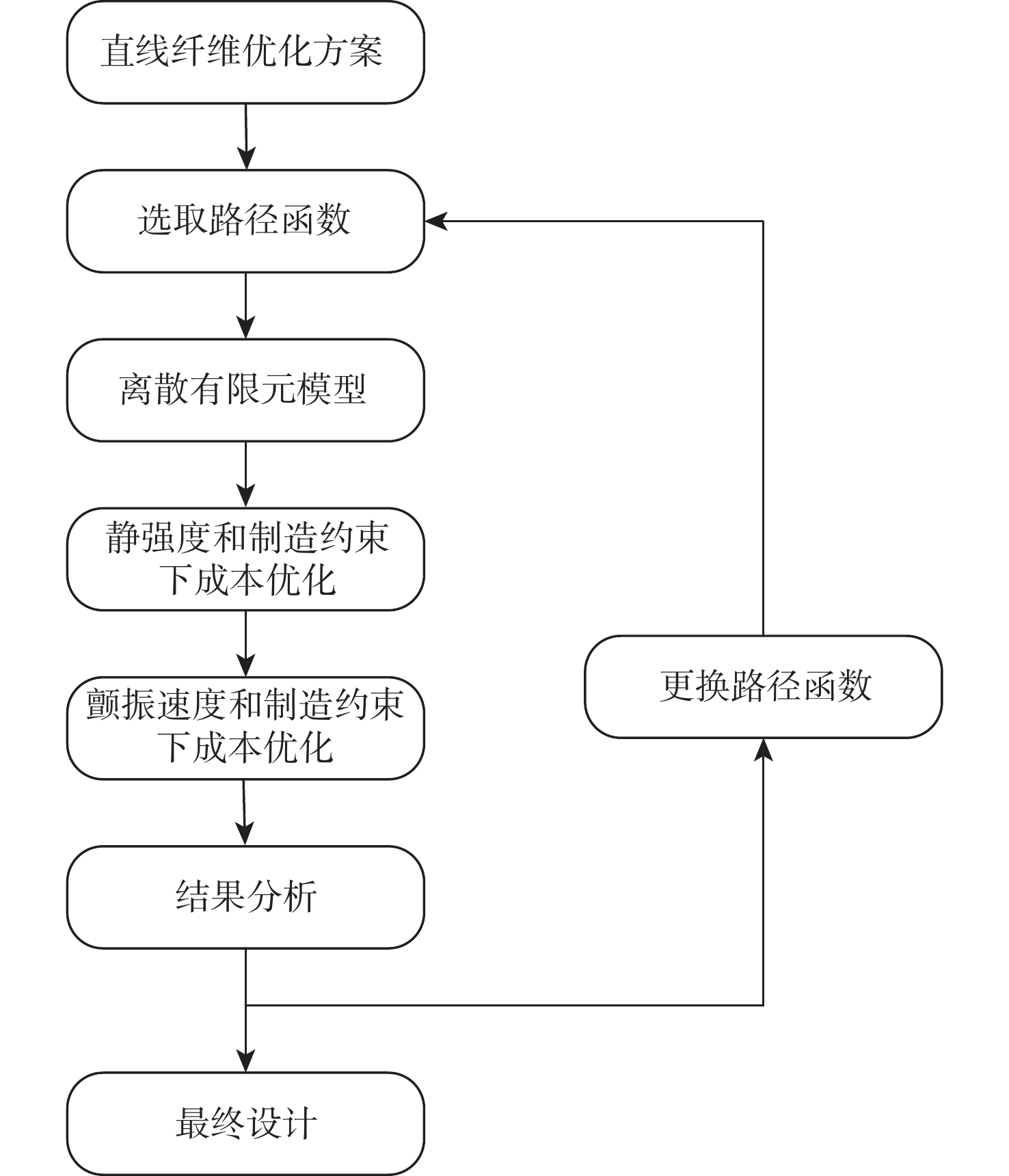
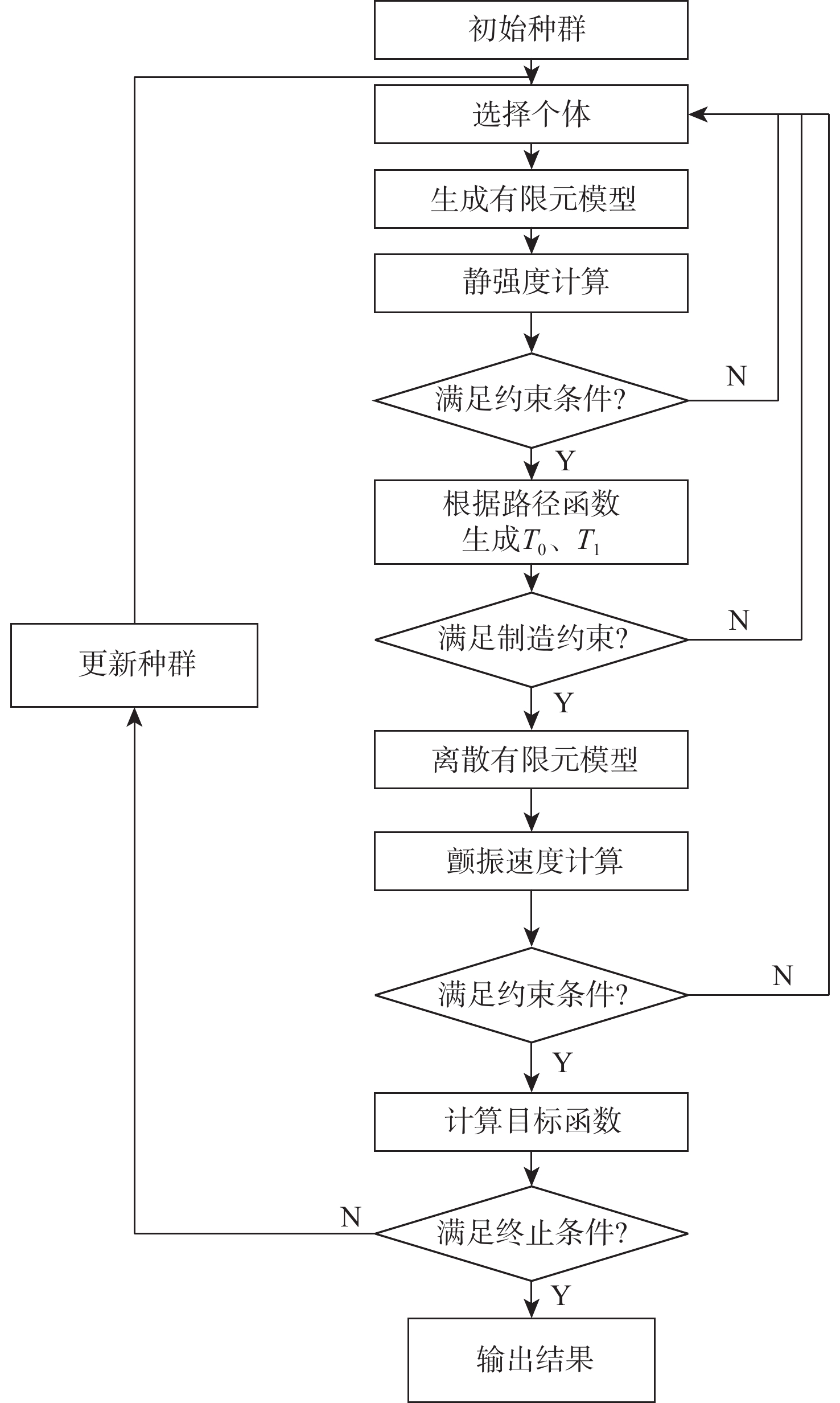
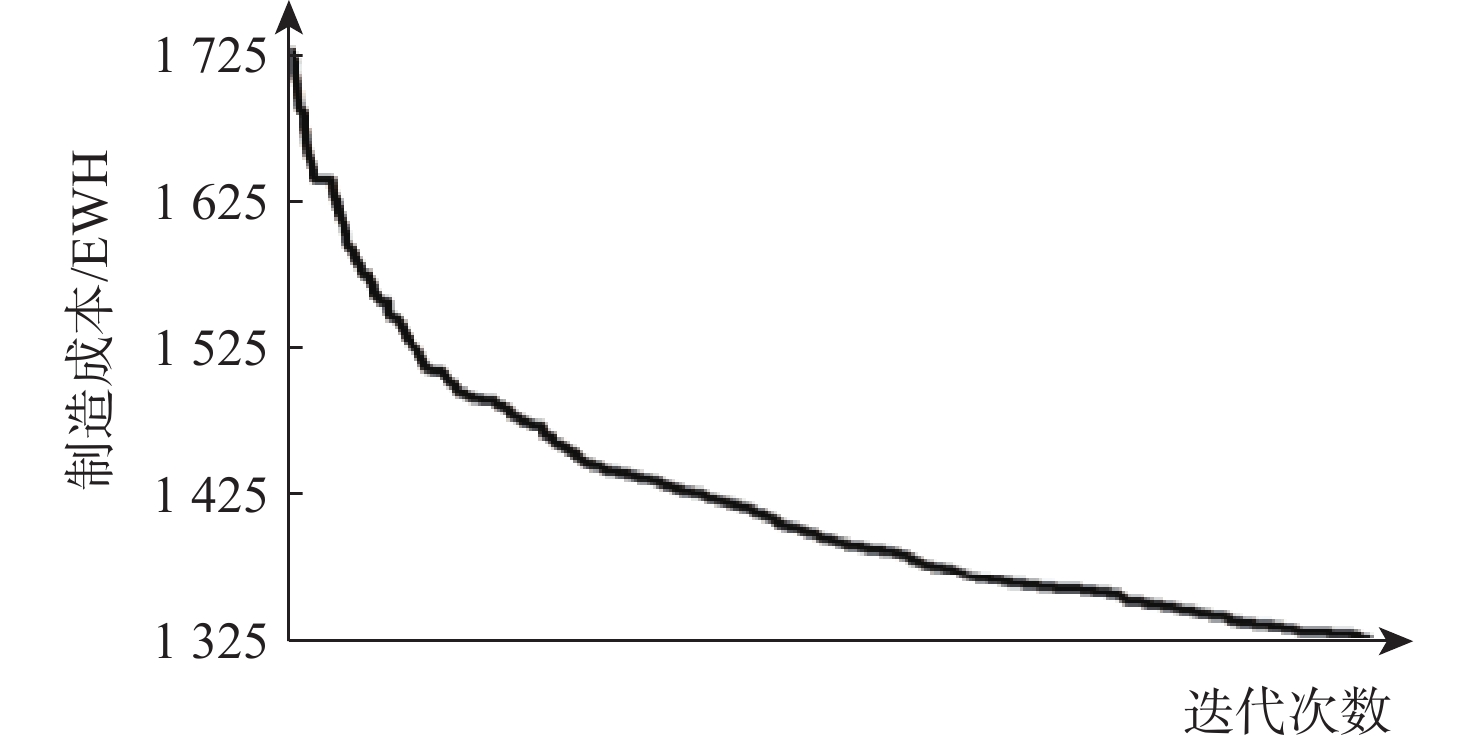
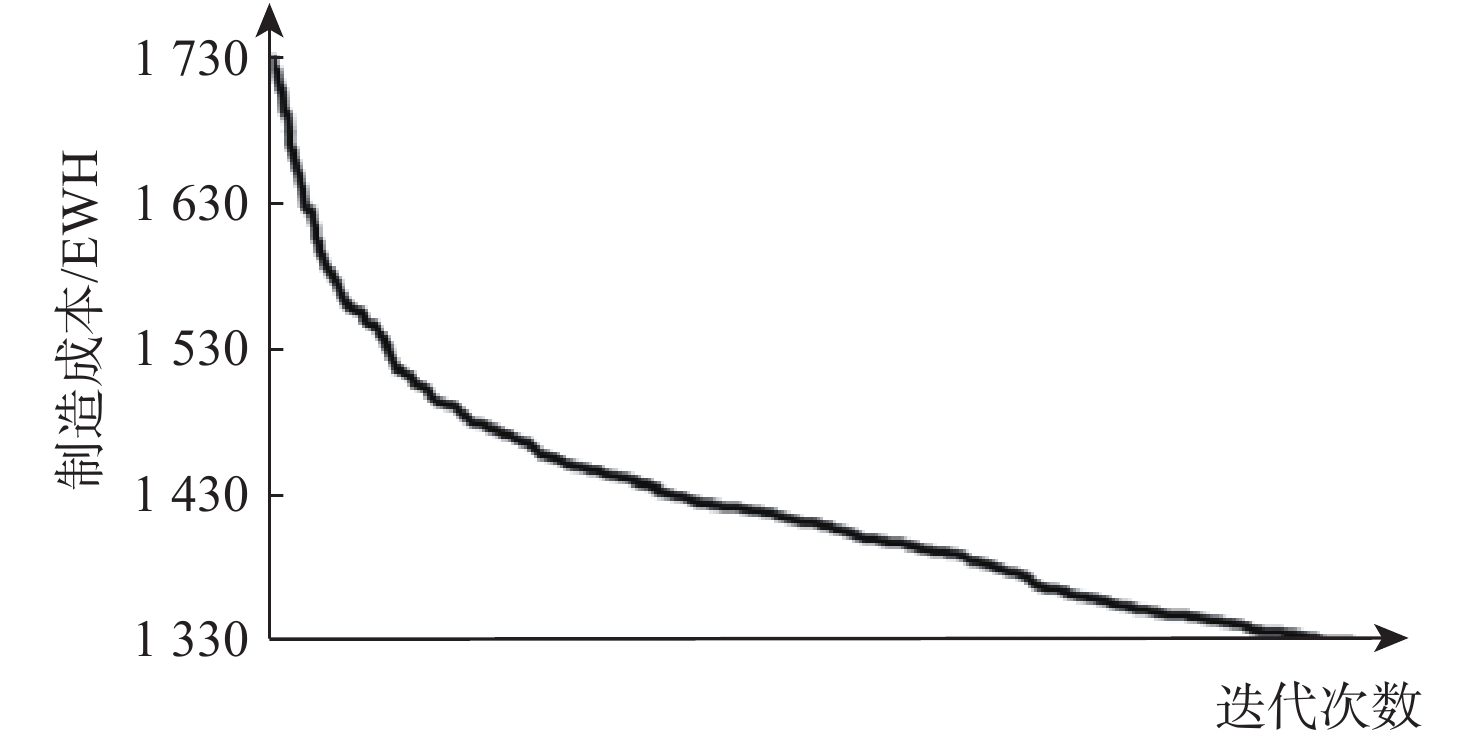
传统的复合材料结构设计方法未能有效利用复合材料的面内设计空间,变刚度结构的实用化为复合材料结构效能的提升提供了新的机会。使用制造工艺成本模型,以制造成本为目标函数,建立结构性能约束和制造约束,通过路径函数法和平移法对一型大展弦比机翼进行变刚度设计,建立了以制造成本为目标的变刚度复合材料结构设计优化方法,实现制造成本减少23.87%,结构减重35.58%,并分析了不同纤维路径对变刚度结构构型设计、性能、质量和制造过程的影响。
Abstract:Due to a number of limitations, traditional composite structure design approaches are unable to completely use the design space of composite. The realization of tow-steered composite brings new opportunities for improvement of the performance of composites. In this research, a tow-steered composite structure design optimization method is established. The optimization method was based on the manufacturing process cost model, manufacturing cost was set as the target function, performance and manufacturing constraints were established, and the fiber path function method and shifted method were selected. On a high respect ratio wing, the tow-steered design optimization realized a 23.87% deduction on manufacturing cost and a 35.58% deduction on structural weight. The research further analyzed the impacts fiber path exerts on configuration, performance, weight, and manufacturing processes.
-
Key words:
- composite /
- tow-steer /
- manufacturing cost /
- structure optimization /
- genetic algorithm
-
表 1 机翼基本参数
Table 1. Basic parameters of wing
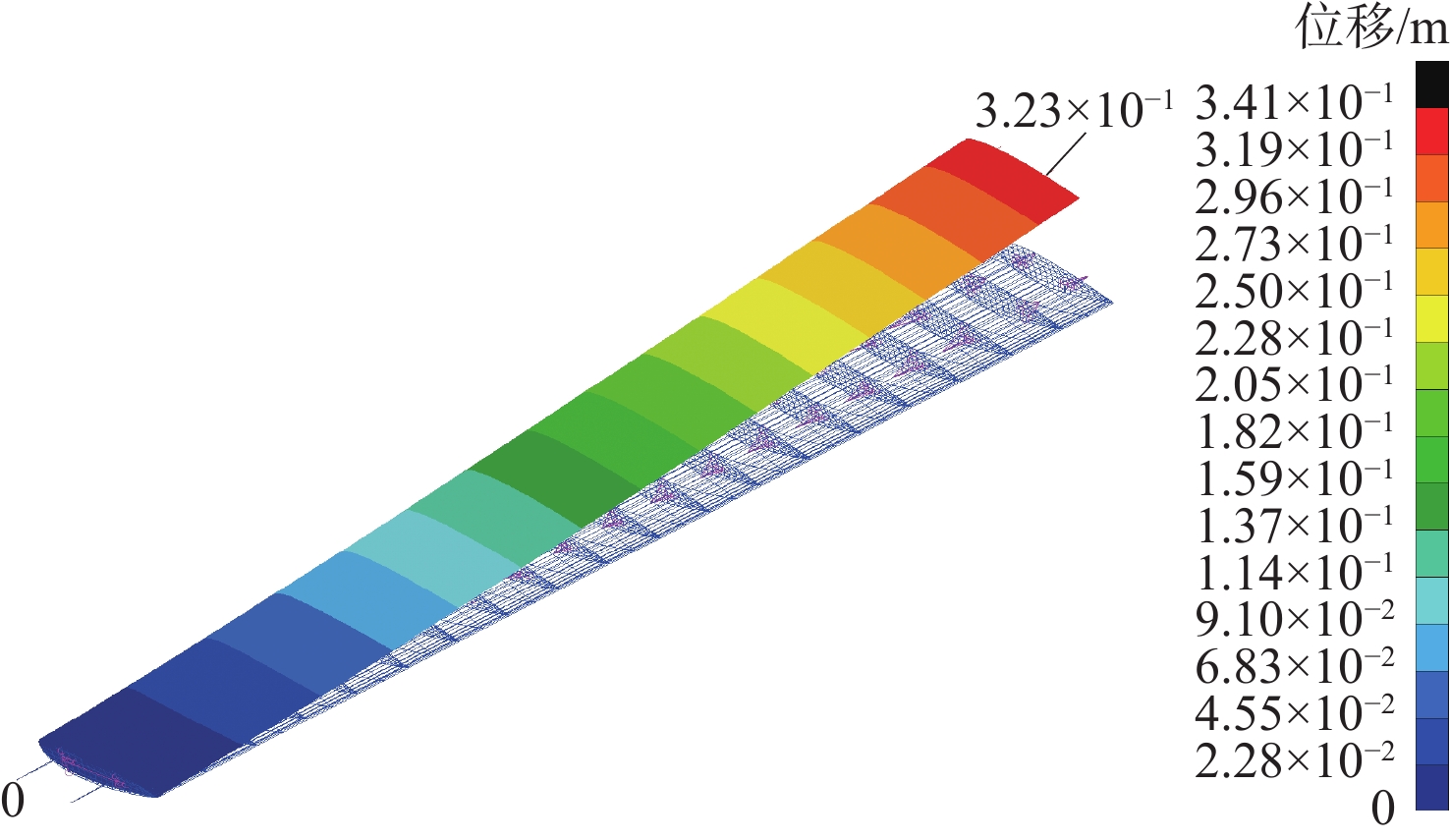
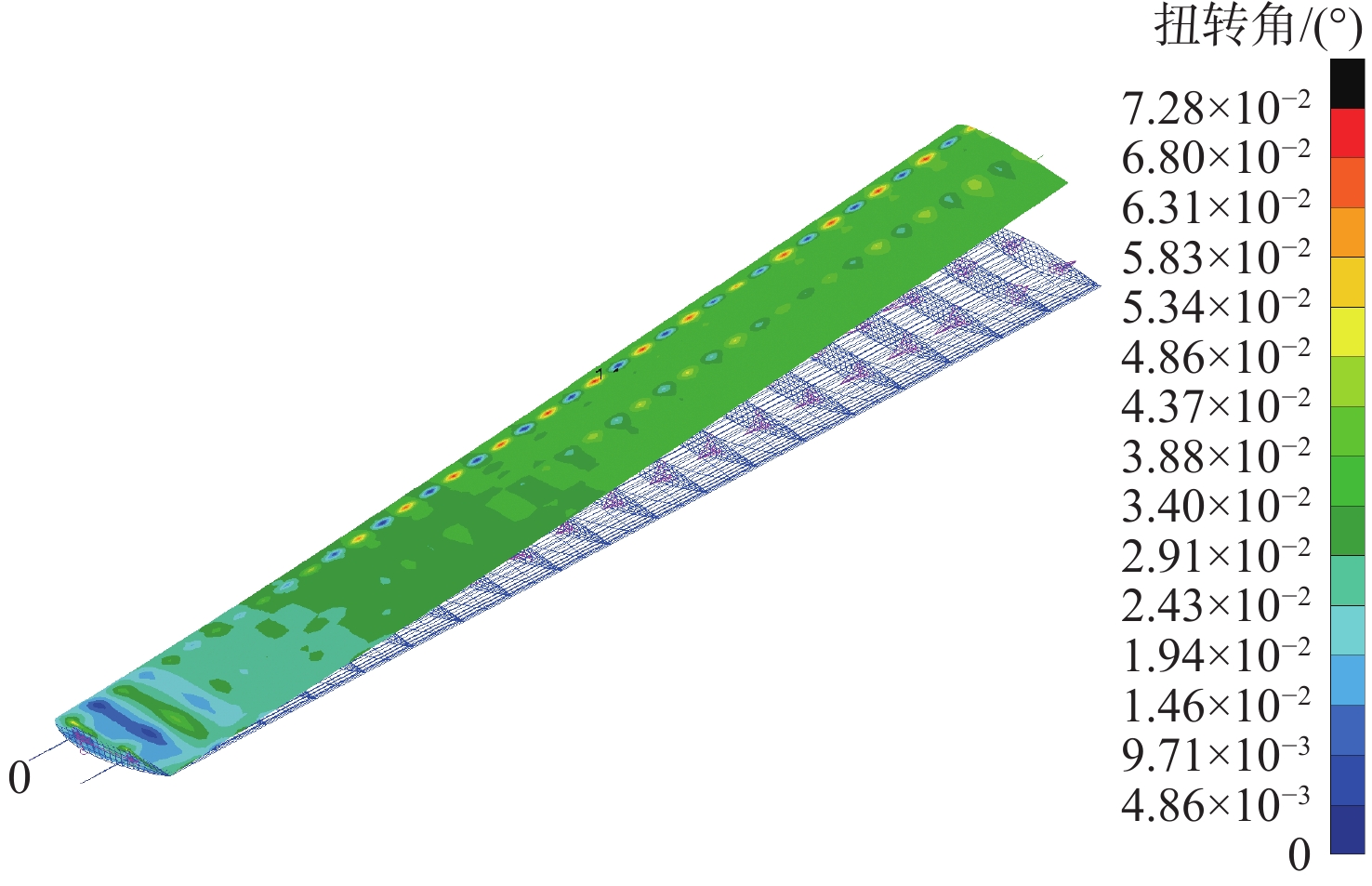
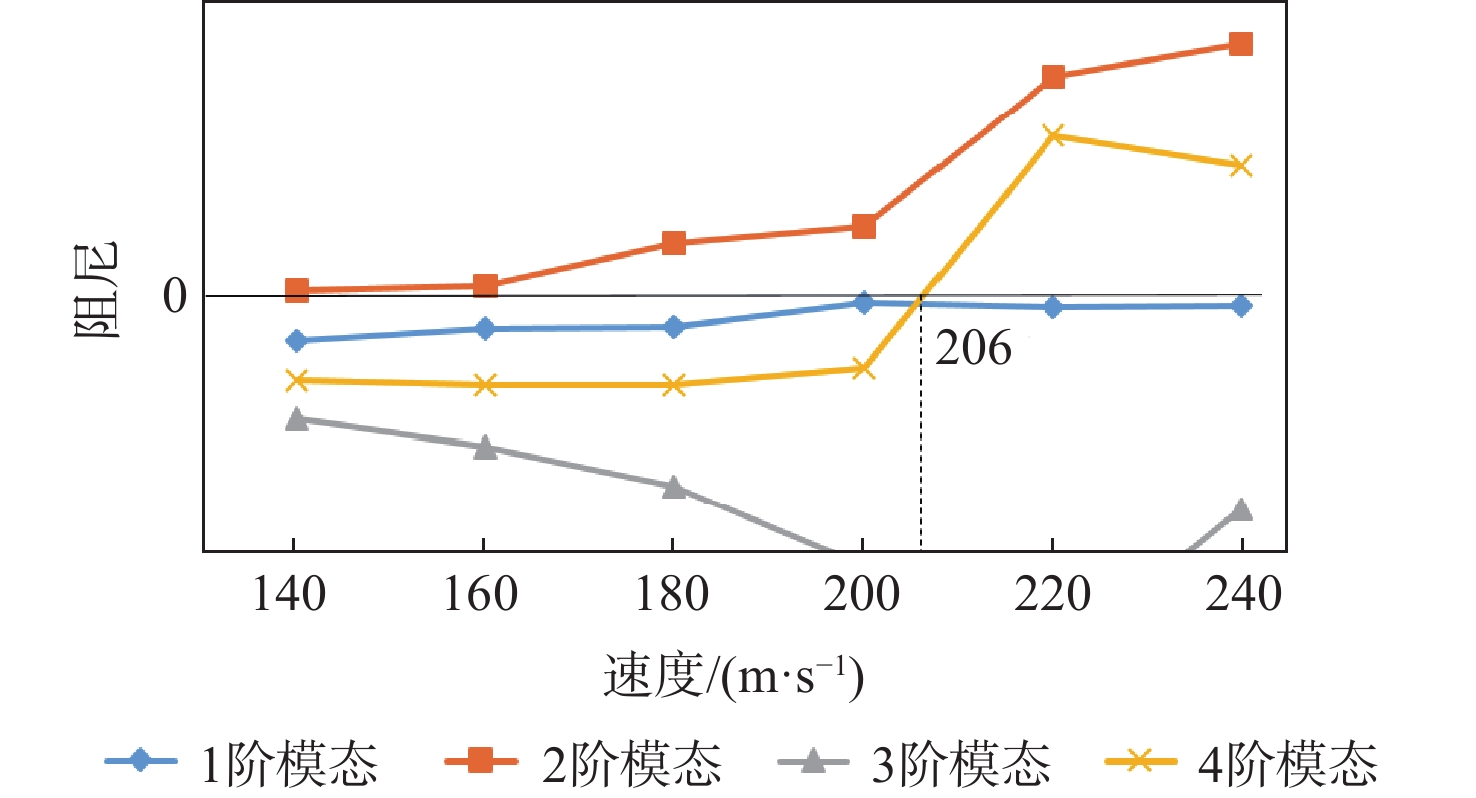
参数 初始值 翼展/m 20 弦长/m 1.75 翼肋数量 19 蒙皮厚度/mm 3.3 蒙皮层数 22 翼肋厚度/mm 1.8 翼肋层数 12 梁边长/mm 101 翼尖最大位移/m 0.323 翼尖最大扭角/(°) 2.44 颤振速度/(m·s−1) 206 结构质量/kg 535.08 表 2 优化结果
Table 2. Optimization results
方案 制造成本/
EWH蒙皮厚
度/mm蒙皮
层数翼肋厚
度/mm翼肋
层数梁边
长/mm翼尖最大
位移/m翼尖最大
扭角/(°)颤振速度/
(m·s−1)结构质
量/kg线性函数 1326.17 2.4 16 1.8 12 83 0.327 3.19 205 351.87 抛物线函数 1331.92 1.5 10 1.8 12 84 0.325 3.09 205 346.52 正弦函数 1317.66 1.8 12 1.8 12 83 0.324 3.17 205 344.68 初始方案 1730.75 3.3 22 1.8 12 101 0.323 2.44 206 535.08 -
[1] WEISSHAAR T A. Aeroelastic tailoring of forward swept composite wings[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 1981, 18(8): 669-676. doi: 10.2514/3.57542 [2] STANFORD B K, JUTTE C V. Comparison of curvilinear stiffeners and tow steered composites for aeroelastic tailoring of aircraft wings[J]. Computers & Structures, 2017, 183: 48-60. [3] WANG Z X, WAN Z Q, GROH R M J, et al. Aeroelastic and local buckling optimisation of a variable-angle-tow composite wing-box structure[J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 258: 113201. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.113201 [4] ALHAJAHMAD A, MITTELSTEDT C. Minimum weight design of curvilinearly grid-stiffened variable-stiffness composite fuselage panels considering buckling and manufacturing constraints[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2021, 161: 107526. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2021.107526 [5] BROOKS T R, MARTINS J R R A, KENNEDY G J. Aerostructural tradeoffs for tow-steered composite wings[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2020, 57(5): 787-799. doi: 10.2514/1.C035699 [6] PEREIRA D A, SALES T P, RADE D A. Multi-objective frequency and damping optimization of tow-steered composite laminates[J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 256: 112932. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112932 [7] BUTLER R, BAKER N, LIU W L, et al. Damage tolerance of buckling optimized variable angle tow panels[C]//Proceedings of the 50th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2009: 2443. [8] ZHANG B, CHEN K L, ZU L. Aeroelastic tailoring method of tow-steered composite wing using matrix perturbation theory[J]. Composite Structures, 2020, 234: 111696. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111696 [9] STODIECK O, COOPER J E, WEAVER P M, et al. Aeroelastic tailoring of a representative wing box using tow-steered composites[J]. AIAA Journal, 2017, 55(4): 1425-1439. doi: 10.2514/1.J055364 [10] STODIECK O, COOPER J E, WEAVER P M, et al. Optimization of tow-steered composite wing laminates for aeroelastic tailoring[J]. AIAA Journal, 2015, 53(8): 2203-2215. doi: 10.2514/1.J053599 [11] 李飞, 聂国隽. 基于连续丝束剪切技术的变角度复合材料层合板的热屈曲分析[J]. 力学季刊, 2019, 40(2): 265-273. doi: 10.15959/j.cnki.0254-0053.2019.02.005LI F, NIE G J. Thermal buckling analysis of VAT composite laminates fabricated by continuous tow shearing[J]. Chinese Quarterly of Mechanics, 2019, 40(2): 265-273(in Chinese). doi: 10.15959/j.cnki.0254-0053.2019.02.005 [12] WU K, TATTING B, SMITH B, et al. Design and manufacturing of tow-steered composite shells using fiber placement[C]//Proceedings of the 50th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2009: 2700. [13] XIAO Z F, ACKERMANN A, HARRISON P. Manual 2-dimensional fabric steering, for the manufacture of variable stiffness panels[J]. Procedia Manufacturing, 2020, 47: 24-28. doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2020.04.111 [14] 孔斌, 顾杰斐, 陈普会, 等. 变刚度复合材料结构的设计、制造与分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(10): 2121-2133. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20170829.006KONG B, GU J F, CHEN P H, et al. Design, manufacture and analysis of variable-stiffness composite structures[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2017, 34(10): 2121-2133(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20170829.006 [15] HAO P, LIU D C, WANG Y, et al. Design of manufacturable fiber path for variable-stiffness panels based on lamination parameters[J]. Composite Structures, 2019, 219: 158-169. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.03.075 [16] SOHOULI A, YILDIZ M, SULEMAN A. Cost analysis of variable stiffness composite structures with application to a wind turbine blade[J]. Composite Structures, 2018, 203: 681-695. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.07.049 [17] CHEN S Z, LI D C, XIANG J W, et al. Composite manufacturing cost model targeting on design optimization[J]. Applied Composite Materials, 2020, 27(5): 673-691. doi: 10.1007/s10443-020-09828-0 [18] KIM B C, POTTER K, WEAVER P M. Continuous tow shearing for manufacturing variable angle tow composites[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2012, 43(8): 1347-1356. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2012.02.024 -








 下载:
下载: