Hydroplaning risk of aircraft tire based on variable weight theory-normal cloud model
-
摘要:
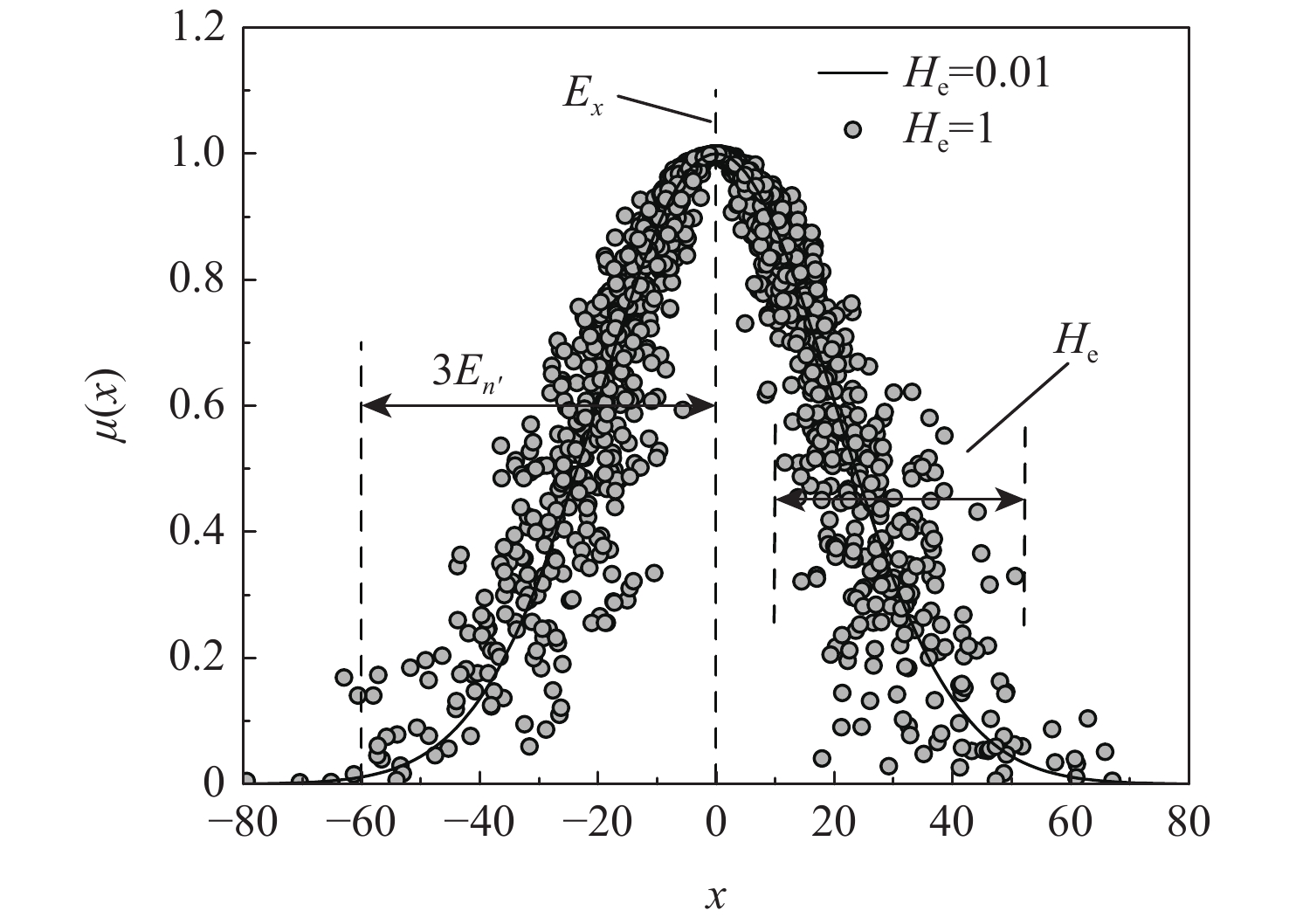
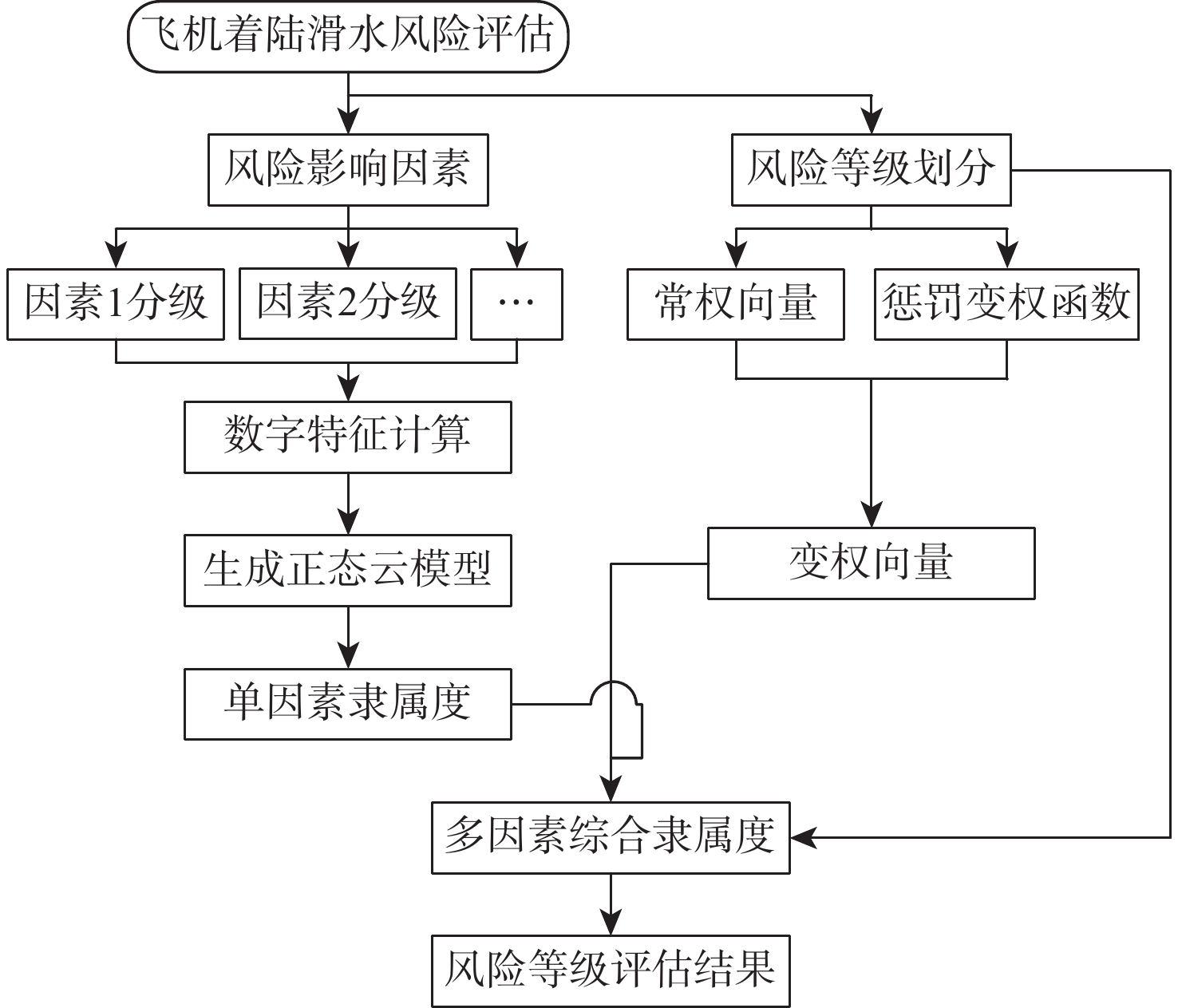
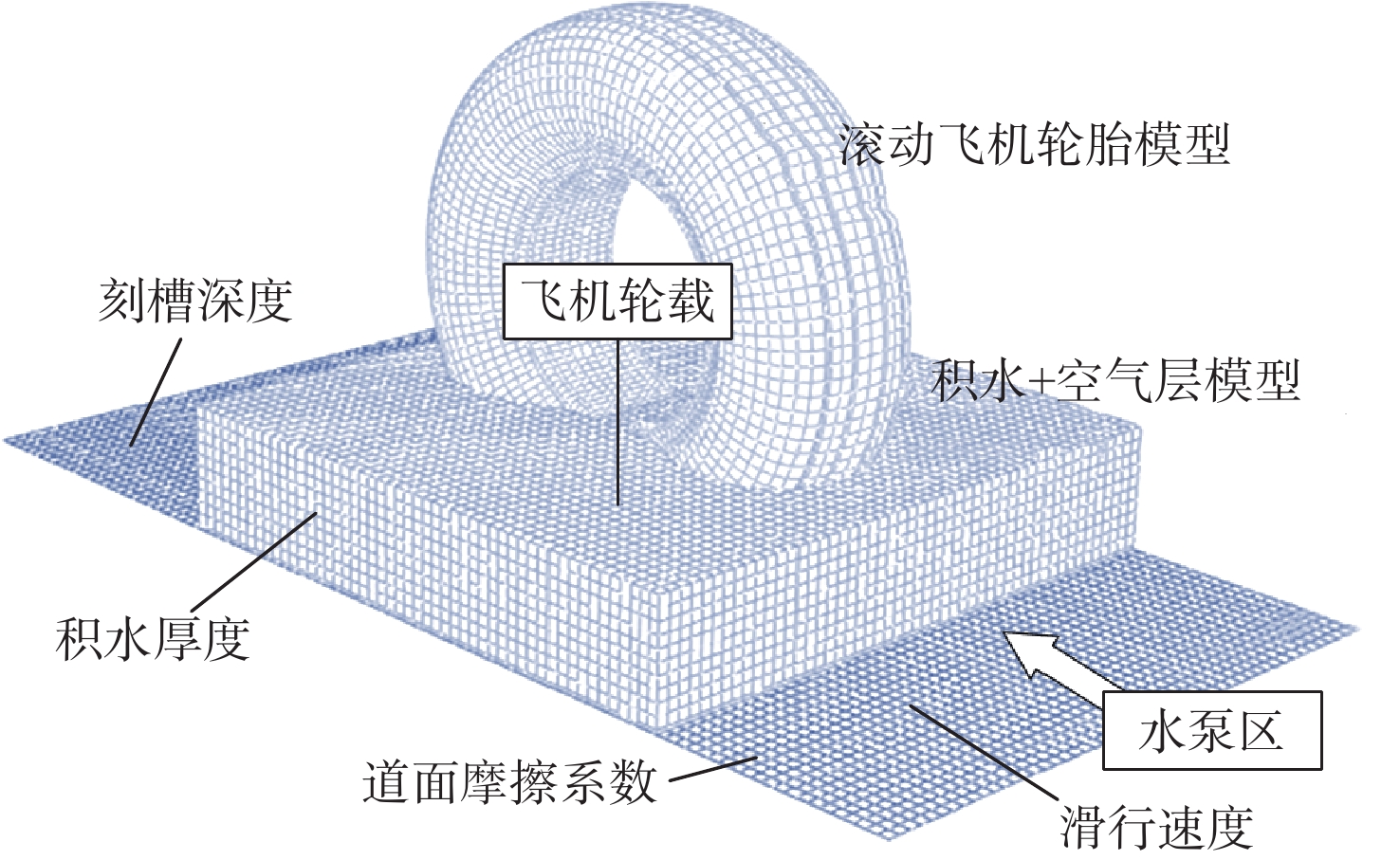
针对飞机轮胎滑水行为的随机性和模糊性特征,提出基于正态云模型的滑水安全评价分析方法。引入变权理论动态调整权值,采用惩罚性变权函数降低常权权值对评价结果的主观影响。构建飞机轮胎滑水流固耦合仿真分析模型,选取飞机轮载、滑行速度、积水厚度、道面摩擦系数及刻槽深度作为风险影响因素,基于单因素云模型数字特征及变权向量求解综合隶属度,建立多元决策下的飞机滑水风险等级及划分标准。以某山区多雨机场轮胎滑水事件为实例进行验证,结果表明:以传统临界滑水速度指标进行条件判定仅得出允许起降的一般结论;对比常权和变权评价结果,工况1安全系数由1.09提高至1.17,工况2由2.09提高至2.94,可定量描述道面起降环境差异,滑水风险仍在可接受范围内,变权评价结果偏于保守;工况3安全系数由3.13提高至3.74,滑水风险上升至Ⅳ级,即使道面积水厚度符合上限要求,轮胎滑水发生几率仍有可能显著提高,与实际风险情况基本一致,对道面运行安全分级管理具备参照性。
Abstract:Aiming at the randomness and fuzziness features of hydroplaning behavior of aircraft tires, a new safety evaluation methodology of tire hydroplaning is established on the basis of normal cloud model. The variable weight theory is adopted in order to adjust the weight value dynamically. The penalty function of variable weight is used to reduce the subjective impact of constant weight value on evaluation results. A fluid-solid coupling model of aircraft tire landing on wet pavement is developed for numerical analysis. The selection of five independent variables as the influencing determinants of hydroplaning risk includes aircraft wheel load, taxiing speed, water-film thickness, pavement friction coefficient, and groove depth. The comprehensive membership degree is then calculated based on the digital features of the single-factor cloud model and variable weight vector. The risk level and classification standard of aircraft tire hydroplaning is then established by multivariate decision. The case study of several accident symptoms of tire hydroplaning that took place in an airport located in a rainy mountainous area indicates that only a simplified conclusion of allowed/not-allowed landing or taking off of aircraft can be obtained by using critical hydroplaning speed as an evaluation criterion. By comparing the evaluation results of constant weight and variable weight theory, the safety factor of Case 1 is increased from 1.09 to 1.17 and that of Case 2 is increased from 2.09 to 2.94. The difference in airport runways under different running conditions can be quantitatively described. Although the risk levels of tire hydroplaning are both within the acceptable range, evaluation results derived from variable weight theory can be more conservative. As for Case 3, the safety factor is increased from 3.13 to 3.74 and the risk level is increased to level IV(unacceptable). Although the water-film thickness on the pavement surface complies with the top limit criteria, it is still possible to greatly increase the likelihood of tire hydroplaning, which is compatible with the actual risk scenario. The conclusions can be used as a reference for the classified safety management of pavement operation.
-
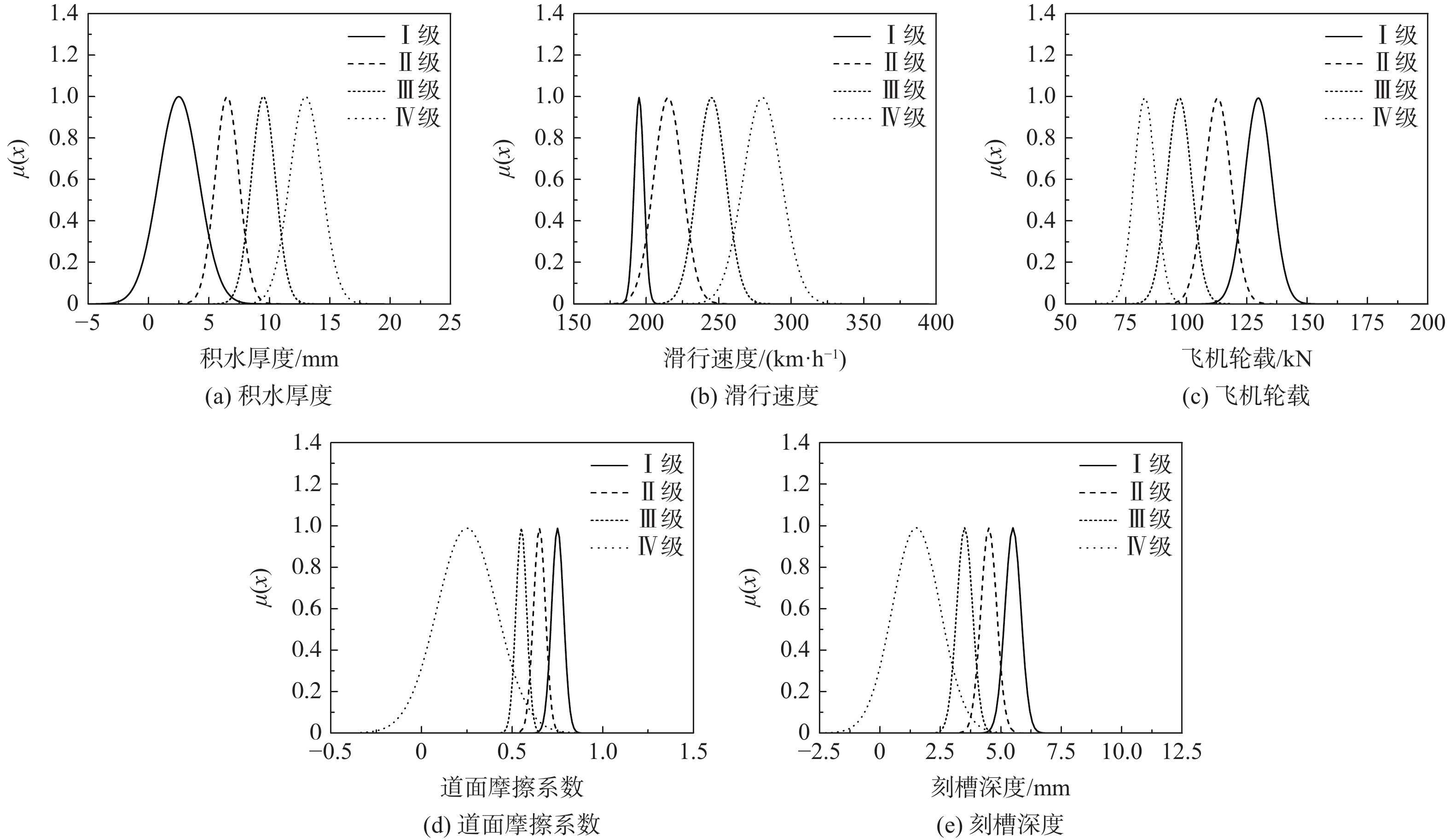
表 1 飞机滑水风险因素及分级
Table 1. Aircraft hydroplaning evaluation index and classification
风险
等级滑行速度/
(km∙h−1)积水厚
度/mm飞机轮
载/kN刻槽深
度/mm道面摩
擦系数Ⅰ级 190
~2000~5 123.1
~138.05~6 0.7~0.8 Ⅱ级 200
~2305~8 107.3
~123.14~5 0.6~0.7 Ⅲ级 230
~2608~11 91.7
~107.33~4 0.5~0.6 Ⅳ级 260
~30011~15 75.8
~91.70~3 0~0.5 表 2 正态云模型数字特征
Table 2. Digital features of normal cloud model
影响因素 滑行速度/(km∙h−1) 积水厚度/mm 飞机轮载/kN 刻槽深度/mm 道面摩擦系数 I级 (195,3.33,0.01) (2.5,1.67,0.01) (129.8,5.7,0.01) (5.5,0.33,0.01) (0.75,0.03,0.01) II级 (215,10,0.01) (6.5,1,10.01) (113.0,5.5,0.01) (4.5,0.33,0.01) (0.65,0.03,0.01) III级 (245,10,0.01) (9.5,1,0.01) (97.1,5.1,0.01) (3.5,0.33,0.01) (0.55,0.03, 0.01) IV级 (280,13.3,0.01) (13,1.33,0.01) (82.8,4.5,0.01) (1.5,1,0.01) (0.25,0.166, 0.01) 表 3 轮胎水滑事件影响因素基本参数
Table 3. Basic parameters of influencing factors of aircraft tire hydroplaning symptoms
工况 滑行速
度/(km∙h−1)积水厚
度/mm飞机轮
载/kN刻槽深
度/mm道面摩
擦系数1 220 3 138.8 6 0.76 2 250 5 100.4 5 0.66 3 280 8 76.5 3 0.60 表 4 不同工况下飞机滑水风险安全性评价
Table 4. Safety evaluation of aircraft hydroplaning under different conditions
工况 评价
方法安全
系数安全等级 规范判定 1 常权 1.09 Ⅰ级 允许起降 本文方法 1.17 Ⅰ级 2 常权 2.09 Ⅱ级 允许起降 本文方法 2.94 Ⅲ级 3 常权 3.13 Ⅲ级 允许起降 本文方法 3.73 Ⅳ级 -
[1] 余治国, 李曙林, 朱青云. 机轮动力滑水机理分析[J]. 空军工程大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 5(5): 9-11.YU Z G, LI S L, ZHU Q Y. Mechanism analysis of an aircraft tire dynamic hydroplaning[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University (Natural Science Edition), 2004, 5(5): 9-11(in Chinese). [2] 蔡靖, 许诤. 沟槽磨损对飞机轮胎滑水影响仿真分析[J]. 中国民航大学学报, 2020, 38(2): 38-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5590.2020.02.008CAI J, XU Z. Simulation analysis on influence of groove abrasion on aircraft hydroplaning[J]. Journal of Civil Aviation University of China, 2020, 38(2): 38-43(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5590.2020.02.008 [3] 朱兴一, 庞亚凤, 杨健, 等. 湿滑条件下基于真实纹理道面的机轮着陆滑水行为解析[J]. 中国公路学报, 2020, 33(10): 159-170.ZHU X Y, PANG Y F, YANG J, et al. Analysis on the hydroplaning of aircraft tire under real texture pavement conditions[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2020, 33(10): 159-170(in Chinese). [4] PURBA J H. A fuzzy-based reliability approach to evaluate basic events of fault tree analysis for nuclear power plant probabilistic safety assessment[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2014, 70: 21-29. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2014.02.022 [5] 朱晟泽. 基于路面宏观纹理的轮胎抗滑行为数值模拟研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2017: 89-114.ZHU S Z. Numerical simulation of tire skid resistance based on pavement macro-texture[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2017: 89-114 (in Chinese). [6] 冯停. 湿滑路面轮胎滑水机理研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛理工大学, 2018: 51-62.FENG T. The study of tire hydroplaning mechanism on wet road[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao Tehcnology University, 2018: 51-62 (in Chinese). [7] 黄晓明, 刘修宇, 曹青青, 等. 积水路面轮胎部分滑水数值模拟[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 45(9): 113-121.HUANG X M, LIU X Y, CAO Q Q, et al. Numerical simulation of tire partial hydroplaning on flooded pavement[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2018, 45(9): 113-121(in Chinese). [8] FWA T F, PASINDU H R, ONG G P. Critical rut depth for pavement maintenance based on vehicle skidding and hydroplaning consideration[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2012, 138(4): 423-429. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)TE.1943-5436.0000336 [9] BENEDETTO A. A decision support system for the safety of airport runways: The case of heavy rainstorms[J]. Transportation Research Part A:Policy and Practice, 2002, 36(8): 665-682. doi: 10.1016/S0965-8564(01)00029-5 [10] Aviation Safety Network. Accident description [DB/OL]. (2020-08-01) [2020-10-01]. [11] 徐征捷, 张友鹏, 苏宏升. 基于云模型的模糊综合评判法在风险评估中的应用[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2014, 14(2): 69-72.XU Z J, ZHANG Y P, SU H S. Application of risk assessment on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method based on the cloud model[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2014, 14(2): 69-72(in Chinese). [12] 王贺, 刘高峰, 王慧敏. 基于云模型的城市极端雨洪灾害预警研究[J]. 水利经济, 2014, 32(4): 59-62,74.WANG H, LIU G F, WAGN H M. Warning of urban extreme rainstorm flood disasters based on cloud model[J]. Journal of Economics of Water Resources, 2014, 32(4): 59-62,74(in Chinese). [13] LI D Y, LIU C Y, GAN W Y. A new cognitive model: Cloud model[J]. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2009, 24(3): 357-375. doi: 10.1002/int.20340 [14] 唐家文, 董兵, 王超峰. 基于云模型的空管安全运行保障能力评价[J]. 航空工程进展, 2021, 12(4): 59-67.TANG J W, DONG B, WANG C F. Evaluation on safe operation support ability of air traffic mangement based on cloud model[J]. Advances in Aeronautical Science and Engineering, 2021, 12(4): 59-67(in Chinese). [15] 史佳辉, 徐吉辉, 陈玉金, 等. 基于交互作用矩阵—多维云模型的飞机重着陆风险评估方法研究[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(10): 3026-3032.SHI J H, XU J H, CHEN Y J, et al. Research on risk assessment method of aircraft heavy landing based on interaction matrix—multidimensional cloud model[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(10): 3026-3032(in Chinese). [16] 刘伟, 韩莉. 基于云模型的综合保障评估方法研究[J]. 科技创新与应用, 2017(5): 67-69.LIU W, HAN L. Research on comprehensive support evaluation method based on cloud model[J]. Technology Innovation and Application, 2017(5): 67-69(in Chinese). [17] 华攸金, 李希建, 陈刘瑜. 基于变权与正态云理论的煤矿安全评价及应用[J]. 煤矿安全, 2020, 51(3): 239-242.HUA Y J, LI X J, CHEN L Y. Coal mine safety evaluation and application based on variable weight and normal cloud theory[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2020, 51(3): 239-242. [18] 王洪利, 冯玉强. 基于云模型具有语言评价信息的多属性群决策研究[J]. 控制与决策, 2005, 20(6): 679-681.WANG H L, FENG Y Q. On multiple attribute group decision making with linguistic assessment information based on cloud model[J]. Control and Decision, 2005, 20(6): 679-681(in Chinese). [19] LIN C J, ZHANG M, LI L P, et al. Risk assessment of tunnel construction based on improved cloud model[J]. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities, 2020, 34(3): 04020028. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)CF.1943-5509.0001421 [20] 宗一鸣. 湿滑道面条件下轮胎力学行为与飞机着陆安全问题研究[D]. 天津: 中国民航大学, 2017.ZONG Y M. Study on the mechanical properties of aircraft tire and safety problem in landing on wet-pavement[D]. Tianjin: Civil Aviation University of China, 2017 (in Chinese). [21] 牛亚东, 张思祥, 田广军, 等. 机场跑道摩擦系数影响因素研究[J]. 应用力学学报, 2021, 38(2): 715-720.NIU Y D, ZHANG S X, TIAN G J, et al. Research on influencing factors of friction coefficient in airport runway[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2021, 38(2): 715-720(in Chinese). [22] 孙晓, 杨淑芳, 武磊, 等. 基于博弈论-云模型的隧道围岩稳定性分析模型研究[J]. 有色金属工程, 2020, 10(10): 112-119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2020.10.017SUN X, YANG S F, WU L, et al. Study on the stability analysis model of tunnel surrounding rock based on the combined weighting cloud model of game theory[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2020, 10(10): 112-119(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2020.10.017 [23] OH C W, KIM T W, JEONG H Y, et al. Hydroplaning simulation for a straight-grooved tire by using FDM, FEM and an asymptotic method[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2008, 22(1): 34-40. doi: 10.1007/s12206-007-1004-y [24] 梁辉如, 王永东, 彭浩, 等. 基于正态云理论的软弱隧道围岩分级[J]. 重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 40(11): 82-87.LIANG H R, WANG Y D, PENG H, et al. Classification of soft surrounding rock of tunnel based on normal cloud theory[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science), 2021, 40(11): 82-87(in Chinese). [25] 胡皓, 李德清, 赵娜, 等. 因素状态值为模糊数的变权综合决策方法[J]. 军械工程学院学报, 2014, 26(5): 75-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2956.2014.05.016HU H, LI D Q, ZHAO N, et al. Variable weights synthesis decision making based on fuzzy numbers[J]. Journal of Ordnance Engineering College, 2014, 26(5): 75-78(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2956.2014.05.016 [26] 李德清, 李洪兴. 状态变权向量的性质与构造[J]. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 38(4): 455-461.LI D Q, LI H X. The properties and construction of state variable weight vectors[J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science), 2002, 38(4): 455-461(in Chinese). 期刊类型引用(3)
1. 贾静焕,骆晨,孙志华,詹中伟,赵明亮. 航空发动机典型连接件腐蚀仿真分析. 中国腐蚀与防护学报. 2024(04): 979-986 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 吴正江,李开伟,毛旭耀,张润林,伍健,侯健,宋卿源,张迪. 新型平衡舵阴极保护设计与保护效果评价. 装备环境工程. 2024(06): 111-118 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 王育鑫,吴波,戴乐阳,胡科峰,吴建华,杨阳,闫福磊,张贤慧. 低合金钢在模拟海洋低温环境下的电偶腐蚀研究. 中国腐蚀与防护学报. 2022(06): 894-902 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(2)
-







 下载:
下载:
 百度学术
百度学术

