Prediction of ground air conditioner energy consumption based on improved long short-term memory neural network
-
摘要:
在机场运行管理中,地面空调是对飞机客舱进行降温除湿的主要设备,准确预测出其在工作过程中的耗电量对于建设绿色机场具有重要意义。地面空调能耗受多维因素的影响,为提高预测精度,提出一种基于改进双向长短时记忆(BiLSTM)神经网络的飞机地面空调能耗预测方法。所提方法使用BiLSTM神经网络和注意力机制构造模型的预测部分,可以充分挖掘和利用数据中的时间序列特征;并以预测精度最优为指标,提出一种基于改进蚁狮优化(IALO)算法的超参数优化算法,与标准蚁狮优化算法相比,改进蚁狮优化算法在随机游走空间缩小机制中改进了收缩因子并赋予收缩系数一定的随机性,同时引入普通蚁狮权重系数动态调整机制,提高所提算法的收敛速度及寻优能力。在实际数据集上进行仿真可知,所提方法预测结果的均方误差为6.045,平均绝对百分比误差为0.928%,决定系数为0.956。通过与其他多种预测方法比较,充分证明所提方法具有准确度高、适应性强等优点。
-
关键词:
- 地面空调 /
- 能耗预测 /
- 双向长短时记忆神经网络 /
- 注意力机制 /
- 蚁狮优化
Abstract:Ground air conditioners are the main equipment for cooling and dehumidification of airplane cabins, so accurate prediction of their energy consumption in the working process plays an important role in building green airports. The energy consumption of the ground air conditioner is affected by multidimensional factors. To improve the accuracy of energy consumption prediction, this study presents a method based on an improved bidirectional long short-term memory (BiLSTM) neural network. This method uses BiLSTM neural network and attention mechanism to construct the predictive part of the model, which can extract and utilize the time series characteristics of the data. Taking the optimal prediction accuracy as the index, this study also proposes a hyperparameter optimization method based on the improved ant lion optimization algorithm. Compared with the standard algorithm, the improved ant lion optimization (IALO) algorithm improves the shrinkage factor in the random walk space reduction mechanism, giving the shrinkage coefficient some randomness. It also introduces the dynamic adjustment mechanism of the ordinary ant lion weight coefficient, which improves the rate of convergence and optimization capabilities of the algorithm. The mean square error of the prediction result is 6.045, the mean absolute percentage error is 0.928%, and the coefficient of determination is 0.956. Compared with other prediction methods, the proposed method has higher accuracy and stronger adaptation.
-
近些年来,中国政府正在大力推进绿色减排技术的研发及推广,并将“双碳”战略写进国家规划。为响应国家号召,中国民用航空局提出建设绿色机场,包括资源节约、运行高效、低碳减排等内容,建设绿色机场离不开对机场设备智慧化、绿色化的研究。为减少使用高污染、高价格的航空煤油,航空公司主要使用地面空调设备替代机载空调对停靠在地面的飞机进行通风、降温和除湿。准确预测飞机地面空调能耗,可以为机场控制能源消耗、合理分配电力资源提供科学的参考,满足高效、节能及保证客舱热舒适性等需求。
目前,关于地面空调能耗预测的研究主要是利用神经网络建立输入与输出之间的映射关系,假设该映射关系在未知数据集上仍然成立,将未知数据集的输入代入映射关系中,得到的输出即为预测结果。王修岩等[1]使用小波神经网络对飞机地面空调能耗进行预测,利用珊瑚礁和粒子群联合算法优化模型中的超参数;林家泉等[2]提出一种基于改进粒子群优化(improved particle swarm optimization, IPSO)Elman模型的飞机地面空调能耗预测方法。文献[1-2]关于飞机地面空调能耗预测的研究具有一定的价值,但未能有效利用数据中的时间规律,使用的模型也较为简单,预测精度仍有提升的空间。文献[3-4]提出长短时记忆(long short-term memory, LSTM)神经网络,其可对流动的信息进行选择性的添加或删除,LSTM神经网络及其变体是目前在时间序列预测问题研究中应用最广泛最有效的模型之一,史亚菲等[5]提出一种基于LSTM神经网络的时间触发以太网(time-triggered ethernet, TTE)网络约束流量预测方法,Cui等[6]使用LSTM神经网络预测电力负荷,文献[3-6]在预测精度上有一定的提升,但忽视了LSTM神经网络的3点不足。首先,LSTM神经网络只能挖掘来自过去的时间序列特征,所以有学者使用2个方向相反的LSTM神经网络组成双向长短时记忆(Bi-directional long short-term memory, BiLSTM)神经网络,并将其应用在时间序列预测领域中。文献[7-8]表明:与单层LSTM模型相比,BiLSTM神经网络能够对数据进行更多的训练,通过挖掘更多的时间序列特征来提高预测精度。其次,LSTM神经网络无法区分时间序列特征的重要程度,容易遗漏重要特征。针对该问题,众多学者在预测模型中添加注意力机制(attention mechanism, AM)[9-11]来提高预测精度,注意力机制是一种通过赋予特征不同的权重来优化资源分配、改善预测结果的机制。最后,LSTM神经网络的预测精度与超参数的配置有很大的关系,尤其是含有多超参数的模型,只有配置合适的超参数组合才可以充分发挥模型的预测性能。对于搜索范围较大的超参数,手动或暴力调参存在计算成本高、耗费时间长等问题[12-13],于是有学者使用群智能优化算法提高超参数寻优的效率,龙远等[14]使用粒子群优化(particle swarm optimization, PSO)算法优化反向传播(back propagation, BP)神经网络,通过仿真证明PSO-BP模型在平流层风场短期快速预测问题上有效,但PSO算法存在调节参数多的问题,会带来新的调参问题;Yuan等[15]使用蚁狮优化(ant lion optimizer, ALO)算法优化LSTM神经网络的隐层神经元数量及学习率,并通过预测月度径流证明LSTM-ALO模型具有预测精度高的优点,但该模型仅考虑超参数少的情形,对于超参数数量多、搜索空间复杂的问题,需要更进一步的研究。
结合上述分析,本文提出一种可用于地面空调能耗预测的融合改进蚁狮优化算法和注意力机制的双向长短时记忆(improved ant lion optimizer-attention mechanism-Bi-directional long short-term memory, IALO-AM-BiLSTM)神经网络模型。该模型分为预测部分和超参数优化部分,预测部分先利用BiLSTM神经网络充分挖掘数据的双向时间序列特征,然后通过注意力机制突出重要特征对预测结果的影响;超参数优化部分使用所提出的改进蚁狮优化(improved ant lion optimizer,IALO)算法寻找使预测结果最优的超参数组合。采用中国东部某机场夏季地面空调设备工作的能耗数据作为数据样本,将IALO-AM-BiLSTM模型与BP、LSTM、BiLSTM、AM-BiLSTM、PSO-AM-BiLSTM、ALO-AM-BiLSTM等多种模型进行对比,仿真结果表明,IALO-AM-BiLSTM模型在预测精度和拟合优度上都具有显著的优势。
1. 相关理论
1.1 双向长短时记忆神经网络
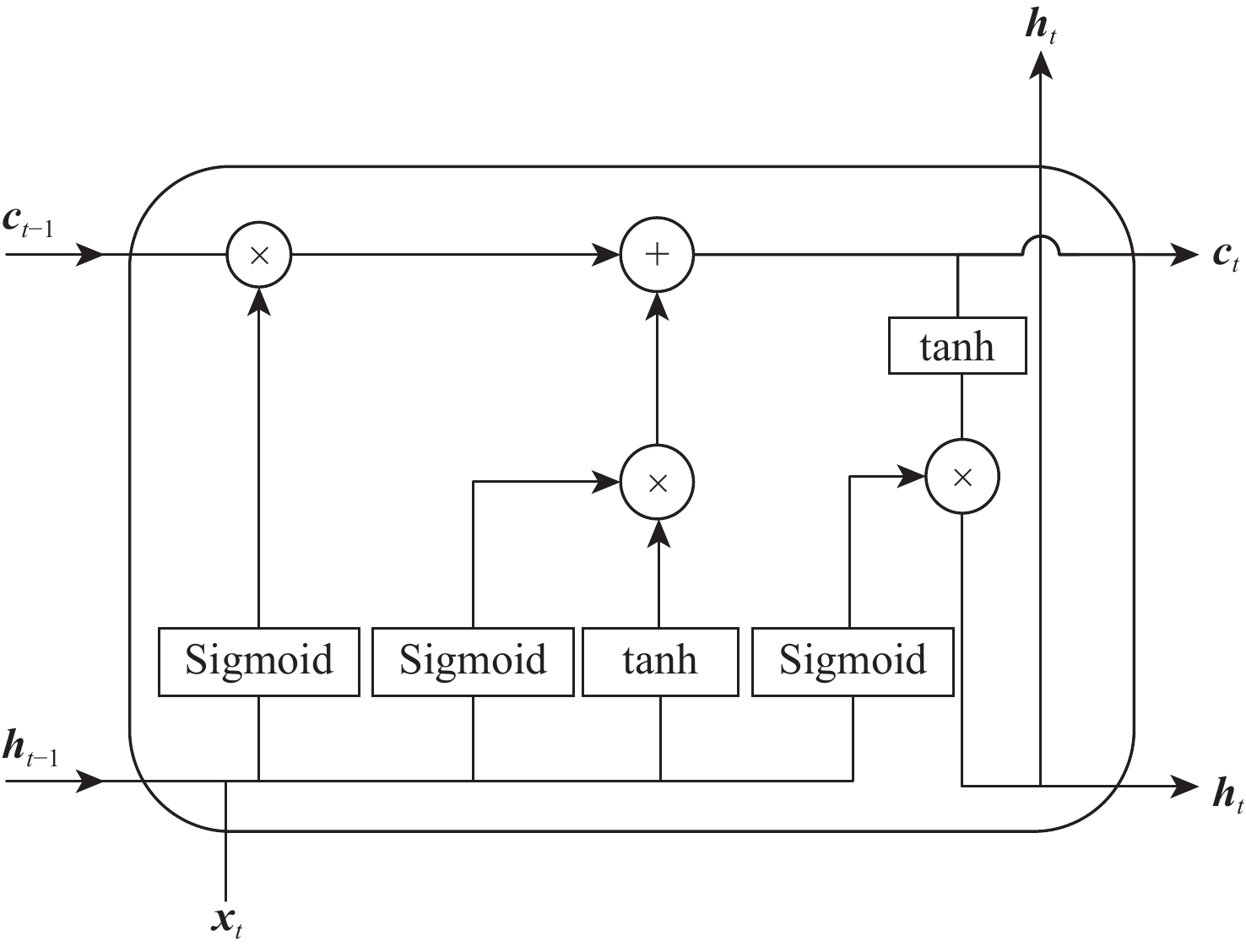
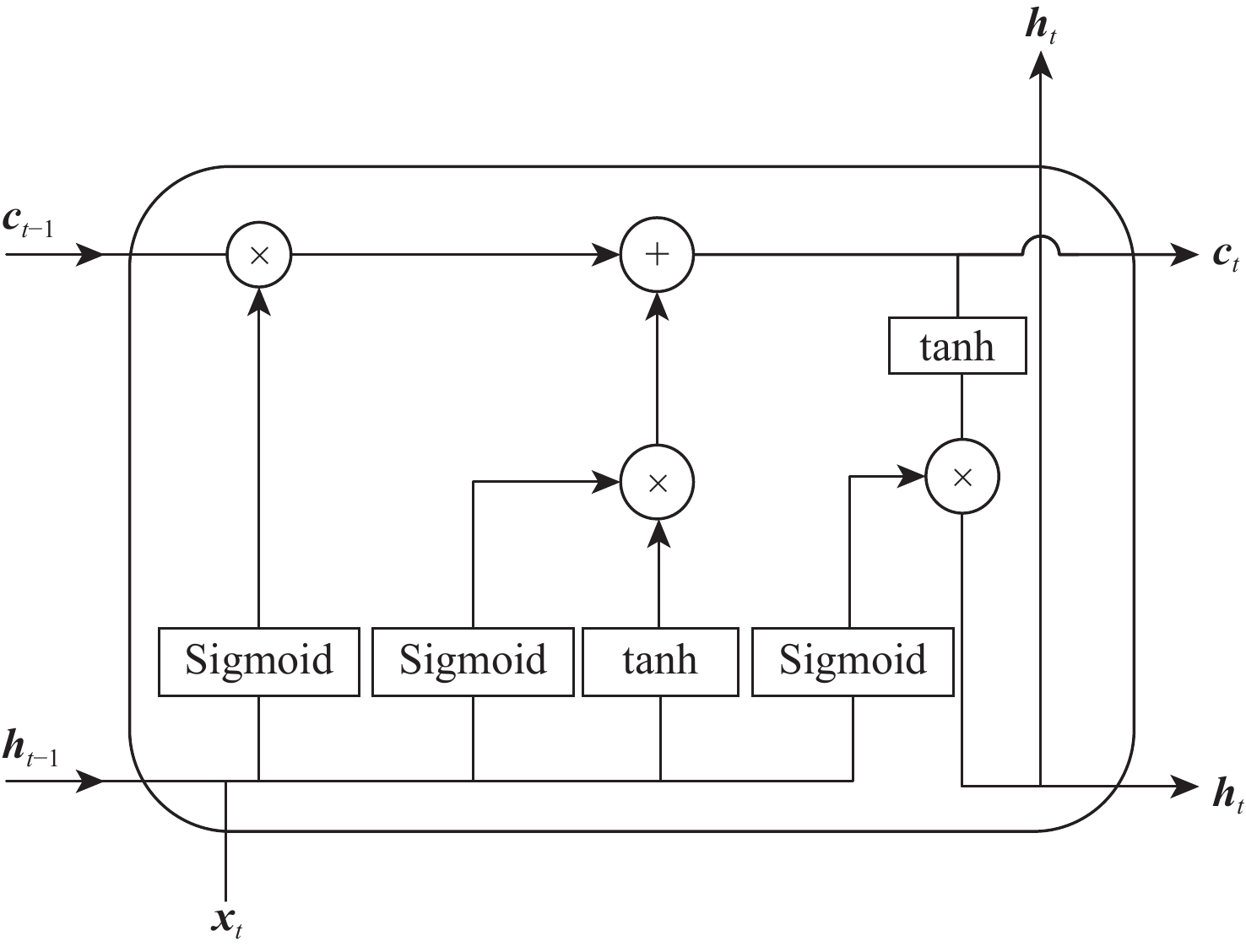
LSTM神经网络是由许多重复的基本单元组成的链式结构,基本单元具有长期状态ct、短期状态ht这2个状态,以及输入门、遗忘门和输出门3个门结构,通过3个门的计算可以删除或增加信息到基本单元状态,基本单元的结构如图1所示[3],具体运算过程如式(1)~式(6)所示[3]。
ft=σ(Wf⋅[ht−1,xt]+bf) (1) it=σ(Wi⋅[ht−1,xt]+bi) (2) ˜ct=tanh(Wc⋅[ht−1,xt]+bc) (3) ct=ft⋅ct−1+it⋅˜ct (4) ot=σ(Wo⋅[ht−1,xt]+bo) (5) ht=ot⋅tanh(ct) (6) 式中:[ht−1, xt]为上一时刻输出ht−1和当前时刻输入xt的拼接向量;Wf、Wi、Wc、Wo分别为遗忘门、输入门、基本单元状态、输出门的权重矩阵;bf、bi、bc、bo分别为遗忘门、输入门、基本单元状态、输出门的偏置项;σ( )为Sigmoid激活函数;tanh( )为tanh激活函数。
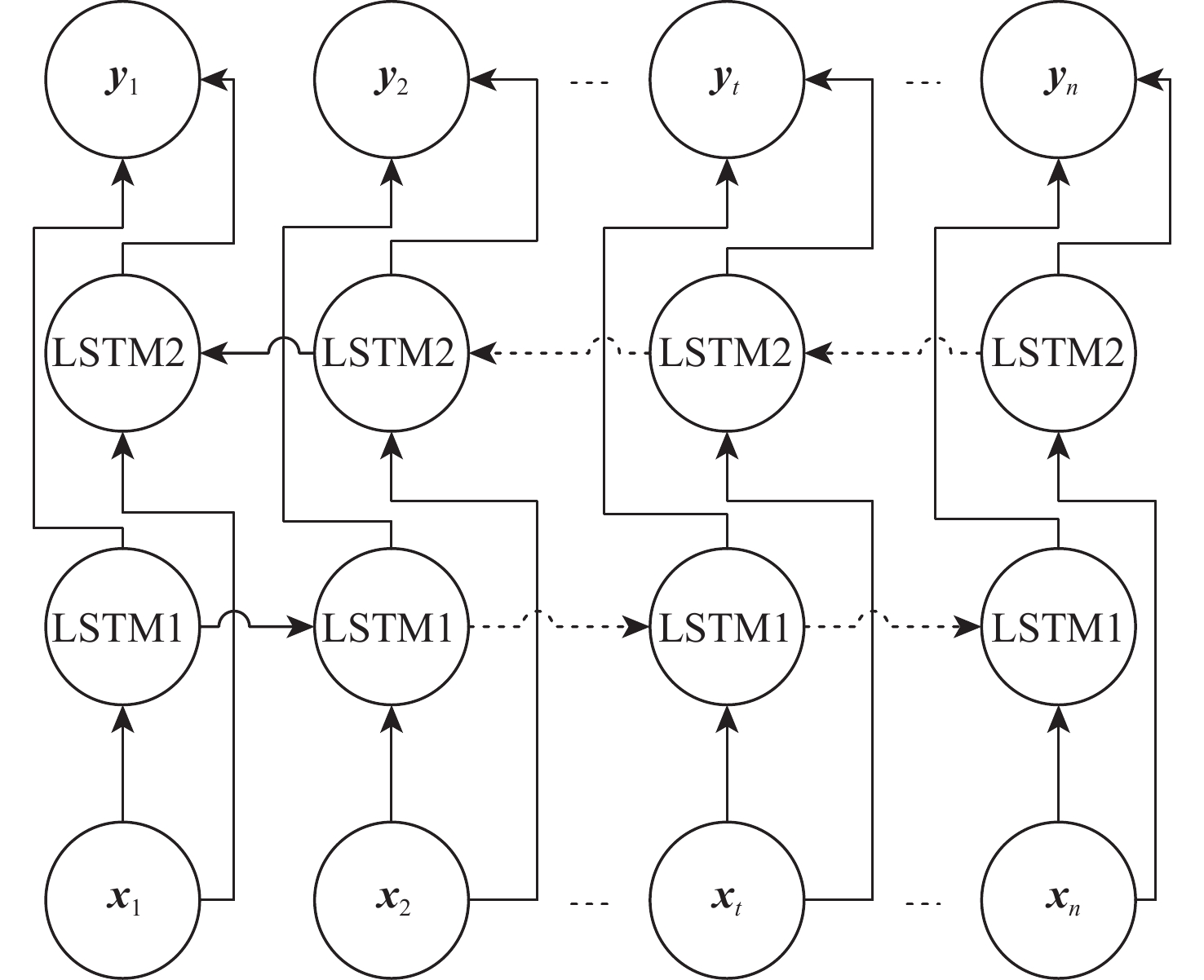
BiLSTM神经网络是由2个方向相反的LSTM神经网络组合而成,结构如图2所示[16],其中将前向LSTM神经网络记作LSTM1,后向LSTM神经网络记作LSTM2。
这2个LSTM神经网络具有相同的网络结构和不同的权重矩阵、偏置项,每个时刻都会计算出前向LSTM1的输出h1t和来自后向LSTM2的输出h2t,将h1t和h2t结合起来便得到了BiLSTM的输出yt,其数学表达式为[16]
h1t=f(ω1⋅[h1t,xt]+b1) (7) h2t=f(ω2⋅[h2t−1,xt]+b2) (8) yt=g(v⋅[h1t,h2t]+c) (9) 式中:ω1和b1分别为LSTM1的权重矩阵和偏置项;ω2和b2分别为LSTM2的权重矩阵和偏置项;v和c分别为计算输出的权重矩阵和偏置项。
1.2 注意力机制
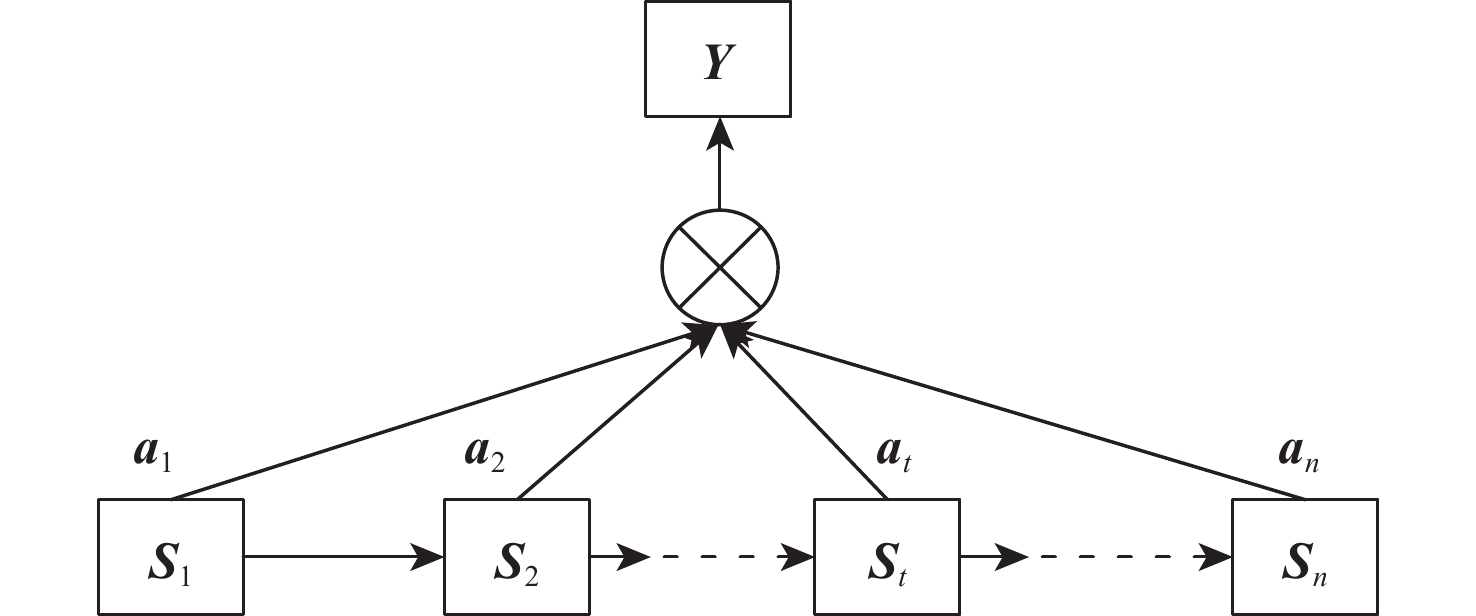
注意力机制是一种可以让模型对更重要的信息给予更多的关注,并对其进行学习吸收的技术。在时间序列预测任务中,可以利用注意力机制对隐含层的每个状态赋予不同的权重,然后根据权重进行加权运算,达到优化预测结果的目的。注意力机制的结构如图3所示[9],图中St为隐含层t时刻的状态。
注意力机制的运算过程分为3个阶段[9],第1阶段通过打分函数计算每个时刻隐含层状态St的注意力得分,计算式为
et=score(St)=tanh(St⋅θ+b) (10) 式中:θ和b分别为打分函数的权重矩阵和偏置项。
第2阶段利用softmax层对第1阶段的et进行归一化操作,求出每个时刻的对应权重值,计算式为
at=softmax(et)=exp(et)n∑t=0exp(et) (11) 第3阶段将每个时刻的权重值at与隐含层对应的状态St进行加权求和,即为经过AM层后的输出Y,计算式为
Y=n∑t=1(at⋅St) (12) 1.3 蚁狮优化算法
ALO算法的灵感源于自然界中蚁狮捕食蚂蚁,其使用了随机游走、轮盘赌策略和精英策略等多种机制,与遗传算法、PSO算法相比,具有调节参数少、收敛速度快及全局能力强等优点[17-18],运算步骤如下[18]。
步骤 1 随机初始化蚂蚁和蚁狮的位置Xn,d,如式(13)所示。每个位置都代表问题的一个解,根据给定的适应度函数可以计算出相应的适应度值,选取适应度值最佳的为精英蚁狮,记作RE。
Xn,d=Ld+srand(Ud−Ld) (13) 式中:n=1,2,···,N(N为蚂蚁和蚁狮的个数);d=1,2,···,D(D为变量个数);Ld为第d个变量的下限;srand为0~1之间的随机数; Ud为第d个变量的上限。
步骤 2 ALO算法使用随机游走模拟蚂蚁的游走过程,随机游走步数集X(t)的数学表达式为
X(t)={0,cum[2r(t1)−1],⋯,cum[2r(tk)−1]} (14) r(t)={1srand>0.50srand⩽ (15) X_i^t = \frac{{\left[ {X\left( t \right) - {a_i}} \right] \left( {d_i^t - c_i^t} \right)}}{{\left( {{d_i} - {a_i}} \right)}} + c_i^t (16) 式中:cum()为计算累计和的函数;tk表示第k次迭代,k为最大迭代次数;Xit表示第i维变量在第t次迭代时的归一化位置;ai和di分别为第i维变量随机游走的最小值和最大值;cit和dit分别为第i维变量在第t代随机游走的最小值和最大值。
步骤 3 令cit和dit定义的超球体为蚂蚁随机游走的搜索空间,为了加快捕捉过程,随机游走空间会不断缩小。其表达式如式(17)~式(20)所示。
c_i^t = A_i^t + \frac{{{c^t}}}{I} (17) {d}_i^{\,t} = A_i^t + \frac{{{d^{\,t}}}}{I} (18) I = {10^\omega }\frac{t}{{T}} (19) \omega = \left\{ \begin{gathered} 2\quad\quad t > 0.1T \\ 3\quad\quad t > 0.5T \\ 4\quad\quad t > 0.75T \\ 5\quad\quad t > 0.9T \\ 6\quad\quad t > 0.95T \\ \end{gathered} \right. (20) 式中:ct和d^{\,t}分别为第t次迭代时所有变量的最小值和最大值;Ait为第t次迭代时第i个蚁狮的位置;I为随机游走空间的收缩系数;ω为收缩因子;t为当前迭代次数;T为最大迭代次数。
步骤 4 每次迭代中适应度值最优的蚁狮被保存为精英蚁狮,再通过轮盘赌抽出一只普通蚁狮,每只蚂蚁都围绕着普通蚁狮和精英蚁狮进行随机游走,蚂蚁位置的更新式为
N_i^t = \frac{{R_{{\rm{A}}}^t + R_{{\rm{E}}}^t}}{2} (21) 式中:N{{_{i}} ^t}为第t次迭代时第i个蚂蚁的位置;R{{_{\rm{A}}} ^t}为蚂蚁在第t次迭代的普通蚁狮周围随机游走产生的值;R{{_{\rm{E}}} ^t}为蚂蚁在第t次迭代的精英蚁狮周围随机游走产生的值。
步骤 5 蚂蚁最终会被蚁狮捕食,若蚂蚁的适应度值比对应蚁狮的更优,就用蚂蚁的位置替换蚁狮的位置,表达式如式(22)所示。然后比较蚁狮和精英蚁狮的适应度值,将适应度值更优的保存为下一次迭代中的精英蚁狮。
\left\{\begin{aligned} &{A}_{i}^{t}={N}_{i}^{t}\\ &f\left({N}_{i}^{t}\right) > f\left({A}_{i}^{t}\right) \end{aligned}\right. (22) 2. IALO-AM-BiLSTM模型
将影响飞机地面空调能耗的因素归为3类:①包括环境温度、环境湿度、光照强度等外环境条件;②包括舱内空间、舱内初始温度、舱内初始湿度等内环境初始条件;③包括工作完成后的温度、工作完成后的湿度等内环境目标条件。其中对地面空调能耗影响较大的外环境条件具有较强的时间规律,因此,可将时间序列预测的思想引入飞机地面空调能耗预测的研究中,通过加强利用数据的时间序列特征提高预测精度。
在此基础上,本文提出IALO-AM-BiLSTM模型,该模型包括预测部分和超参数优化部分,其中预测部分通过将BiLSTM神经网络和注意力机制结合起来,加强对数据中时间序列特征的利用;超参数优化部分是利用IALO算法自动寻找使预测效果最优的超参数组合,IALO算法是在标准ALO算法上,改进了1.3节中步骤3中的蚂蚁随机游走空间缩小机制和步骤4中的蚂蚁位置更新机制。
2.1 预测部分
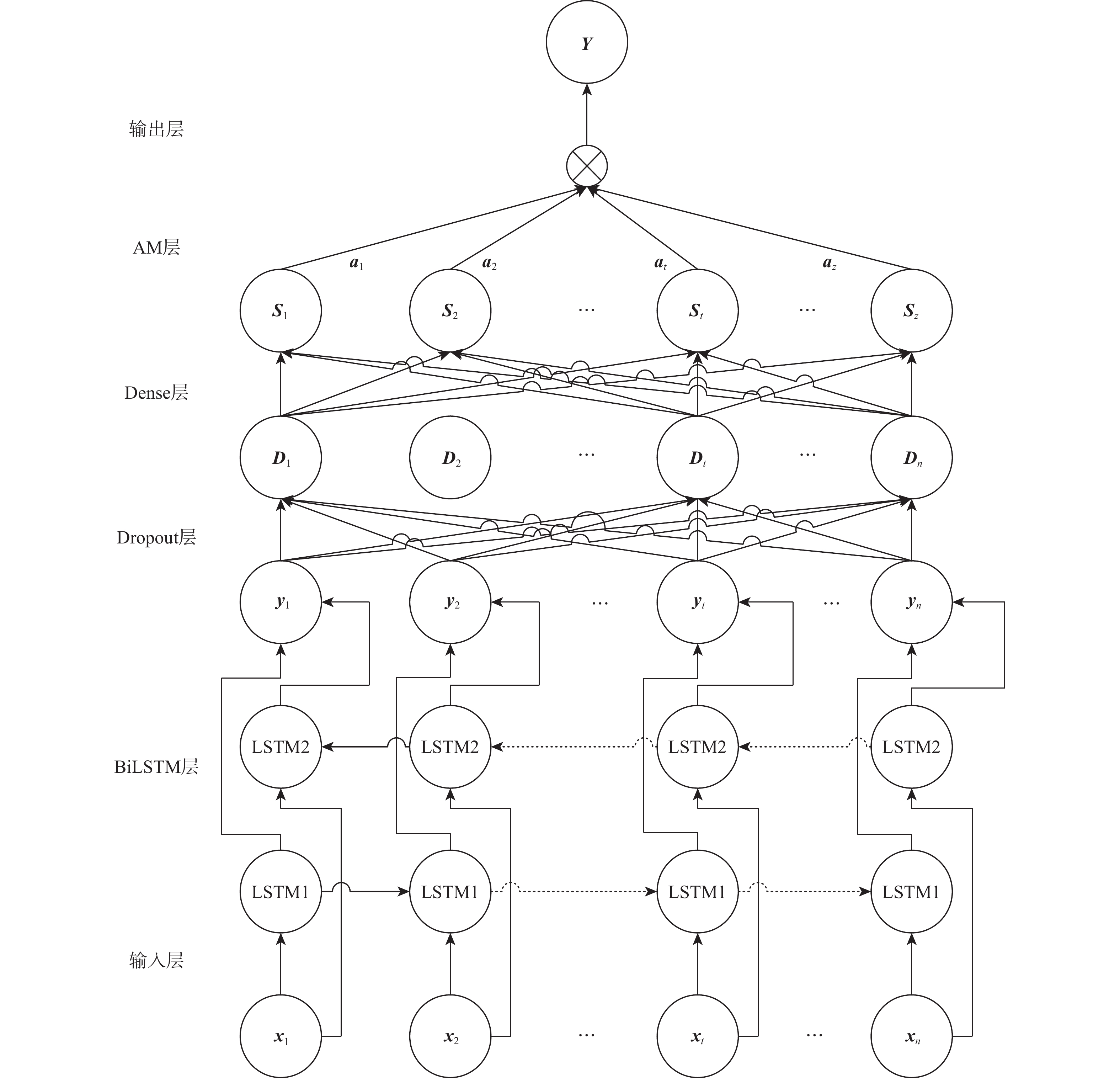
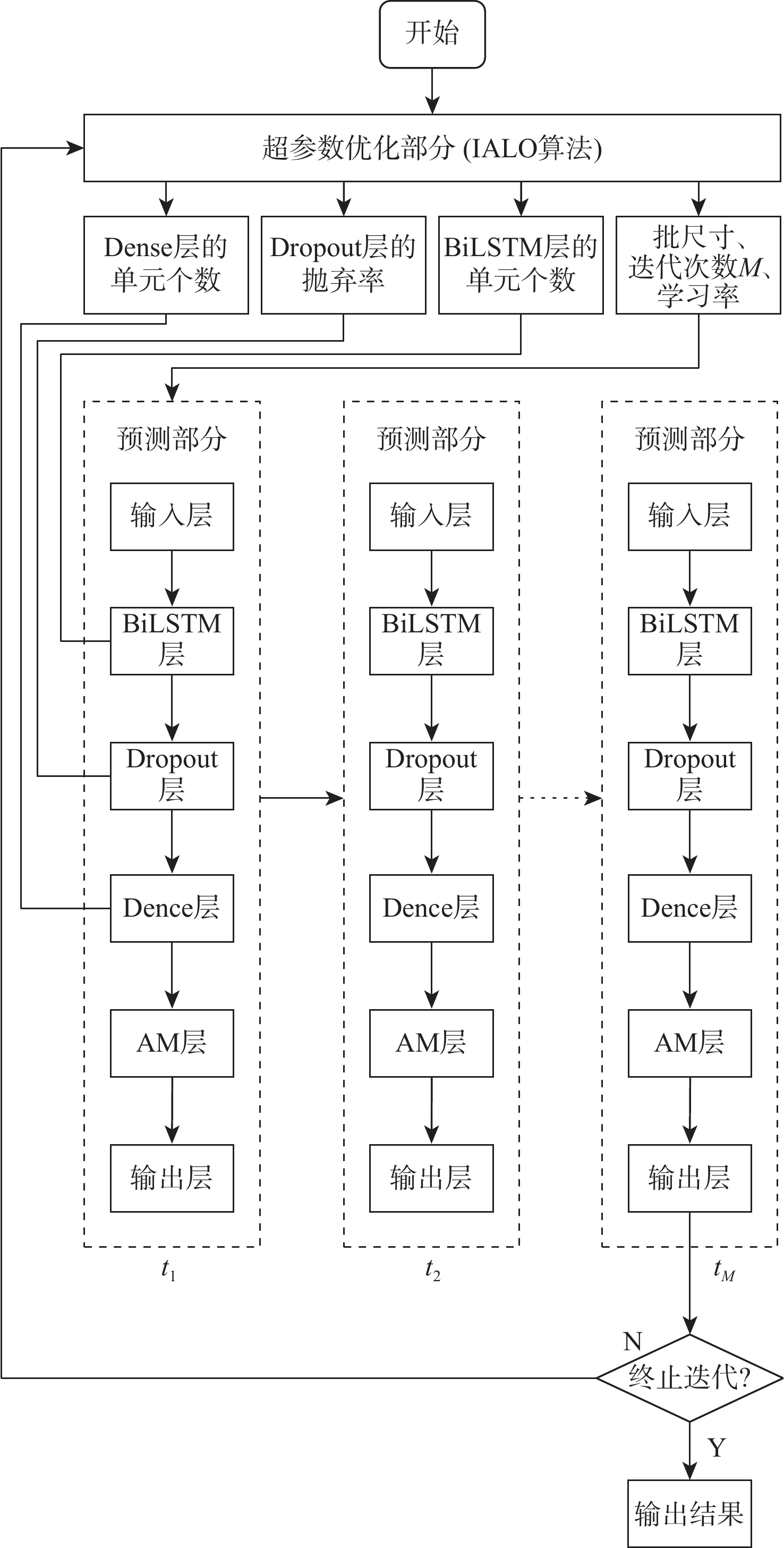
预测部分以BiLSTM神经网络和注意力机制为主,同时引入Dropout避免因训练数据较少而产生过拟合的现象。所构造的预测部分包括输入层、BiLSTM层、Dropout层、Dense层、AM层、输出层6层网络,其结构如图4所示。
各网络层的作用如下:
1) 输入层。将每个时刻的环境特征数据(即初始温度、初始湿度、最终温度及最终湿度)作为模型的输入,t时刻的输入为
{{\boldsymbol{x}}_t} = \left[ {{P_t},{Q_t},{H_t},{M_t}} \right] (23) 式中:Pt为t时刻地面空调工作前客舱的初始温度;Qt为t时刻地面空调工作完成后客舱的最终温度;Ht为t时刻地面空调工作前客舱的初始湿度;Mt为t时刻地面空调工作完成后客舱的最终湿度。
2) BiLSTM层。利用2个方向相反的LSTM神经网络对t时刻的输入序列xt进行计算,将其输出yt视为地面空调能耗数据的双向时间序列特征。
3) Dropout层。对地面空调能耗数据的双向时间序列特征按抛弃率进行随机抛弃,目的在于抑制过拟合,提高模型的鲁棒性[19-20]。
4) Dense层。将Dropout层的输出在Dense层进行非线性变换,以增强时间序列特征与预测结果之间的联系。
5) AM层。将Dense层的输出隐藏状态视为AM层的输入,并根据式(10)~式(12)计算出t时刻AM层的输出St。
6) 输出层。使用全连接层对AM层输出进行降维计算,其激活函数为sigmoid函数,最终输出结果Y即为预测时刻地面空调工作的耗电量。
2.2 超参数优化部分
选取合适的超参数对于充分发挥模型的预测性能至关重要,不合适的超参数优化方法会存在浪费时间、浪费资源或预测性能发挥不稳定、不充分等缺点。考虑到所提出的预测部分含有较多的超参数,提出一种用于多超参数优化的IALO算法,以解决标准ALO算法在处理复杂的多维搜索空间时,存在的寻优难度大、收敛速度慢等缺点。提出的2种改进机制具体如下。
2.2.1 随机游走空间缩小机制
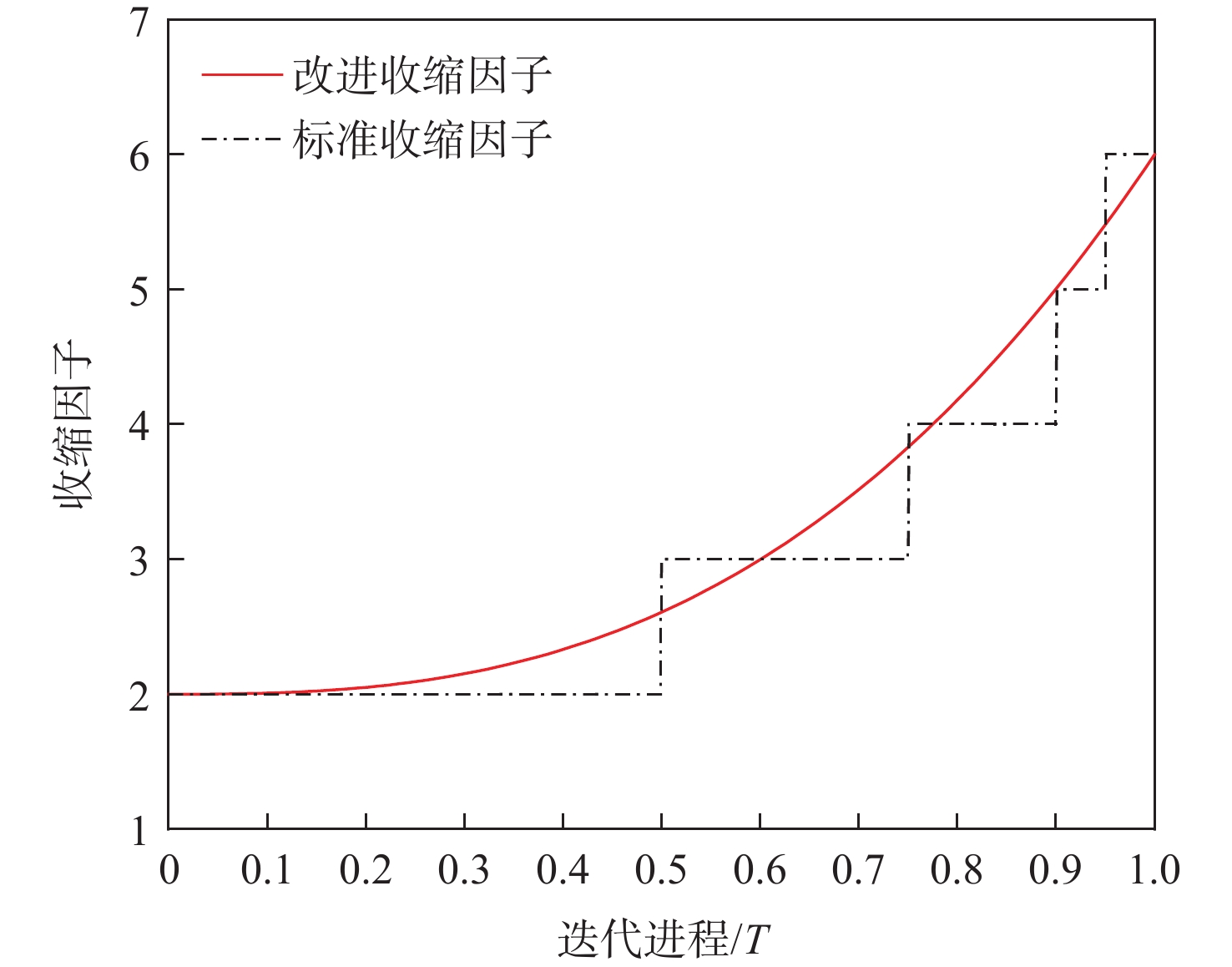
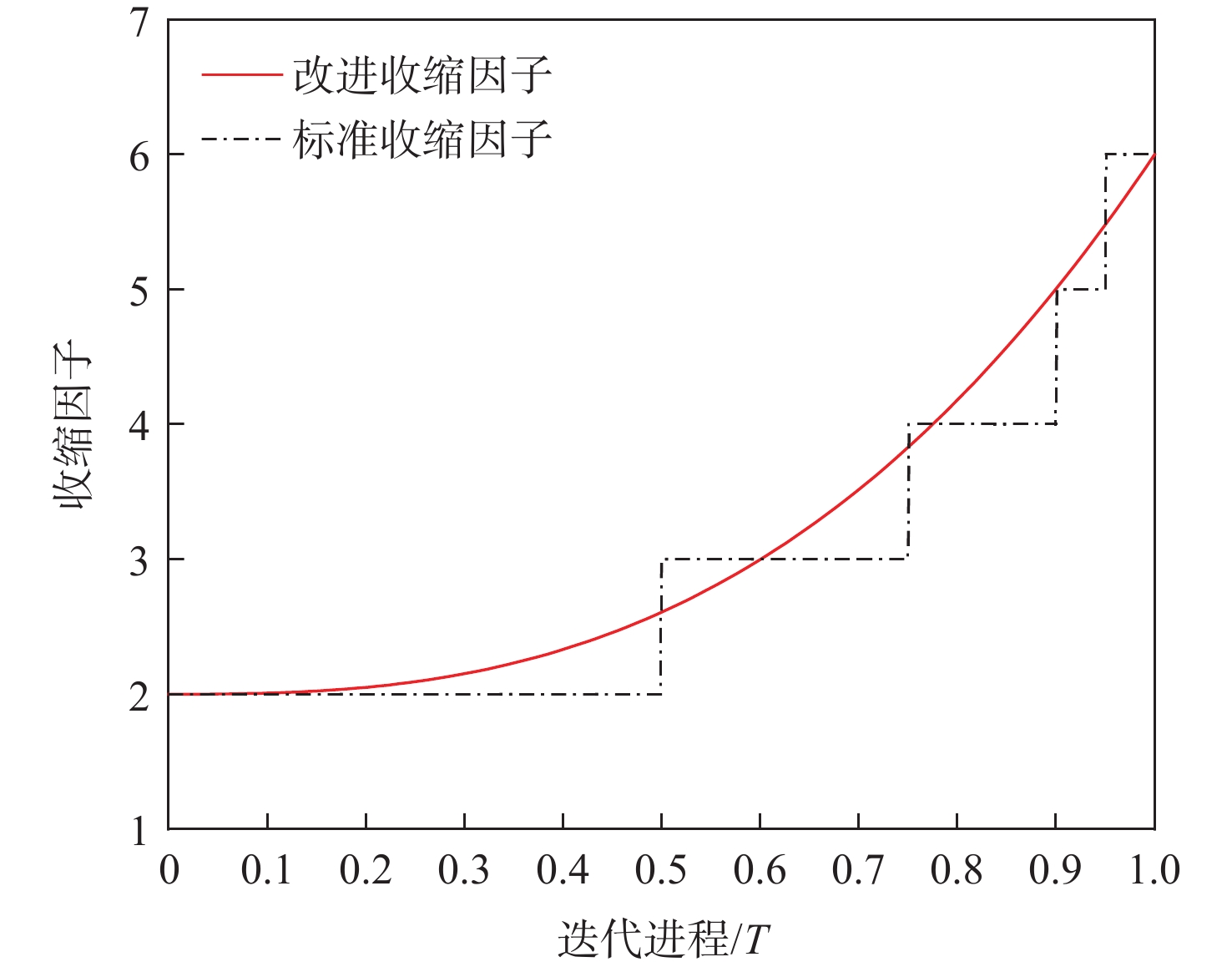
由式(17)~式(20)可知,收缩因子ω为分段常值函数,使随机游走空间随着迭代次数增加而分段线性缩小。标准随机游走空间缩小机制存在3点不足:①搜索空间在分段点处较大幅度的阶梯变化会遗漏某些区域,可能错过最优解;②搜索空间的分段缩小过程缓慢且不均匀,导致收敛速度较慢;③在同一阶段的迭代过程中,所有蚂蚁的随机游走空间完全一致,不仅降低了算法的多样性,还浪费了算力。
为改善算法的寻优性能、收敛性能及多样性,提出一种具有一定随机性的连续非线性随机游走空间缩小机制。改进后的数学表达式如式(24)~式(25)所示。
\omega = 2 + 4 {\left( {\frac{t}{{T}}} \right)^{{\rm{e}}}} (24) I = {10^\omega }\frac{t}{{T}}\left[ {0.8 + \sin \left( {\frac{{{{\text{π}} }t}}{{4{T}}} s_{\text{rand}}} \right)} \right] (25) 该机制主要改进了收缩因子ω,收缩因子调节过程如图5所示。
由图5可以看出,改进收缩因子ω仍可以满足收缩尺度变化需求;改进收缩因子ω具有了连续性,可以避免在寻优过程遗漏某些区域。
此外,在收缩系数I内添加了随机部分,不仅有效增强了算法的多样性,还可以在迭代后期加快收敛。
2.2.2 蚂蚁位置更新机制
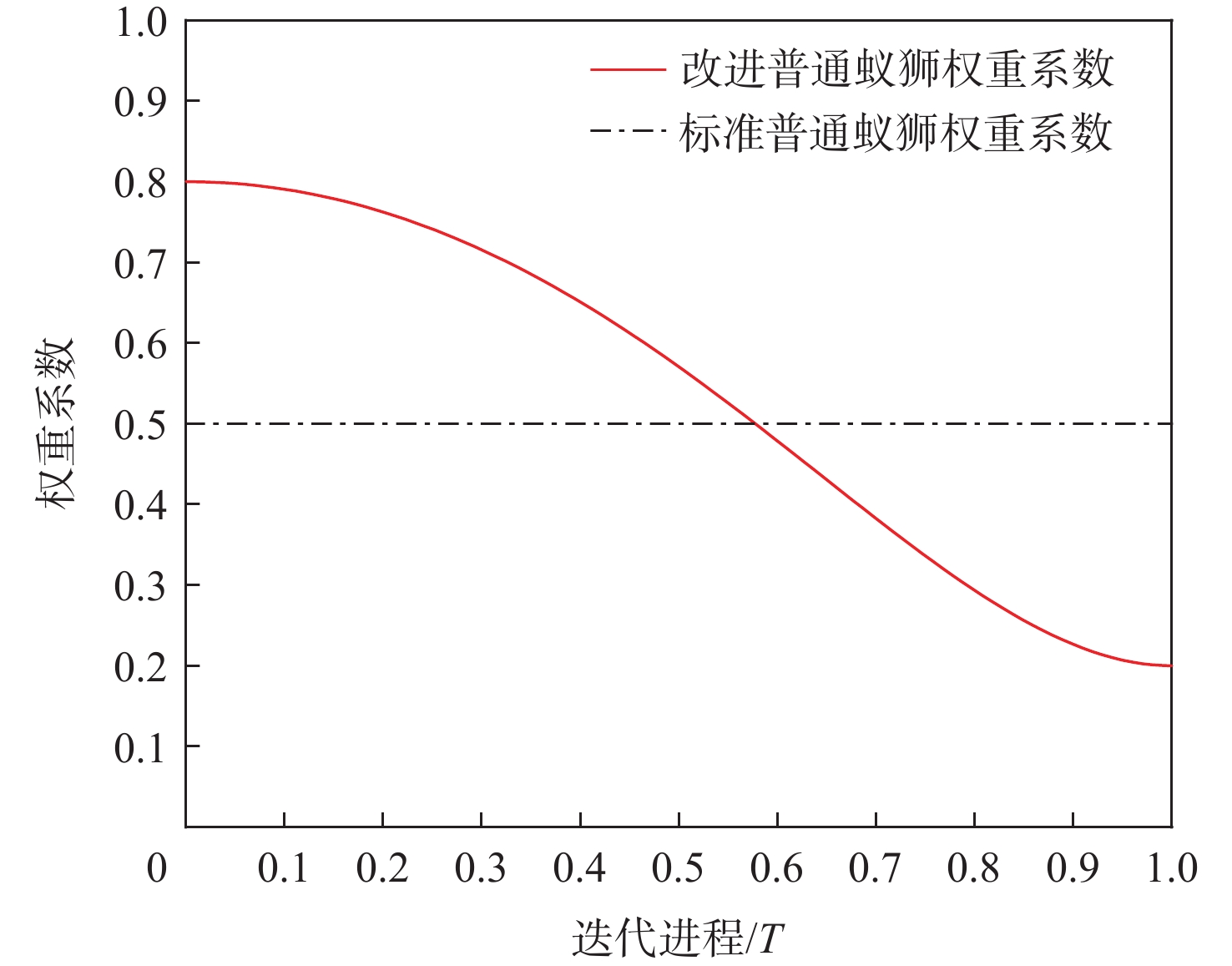
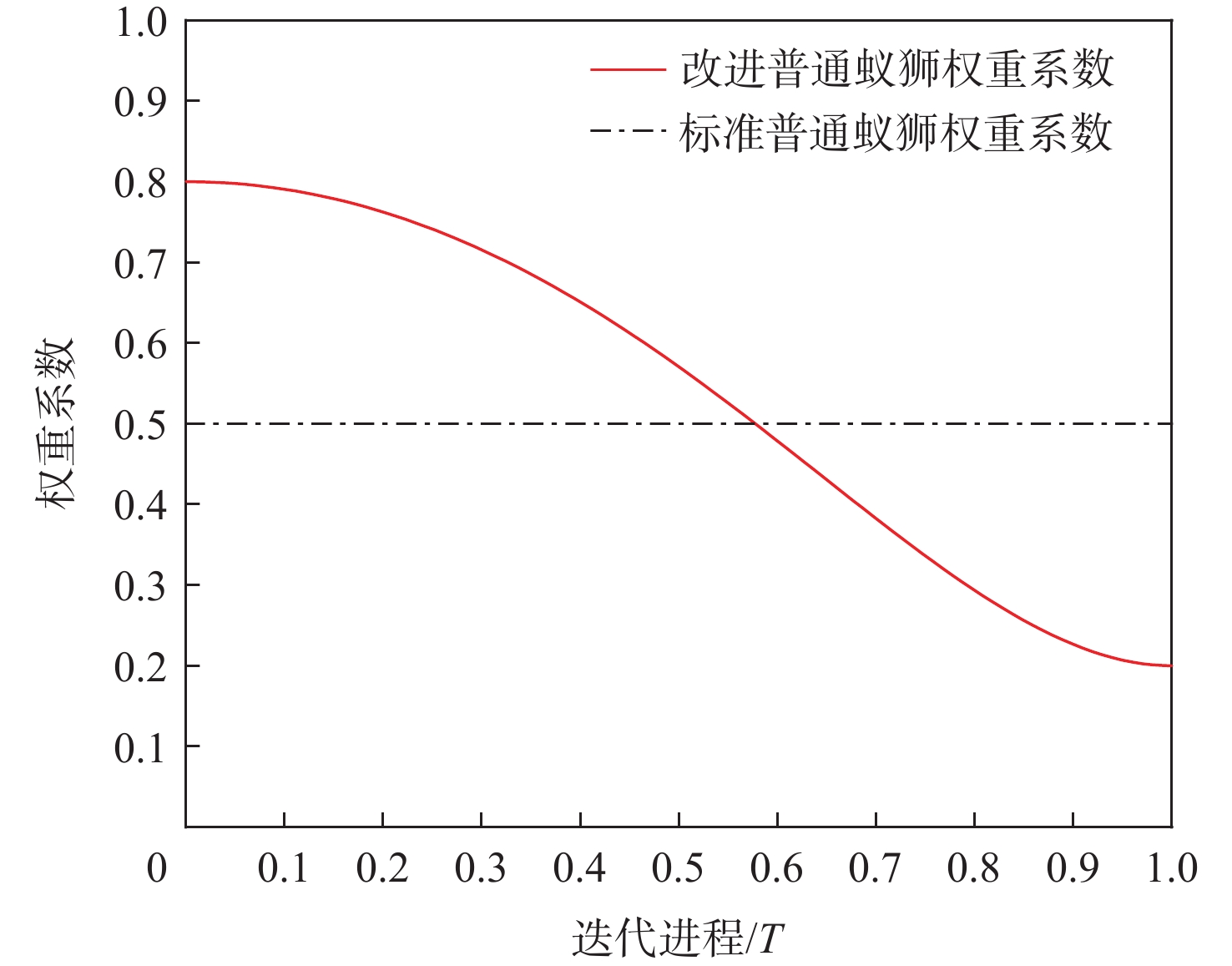
在标准ALO算法中,蚂蚁通过围绕着精英蚁狮和通过轮盘赌抽取的普通蚁狮进行随机游走来更新自己的位置,其中普通蚁狮主要影响算法的全局搜索能力,精英蚁狮主要影响算法的局部寻优能力,二者在蚂蚁位置更新时的权重均恒为0.5。但在实际迭代过程中,不同时期对全局搜索能力和局部寻优能力的需求存在差异,迭代的前中期需要更强的全局搜索能力,以增加种群的多样性,避免陷入局部最优解;而迭代的后期需要更强的局部寻优能力,以提高在全局最优点附近的收敛速度,找到更优的解。
为满足不同时期算法对全局搜索能力和局部寻优能力的差异性需求,提出一种可以根据迭代次数非线性动态调整普通蚁狮权重系数β的方法,如式(26)~式(27)所示。
\,\beta = {{\beta }_{{\max}}} + \left( {{{\beta }_{\max }} - {{\beta }_{\min }}} \right)\sin \left[ {\frac{{\text{π}}}{2} {{\left( {\frac{t}{{T}}} \right)}^2} + {{\text{π}}}} \right] (26) A_i^t = \beta R_{{\rm{A}}}^t + \left( {1 - \beta } \right)R_{{\rm{E}}}^t (27) 式中:βmax=0.8;βmin=0.2。
普通蚁狮权重系数β随迭代次数变化曲线如图6所示,可以看出采用该调节方法后,IALO算法在迭代的前期拥有更强的全局寻优能力,以较为缓慢的速度降低全局寻优能力,到了迭代中期仍以全局寻优为主,从而在全局范围搜寻到更优的解区域,避免陷入局部最优陷阱。然后以更快的速度增强局部寻优能力,使迭代后期以局部寻优为主,保证算法可以充分寻找全局最优区域的局部最优解。
2.3 构造模型
将所提出的预测部分和超参数优化部分进行融合,构造出IALO-AM-BiLSTM模型,其构造过程如下:①使用超参数优化部分提供的初始超参数配置预测部分;②预测部分进行迭代运算; ③超参数优化部分根据预测部分迭代运算的输出结果对超参数进行优化; ④判断是否满足终止条件,若不满足则使用更新后的超参数配置预测部分,返回过程2,若满足则输出结果,并得到超参数最优的预测模型。
IALO-AM-BiLSTM模型的结构如图7所示。
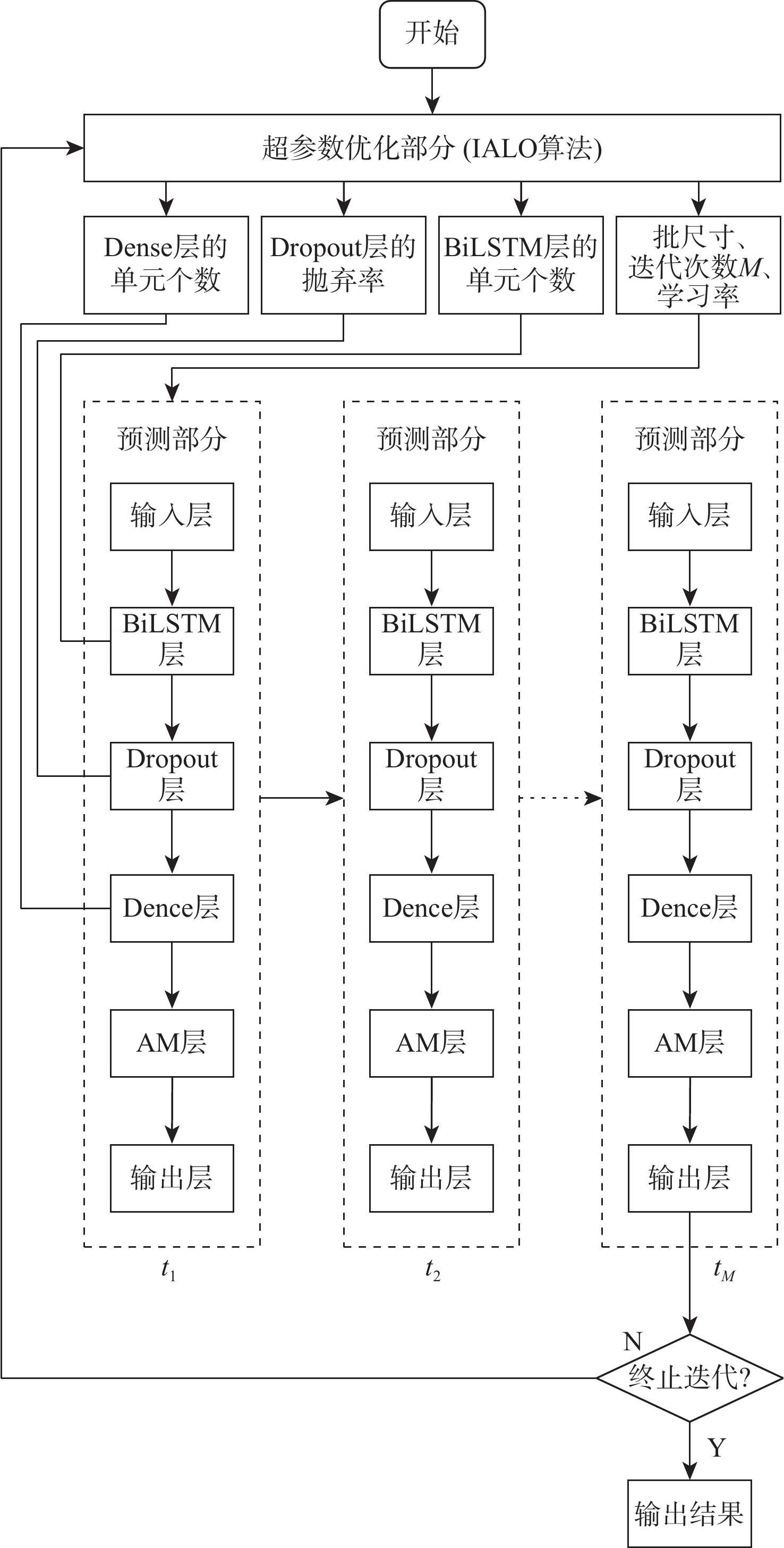
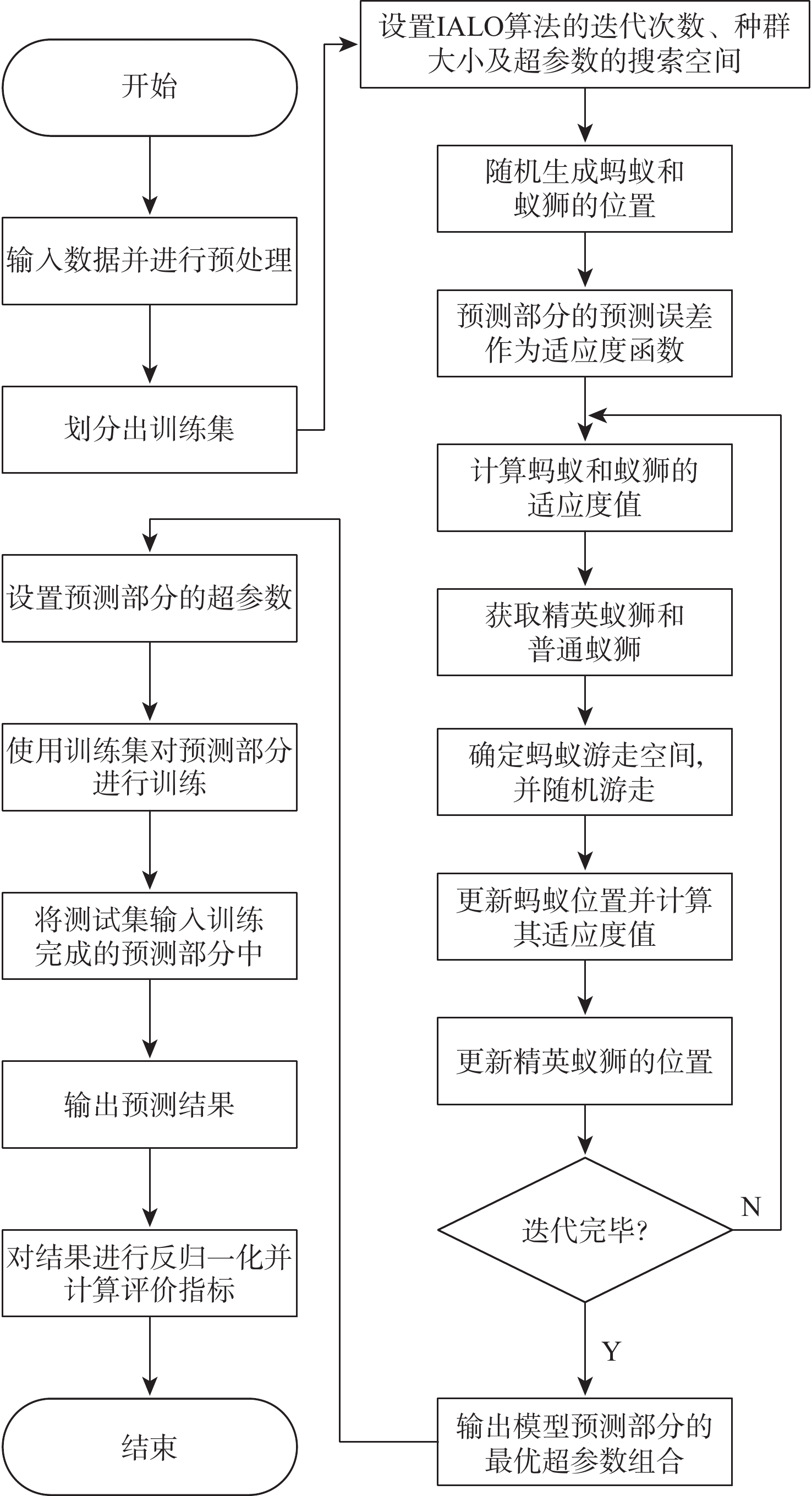
2.4 模型的训练流程
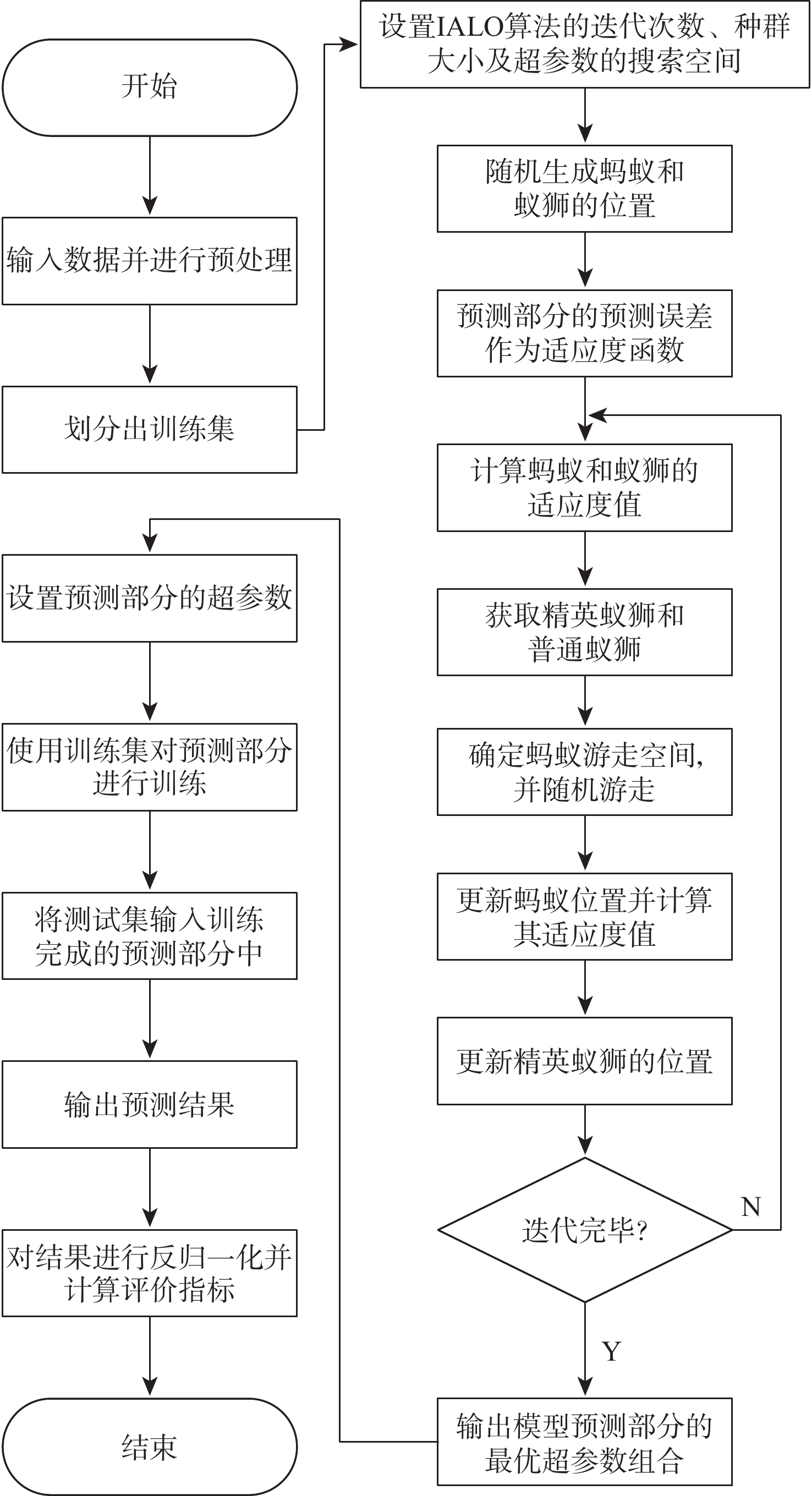
本文提出的IALO-AM-BiLSTM模型的训练流程如图8所示,具体训练步骤如下。
步骤 1 将数据集按7:3的比例划分为训练集和测试集,使用最值归一化法分别对其进行处理,计算式为
{{\boldsymbol{x}}_{{\rm{e}}}} = \frac{{{{\boldsymbol{x}}_{{\rm{a}}}} - {{\boldsymbol{x}}_{\min }}}}{{{{\boldsymbol{x}}_{\max }} - {{\boldsymbol{x}}_{\min }}}} (28) 式中:xe为归一化之后的输入数据;xa为原始的输入数据;xmax和xmin为原始数据中各变量的最大值和最小值。
步骤 2 将模型预测部分的批尺寸、BiLSTM层的单元个数、Dropout层的抛弃率、Dense层的单元个数、迭代次数、学习率等超参数设为寻优对象并确定各自的搜索空间。
步骤 3 设置IALO算法的迭代次数T、种群大小N、变量个数D。
步骤 4 对蚂蚁和蚁狮的位置进行随机初始化,用训练集训练模型的预测部分,选取预测误差的均方误差(MSE)为适应度函数,并计算每个位置对应的适应度值。MSE的计算式为
E_{\text{MSE}} = \frac{1}{m}\sum\limits_{i = 1}^m {{{\left( {{y_i} - f\left( {{x_i}} \right)} \right)}^2}} (29) 式中:yi为真实值;f(xi)为预测值;m为样本数量。
步骤 5 根据适应度值确定精英蚁狮,并通过轮盘赌抽取普通蚁狮。
步骤 6 根据式(17)和式(18)及式(24)和式(25)更新随机游走空间,蚂蚁分别围绕精英蚁狮和普通蚁狮进行随机游走。
步骤 7 根据式(26)和式(27)确定蚂蚁的最终位置,计算其适应度值,再与精英蚁狮的适应度值对比,根据式(22)更新精英蚁狮的位置。
步骤 8 判断是否满足终止条件,若满足则输出最优位置,否则返回步骤4。终止条件为达到最大迭代次数。
步骤 9 使用IALO算法得到的最优超参数组合配置模型的预测部分,并用训练集对其进行训练。
步骤 10 将测试集的特征数据输入训练好的模型中,输出预测结果。
步骤 11 对预测结果进行反归一化,与测试集的目标数据对比,并结合评价指标对其进行分析。
3. 算例验证
3.1 数据来源
采集中国东部某机场在夏季使用地面空调为飞机客舱降温除湿的相关数据作为数据集,其中地面空调的制冷量均为150 kW,飞机型号均为波音737-800。该数据集共300组,包括工作前的初始温度和初始湿度,工作完成后的最终温度和最终湿度及全过程的耗电量,其中初始温度、初始湿度、最终温度及最终湿度作为特征数据,耗电量作为目标数据。部分样本数据如表1所示。
表 1 部分样本数据Table 1. Partial sample data初始温度/℃ 初始湿度/% 最终温度/℃ 最终湿度/% 耗电量/kW 32.5 57.5 24.7 37.9 181.33 31.3 63.9 23.8 36.2 165.24 32.6 49.9 25.0 24.7 178.26 35.2 68.2 25.2 36.0 186.14 33.2 72.8 24.5 37.0 169.94 31.2 62.8 27.6 35.1 147.79 3.2 评价指标
选取MSE、平均绝对百分比误差(MAPE)和决定系数(R2)作为评价指标,其中MSE、MAPE的值越小,说明预测结果越接近真实值,预测精度越高;R2的值越接近1,说明拟合优度越大,自变量对因变量的解释程度越高,所建立的模型越好。MSE的计算如式(29)所示,其余评价指标的计算如式(30)和式(31)所示。
E_ {\text{MAPE}} = \frac{{100\% }}{m}\sum\limits_{i = 1}^m {\left| {\frac{{{y_i} - f\left( {{x_i}} \right)}}{{f\left( {{x_i}} \right)}}} \right|} (30) {R^2} = 1 - \frac{{\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^m {{{\left( {{y_i} - f\left( {{x_i}} \right)} \right)}^2}} }}{{\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^m {{{\left( {{y_i} - {{\bar y}_i}} \right)}^2}} }} (31) 式中: {\bar y_i} 为真实值的平均数。
3.3 超参数优化结果与分析
本文所提IALO-AM-BiLSTM模型中的超参数包括批尺寸、BiLSTM层的单元个数、Dense层的单元个数、迭代次数、Dropout层的抛弃率、学习率等,其组合形式对模型的预测结果具有很大的影响。在综合考虑实例具体情况和搜索效率的基础上设置超参数的搜索空间,如表2所示。
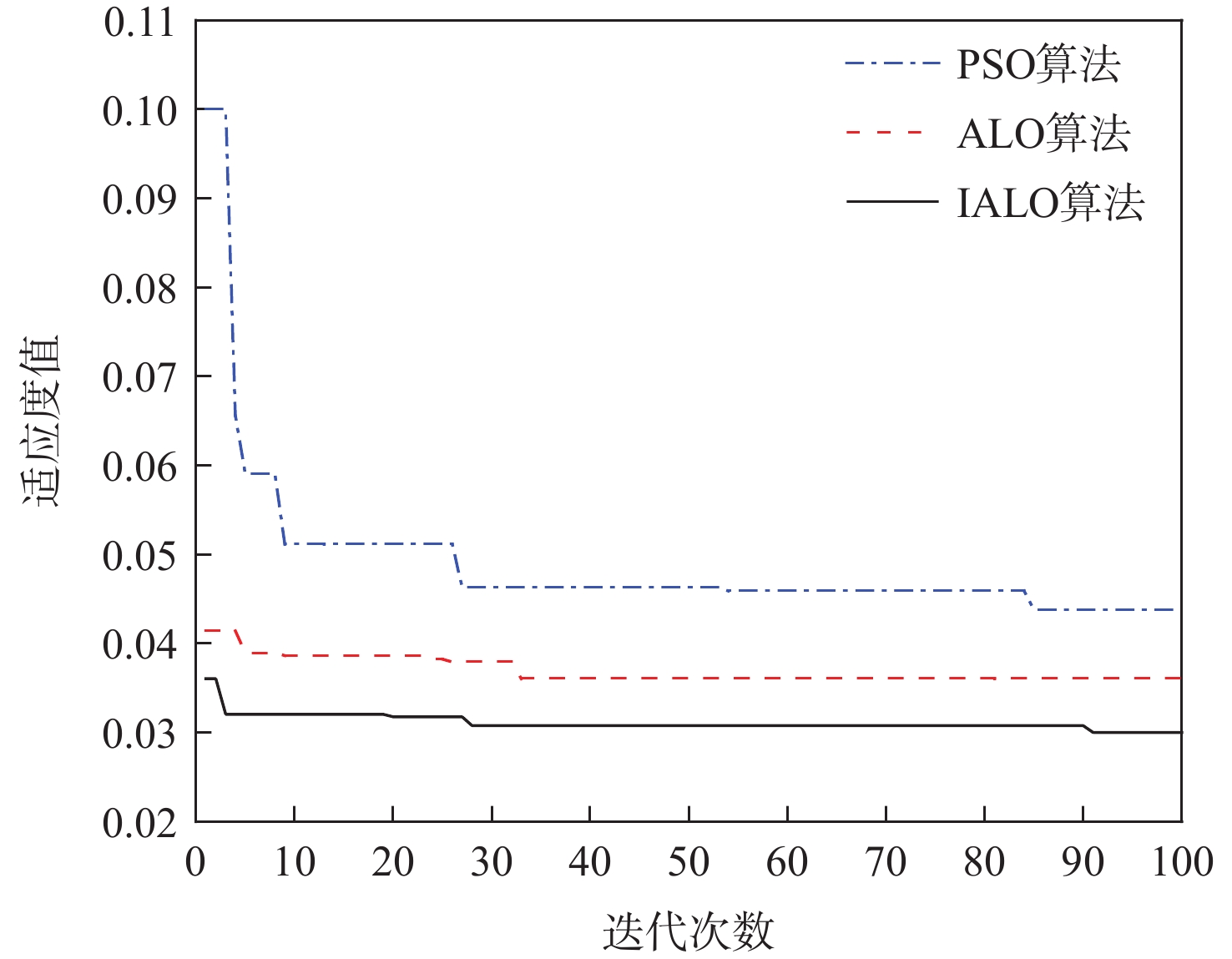
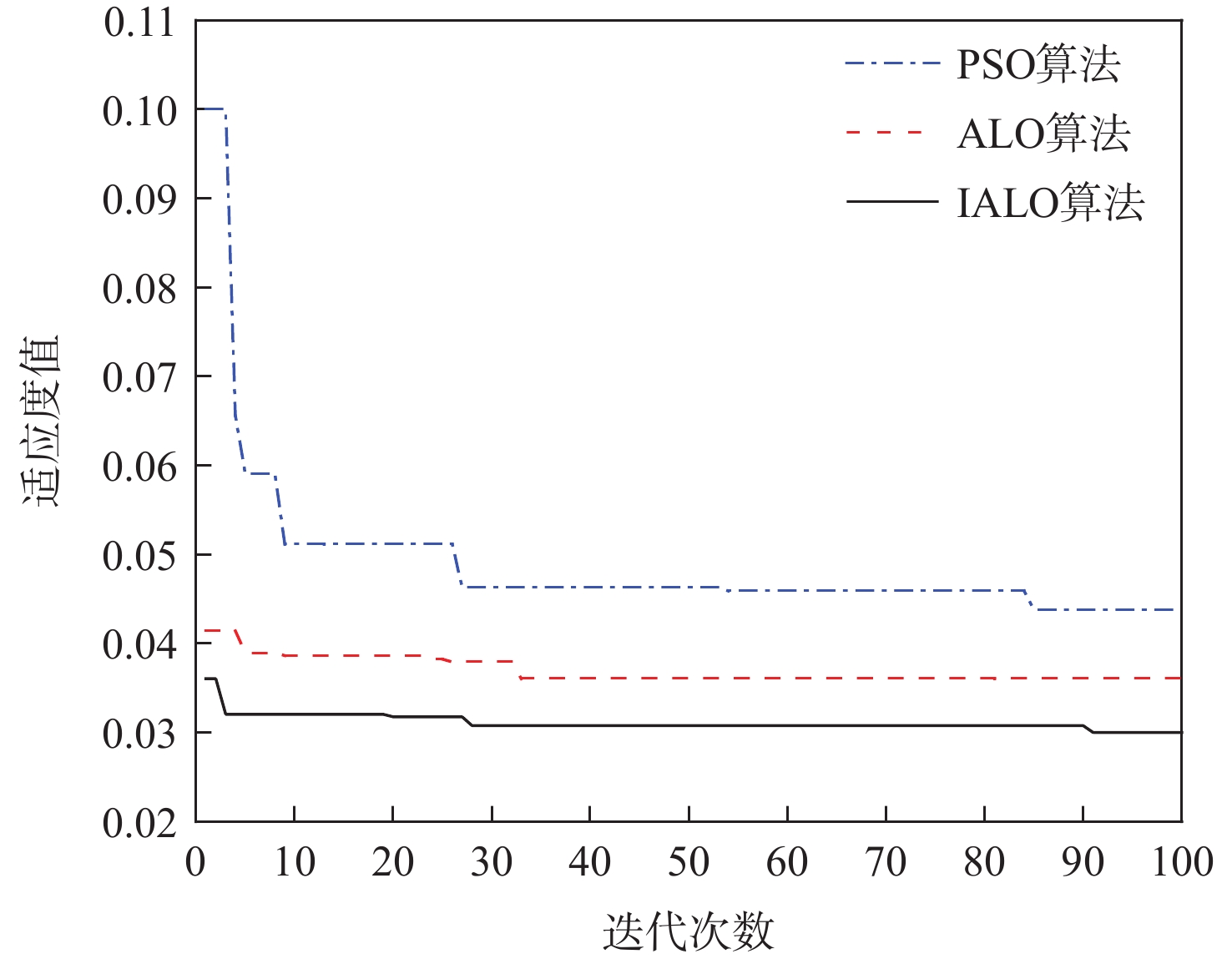
表 2 超参数搜索空间Table 2. Search space of hyperparameters超参数 搜索空间 批尺寸 1~20 学习率 0.0001~0.01 迭代次数 300~500 BiLSTM层的单元个数 10~200 Dense层的单元个数 10~200 Dropout层的抛弃率 0.1~0.9 选取PSO-AM-BiLSTM、ALO-AM-BiLSTM作为对比模型,使用训练集对各模型的超参数优化部分进行训练,其迭代次数均设置为100,种群规模均为50。各算法的迭代过程如图9所示。
从图9可以看出,IALO算法的寻优结果显著优于PSO算法和ALO算法;ALO算法虽然在迭代前期具有良好的寻优能力,但在迭代过程的中后期无法跳出局部最优陷阱;IALO算法不仅在迭代前期具有优异的寻优效果,在迭代后期也能进一步优化寻优结果,证明IALO算法在整个迭代过程中都具有很好的全局寻优能力和局部寻优能力。
各超参数优化算法最终寻找到的最优超参数组合如表3所示。
表 3 各算法的最优超参数组合Table 3. Optimal hyperparameter combination of different algorithms算法 批尺寸 BiLSTM层的
单元个数Dense层的
单元个数迭代次数 Dropout层的
抛弃率学习率 PSO 1 200 96 499 0.1 0.01 ALO 8 65 67 487 0.2 0.0077 IALO 2 36 121 324 0.2 0.0064 3.4 预测结果与分析
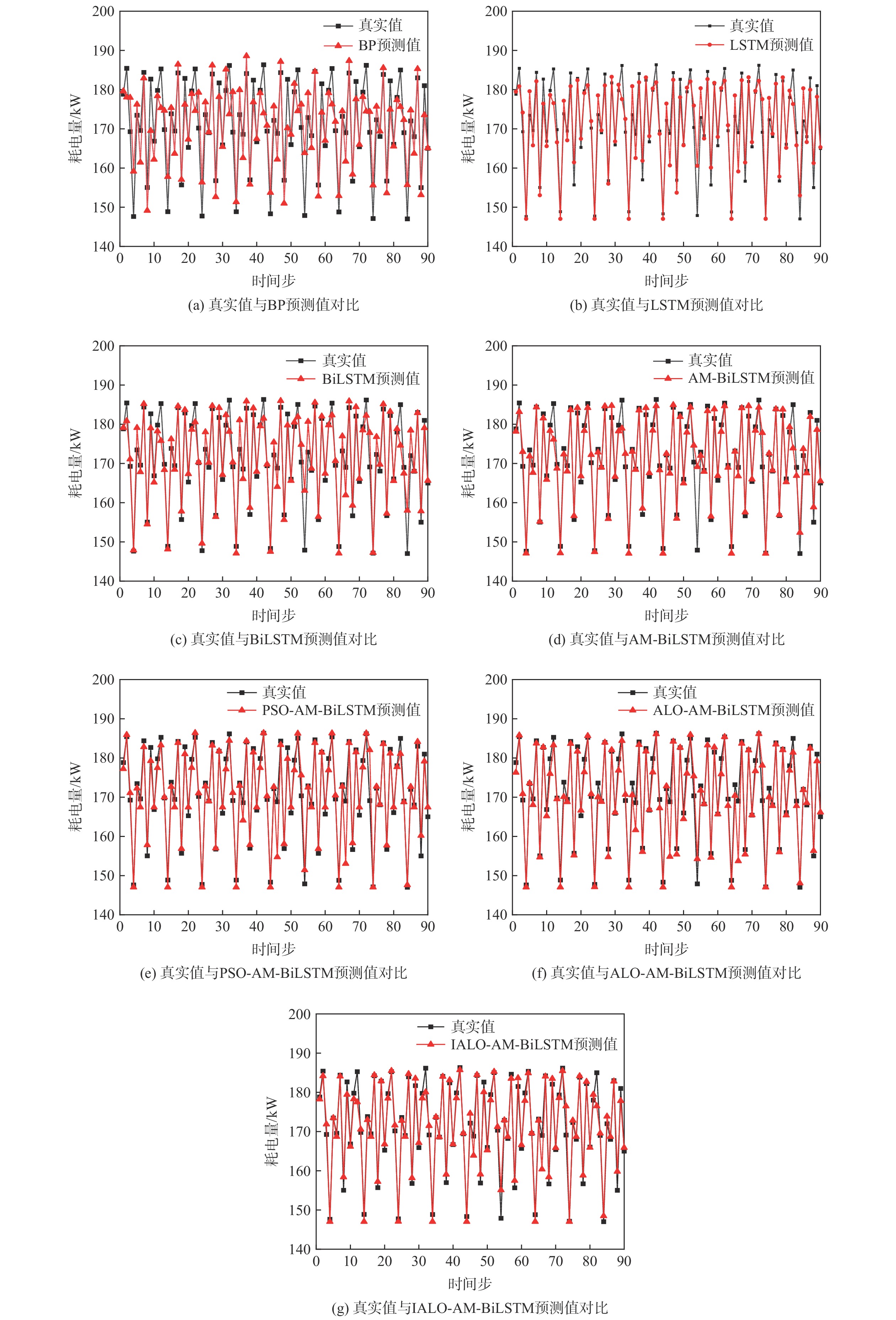
利用各超参数优化算法得到最优超参数组合配置各自的预测模型,在测试集上进行预测,将预测结果与根据经验手动调参的BP模型、LSTM模型、BiLSTM模型、AM-BiLSTM模型的预测结果对比,各模型预测值和真实值的对比如图10所示。
为了科学评价各模型的性能,使用MSE、MAPE和R2等评价指标对各模型的预测结果进一步分析,分析结果如表4所示。
表 4 不同模型预测结果对比(测试集)Table 4. Comparison of prediction results based on different models (test set)模型 MSE MAPE/% R2 BP 37.159 2.842 0.728 LSTM 17.257 1.870 0.874 BiLSTM 14.326 1.504 0.895 AM-BiLSTM 11.145 1.083 0.918 PSO-AM-BiLSTM 9.196 1.068 0.927 ALO-AM-BiLSTM 9.411 1.041 0.931 IALO-AM-BiLSTM 6.045 0.928 0.956 通过分析表4的各项指标可以得出:①IALO-AM-BiLSTM模型的预测结果在MSE、MAPE、R2等多项指标上都优于其他模型;②提取更多时间序列特征有助于提高模型的预测精度及拟合优度;③在模型中引入注意力机制能够提高时序特征的利用率及模型的预测精度;④IALO算法在超参数寻优上优于PSO算法和ALO算法,可以更充分地发挥AM-BiLSTM模型的预测性能。
4. 结 论
1) 在分析地面空调能耗影响因素的基础上,通过提高时间序列特征的利用效率来提高预测精度,本文模型可通过BiLSTM神经网络充分挖掘出数据的时间序列特征,结合注意力机制赋予各特征不同的权重。经仿真验证,增强对时间序列特征的利用可以显著地提高地面空调能耗预测的精度。
2) 本文提出2种优化机制来改进ALO算法,一种是基于非线性动态调整蚁狮权重系数的蚂蚁位置更新机制,另一种是具有一定随机性的连续非线性随机游走空间缩小机制。这2种优化机制可提高算法的收敛速度、寻优性能及多样性,增强IALO算法处理具有复杂搜索空间的超参数优化问题的能力,进一步提升了模型的预测精度和拟合优度。
-
表 1 部分样本数据
Table 1. Partial sample data
初始温度/℃ 初始湿度/% 最终温度/℃ 最终湿度/% 耗电量/kW 32.5 57.5 24.7 37.9 181.33 31.3 63.9 23.8 36.2 165.24 32.6 49.9 25.0 24.7 178.26 35.2 68.2 25.2 36.0 186.14 33.2 72.8 24.5 37.0 169.94 31.2 62.8 27.6 35.1 147.79 表 2 超参数搜索空间
Table 2. Search space of hyperparameters
超参数 搜索空间 批尺寸 1~20 学习率 0.0001~0.01 迭代次数 300~500 BiLSTM层的单元个数 10~200 Dense层的单元个数 10~200 Dropout层的抛弃率 0.1~0.9 表 3 各算法的最优超参数组合
Table 3. Optimal hyperparameter combination of different algorithms
算法 批尺寸 BiLSTM层的
单元个数Dense层的
单元个数迭代次数 Dropout层的
抛弃率学习率 PSO 1 200 96 499 0.1 0.01 ALO 8 65 67 487 0.2 0.0077 IALO 2 36 121 324 0.2 0.0064 表 4 不同模型预测结果对比(测试集)
Table 4. Comparison of prediction results based on different models (test set)
模型 MSE MAPE/% R2 BP 37.159 2.842 0.728 LSTM 17.257 1.870 0.874 BiLSTM 14.326 1.504 0.895 AM-BiLSTM 11.145 1.083 0.918 PSO-AM-BiLSTM 9.196 1.068 0.927 ALO-AM-BiLSTM 9.411 1.041 0.931 IALO-AM-BiLSTM 6.045 0.928 0.956 -
[1] 王修岩, 刘艳敏, 张革文, 等. 基于PSO和CRO联合算法的飞机客舱能耗预测[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2018, 30(8): 3074-3081.WANG X Y, LIU Y M, ZHANG G W, et al. Prediction of aircraft cabin energy consumption based on PSO and CRO algorithms[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2018, 30(8): 3074-3081(in Chinese). [2] 林家泉, 孙凤山, 李亚冲, 等. 基于IPSO-Elman神经网络的飞机客舱能耗预测[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(7): 323614.LIN J Q, SUN F S, LI Y C, et al. Prediction of aircraft cabin energy consumption based on IPSO-Elman neural network[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(7): 323614(in Chinese). [3] GERS F A, SCHMIDHUBER J, CUMMINS F. Learning to forget: Continual prediction with LSTM[J]. Neural Computation, 2000, 12(10): 2451-2471. doi: 10.1162/089976600300015015 [4] HOCHREITER S, SCHMIDHUBER J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735-1780. doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 [5] 史亚菲, 李峭, 熊华钢. 基于LSTM的TTE网络速率约束流量预测[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(4): 822-829.SHI Y F, LI Q, XIONG H G. Rate-constrained traffic prediction of TTE network based on LSTM[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(4): 822-829(in Chinese). [6] CUI C, HE M, DI F C, et al. Research on power load forecasting method based on LSTM model[C]//2020 IEEE 5th Information Technology and Mechatronics Engineering Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 1657-1660. [7] SIAMI-NAMINI S, TAVAKOLI N, NAMIN A S. The performance of LSTM and BiLSTM in forecasting time series[C]//2019 IEEE International Conference on Big Data. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 3285-3292. [8] ZHANG L, LIU P, ZHAO L, et al. Air quality predictions with a semi-supervised bidirectional LSTM neural network[J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 2021, 12(1): 328-339. doi: 10.1016/j.apr.2020.09.003 [9] 赵兵, 王增平, 纪维佳, 等. 基于注意力机制的CNN-GRU短期电力负荷预测方法[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43(12): 4370-4376.ZHAO B, WANG Z P, JI W J, et al. A short-term power load forecasting method based on attention mechanism of CNN-GRU[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43(12): 4370-4376(in Chinese). [10] JING H, HAN L, GAO Z. Wind power ramp forecast based on feature extraction using convolutional neural network[J]. Dianli Xitong Zidonghua/Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45(4): 98-105. [11] ZHANG W, ZHU F, CHEN Y, et al. Bus passenger flow forecast based on attention and time-sharing graph convolutional network[J]. Moshi Shibie yu Rengong Zhineng/Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 34(2): 167-175. [12] TAN R K, BORA Ş. Parameter tuning in modeling and simulations by using swarm intelligence optimization algorithms[C]//2017 9th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Communication Networks. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 148-152. [13] PHAN H D, ELLIS K, BARCA J C, et al. A survey of dynamic parameter setting methods for nature-inspired swarm intelligence algorithms[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2020, 32(2): 567-588. doi: 10.1007/s00521-019-04229-2 [14] 龙远, 邓小龙, 杨希祥, 等. 基于PSO-BP神经网络的平流层风场短期快速预测[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(10): 1970-1978.LONG Y, DENG X L, YANG X X, et al. Short-term rapid prediction of stratospheric wind field based on PSO-BP neural network[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(10): 1970-1978(in Chinese). [15] YUAN X H, CHEN C, LEI X H, et al. Monthly runoff forecasting based on LSTM-ALO model[J]. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 2018, 32(8): 2199-2212. doi: 10.1007/s00477-018-1560-y [16] CHENG H Y, DING X W, ZHOU W N, et al. A hybrid electricity price forecasting model with Bayesian optimization for German energy exchange[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2019, 110: 653-666. [17] YE Z W, TANG Y Z, LIU W, et al. Learning parameters in deep belief networks through ant lion optimization algorithm[C]//2019 10th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Data Acquisition and Advanced Computing Systems: Technology and Applications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 548-551. [18] MIRJALILI S. The ant lion optimizer[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2015, 83: 80-98. doi: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2015.01.010 [19] SRIVASTAVA N, HINTON G E, KRIZHEVSKY A, et al. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2014, 15: 1929-1958. [20] LIM H I. A study on dropout techniques to reduce overfitting in deep neural networks[C]//Advanced Multimedia and Ubiquitous Engineering. Berlin: Springer, 2021: 133-139. 期刊类型引用(4)
1. 李鹏,肖辉,李秀花,赵恒,邵頲. 基于遗传算法优化Seq2Seq模型的建筑空调电能预测研究. 电气应用. 2025(02): 30-35 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 朱杰克,刘潇晗,汤毅. 基于数值模拟的宁波某超高层建筑空调负荷研究. 建筑施工. 2025(03): 485-489 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 刘涵,林家泉. 基于IPSO-AM-LSTM的飞机地面空调能耗预测. 北京航空航天大学学报. 2024(11): 3595-3602 .  本站查看
本站查看4. 蔡霞,王可,郑军红,何利力. 面向制造企业动力能源的智能供应与管控研究. 工程设计学报. 2024(06): 697-706 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(6)
-








 下载:
下载:









 下载:
下载:
 百度学术
百度学术