-
摘要:
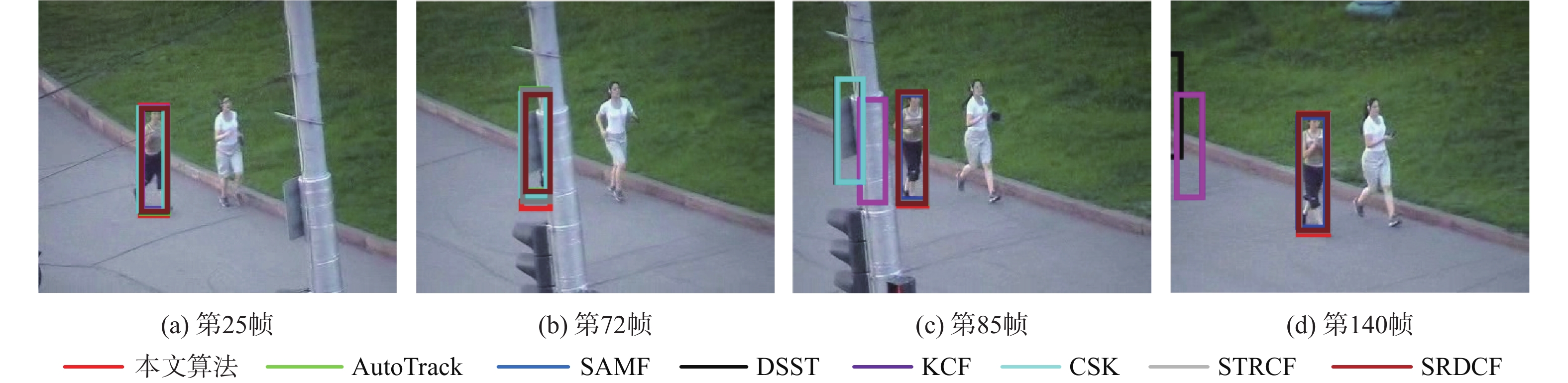
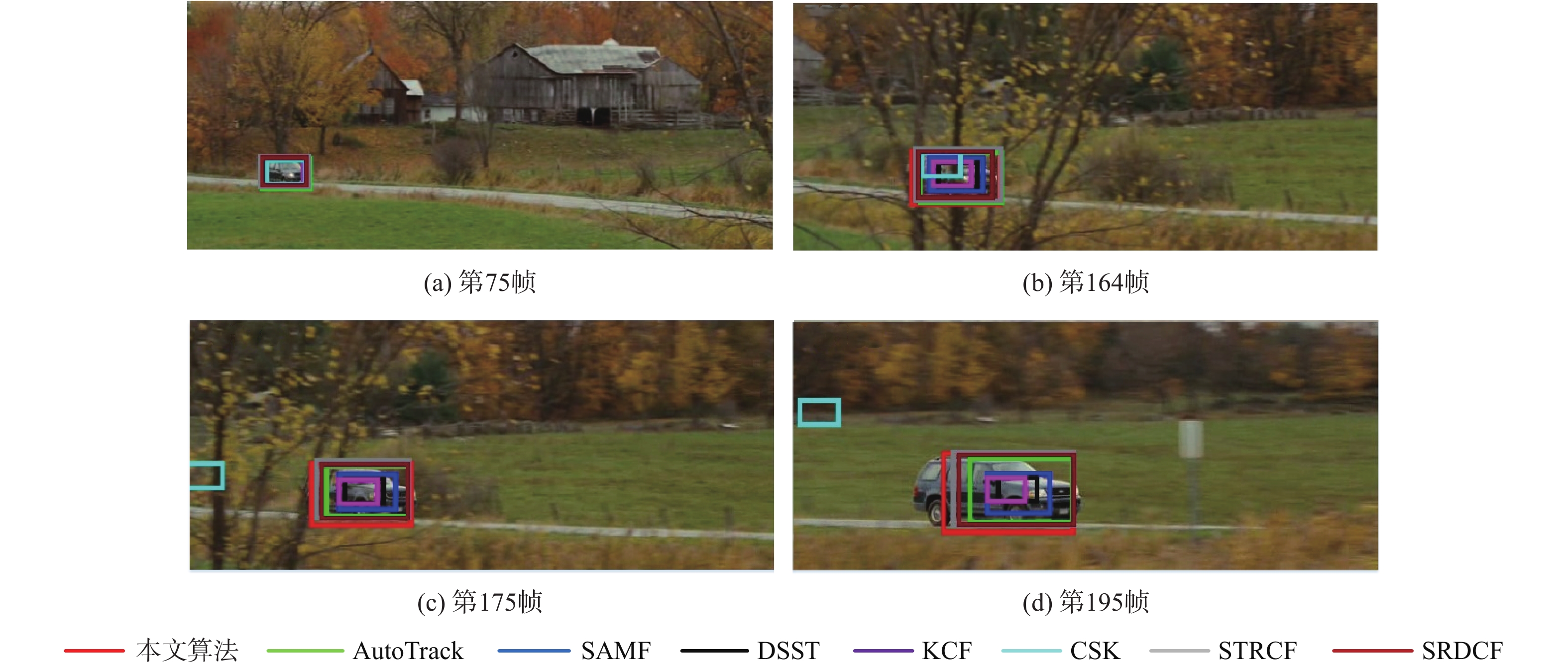
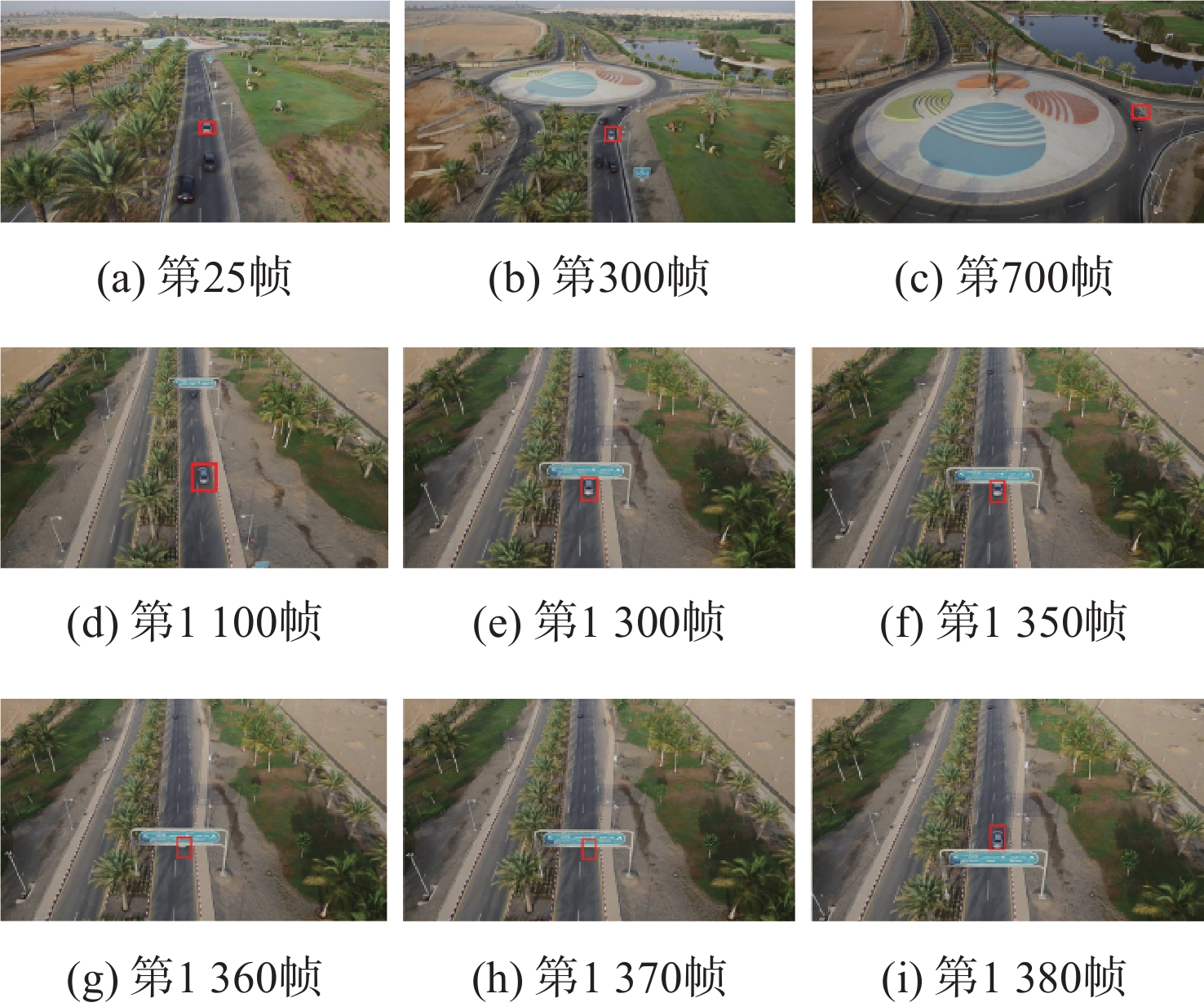
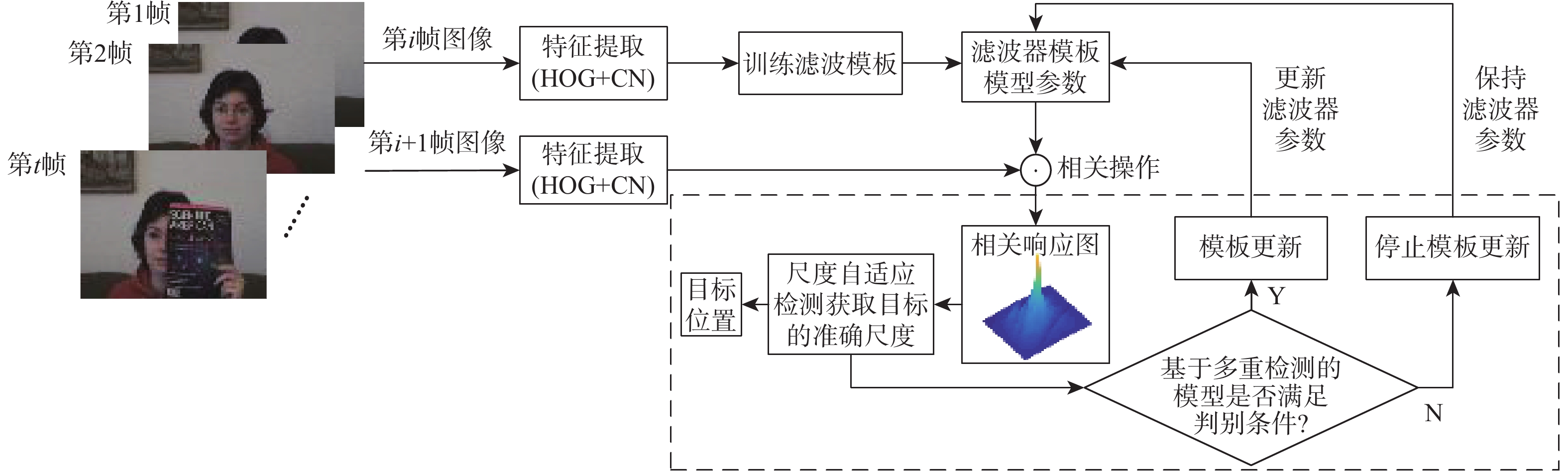
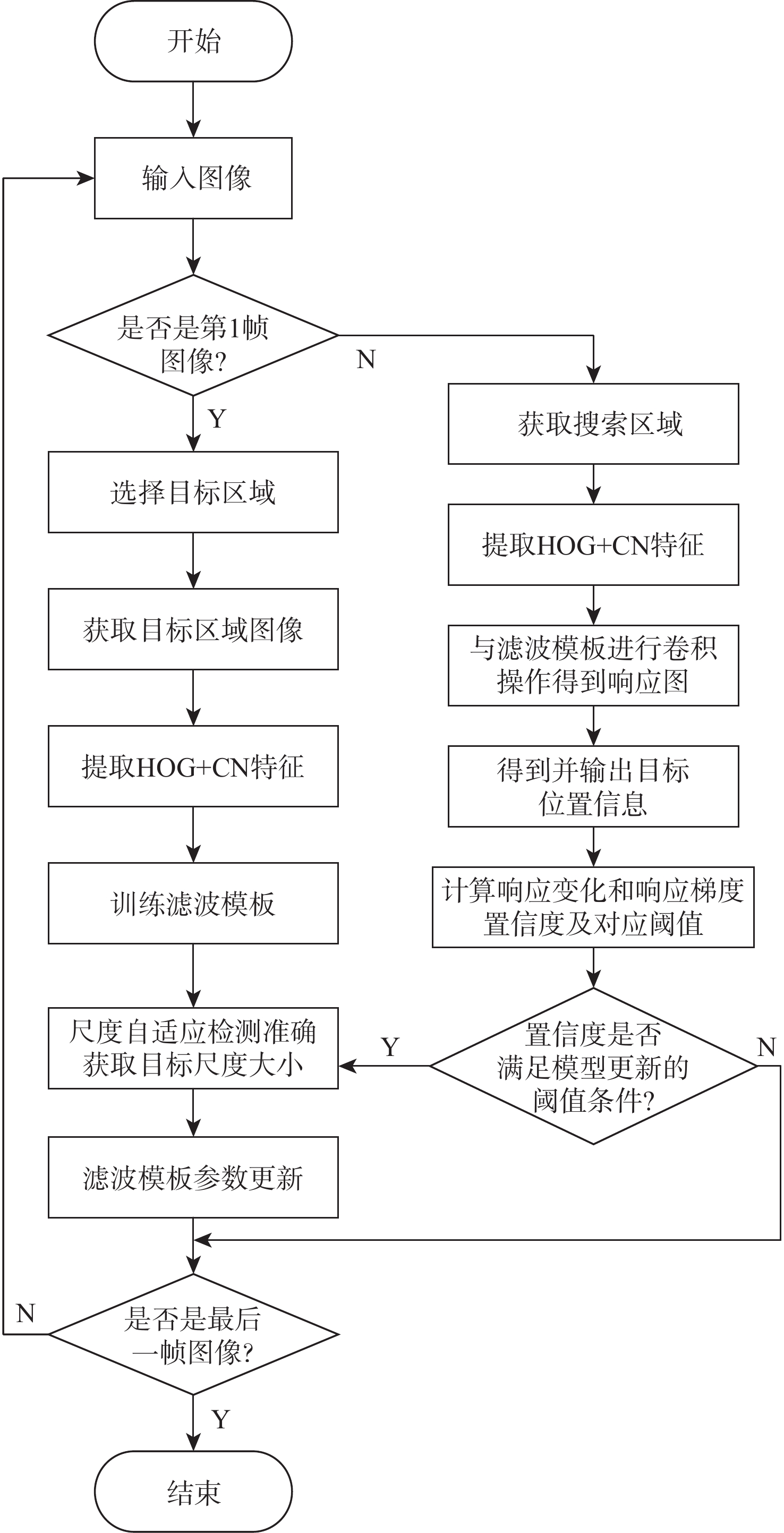
针对无人机(UAV)目标跟踪过程中遇到目标被障碍物遮挡时跟踪效果不佳的问题,提出一种多重检测的抗遮挡目标跟踪算法。在基于时空正则化相关滤波算法的框架下通过融合多种置信度函数,设计了一种响应置信度判别方法;为了具体了解目标被遮挡情况,将响应差值变化和响应梯度变化结合在一起作为判断是否更新滤波模板参数的依据;设计了一种融合分块思想与金字塔尺度池的尺度估计方法来解决目标在图像中尺度大小变化问题。所提算法在UAV数据集上相较于其他7种算法有不错的表现,在跟踪过程中面对目标遮挡、尺度变化和快速移动问题的跟踪精度和成功率上都有明显的提升。结果表明:所提算法能够更好地应对UAV在目标跟踪过程中出现的目标遮挡和尺度变化的问题,具有良好的快速性、准确性和鲁棒性。
Abstract:In this research, a multi-detection anti-occlusion target tracking method is suggested to address the issue of poor tracking effect when unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) targets are occluded by obstacles during the target tracking process. A response confidence discrimination method is designed by fusing various confidence functions under the framework of a spatiotemporal regularization correlation filtering algorithm. In order to understand the occlusion situation, the change of response difference and response gradient are combined together as the basis to judge whether to update the filter template parameters. A scale estimation method combining the block idea and pyramid scale pool is designed to solve the problem of the scale variation of the target in the image. Compared with the other seven algorithms, the proposed algorithm performs well in the UAV data set, and significantly improves the tracking accuracy and success rate in the face of target occlusion, scale change, and fast movement problems in the tracking process. The findings demonstrate that the multi-detection-based anti-occlusion target tracking algorithm has good speed, accuracy, and robustness and can more effectively address the issues of target occlusion and dimension change in the process of UAV target tracking.
-
表 1 8种算法在UAV123数据集上的性能对比
Table 1. Performance comparison of 8 algorithms on UAV123 dataset
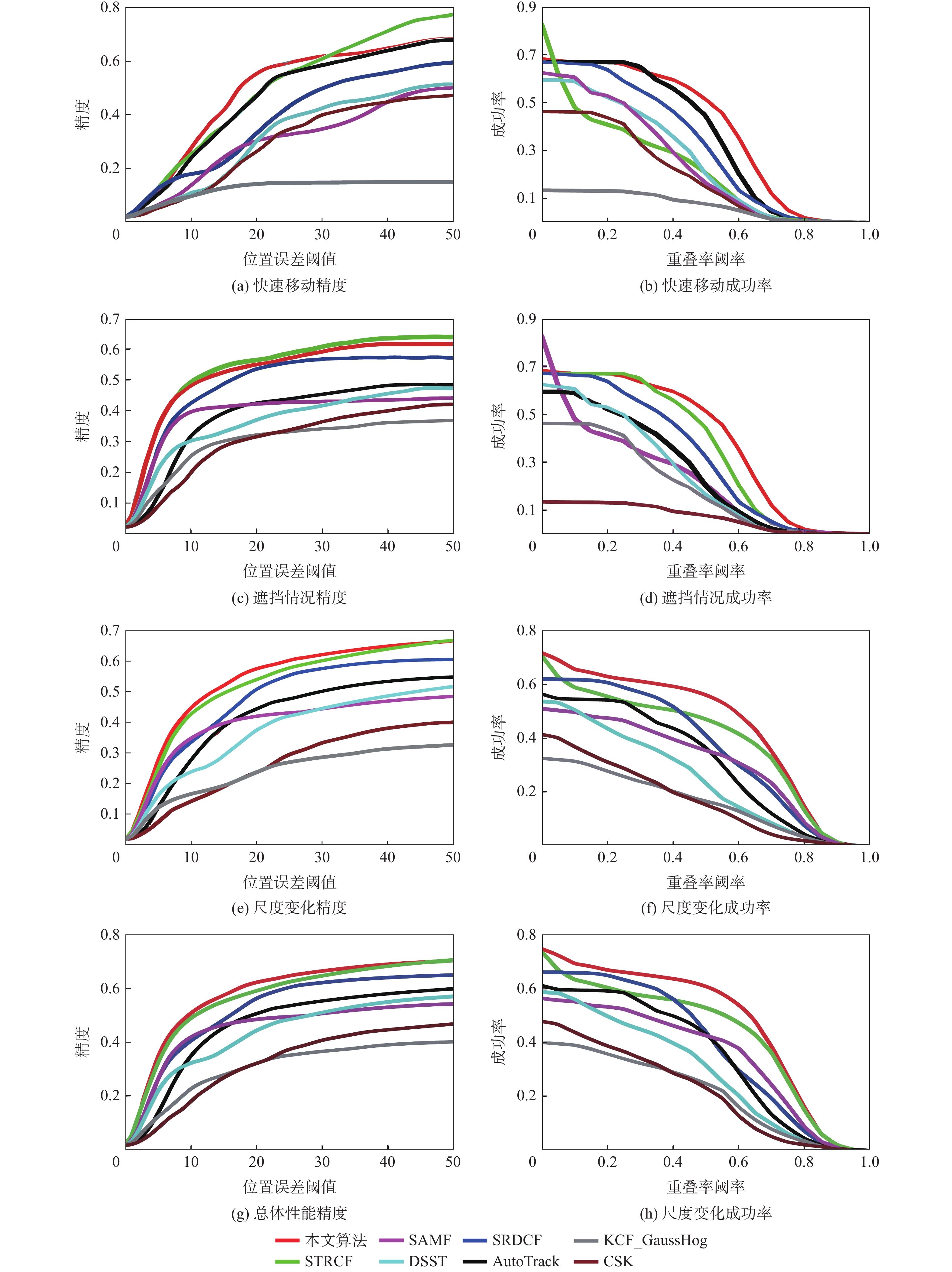
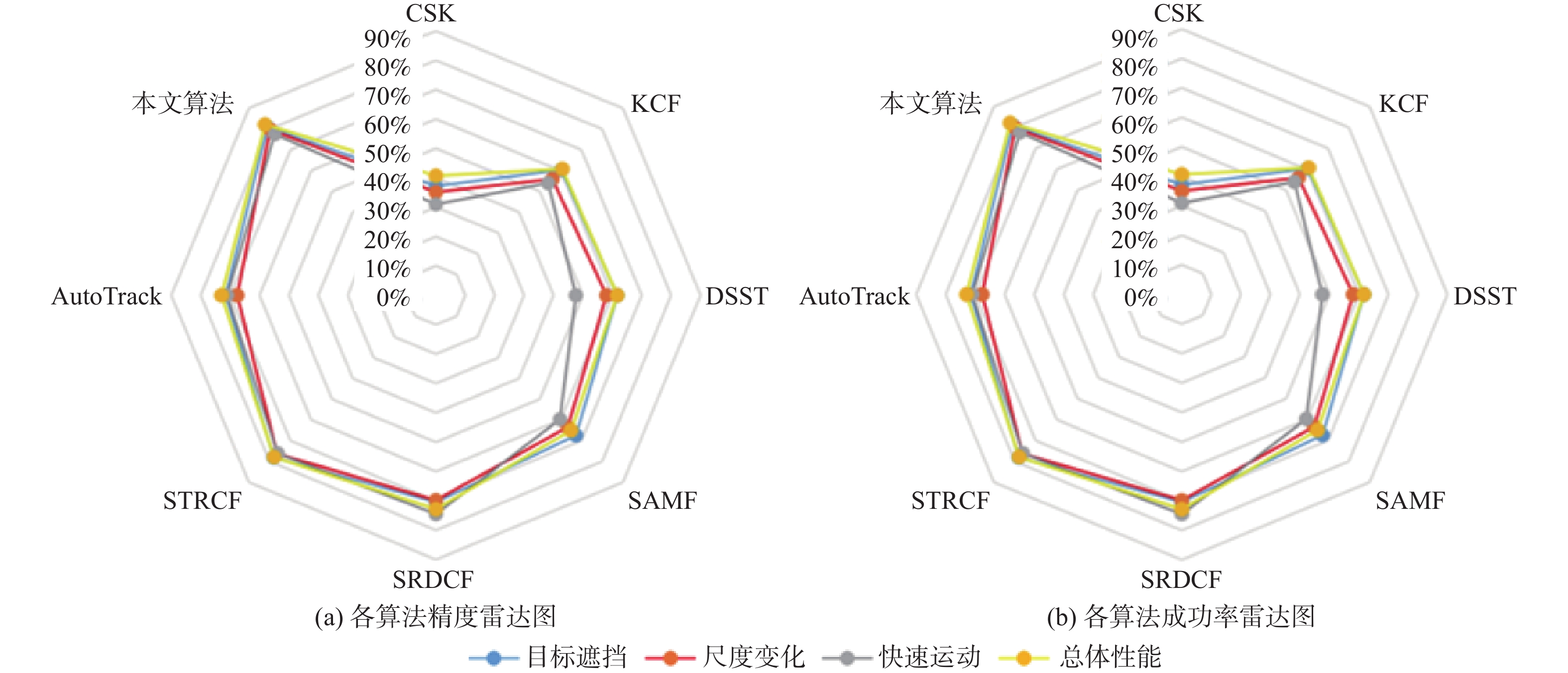
% 算法 精度 成功率 快速运动 遮挡 尺度变化 总体性能 快速运动 遮挡 尺度变化 总体性能 CSK 26.2 31.6 23.8 32.1 14.6 22.8 15.2 23.2 KCF 14.1 32.2 23.8 32.2 7.6 26.6 16.5 24.8 DSST 30.1 37.1 37.6 44.5 20.0 28.9 23.1 31.6 SAMF 30.3 42.2 42.0 48.5 16.4 37.5 35.3 42.5 SRDCF 33.0 53.6 50.8 56.3 32.1 39.4 40.9 44.0 STRCF 47.3 56.5 54.0 59.1 20.4 51.2 47.0 52.9 AutoTrack 46.9 42.5 44.4 50.6 44.1 32.3 36.4 43.3 本文算法 55.4 55.0 57.4 62.2 51.1 53.1 55.9 60.8 表 2 8种算法在DTB70数据集上的性能对比
Table 2. Performance comparison of 8 algorithms on DTB70 dataset
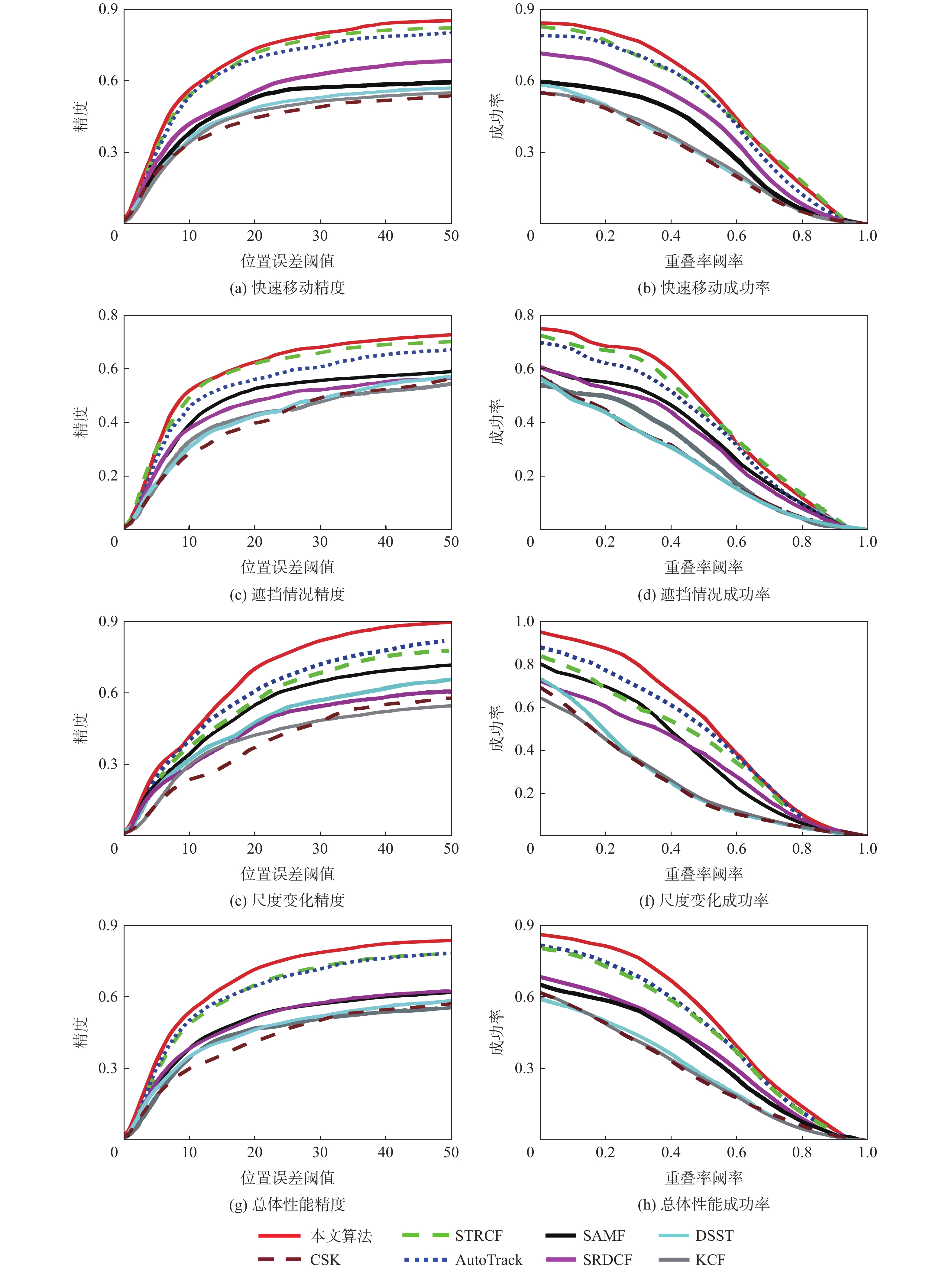
% 算法 精度 成功率 快速运动 遮挡 尺度变化 总体性能 快速运动 遮挡 尺度变化 总体性能 CSK 44.3 39.7 37.0 41.5 27.2 24.4 23.9 27.2 KCF 47.0 42.9 42.2 46.3 28.0 27.0 24.0 28.0 DSST 48.5 42.3 47.3 46.3 28.1 24.4 25.5 27.6 SAMF 52.8 52.5 54.9 52.0 33.4 32.5 37.3 33.9 SRDCF 55.4 47.8 46.2 51.2 39.8 31.0 35.9 36.3 STRCF 71.3 61.7 56.8 64.9 46.7 40.0 41.7 43.7 AutoTrack 69.1 55.9 60.6 64.5 45.7 37.2 45.9 44.2 本文算法 73.1 62.4 70.0 71.5 49.0 41.2 50.2 47.9 表 3 8种算法在OTB100数据集上的性能对比
Table 3. Performance comparison of 8 algorithms on OTB100 dataset
% 算法 精度 成功率 快速运动 遮挡 尺度变化 总体性能 快速运动 遮挡 尺度变化 总体性能 CSK 31 37.2 35.1 40.7 29.9 27.4 27 33.6 KCF 54 60.4 56 60.8 43.6 44.2 38.2 46.3 DSST 47.6 61.7 58 61.7 38.8 42.6 39.4 46.8 SAMF 59.7 67.4 63.4 65 51.1 56.6 52 55 SRDCF 74.5 70.4 69.8 72.8 68.9 61.9 62.7 65.8 STRCF 76.1 78.1 76.3 77.9 70.8 69.9 67.7 70.4 AutoTrack 71 71.5 67.6 72.9 65.1 62.5 57.9 64.9 本文算法 77.6 81 79.8 82.2 71.1 70.7 71.8 73.8 表 4 各个算法在3种数据集上的平均实时性能
Table 4. Average real-time performance of each algorithm on three kinds of datasets
算法 实时性能/(帧·s−1) CSK 118 KCF 112 DSST 32 SAMF 26 SRDCF 88 STRCF 101 AutoTrack 110 本文算法 93 -
[1] BONATTI R, HO C, WANG W S, et al. Towards a robust aerial cinematography platform: Localizing and tracking moving targets in unstructured environments[C]// 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 229-236. [2] LI R, PANG M J, ZHAO C, et al. Monocular long-term target following on UAVs[C]// 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 29-37. [3] LUKEŽIC A, VOJÍR T, ZAJC L C, et al. Discriminative correlation filter with channel and spatial reliability[C]// 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 4847-4856. [4] BOLME D S, BEVERIDGE J R, DRAPER B A, et al. Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters[C]// 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 2544-2550. [5] HENRIQUES J F, CASEIRO R, MARTINS P, et al. Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2012: 702-715. [6] HENRIQUES J F, CASEIRO R, MARTINS P, et al. High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(3): 583-596. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2345390 [7] NAM H, HAN B. Learning multi-domain convolutional neural networks for visual tracking[C]// 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 4293-4302. [8] DANELLJAN M, BHAT G, KHAN F S, et al. ECO: Efficient convolution operators for tracking[C]// 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 6931-6939. [9] WANG L, LIU T, WANG B, et al. Learning hierarchical features for visual object tracking with recursive neural networks[C]// 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 3088-3092. [10] JIANG M X, HAI T, PAN Z G, et al. Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning for multi-object tracker[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 32400-32407. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2901300 [11] 潘振福, 朱永利. 使用PSR重检测改进的核相关目标跟踪方法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2017, 53(12): 196-202. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1601-0261PAN Z F, ZHU Y L. Improvement for tracker with kernelized correlation filters with PSR redetection[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2017, 53(12): 196-202(in Chinese). doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1601-0261 [12] 侯志强, 韩崇昭. 视觉跟踪技术综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2006, 32(4): 603-617. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2006.04.016HOU Z Q, HAN C Z. A survey of visual tracking[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2006, 32(4): 603-617(in Chinese). doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2006.04.016 [13] MA H Y, ACTON S T, LIN Z L. SITUP: Scale invariant tracking using average peak-to-correlation energy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 3546-3557. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2962694 [14] LI F, TIAN C, ZUO W M, et al. Learning spatial-temporal regularized correlation filters for visual tracking[C]// 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 4904-4913. [15] UZKENT B, SEO Y. EnKCF: Ensemble of kernelized correlation filters for high-speed object tracking[C]// 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1133-1141. [16] LIU S, WANG S, LIU X Y, et al. Fuzzy detection aided real-time and robust visual tracking under complex environments[C]// IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 90-102. [17] HUANG Z Y, FU C H, LI Y M, et al. Learning aberrance repressed correlation filters for real-time UAV tracking[C]// 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 2891-2900. [18] DANELLJAN M, HÄGER G, SHAHBAZ KHAN F, et al. Accurate scale estimation for robust visual tracking[C]// Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference 2014. Nottingham: British Machine Vision Association, 2014: 1064-1075. [19] DANELLJAN M, HÄGER G, KHAN F S, et al. Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking[C]// 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 4310-4318. [20] HENRIQUES J F, CASEIRO R, MARTINS P, et al. Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels[C]//Proceedings of the 12th European conference on Computer Vision—Volume Part IV. New York: ACM, 2012: 702-715. [21] LI Y, ZHU J K. A scale adaptive kernel correlation filter tracker with feature integration[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2015: 254-265. [22] LI Y M, FU C H, DING F Q, et al. AutoTrack: Towards high-performance visual tracking for UAV with automatic spatio-temporal regularization[C]// 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 11923-11932. -








 下载:
下载: