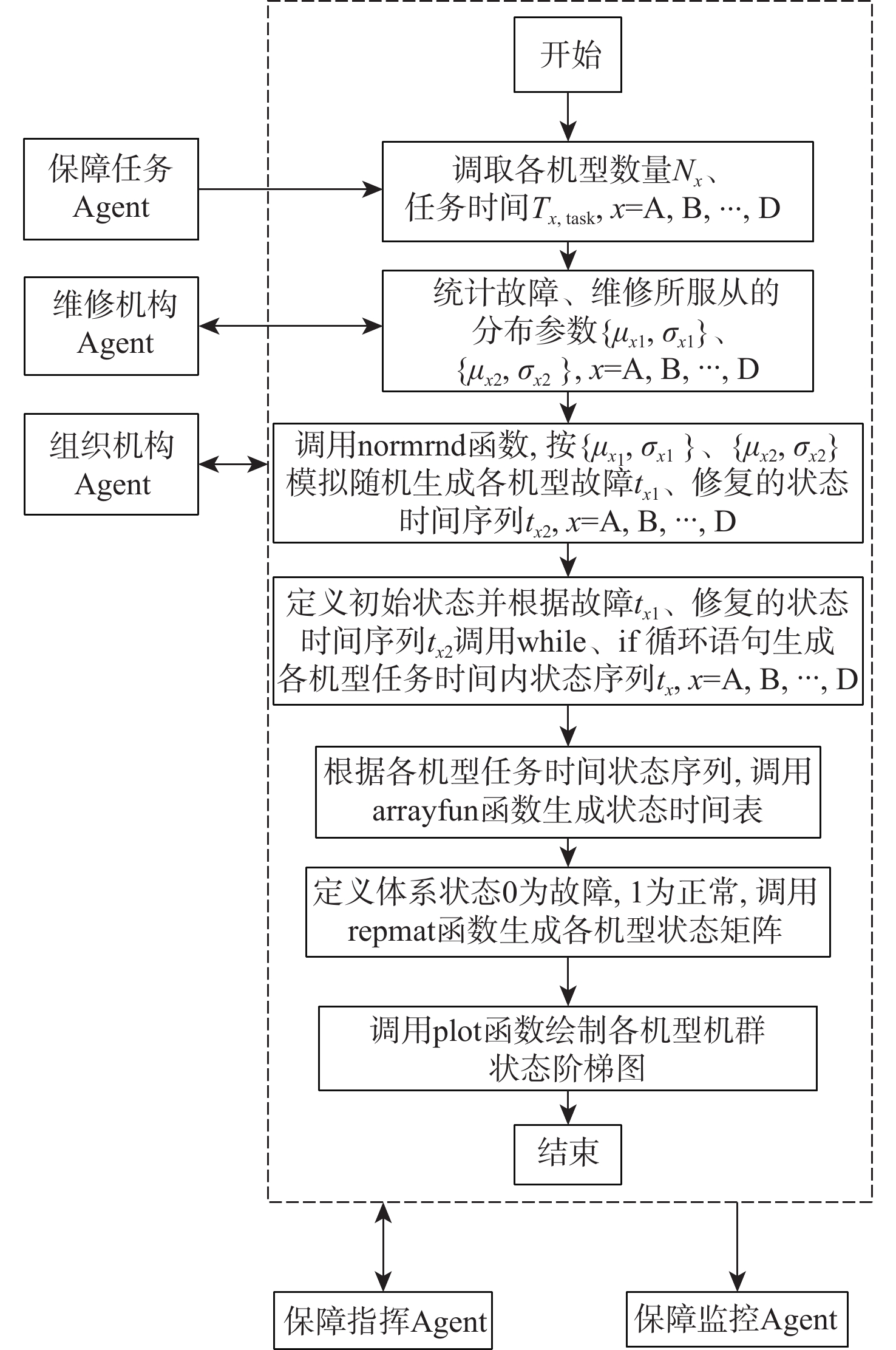
-
摘要:
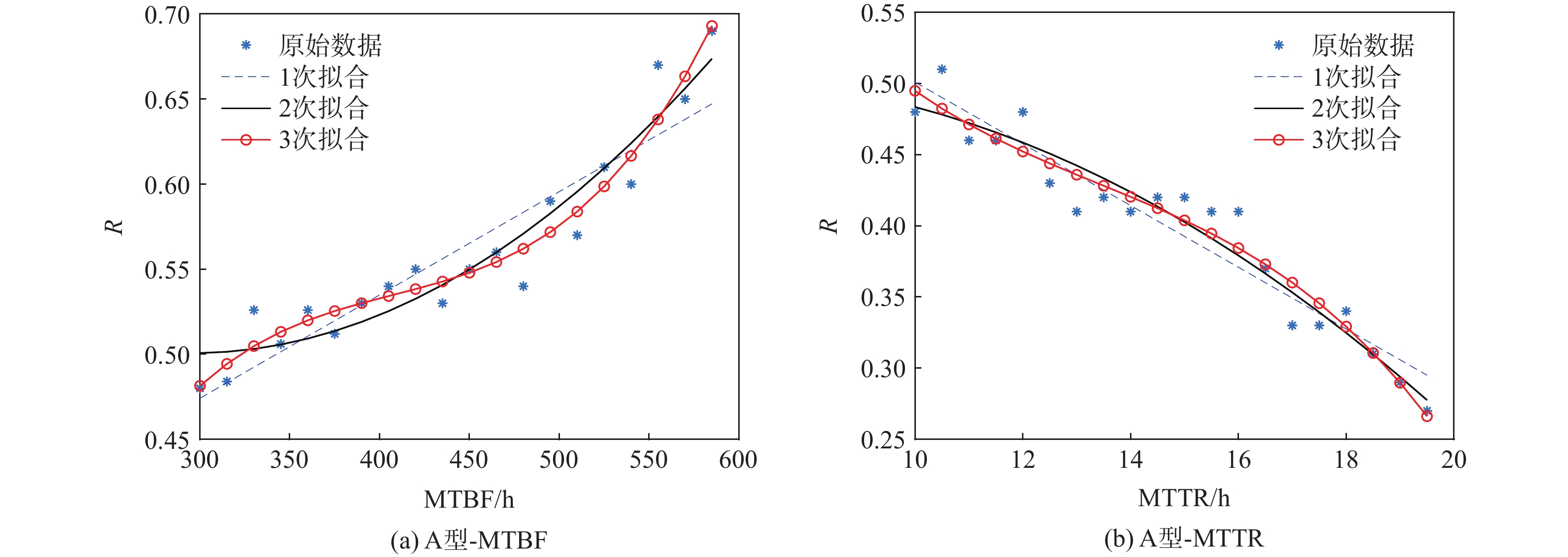
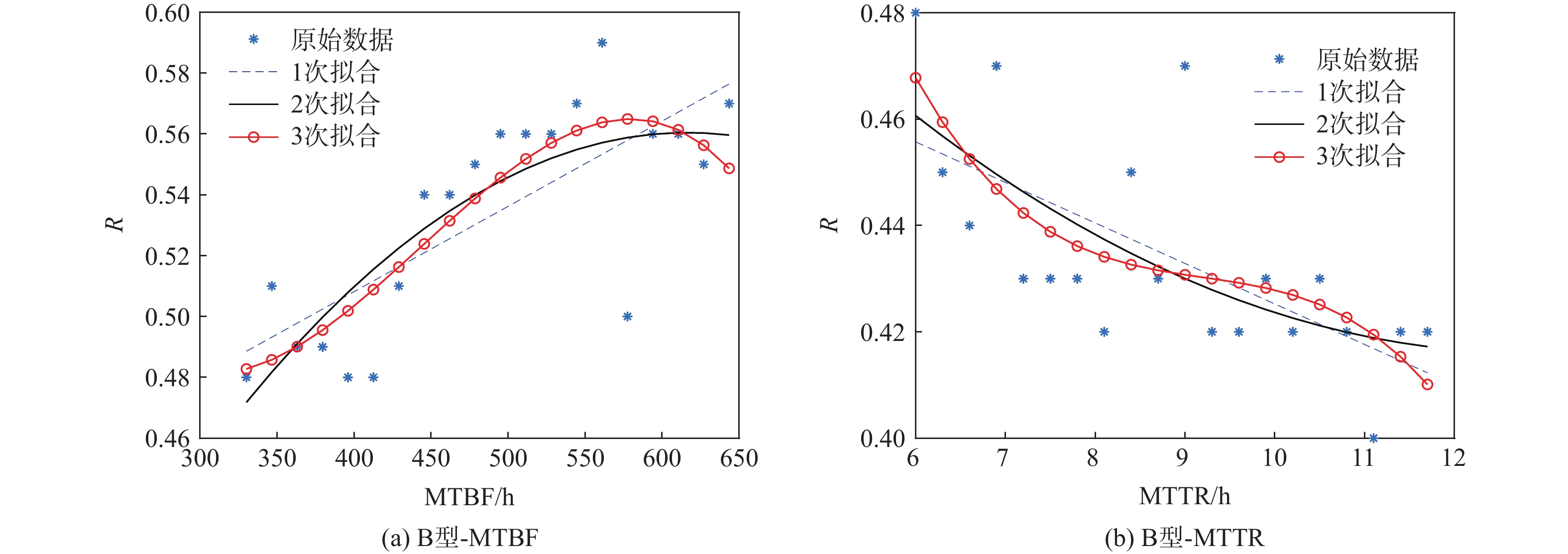
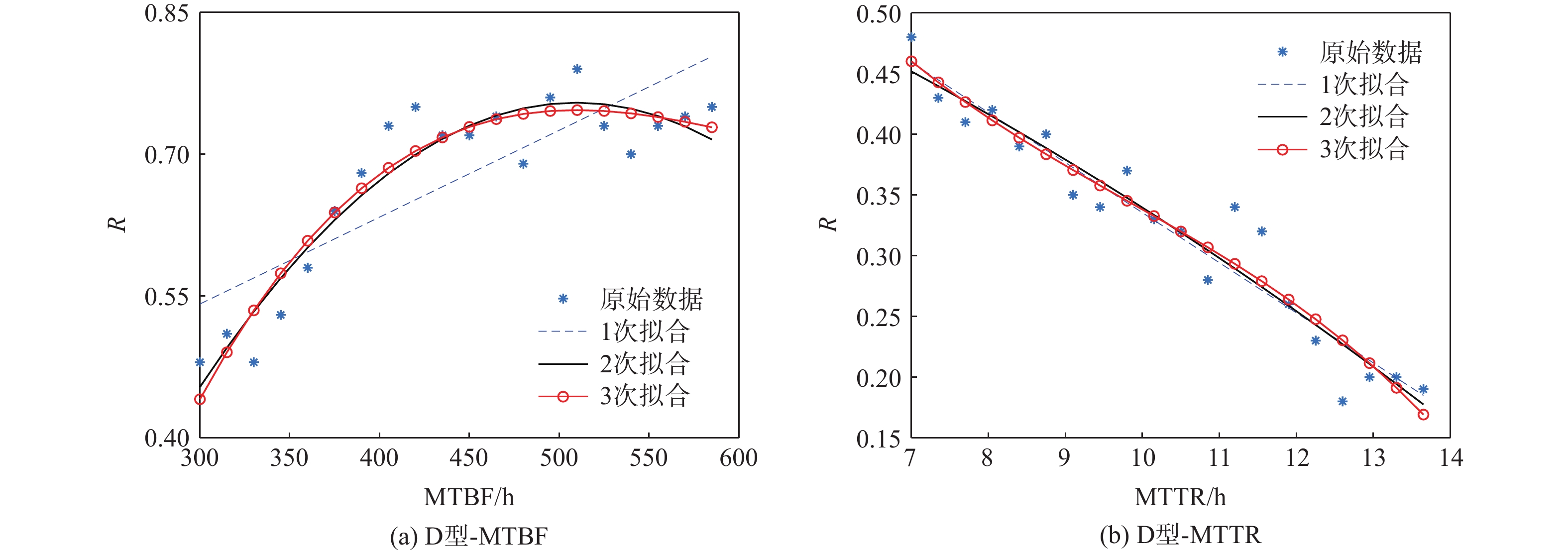
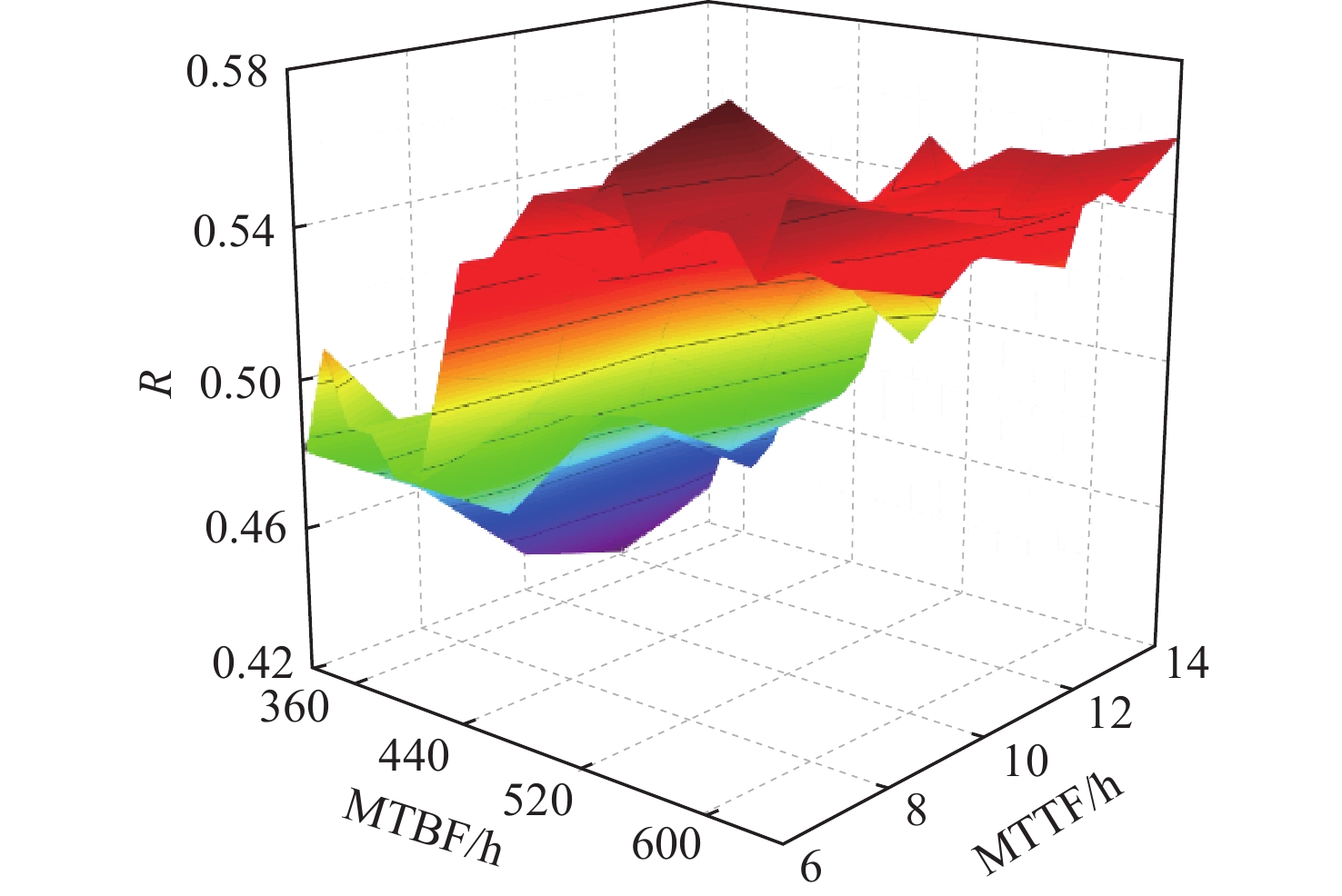
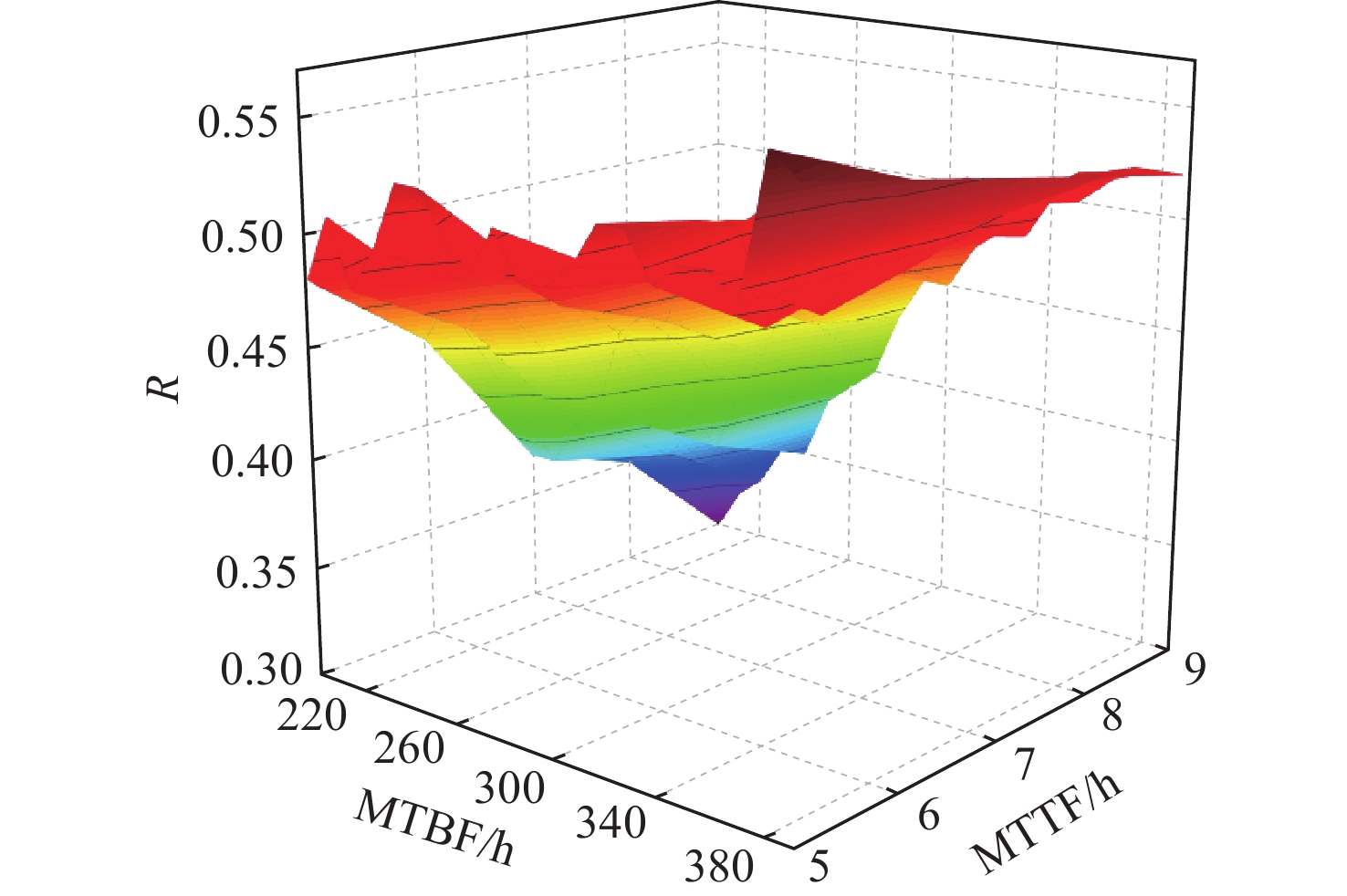
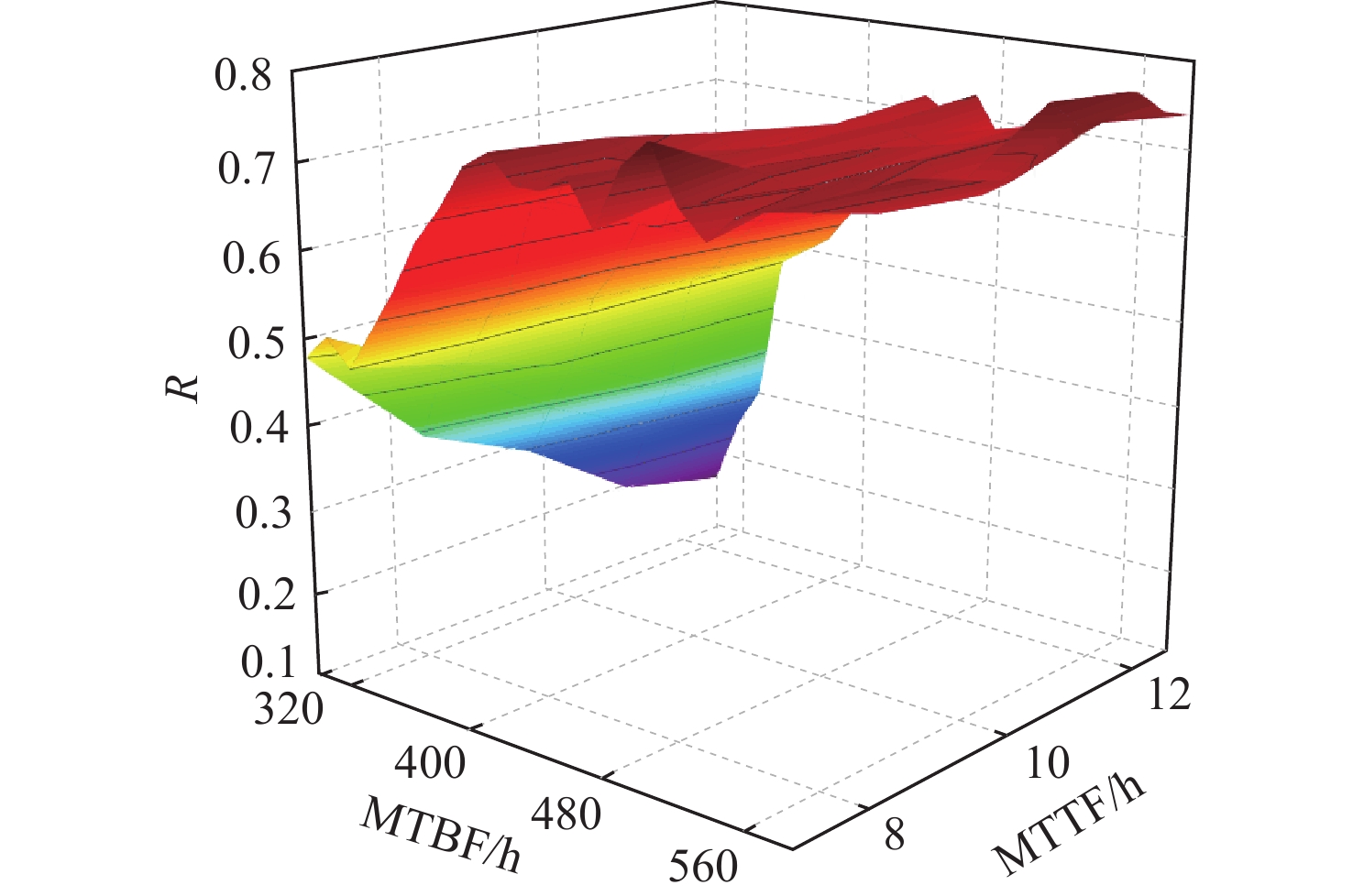
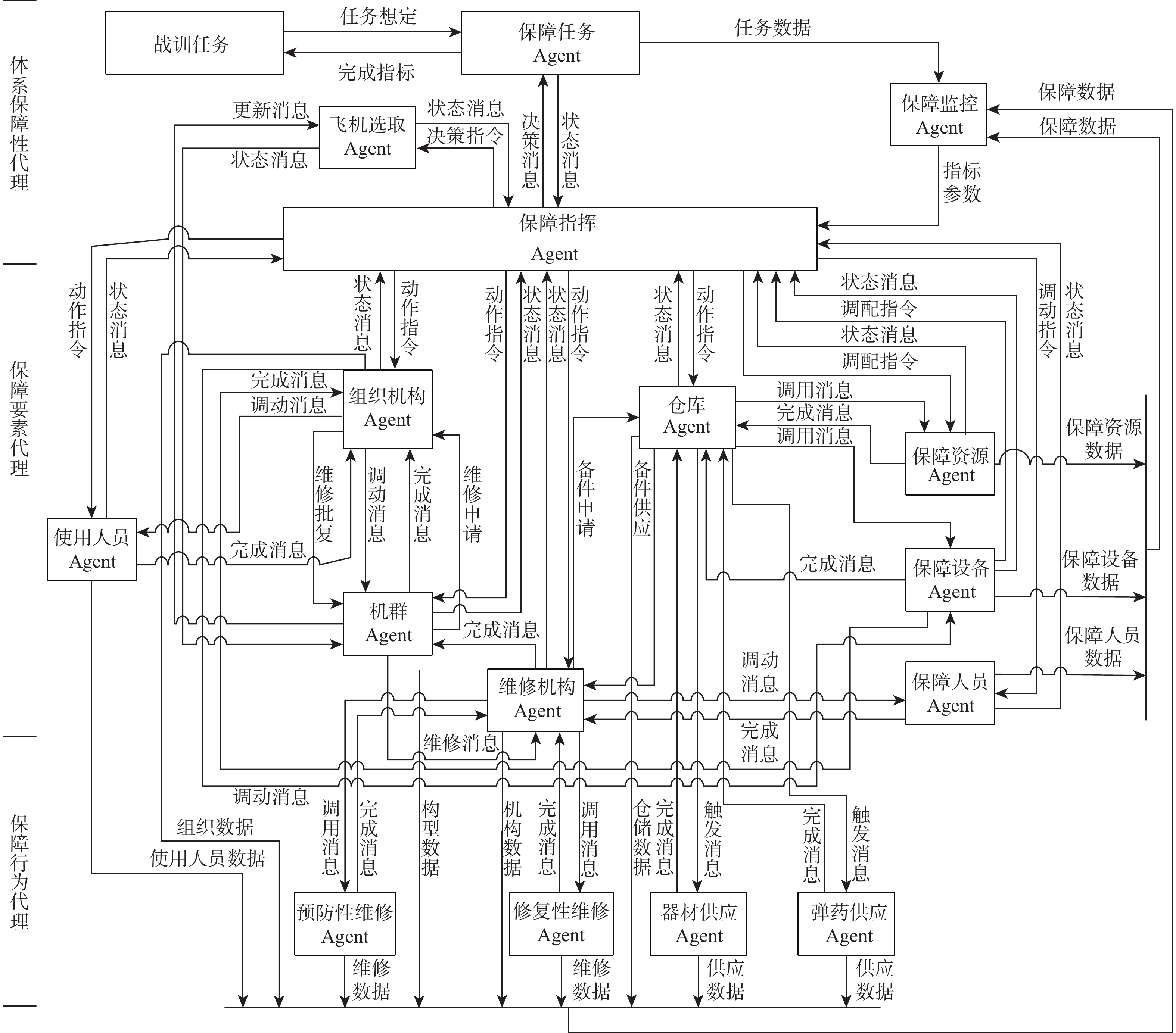
航空机群保障涉及要素广、策略多、交互性强,仿真分析方法是开展飞机保障决策与评估研究的热点和难点。提出一种机群保障仿真评估方法,建立多智能体(Agent)功能类型与交互关系模型;对多Agent结构进行定义,并建立模型;以五型飞机构成的航空机群为仿真对象,以任务成功率为保障指标进行案例验证与仿真计算分析。结果表明:各型飞机平均故障间隔时间(MTBF)、设备故障平均修复时间(MTTR)对任务成功率的影响总体趋势相似,随着MTBF的增加任务成功率提升,随着MTTR的增加任务成功率降低。所提方法能够为航空机群维修保障智能决策提供一种可行、有效的方法手段,支撑基于模型的智能决策优化实现。
Abstract:Aircraft group support involves a wide range of elements, multiple strategies, and strong interaction. Its simulation analysis method is a hot and difficult point in conducting research on aircraft group support decision-making and evaluation. This paper first establishes the multi-agent function type and interaction relationship model; Secondly, defines the multi-agent structure and establish the model; Finally, Using the aircraft group consisting of five types of aircraft as the simulation object, the case validation and simulation analysis are conducted based on the mission success rate as the guarantee indicators. The results show that the mean time between failures (MTBF) and the mean time to repair (MTTR) of various types of fighters have similar effects on the mission success rate. As the MTBF increases, the mission success rate increases. As the MTTR increases, the mission success rate decreases. The proposed support simulation evaluation method can provide a feasible and effective method for the intelligent decision-making of aircraft group maintenance support, and support the realization of model-based intelligent decision-making optimization.
-
Key words:
- aircraft group /
- support /
- multi-agent /
- simulation evaluation /
- sensitivity analysis
-
表 1 仿真计算初始输入
Table 1. Initial input of simulation calculation
机型 数量/架 滞空时间/min 任务时间/min 构型要求(k/n) MTBF/h MTTR/h 第1阶段 第2阶段 第3阶段 第1阶段 第2阶段 第3阶段 A 3 210 12 8 6 1/2 1/2 2/3 [300,20] [10,2] B 10 210 6 7/10 [330,25] [6,2] C 16 90 12 8 6 5/8 7/10 10/16 [200,30] [5,1] D 8 180 8 6 4/6 6/8 [300,50] [7,2] E 6 210 6 4/6 [350,30] [8,2] 表 2 任务强度敏感性分析
Table 2. Mission intensity sensitivity analysis
类别 序号 敏感性因素 R R变化
幅度/%初始值 变化值 各机型
MTBF1 A型-MTBF增
加20%(300~360)0.48 0.526 9.6 2 B型-MTBF增
加20%(330~396)0.48 0.52 8.3 3 C型-MTBF增
加20%(200~240)0.48 0.53 10.4 4 D型-MTBF增
加20%(300~360)0.48 0.58 20.8 5 E型-MTBF增
加20%(350~420)0.48 0.49 2.1 各机型
MTTR6 A型-MTTR增
加20%(10~12)0.48 0.44 −8.3 7 B型-MTTR增
加20%(6~7.2)0.48 0.43 −10.4 8 C型-MTTR增
加20%(5~6)0.48 0.42 −12.5 9 D型-MTTR增
加20%(7~8.4)0.48 0.39 −18.8 10 E型-MTTR增
加20%(8~9.6)0.48 0.41 −14.6 任务
强度11 A型飞机任务强度
降低20%(2/3→1/3)0.48 0.60 25.8 12 B型飞机任务强度
降低20%(5/10→4/10)0.48 0.51 6.9 13 C型飞机任务强度
降低20%(4/10→3/10)0.48 0.56 16.7 14 D型飞机任务强度
降低20%(6/8→5/8)0.48 0.65 35.4 15 E型飞机任务强度
降低20%(4/6→3/6)0.48 0.51 6.3 阶段任
务时间16 第1阶段时间
减少20%(9.6 h)0.48 0.52 8.3 17 第2阶段时间
减少20%(6.4 h)0.48 0.50 4.2 18 第3阶段时间
减少20%(4.8 h)0.48 0.49 2.1 -
[1] 汤润泽, 张承龙, 李林林, 等. 多武器跨域智能协同对空作战应用及关键技术[J]. 现代防御技术, 2021, 49(2): 26-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2021.02.005TANG R Z, ZHANG C L, LI L L, et al. Research on applications and key technologies of multi-weapons in cross-domain intelligent coordination air combat[J]. Modern Defence Technology, 2021, 49(2): 26-34(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2021.02.005 [2] 丁刚, 张琳, 崔利杰, 等. 航空装备体系保障性分析仿真运行控制[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2021, 41(1): 58-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2021.01.014DING G, ZHANG L, CUI L J, et al. Simulation operation control of aviation equipment system of system supportability analysis[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2021, 41(1): 58-62(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2021.01.014 [3] 丁刚, 张琳, 崔利杰, 等. 基于任务的航空装备保障体系概念建模研究[J]. 军事运筹与系统工程, 2020, 34(1): 39-46.DING G, ZHANG L, CUI L J, et al. Research on concept modeling of mission-based aviation equipment support system of systems[J]. Military Operations Research and Systems Engineering, 2020, 34(1): 39-46(in Chinese). [4] 崔利杰, 丛继平, 丁刚, 等. 基于不确定性的航空装备体系保障性评估[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(12): 2452-2461. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2020.0490CUI L J, CONG J P, DING G, et al. Supportability evaluation of aviation equipment system based on uncertainty[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(12): 2452-2461(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2020.0490 [5] 杨东昌, 马永忠, 宋科. 武器装备体系需求论证研究[J]. 中国设备工程, 2021(12): 250-251. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0711.2021.12.158YANG D C, MA Y Z, SONG K. Research on requirement demonstration of weapon equipment system[J]. China Plant Engineering, 2021(12): 250-251(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0711.2021.12.158 [6] 姜忠钦, 张明智, 张斌, 等. 基于仿真的武器装备体系论证关键问题研究[J]. 装备指挥技术学院学报, 2009, 20(5): 19-23.JIANG Z Q, ZHANG M Z, ZHANG B, et al. Study on key questions of weapon system-of-systems demonstration based on simulation[J]. Journal of the Academy of Equipment Command & Technology, 2009, 20(5): 19-23(in Chinese). [7] KAVIARI F, MESGARI M S, SEIDI E, et al. Simulation of urban growth using agent-based modeling and game theory with different temporal resolutions[J]. Cities, 2019, 95: 102387. doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2019.06.018 [8] NGUYEN N D, NGUYEN T, NAHAVANDI S. Multi-agent behavioral control system using deep reinforcement learning[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 359: 58-68. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.05.062 [9] HUANG J, CAO M, ZHOU N, et al. Distributed behavioral control for second-order nonlinear multi-agent systems[J]. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2017, 50(1): 2445-2450. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2017.08.407 [10] 黄柯棣, 刘宝宏, 黄健, 等. 作战仿真技术综述[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2004, 16(9): 1887-1895. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-731X.2004.09.011HUANG K D, LIU B H, HUANG J, et al. A survey of military simulation technologies[J]. Acta Simulata Systematica Sinica, 2004, 16(9): 1887-1895(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-731X.2004.09.011 [11] 李宏亮, 程华, 金士尧. 基于Agent的复杂系统分布仿真建模方法的研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2007, 43(8): 209-213. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2007.08.065LI H L, CHENG H, JIN S Y. Research of modeling method for Agent-based complex systems distributed simulation[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2007, 43(8): 209-213(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2007.08.065 [12] 饶明波. 基于Agent战场仿真实体模型研究与实现[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2011.RAO M B. Agent-based battlefield simulation entity model research and implementation[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2011 (in Chinese). [13] 陈坚, 廖守亿, 邓方林. 基于多Agent系统的计算机生成兵力建模研究[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2008, 30(10): 1924-1928. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2008.10.026CHEN J, LIAO S Y, DENG F L. On modeling computer generated forces based on multi-agent systems[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2008, 30(10): 1924-1928(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2008.10.026 [14] 阿纳达·佩雷兹·卡斯塔诺. 人工智能实战[M]. 敖富江, 周云彦, 李博, 等, 译, 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2019: 27-29, 51-73.AMALDO P C. Practical artificial intelligence[M]. AO F J, ZHOU Y Y, Li B, et al. translated. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2019: 27-29, 51-73 (in Chinese). [15] 武强. 多智能体强化学习在城市交通信号控制中的研究与应用[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2020.WU Q. Research and application of multi-agent reinforcement learning in traffic signal control[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2020 (in Chinese). [16] 梁鹏, 王海燕, 王耀辉. 由反应式Agent构造智能Agent的方法[J]. 东北电力大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 28(2): 94-97.LIANG P, WANG H Y, WANG Y H. The method by reflection type agent structure intelligence agent[J]. Journal of Northeast Dianli University (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 28(2): 94-97(in Chinese). [17] MOSTAFA S A, MUSTAPHA A, GUNASEKARAN S S, et al. An agent architecture for autonomous UAV flight control in object classification and recognition missions[J]. Soft Computing, 2023, 27(1): 391-404. doi: 10.1007/s00500-021-05613-8 [18] TAJALLI S Z, KAVOUSI-FARD A, MARDANEH M. Multi-agent-based optimal power scheduling of shipboard power systems[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2021, 74: 103137. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2021.103137 [19] SHPILEVOY V, SHISHOV A, SKOBELEV P, et al. Multi-agent system “Smart Factory” for real-time workshop management in aircraft jet engines production[J]. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2013, 46(7): 204-209. doi: 10.3182/20130522-3-BR-4036.00025 [20] LU Z Y, ZHUANG Z L, HUANG Z Z, et al. A framework of multi-agent based intelligent production logistics system[J]. Procedia CIRP, 2019, 83: 557-562. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2019.04.116 [21] ZHANG X, SUN Y C, ZHANG Y J, et al. Multi-agent modelling and situational awareness analysis of human-computer interaction in the aircraft cockpit: A case study[J]. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 2021, 111: 102355. doi: 10.1016/j.simpat.2021.102355 [22] LIU X, GE S S. Optimized control for human-multi-robot collaboration via multi-agent adaptive dynamic programming[J]. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2020, 53(2): 9207-9212. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2020.12.2189 [23] ZHANG L X, LI J C, ZHU Y A, et al. Multi-agent reinforcement learning by the actor-critic model with an attention interface[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 471: 275-284. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.06.049 [24] CASTRO B M, MELO Y D AD, SANTOS N F D, et al. Multi-agent simulation model for the evaluation of COVID-19 transmission[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2021, 136: 104645. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104645 [25] VALLEJO D, CASTRO-SCHEZ J J, GLEZ-MORCILLO C, et al. Multi-agent architecture for information retrieval and intelligent monitoring by UAVs in known environments affected by catastrophes[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 87: 103243. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2019.103243 [26] NING H, SHI Y B, GAO X J. Dynamic simulation of the equipment repair support system based on the OPN model[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2011, 23: 284-289. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2011.11.2503 [27] ZHANG W J, KANG R, GUO L H, et al. Study on military equipment support modeling and simulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2005, 18(2): 142-146. doi: 10.1016/S1000-9361(11)60319-1 [28] GRADY J O. System modeling using the DoD architecture framework[C]//System Requirements Analysis. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2006: 275-287. [29] 李亢, 李新明, 刘东. 基于语义元模型的装备体系结构建模方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2015, 37(11): 2503-2512. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2015.11.13LI K, LI X M, LIU D. Modeling method for weapon system of systems structure based on semantic meta-model[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 37(11): 2503-2512(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2015.11.13 [30] 尹丽丽, 寇力, 范文慧. 基于多Agent的装备保障体系分布式建模与仿真方法[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2017, 29(12): 3185-3194. doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.201712032YIN L L, KOU L, FAN W H. Distributed modeling and simulation method of equipment support system based on multi agent[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2017, 29(12): 3185-3194(in Chinese). doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.201712032 [31] 邢彪, 曹军海, 宋太亮. 基于多Agent仿真的装备保障体系供应保障系统设计与实现[J]. 指挥控制与仿真, 2016, 38(2): 102-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3819.2016.02.021XING B, CAO J H, SONG T L. Design and implementation for the supply support system of equipment support system of systems based on multi-agent simulation[J]. Command Control & Simulation, 2016, 38(2): 102-105(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3819.2016.02.021 [32] 尹延涛, 徐衡博, 高杰, 等. 基于Multi-Agent的导弹装备军民一体化维修保障决策支持系统研究[J]. 质量与可靠性, 2012(4): 12-14.YIN Y T, XU H B, GAO J, et al. Research on multi-agent-based decision support system for military-civilian integrated maintenance support of missile equipment[J]. Quality and Reliability, 2012(4): 12-14(in Chinese). [33] 黄海, 曹军海, 单志伟. 基于MAS的装备综合保障仿真系统设计[J]. 装甲兵工程学院学报, 2008, 22(3): 17-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1497.2008.03.005HUANG H, CAO J H, SHAN Z W. Design of the MAS-based material integrated support simulation system[J]. Journal of Academy of Armored Force Engineering, 2008, 22(3): 17-21(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1497.2008.03.005 [34] 王步云, 张国. 一种适用于人工生命作战仿真的混合Agent结构[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2010, 22(11): 2515-2518. doi: 10.16182/j.cnki.joss.2010.11.070WANG B Y, ZHANG G. Mixed agent architecture for warfare-simulation based on artificial life[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2010, 22(11): 2515-2518(in Chinese). doi: 10.16182/j.cnki.joss.2010.11.070 -







 下载:
下载: