Error analysis and suppression of probe system for SERF atomic spin co-magnetometer
-
摘要:
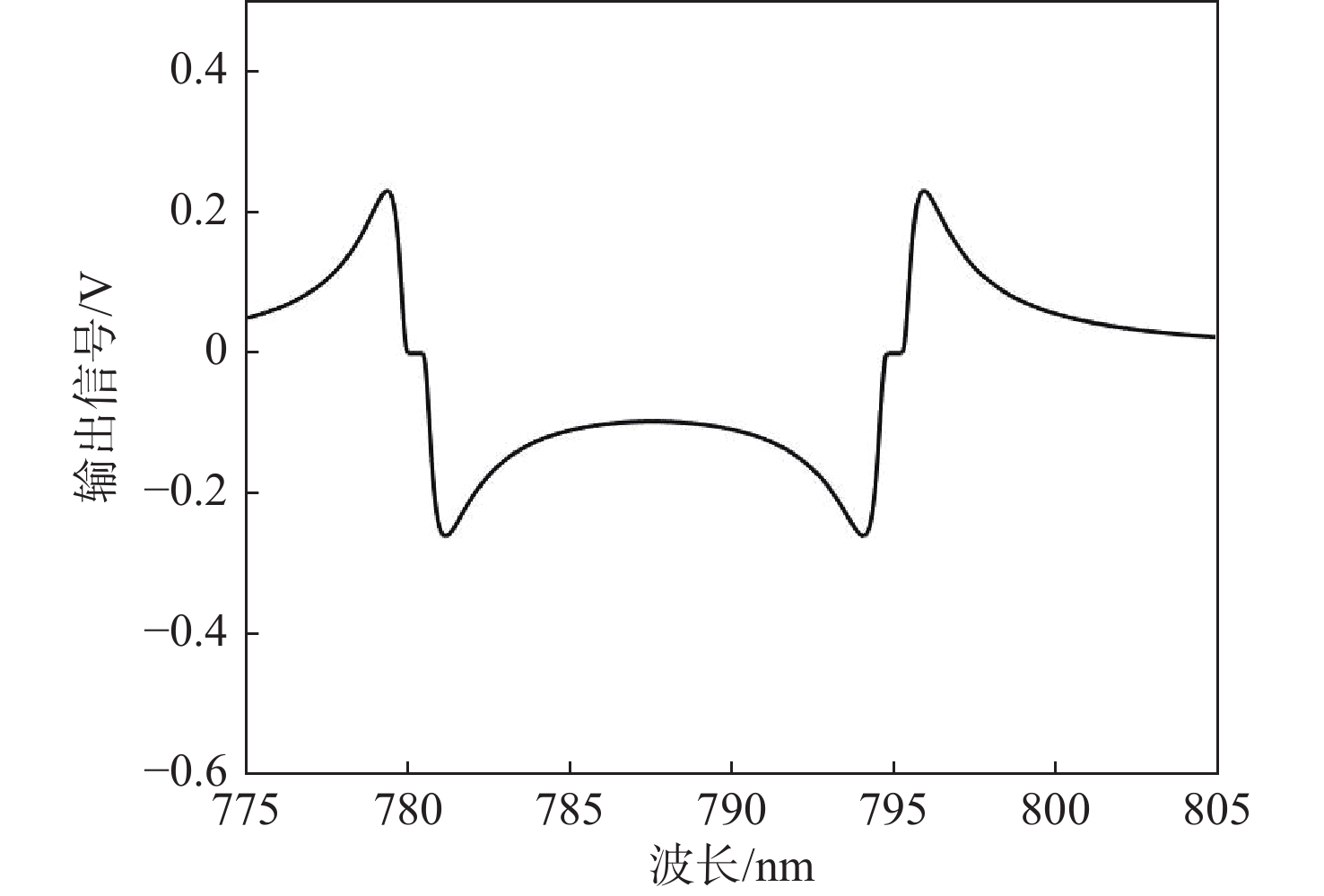
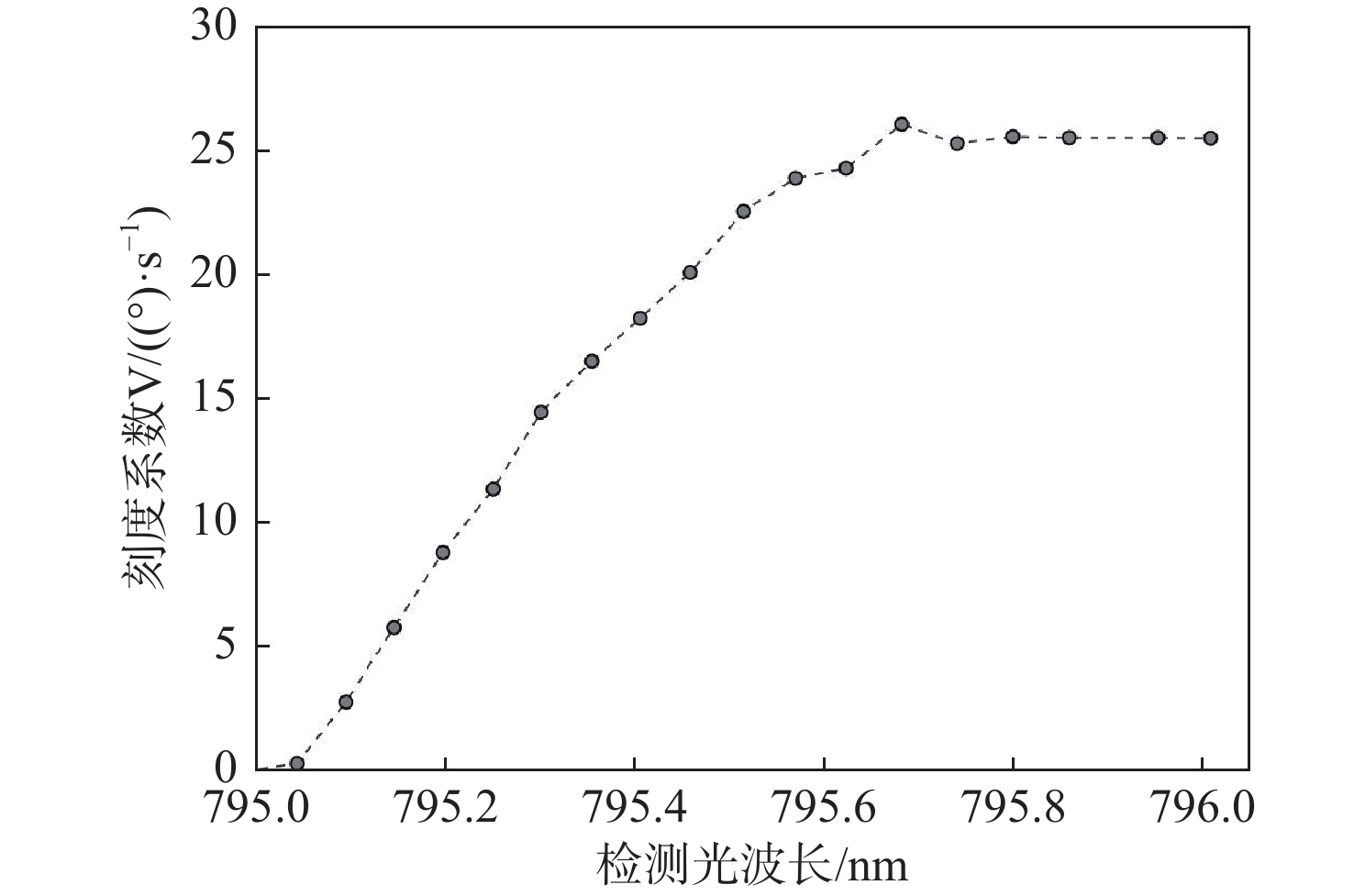
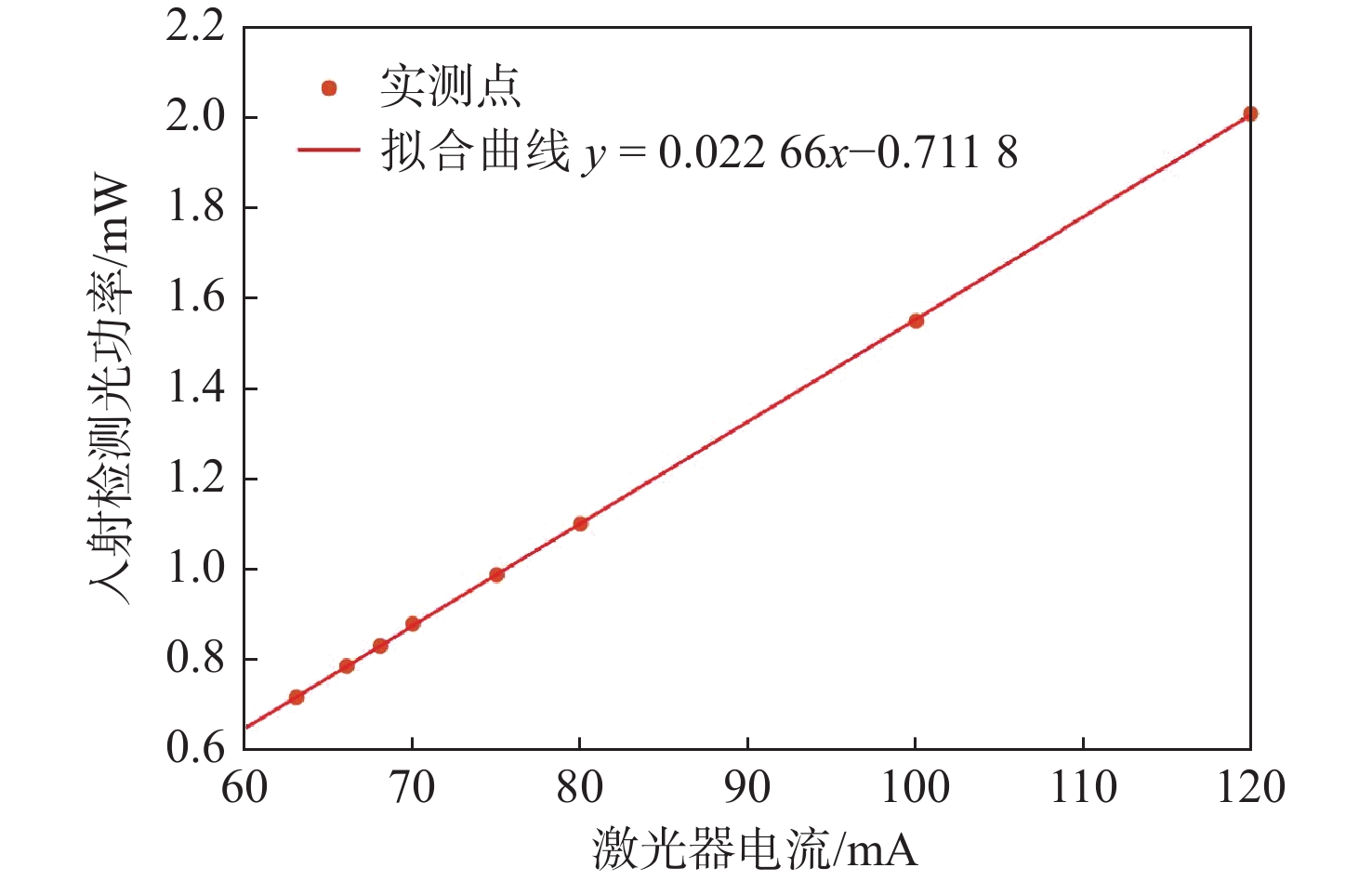
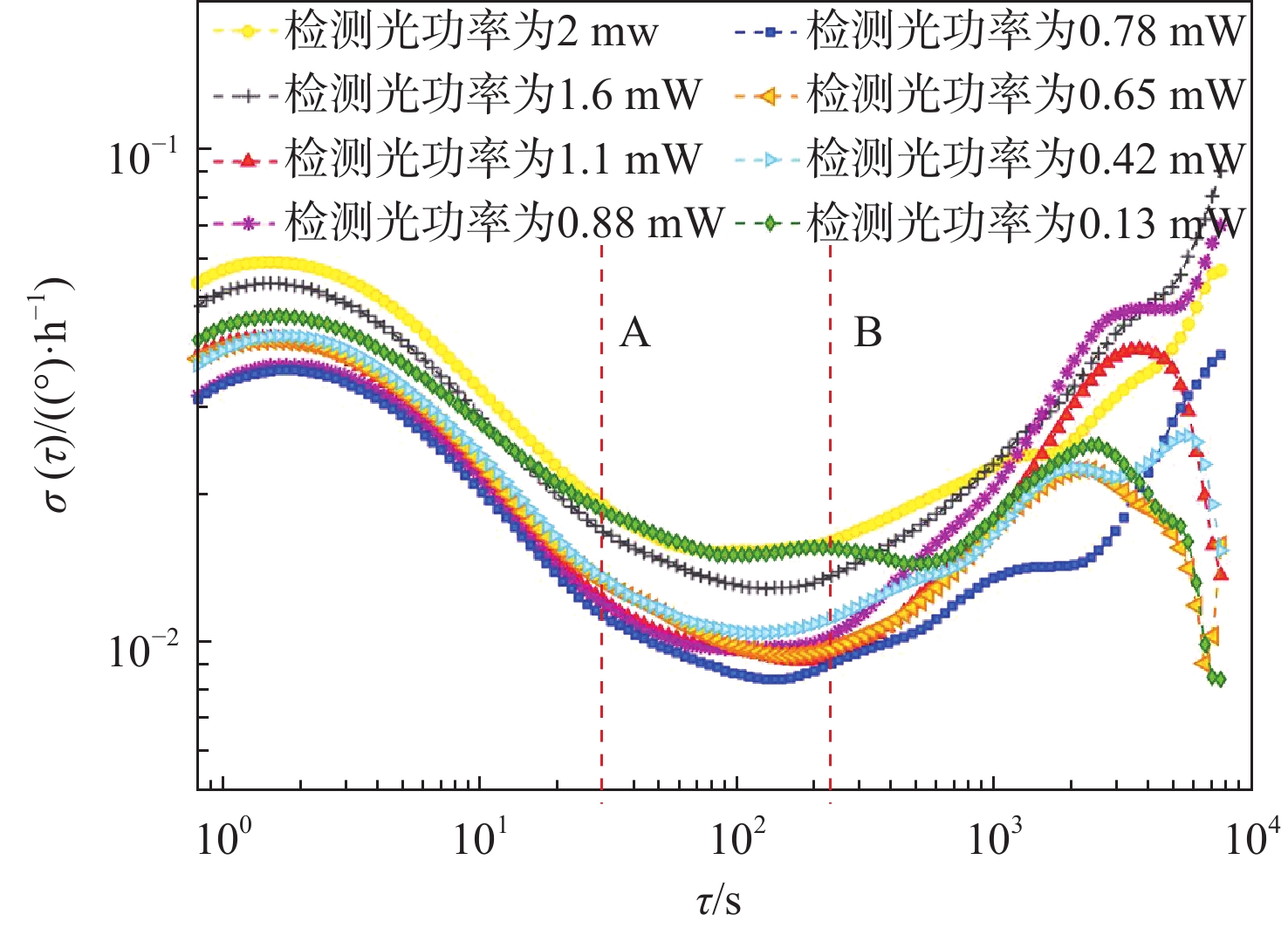
在无自旋交换弛豫(SERF)原子自旋惯性测量装置中,检测系统的性能是决定输出信号灵敏度和稳定性极限的关键因素。为有效抑制SERF原子自旋惯性测量的低频随机噪声,在横向电子自旋极化率稳态解和旋光角表达式的基础上,建立检测相关的输出信号误差机理模型,明确了检测系统影响最终测量信号噪声的主要因素。研究结果表明:检测光入射气室时的初始光强作为信号背景直接引起刻度系数的波动而非作用于电子自旋,而检测光的非理想线偏振导致电子自旋产生横向抽运效果和横向光频移作用,从而引入测量误差。针对检测系统影响测量信号噪声的主要参数,设计了参数优化路径:先通过优化检测光频率,提高惯性测量刻度系数,后通过检测光功率的优化,减小横向抽运效应、横向光频移作用及检测光背景波动。实验表明:通过对比输出信号的Allan方差,优化后SERF原子自旋惯性测量的零偏不稳定性减小了1.8倍,速率斜坡噪声系数从0.124 (º)/h2减小至0.041 (º)/h2,达到了抑制测量信号低频随机噪声的效果。
Abstract:The performance of the probe system is the key factor to determine the sensitivity and stability limit of the spin-exchange relaxation-free (SERF) atomic spin co-magnetometer for inertial measurement. In order to suppress the low-frequency random noise in SERF auto spin co-magnetometer, the error mechanism model for the probe system is established based on the steady-state solution of transverse electron spin polarization and optical rotation angle. The main factors affecting the output signal of the probe system are clarified. According to model analysis, the initial probe light intensity incident on the vapor cell as the signal background directly causes the fluctuation of the scale coefficient rather than the electron spins. In addition, the non-ideal linear polarization of probe light affects the electron spins in a transverse pumping manner and causes a light shift, both of which can cause measurement error. Aiming at the main parameters affecting the noise, the optimization path has been proposed. The probe light frequency has been first optimized to increase the scale coefficient of inertial measurement. Then the transverse pumping rate, light shift, and background fluctuation have been reduced by optimizing the probe light intensity. According to the analysis of Allan variance, the bias instability of SERF auto spin co-magnetometer is suppressed by 1.8 times, and the coefficients of rate ramp are reduced from 0.124 (º)/h2 to 0.041 (º)/h2. Therefore, the effect of reducing the low-frequency random noise in the output signal is achieved.
-
-
[1] 郭雷, 房建成. 导航制导与传感技术研究领域若干问题的思考与展望[J]. 中国科学:信息科学, 2017, 47(9): 1198-1208. doi: 10.1360/N112016-00275GUO L, FANG J C. Recent prospects on some problems of navigation guidance and sensing technology[J]. Scientia Sinica (Informationis), 2017, 47(9): 1198-1208(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/N112016-00275 [2] 薛连莉, 陈少春, 陈效真. 2017年国外惯性技术发展与回顾[J]. 导航与控制, 2018, 17(2): 1-9.XUE L L, CHEN S C, CHEN X Z. Development and review of foreign inertial technology in 2017[J]. Navigation and Control, 2018, 17(2): 1-9(in Chinese). [3] HU Z X, GALLACHER B J. Effects of nonlinearity on the angular drift error of an electrostatic MEMS rate integrating gyroscope[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(22): 10271-10280. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2929352 [4] LEFÈVRE H C. The fiber-optic gyroscope[M]. Boston: Artech House, 1993. [5] LEE B. Review of the present status of optical fiber sensors[J]. Optical Fiber Technology, 2003, 9(2): 57-79. doi: 10.1016/S1068-5200(02)00527-8 [6] KETTERLE W. Nobel lecture: When atoms behave as waves: Bose-Einstein condensation and the atom laser[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2002, 74(4): 1131-1151. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.74.1131 [7] CHU S. Cold atoms and quantum control[J]. Nature, 2002, 416(6877): 206-210. doi: 10.1038/416206a [8] GUSTAVSON T L, BOUYER P, KASEVICH M A. Precision rotation measurements with an atom interferometer gyroscope[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1997, 78(11): 2046-2049. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.78.2046 [9] WOODMAN K F, FRANKS P W, RICHARDS M D. The nuclear magnetic resonance gyroscope: A review[J]. Journal of Navigation, 1987, 40(3): 366-384. doi: 10.1017/S037346330000062X [10] KORNACK T W, GHOSH R K, ROMALIS M V. Nuclear spin gyroscope based on an atomic comagnetometer[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2005, 95(23): 230801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.230801 [11] ALLRED J C, LYMAN R N, KORNACK T W, et al. High-sensitivity atomic magnetometer unaffected by spin-exchange relaxation[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2002, 89(13): 130801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.89.130801 [12] SMICIKLAS M A, BROWN J M, CHEUK L W, et al. New test of local Lorentz invariance using a 21Ne-Rb-K Comagnetometer[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2011, 107(17): 171604. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.171604 [13] SMICIKLAS M A, ROMALIS M V. Test of Lorentz invariance with Rb-21Ne co-magnetometer at the south pole[C]//Proceedings of the Sixth Meeting on CPT and Lorentz Symmetry. Bloomington: World Scientific Publishing House, 2014: 95-98. [14] ROMALIS M V, KORNACK T. Chip-scale combinatorial atomic navigator (C-SCAN) low drift nuclear spin gyroscope: 125560431[R]. Princeton: Princeton University, 2018. [15] LIMES M E, SHENG D, ROMALIS M V. 3He-129Xe comagnetometery using 87Rb detection and decoupling[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2018, 120(3): 033401. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.033401 [16] BUDKER D, GAWLIK W, KIMBALL D F, et al. Resonant nonlinear magneto-optical effects in atoms[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2002, 74(4): 1153-1201. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.74.1153 [17] XING L, ZHAI Y Y, FAN W F, et al. Miniaturized optical rotation detection system based on liquid crystal variable retarder in a K-Rb-21Ne gyroscope[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(26): 38061. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.038061 [18] VASILAKIS G. Precision measurements of spin interactions with high density atomic vapors[D]. Princeton: Princeton University, 2011. [19] CHOUDHURI A R. Classical electrodynamics[J]. Current Science, 2015, 109(3): 632-633. [20] KORNACK T W. A test of CPT and Lorentz symmetry using a K-3He co-magnetometer[D]. Princeton: Princeton University, 2005. [21] 张桂才. 光纤陀螺原理与技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2008.ZHANG G C. The principles and technologies of fiber-optic gyroscope[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2008 (in Chinese). 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 周晓猛,蔡金乐,郭一博,廖云龙. 商用锂离子电池快充降解及热失控特性研究. 中国民航大学学报. 2025(01): 27-32 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 卫寿平,孙杰,李吉刚,周添,陈静,党胜男,唐娜,张帆. 锂离子电池热失控气体产物检测及分析技术研究进展. 储能科学与技术. 2024(11): 4155-4176 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-








 下载:
下载:

 百度学术
百度学术

