Multi-channel wireless sensor system based on CC1310 chip wtih high speed and low power consumption
-
摘要:
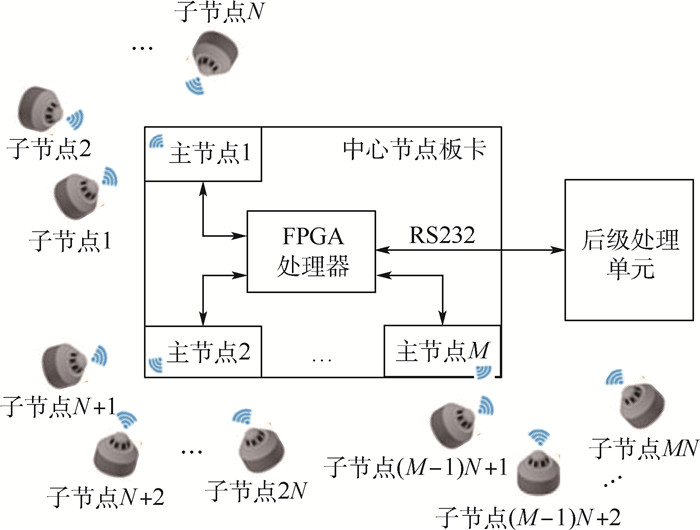
为有效减轻新一代运载火箭传感器数据采集与传输系统的质量, 设计并实现了基于CC1310芯片的无线传感器系统。采用频分复用(FDM)结合时分复用(TDM)的方式完成多节点组网并实施分组管理, 组间频分复用既实现了节点数的扩增, 又提升了传输速率复用倍数, 分组数为4时子节点数量可达100个以上。提出主节点授时法结合多节点分时传输协议的优化设计方法, 保证多节点高精准同步, 避免节点间碰撞, 获得了最优的组内可达速率;设计节点唤醒/休眠模式切换策略, 有效降低了系统功耗。实测结果表明:2个主节点带5个子节点并行工作时, 传输速率可达400 Kbps, 且主节点数量增加时, 系统的传输速率成比例增大;单个子节点忙时功耗不超过60 mW, 闲时功耗不超过12 mW, 平均功耗为15.2 mW, 符合低功耗要求;同时, 所设计的无线传感系统具备良好的可靠性和鲁棒性。
Abstract:In order to effectively reduce the weight of sensor data acquisition and transmission system for the new-generation launch vehicle, a wireless sensor system based on chip CC1310 was designed and implemented. Multi-node networking and group management are accomplished using frequency division multiplexing (FDM) and time division multiplexing (TDM). The FDM scheme among groups not only increases the number of nodes, but also improves the transmission rate multiplexing multiple. When there are four groups, the system is capable of supporting more than 100 sub-nodes. In order to ensure high precision synchronization of multi-nodes, avoid node collisions, and obtain the optimal intra-group achievable rate, we also suggested an optimal method of master node timing in combination with a multi-node time-sharing transfer protocol. Moreover, a node wake-up/idle mode switching strategy is designed to reduce system power consumption effectively. The experimental results show that the transmission rate can reach 400 Kbps when two master nodes work in parallel with five sub-nodes, and the transmission rate will increase proportionally when the number of master nodes rises. The power consumption of the single sub-node is less than 60 mW during work hours and less than 12 mW during idle hours. The average power consumption of the single sub-node is 15.2 mW, which meets the requirements of low power consumption. At the same time, the wireless sensor system designed in this paper has good reliability and robustness.
-
Key words:
- CC1310 /
- wireless network communication /
- time synchronization /
- high rate /
- low power consumption
-
表 1 传感器子节点采集信号与采样率
Table 1. Acquisition signals and sampling rates of sensor sub-nodes
组别(频段/MHz) 子节点编号 模拟信号源 采样率/Hz 1 电池电压 320 第1组(868) 2 1 kHz正弦波 5 120 4 湿度传感器 320 第2组(915) 6 温度传感器 320 8 电池电压 320 表 2 子节点传输速率
Table 2. The transmission rate of sub-nodes
组别(频段/MHz) 子节点编号 传输速率/bps 净荷传输速率/bps 1 68 608 2 560 第1组(868) 2 66 560 40 960 4 67 379 2 560 第2组(915) 6 100 147 2 560 8 101 376 2 560 系统总速率 406 323 51 200 -
[1] PATEL N R, KUMAR S. Wireless sensor networks' challenges and future prospects[C]//International Conference on System Modeling & Advancement in Research Trends. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 60-65. [2] CARMINATI M, KANOUN O, ULLO S L, et al. Prospects of distributed wireless sensor networks for urban environmental monitoring[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2019, 34(6): 44-52. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2019.2916294 [3] WU J, JIANG W, MEI Y, et al. A survey on the progress of testing techniques and methods for wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 4302-4316. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2887246 [4] 罗煜缤, 李洪, 周广铭, 等. 新一代箭载无线传感器网络系统架构综述[J]. 宇航计测技术, 2020, 40(4): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YHJJ202004001.htmLUO Y B, LI H, ZHOU G M, et al. Review on the system architecture of new generation wireless sensor network for rocket[J]. Journal of Astronautical Metrology and Measurement, 2020, 40(4): 1-6(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YHJJ202004001.htm [5] WANG Y, LU J, HAO C, et al. Applicable to launch vehicle data integrated design method of wireless sensor network research[C]//2018 Eighth International Conference on Instrumentation & Measurement, Computer, Communication and Control (IMCCC). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 221-225. [6] WANG H, ZENG H, PING W. Linear estimation of clock frequency offset for time synchronization based on overhearing in wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2016, 20(2): 288-291. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2015.2510645 [7] LEANDRO T B, TALES H, EDISON P. Enhancing time synchronization support in wireless sensor networks[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(12): 2956. doi: 10.3390/s17122956 [8] ABDULKAREM M, SAMSUDIN K, ROKHANI F Z, et al. Wireless sensor network for structural health monitoring: A contemporary review of technologies, challenges, and future direction[J]. Structural Health Monitoring, 2020, 193: 693-735. [9] SUN X, SU Y, HUANG Y, et al. Design and development of a wireless sensor network time synchronization system for photovoltaic module monitoring[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2020, 16(5): 1-8. [10] 庄祎梦, 贺光辉, 陈洪涛, 等. 无线传感器网络高精度时间同步机制[J]. 信息技术, 2017(10): 1-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDZJ201710001.htmZHUANG Y M, HE G H, CHEN H T, et al. Method of highly accurate time synchronization for wireless sensor networks[J]. Information Technology, 2017(10): 1-4(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDZJ201710001.htm [11] 麦军, 邓巧茵, 万智萍. 基于CC2530的ZigBee无线组网温度监测系统的设计[J]. 电子设计工程, 2015, 23(22): 117-121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWDZ201522037.htmMAI J, DENG Q Y, WAN Z P. A ZigBee wireless network temperature monitoring system based on CC2530[J]. Electronic Design Engineering, 2015, 23(22): 117-121(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWDZ201522037.htm [12] SAHITYA G, BALAJI N, NAIDU C D, et al. Designing a wireless sensor network for precision agriculture using Zigbee[C]// IEEE International Advance Computing Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 287-291. [13] NURGALIYEV M, SAYMBETOV A, YASHCHYSHYN Y, et al. Prediction of energy consumption for LoRa based wireless sensors network[J]. Wireless Networks, 2020, 26(5): 3507-3520. doi: 10.1007/s11276-020-02276-5 [14] SOMMER P, MARET Y, DZUNG D. Low-power wide-area networks for industrial sensing applications[C]//IEEE International Conference on Industrial Internet. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 23-32. [15] 周洋. 无线传感网节点低功耗控制技术的研究[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2019: 33-39.ZHOU Y. Research on low power control technology of wireless sensor network nodes[D]. Suzhou: Soochow University, 2019: 33-39(in Chinese). [16] 朱志斌. 基于CC1310的无线传感网络记录仪设计[D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2021: 30-36.ZHU Z B. Design of wireless sensor network recorder based on CC1310[D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2021: 30-36(in Chinese). [17] MAHBUBUR R, DALI I, VENKATA P. et al. Implementation of LPWAN over white spaces for practical deployment[C]//Conference on Internet-of-Things Design and Implementation. New York: ACM, 2019: 178-189. [18] JIAN L, MECHITOV K A, KIM R E, et al. Efficient time synchronization for structural health monitoring using wireless smart sensor networks[J]. Structural Control and Health Monitoring, 2016, 23(3): 470-486. -







 下载:
下载: