-
摘要:
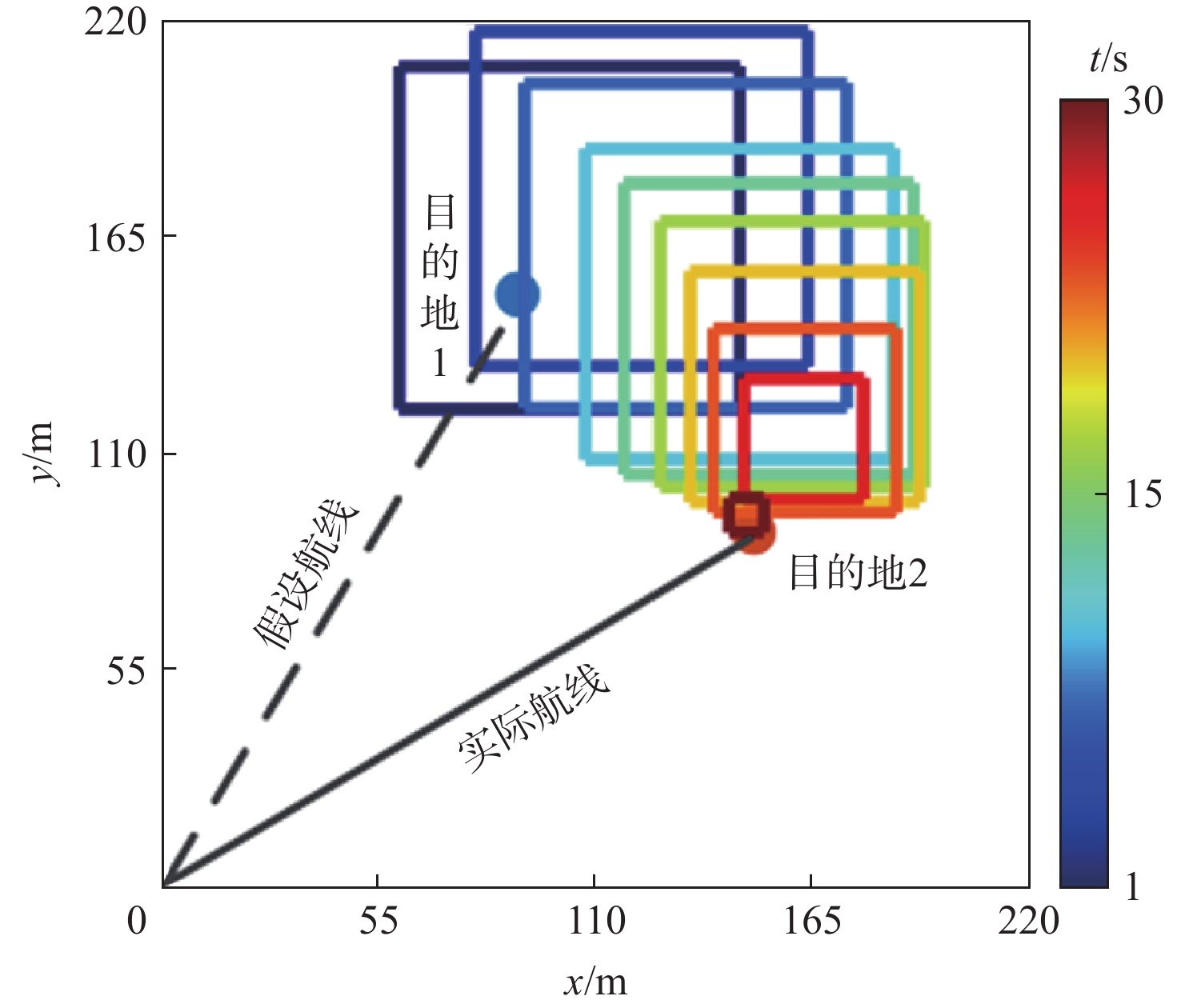
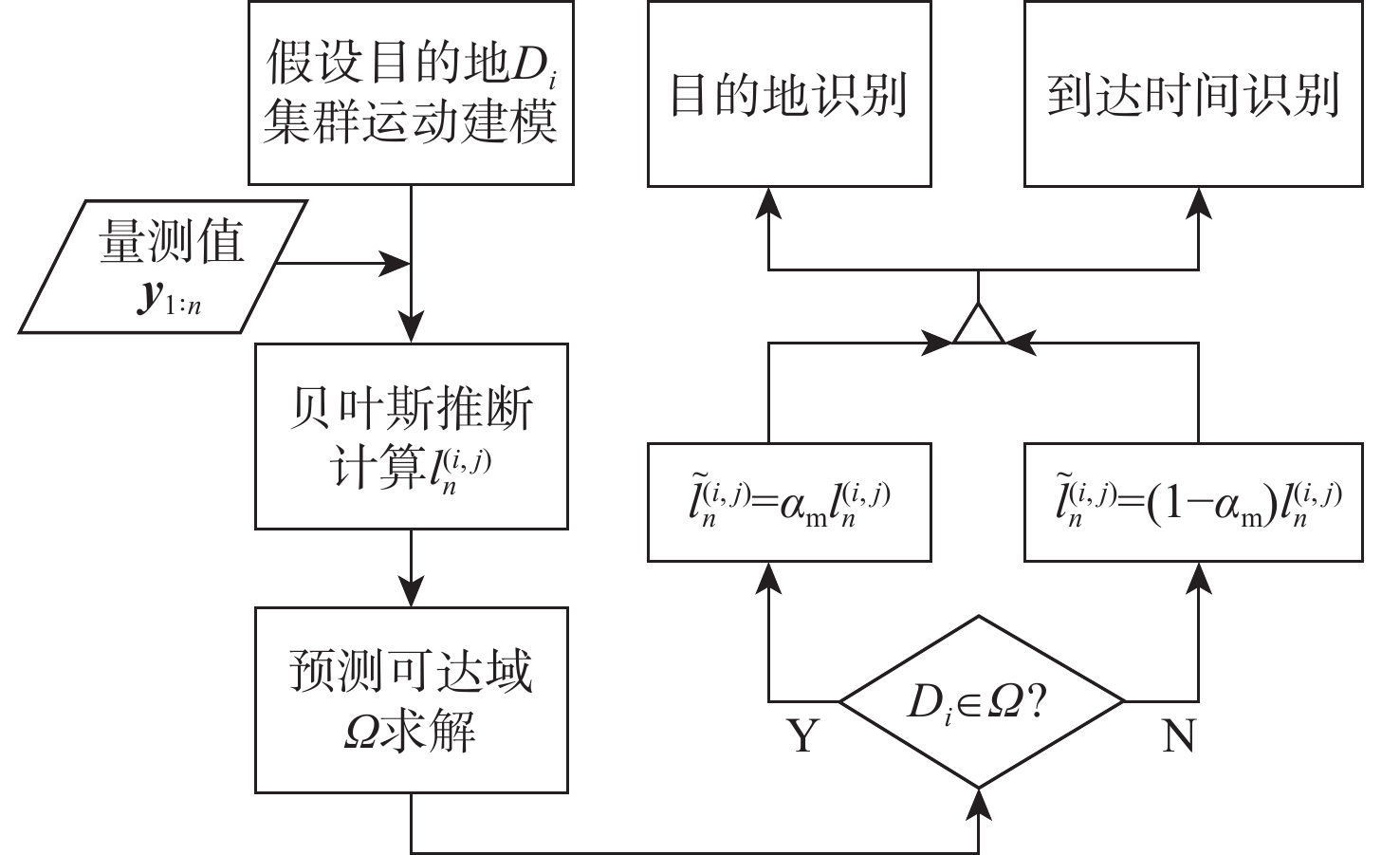
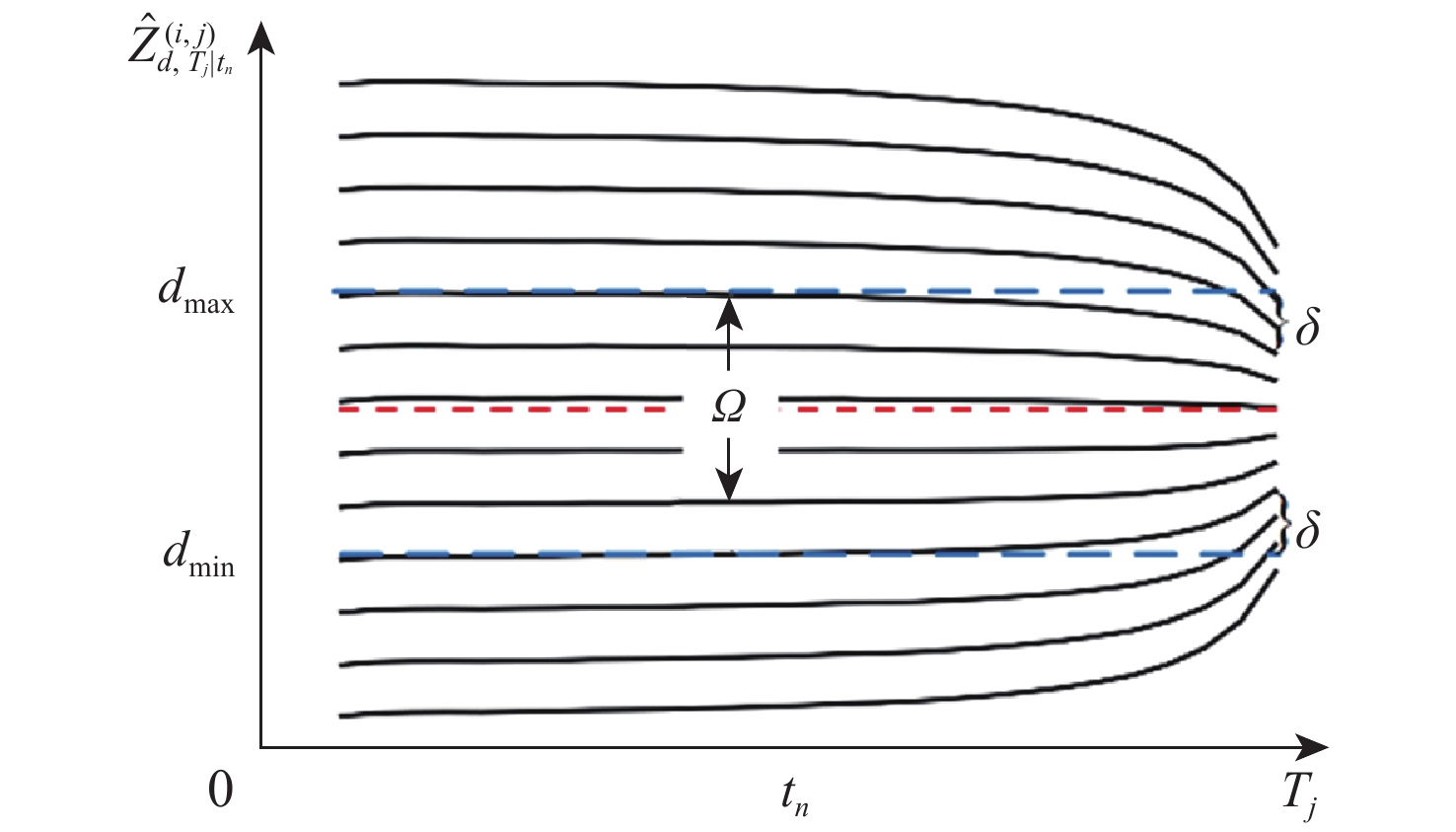
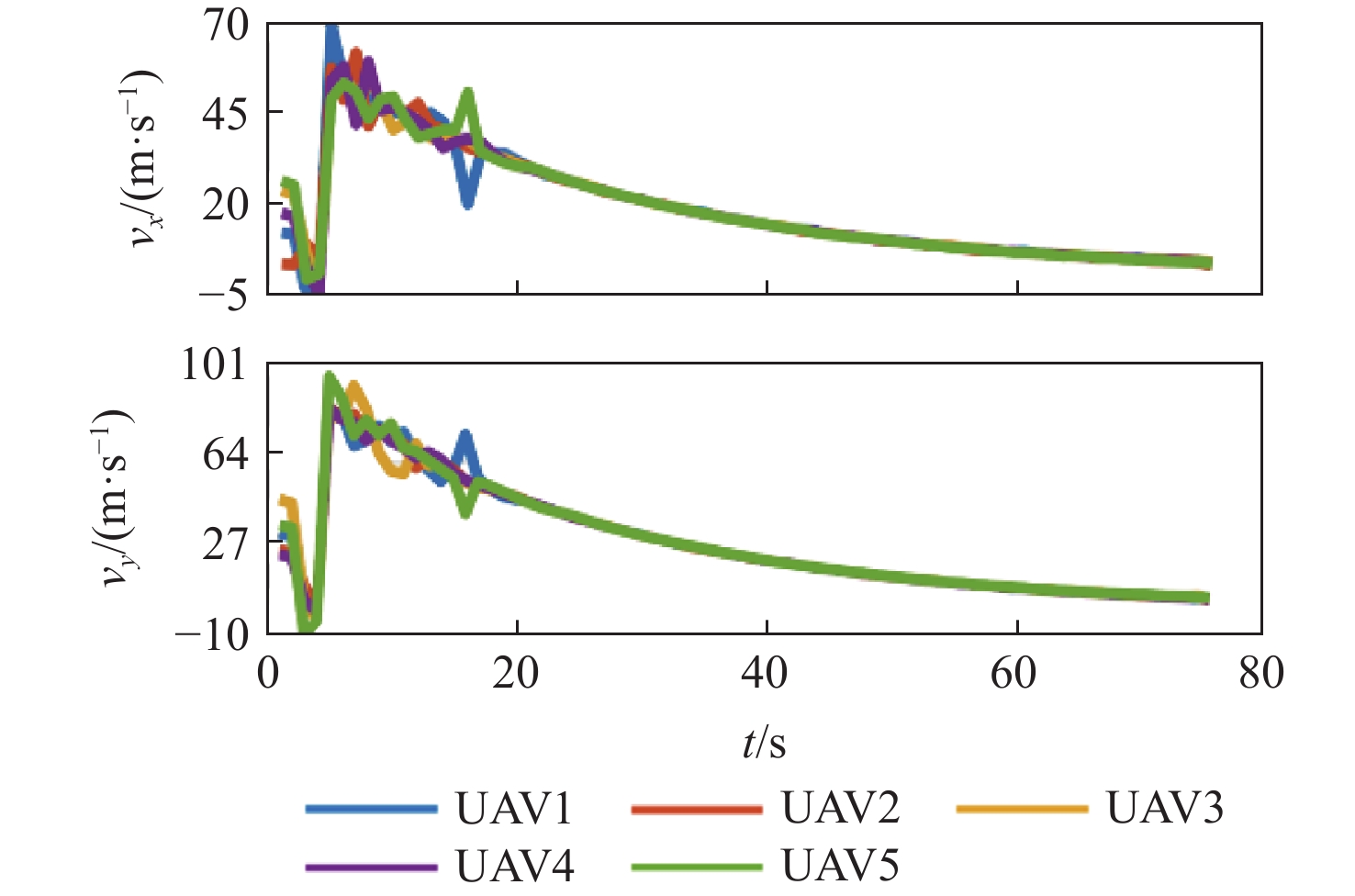
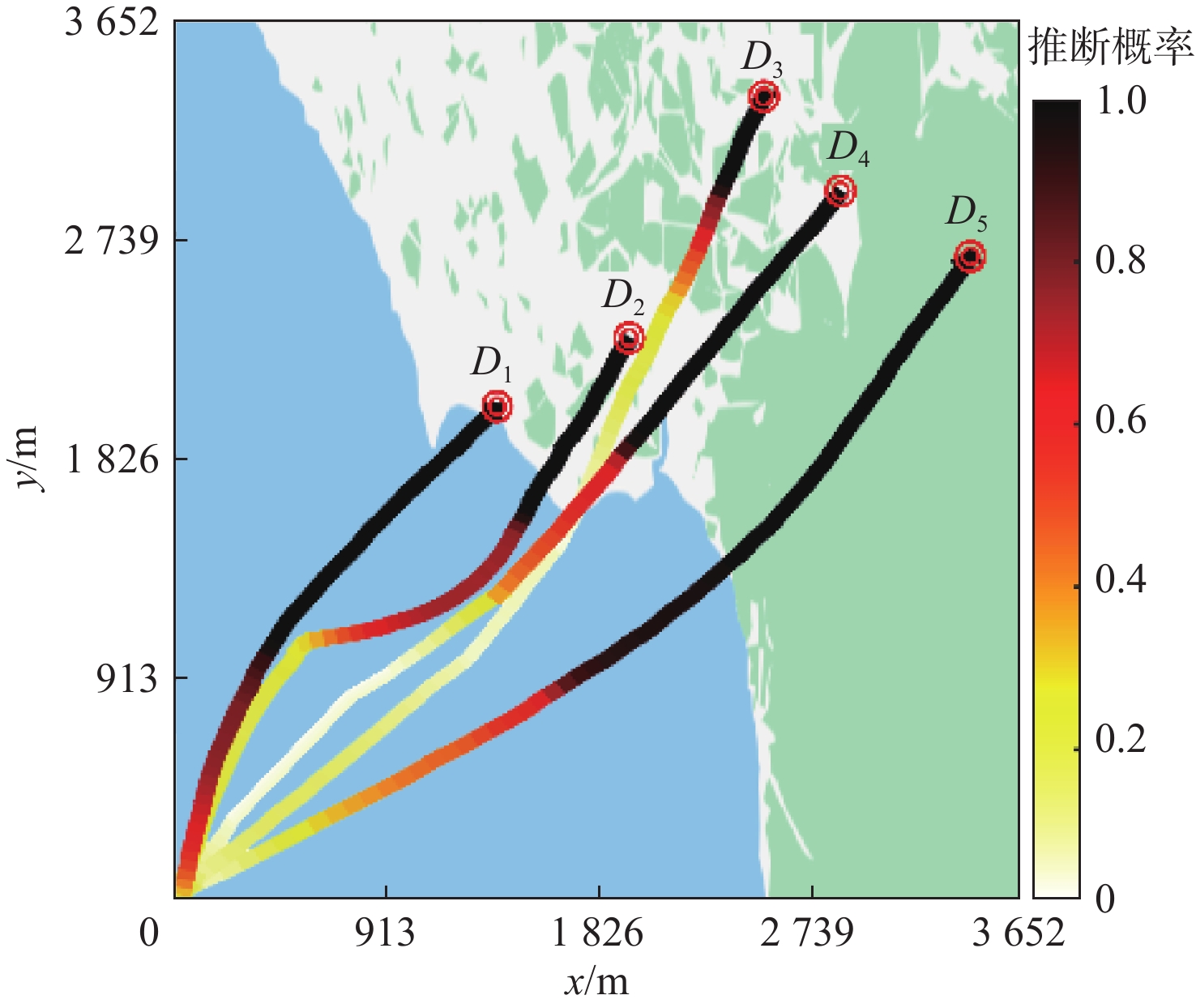
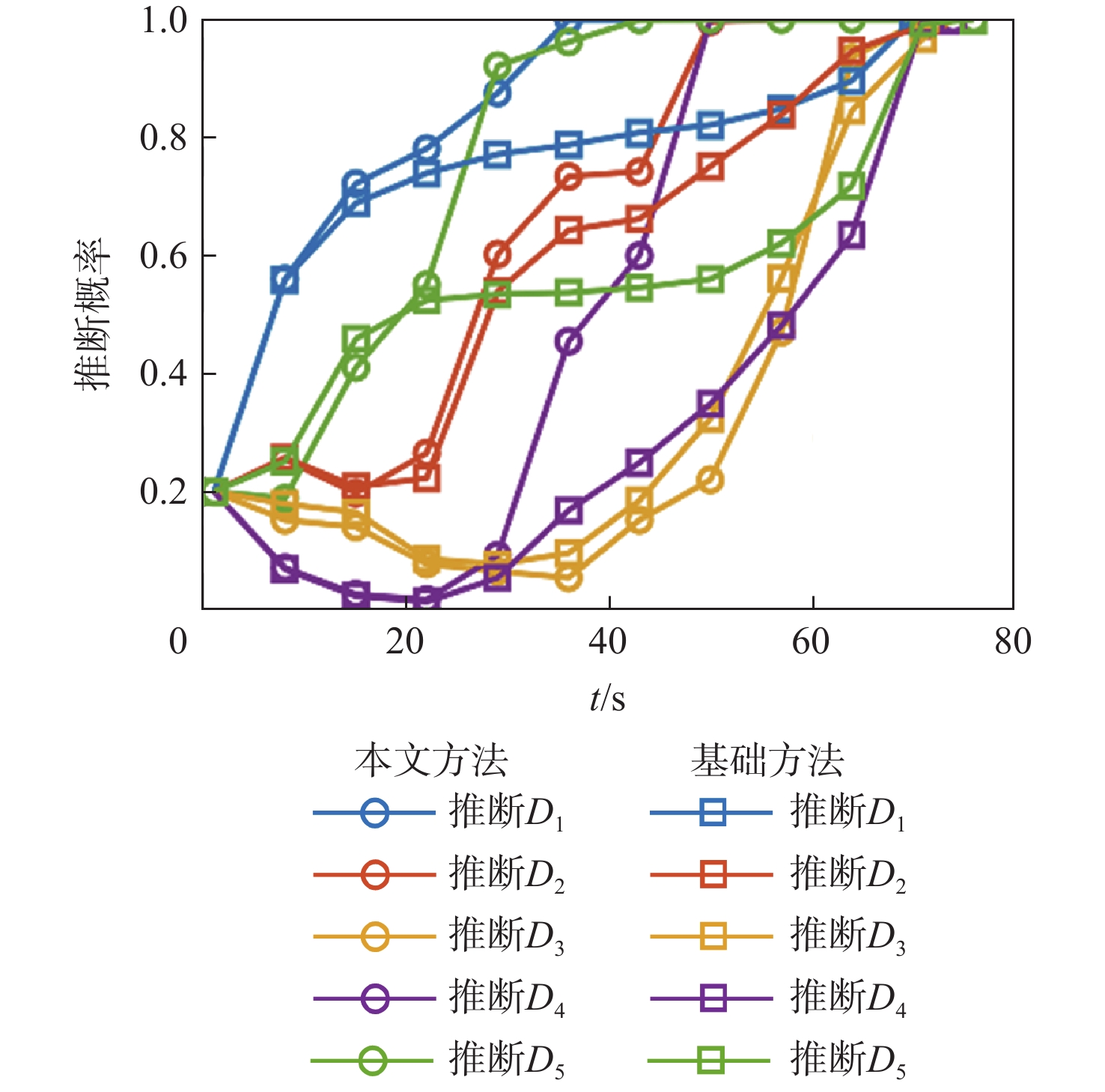
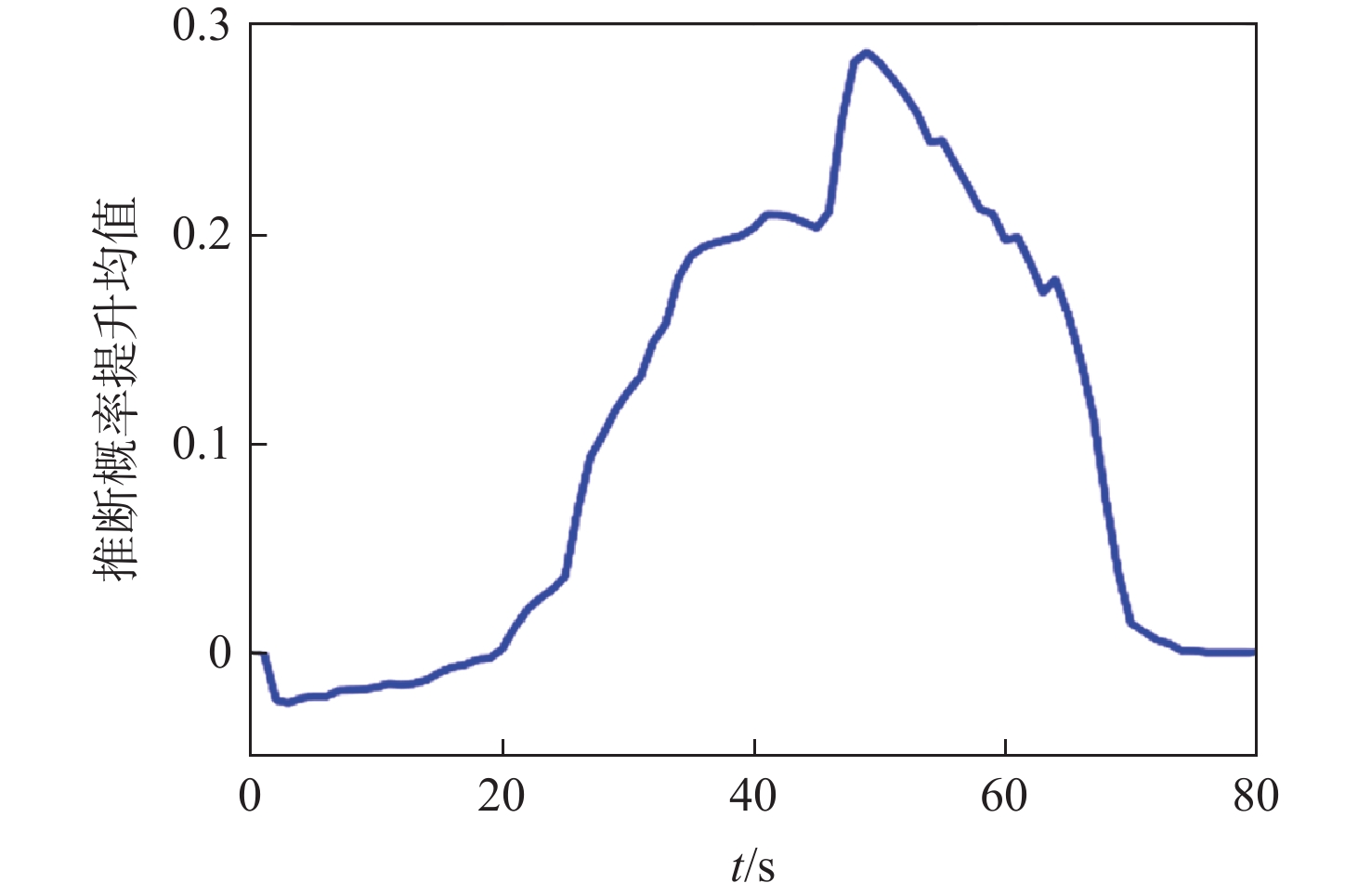
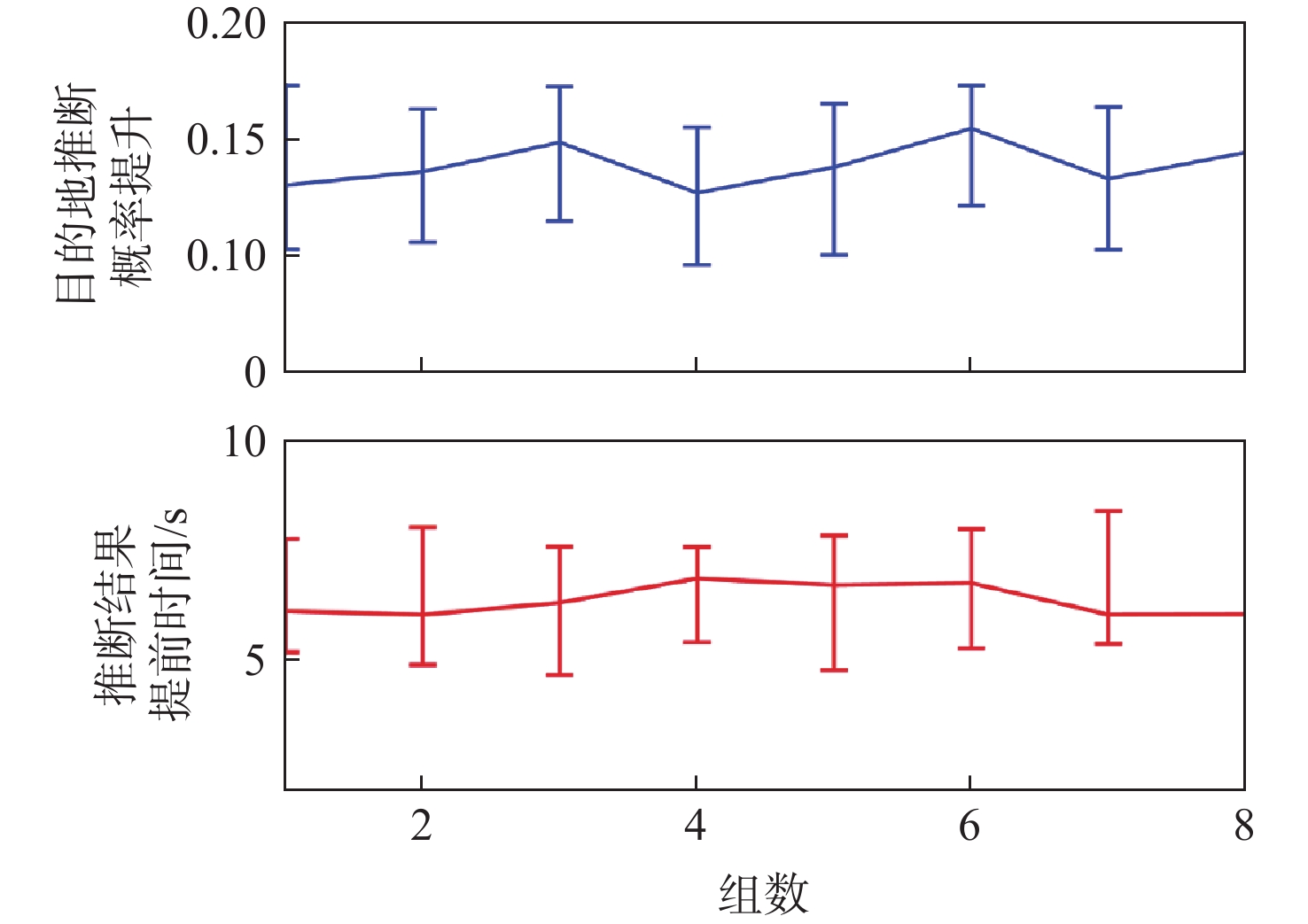
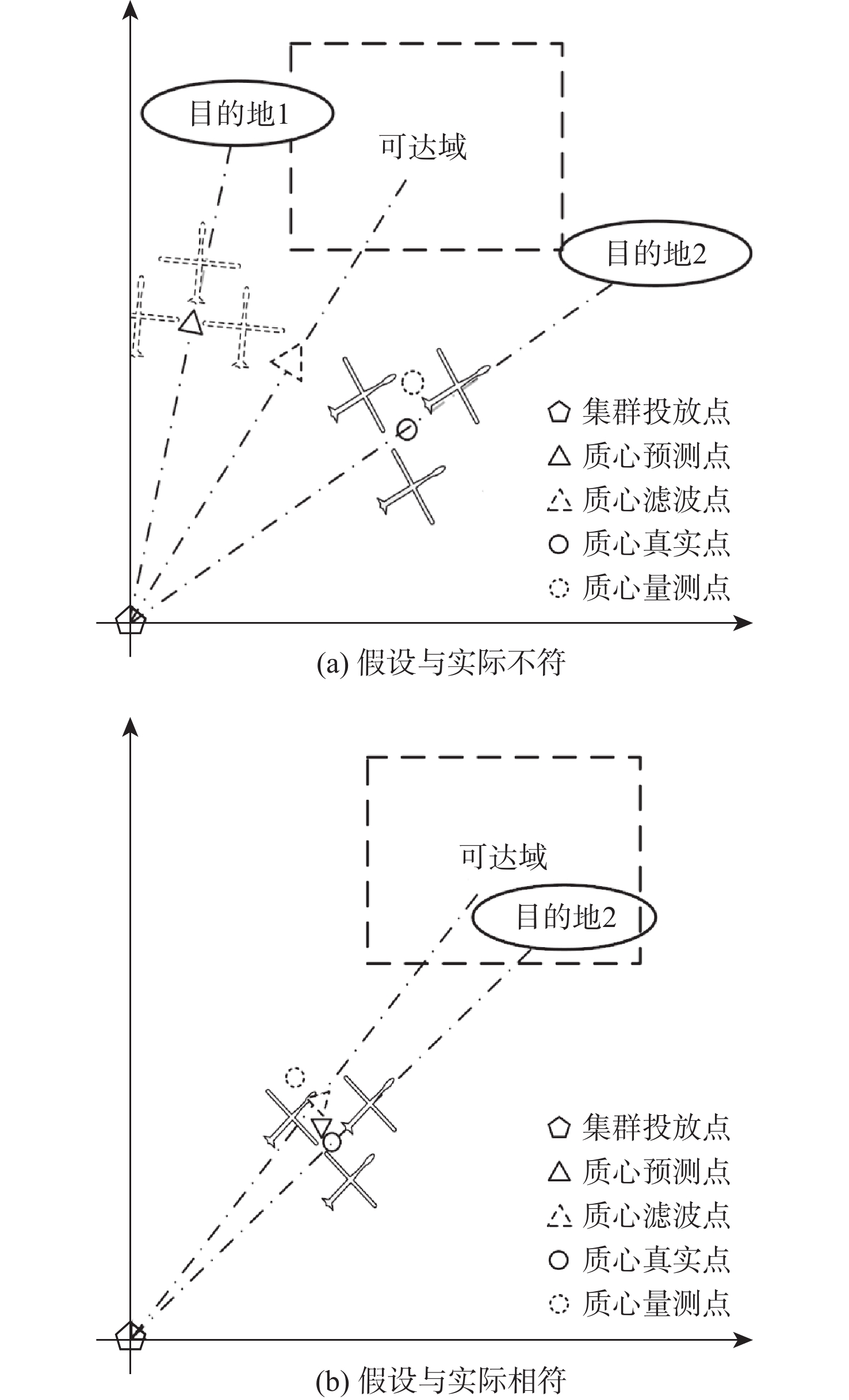
针对无人机集群攻击意图难以有效推断问题,提出基于集群协同规则和具有明确速度定义的综合奥恩斯坦-乌伦贝克(IOU)运动过程推导的马尔可夫桥接分布的无人机集群运动模型,并在此基础上提出基于可达域优化的贝叶斯意图推断方法。利用随机微分方程将所提模型与马尔科夫桥接模型相结合,并推导其在离散空间的表达形式。在基本贝叶斯推断方法的基础上,考虑了所提模型中目的地状态对集群状态的限制作用,通过计算集群可达域,修正量测似然,推导了利用可达域优化贝叶斯推断结果的方法。仿真实验表明:所提模型能够准确模拟集群运动过程并有效推断集群作战意图。
Abstract:Aiming at the problem that it is difficult to infer the attack intention of UAV clusters effectively,in this paper, a UAV cluster motion model is proposed based on cluster coordination rules and a Markov bridging distribution derived from an integrated Ornstein-Uhlenbeck(IOU) motion process with explicit velocity definition. Based on this, a method to optimize the Bayesian intention inference results is proposed by using the idea of the reachable domain.The stochastic differential equation is used to combine the cluster cooperative motion model with the Markov bridge model, and the discrete form of the model is derived. The method of using the reachable domain to optimize the Bayesian intention inference results is derived second, based on the fundamental Bayesian inference method, taking into account the restriction of the destination state on the cluster state, by calculating the reachable domain of the cluster and modifying the measurement likelihood. The results of the simulations demonstrate that the proposed model is capable of simulating the cluster’s movement process with great accuracy and effectively predicting the cluster’s operational intention.
-
表 1 参数定义
Table 1. Parameter definition
dr dm [R11,R12R21,R22] [σx,σy] 15 30 [4,34,1] [3,3] 表 2 目的地位置
Table 2. Location of destination
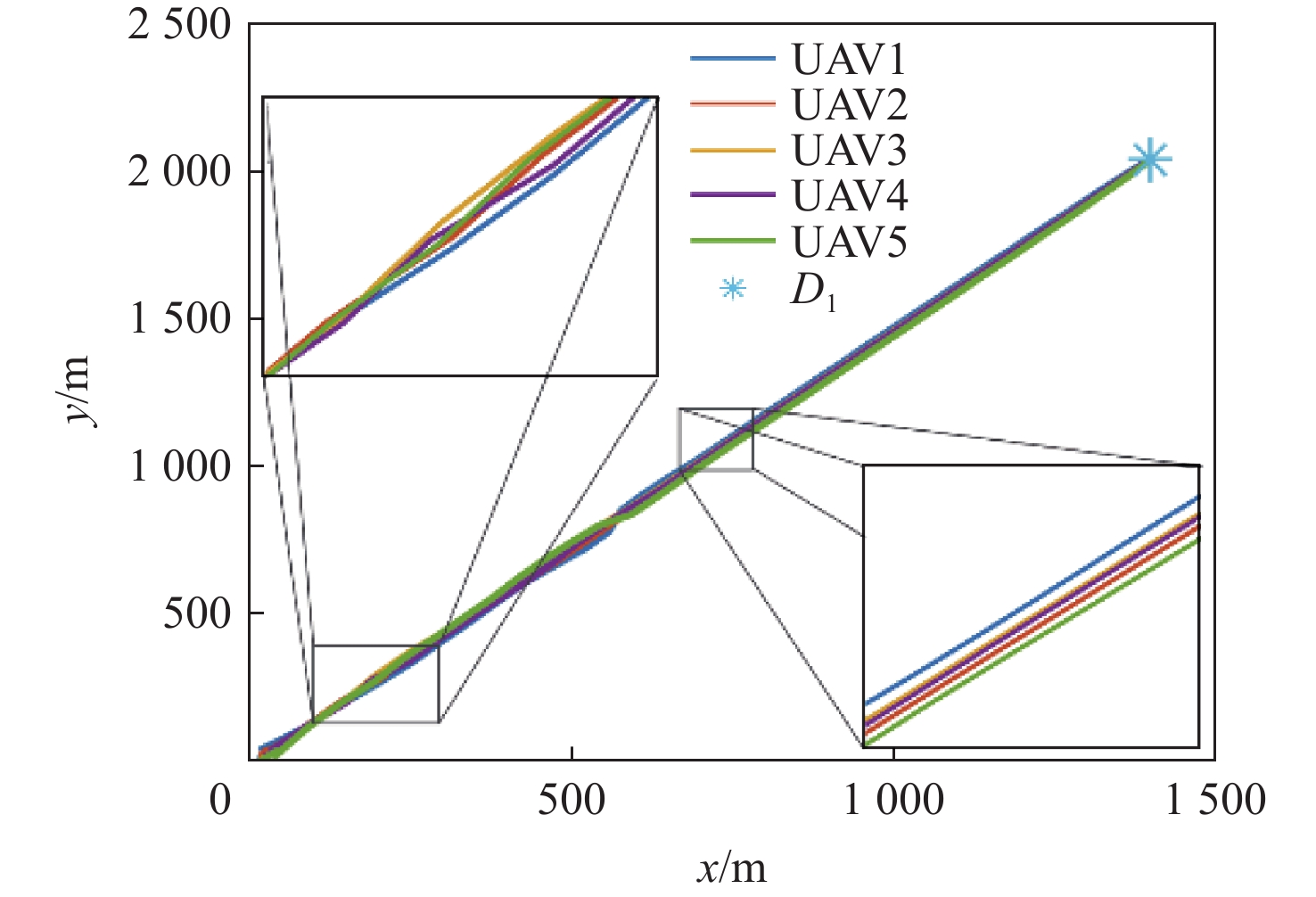
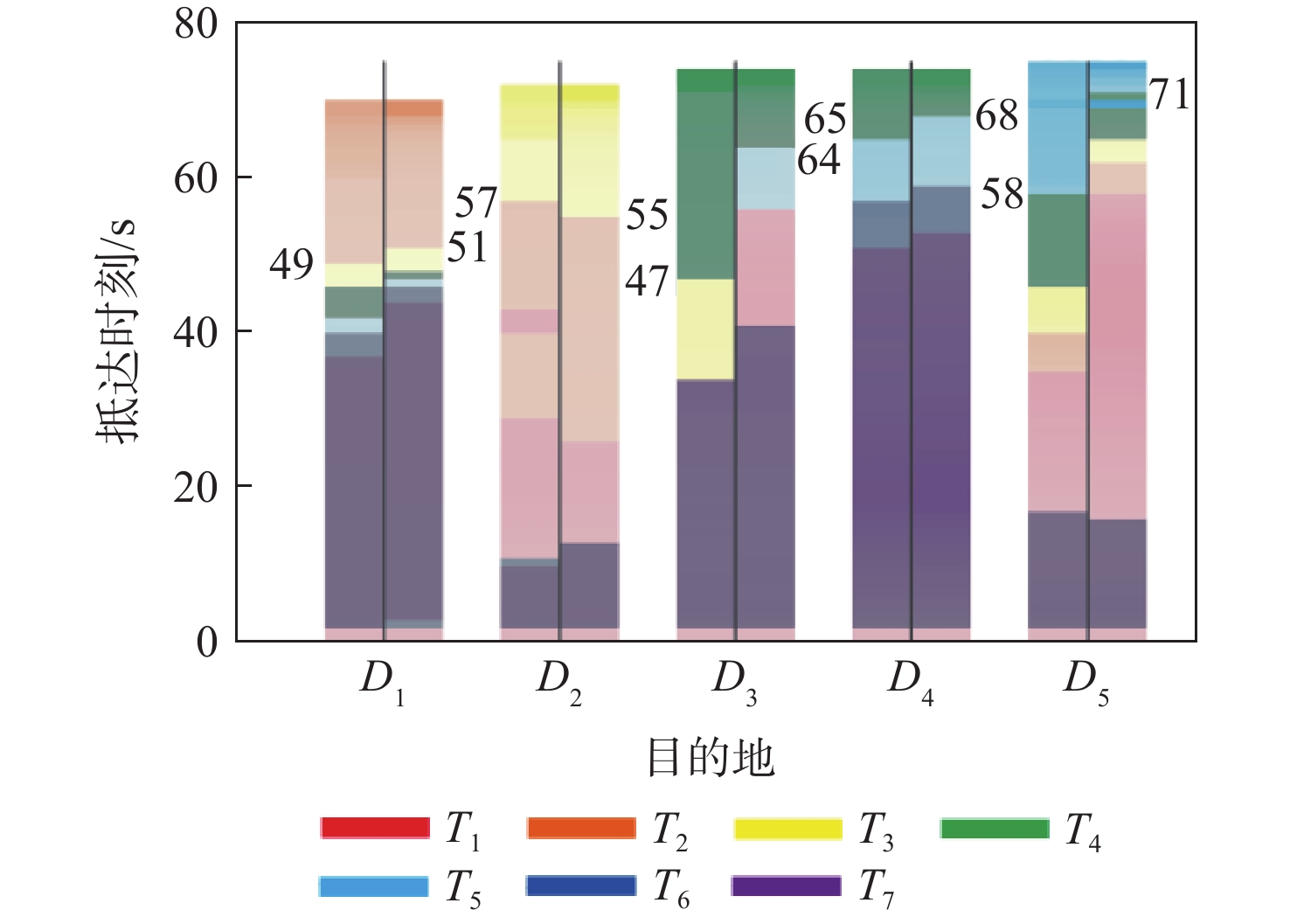
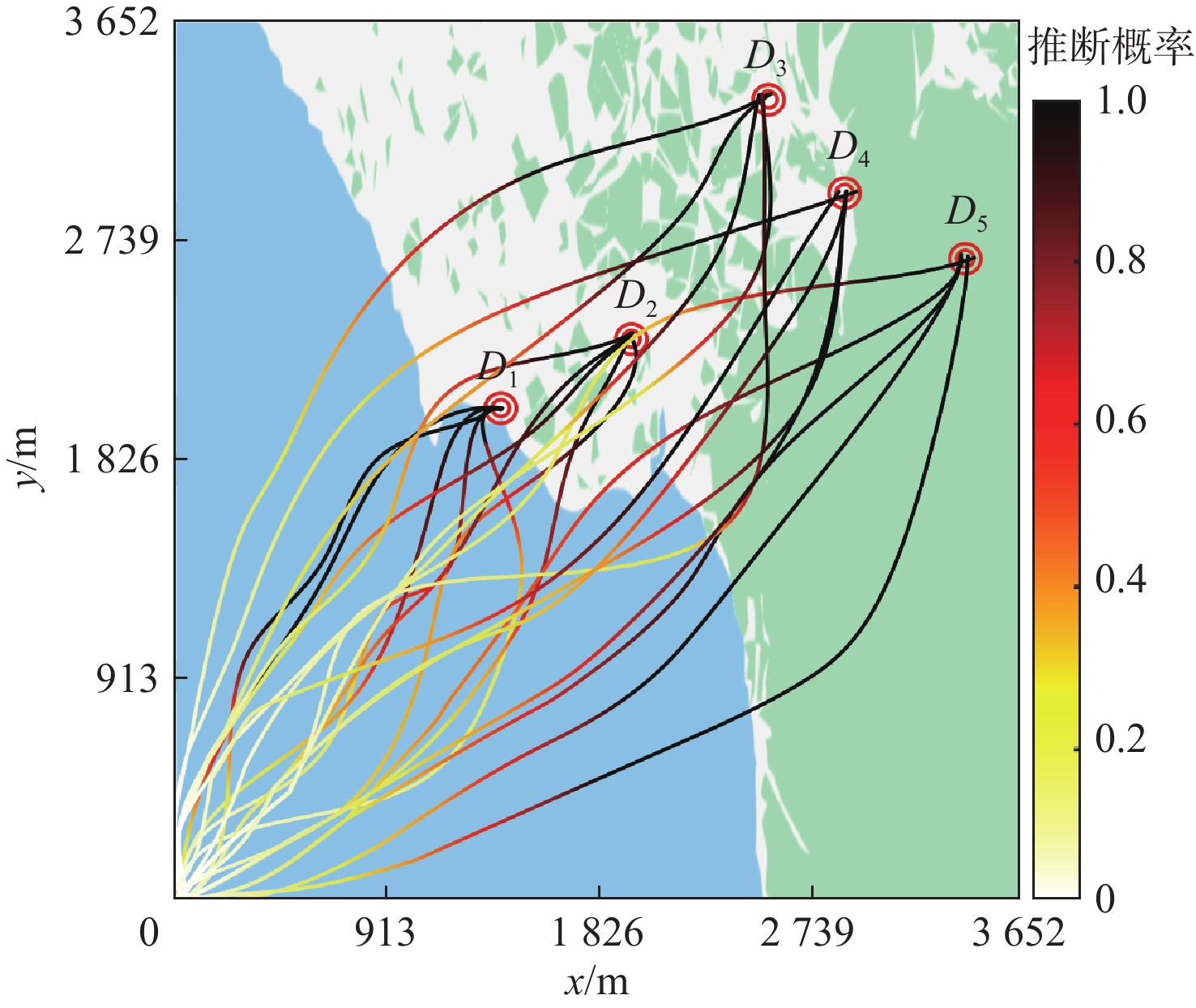
目的地 位置坐标/m 目的地 位置坐标/m D1 (1 400,2 040) D4 (2 880,2 940) D2 (1 960,2 500) D5 (3 440,2 680) D3 (2 560,3 360) -
[1] BORDEAUX J. Self-organized air tasking: Examining a non-hierarchical model for joint air operations[EB/OL]. (2012-10-03)[2021-09-22]. [2] 党爱国, 王坤, 王延密, 等. 无人机集群作战概念发展对未来战场攻防影响[J]. 战术导弹技术, 2019(1): 37-41. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.2019.8.041DANG A G, WANG K, WANG Y M, et al. The impact of UAVs swarming fighting concept development on attack and defense in future battlefield[J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2019(1): 37-41(in Chinese). doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.2019.8.041 [3] MONREALE A, PINELLI F, TRASARTI R, et al. WhereNext: A location predictor on trajectory pattern mining[C]//Proceedings of the 15th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2009: 637-646. [4] 伍之前, 李登峰. 基于推理和多属性决策的空中目标攻击意图判断模型[J]. 电光与控制, 2010, 17(5): 10-13.WU Z Q, LI D F. A model for aerial target attacking intention judgment based on reasoning and multi-attribute decision making[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2010, 17(5): 10-13(in Chinese). [5] 崔洋培, 吴庆宪, 陈谋. 基于自适应神经模糊推理系统的空中目标意图预测[C]//第15届中国系统仿真技术及其应用学术会议论文集, 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2014: 277-281.CUI Y P, WU Q X, CHEN M. Aerial target intention prediction based on adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system[C]//Proceedings of the 15th China Symposium on System Simulation Technology and Its Application. Hefei : University of Science and Technology of China Press , 2014: 277-281 (in Chinese). [6] REYNOLDS C W. Flocks, herds and schools: A distributed behavioral model[C]//Proceedings of the 14th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques. New York: ACM, 1987: 25-34. [7] VICSEK T, CZIRÓK A, BEN-JACOB E, et al. Novel type of phase transition in a system of self-driven particles[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1995, 75(6): 1226-1229. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.75.1226 [8] COUZIN I D, KRAUSE J, FRANKS N R, et al. Effective leadership and decision-making in animal groups on the move[J]. Nature, 2005, 433(7025): 513-516. doi: 10.1038/nature03236 [9] ROMANCZUK P, BÄR M, EBELING W, et al. Active brownian particles: From individual to collective stochastic dynamics[J]. The European Physical Journal Special Topics, 2012, 202(1): 1-162. doi: 10.1140/epjst/e2012-01529-y [10] MOGILNER A, EDELSTEIN-KESHET L, BENT L, et al. Mutual interactions, potentials, and individual distance in a social aggregation[J]. Journal of Mathematical Biology, 2003, 47(4): 353-389. doi: 10.1007/s00285-003-0209-7 [11] DUSTIN J N. Exploitation of self organization in UAV swarms for optimization in combat environments [D]. Ohio : Air Force Institute of Technology, 2008. [12] AHMAD B I, MURPHY J, LANGDON P M, et al. Destination inference using bridging distributions[C]//2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing . Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 5585-5589. [13] AHMAD B I, MURPHY J K, LANGDON P M, et al. Bayesian intent prediction in object tracking using bridging distributions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2018, 48(1): 215-227. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2016.2629025 [14] STONE L D, STREIT R L, CORWIN T L, et al. Bayesian multiple target tracking[M]. Norwood : Artech House Publishers , 2013: 82-83. [15] PANG S K, LI J, GODSILL S J. Detection and tracking of coordinated groups[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(1): 472-502. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5705687 [16] PANG S K, LI J, GODSILL S J. Models and algorithms for detection and tracking of coordinated groups[C]//2008 IEEE Aerospace Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2008: 1-17. [17] AHMAD B I, MURPHY J K, LANGDON P M, et al. Intent inference for hand pointing gesture-based interactions in vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016, 46(4): 878-889. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2015.2417053 [18] OKSENDAL B. Stochastic differential equations: An introduction with applications[M]. Beilin: Springer, 2013. [19] HAUG A J. Bayesian estimation and tracking: A practical guide[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. , 2012. [20] 史小斌, 顾红, 苏卫民, 等. 地面侦察雷达目标威胁度评估方法研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2015, 36(6): 1128-1135.SHI X B, GU H, SU W M, et al. Study of target threat assessment for ground surveillance radar[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2015, 36(6): 1128-1135(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: