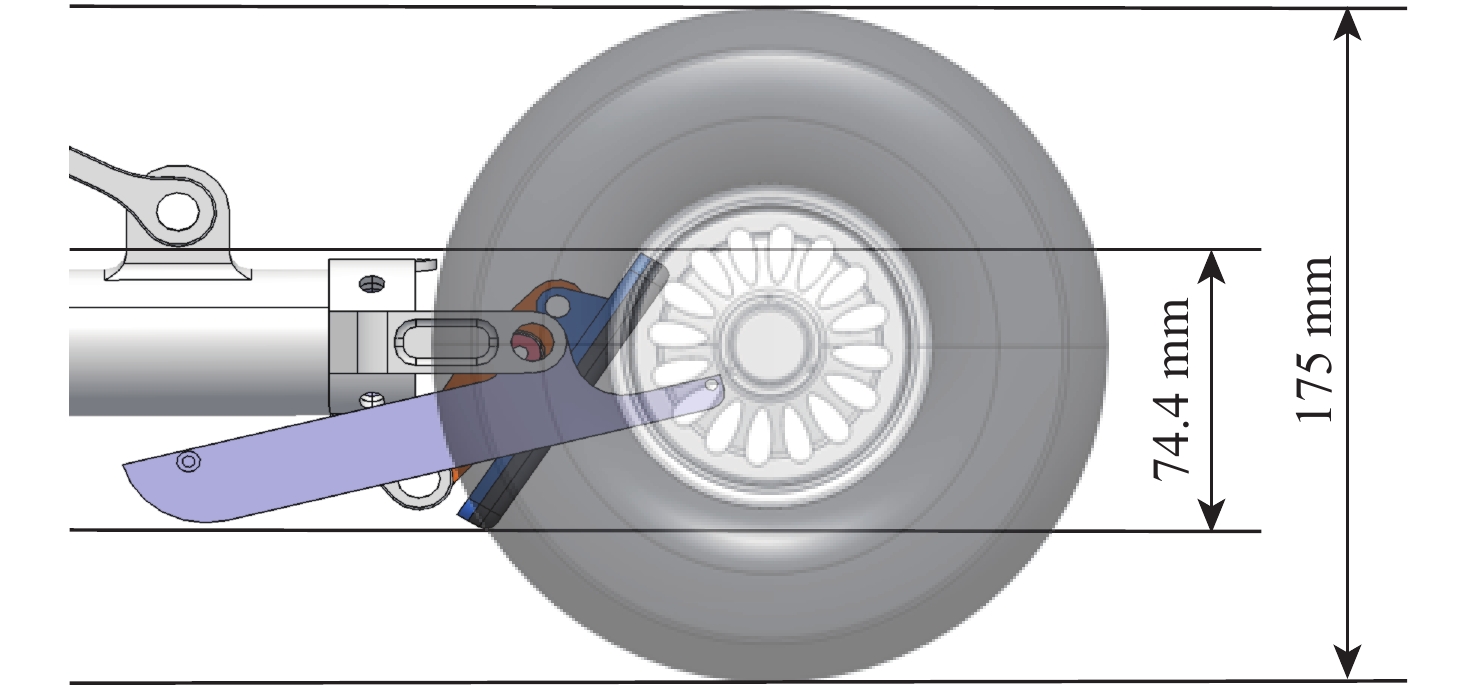
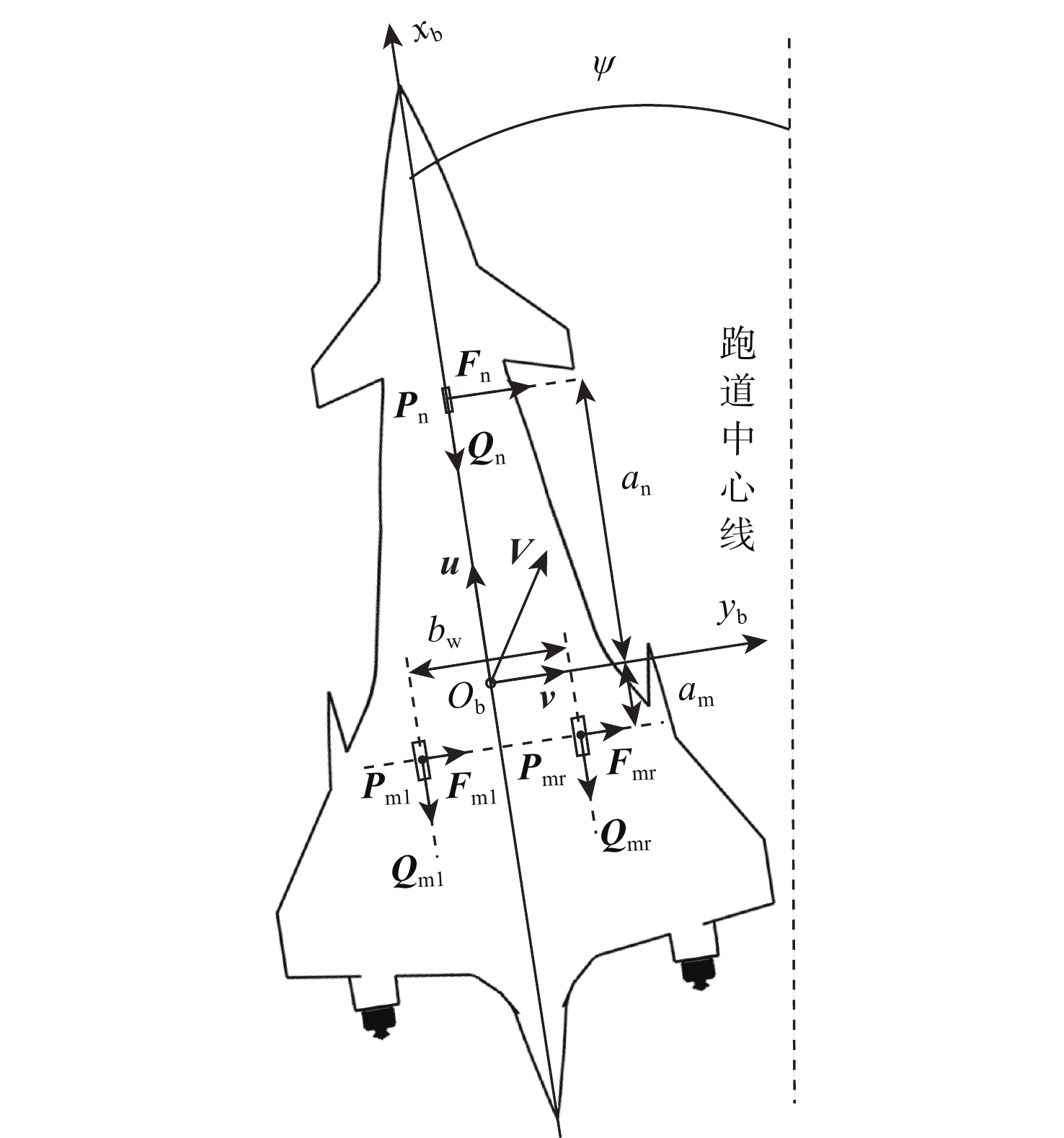
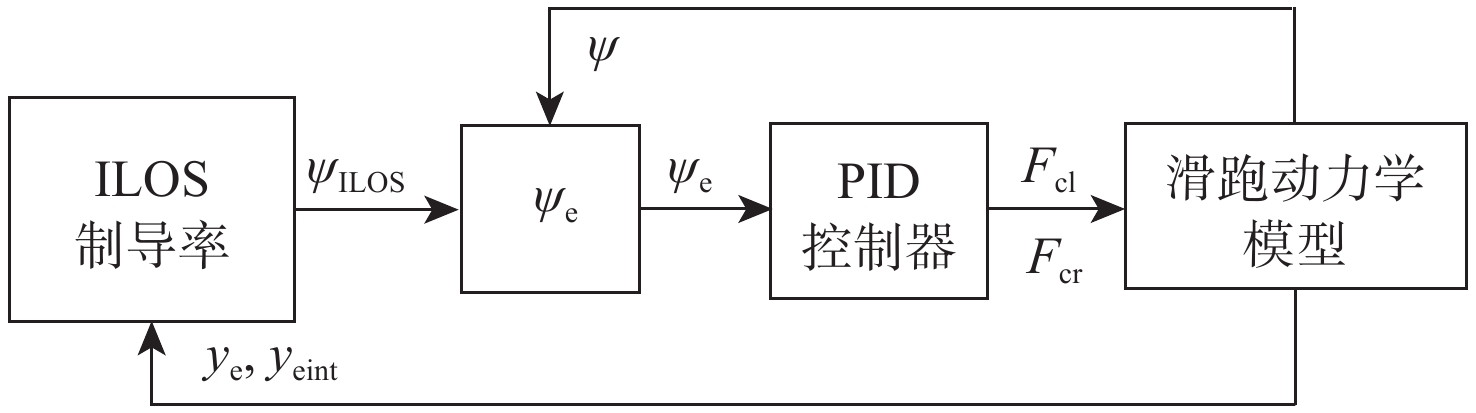
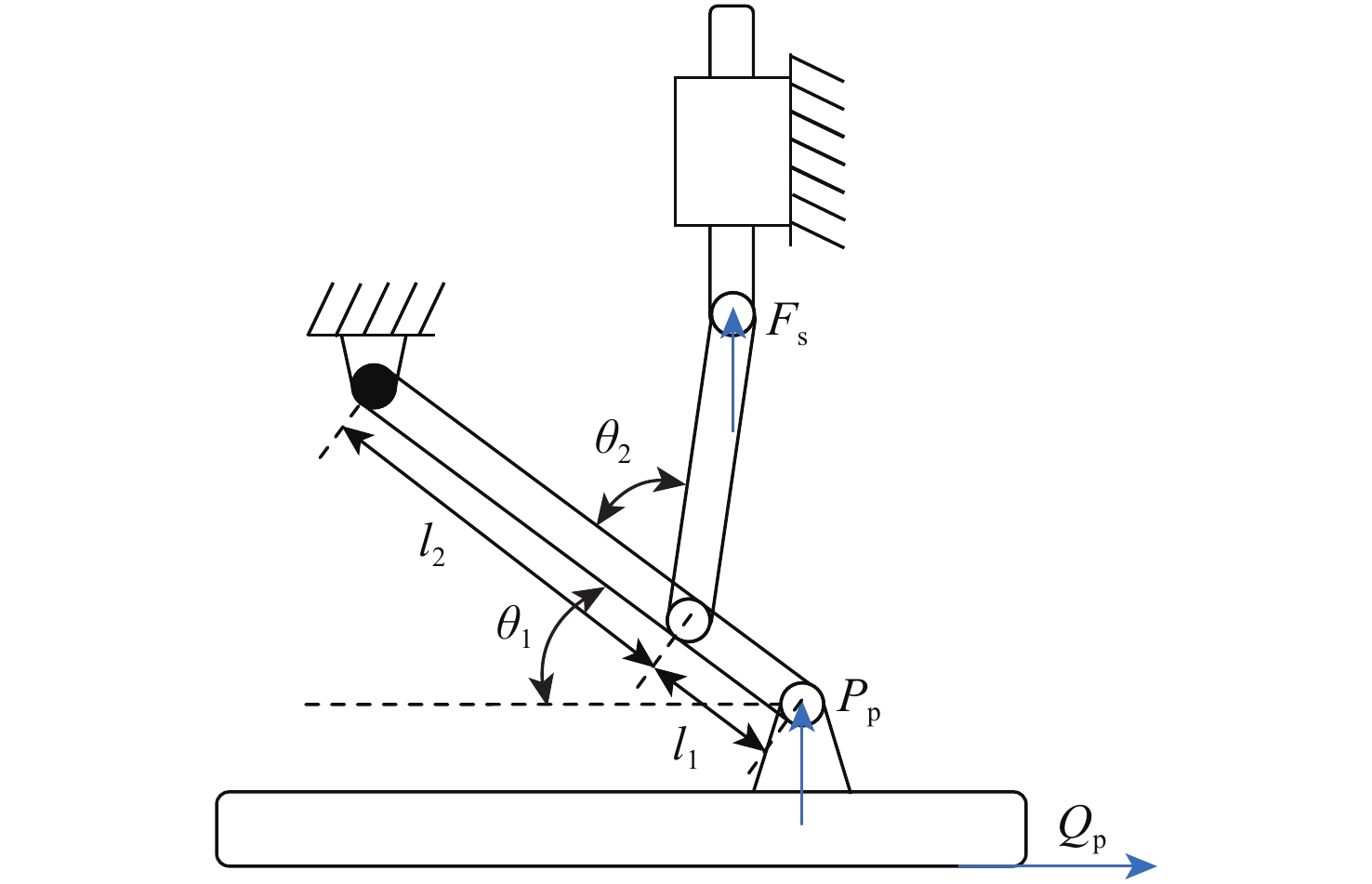
Taxiing deviation-correction control of a new variable-friction equipped-skid aircraft
-
摘要:
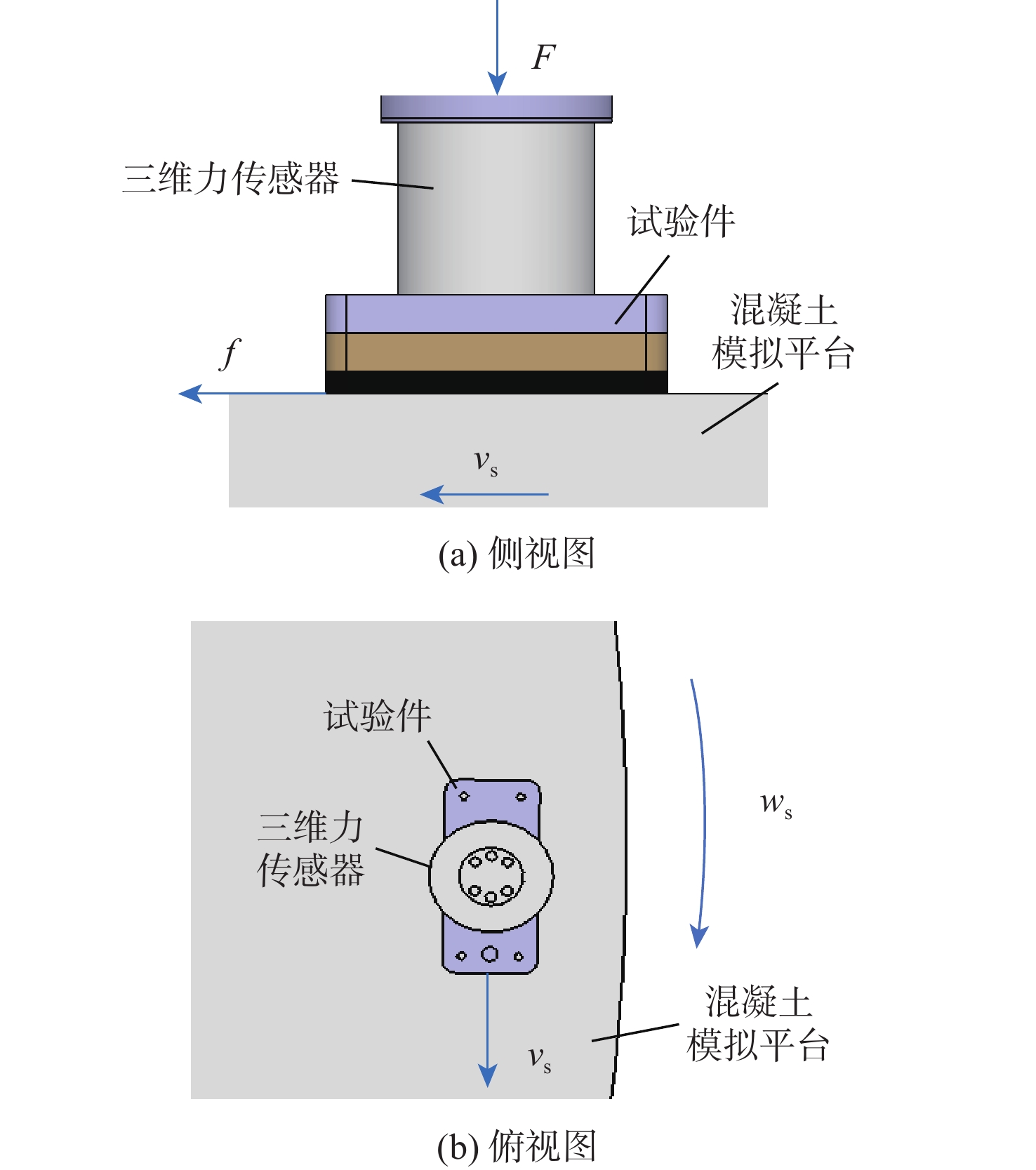
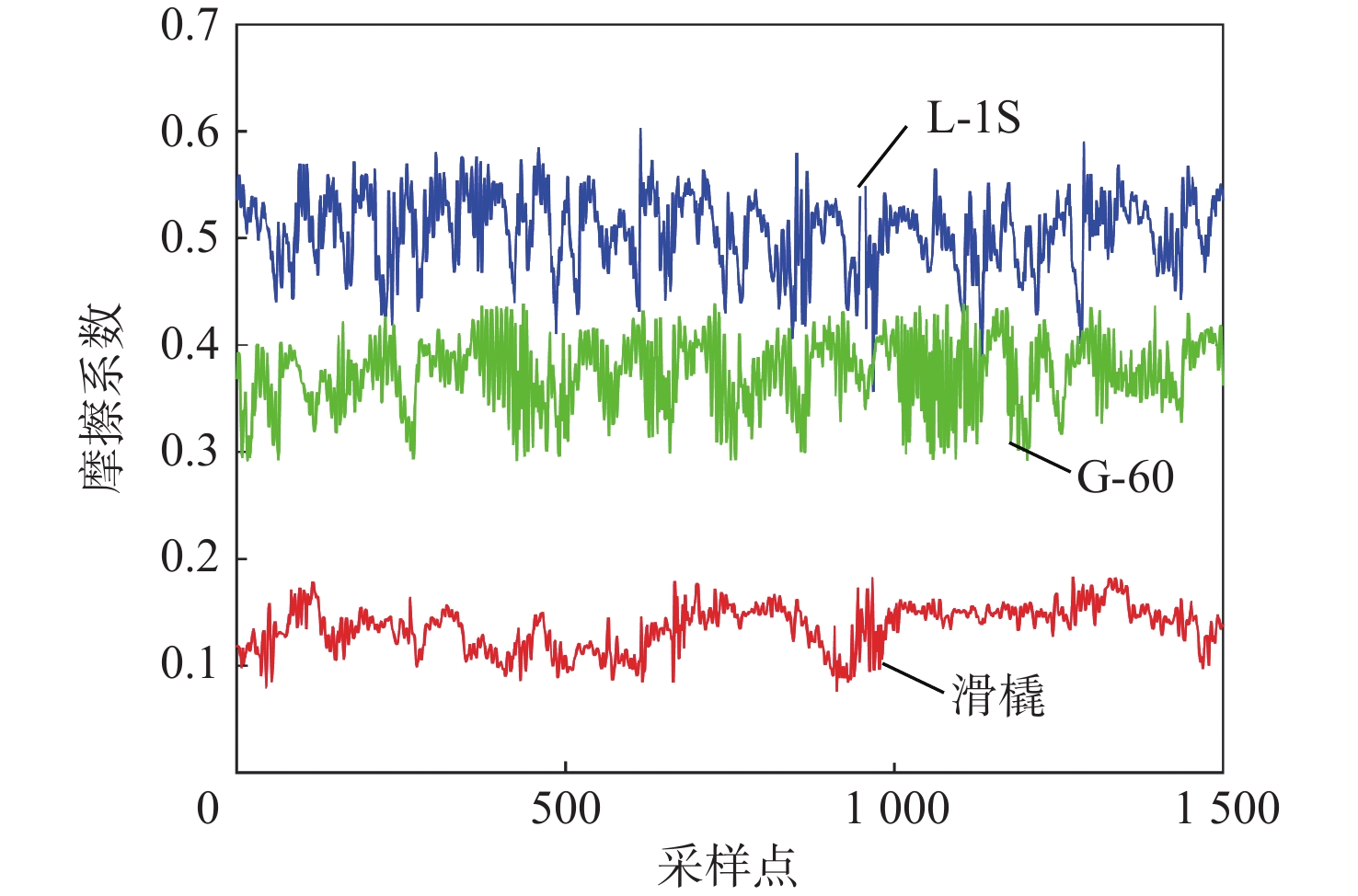
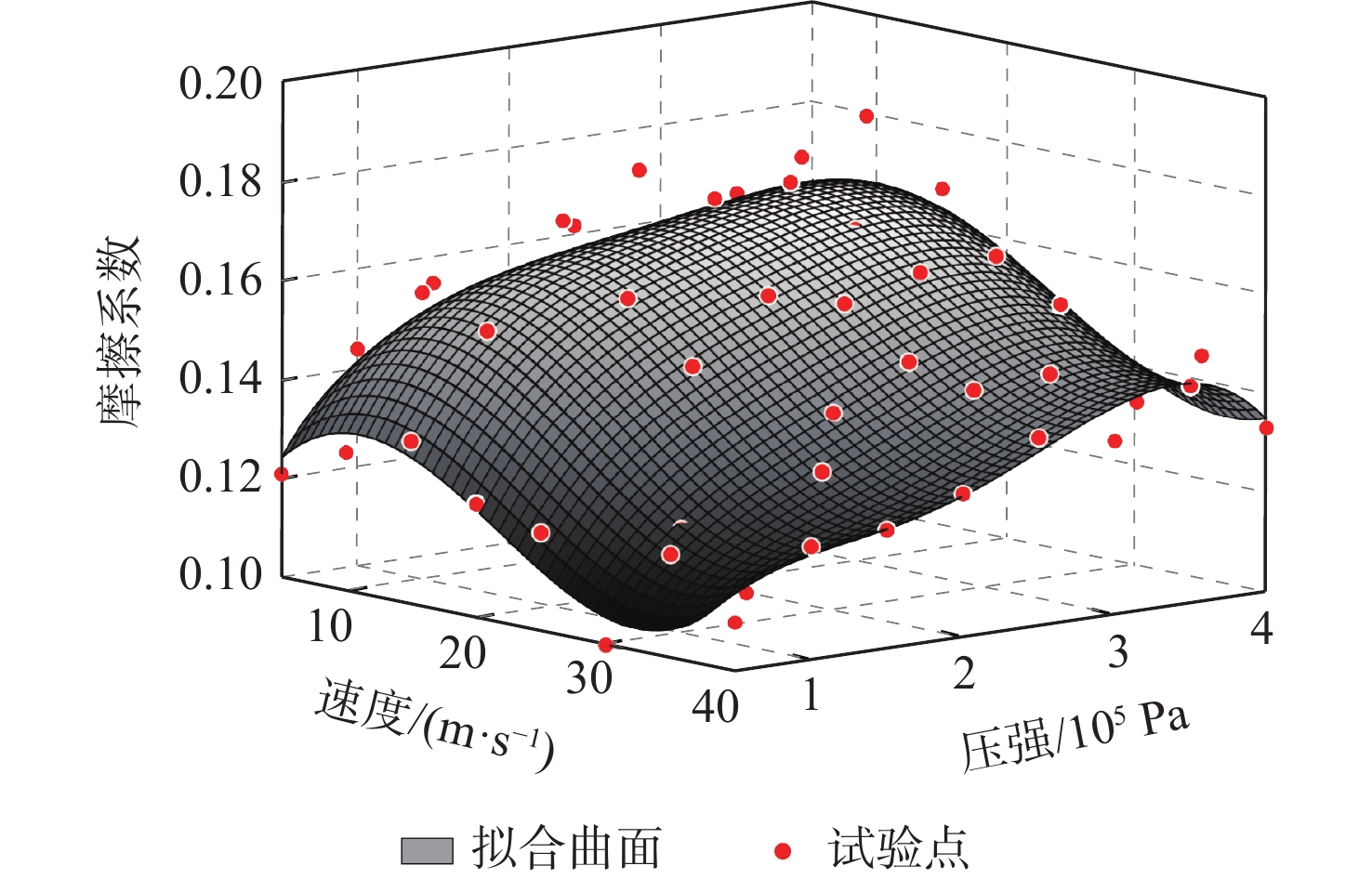
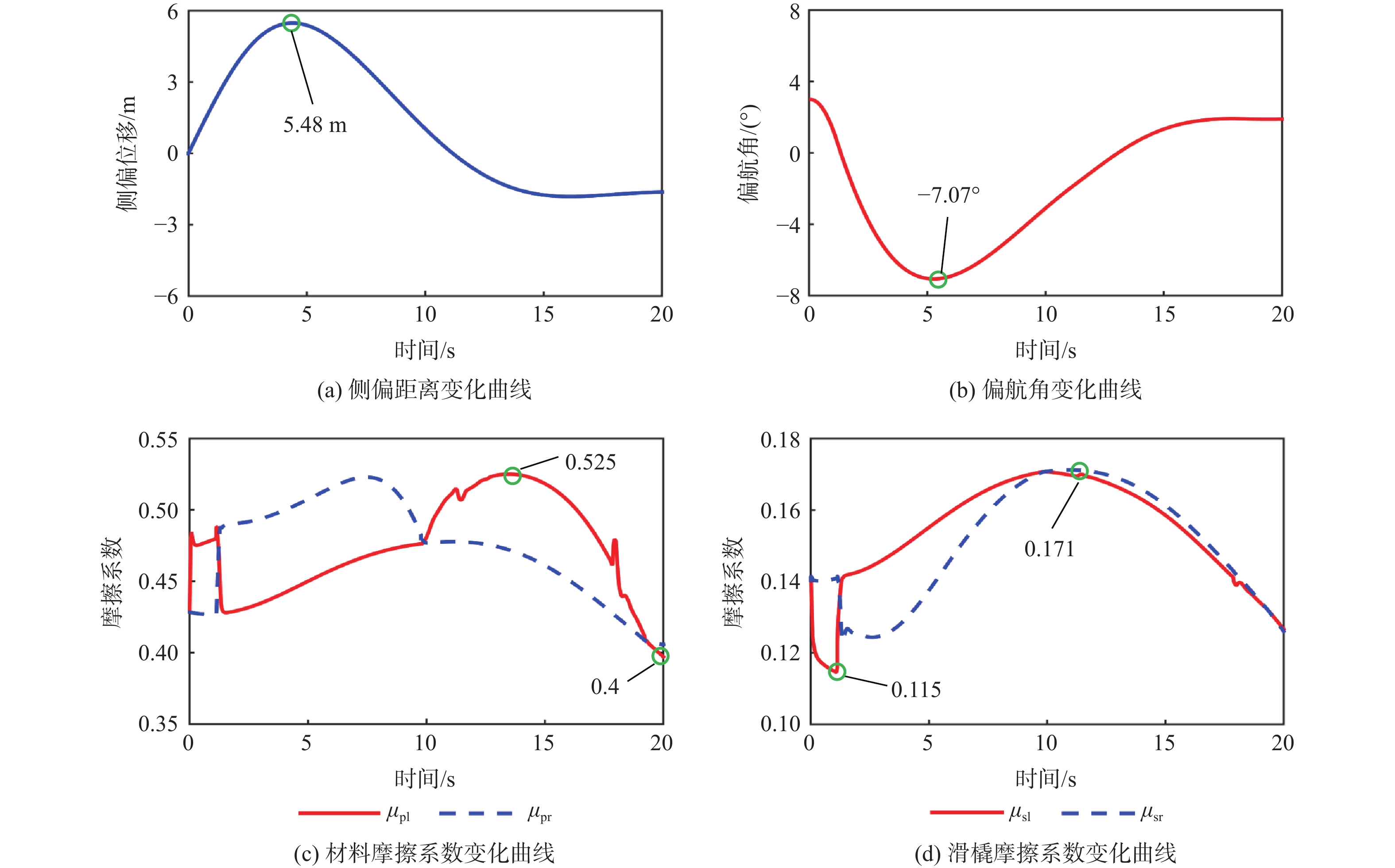
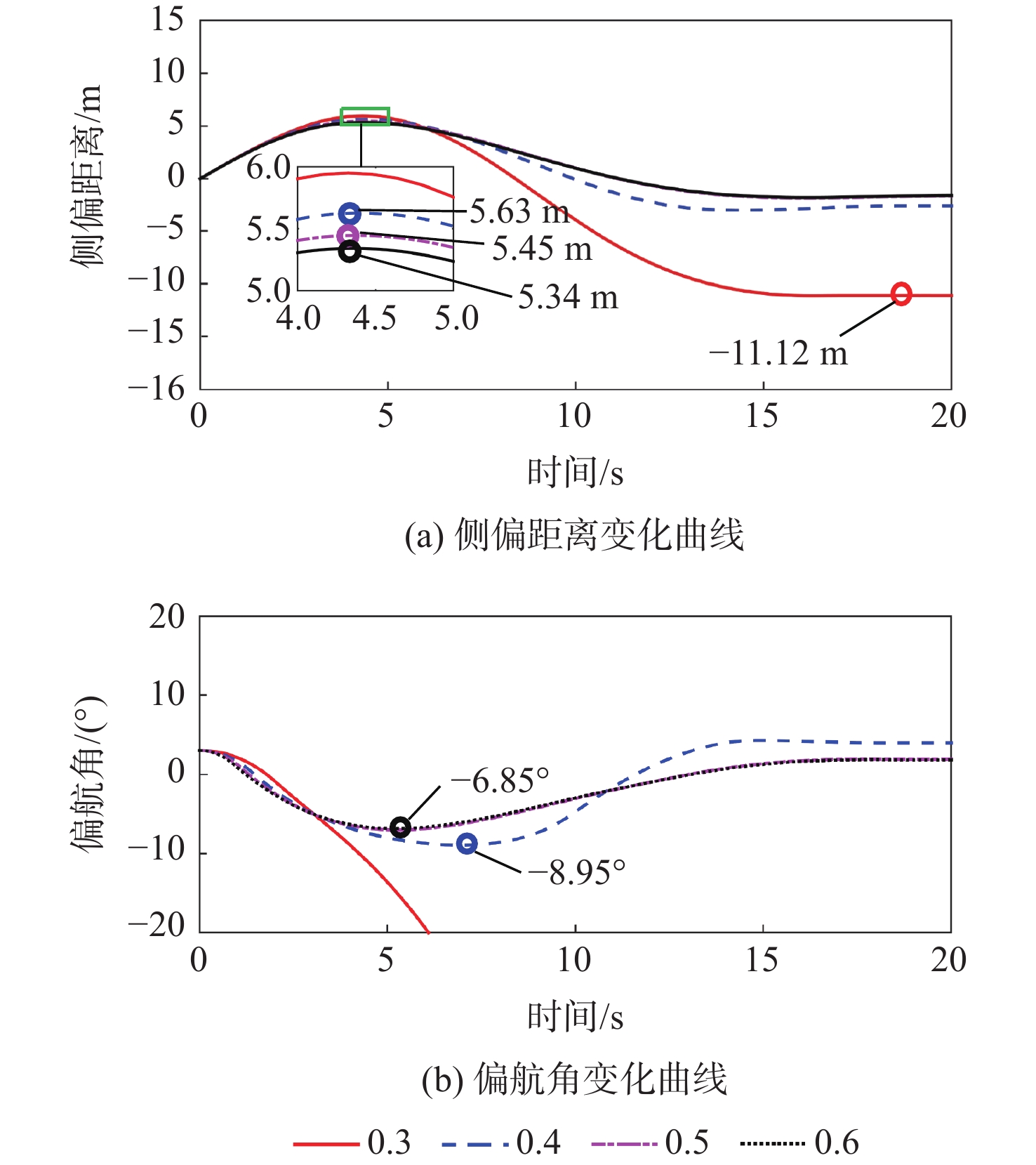
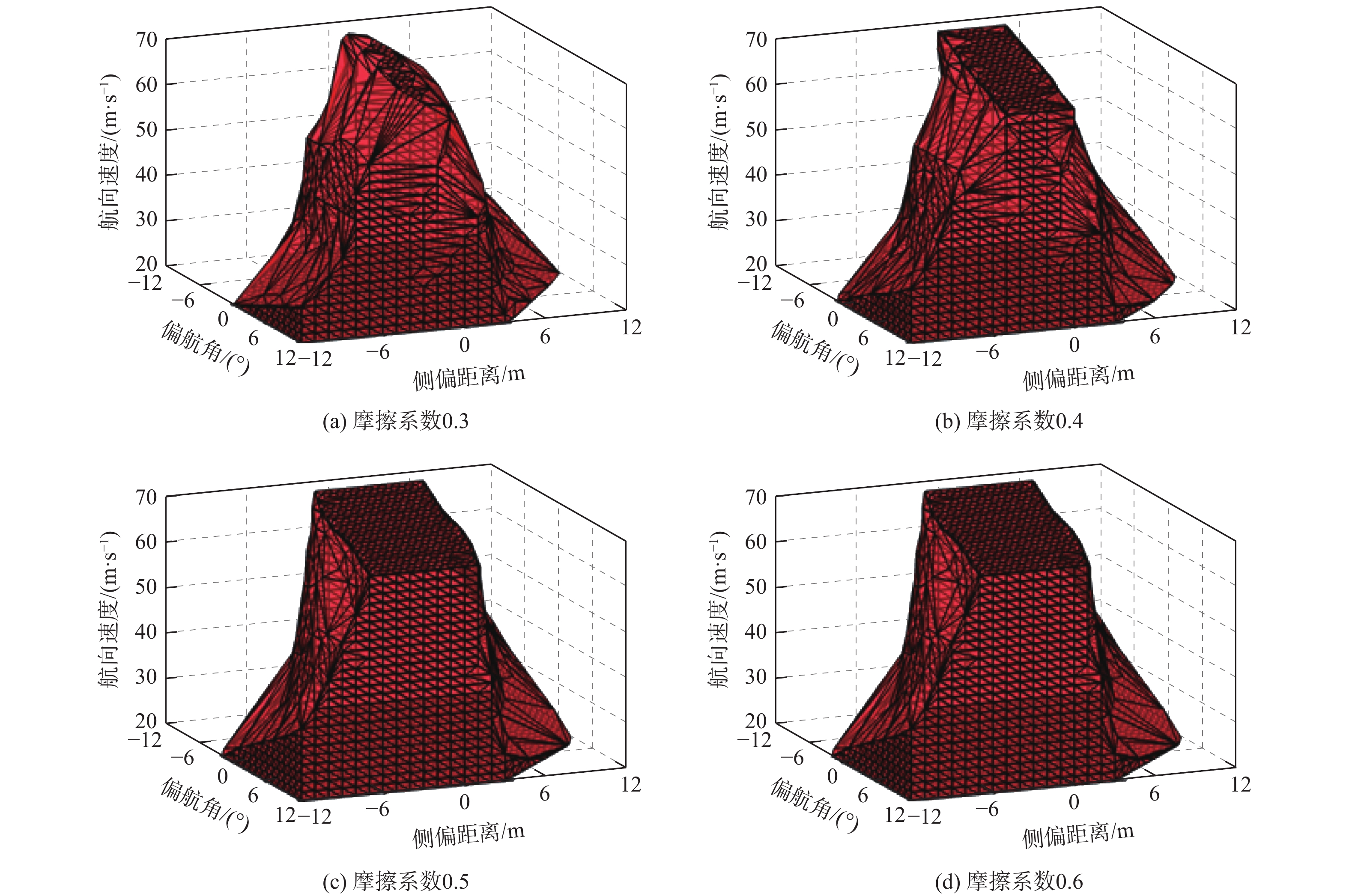
相较于轮式起落架,结构轻巧紧凑的滑橇式起落架更适用于扁平化的高超声速飞行器,然而前轮后橇布局所固有的地面力学特性使得飞行器在中速滑跑阶段存在严重的航向失稳问题。针对滑橇式飞行器滑跑航向稳定性较差的问题,提出了一种具备航向增稳功能的新型变摩擦滑橇式起落架。建立了滑橇式飞行器的非线性地面滑跑动力学模型,考虑了气动载荷、地面载荷和纠偏机构模型;基于摩擦特性试验结果得到了滑橇及摩擦材料摩擦系数的多参数拟合公式,并将其代入所提滑跑模型以提高精度;引入积分视线(ILOS)法建立了滑橇式飞行器滑跑纠偏控制系统,并采用粒子群算法优化控制参数。试验结果表明:滑橇及摩擦材料的摩擦系数均随速度和压强的增加先增大后减小;典型初始工况下的滑跑仿真结果验证了基于变摩擦滑橇纠偏控制的有效性;当摩擦材料摩擦系数从0.3增至0.4时,飞行器地面滑跑安全边界提升16.6%。
Abstract:Flat hypersonic aircraft are better suited to skid landing gear than wheeled landing gear because of its light weight and compact design. However, the inherent characteristic of the wheel skid layout causes the problem of heading instability during mid-speed taxiing. Aiming at the problem, a variable-friction skid landing gear with a directional stability augmentation function is designed. Firstly, a nonlinear ground taxiing model is established, considering aerodynamic forces, ground forces, correction mechanism model, and deviation-correction control system.The ground friction characteristics experiment findings are then used to create the multi-parameter fitting polynomials of the friction coefficients of the skid and material, which are then incorporated into the dynamic model discussed earlier. Finally, an integral line of sight (ILOS) guidance is introduced to realize the effective tracking of the runway centerline during the rollout phase. Particle swarm optimization is introduced to optimize control parameters. Results show that the friction coefficients of the skid and the material first increase and then decrease with the increase of speed and pressure. The effectiveness of the deviation-correction control system is verified by taxiing simulation results under typical initial conditions. The safety set of taxiing increases by 16.6% when the friction coefficient of the friction material increases from 0.3 to 0.4.
-
表 1 拟合多项式的系数
Table 1. Coefficients of fitting polynomials
系数 滑橇摩擦系数${\mu _{\text{s}}}$ 材料摩擦系数${\mu _{\text{p}}}$ p00 0.067 0.3907 p10 0.00529 0.01364 p01 1.009×10−6 1.798×10−6 p20 −3.418×10−4 −6.458×10−4 p11 1.404×10−8 −6.084×10−8 p02 −6.93×10−12 −1.092×10−11 p30 5.825×10−6 8.209×10−6 p21 −5.442×10−6 2.545×10−9 p12 2.115×10−14 2.671×10−14 p03 1.938×10−17 3.134×10−17 p31 −4.945×10−12 −3.235×10−11 p22 1.729×10−15 −6.44×10−16 p13 −1.438×10−19 3.3×10−20 p04 −1.814×10−23 −3.337×10−23 -
[1] 张丽静, 刘东升, 于存贵, 等. 高超声速飞行器[J]. 航空兵器, 2010, 17(2): 13-16.ZHANG L J, LIU D S, YU C G, et al. Hypersonic aircraft[J]. Aero Weaponry, 2010, 17(2): 13-16(in Chinese). [2] 杜善义, 方岱宁, 孟松鹤, 等. “近空间飞行器的关键基础科学问题”重大研究计划结题综述[J]. 中国科学基金, 2017, 31(2): 109-114.DU S Y, FANG D N, MENG S H, et al. Review of the achievements of major research plan on “key fundamental scientific problems on hypersonic vehicle”[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2017, 31(2): 109-114(in Chinese). [3] 黄伟, 罗世彬, 王振国. 临近空间高超声速飞行器关键技术及展望[J]. 宇航学报, 2010, 31(5): 1259-1265.HUANG W, LUO S B, WANG Z G. Key techniques and prospect of near-space hypersonic vehicle[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2010, 31(5): 1259-1265(in Chinese). [4] 李宪开, 王霄, 柳军, 等. 水平起降高超声速飞机气动布局技术研究[J]. 航空科学技术, 2020, 31(11): 7-13.LI X K, WANG X, LIU J, et al. Research on the aerodynamic layout design for the horizontal take-off and landing hypersonic aircraft[J]. Aeronautical Science & Technology, 2020, 31(11): 7-13(in Chinese). [5] 朱林昊, 邹泽铧, 印寅, 等. 面向狭小空间的起落架收放轨迹智能设计方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(12): 2560-2570.ZHU L H, ZOU Z H, YIN Y, et al. Intelligent design method of landing gear retraction and extension trajectory for narrow space[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(12): 2560-2570(in Chinese). [6] 张猛. 着陆过程航空轮胎热-力学特性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019: 53-57.ZHANG M. Study on thermal-mechanical characteristics of aircraft tires during landing[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019: 53-57(in Chinese). [7] 段卓毅. X系列飞行器概览[M]. 北京: 航空工业出版社, 2017: 267-351.DUAN Z Y. Survey of X-planes[M]. Beijing: Aviation Industry Press, 2017: 267-351(in Chinese). [8] SEEDHOUSE E. SpaceX[M]. SpaceX's Dragon: America's Next Generation Spacecraft. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 1-9. [9] LEMAY D, CHAMAILLARD Y, BASSET M, et al. Gain-scheduled yaw control for aircraft ground taxiing[J]. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2011, 44(1): 12970-12975. doi: 10.3182/20110828-6-IT-1002.00692 [10] 王勇, 王英勋. 无人机滑跑纠偏控制[J]. 航空学报, 2008, 29(增刊1): 142-149.WANG Y, WANG Y X. Lateral deviation correction control for UAV taxiing[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2008, 29(Sup 1): 142-149(in Chinese). [11] YIN Q Z, NIE H, WEI X, et al. Aircraft electric anti-skid braking and combined direction control system using co-simulation and experimental methods:[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part G:Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2020, 234(2): 173-191. doi: 10.1177/0954410019852825 [12] 李继广, 董彦非, 杨芳, 等. 基于反步控制方法的菱形翼无人机起飞滑跑控制[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(3): 496-504.LI J G, DONG Y F, YANG F, et al. Takeoff taxiing control of joined-wing UAV based on backstepping method[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(3): 496-504(in Chinese). [13] LI X B, WEI X H, WANG Y A, et al. Nonlinear tracking deviation correction control of airplanes in high-speed landing taxiing[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2020, 43(12): 2413-2424. doi: 10.2514/1.G005232 [14] 黄平. 摩擦学教程[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2008: 60-74.HUANG P. Tribology course[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2008: 60-74(in Chinese). [15] 魏兵辉, 孙琨, 王云鹏, 等. 高速干滑动摩擦系数的有限元仿真计算研究[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2020, 54(6): 82-89.WEI B H, SUN K, WANG Y P, et al. Finite element prediction for friction coefficient of high speed dry sliding[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2020, 54(6): 82-89(in Chinese). [16] 魏龙, 张鹏高, 刘其和, 等. 接触式机械密封端面摩擦系数影响因素分析与试验[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2016, 36(3): 354-361.WEI L, ZHANG P G, LIU Q H, et al. Influencing factors analysis and experiments of friction coefficient between the end faces for contact mechanical seals[J]. Tribology, 2016, 36(3): 354-361(in Chinese). [17] WU B Z, QIN D T, HU J J, et al . Experimental data mining research on factors influencing friction coefficient of wet clutch[J]. Journal of Tribology’ 2021, 143(12): 121802. [18] 陶润, 侯之超. 受径向力滚动轴承摩擦力矩的测试和函数拟合[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 54(6): 744-749.TAO R, HOU Z C. Measurement and curve fitting of the friction torque of rolling bearings subjected to radial loads[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2014, 54(6): 744-749(in Chinese). [19] SADIEN E, ROOS C, BIROUCHE A, et al. Control design oriented modeling of an on-ground aircraft[C]//2018 17th European Control Conference (ECC). Limassol: IEEE Press, 2018: 2757-2762. [20] 李洁玉. 高速水平回收无人机综合纠偏方法研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2017: 9-13.LI J Y. Research on lateral deviation correction control for high-speed UAV of horizontal recovery[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics , 2017: 9-13(in Chinese). [21] SUJIT P B, SARIPALLI S, SOUSA J B. Unmanned aerial vehicle path following: A survey and analysis of algorithms for fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicless[J]. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 2014, 34(1): 42-59. doi: 10.1109/MCS.2013.2287568 [22] PANTELEY E, LORIA A. On global uniform asymptotic stability of nonlinear time-varying systems in cascade[J]. Systems & Control Letters, 1998, 33(2): 131-138. [23] 瞿洋, 徐海祥, 余文曌, 等. 基于ILOS的欠驱船舶循迹控制[J]. 武汉理工大学学报(交通科学与工程版), 2016, 40(5): 834-838.QU Y, XU H X, YU W Z, et al. Integral line-of-sight guidance for path following of underactuated marine surface vessels[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Transportation Science & Engineering), 2016, 40(5): 834-838(in Chinese). [24] LIANG T T, YIN Q Z, FANG W G, et al. The maximum taxiing safe set of the wheelskid aircraft under op-timal control of rudder[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part G: Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2021, 235(15): 2274-2287. doi: 10.1177/0954410021995382 [25] 王海涛, 蒋经凯. 飞机起落架主动控制与滑跑性能优化研究[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2013, 31(2): 223-228.WANG H T, JIANG J K. Active control of landing gear and taxiing performance optimization[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2013, 31(2): 223-228(in Chinese). [26] EBERHART R, KENNEDY J. A new optimizer using particle swarm theory[C]// Micro Machine and Human Science, 1995. MHS '95. Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Micro Machine and Human Science. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1995: 39-43 -








 下载:
下载: